#1099 deadlines
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Easy Online 1099 Filing Method
Filing 1099s online can be a straightforward process. Here's a simple step-by-step guide to help you file 1099s online:
1. Gather the necessary information: Collect all the required information for each recipient, including their name, address, Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN), and the amount paid to them during the tax year.
2. Choose an online filing service: There are various online platforms and tax software available that can help you file 1099s electronically. Look for a reputable service that is user-friendly and provides secure transmission of sensitive data.
3. Create an account: Sign up for an account on the chosen online filing service. You may need to provide some basic information to set up your account.
4. Enter recipient information: Enter the details of each recipient and the corresponding payment amounts into the online form. Most services provide an intuitive interface to guide you through this process.
5. Verify the information: Double-check all the entered information to ensure its accuracy. Filing incorrect information can lead to penalties, so it's essential to review everything carefully.
6. Review IRS rules and deadlines: Familiarize yourself with the IRS rules and deadlines for filing 1099 forms. Make sure you complete the filing before the due date to avoid any late filing penalties.
7. Submit the 1099 forms: Once you've reviewed and confirmed all the information, submit the 1099 forms electronically through the online service. The platform will typically have a button or option to submit the forms to the IRS directly.
8. Pay the filing fee (if applicable): Some online services may charge a small fee for filing 1099s electronically. If there is a fee, pay it using the provided payment method.
9. Keep a copy for your records: After filing, save a copy of the filed 1099 forms for your records. This is essential for your own accounting and as a backup in case any issues arise in the future.
10. Notify recipients: Inform your recipients that you have filed 1099s reporting their income. They will need this information when they file their own taxes.
Remember, if you're unsure about any aspect of filing 1099s, it's always a good idea to consult with a tax professional or accountant for guidance. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
#1099 online filing#1099 online#1099 filing#efile 1099 form#irs form 1099#ors form 1099 online filing#irs rules#1099 penalties#1099 deadlines#1099 nec#1099 misc#1099 div#1099 int#1099 k#1099 r#1099 a#1099 s
0 notes
Text
#Tax filing for freelancers#Freelance tax deductions#Self-employed tax tips#Maximize tax returns freelancers#Freelancer tax guide#Tax tips for self-employed#Independent contractor taxes#Minimize tax stress#Tax filing deadlines freelancers#Business expense deductions#Freelance income reporting#Home office tax deductions#Estimated tax payments freelancers#Tax software for freelancers#Tax planning for freelancers#1099 tax forms guidance#Self-employed retirement deductions#Health insurance deductions freelancers#Tax credits for freelancers#Record keeping for freelance taxes
0 notes
Text
Navigating Tax Season: Deciphering the 1098 vs. 1099 Forms
For small business owners, tax time often descends like a fog, obscuring the clarity of financial records and demanding sudden mastery of arcane IRS forms. Among these, Form 1098 and Form 1099 stand out as essential instruments for recording and reporting various financial transactions. Understanding the distinctions between these two forms is crucial for ensuring compliance and accurate reporting. In this comprehensive exploration, we will demystify the differences between Form 1098 and Form 1099, providing you with the knowledge to sail through tax season unscathed.
Form 1098: A Mortgage Interest Report
Form 1098 is a document issued by lenders indicating mortgage interest payments made by a taxpayer over the course of the year. It is crucial for homeowners who seek to claim deductions for mortgage interest on their federal tax returns. This form can also be applicable to small business owners who utilize real estate within their operations.
What Does Form 1098 Cover?
Form 1098 covers reported interest payments on a mortgage including if a taxpayer paid more than $600 in interest during the tax year. This form is essential, as it enables taxpayers to minimize their taxable income by claiming deductions on their mortgage interest.
Who Receives Form 1098?
The borrower of a mortgage receives Form 1098 from their lender, which could be a bank, credit union, or mortgage company. It's imperative for the lender to provide a copy of Form 1098 to both the borrower and the IRS.
Form 1099: Diverse Vendor Payments
Form 1099, on the other hand, is a more versatile creature. It covers a broad range of payments made by businesses to vendors, contractors, and freelancers. This form is used to report various types of income not found on W-2 forms, which are typically used for salaried employees.
What Does Form 1099 Include?
