#Alkaline Phosphatase
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
#Telfairia occidentalis#Mucuna pruriens#Phytochemical#Haemoglobin#Aspartate transaminase#Alkaline phosphatase
1 note
·
View note
Text

Liver function assessments, often known as hepatic function evaluations or liver enzyme examinations, comprise a battery of blood tests designed to appraise the liver's state and operational competence. These evaluations offer valuable insights into diverse aspects of liver well-being and have the potential to reveal possible concerns. The central components scrutinized in liver function assessments encompass:
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): ALT is an enzyme primarily situated in the liver. Elevated ALT levels in the bloodstream are a robust indication of liver impairment, typically attributed to conditions like viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST): AST is another liver enzyme, though it is also found in other tissues such as the heart and muscles. Elevated AST levels can imply liver damage, but it is imperative to consider the clinical context as they can also signal heart-related issues.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): ALP is an enzyme present in several organs, including the liver, bones, and biliary system. Elevated ALP levels may be a marker of liver disorders, but they can also relate to bone conditions or biliary tract complications.
Total Bilirubin: Bilirubin, a yellow pigment generated during the breakdown of red blood cells, is metabolized by the liver. Increased bilirubin levels can signify liver difficulties like hepatitis or obstruction in the bile duct.
Albumin: Albumin is a protein produced by the liver. Reduced levels of albumin in the bloodstream could indicate liver maladies or malnutrition.
Total Protein: This test measures the overall protein concentration in the blood, encompassing albumin and other proteins. Irregular total protein levels might be associated with liver conditions or kidney issues.
Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR): These assessments gauge the blood's clotting ability. The liver manufactures clotting factors, and deviations in PT and INR may suggest liver ailments or a requirement for monitoring anticoagulant treatment. These assessments for liver function stand as essential instruments for appraising the liver's health and its capability to perform crucial functions.
Full body checkups at Saifee Hospital Mumbai or other reputed hospitals in Mumbai usually include liver function tests, that help you in assessing your liver health and your general health as well.
0 notes
Text
@frau-lines freaks
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

Learn to interpret your liver function test results with our comprehensive guide. Understand commonly used liver tests and their implications for your health.
Do Visit: https://www.healixhospitals.com/blogs/reading-and-interpreting-your-liver-function-test-a-guide-to-commonly-used-liver-tests
#Liver Function Test#Liver Health#Diagnostic Tests#Liver Enzymes#Blood Tests#Hepatic Function#Liver Panel#Bilirubin Levels#Liver Disease#Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)#Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)#Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)#Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)#Liver Health Markers#Hepatobiliary Disorders#Serum Biomarkers#Hepatic Enzymes#Liver Damage#Medical Laboratory Tests#Hepatology
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is the treatment for high alkaline phosphatase?
If you are struggling with high alkaline phosphatase levels, get insights into effective treatment options in our blog on High Alkaline Phosphatase Treatments Approaches."
0 notes
Text
Understanding Liver Function Test
What is a liver function test?
A liver function test is a blood test that measures the levels of various enzymes and proteins in your blood. These substances are produced by the liver, and they can be a sign of liver damage or disease.
#liver function test#Bilirubin#Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)#Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)#and Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
0 notes
Text
The Use of Goat Anti-Llama Alkaline Phosphatase to Study the Sheep Endothelin A Receptor
The intricate world of molecular biology has unlocked numerous doorways to understanding complex cellular processes. One such profound area of research revolves around the sheep endothelin A receptor, a critical player in regulating vasomotor activity and blood pressure. Delving deep into the workings of this receptor has not only broadened our scientific horizons but also paved the way for novel therapeutic strategies. And, what's remarkable is the tool we've employed in this quest - the goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase. Here's an exploration of this compelling journey.
The Sheep Endothelin A Receptor: A Brief Overview, The sheep endothelin A receptor belongs to the endothelin receptor group, primarily responsible for vasoconstriction. Aberrant function or expression of this receptor can lead to a range of cardiovascular conditions, hence, making it a promising target for therapeutic interventions.
Alkaline Phosphatase: The Unsung Hero of Enzyme Markers, Before we bridge the connection between the sheep endothelin A receptor and the goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase, it's crucial to grasp the importance of Alkaline Phosphatase (AP). AP is an enzyme commonly employed as a marker in various immunoassays. Due to its unique ability to catalyze reactions that produce a colored or luminescent product, it is widely used in visualization techniques.
