#Additional Chief Secretary Appointment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Avinash Kumar Appointed Additional Chief Secretary To CM Hemant Soren
New Government Formation Underway With Cabinet Expansion Expected Tuesday Congress leaders in Delhi to discuss potential ministerial changes. RANCHI – Senior bureaucrat Avinash Kumar has been appointed as Additional Chief Secretary to newly sworn-in Chief Minister Hemant Soren. "The Department of Personnel Administrative Reforms and Official Language has issued a notification for Kumar’s…
#Additional Chief Secretary Appointment#Avinash Kumar Appointment#राज्य#Congress Ministerial Changes#Hemant Soren Oath Ceremony#Hemant Soren Third Term#Jamshedpur political news#Jharkhand cabinet expansion#Jharkhand government formation#Jharkhand political developments#Jharkhand Secretariat Meeting#state
0 notes
Text
Major bureaucratic reshuffle in Tamil Nadu, IAS Dheeraj Kumar Appointed as New Home Secretary.

Chennai: The Tamil Nadu government announced a major reshuffle of IAS officers. IAS Dheeraj Kumar has been appointed as the Government, Home, Prohibition, and Excise Department’s Additional Chief Secretary. IAS P Amudha previously held the position and has now been appointed Principal Secretary to the Government, Revenue, and Disaster Management Department.
ALSO READ MORE- https://apacnewsnetwork.com/2024/07/tamil-nadu-government-appoints-ias-dheeraj-kumar-as-new-home-secretary-amidst-multiple-bureaucratic-transfers/
#Additional Chief Secretary Animal Husbandry Dairying Fisheries#Chief Secretary and Commissioner of Greater Chennai Corporation#Dalit Bahujan Samaj Party#IAS Dheeraj Kumar#IAS Har Sahay Meena#IAS K Gopal#IAS K Gopal Additional Chief Secretary Animal Husbandry Dairying Fisheries#IAS P Amudha#IAS S Madumathi as Secretary School Education#IAS Veera Raghava Rao#J Radhakrishnan#J Radhakrishnan Chief Secretary and Commissioner of Greater Chennai Corporation#new Home Secretary amidst multiple bureaucratic transfers#Tamil Nadu Government#Tamil Nadu government appoints IAS Dheeraj Kumar
0 notes
Text

Make that Trump and D.C. Be sure to read the caption.
[Thanks Steve Jennings]
* * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
June 2, 2025
Heather Cox Richardson
Jun 03, 2025
The Republicans’ giant budget reconciliation bill has focused attention on the drastic cuts the Trump administration is making to the American government. On Friday, when a constituent at a town hall shouted that the Republicans’ proposed cuts to Medicaid, the federal healthcare program for low-income Americans, meant that “people will die,” Senator Joni Ernst (R-IA) replied, “Well, we are all going to die.”
The next day, Ernst released a video purporting to be an apology. It made things worse. “I made an incorrect assumption that everyone in the auditorium understood that, yes, we are all going to perish from this Earth. So, I apologize. And I’m really, really glad that I did not have to bring up the subject of the tooth fairy as well. But for those that would like to see eternal and everlasting life, I encourage you to embrace my lord and savior, Jesus Christ," she said.
Ernst blamed the “hysteria that’s out there coming from the left” for the outcry over her comments. Like other Republicans, she claims that the proposed cuts of more than $700 billion in Medicaid funding over the next ten years is designed only to get rid of the waste and fraud in the program. Thus, they say, they are actually strengthening Medicaid for those who need it.
But, as Linda Qiu noted in the New York Times today, most of the bill’s provisions have little to do with the “waste, fraud, and abuse” Republicans talk about. They target Medicaid expansion, cut the ability of states to finance Medicaid, force states to drop coverage, and limit access to care. And the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office (CBO) says the cuts mean more than 10.3 million Americans will lose health care coverage.
House speaker Mike Johnson has claimed that those losing coverage will be 1.4 million unauthorized immigrants, but this is false. As Qiu notes, although 14 states use their own funds to provide health insurance for undocumented immigrant children, and seven of those states provide some coverage for undocumented pregnant women, in fact, “unauthorized immigrants are not eligible for federally funded Medicaid, except in emergency situations.” Instead, the bill pressures those fourteen states to drop undocumented coverage by reducing their federal Medicaid funding.
MAGA Republicans claim their “One Big, Beautiful Bill”—that’s its official name—dramatically reduces the deficit, but that, too, is a lie.
On Thursday, May 29, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt claimed the measure would carry out “the largest deficit reduction in nearly 30 years with $1.6 trillion in mandatory savings.” She echoed forty years of Republican claims that the economic growth unleashed by the measure would lead to higher tax revenues, a claim that hasn’t been true since Ronald Reagan made it in the 1980s.
In fact, the CBO estimates that the tax cuts and additional spending in the measure mean “[a]n increase in the federal deficit of $3.8 trillion.” As G. Elliott Morris of Strength in Numbers notes, the CBO has been historically very reliable, but Leavitt and House speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) tried to discount its scoring by claiming, as Johnson said: “They are historically totally unreliable. It’s run by Democrats.”
The director of the CBO, economist Philip Swagel, worked as chief of staff and senior economist at the Council of Economic Advisors during the George W. Bush administration. He was appointed in 2019 with the support of Senate Budget Committee chair Michael Enzi (R-WY) and House Budget Committee chair John Yarmuth (D-KY). He was reappointed in 2023 with bipartisan support.
Republican cuts to government programs are a dramatic reworking of America’s traditional evidence-based government that works to improve the lives of a majority of Americans. They are replacing that government with an ideologically driven system that concentrates wealth and power in a few hands and denies that the government has a role to play in protecting Americans.
And yet, those who get their news by watching the Fox News Channel are likely unaware of the Republicans’ planned changes to Medicaid. As Aaron Rupar noted, on this morning’s Fox and Friends, the hosts mentioned Medicaid just once. They mentioned former president Joe Biden 39 times.
That change shows dramatically in cuts to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA is an agency in the Commerce Department, established under Republican president Richard Nixon in 1970, that monitors weather conditions, storms, and ocean currents. The National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather, wind, and ocean forecasts, is part of NOAA.
NWS forecasts annually provide the U.S. with an estimated $31.5 billion in benefits as they enable farmers, fishermen, businesspeople, schools, and individuals to plan around weather events.
As soon as he took office, Trump imposed an across-the-board hiring freeze, and billionaire Elon Musk’s “Department of Government Efficiency” fired probationary employees and impounded funds Congress had appropriated. Now, as hurricane season begins, experts in storms and disasters are worried that the NOAA will be unable to function adequately.
Cuts to the NWS have already meant fewer weather balloons and thus less data, leaving gaps in information for a March ice storm in Northern Michigan and for storms and floods in Oklahoma in April. Oliver Milman of The Guardian reported today that 15 NWS offices on the Gulf of Mexico, a region vulnerable to hurricanes, are understaffed after losing more than 600 employees. Miami’s National Hurricane Center is short five specialists. Thirty of the 122 NWS stations no longer have a meteorologist in charge, and as of June 1, seven of those 122 stations will not have enough staff to operate around the clock.
On May 5, the five living former NWS leaders, who served under both Democratic and Republican presidents, wrote a letter to the American people warning that the cuts threaten to bring “needless loss of life.” They urged Americans to “raise your voice” against the cuts.
Trump’s proposed 2026 budget calls for “terminating a variety of climate-dominated research, data, and grant programs” and cutting about 25% more out of NOAA’s funding.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has also suffered dramatic cuts as Trump has said he intends to push disaster recovery to the states. The lack of expertise is taking a toll there, too. Today staff members there said they were baffled after David Richardson, the head of the agency, said he did not know the United States has a hurricane season. (It does, and it stretches from June 1 to the end of November.) Richardson had no experience with disaster response before taking charge of FEMA.
Trump’s proposed cuts to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are even more draconian. On Friday, in a more detailed budget than the administration published in early May, the administration called for cuts of 43% to the NIH, about $20 billion a year. That includes cuts of nearly 40% to the National Cancer Institute. At the same time, the administration is threatening to end virtually all biomedical research at universities.
On Friday, May 23, the White House issued an executive order called “Restoring Gold Standard Science.” The order cites the COVID-19 guidance about school reopenings from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to claim that the federal government under President Joe Biden “used or promoted scientific information in a highly misleading manner.” (Schools closed in March 2020 under Trump.) The document orders that “[e]mployees shall not engage in scientific misconduct” and, scientists Colette Delawalla, Victor Ambros, Carl Bergstrom, Carol Greider, Michael Mann, and Brian Nosek explain in The Guardian, gives political appointees the power to silence any research they oppose “based on their own ‘judgment.’” They also have the power to punish those scientists whose work they find objectionable.
The Guardian authors note that science is “the most important long-term investment for humanity.” They recall the story of Soviet biologist Trofim Lysenko, who is a prime example of the terrible danger of replacing fact-based reality with ideology.
As Sam Kean of The Atlantic noted in 2017, Lysenko opposed science-based agriculture in the mid-20th century in favor of the pseudo-scientific idea that the environment alone shapes plants and animals. This idea reflected communist political thought, and Lysenko gained the favor of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin. Lysenko claimed that his own agricultural techniques, which included transforming one species into another, would dramatically increase crop yields. Government leaders declared that Lysenko’s ideas were the only correct ones, and anyone who disagreed with him was denounced. About 3,000 biologists whose work contradicted his were fired or sent to jail. Some were executed. Scientific research was effectively banned.
In the 1930s, Soviet leaders set out to “modernize” Soviet agriculture, and when their new state-run farming collectives failed, they turned to Lysenko to fix the problem with his new techniques. Almost everything planted according to his demands died or rotted. In the USSR and in China, which adopted his methods in the 1950s, at least 30 million people died of starvation.
“[W]hen the doctrines of science and the doctrines of communism clashed, he always chose the latter—confident that biology would conform to ideology in the end,” Kean said of Lysenko. He concludes: “It never did.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters From Am American#heather cox richardson#Lysenko#Scientific research#history#Joseph Stalin#National Institute of Health#“one big beautiful bill”#Joni Ernst#fraud waste and abuse
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

"defending civilization against bugs"
lol the mosquito sculpture

see Pratik Chakrabarti's Medicine and Empire: 1600-1960 (2013) and Bacteriology in British India: Laboratory Medicine and the Tropics (2012)
---
Sir Ronald Ross had just returned from an expedition to Sierra Leone. The British doctor had been leading efforts to tackle the malaria that so often killed English colonists in the country, and in December 1899 he gave a lecture to the Liverpool Chamber of Commerce [...]. [H]e argued that "in the coming century, the success of imperialism will depend largely upon success with the microscope."
Text by: Rohan Deb Roy. "Decolonise science - time to end another imperial era." The Conversation. 5 April 2018.