Form 1099 encompasses several different types, each representing a specific category of income. The most common types of Form 1099 include:
1099-NEC for non-employee compensation
1099-K for payments received through card transactions or third-party networks
1099-DIV for dividends and distributions
1099-INT for interest income
1099-MISC for miscellaneous income
Who Receives Form 1099?
Entities that pay $600 or more in the course of their trade or business to an individual or unincorporated business must issue a Form 1099 to those recipients as well as report the information to the IRS.
Key Differences Between 1099 and 1098
We can now turn to the principal distinctions between 1098 and 1099 forms. Knowing these differences is vital when categorizing payments or recording mortgage interest for tax purposes.
Purpose of Each Form
Form 1098 is specifically designed to report mortgage interest, facilitating the deduction process for homeowners. It has a clear and narrow purpose.
Form 1099, on the other hand, is broader in scope. It's multifunctional, covering a variety of transactions ranging from rental income to prizes and awards.
Information Provided
Form 1098 shows deductible mortgage interest—this amount is detailed and includes the mortgage loan principle, aggregate of real estate taxes, and any points you paid during the tax year.
In contrast, Form 1099 provides a wide array of information depending on the specific 1099 type, ranging from compensation to interest and dividends.
Recipients of Each Form
The 1098 form is solely for individuals who have paid or received mortgage interest. It is not issued to businesses or for services rendered.
Form 1099, however, can be issued to any individual who has received reportable income from business transactions, regardless of whether they are an employee or contractor.
Reporting Timeline
Typically, businesses are required to provide 1099 forms to recipients by January 31. For Form 1098, the deadline is the same as for the IRS filing, typically the following February 15.
Utilizing Forms 1098 and 1099 for Small Business Success
For small business owners, the effective use of Forms 1098 and 1099 can be a strategic part of their financial management. Whether leveraging the mortgage interest deduction to reduce personal taxable income or properly reporting various streams of income through Form 1099, these forms play a vital role in tax liability.
Understanding and attention to detail when dealing with Form 1098 and the various 1099 types can ensure that you are not only compliant but also making the most of any available tax benefits. Engaging with knowledgeable tax professionals can further enhance your tax season experience, allowing you to focus on the growth and success of your business.
In conclusion, these seemingly arcane forms—1098 and 1099—align with critical elements of personal and business financial transactions. They offer both the relief of tax deductions and the rigor of detailed income reporting. By ensuring you understand their roles and applications, you will arm yourself with the knowledge necessary not only to survive but to thrive during tax season.
@erastaffingsolutions
#erastaffingsolutions#era#hrsolution#workfocesolution#aorservice#1098vs1099#1099vs1098#differencebetween1098and1099#differencebetween1099and1098#1099formvs1098
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Preparing For Tax Season: A Checklist For Business Owners

As tax season approaches, business owners must prepare diligently to ensure a smooth and accurate filing process. By taking a proactive approach and organizing financial records in advance, entrepreneurs can minimize stress, reduce the risk of errors, and potentially identify opportunities for tax savings.
Here's a comprehensive checklist to guide business owners in preparing for the upcoming tax season.
Organize Financial Records: Start by organizing all financial records, including income statements, expense receipts, invoices, and bank statements. Keeping these documents in an orderly manner will streamline the tax preparation process and help ensure that nothing is overlooked.
Review Business Structure: Assess whether the current business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation) is still the most advantageous for your situation. Changes in business operations or financial circumstances may warrant a reevaluation of your business structure for optimal tax efficiency.
Update Employee Information: Ensure that employee information is up-to-date. Verify Social Security numbers, addresses, and other relevant details. This information is critical for accurate payroll reporting and compliance with tax regulations.
Check Compliance with Tax Law Changes: Stay informed about any changes in tax laws that may affect your business. Tax regulations are subject to updates, and being aware of changes ensures that your business remains in compliance and takes advantage of any new opportunities for deductions or credits.
Verify Vendor and Contractor Information: Confirm that you have accurate information for vendors and contractors, especially if you are required to issue 1099 forms. Having correct details, such as Tax Identification Numbers, will help prevent issues with the IRS and other tax authorities.