Goat Anti-Llama Alkaline Phosphatase: The Molecular Workhorse, The use of antibodies as tools in molecular research is not new. They are known for their specificity, binding precisely to their target, and acting as beacons in a cellular maze. The goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase is a special type of secondary antibody. This means it doesn't bind directly to the molecule of interest (in this case, the sheep endothelin A receptor). Instead, it binds to another primary antibody that recognizes and attaches to the receptor.
So, why use a goat-derived antibody against llama? It's a matter of cross-reactivity and specificity. Given the vast evolutionary distance between goats and llamas, there's a reduced likelihood of the goat antibody recognizing and binding to non-specific proteins in the llama. This minimizes background noise and false signals in experiments.
The Intersection: How It Benefits Sheep Endothelin A Receptor Research, By conjugating goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase with a primary antibody specific for the sheep endothelin A receptor, researchers can effectively tag the receptor. Once this receptor is tagged, the AP can catalyze its substrate, producing a visible reaction. This allows scientists to track, visualize, and quantify the presence, location, and behavior of the sheep endothelin A receptor in various samples.
This method not only offers an efficient way to study the receptor but also provides high accuracy, reducing the chances of erroneous interpretations.
Final Thoughts: The dance of molecules within a cell, as complex as it may sound, can be beautifully understood with the right tools and techniques. By integrating the specificity of the goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase with the critical insights into the sheep endothelin A receptor, science has once again showcased its brilliance. This endeavor reflects not only the depth of our molecular understanding but also the creative means by which we explore it.
0 notes
Text
Beginning of clinical studies for llama-antibody-based treatment of COVID-19
Clinical trials for a coronavirus therapy produced using antibodies collected from the animals begin, suggesting that a four-year-old llama named Winter may have played a crucial part in the global fight against COVID-19. Scientists at the VIB-UGent Center for Medical Biotechnology in Ghent have found that Winter's goat anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase mitigates the severity of coronavirus infections. They have started Phase 1 studies of their medication based on the llama antibodies.
0 notes
Text
Get aware with Secondary Antibodies conjugated with Alkaline Phosphatase
High-activity AP-conjugated secondary rabbit anti-llama Alkaline Phosphatase antibodies are included in a table below, organized by specific use case. Recommended substrates for chemiluminescent and colorimetric detection methods are included in the tables used to choose AP-linked secondary antibodies.
0 notes
Text

I drew Minifit and Erwin! OCs belong to @alkaline-phosphatase hope you like them! 😅
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have a very rare disease, hooray! Under a cut in case I ramble, not for content warning. I won't be talking about anything explicit.
It's official: I have hypophosphatasia, which is a genetic mutation that causes a deficiency of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) which is used for building bones and metabolizing vitamin B6 into energy, among other things.
Ever since I started getting my lab results mailed to me as an adult, I've had low ALP. But most doctors either only know about the more severe infantile form of HPP, or they don't know about it at all. So it's understandable that they always wrote something like "Low ALP isn't a concern", because most doctors only look for high ALP (which indicates liver problems). I'm accustomed to doing research into medical things, but even I didn't have reason to suspect HPP because most of the information (at least in the past) focused on the severe form.
I didn't look hard enough. Childhood-onset HPP is a thing and it isn't fatal, just painful and annoying. And that's what I have. The signs were there as a kid: disliking standing, finding it easier to walk than stand, difficulty with stairs, "growing pains", less energy and muscle strength than my peers. But none severe enough to catch the attention of teachers or pediatricians. In the US you can only get treatment if symptoms presented before 18 (adult-onset is also a thing but the FDA doesn't care about those people*), so when I was gathering data for the endocrinologist I thought back to my childhood for anything out of the ordinary. One memory that stood out to the doctor and my case managers was the time my classmate broke his leg in fourth grade. He had crutches, and - as our rural school somehow managed to be fairly progressive and inclusive in 1993 - he chose to allow the rest of us to try them, so we could have empathy for him. When I tried them, I remember feeling relief. I though this was cool, there was less weight on my legs but I could still move! It did not occur to me that that isn't a normal thing for a ten-year-old to think. I think it was the pharmacy case manager that went "OH" at this memory.