---
---
---
[A]s [...] Diane Nelson explains: The creation of transportation infrastructure such as canals and railroads, the deployment of armies, and the clearing of ground to plant tropical products all had to confront [...] microbial resistance. The French, British, and US raced to find a cure for malaria [...]. One French colonial official complained in 1908: “fever and dysentery are the ‘generals’ that defend hot countries against our incursions and prevent us from replacing the aborigines that we have to make use of.” [...] [T]ropical medicine was assigned the role of a “counterinsurgent field.” [...] [T]he discovery of mosquitoes as malaria and yellow fever carriers reawakened long-cherished plans such as the construction of the Panama Canal (1904-1914) [...]. In 1916, the director of the US Bureau of Entomology and longtime general secretary of the American Association for the Advancement of Science rejoiced at this success as “an object lesson for the sanitarians of the world” - it demonstrated “that it is possible for the white race to live healthfully in the tropics.” [...] The [...] measures to combat dangerous diseases always had the collateral benefit of social pacification. In 1918, [G.V.], president of the Rockefeller Foundation, candidly declared: “For purposes of placating primitive and suspicious peoples, medicine has some decided advantages over machine guns." The construction of the Panama Canal [...] advanced the military expansion of the United States in the Caribbean. The US occupation of the Canal Zone had already brought racist Jim Crow laws [to Panama] [...]. Besides the [...] expansion of vice squads and prophylaxis stations, during the night women were picked up all over the city [by US authorities] and forcibly tested for [...] diseases [...] [and] they were detained in something between a prison and hospital for up to six months [...] [as] women in Panama were becoming objects of surveillance [...].
Text by: Fahim Amir. "Cloudy Swords." e-flux Journal Issue #115. February 2021.
---
---
---
Richard P. Strong [had been] recently appointed director of Harvard’s new Department of Tropical Medicine [...]. In 1914 [the same year of the Panama Canal's completion], just one year after the creation of Harvard’s Department of Tropical Medicine, Strong took on an additional assignment that cemented the ties between his department and American business interests abroad. As newly appointed director of the Laboratories of the Hospitals and of Research Work of United Fruit Company, he set sail in July 1914 to United Fruit plantations in Cuba, Guatemala, Honduras, Costa Rica, and Panama. […] As a shareholder in two British rubber plantations, [...] Strong approached Harvey Firestone, chief executive of the tire and rubber-processing conglomerate that bore his name, in December 1925 with a proposal [...]. Firestone had negotiated tentative agreements in 1925 with the Liberian government for [...] a 99-year concession to optionally lease up to a million acres of Liberian land for rubber plantations. [...]
[I]nfluenced by the recommendations and financial backing of Harvard alumni such as Philippine governor Gen. William Cameron Forbes [the Philippines were under US military occupation] and patrons such as Edward Atkins, who were making their wealth in the banana and sugarcane industries, Harvard hired Strong, then head of the Philippine Bureau of Science’s Biological Laboratory [where he fatally infected unknowing test subject prisoners with bubonic plague], and personal physician to Forbes, to establish the second Department of Tropical Medicine in the United States [...]. Strong and Forbes both left Manila [Philippines] for Boston in 1913. [...] Forbes [US military governor of occupied Philippines] became an overseer to Harvard University and a director of United Fruit Company, the agricultural products marketing conglomerate best known for its extensive holdings of banana plantations throughout Central America. […] In 1912 United Fruit controlled over 300,000 acres of land in the tropics [...] and a ready supply of [...] samples taken from the company’s hospitals and surrounding plantations, Strong boasted that no “tropical school of medicine in the world … had such an asset. [...] It is something of a victory [...]. We could not for a million dollars procure such advantages.” Over the next two decades, he established a research funding model reliant on the medical and biological services the Harvard department could provide US-based multinational firms in enhancing their overseas production and trade in coffee, bananas, rubber, oil, and other tropical commodities [...] as they transformed landscapes across the globe.
Text by: Gregg Mitman. "Forgotten Paths of Empire: Ecology, Disease, and Commerce in the Making of Liberia's Plantation Economy." Environmental History, Volume 22, Number 1. January 2017. [Text within brackets added by me for clarity and context.]
---
---
---
[On] February 20, 1915, [...] [t]o signal the opening of the Panama-Pacific International Exposition (PPIE), [...] [t]he fair did not officially commence [...] until President Wilson [...] pressed a golden key linked to an aerial tower [...] whose radio waves sparked the top of the Tower of Jewels, tripped a galvanometer, [...] swinging open the doors of the Palace of Machinery, where a massive diesel engine started to rotate. [...] [W]ith lavish festivities [...] nineteen million people has passed through the PPIE's turnstiles. [...] As one of the many promotional pamphlets declared, "California marks the limit of the geographical progress of civilization. For unnumbered centuries the course of empire has been steadily to the west." [...] One subject that received an enormous amount of time and space was [...] the areas of race betterment and tropical medicine. Indeed, the fair's official poster, the "Thirteenth Labor of Hercules," [the construction of the Panama Canal] symbolized the intertwined significance of these two concerns [...]. [I]n the 1910s public health and eugenics crusaders alike moved with little or no friction between [...] [calls] for classification of human intelligence, for immigration restriction, for the promotion of the sterilization and segregation of the "unfit," [...]. It was during this [...] moment, [...] that California's burgeoning eugenicist movement coalesced [...]. At meetings convened during the PPIE, a heterogenous group of sanitary experts, [...] medical superintendents, psychologists, [...] and anthropologists established a social network that would influence eugenics on the national level in the years to come. [...]
In his address titled "The Physician as Pioneer," the president-elect of the American Academy of Medicine, Dr. Woods Hutchinson, credited the colonization of the Mississippi Valley to the discovery of quinine [...] and then told his audience that for progress to proceed apace in the current "age of the insect," the stringent sanitary regime imposed and perfected by Gorgas in the Canal Zone was the sine qua non. [...]
Blue also took part in the conference of the American Society for Tropical Medicine, which Gorgas had cofounded five years after the annexation of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Invoking the narrative of medico-military conquest [...], [t]he scientific skill of the United States was also touted at the Pan-American Medical Congress, where its president, Dr. Charles L. Reed, delivered a lengthy address praising the hemispheric security ensured by the 1823 Monroe Doctrine and "the combined genius of American medical scientists [...]" in quelling tropical diseases, above all yellow fever, in the Canal Zone. [...] [A]s Reed's lecture ultimately disclosed, his understanding of Pan-American medical progress was based [...] on the enlightened effects of "Aryan blood" in American lands. [...] [T]he week after the PPIE ended, Pierce was ordered to Laredo, Texas, to investigate several incidents of typhus fever on the border [...]. Pierce was instrumental in fusing tropical medicine and race betterment [...] guided by more than a decade of experience in [...] sanitation in Panama [...]. [I]n August 1915, Stanford's chancellor, David Starr Jordan [...] and Pierce were the guests of honor at a luncheon hosted by the Race Betterment Foundation. [...] [At the PPIE] [t]he Race Betterment booth [...] exhibit [...] won a bronze medal for "illustrating evidences and causes of race degeneration and methods and agencies of race betterment," [and] made eugenics a daily feature of the PPIE. [...] [T]he American Genetics Association's Eugenics Section convened [...] [and] talks were delivered on the intersection of eugenics and sociology, [...] the need for broadened sterilization laws, and the medical inspection of immigrants [...]. Moreover, the PPIE fostered the cross-fertilization of tropical medicine and race betterment at a critical moment of transition in modern medicine in American society.
Text by: Alexandra Minna Stern. Eugenic Nation: Faults and Frontiers of Better Breeding in Modern America. Second Edition. 2016.
#literally that post i made earlier today about frustration of seeing the same colonial institutions and leaders showing up in every story#about plantations and forced labor my first draft i explicitly mentioned the harvard school tropical medicine and kew royal botanic garden#abolition#ecology#imperial#colonial#bugs#indigenous#multispecies#civilization vs bugs#tidalectics#archiepalgos#my writing i guess
325 notes
·
View notes
Text
Steve Contorno at CNN:
Donald Trump has lately made clear he wants little to do with Project 2025, the conservative blueprint for the next Republican president that has attracted considerable blowback in his race for the White House. “I have no idea who is behind it,” the former president recently claimed on social media. Many people Trump knows quite well are behind it. Six of his former Cabinet secretaries helped write or collaborated on the 900-page playbook for a second Trump term published by the Heritage Foundation. Four individuals Trump nominated as ambassadors were also involved, along with several enforcers of his controversial immigration crackdown. And about 20 pages are credited to his first deputy chief of staff. In fact, at least 140 people who worked in the Trump administration had a hand in Project 2025, a CNN review found, including more than half of the people listed as authors, editors and contributors to “Mandate for Leadership,” the project’s extensive manifesto for overhauling the executive branch.
Dozens more who staffed Trump’s government hold positions with conservative groups advising Project 2025, including his former chief of staff Mark Meadows and longtime adviser Stephen Miller. These groups also include several lawyers deeply involved in Trump’s attempts to remain in power, such as his impeachment attorney Jay Sekulow and two of the legal architects of his failed bid to overturn the 2020 presidential election, Cleta Mitchell and John Eastman. To quantify the scope of the involvement from Trump’s orbit, CNN reviewed online biographies, LinkedIn profiles and news clippings for more than 1,000 people listed on published directories for the 110 organizations on Project 2025’s advisory board, as well as the 200-plus names credited with working on “Mandate for Leadership.”
Overall, CNN found nearly 240 people with ties to both Project 2025 and to Trump, covering nearly every aspect of his time in politics and the White House – from day-to-day foot soldiers in Washington to the highest levels of his government. The number is likely higher because many individuals’ online résumés were not available. In addition to people who worked directly for Trump, others who participated in Project 2025 were appointed by the former president to independent positions. For instance, Federal Communications Commissioner Brendan Carr authored an entire chapter of proposed changes to his agency, and Lisa Correnti, an anti-abortion advocate Trump appointed as a delegate to the United Nations Commission on the Status of Women, is among the contributors. Several people involved in Project 2025 didn’t serve in the Trump administration but were influential in shaping his first term. One example is former US Attorney Brett Tolman, a leading force behind the former president’s criminal justice reform law who later helped arrange a pardon for Charles Kushner, the father of Trump’s son-in-law. Tolman is listed as a contributor to “Mandate for Leadership.”
The extensive overlap between Project 2025 and Trump’s universe of allies, advisers and former staff complicates his efforts to distance himself from the work. Trump’s campaign has sought for months to make clear that Project 2025 doesn’t speak for them amid an intensifying push by President Joe Biden and Democrats to tie the Republican standard bearer to the playbook’s more controversial policies.
[...]