Inventory and Depreciation: Review your inventory and assess whether any adjustments are needed. Additionally, evaluate the depreciation of assets and update records accordingly. Accurate depreciation calculations can impact your business's taxable income.
Maximize Deductions and Credits: Identify potential deductions and tax credits that your business may be eligible for. This could include business expenses, home office deductions, research and development credits, and more. Consult with a tax professional to ensure you are taking full advantage of available tax-saving opportunities.
Healthcare Reporting: If you provide health insurance to employees, ensure that you comply with reporting requirements. This includes providing necessary forms such as W-2s and 1095s to employees and filing corresponding documents with the appropriate tax agencies.
Estimated Tax Payments: Review your estimated tax payments for the year. If necessary, make any final estimated tax payments before the tax filing deadline to avoid penalties and interest. Accurate estimates can prevent surprises when it comes time to settle your tax liability.
Evaluate Retirement Contributions: Consider maximizing contributions to retirement plans, such as a 401(k) or SEP-IRA. These contributions can provide tax benefits while helping you plan for the future. Ensure that contributions are made by the applicable deadlines.
Review Losses and Gains: Assess capital losses and gains from investments. Consider strategic moves to offset gains with losses, which can impact your overall tax liability. Consult with a financial advisor to explore the best options for your specific situation.
Engage a Tax Professional: Enlist the services of the best tax preparer for small businesses in Mayfield Heights OH to review your financial records. A tax professional can provide valuable insights and help navigate complex tax regulations.
Familiarize Yourself with Filing Deadlines: Be aware of key tax deadlines for your business, including filing dates for federal and state taxes. Failing to meet deadlines can result in penalties, so mark important dates on your calendar and plan accordingly.
By diligently following this tax season checklist, business owners can position themselves for a successful and stress-free tax filing process. Taking the time to organize financial records, stay informed about tax law changes, and leverage available deductions and credits can contribute to a positive outcome and financial stability for the business.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

TAX PREPARATION BEST PRACTICES FOR A STRESS-FREE FILING SEASON
As we inch closer to the infamous tax filing season, the palpable tension in the air becomes almost unavoidable. For many, the thought of navigating the labyrinthine tax codes and forms is enough to induce a cold sweat. But it doesn't always have to be this way.
With a little forethought and meticulous planning, tax preparation can be a breezy, walk-in-the-park experience, saving you not only precious time but also potential penalties for mistakes or late submissions.
In this article, we'll dive headfirst into a wealth of expert tips, savvy strategies, and best practices for tax preparation that promise to transform your filing season from a stress-inducing nightmare into a seamless and orderly process.
From understanding how to maximize your deductions, to organizing your financial paperwork, to deciding whether to enlist the help of a professional, we'll equip you with all the tools and knowledge you need to tackle your tax preparation with confidence and ease.
Organize Your Financial Records
The foundation of a smooth tax preparation process is well-organized financial records. To ensure accuracy and efficiency in preparing your taxes, follow these steps for organizing your financial documents:
1. Gather all essential documents: Begin by collecting critical financial records related to your income, deductions, and credits. These may include W-2 forms, 1099 forms, bank statements, receipts for charitable donations, and business expense documentation.
2. Categorize and sort your records: Separate your financial documents into clearly defined categories, such as income, business expenses, and deductions. This approach will make it easier to locate and reference specific documents when preparing your tax return.
3. Use a system for tracking expenses: Implementing a consistent method for recording and tracking your expenses throughout the year, such as financial software or a dedicated expense journal, can greatly simplify the tax preparation process.
4. Store documents securely: Keep your financial records in a secure location, whether it's a physical filing cabinet or encrypted digital storage. This ensures easy access to essential information while protecting your sensitive financial data.
Understand Your Tax Obligations and Deadlines
Staying informed about your tax obligations and deadlines is essential for avoiding penalties or other consequences. To ensure you're educated and prepared for tax season, consider the following tips:
1. Stay up-to-date on tax laws: Tax laws and regulations can change frequently, so make a point to stay informed about any updates or changes that may impact your tax return.
2. Identify the appropriate tax forms: Depending on your financial circumstances, you may need to complete various tax forms. Ensure you've correctly identified and obtained the necessary forms prior to beginning your tax preparation process.