So HPP is at least a major contributor to my ongoing struggles with chronic fatigue and weakness. It may not be the only one, but it needs to be treated even if only to protect my bones as I get older. ALP is needed to metabolize vitamin B6 as well as make bones though, and Strensiq (a lab-created form of ALP) is known to break down B6. It's so good at it in fact that you can't really get a B6 blood test to be accurate if you're on Strensiq, because the drug will keep eating the B6 in the vial! So we're hopeful that Strensiq will make me feel better, even though it's really made with people with soft bones in mind. The fact that I haven't broken a bone going up the stairs like many people do may make it difficult to get Medicare to approve the prescription. Thankfully, not only am I perfectly willing to fight about it, I have a team to fight alongside me. HPP is so rare that the manufacturer and pharmacy for Strensiq have enough resources to assign each patient case managers to assist with everything from insurance to learning about the drug and how to take it (it's a subcutaneous injection), and also there's Soft Bones, the largest patient advocacy group for HPP in the US. I've already touched base with them and they're standing ready to assist if needed.
Also Alexion sent me this frickin adorable kids' book with the information packet:


*Forgot the note I was going to add about this. The reason the FDA doesn't authorize Strensiq for adult-onset is probably because studies didn't show as dramatic an improvement for adults compared to kids. But I think that's stupid. For one thing the disease is rare so studies are always small and there aren't very many of them. For another, of course the improvement in kids is more dramatic, their disease is more severe. Japan is the only country that allows Strensiq for adult-onset, as far as I'm aware.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Physiology Of The Liver
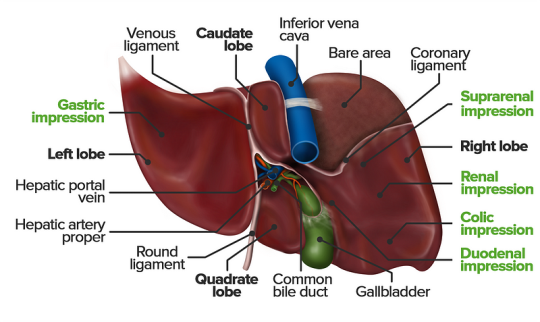
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous functions including metabolism, immunity, digestion, detoxification, and vitamin storage. It weighs around 2% of an adult’s body weight and is unique due to its dual blood supply from the portal vein (75%) and the hepatic artery (25%).
Cellular Structure
The liver’s functional unit is the lobule, which is hexagonal in shape. Each corner of the hexagon has a portal triad consisting of the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. The lobule is composed mainly of hepatocytes, which have distinct apical and basolateral membranes. Hepatocytes are categorized into three zones based on their function and blood supply:
Zone I (periportal region): Closest to the blood supply, involved in oxidative metabolism (e.g., gluconeogenesis, bile formation).
Zone II (pericentral region): Sits between Zones I and III.
Zone III: Farthest from the blood supply, primarily involved in detoxification and biotransformation.
Blood and bile flow in opposite directions within the liver. The space of Disse, between the hepatocytes and the sinusoidal lumen, contains Kupffer cells (macrophages) and Ito cells (fat-storing stellate cells).
Development
The liver develops from endodermal cells of the foregut as the hepatic diverticulum around the fourth week of embryonic development. It undergoes complex differentiation influenced by various pathways (e.g., Wnt/β-catenin, FGF). By the sixth week, the liver participates in hematopoiesis, and hepatocytes begin bile production by the 12th week.
Organ Systems and Functions
The liver interacts with multiple body systems:
Digestive and Metabolic Roles: Aids in digestion, stores fat-soluble vitamins, and handles cholesterol.
Hematological Functions: Produces clotting factors and proteins.
Detoxification: Metabolizes drugs and other xenobiotics through phase I (oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis) and phase II (conjugation) reactions.
Bilirubin Metabolism: Converts heme to unconjugated bilirubin, then conjugates it for excretion.
Hormonal and Protein Synthesis: Involved in thyroid hormone activation and synthesis of nearly all plasma proteins.
Related Testing
Liver function tests (LFTs), including ALT, AST, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), help assess liver health. Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT, and MRI are also employed to identify liver abnormalities.
Pathophysiology
Cirrhosis results from chronic liver injury (e.g., due to alcoholism, hepatitis B and C), leading to fibrosis and necrosis. It causes symptoms like portal hypertension, coagulopathy, and jaundice. Hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E), autoimmune diseases (e.g., primary biliary cholangitis), and metabolic conditions (e.g., non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) also contribute to liver pathology.