Heritage plan becomes a political headache
Behind Project 2025 is the Heritage Foundation, a 51-year-old conservative organization that aligned itself with Trump not long after his 2016 victory. Heritage is led by Kevin Roberts, a Trump ally whom the former president praised as “doing an unbelievable job” on a February night when they shared the same stage. Heritage conceived Project 2025 to begin planning so a Republican president could hit the ground running after the election. One of its priorities is creating a roadmap for the first 180 days of the new administration to quickly reorient every federal agency around its conservative vision. Described on its website as “a movement-wide effort guided by the conservative cause to address and reform the failings of big government and an undemocratic administrative state,” Project 2025 also aims to recruit and train thousands of people loyal to the conservative movement to fill federal government positions.
[...]
Vast network of Trump allies
However, Trump’s attempts to distance himself from Project 2025 have already encountered credibility challenges. The person overseeing Project 2025, Paul Dans, was a top official in Trump’s White House who has previously said he hopes to work for his former boss again. Shortly after Trump’s Truth Social post last week, Democrats noted a recruitment video for Project 2025 features a Trump campaign spokeswoman. On Tuesday, the Biden campaign posted dozens of examples of connections between Trump and Project 2025. CNN’s review of Project 2025’s contributors also demonstrated the breadth of Trump’s reach through the upper ranks of the vast network of organizations working to move the country in a conservative direction – from women’s groups and Christian colleges to conservative think tanks in Texas, Alabama and Mississippi. New organizations centered around Trump’s political movement, his conspiracy theories around his electoral defeats and his first-term policies are deeply involved in Project 2025 as well. One of the advisory groups, America First Legal, was started by Miller, a key player in forming Trump’s immigration agenda. Another is the Center for Renewing America, founded by Russ Vought, former acting director of the Office of Management and Budget, who wrote for Project 2025 a detailed blueprint for consolidating executive power. Vought recently oversaw the Republican Party committee that drafted the new platform heavily influenced by Trump.
In addition to Vought, two other former Trump Cabinet secretaries wrote chapters for “Mandate for Leadership”: Housing and Urban Development Secretary Ben Carson and acting Defense Secretary Christopher Miller. Three more former department heads – National Intelligence Director John Ratcliffe, acting Transportation Secretary Steven Bradbury and acting Labor Secretary Patrick Pizzella – are listed as contributors.
CNN reports that at least 140 people who worked for Donald Trump’s administration are involved in The Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025. This should put an end to the nonsensical lie that Trump “know[s] nothing about Project 2025.”
See Also:
MMFA: Trump and his allies are denying any association to Project 2025 and its architects. History speaks for itself.
#Project 2025#Donald Trump#Trump Administration#Brett Tolman#Jay Sekulow#Stephen Miller#Brendan Carr#Lisa Correnti#Mark Meadows#Cleta Mitchell#John Eastman#Kevin Roberts#Ben Carson#Paul Dans#John Ratcliffie#Frank Wuco#Michael Pack
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
In Moscow, it was like Christmas, Easter, and New Year’s all rolled into one. In a gushing readout of his call with Russian President Vladimir Putin, U.S. President Donald Trump announced the immediate start of negotiations about the future of Ukraine—without preconditions or other countries at the table. Earlier, U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth ruled out NATO membership for Ukraine and any chance of a return to the country’s internationally recognized borders, fulfilling two key Russian conditions. On the same day, the U.S. Senate confirmed Tulsi Gabbard, whose talking points often align with Kremlin propaganda, as the next director of national intelligence.
The Kremlin and its media machine have not been this ecstatic since the launch of Putin’s “special military operation” on Feb. 24, 2022, when for a day or two it actually looked as if Russian forces would overrun Ukraine without much of a fight. “Trump is now doing our job for us” by “sawing” Europe into pieces, Russian talk show host Evgeny Popov told his viewers. His giddy, smiling co-host, Olga Skabeeva, described the turn of events as having been “unimaginable” and “unthinkable” before. On another show, the pundit Sergey Mikheev was elated by another Hegseth remark that was widely interpreted to mean that Washington was reconsidering its security commitment to Europe. Mikheev concluded that Russia was finally free to strike Brussels, London, and Paris. Some pundits basked in the fact that it was Trump who reached out to Putin. “It’s as if Julius Ceasar himself telephoned a barbarian,” Mosfilm studio chief Karen Shakhnazarov commented on another show.
Pundits, bloggers, and officials across Moscow echoed the triumphalism. From their vantage point, fortune has finally turned Russia’s way following three years of humiliating setbacks, including Ukraine’s surprise conquest of a slice of Russia last summer. Since Wednesday, Ukraine looks abandoned by its allies, Europe is as effete and paralyzed as ever, and the Americans are handing Russia a series of gifts by dismantling their alliances and making massive concessions before negotiations even begin. Among Trump’s major appointments, there is not a single official with expert knowledge or experience in the region—not even Keith Kellogg, his special representative for Ukraine and Russia. There is no doubt that the Kremlin will exploit this institutional ignorance to its benefit.
But what is especially delightful to Putin and his cronies is the humiliating exclusion of Ukraine and its European allies from the deal that Trump is eager to personally strike with Putin. Aleksandr Kots, a pro-Putin war reporter, is skeptical that Trump is really Russia’s friend, but for now he celebrates the fact that there are “two men deciding” Ukraine’s fate while Europe is reduced to providing “backup vocals” in the upcoming negotiations. Trump’s own former national security advisor, John Bolton, perfectly captured the exuberance on CNN: “They’re drinking vodka straight out of the bottle in the Kremlin tonight,” he said shortly after the Trump-Putin call.
The Kremlin’s media machine is rightfully celebrating, given how much of what Moscow wants it has just gotten. But underneath the giddiness, much skepticism remains. Russian officials have been burned by Trump’s unpredictability before, and they still seem less exuberant today than in 2016. Then, Trump’s surprise election victory triggered near-fanatical enthusiasm in Moscow, only to end in disappointment. Not only did Trump fail to roll back the Obama administration’s sanctions on Russia, but he actually signed an additional sanctions package soon after taking office.
The current exuberant mood also hides some fundamental obstacles to any negotiated end to the war. Even as Trump meets some of Putin’s preconditions, the Kremlin’s uncompromising rhetoric doesn’t leave much wiggle room elsewhere. Putin has not backed down an inch from his demands that Ukraine surrender even those territories that Russian forces never managed to occupy. Naturally, this is completely unacceptable to Ukraine, setting the talks up for failure from the start.
Russia also doesn’t have a lot of military leverage to dictate its terms. The widespread narrative that Russia is relentlessly advancing with time on its side collapses when you look at the minuscule gains and tremendous toll in Russian lives and equipment. The Russian army is decimated; of its prewar stock of more than 11,000 tanks, for example, barely 3,000 remain—many of them rusted, turretless husks. Seven months after Ukraine occupied parts of Russia’s Kursk region, Russian and North Korean forces still have not managed to retake them; last week, it was the Ukrainians who were advancing there again. Meanwhile, Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov has categorically ruled out territorial swaps—occupied Russia for parts of occupied Ukraine—which further complicates any cease-fire deal.
That said, Ukraine is also exhausted, and neither side has the momentum for a decisive victory. Furthermore, none of Russia’s allies has managed to change the war’s course in Russia’s favor—neither Iran with its missiles and drones nor North Korea with its troops, artillery, and ammunition. Russia’s only remaining hope is that Trump abandons Ukraine, but the Kremlin has no real way to steer his whims and caprices other than by massaging his fragile ego. In this sense, Moscow is as dependent on Trump’s unpredictable decisions as Kyiv. Even as the Kremlin’s media lackeys celebrate, Russian Telegram channels reflect the more sober reality. There, commentators oscillate between euphoria and despair, unsure whether Trump’s next social media post will hand them victory or abandon their cause.
In the end, it will boil down to whoever offers Trump the most convincing flattery or clearest benefit. Putin, as a former KGB handler, quickly figured this out; instead of lashing out at Trump’s earlier threats of pressuring Russia, Putin chose to appeal to Trump’s transparent private obsessions, such as his claim that he won the 2020 U.S. presidential election. Ukraine, in turn, seems to be biding time in hopes that Putin’s inflexible demands and combative nature finally exasperate Trump.
It’s a calculated gamble on Ukraine’s part—and likely its best option. Russia’s resources, while enormous, are not infinite. Putin doesn’t have a lot of time to wait for Ukraine to collapse or Western support to wither away. His threats and red lines have consistently turned out to be hollow. Since the failure of the initial invasion plan, his theory of victory has always revolved around dividing the West and undermining its support for Ukraine. Trump’s return to the White House was always part of that strategy. It’s early days, but we may soon see whether Putin’s strategy pays off—and this week’s champagne toasts in Moscow were warranted.
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
[“American diagrams of the NLF command structure tend to show a hierarchical organization in which the lines of authority run solidly from top to bottom — as was the case within the GVN. In fact, the operations of the Front presented an almost antithetical picture to that of the GVN, in part for the excellent reason that its supply of men, goods, and intelligence came from the bottom up rather than from the top down.
The GVN combined an almost total lack of central planning with a highly centralized administration. The Front combined a complete central planning system with a highly decentralized administration. At least until 1966, when the American armed forces began to depopulate the countryside and to drive the NLF to dependence on the North Vietnamese, the Front’s developed village, district, and provincial organizations were almost entirely self-sufficient. Each village, for instance, supported its own militia and its own intelligence, education, and welfare services, and its own public works projects. The village committees could survive in logistical isolation for long periods of time. This decentralization gave an enormous flexibility. It also enforced cooperation between the civil and military authorities and between the higher and lower levels of the bureaucracy.
The provincial and national battalions depended on the district and village committees for intelligence, if not for some part of their supplies, and thus their commanders had to take directives from the civilians — even those in the lower echelons of the bureaucracy. Brought into the military councils, the village cadres could, for their part, coordinate all of the local government activities. They could prepare propaganda campaigns in conjunction with military operations and they could (unlike the GVN village and district chiefs) work with the peasants without fear that their efforts would be brought to naught by an ill-timed movement of troops. This system insured a degree of local influence over national affairs that did not begin to exist within the GVN.
The NLF village leaders had to accept policy from above. But with their own militia, and their own local supply lines and intelligence services, they had a great deal more power vis-à-vis the central command than any GVN village council — appointed or elected.
The NLF leaders instructed their cadres in this distribution of power by the very style in which they lived. Even the highest of the Front cadres showed no outward sign of rank. The highest of them dressed in the black pajamas of the peasants and held titles no more impressive than that of “chairman,” “secretary,” or “cadre.” Unlike the regular North Vietnamese army, the People’s Liberation Army of the south conferred no permanent titles at all. An officer would be designated “commander of the nth battalion” or “the nth regiment,” never Colonel X or General Y. This anonymity served as a security precaution, but it also served to reinforce the idea that rank was not a ritual station gained by long tenure or ritual actions. Rank was a responsibility earned and held by continuing positive achievement. In fact, all diagrams of the NLF tend to be confusing and to some degree deceptive, for in addition to its vertical chain of command the Front possessed a strong lateral element in the form of the People’s Revolutionary Party. PRP cadres participated in all of the Front organizations from the village level up, but their chain of command ran parallel to, and to some extent independently of, the NLF itself.