3. Familiarize yourself with relevant tax credits and deductions: Research and understand the tax credits and deductions available to you, enabling you to maximize your tax savings.
4. Be aware of tax deadlines: Missing tax filing deadlines can result in costly penalties. Mark the relevant tax deadlines on your calendar, and consider filing your return early to avoid last-minute stress.
Avoid Common Tax Filing Mistakes
Mistakes during the tax preparation process can lead to delays, penalties, or even audits. To safeguard against errors, follow these guidelines:
1. Double-check your personal information: Confirm that critical details, such as your Social Security number and address, are correct on your tax return.
2. Report all income: Ensure that you report all forms of income, including freelance work, investment income, or gig economy earnings.
3. Verify your deductions and credits: Carefully review your deductions and credits to ensure you’ve followed the guidelines and have correctly calculated the amounts claimed.
4. File electronically: Electronic filing reduces the likelihood of errors and offers faster processing times for tax refunds.
Partner with Advance Tax Relief for Expert Tax Preparation
Enlisting professional tax preparation assistance from Advance Tax Relief offers numerous benefits, including:
1. Accurate and compliant tax filings: Experienced tax professionals possess thorough knowledge of tax laws and regulations, ensuring your return is completed accurately and in compliance with current tax legislation.
2. Time-saving convenience: Outsourcing your tax preparation can free up valuable time, allowing you to focus on your personal and professional goals without the distraction of tax season stress.
3. Proactive tax planning: Advance Tax Relief can also assist with proactive tax planning strategies, identifying opportunities for tax savings and advising on strategies to minimize your tax liability for future filing seasons.
4. Audit support and representation: Should you face an IRS audit, Advance Tax Relief can provide expert guidance, support, and representation throughout the process, alleviating your concerns and simplifying a potentially overwhelming experience.
Achieve a Stress-free Filing Season with Advance Tax Relief
Implementing best practices for tax preparation can help ensure a smooth, stress-free filing season, allowing you to concentrate on your financial objectives with confidence. Advance Tax Relief, a leading tax resolution company in Houston, Texas, is dedicated to providing expert tax preparation services, ensuring accuracy and compliance in your tax filings, and offering support for future tax planning and potential audit situations.
Discover how our experienced team can simplify the tax preparation process, enabling you to approach each filing season with confidence and ease. Contact us today to explore our comprehensive tax solutions and services and begin your journey towards a hassle-free tax filing experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, it’s me the cat artist that is also a Certified Public Accountant in the US. I would love to make art for a living but instead I do taxes (which is why I haven’t been posting as much art since it’s tax season). I have a Masters in Taxation and have been doing this for 10 years. With that said, this is not legal or tax advice and you should consult your tax preparer.
Let’s break down what could happen if you don’t do your taxes right.
In most instances, the IRS will send you a notice first.
So if you forget to include something that was reported to the IRS, like a W-2 or 1099, they may just correct it by including in and recalculating your taxes for you. This will result in a notice and it will indicate if you are getting an additional refund or if you owe additional taxes.
You forgot to file your tax return timely. There will be a late filing penalty and interest. From the IRS website:
“The Failure to File penalty is 5% of the unpaid taxes for each month or part of a month that a tax return is late. The penalty won't exceed 25% of your unpaid taxes.”
There’s more to it but generally it will depend on your situation. Typically if you tax is calculated at zero, then a penalty won’t be assessed. Not everyone has to file a tax return, and I would recommend this page on the IRS website on who must file. In general, even if you don’t have to file it’s a good idea to do it anyways just so that there’s a record of it.
Another thing that could happen is the IRS decides to audit your tax return. This is where they think maybe something didn’t get reported correctly and they want to show additional support. The IRS website has a whole section on this. Based on my general understanding of the user base on tumblr, this is very unlikely to happen to most people who are reading this. If it does, hire an accountant who knows what they’re doing to help you. Typically the more money you make, the more likely you are to get picked for an audit.