Clinical Significance
Understanding liver physiology helps manage conditions like viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, benign liver lesions, and liver cancers. Early detection through appropriate testing and management strategies is essential for preventing end-stage liver disease and improving patient outcomes
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at [email protected] and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#medical help#academic assignments#university student#medical university#university life#university#studying#study motivation#study blog#studyblr community#study inspiration#studyspo#studyblr#student#study aesthetic#medical student#aesthetic#medical school#case study
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
how is psilocybin metabolized?
To metabolize is to breakdown a chemical to its simpler component forms for cells to use. Psilocybin is a psychedelic compound found in fungi of several genera including Psilocybe, Panaeolus, and Copelandia. Inside the body, it influences the functional molecular mechanisms of several organs, mainly the brain, kidneys, and liver. On its own psilocybin is not as effective. To produce its infamous hallucinogenic effect in the brain, it must be converted to psilocin. Psilocin is the main active molecule, which is derived from the prodrug psilocybin.
There are two ways of getting these metabolites inside the body: oral ingestion (for example, eating the "magic mushrooms") and intravenous injection. When orally ingested, the mushrooms are digested in the usual way. Eventually, the psilocybin in the mushrooms reaches the liver where it is converted to psilocin. An enzyme, alkaline phosphatase, acts on psilocybin such that its phosphate group (PO₄³⁻) is replaced with a hydroxyl group (−OH). Psilocin is further acted upon by diverse enzymes to obtain products which are either excreted through urine or contribute to other functions in hepatocytes (liver cells) as psilocin metabolites.
There is a format to convert chemical equations to sentences. Nevertheless, I firmly believe that one must have the convenience of remembering their organic chemistry without having a stroke. Behold,
psilocin + monoamine oxidase = 4-hydroxyindole-3-acetaldehyde
psilocin + glucuronosyltransferase = psilocin glucoronide (PCG)
psilocin + aldehyde reductase = 4-hydroxytryptophol
psilocin + aldehyde dehydrogenase = 4-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (4HIAA)
The fates of each of these products are an elaborate article on their own, and I will be happy to write them should you be interested. Let me know!
Now, we remember that the primary effects due to which human beings consume psilocybin-containing mushrooms are caused by psilocin in the brain. The exact step-by-step mechanism has not yet been outlined; however, general molecular interactions have been found in studies. This psychoactive compound shows an interesting resemblance to serotonin the neurotransmitter. The psilocin binds to 5-HT2A (a molecule in a cell membrane which responds specifically to serotonin i.e., a serotonin receptor) with high affinity, which is believed to be essential for hallucinogenic effect. It also binds to other receptors with varying affinities, although their significance is yet to be understood.
Psilocybin and its metabolized products are completely removed from the body after 24 hours of consumption. The kidneys take pride in detoxifying circulating blood by creating the waste product urine; psilocin consumed can be detected in blood plasma 6-8 hours after consumption. Majority of the psilocin excreted through urine is in the form of psilocin-O-glucoronide. Psilocybin that remains psilocybin is also excreted through urine by the kidneys.
Introducing psilocybin in the body through veins produces effects of similar intensity as the former method. Whereas it remains as an active compound in the blood for a shorter duration. Turton et. al. conducted an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) study to compare the subjective experience of intravenous psilocybin injection interestingly explains how their participants’ descriptions of their experiences were influenced by the MRI scanner environment and the 1960s, when psychedelics were first introduced to western culture.
bibliography:
Passie T, Seifert J, Schneider U, Emrich HM. The pharmacology of psilocybin. Addiction biology. 2002 Oct;7(4):357-64.
Tylš F, Páleníček T, Horáček J. Psilocybin–summary of knowledge and new perspectives. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Mar 1;24(3):342-56.
Turton S, Nutt DJ, Carhart-Harris RL. A qualitative report on the subjective experience of intravenous psilocybin administered in an FMRI environment. Current Drug Abuse Reviews. 2014 Aug 1;7(2):117-27.
#psilocybe cubensis#psilocybe azurescens dried#psilocybe semilanceata#magic mushies#magic mushrooms#metabolites#mushrooms#altered my brain chemistry#psilocybin research#science side of tumblr#science side explain#science side help me
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reading And Interpreting Your Liver Function Test - A Guide To Commonly Used Liver Tests

The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous metabolic functions in the body, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and bile production. Monitoring liver health is crucial for early detection and management of liver diseases. One of the primary tools for assessing liver function is the Liver Function Test (LFT). In this guide, we will delve into the commonly used liver tests, how to interpret the results, and what they indicate about your liver health.