To visualize the NLF it is necessary to imagine not a diagram but a three-dimensional cone with a core of denser material corresponding to the PRP. The role of the PRP was much the same as that of the Communist parties in China and the Soviet Union. Its function was to provide political education and “correct” political leadership at all levels of the bureaucracy. In the villages the Party cadres created and directed all of the Front organizations from their positions within the administrative committees. In the military units and in the district and provincial headquarters they acted as “generalists” amid specialists, coordinating the military, administrative, and logistical machinery so that it served the overall political aims of the Front. The Party cadres held veto power over all military activities and authority over all aspects of the political struggle. The Party, in sum, was the government of the NLF. Government, as it were from the inside out rather than strictly from the top down, presented certain practical advantages to the NLF in its conduct of the political struggle and the guerrilla war.
As most American analysts recognized, the presence of Party cadres at all levels of the command helped to prevent ideological splits and bureaucratic snafus in a struggle where all forms of communication had to be kept to the minimum. The Party was in fact the key to the ability of the NLF to provide centralized policy control with a decentralized administration.
Less obvious to American analysts was the fact that government by the Party constituted a part of the solution to the problem of mandarinism that plagued the GVN. Within the GVN an official would look upon promotion as a movement upwards, a gain in power, wealth, and prestige. Because of the PRP, however, the NLF presented a very different picture even to its newest recruits. A guerrilla fighter could, he knew, rise upwards through the ranks to control more men, but he could not gain real power until he joined the Party. And to join the Party was to move not upwards but inwards; it was a promotion but it was also a demotion in the sense that it meant no rise in wealth or outward status, but, on the contrary, obedience to a discipline much more severe than that exacted from the ordinary NLF member. The Party cadre had to serve as an example of courage, discipline, and abstemiousness. He had, in other words, to descend to the status of a model “servant of the people.”]
frances fitzgerald, from fire in the lake: the vietnamese and the americans in vietnam, 1972
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Vice Admiral Sir Timothy Laurence appointed Patron of the International Maritime Rescue Federation
Vice Admiral Sir Timothy Laurence, the husband of Her Royal Highness the Princess Royal, has been named the Patron of the International Maritime Rescue Federation (IMRF), the world’s leading organisation for developing and improving maritime search and rescue (SAR) capabilities.
He replaces Sir Efthimios Mitropoulos, the Secretary-General Emeritus of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), who stepped down earlier this year, having been in the role since 2012.
Sir Tim holds a distinguished career as part of the UK’s Royal Navy, serving from the early 1970s upon leaving the University of Durham before retiring in 2010. His strong interest and background in maritime led to him being appointed to the Governing Council of the UK’s Royal National Lifeboat Institution in 2004, then to the Trustee Board and Chairman of the Operations Committee in 2011. He later became Deputy Chairman of the RNLI Board and, on retirement from the Board in 2020, became a Vice President.
As Patron, Sir Tim will become a leading voice and advocate for the work of the IMRF and maritime SAR organisations around the world, which continues to play a critical role in protecting and saving lives at sea.
“It is an honour to be appointed the new Patron of the IMRF, and I look forward to working closely with the organisation, its members and SAR personnel worldwide to advance the cause of safety at sea,” Sir Tim said.
Speaking about the appointment, Jacob Tas, Chair of the IMRF, said, “I am delighted that Sir Tim Laurence has accepted our invitation to become the new Patron of the IMRF. His tenure at the UK’s Royal Navy and his dedication to public service means he will be a fantastic supporter of the IMRF’s global work and the critical importance of maritime SAR organisations globally.”
Caroline Jupe, Chief Executive Officer of the IMRF, said, “The IMRF and its membership continue to play a major role in the maritime SAR sector as we look to prevent loss of life in the world’s waters. I am thrilled that Sir Tim has agreed to join the IMRF community as our new Patron, and I’m excited to see how we can work together to bolster the maritime SAR sector, tackle critical issues facing the sector and advance key initiatives to improve the lives of those working in a challenging industry.”
In addition to its work providing guidance and best practice for SAR operations, the IMRF has also launched a number of critical initiatives to improve the wellness and efficiency of SAR personnel, including its #WomenInSAR campaign, its #SARyouOK? mental health initiative and its #FutureSAR climate change awareness campaign.
#yaaaay#a tim patronage#ffs charles just make him a working royal already#tim laurence#timothy laurence#tim does stuff#british royal family#brf#princess anne#princess royal
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
June 2, 2025
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
JUN 3
READ IN APP
The Republicans’ giant budget reconciliation bill has focused attention on the drastic cuts the Trump administration is making to the American government. On Friday, when a constituent at a town hall shouted that the Republicans’ proposed cuts to Medicaid, the federal healthcare program for low-income Americans, meant that “people will die,” Senator Joni Ernst (R-IA) replied, “Well, we are all going to die.”
The next day, Ernst released a video purporting to be an apology. It made things worse. “I made an incorrect assumption that everyone in the auditorium understood that, yes, we are all going to perish from this Earth. So, I apologize. And I’m really, really glad that I did not have to bring up the subject of the tooth fairy as well. But for those that would like to see eternal and everlasting life, I encourage you to embrace my lord and savior, Jesus Christ," she said.
Ernst blamed the “hysteria that’s out there coming from the left” for the outcry over her comments. Like other Republicans, she claims that the proposed cuts of more than $700 billion in Medicaid funding over the next ten years is designed only to get rid of the waste and fraud in the program. Thus, they say, they are actually strengthening Medicaid for those who need it.
But, as Linda Qiu noted in the New York Times today, most of the bill’s provisions have little to do with the “waste, fraud, and abuse” Republicans talk about. They target Medicaid expansion, cut the ability of states to finance Medicaid, force states to drop coverage, and limit access to care. And the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office (CBO) says the cuts mean more than 10.3 million Americans will lose health care coverage.
House speaker Mike Johnson has claimed that those losing coverage will be 1.4 million unauthorized immigrants, but this is false. As Qiu notes, although 14 states use their own funds to provide health insurance for undocumented immigrant children, and seven of those states provide some coverage for undocumented pregnant women, in fact, “unauthorized immigrants are not eligible for federally funded Medicaid, except in emergency situations.” Instead, the bill pressures those fourteen states to drop undocumented coverage by reducing their federal Medicaid funding.
MAGA Republicans claim their “One Big, Beautiful Bill”—that’s its official name—dramatically reduces the deficit, but that, too, is a lie.
On Thursday, May 29, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt claimed the measure would carry out “the largest deficit reduction in nearly 30 years with $1.6 trillion in mandatory savings.” She echoed forty years of Republican claims that the economic growth unleashed by the measure would lead to higher tax revenues, a claim that hasn’t been true since Ronald Reagan made it in the 1980s.
In fact, the CBO estimates that the tax cuts and additional spending in the measure mean “[a]n increase in the federal deficit of $3.8 trillion.” As G. Elliott Morris of Strength in Numbers notes, the CBO has been historically very reliable, but Leavitt and House speaker Mike Johnson (R-LA) tried to discount its scoring by claiming, as Johnson said: “They are historically totally unreliable. It’s run by Democrats.”
The director of the CBO, economist Philip Swagel, worked as chief of staff and senior economist at the Council of Economic Advisors during the George W. Bush administration. He was appointed in 2019 with the support of Senate Budget Committee chair Michael Enzi (R-WY) and House Budget Committee chair John Yarmuth (D-KY). He was reappointed in 2023 with bipartisan support.
Republican cuts to government programs are a dramatic reworking of America’s traditional evidence-based government that works to improve the lives of a majority of Americans. They are replacing that government with an ideologically driven system that concentrates wealth and power in a few hands and denies that the government has a role to play in protecting Americans.
And yet, those who get their news by watching the Fox News Channel are likely unaware of the Republicans’ planned changes to Medicaid. As Aaron Rupar noted, on this morning’s Fox and Friends, the hosts mentioned Medicaid just once. They mentioned former president Joe Biden 39 times.
That change shows dramatically in cuts to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA is an agency in the Commerce Department, established under Republican president Richard Nixon in 1970, that monitors weather conditions, storms, and ocean currents. The National Weather Service (NWS), which provides weather, wind, and ocean forecasts, is part of NOAA.
NWS forecasts annually provide the U.S. with an estimated $31.5 billion in benefits as they enable farmers, fishermen, businesspeople, schools, and individuals to plan around weather events.
As soon as he took office, Trump imposed an across-the-board hiring freeze, and billionaire Elon Musk’s “Department of Government Efficiency” fired probationary employees and impounded funds Congress had appropriated. Now, as hurricane season begins, experts in storms and disasters are worried that the NOAA will be unable to function adequately.
Cuts to the NWS have already meant fewer weather balloons and thus less data, leaving gaps in information for a March ice storm in Northern Michigan and for storms and floods in Oklahoma in April. Oliver Milman of The Guardian reported today that 15 NWS offices on the Gulf of Mexico, a region vulnerable to hurricanes, are understaffed after losing more than 600 employees. Miami’s National Hurricane Center is short five specialists. Thirty of the 122 NWS stations no longer have a meteorologist in charge, and as of June 1, seven of those 122 stations will not have enough staff to operate around the clock.
On May 5, the five living former NWS leaders, who served under both Democratic and Republican presidents, wrote a letter to the American people warning that the cuts threaten to bring “needless loss of life.” They urged Americans to “raise your voice” against the cuts.
Trump’s proposed 2026 budget calls for “terminating a variety of climate-dominated research, data, and grant programs” and cutting about 25% more out of NOAA’s funding.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has also suffered dramatic cuts as Trump has said he intends to push disaster recovery to the states. The lack of expertise is taking a toll there, too. Today staff members there said they were baffled after David Richardson, the head of the agency, said he did not know the United States has a hurricane season. (It does, and it stretches from June 1 to the end of November.) Richardson had no experience with disaster response before taking charge of FEMA.
Trump’s proposed cuts to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are even more draconian. On Friday, in a more detailed budget than the administration published in early May, the administration called for cuts of 43% to the NIH, about $20 billion a year. That includes cuts of nearly 40% to the National Cancer Institute. At the same time, the administration is threatening to end virtually all biomedical research at universities.
On Friday, May 23, the White House issued an executive order called “Restoring Gold Standard Science.” The order cites the COVID-19 guidance about school reopenings from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to claim that the federal government under President Joe Biden “used or promoted scientific information in a highly misleading manner.” (Schools closed in March 2020 under Trump.) The document orders that “[e]mployees shall not engage in scientific misconduct” and, scientists Colette Delawalla, Victor Ambros, Carl Bergstrom, Carol Greider, Michael Mann, and Brian Nosek explain in The Guardian, gives political appointees the power to silence any research they oppose “based on their own ‘judgment.’” They also have the power to punish those scientists whose work they find objectionable.
The Guardian authors note that science is “the most important long-term investment for humanity.” They recall the story of Soviet biologist Trofim Lysenko, who is a prime example of the terrible danger of replacing fact-based reality with ideology.