If you disagree with an assessment made by the IRS, you can push back typically by going through the legal process. Here’s a nifty flowchart on it:
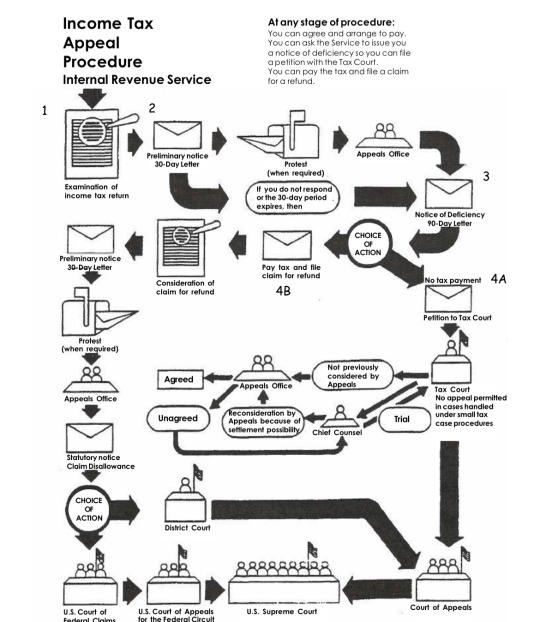
So like, the IRS is not going to send the police to your house if you don’t pay your taxes or don’t file. If it turns out you did something illegal or committed tax fraud, that’s a different story.
Also like, if you owe taxes and cannot afford to pay them, the IRS website has a section on that as well. They will typically try to work with you and your situation to get things settled.
I hope that this will help someone feel a little less anxious about taxes.
Deadline this year for individual income tax returns is April 15th, 2024, so at the time of writing this you’ve still got a month to file. And you can always file an extension for time to file, which is not an extension for time to pay.
I like answering questions and sharing my knowledge, so feel free to reach out. I will preface that anything I write here on tumblr is not legal or tax advice and you should consult your tax preparer.

166. IRS
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Streamline Business Tax Preparation with Technology?

Corporate tax preparation can be a time-consuming and complex process for businesses, but leveraging the right technology can make it more efficient, accurate, and stress-free. With automation, cloud-based software, and artificial intelligence (AI)-powered tools, businesses can simplify tax compliance, reduce errors, and save valuable time. Here’s how technology can help streamline business tax preparation.
1. Use Cloud-Based Accounting Software
Cloud-based accounting software, such as QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks, allows businesses to manage their financial data in real-time. These platforms automate income and expense tracking, generate financial reports, and integrate with tax preparation software to ensure accurate calculations. Since data is stored securely in the cloud, businesses can access their financial records from anywhere, making tax filing easier and more organized.
2. Automate Expense Tracking and Deductions
Manually tracking expenses and deductions can be tedious, but automation tools simplify this process. Receipt scanning apps like Expensify or Dext automatically categorize expenses and sync them with accounting software. Additionally, AI-powered solutions can analyze transactions and identify potential tax deductions, ensuring businesses don’t miss out on savings.
3. Integrate Payroll and Tax Systems
For businesses with employees, payroll taxes are a crucial component of tax preparation. Payroll management software like Gusto, ADP, or Paychex automates payroll tax calculations, withholds the correct amounts, and generates necessary tax forms, such as W-2s and 1099s. Integrating payroll and tax software minimizes errors and ensures compliance with federal and state tax regulations.
4. Leverage Tax Preparation Software
Dedicated tax preparation software, such as TurboTax Business, TaxSlayer, and H&R Block, simplifies tax filing by guiding users through step-by-step processes. These platforms integrate with accounting software, automatically importing financial data and calculating tax liabilities. Many also include e-filing options, allowing businesses to submit returns electronically for faster processing.
5. Utilize AI and Machine Learning
AI-driven tax solutions analyze financial data to detect anomalies, predict future tax liabilities, and suggest strategies to optimize tax savings. Some AI tools also assist with compliance by keeping track of changing tax laws and ensuring businesses remain up to date with regulatory requirements.
6. Digitize Document Management
Maintaining organized financial records is essential for smooth tax preparation. Cloud-based document management systems like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive help businesses store and categorize tax-related documents digitally. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology further enhances efficiency by converting scanned receipts and invoices into searchable text.
7. Schedule Automated Tax Reminders
Missing tax deadlines can lead to penalties and interest charges. Tax software and calendar apps can send automated reminders for estimated tax payments, filing deadlines, and other obligations. Businesses can set up alerts through apps like Trello, Asana, or Google Calendar to ensure timely compliance.