Understanding Liver Function Tests
Liver Function Tests (LFTs) are a group of blood tests that provide valuable insights into the health and function of the liver. These tests measure various enzymes, proteins, and substances in the blood that are indicative of liver health.
Key components of Liver Function Tests
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT): Elevated levels suggest liver damage, commonly caused by conditions like hepatitis or fatty liver disease.
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST): Similar to ALT, elevated AST levels indicate liver damage but may also be elevated in conditions affecting the heart or muscles.
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): Elevated ALP levels may suggest liver or bone disease.
Total Bilirubin: Increased levels may indicate liver dysfunction or obstruction of bile ducts.
Albumin and Total Protein: These are measures of liver synthetic function; decreased levels may suggest liver disease.
What are the causes of abnormal liver function test results?
Causes of abnormal liver function test results can vary and may indicate different underlying conditions. Some common causes include:
1. Build-up of Fat in the Liver:
* Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) can lead to abnormal liver function tests, especially in overweight or obese individuals.
2. Liver Inflammation and Damage:
* Infections, toxic substances like alcohol or certain medications, and immune conditions can cause liver inflammation and subsequent abnormal test results.
3. Liver Overworking:
* When the liver is under stress from processing medicines or toxic substances like alcohol or paracetamol, it can result in abnormal liver function tests.
4. Bile Duct Blockage:
* Blockages in the bile ducts, such as by gallstones, can lead to abnormal liver function test results.
5. Liver Conditions and Diseases:
* Underlying conditions like Wilson's disease, haemochromatosis, or Gilbert's syndrome can affect liver function and result in abnormal test values.
6. Liver Injury:
* Physical injury to the liver, trauma, or presence of abscesses or tumors within the liver can cause abnormal liver function tests.
7. Medications and Supplements:
* Certain medications, over-the-counter drugs, herbal remedies, and traditional medicines can also impact liver function test results.
8. Other Factors:
* Factors like high alcohol intake, viral infections, autoimmune conditions, metabolic liver diseases, heart problems, and tumors in the liver can contribute to abnormal liver function tests.
Continue Reading: https://www.healixhospitals.com/blogs/reading-and-interpreting-your-liver-function-test-a-guide-to-commonly-used-liver-tests
#Liver Function Test#Liver Health#Diagnostic Tests#Liver Enzymes#Blood Tests#Hepatic Function#Liver Panel#Bilirubin Levels#Liver Disease#Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)#Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)#Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)#Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)#Liver Health Markers#Hepatobiliary Disorders#Serum Biomarkers#Hepatic Enzymes#Liver Damage#Medical Laboratory Tests#Hepatology
1 note
·
View note
Text
I'm on OB rotation again. I asked the attending what are things the PCP should know about prenatal and postpartum pts. Stuff we discussed:
SSRIs can be continued during pregnancy. I often see patients on Zoloft during pregnancy if they need an antidepressant. In fact, I just started a prenatal patient on Zoloft the other day in clinic. It is safe to continue SSRIs during pregnancy because you should treat the patient's depression. Babies can come out sort of jittery because of the SSRI, but that goes away.
Postpartum patients will have bleeding somewhat similar to a menstrual period right after giving birth. It starts to decrease and becomes like a brownish color and can last up to 6 weeks postpartum. Any bleeding beyond that point is abnormal.
There is some evidence that if you have estrogen-containing birth control, it can decrease milk supply. Actually, I had a patient in clinic recently who was seen by an attending and he started her on a progesterone only birth control so that it would not affect her milk supply. Estrogen decreases the patient's milk supply, so patients who plan to breast-feed should not be started on estrogen-containing birth control. Right after giving birth, your body has increased amounts of estrogen, so you would not start estrogen containing birth control until at least 6 weeks postpartum anyway. Increasing estrogen immediately postpartum increases risk of blood clots. For patients who plan to breastfeed and want to be on an oral contraceptive, use progesterone only oral contraceptives until she stops breastfeeding.
If the mother is breastfeeding at least every 4 hours, then this can be used for contraception. It's about 80% effective. Once baby starts sleeping through the night or once baby starts feeding more than every 4 hours, this method won't work! If you go more than 4 hours without breastfeeding, breastfeeding will not protect you from pregnancy! You can also ovulate before your menstrual period returns, so you can't say you can't get pregnant because your period has not returned yet!