As Sam Kean of The Atlantic noted in 2017, Lysenko opposed science-based agriculture in the mid-20th century in favor of the pseudo-scientific idea that the environment alone shapes plants and animals. This idea reflected communist political thought, and Lysenko gained the favor of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin. Lysenko claimed that his own agricultural techniques, which included transforming one species into another, would dramatically increase crop yields. Government leaders declared that Lysenko’s ideas were the only correct ones, and anyone who disagreed with him was denounced. About 3,000 biologists whose work contradicted his were fired or sent to jail. Some were executed. Scientific research was effectively banned.
In the 1930s, Soviet leaders set out to “modernize” Soviet agriculture, and when their new state-run farming collectives failed, they turned to Lysenko to fix the problem with his new techniques. Almost everything planted according to his demands died or rotted. In the USSR and in China, which adopted his methods in the 1950s, at least 30 million people died of starvation.
“[W]hen the doctrines of science and the doctrines of communism clashed, he always chose the latter—confident that biology would conform to ideology in the end,” Kean said of Lysenko. He concludes: “It never did.”
—
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Garter and Silk
No, not the name of a pair of detectives with red hot chemistry solving murders, but two items somewhat relevant to this story.
The Right Hon. the Earl of Thornaby, K.G. is the holder of two very important titles in the UK. Right Honourable means he is a Privy Counsellor, a title given to high-ranking politicians and which gives them access to highly secret information. You retain membership for life unless you resign or do something really stupid.
But I'm going to talk more about a organisation with a somewhat silly name. K.G. stands for "Knight of the Garter", which means Thornaby is a member of the Order of the Garter. Covering England and Wales, this is the highest state honour you can get that does not involve the serious possiblity of dying getting it; the two above it being the Victoria and George Crosses. Scotland has the Order of the Thistle, just below it in precedence. Ireland had the Order of St Patrick; with no new member added since 1936 and the last surviving member dying in 1974, it is essentially defunct.
Tradition has it that the order was founded by Edward III in 1348, but records suggest it was actually slightly early. The most popular version of the name is that a woman at a dance in Calais had her garter fall down. As courtiers sniggered at the wardrobe malfunction, Edward picked up the garter, returned it and said "Honi soit qui mal y pense!", which is generally translated as "Shame on him who thinks evil of it". The story comes from the 1460s and may well have been conocted to explain why the order was named after what was then a feminine garment.
As you can see from the link, the blue belt has a prominent role in the royal coat of arms used outside of Scotland. The Scottish version has the Order of the Thistle's motto Nemo me impune lacessit or "No-one provokes me with impunity", which definitely sounds more stereotypically Scottish!
It also features in the simplified version of the arms used by the British government, featuring on all British passports.
Membership is limited to the monarch (of course currently Charles III), the Prince of Wales (Prince Williams) and 24 living members. There are also Royal Knights and Ladies, basically members of the Royal Family like Queen Camilla, the Duke of Edinburgh (Prince Edward) or the Duke of Kent (the other Prince Edward). In addition, there are Stranger Knights and Ladies, covering a good proportion of Europe's monarchs, active or retired. Both the former and current Japanese Emperors are there; Hirohito was thrown out in 1941 for obvious reasons, but reinstated in 1971.
The latter two do not count towards the total.
The current membership gives you an idea of the sort of people who get this honour. For example:
Former Cabinet Secretary Lord Butler of Brockwell, also known for the Butler Inquiry into intelligence used to justify the Iraq War.
Sir John Major and Sir Tony Blair, former Prime Ministers.
Lord King of Lothbury, former Governor of the Bank of England.
Marshal of the Royal Air Force The Lord Stirrup, former Chief of the Defence. Or Jock Stirrup.
Lord Lloyd-Webber. Yes, the musicals guy.
The 7th Marquess of Salisbury, also a former Cabinet minister. Descended from the PM at the time of "Knees of the Gods" and all the way back to William Cecil, chief minister to Elizabeth I; the Cecil family have long been friends with the royals.
There are currently three vacancies.
Until 1946, appointments to the Order were made by the monarch on advice from the government... with all the potential for patronage that would involve. Edward VII threw a major tantrum in 1902-1903 over giving it to Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar, the Shah of Iran, because the guy wasn't a Christian. An alternative design for the badge minus the Cross of St George was drawn up... and Bertie literally threw it out of the porthole of his yacht. He eventually had to back down though.
However, in 1946, Clement Attlee and Winston Churchill, at the time Prime Minister and Leader of the Opposition respectively, agreed that the honour would go back to the monarch. Elizabeth II would make them both Knights of the Garter.
****
So, onto the Silk part. "Kingsmill, Q.C." is a "Queen's Counsel", meaning he is a highly experienced lawyer appointed from the profession. You'd want one of these if you were up on a charge in the Old Bailey.
As a QC, he would have the right to wear a silk gown when in court, hence the nickname of "silks". At the time they were appointed by the monarch on advice from the government; since 2004 a selection panel makes the decision and it's a formality from there on in.
This story is set in 1893 when Queen Victoria was on the throne. When the reigning monarch is male, like at the moment, these people are known as King's Counsel or KC. The changeover is immediate; when Elizabeth II died in 2022, the head of the Bar Council signed off his tribute with "KC", causing some moderate confusion and necessitating a clarification on that matter:
The current Prime Minister, Sir Keir Starmer is a KC by virtue of having made a silk in 2002 as a barrister; he would later head the Crown Prosecution Service. His knighthood is the Order of the Bath. Others may make the jokes.
Sitting MPs who were barristers were made silks automatically until the 1990s; the top law officers of the government get the title as well. This is not necessarily a popular decision with other lawyers, especially if the person has little recent legal experience.
There was a BBC TV series that ran from 2011 to 2014 called Silk about a chamber of lawyers in London; including some QCs. The first season features Natalie Dormer before she joined the cast of Game of Thrones.
****
It is entirely possible to be a Silk Garter i.e. have both honours. There is currently one in fact - Baron Phillips of Worth Matravers, former President of our Supreme Court.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
HELSINKI (AP) — Estonia’s president formally appointed the Baltic country’s new government on Monday after lawmakers gave the green light to Prime Minister-designate Kristen Michal’s three-party coalition Cabinet.
Addressing the new Cabinet, which is to be sworn in Tuesday, President Alar Karis said the government's comfortable majority in the 101-seat Riigikogu, or Parliament, brings along “special responsibility."
Under a revised government program agreed on Friday, Michal’s first Cabinet will focus on improving Estonia’s ailing state finances, among other things, through hiking income tax and value added tax, in addition to raising the excise tax on alcohol, tobacco and gasoline.
In a 64-27 vote, lawmakers approved the proposed government of Michal, who is a seasoned politician but a first-time prime minister, from the governing center-right Reform Party.
The 49-year-old Michal, who earlier served as climate, justice and economics minister, was tapped to become Estonia’s new prime minister in late June, just days after his predecessor Kaja Kallas was chosen to be the European Union’s new foreign policy chief — a post she will take up later this year.
Kallas, Estonia’s first female head of government, formally resigned a week ago after which Michal started sounding possibilities for a broad-based coalition Cabinet. Following intense talks with parties last week, he decided to stick with the composition of Kallas’ outgoing government with senior partner Reform Party supported by the center-left Social Democrats and the liberal Estonia 200 party.
In addition to finances, the new Cabinet also pledges to continue investing strongly into defense and security in the small NATO nation of 1.3 million that borders Russia to the east.
In the key Cabinet posts, Margus Tsahkna from Estonia 200 will continue as foreign minister and Social Democrat Lauri Läänemets as interior minister. Reform’s veteran politician Jürgen Ligi makes a return to a government post and takes over the finance minister portfolio.
Michal has been active in the Reform Party, Estonia’s dominant party, since the late 1990s. He served as minister for climate affairs in Kallas’ last Cabinet, which took office in April 2023.
Michal also served as Reform’s party secretary and as a member of Tallinn City Council. He is set to take over Reform's chairmanship from Kallas in the fall.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Independent review panel releases final report on UNRWA
An independent panel released its much-awaited report on Monday about the UN relief agency for Palestine refugees (UNRWA), providing 50 recommendations and noting that Israeli authorities have yet to provide proof of their claims that UN staff are involved with terrorist organisations.
“Israel made public claims that a significant number of UNRWA employees are members of terrorist organisations. However, Israel has yet to provide supporting evidence of this,” according to the 54-page final report, Independent review of mechanisms and procedures to ensure adherence by UNRWA to the humanitarian principle of neutrality. The UN Secretary-General, who received the final report at the weekend, had appointed the independent review group days after Israel announced the allegations against UNRWA, which employees 30,000 people and serves 5.9 million Palestine refugees in the West Bank, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria and war-torn Gaza. The much-awaited final report found that UNRWA, established by the General Assembly in 1949, has extensive tools in place to ensure it remains unbiased in its work and routinely provides Israel with employee lists and “the Israeli Government has not informed UNRWA of any concerns relating to any UNRWA staff based on these staff lists since 2011.”
UNRWA has ‘most elaborate’ rules within UN system
“The set of rules and the mechanisms and procedures in place [at UNRWA] are the most elaborate within the UN system, precisely because it is such a difficult issue to work in such a complex and sensitive environment,” Catherine Colonna, former French foreign minister and head of the review group, told journalists at UN Headquarters following the report’s launch. “What needs to be improved will be improved. I’m confident that implementing these measures will help UNRWA deliver on its mandate.” Strongly encouraging "the international community to work side by side with the agency so it can perform its mission and overcome the challenges when they are there", she said “this is the purpose of the review.” In its nine-week-long review of existing mechanisms, the group conducted more than 200 interviews, met with Israeli and Palestinian authorities and directly contacted 47 countries and organisations, presenting a set of 50 recommendations on issues ranging from education to fresh vetting processes for recruiting staff.
Report steers new UN action plan
The report’s recommendations include creating a centralised “neutrality investigations unit”, rolling out an updated Code of Ethics and associated training to all staff, and identifying and implementing additional ways to screen UNRWA applicants at an early stage of the recruitment process. The report also suggested exploring the possibility of third-party monitoring for sensitive projects and establishing a framework with interested donors to ensure transparency. In a statement on Monday, the UN Secretary-General’s Spokesperson said the UN chief accepts the recommendations contained in Ms. Colonna’s report. He has agreed with Commissioner General Philippe Lazzarini that UNRWA, with the Secretary-General’s support, will establish an action plan to implement the recommendations contained in the final report.”
Claims financially hobbled UNRWA
According to the review group’s final report, Israel’s claims against UNRWA triggered the suspension of funding amounting to around $450 million. The direct impact of Israel’s allegations swiftly hobbled UNRWA’s ability to continue its work. Operating solely on voluntary donations, UNRWA saw major donors, including the United States, cancelling or suspending funds for the agency. In April, Washington banned funding for UNRWA until at least 2025, but other donors have pledged additional funding or restored their donations. The new report recommended increasing the frequency and strengthening the transparency of UNRWA’s communication with donors on its financial situation and on neutrality allegations and breaches. The review group suggested regular updates and “integrity briefings” for donors interested in supporting UNRWA on integrity and related issues.
[keep reading]
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In this excerpt from Superpredator: Bill Clinton’s Use and Abuse of Black America, we examine the Clintons’ involvement in the country’s affairs during Hillary Clinton’s time at the State Department.

Their actions in the country were shameful and shouldn’t be defended…
Bill and Hillary Clinton had long shared a personal interest in Haiti, dating back to the time of their honeymoon, part of which was spent in Port-au-Prince. In his autobiography, Bill says that his understanding of God and human nature were profoundly transformed when they witnessed a voodoo ceremony in which a woman bit the head off a live chicken. Hillary Clinton says the two of them “fell in love” with Haiti and they had developed a “deep connection” to the country. So when Hillary Clinton became Secretary of State in 2009, she consciously made the redevelopment of Haiti one of her top priorities. The country, she announced, would be a laboratory where the United States could “road-test new approaches to development,” taking advantage of what she termed “the power of proximity.” She intended to “make Haiti the proving ground for her vision of American power.” Hillary Clinton selected her own chief of staff, Cheryl Mills, to run the Haiti project.
Mills would be joined by Bill Clinton, who had been deputized by the U.N. as a “special envoy” to Haiti. Bill’s role was not well-defined, and Haitians were curious about what was in store. Mills wrote in an email to Hillary Clinton that Haitians saw Bill’s appointment as “a step toward putting Haiti in a protectorate or trusteeship status.” Soon, “joking that he must be coming back to lead a new colonial regime,” the Haitian media “dubbed him Le Gouverneur.”
The project was heavily focused on increasing Haiti’s appeal to foreign corporations. As Politico reported, Clinton’s experiment “had business at its center: Aid would be replaced by investment, the growth of which would in turn benefit the United States.”
One of the first acts in the new “business-centered” Haiti policy involved suppressing Haiti’s minimum wage. A 2009 Haitian law raised the minimum wage to 61 cents an hour, from 24 cents an hour previously. Haitian garment manufacturers, including contractors for Hanes and Levi Strauss, were furious, insisting that they were only willing to agree to a seven-cent increase. The manufacturers approached the U.S. State Department, who brought intense pressure to bear against Haitian President René Préval, working to “aggressively block” the 37-cent increase. The U.S. Deputy Mission Chief said a minimum-wage increase “did not take economic reality into account” and simply “appealed to the unemployed and underpaid masses.” But as Ryan Chittum of the Columbia Journalism Review explained, the proposed wage increase would have been only the most trivial additional expense for the American garment manufacturers:
As of last year Hanes had 3,200 Haitians making t-shirts for it. Paying each of them two bucks a day more would cost it about $1.6 million a year. Hanesbrands Incorporated made $211 million on $4.3 billion in sales last year, and presumably it would pass on at least some of its higher labor costs to consumers. Or better yet, Hanesbrands CEO Richard Noll could forego some of his rich compensation package. He could pay for the raises for those 3,200 t-shirt makers with just one-sixth of the $10 million in salary and bonus he raked in last year.
The truth of the “economic reality” was that the Haitian undergarment sector was hardly likely to become wildly less competitive as a result of the increase. The effort to suppress the minimum wage was not solely a Clinton project. It was also a “concerted effort on the part of Haitian elites, factory owners, free trade proponents, U.S. politicians, economists, and American companies.” But it was in keeping with the State Department’s priorities under Clinton, which prioritized creating a favorable business climate. It was that same familiar Clinton move “from aid to trade.” Bill Clinton’s program for Haitian development, designed by Oxford University economist Paul Collier, “had garment exports at its center.” Collier wrote that because of “propitious” factors like “poverty and [a] relatively unregulated labor market, Haiti has labor costs that are fully competitive with China.” But the Clintons’ role in Haiti would soon expand even further. In 2010, the country was struck by the worst earthquake in its history. The disaster killed 160,000 people and displaced over 1.5 million more.
(The consequences of the earthquake were exacerbated by the ruined state of the Haitian food economy, plus the concentration of unemployed Haitian farmers in Port-au-Prince.) Bill Clinton was soon put in charge of the U.S.-led recovery effort. He was appointed to head the Interim Haiti Recovery Commission (IHRC), which would oversee a wide range of rebuilding projects.
At President Obama’s request, Clinton and George W. Bush created the “Clinton-Bush Haiti Fund,” and began aggressively fundraising around the world to support Haiti in the earthquake’s aftermath. (With Hillary Clinton as Secretary of State overseeing the efforts of USAID, the Clintons’ importance to the recovery could not be overstated; Bill’s appointment meant that “at every stage of Haiti’s reconstruction—fundraising, oversight and allocation—a Clinton was now involved.”
Clinton announced that Haiti would be a laboratory where the United States could road-test new approaches to development, taking advantage of “the power of proximity.”
Despite appearances, the Clinton-Bush fund was not focused on providing traditional relief. As they wrote, “[w]hile other organizations in Haiti are using their resources to deliver immediate humanitarian aid, we are using our resources to focus on long-term development.” While the fund would advertise that “100% of donations go directly to relief efforts,” Clinton and Bush adopted an expansive definition of “relief” efforts, treating luring foreign investment and jobs as a crucial part of earthquake recovery. On their website, they spoke proudly of what the New York Daily News characterized as a program of “supporting longterm programs to develop Haiti’s business class.”
The strategy was an odd one. Port-au-Prince had been reduced to ruin, and Haitians were crowded into filthy tent cities, where many were dying of a cholera outbreak (which had itself been caused by the negligence of the United Nations). Whatever value building new garment factories may have had as a longterm economic plan, Haitians were faced with somewhat more pressing concerns like the basic provision of shelter and medicine, as well as the clearing of the thousands of tons of rubble that filled their streets.
The Clinton-led recovery was a disaster. A year after the earthquake, a stinging report from Oxfam singled out Clinton’s IHRC as creating a “quagmire of indecision and delay” that had made little progress toward successful earthquake recovery. Oxfam found that:
…less than half of the reconstruction aid promised by international donors has been disbursed. And while some of that money has been put toward temporary housing, almost none of the funds have been used for rubble removal.
Instead, the Clinton Foundation, IHRC, and State Department created what a Wall Street Journal writer called “a mishmash of low quality, poorly thought-out development experiments and half-finished projects.” A Haitian IHRC members lamented that the commission had produced “a disparate bunch of approved projects. . . [that] do not address as a whole either the emergency situation or the recovery, let alone the development, of Haiti.” A 2013 investigation by the Government Accountability Office found that most money for the recovery was not being dispersed, and that the projects that were being worked on were plagued by delays and cost overruns. Many Clinton projects were extravagant public relations affairs that quickly fizzled. For example, The Washington Post reported that:
…[a] 2011 housing expo that cost more than $2 million, including $500,000 from the Clinton Foundation, was supposed to be a model for thousands of new units but instead has resulted in little more than a few dozen abandoned model homes occupied by squatters.
Other Clinton ventures were seen as “disconnected from the realities of most people in the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere.” Politico reported that many Clinton projects “have primarily benefited wealthy foreigners and the island’s ruling elite, who needed little help to begin with.” For example, “the Clinton Bush Haiti Fund invested more than $2 million in the Royal Oasis Hotel, where a sleek suite with hardwood floors costs more than $200 a night and the shops sell $150 designer purses and $120 men’s dress shirts.”

Predictably, the Royal Oasis didn’t do an especially roaring trade; The Washington Post reported that “[o]ne recent afternoon, the hotel appeared largely empty, and with tourism hardly booming five years after the quake, locals fear it may be failing.”
In a country with a 30-cent minimum wage, investing recovery dollars in a luxury hotel was not just offensive, but economically daft.
Sometimes the recovery projects were accused not only of being pointless, but of being downright harmful. For instance, Bill Clinton had proudly announced that the Clinton Foundation would be funding the “construction of emergency storm shelters in Léogâne.” But an investigation of the shelters that the Foundation had actually built found that they were “shoddy and dangerous” and full of toxic mold.
The Nation discovered, among other things, that the temperature in the shelters reached over 100 degrees, causing children to experience headaches and eye irritations (which may have been compounded by the mold), and that the trailers showed high levels of carcinogenic formaldehyde, linked to asthma and other lung diseases.
The Clinton Foundation had subcontracted the building of the shelters to Clayton Homes, a firm that had already been sued in the United States by the Federal Emergency Management Administration (FEMA) for “having provided formaldehyde-laced trailers to Hurricane Katrina victims.” (Clayton Homes was owned by Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway, and Buffett had been a longstanding major donor to the Clinton Foundation.)
The Nation’s investigation reported on children whose classes were being held in Clinton Foundation trailers. Their semester had just been cut short, and the students sent home, because the temperature in the classrooms had grown unbearable. The misery of the students in the Clinton trailers was described:
Judith Seide, a student in Lubert’s sixth-grade class [explained that] she and her classmates regularly suffer from painful headaches in their new Clinton Foundation classroom. Every day, she said, her “head hurts and I feel it spinning and have to stop moving, otherwise I’d fall.” Her vision goes dark, as is the case with her classmate Judel, who sometimes can’t open his eyes because, said Seide, “he’s allergic to the heat.” Their teacher regularly relocates the class outside into the shade of the trailer because the swelter inside is insufferable.
Sitting in the sixth-grade classroom, student Mondialie Cineas, who dreams of becoming a nurse, said that three times a week the teacher gives her and her classmates painkillers so that they can make it through the school day. “At noon, the class gets so hot, kids get headaches,” the 12-year-old said, wiping beads of sweat from her brow. She is worried because “the kids feel sick, can’t work, can’t advance to succeed.”
The most notorious post-earthquake development project, however, was the Caracol industrial park. The park was pitched as a major job creator, part of the goal of helping Haiti “build back better” than it was before.
The State Department touted the prospect of 100,000 new jobs for Haitians, with Hillary Clinton promising 65,000 jobs within five years. The industrial park followed the Clintons’ preexisting development model for Haiti: public/private partnerships with a heavy emphasis on the garment industry.
Even though there were still hundreds of thousands of evacuees living in tents, the project was based on “the more expansive view that, in a desperately poor country where traditional foreign aid has chronically failed, fostering economic development is as important as replacing what fell down.” Much of the planning was focused on trying to lure a South Korean clothing manufacturer to set up shop there, by plying them with U.S. taxpayer funding.
The Caracol project was “the centerpiece” of the U.S.’s recovery effort. A gala celebrating its opening featured the Clintons and Sean Penn, and it was treated as the emblem of the new, “better” Haiti, that would demonstrate the country’s commitment to being “open for business.” In order to build the park, hundreds of poor farmers were evicted from their land, so that millions of dollars could be spent transforming it.