I asked the attending I worked with today about how she goes about prescribing birth control. She said she will usually start with Sprintec. It's usually covered by insurance and if it's not covered, it's pretty affordable. She also said Junel is pretty well tolerated. Certain progestins in certain brands of birth control may work better for certain things like acne control, but she didn't have as much knowledge on that. I'll ask another attending again about that. I usually start people on Sprintec as well.
PCP should know that alkaline phosphatase is high in pregnant patients. It comes from the placenta. So don't be freaked out by that.
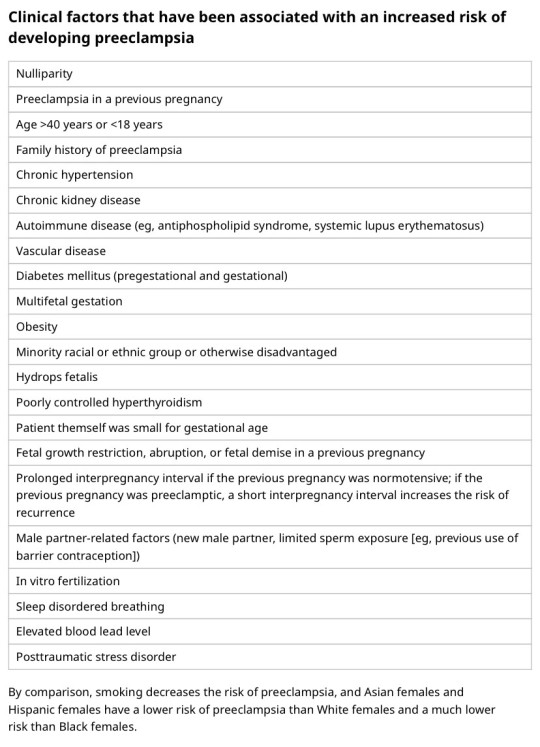
You should know HTN in pregnancy and preeclampsia workup. High BP is 140/90. Severely high BP is 160/110. Swelling occurs in many pregnant pts, but that should also alert you to start preeclampsia workup.
[Preeclampsia w/u from UpToDate:
Diagnostic evaluation
•Laboratory – Patients with suspected preeclampsia should have a complete blood count with platelets, creatinine level, liver chemistries, and determination of urinary protein excretion.
•Fetal status – Fetal status is assessed concurrently or postdiagnosis, depending on the degree of concern during maternal evaluation. At a minimum, a nonstress test or biophysical profile is performed if appropriate for gestational age. Ultrasound is used to evaluate amniotic fluid volume and estimate fetal weight, given the increased risk for oligohydramnios and growth restriction.
•Consultation with the neurology service is generally indicated in patients with neurologic deficits/abnormal neurologic examination, which may include ocular symptoms or a severe persistent headache that does not respond to initial routine management of preeclampsia.]
An important thing to review is physiology of pregnancy. Blood volume increases during pregnancy, so there are lots of new RBCs and that will throw off a HgbA1c reading, therefore HgbA1c is not measured during pregnancy and will not be accurate! My attending today told me there was a midwife who offered pts either HgbA1c or oral glucose tolerance tests to screen for gestational DM. The HgbA1c is not accurate in pregnancy, so this should not be done. That would be bad to miss a diagnosis of gestational diabetes. You have to wait until 3 months postpartum to measure HgbA1c to get an accurate reading. Had a pt who did not have a PCP prior to getting pregnant, was on insulin during the pregnancy, and after giving birth, still needs to establish with PCP for diabetes f/u. After you give birth, you insulin needs drastically change, so you don't need as much as you did when you were pregnant. So I stopped her insulin and advised that she f/u with her new PCP for diabetes care.
I still need to review fetal heart tracings. The attending today said the first thing to look at is the baseline (the baseline HR should be about 160 beats/min), then the variability, then look for accelerations and decelerations. If more than 32 weeks GA, accelerations are 15 beats/min above the baseline lasting at least 15 seconds. Early decelerations are representative of compression of the fetal head, which is normal during labor as baby moves down the pelvis/birth canal. Variable decelerations look sharper like a "V" and can represent compression of the umbilical cord. Late decelerations represent placental insufficiency.
ACOG has very helpful practice bulletins.