But the project was a terrible disappointment. After four years, it was only operating at 10% capacity, and the jobs had failed to materialize:
Far from 100,000 jobs—or even the 60,000 promised within five years of the park’s opening— Caracol currently employs just 5,479 people full time. That comes out to roughly $55,000 in investment per job created so far; or, to put it another way, about 30 times more per job than the average [Caracol] worker makes per year. The park, built on the site of a former U.S. Marine-run slave labor camp during the 1915-1934 U.S. occupation, has the best-paved roads and manicured sidewalks in the country, but most of the land remains vacant.
Most of the seized farmland went unused, then, and even for the remaining farmers, “surges of wastewater have caused floods and spoiled crops.” Huge queues of unemployed Haitians stood daily in front of the factory, awaiting jobs that did not exist. The Washington Post described the scene:
Each morning, crowds line up outside the park’s big front gate, which is guarded by four men in crisp khaki uniforms carrying shotguns. They wait in a sliver of shade next to a cinder-block wall, many holding résumés in envelopes. Most said they have been coming every day for months, waiting for jobs that pay about $5 a day. From his envelope, Jean Mito Palvetus, 27, pulled out a diploma attesting that he had completed 200 hours of training with the U.S. Agency for International Development on an industrial sewing machine. “I have three kids and a wife, and I can’t support them,” he said, sweating in the hot morning sun. “I have a diploma, but I still can’t get a job here. I still have nothing.”
For some, the Caracol project perfectly symbolized the Clinton approach: big promises, an emphasis on sweatshops, incompetent management, and little concern for the actual impact on Haitians. “Caracol is a prime example of bad help,” as one Haiti scholar put it. “The interests of the market, the interest of foreigners are prioritized over the majority of people who are impoverished in Haiti.”
But, failure as it may have been, the Caracol factory was among the more successful of the projects, insofar as it actually came into existence.
A large amount of the money raised by Bill Clinton after the earthquake, and pledged by the U.S. under Hillary Clinton, simply disappeared without a trace, its whereabouts unknown.
As Politico explained:
Even Bill’s U.N. Office of the Special Envoy couldn’t track where all of [it] went—and the truth is that still today no one really knows how much money was spent “rebuilding” Haiti. Many initial pledges never materialized. A whopping $465 million of the relief money went through the Pentagon, which spent it on deployment of U.S. troops—20,000 at the high water mark, many of whom never set foot on Haitian soil.
That money included fuel for ships and planes, helicopter repairs and inscrutables such as an $18,000 contract for a jungle gym… Huge contracts were doled out to the usual array of major contractors, including a $16.7 million logistics contract whose partners included Agility Public Warehousing KSC, a Kuwaiti firm that was supposed to have been blacklisted from doing business with Washington after a 2009 indictment alleging a conspiracy to defraud the U.S. government during the Iraq War.
The recovery under the Clintons became notorious for its mismanagement. Clinton staffers “had no idea what Haiti was like and had no sensitivity to the Haitians.” They were reportedly rude and condescending toward Haitians, even refusing to admit Haitian government ministers to meetings about recovery plans.
While the Clintons called in high-profile consulting firms like McKinsey to draw up plans, they had little interest in listening to Haitians themselves.
The former Haitian prime minister spoke of a “weak” American staff who were “more interested in supporting Clinton than helping Haiti.”
One of those shocked by the failure of the recovery effort was Chelsea Clinton, who wrote a detailed email to her parents in which she said that while Haitians were trying to help themselves, every part of the international aid effort, both governmental and nongovernmental, was falling short. “The incompetence is mind numbing,” she wrote. Chelsea produced a detailed memorandum recommending drastic steps that needed to be taken in order to get the recovery on track. But the memo was kept within the Clinton family, released only later under a Freedom of Information Act disclosure of Hillary’s State Department correspondence.
If it had come out at the time, as Haiti journalist Jonathan Katz writes, it “would have obliterated the public narrative of helpful outsiders saving grateful earthquake survivors that her mother’s State Department was working so hard to promote.”
The Clintons’ Haiti recovery ended with a whimper. The Clinton-Bush Haiti Fund distributed the last of its funds in 2012 and disbanded, without any attempt at further fundraising. The IHRC “quietly closed their doors” in October of 2011, even though little progress had been made. As the Boston Review’s Jake Johnston explained, though hundreds of thousands remained displaced, the IHRC wiped its hands of the housing situation:
[L]ittle remained of the grand plans to build thousands of new homes. Instead, those left homeless would be given a small, one-time rental subsidy of about $500. These subsidies, funded by a number of different aid agencies, were meant to give private companies the incentive to invest in building houses. As efforts to rebuild whole neighborhoods faltered, the rental subsidies turned Haitians into consumers, and the housing problem was handed over to the private sector.
The Clintons themselves simply stopped speaking about Haiti..
After the first two years, they were “nowhere to be seen” there, despite Hillary’s having promised that her commitment to Haiti would long outlast her tenure as Secretary of State. Haiti has been given little attention during Hillary Clinton’s presidential campaign, even though the Haiti project was ostensibly one of great pride for both Clintons.
The widespread consensus among observers is that the Haiti recovery, which TIME called the U.S.’s “compassionate invasion,” was a catastrophically mismanaged disappointment. Jonathan Katz writes that “it’s hard to find anyone these days who looks back on the U.S.-led response to the January 12, 2010, Haiti earthquake as a success.” While plenty of money was channeled into the country, it largely went to what were “little more than small pilot projects—a new set of basketball hoops and a model elementary school here, a functioning factory there.”
The widespread consensus is that the Haiti recovery was a catastrophically mismanaged disappointment.
The end result has been that little has changed for Haiti. “Haitians find themselves in a social and economic situation that is worse than before the earthquake,” reports a Belgian photojournalist who has spent 10 years in Haiti:
Everyone says that they’re living in worse conditions than before… When you look at the history of humanitarian relief, there’s never been a situation when such a small country has been the target of such a massive influx of money and assistance in such a short span of time… On paper, with that much money in a territory the size of Haiti, we should have witnessed miracles; there should have been results.
“If anything, they appear worse off,” says Foreign Policy of Haiti’s farmers. “I really cannot understand how you could raise so much money, put a former U.S. president in charge, and get this outcome,” said one Haitian official. Indeed, the money donated and invested was extraordinary. But nobody seems to know where it has gone.
Haitians direct much of the blame toward the Clintons.
As a former Haitian government official who worked on the recovery said, “[t]here is a lot of resentment about Clinton here. People have not seen results. . .. They say that Clinton used Haiti.” Haitians “increasingly complain that Clinton-backed projects have often helped the country’s elite and international business investors more than they have helped poor ‘Haitians.” There is a “suspicion that their motives are more to make a profit in Haiti than to help it.” And that while “striking a populist pose, in practice they were attracted to power in Haiti.”
But perhaps we should be more forgiving of the Clintons’ conduct during the Haitian recovery. After all, instead of doing true harm, the Clintons simply failed to do much good. And perhaps it’s better to have a luxury hotel than not to have one, better to have a few jobs than none at all. Thanks to Bill Clinton, there’s a gleaming new industrial park, albeit one operating at a fraction of its capacity.
Yet it’s a mistake to measure Clinton against what would have happened if the United States had done nothing at all for Haiti. The question is what would have happened if a capable, nonfamous administrator, rather than a globetrotting narcissist, had been placed in charge.
Tens of millions of dollars were donated toward the Haiti recovery by people across the world; it was an incredible outpouring of generosity. The squandering of that money on half-baked development schemes (mainly led by cronies), and the ignoring of Haitians’ own demands, mean that Clinton may have caused considerable harm through his failure.
Plenty of people died in tent cities that would not have died if the world’s donations had been used effectively
Democrats have bristled at recent attempts by Donald Trump to criticize Hillary Clinton over her record in Haiti. Jonathan Katz, whose in-depth reporting from Haiti was stingingly critical of the Clintons, has now changed his tune, insisting that we all bear the responsibility for the failed recovery effort. When Trump accused the Clintons of squandering millions building “a sweatshop” in Haiti in the form of the Caracol park, media fact-checkers quickly insisted he was spewing Pinocchios.
The Washington Post said that while Clinton Foundation donors may have financially benefited from the factory-building project, they benefited “writ large” rather than “directly.” The Post cited the words of the factory’s spokesman as evidence that the factory was not a sweatshop, and pointed out that Caracol workers earned at least “minimum wage” (failing to mention that minimum wage in Haiti remains well under a dollar). PolitiFact also rated the sweatshop claim “mostly false,” even though Katz notes “long hours, tough conditions, and low pay” at the factory and PolitiFact acknowledges the “ongoing theft of legally-earned wages.”
Defending the Clintons’ Haiti record is an impossible endeavor, one Democrats should probably not bother attempting. As the Center for Economic and Policy Research, which has studied the recovery, noted, when it comes to the Clinton-led recovery mission, “it’s hard to say it’s been anything other than a failure.” Haitians are not delusional in their resentment of the Clintons; they have good reason to feel as if they were used for publicity, and discarded by the Clintons when they became inconvenient.
None of this means that one should vote for Donald Trump for president. His tears for Haiti are those of a highly opportunistic crocodile, and his interest in the country’s wellbeing began at the precise moment that it could be used a bludgeon with which to beat his political opponent. As we have previously noted in this publication, one does not need to be convinced that Hillary Clinton is an honorable person in order to be convinced that she is the preferable candidate. It is important, however, not to maintain any illusions, not to stifle or massage the truth in the service of short-term electoral concerns. It remains simultaneously true that a Clinton presidency is our present least-worst option and that what the Clintons did to Haiti was callous, selfish, and indefensible.
More on Clinton involvement in Haiti can be found in Superpredator: Bill Clinton’s Use and Abuse of Black America.
#What The Clintons Did To Haiti#Haiti#clinton foundation#theft of a nation#superpredator#Superpredator: Bill Clinton’s Use and Abuse of Black America.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Full-scale Pre-poll Preparations Underway as ECI Team Plans Visit to State from October 3

Preparations for the upcoming Assembly elections in the state are in full swing, as the Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) Vikas Raj announced that a team from the Election Commission of India (ECI) is scheduled to visit the state from October 3. During this three-day tour, the ECI team will engage with various stakeholders, assess the state's poll preparedness, and interact with voters.
Speaking at the inauguration of the media center at BRKR Bhavan, Vikas Raj stated that the ECI team would hold meetings with the CEO's office, political parties, chief secretary, director general of police (DGP), district collectors, district police officials, and other key stakeholders. More than 20 agencies, including both Central and State entities, have been identified for the implementation of the model code of conduct, and a meeting with these agencies is scheduled.
The CEO also provided updates on electoral rolls, stating that almost 15 lakh additions have been made since January 2023, and around 3.38 lakh voter names were removed during the Special Summary Revision of Rolls. The upcoming elections will witness the participation of nearly 6.99 lakh new voters, with efforts underway to encourage the enrollment of more women voters through active campaigns.
Once the final electoral rolls are published early next month, the focus will shift to the districts, involving tasks such as appointing presiding officers and polling officers, identifying strongrooms, and preparing polling stations. Officials will undergo training to ensure the smooth conduct of the elections.
Vikas Raj emphasized that the electoral rolls are currently robust, addressing complaints of bogus votes made by some political leaders. He assured a thorough investigation into each complaint, with details to be shared with complainants and representatives of all political parties.
You May also Like to Read About Google Ads Agency in Dubai
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Judd Legum at Popular Information:
Project 2025 is a radical blueprint for a potential second Trump administration, spearheaded by the right-wing Heritage Foundation. The plan calls for withdrawing approval for the abortion pill, banning pornography, slashing corporate taxes, abolishing the Department of Education, replacing thousands of experienced federal workers with political appointees, imposing a "biblically based… definition of marriage and families," and placing the Justice Department and other independent agencies under the direct control of the president. These and other provisions of Project 2025 are quite unpopular. As Project 2025 has gained notoriety — thanks to actor Taraji P. Henson and others — Trump has sought to distance himself from the effort. On July 5, Trump posted on Truth Social that he knows "nothing about Project 2025," has "no idea who is behind it," and has "nothing to do with them."
This is false. The co-editors of Project 2025, Paul Dans and Steven Groves, both held high-ranking positions in the Trump administration. Under Trump, Dans served as Chief of Staff at the Office of Personnel Management, the agency responsible for staffing the federal government, and was a senior advisor at the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). Groves served Trump in the White House as Deputy Press Secretary and Assistant Special Counsel. Project 2025's two associate directors, Spencer Chretien and Troup Hemenway, are also tightly connected with Trump. Chretien was Special Assistant to President Donald J. Trump and Associate Director of Presidential Personnel, "helping to identify, recruit, and place hundreds of political appointees at all levels of government." Previously, Trump appointed Chretien to a position at HUD. Hemenway also served as an Associate Director of Presidential Personnel and previously worked on Trump's 2016 campaign and Trump's 2016 transition team.
Project 2025's 922-page policy agenda has 30 chapters and 34 authors. Twenty-five of Project 2025's authors served as members of the Trump administration. Another Project 2025 author, Stephen Moore, was nominated by Trump to the Federal Reserve but forced to withdraw "over his past inflammatory writings about women." Further, William Walton, the co-author of the chapter on the Department of the Treasury, was a key member of Trump's transition team. All told, of the 38 people responsible for writing and editing Project 2025, 31 were appointed or nominated to positions in the Trump administration and transition. In other words, while Trump claims he has "nothing to do" with the people who created Project 2025, over 81% had formal roles in his first administration.
Here is the complete list of the 31 authors and editors of Project 2025 that have formal connections to the Trump administration.
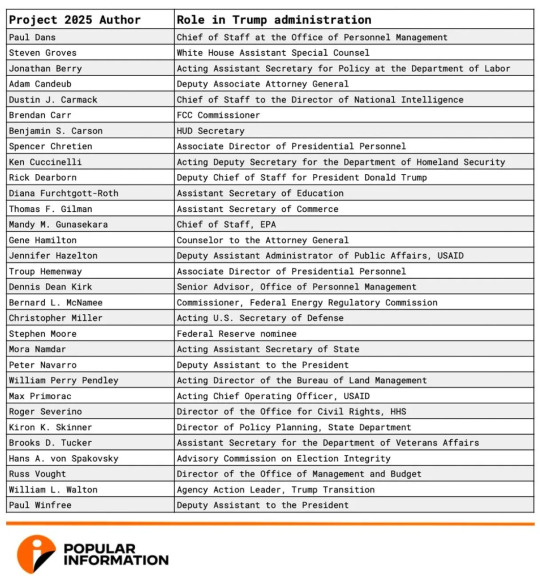
In addition to a detailed policy agenda, Project 2025 also involves the training and recruitment of political appointees for a potential second Trump administration. One key component of this effort is the "Presidential Administration Academy," which Heritage bills as "a one-of-a-kind educational and skill-building program designed to prepare and equip future political appointees now to be ready on Day One of the next conservative Administration." Among the program instructors is Karoline Leavitt, the national press secretary for the 2024 Trump campaign and an assistant press secretary during the Trump administration. Leavitt co-teaches a video course on "The Art of Professionalism." She also appears in a promotional video for the academy.
Also appearing in the video is top Trump advisor Stephen Miller. Despite his role in the academy, Miller claims he has "never been involved with Project 2025." Miller's organization, America First Legal, is a member of the Project 2025 advisory board.
Popular Information exposes Donald Trump's deranged lie that he has "nothing to do with them", as 31 of the 38 authors of Project 2025 were in the Trump Administration in some capacity, including Paul Dans, Peter Navarro, Stephen Moore, Ken Cuccinelli, and Russ Vought.
See Also:
Right Wing Watch: Trump Team Lies About Project 2025 Reveal its Potential to Cost Him the Election
MMFA: Donald Trump on Heritage’s Kevin Roberts, who oversees Project 2025: “He’s going to be so incredible”
#Project 2025#Donald Trump#The Heritage Foundation#Truth Social#Taraji P. Henson#Troup Hemenway#Spencer Chretien#Paul Dans#Karoline Leavitt#Stephen Miller#Steven Groves#Trump Administration#Stephen Moore#Roger Severino#Russ Vought#Trump Administration II
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Texas public college and university presidents will be able to take control of their faculty governing bodies if Gov. Greg Abbott signs a bill now before him.
“Shared governance structures may not be used to obstruct, delay, or undermine necessary institutional reforms or serve as a mechanism for advancing ideological or political agendas,” says Senate Bill 37, which the Republican-dominated State Legislature passed May 31. Multiple states have considered GOP bills targeting shared governance, but SB 37 is a sweeping example.
It says that “only the governing board of an institution of higher education may establish a faculty council or senate.”
“The board of regents has to decide whether or not there will even be one, that’s problem No. 1,” said Brian Evans, president of the Texas American Association of University Professors–American Federation of Teachers Conference.
If a college or university board decides to keep a faculty governing body, the institution’s president gets to prescribe how it conducts meetings. The president also gets to pick the “presiding officer, associate presiding officer, and secretary.”
In addition, unless the college or university’s board decides otherwise, faculty senates and councils must shrink to no more than 60 members.
Those remaining 60 would have to include at least two representatives from each of the colleges and schools that comprise the institution—including what the bill describes vaguely as “one member appointed by the president or chief executive officer of the institution” and the rest elected by the faculty of the particular school or college. This could mean that half of a faculty senate or council would be chosen by the president if an institution’s board doesn’t grant exemptions from these requirements.
Andrew Klein, speaker of the Texas A&M University Faculty Senate, said the biggest concern among his 122 senators is the 60-senator limit, which will take effect unless the Texas A&M System Board of Regents grants an exemption. Klein questioned how a senate that small could represent 4,300 faculty across the university, and how a requirement for at least two representatives per college or school would provide fair representation when the College of Arts and Sciences has over 800 faculty, compared to a number in the low double-digits at the School of Engineering Medicine.
“With 60 people, that’s not enough different viewpoints that can be brought to bear on questions, given our complexity,” Klein said.
In another blow to faculty control of their own governance bodies, SB 37 establishes term limits for faculty senate and council members—and allows presidential appointees to serve longer than the elected members. The presidential appointees would get to serve six consecutive years before having to take two off, while the elected members could only serve two years before the mandatory two-year break.
A faculty senate or council member could also have their seat stripped at any time; the bill says the provost can recommend to the president that members be “immediately removed” for failing to attend meetings or conduct their “responsibilities within the council’s or senate’s parameters” or for “similar misconduct.”
“It’s no longer an elected faculty voice,” Evans said. “It’s controlled by the administration.”
The bill still says that faculty senates or councils can hold votes of no confidence in administrators. But its language elsewhere stresses that faculty governance has no final say over anything.
“A faculty council or senate is advisory only and may not be delegated the final decision-making authority on any matter,” the bill says. (The faculty senate leaders at Texas A&M University at College Station and the University of Houston said their bodies are already advisory.)
Ultimately, the bill defines shared governance in a way that stresses the supremacy of college and university boards, which are composed of gubernatorial appointees who are confirmed by the state Senate.
“The governing board of the institution exercises ultimate authority and responsibility for institutional oversight, financial stewardship, and policy implementation, while allowing for appropriate consultation with faculty, administrators, and other stakeholders on matters related to academic policy and institutional operations,” the bill says. “The principle of shared governance may not be construed to diminish the authority of the governing board to make final decisions in the best interest of the institution, students, and taxpayers.”
In addition to overhauling faculty senates, SB 37 would require the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board to establish an advisory committee that would review general education requirements statewide and be responsible for considering methods for “condensing the number of general education curriculum courses required.” Furthermore, colleges and universities would be required to review minors and certificate programs every five years “to identify programs with low enrollment that may require consolidation or elimination,” according to the bill.
Dan Price, president-elect of the University of Houston Faculty Senate, said this goes “hand in hand” with the Legislature’s efforts to diminish faculty senate power.
“The ways in which the humanities could be really transformed, I think that’s not well considered,” he said.
‘Woke College Professors’
Will Abbott, a Republican, sign this into law? His press secretary, Andrew Mahaleris, didn’t directly answer in an email to Inside Higher Ed.
“More than 1,000 pieces of legislation have been sent to Governor Abbott’s desk and he is closely reviewing them all,” he wrote.
But Mahaleris’s email indicated that the governor is strongly in favor of reducing faculty power.
“Governor Abbott was clear in his State of the State address: Woke college professors have too much influence over who is hired to educate our kids,” Mahaleris wrote. “Texas needs legislation that prohibits professors from having any say over employment decisions.”
Lt. Gov. Dan Patrick, who leads the Texas Senate, also touted the bill. Upon the Legislature’s adjournment, he issued a statement calling it the “Senate’s most conservative and successful legislative session.” He attributed that in part to SB 37, which he said was about “reforming liberal faculty control over universities.”
The author of the introduced version of the bill, Republican senator Brandon Creighton, didn’t respond to Inside Higher Ed’s requests for an interview or to written questions last week.
For faculty, Abbott’s decision on the bill is merely the first step. If he signs it, they’ll still be looking to their institutions’ boards to decide whether, and how, their faculty senates and councils can continue to operate.
“I really don’t have a good idea of what we’re going to look like next year,” said Klein, the speaker of the Texas A&M University Faculty Senate.
Price, the University of Houston Faculty Senate president-elect, said he thinks the bill is partly “based on a misunderstanding of what faculty senates had been doing. It assumed that faculty senates were run much more like unions.” He said there was “a lot of animosity toward faculty senates.”
“We’ve got work to do to make sure that the public sees the value of faculty,” Price said, along with the values of open inquiry and “faculty having real and influential voices and choice of curriculum.”
4 notes
·
View notes