I can't take screen shots on my work laptop, so I'm just going to summarize gestational HTN w/u from UpToDate:
Gestational HTN: New onset of systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg on at least 2 occasions 4 hours apart after 20 weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive individual
And:
No proteinuria
No signs/symptoms of preeclampsia-related end-organ dysfunction (eg, thrombocytopenia, renal insufficiency, elevated liver transaminases, pulmonary edema, cerebral or visual symptoms)
Preeclampsia: New onset of systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg on at least 2 occasions at least 4 hours apart after 20 weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive individual. Patients with systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mmHg should have blood pressure confirmed within a short interval (minutes) to facilitate timely administration of antihypertensive therapy.
And:
Proteinuria (≥300 mg per 24-hour urine collection [or this amount extrapolated from a timed collection], or protein:creatinine ratio ≥0.3, or urine dipstick reading ≥2+ [if other quantitative methods are not available]).
In a patient with new-onset hypertension without proteinuria, the diagnosis of preeclampsia can still be made if any features of severe disease are present.
Preeclampsia with severe features: In a patient with preeclampsia, presence of any of the following findings are features of severe disease:
Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mmHg on 2 occasions at least 4 hours apart (unless antihypertensive therapy is initiated before this time)
Thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100,000/microL)
Impaired liver function as indicated by liver transaminase levels at least twice the normal concentration or severe persistent right upper quadrant or epigastric pain unresponsive to medication and not accounted for by alternative diagnoses, or both
Progressive renal insufficiency (serum creatinine concentration >1.1 mg/dL [97 micromol/L] or doubling of the serum creatinine concentration in the absence of other renal disease)
Pulmonary edema
Persistent cerebral or visual disturbances
Eclampsia: A generalized seizure in a pt with preeclampsia that cannot be attributed to other causes.
HELLP syndrome: hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets. Hypertension may be present (HELLP in such cases is often considered a variant of preeclampsia).
Chronic (pre-existing) hypertension: hypertension diagnosed or present before pregnancy or on at least 2 occasions before 20 weeks of gestation. Hypertension that is first diagnosed during pregnancy and persists for at least 12 weeks postpartum is also consider chronic hypertension.
Blood pressure criteria during pregnancy are:
Systolic ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic ≥90 mmHg
Prepregnancy and 12 weeks postpartum blood pressure criteria are:
Stage 1 – Systolic 130 to 139 mmHg or diastolic 80 to 89 mmHg
Stage 2 – Systolic ≥140 mmHg or diastolic ≥90 mmHg
Chronic HTN with superimposed preeclampsia*:
Any of these findings in a patient with chronic hypertension:
A sudden increase in blood pressure that was previously well-controlled or an escalation of antihypertensive therapy to control blood pressure
New onset of proteinuria or a sudden increase in proteinuria in a patient with known proteinuria before or early in pregnancy
Significant new end-organ dysfunction consistent with preeclampsia after 20 weeks of gestation or postpartum
*Precise diagnosis is often challenging. High clinical suspicion is warranted given the increase in maternal and fetal-neonatal risks associated with superimposed preeclampsia.
Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia with severe features:
Any of these findings in a patient with chronic hypertension and superimposed preeclampsia:
Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mmHg despite escalation of antihypertensive therapy
Thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100,000/microL)
Impaired liver function as indicated by liver transaminase levels at least twice the normal concentration or severe persistent right upper quadrant or epigastric pain unresponsive to medication and not accounted for by alternative diagnoses, or both
New-onset or worsening renal insufficiency
Pulmonary edema
Persistent cerebral or visual disturbances
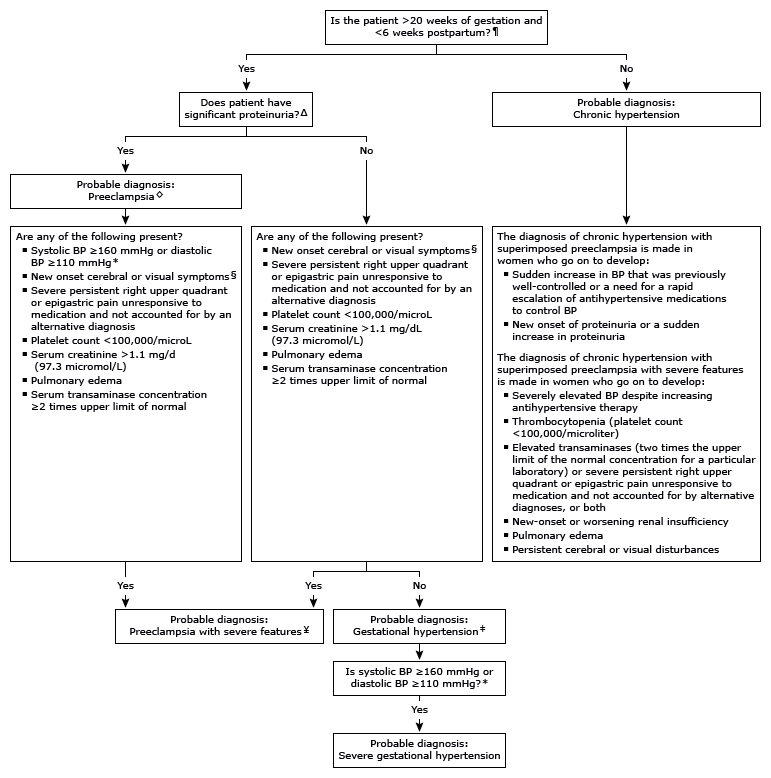
A reduction in blood pressure early in pregnancy is a normal physiologic occurrence. For this reason, women with chronic hypertension may be normotensive at their first few prenatal visits. Later in pregnancy, when their blood pressure returns to its prepregnancy baseline, they may appear to be developing preeclampsia or gestational hypertension if there are no documented prepregnancy blood pressure measurements.
BP: blood pressure.
* Blood pressure should be elevated on at least two occasions at least four hours apart. However, if systolic pressure is ≥160 mmHg or diastolic pressure is ≥110 mmHg, confirmation after a short interval, even within a few minutes, is acceptable to facilitate timely initiation of antihypertensive therapy.
¶ The onset of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension is almost always after 20 weeks of gestation. Preeclampsia before 20 weeks of gestation may be associated with a complete or partial molar pregnancy or fetal hydrops. Postpartum preeclampsia usually presents within two days of delivery. The term "delayed postpartum preeclampsia" is used for signs and symptoms of the disease leading to readmission more than two days but less than six weeks after delivery.
Δ Significant proteinuria is defined as ≥0.3 g in a 24-hour urine specimen or protein/creatinine ratio ≥0.3 (mg/mg) (34 mg/mmol) in a random urine specimen or dipstick ≥1+ if a quantitative measurement is unavailable.
◊ Almost all women with the new onset of hypertension and proteinuria at this gestational age or postpartum have preeclampsia, but a rare patient may have occult renal disease exacerbated by the physiologic changes of pregnancy. An active urine sediment (red and white cells and/or cellular casts) is consistent with a proliferative glomerular disorder but not a feature of preeclampsia. Women with chronic hypertension who had proteinuria prior to or in early pregnancy may develop superimposed preeclampsia. This can be difficult to diagnose definitively, but should be suspected when blood pressure increases significantly (especially acutely) in the last half of pregnancy/postpartum or signs/symptoms associated with the severe end of the disease spectrum develop.
§ Photopsia (flashes of light), scotomata (dark areas or gaps in the visual field), blurred vision, or temporary blindness (rare); severe headache (ie, incapacitating, "the worst headache I've ever had") or headache that persists and progresses despite analgesic therapy; altered mental status. Seizure occurrence upgrades the diagnosis to eclampsia.¥ The differential diagnosis of preeclampsia with severe features includes but is not limited to:
Antiphospholipid syndrome
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
The laboratory findings in these disorders overlap with those in preeclampsia with severe features. (Refer to table in the UpToDate topic on the clinical manifestations and diagnosis of preeclampsia.) The prepregnancy history, magnitude and spectrum of laboratory abnormalities, and additional presence of signs and symptoms not typically associated with preeclampsia help in making the correct diagnosis, which is not always possible during pregnancy.
In addition, a variety of medical disorders may be associated with hypertension and one or more of the signs and symptoms that occur in women with preeclampsia with severe features. These patients can usually be distinguished from patients with preeclampsia by taking a detailed history, performing a thorough physical examination, and obtaining relevant laboratory studies.‡ In contrast to preeclampsia, gestational hypertension is not associated with end-organ involvement, so neither proteinuria nor the symptoms or laboratory findings of preeclampsia are present.
#OB#OBGYN#birth control#gestational HTN#preeclampsia#eclampsia#breastfeeding#gestational diabetes#fetal heart tracing#FHT
2 notes
·
View notes