Conclusion
Technology has transformed business tax preparation, making it more efficient and accurate. By adopting cloud-based accounting software, automating expense tracking, integrating payroll systems, leveraging AI, and digitizing document management, businesses can streamline tax processes and reduce the risk of errors. Investing in the right tax technology ensures smoother compliance, minimizes stress, and helps businesses focus on growth.
0 notes
Text
Simple Tax Strategies to Boost Your Refund

As tax season approaches, understanding deductions and credits can help you keep more money in your pocket. Many people miss out on opportunities to reduce their tax bill simply because they don’t explore the full range of benefits available.
How to Maximize Your Tax Refund
Tax deductions lower your taxable income, while tax credits reduce the amount of tax owed. Knowing the difference and applying both correctly can significantly impact your refund. For instance, the Child Tax Credit for 2024 provides $2,000 per qualifying child, and the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) offers up to $7,830 for lower-income households.
Key Tax Deductions and Credits to Consider
Charitable Donations: You can deduct mileage for charity work at 14 cents per mile in 2024.
Medical Expenses: If medical costs exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income (AGI), they may be deductible.
Standard Deduction: For 2024, the single filer deduction is $14,600, while married couples filing jointly can deduct $29,200.
Retirement Contributions: Contributions to traditional IRAs lower taxable income and can be made until tax filing time.
Organizing Your Tax Documents
Keeping tax documents organized ensures you don’t miss out on valuable deductions. Essential documents include:
Receipts for charitable donations
Medical expense records
Business-related expenses
Investment statements
Using apps and cloud services can simplify tracking expenses and storing receipts. The IRS recommends keeping tax records for at least three years.
Key Tax Deadlines to Remember
January 31, 2025: Deadline for employers to send W-2s and 1099s.
April 15, 2025: Tax return due date (also the last day to contribute to an IRA for the 2024 tax year).
October 15, 2025: Extended tax return deadline.
Planning ahead helps avoid last-minute stress and ensures you take advantage of all eligible deductions.
Using Tax Software and Tools
Tax software simplifies filing and ensures accuracy. Popular options include TurboTax and TaxAct, which offer tools to help maximize refunds by identifying deductions and credits you might otherwise miss.
Features to look for in tax software:
Automated deduction and credit identification
Accuracy and efficiency in tax filing
Cost-saving strategies
Choosing Between Standard and Itemized Deductions
The standard deduction is straightforward and works well for many taxpayers. However, itemizing can be more beneficial if you have significant expenses, such as:
Mortgage interest and property taxes
Charitable contributions
High medical expenses
A tax refund calculator can help determine whether itemizing or taking the standard deduction is best for your situation.
Making Use of Retirement Accounts
Contributing to retirement accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, lowers taxable income. For 2024, the contribution limits are:
IRA: $7,000
401(k): $23,000
Those 50 and older can contribute additional catch-up amounts, further reducing taxable income. Understanding withdrawal rules is also important to avoid penalties.
Considering Education-Related Expenses
Education tax credits can reduce what you owe. The American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) provides up to $2,500 per eligible student. The Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC) offers up to $2,000 per return for tuition and fees. Additionally, the Tuition and Fees Deduction can lower taxable income by up to $4,000.
Homeowner Benefits and Deductions
Owning a home comes with tax advantages, including:
Mortgage Interest Deduction: Allows deductions for interest on loans up to $750,000.
Property Tax Deduction: Deduct up to $10,000 in state and local taxes ($5,000 for single filers).
Energy Efficiency Credits: Get a 30% credit for installing solar panels or energy-efficient improvements.
Seeking Professional Help
Hiring a tax professional can be beneficial for complex tax situations. They help maximize refunds, ensure compliance, and reduce the risk of audits. A tax expert can also guide self-employed individuals on estimated payments and deductions.
Reviewing Your Tax Returns
Double-checking your return can prevent costly mistakes. Reviewing for missed deductions and tax law changes ensures accuracy. If you expect a large refund, adjusting your W-4 to optimize withholdings may provide more take-home pay throughout the year.
By staying informed and proactive, you can take full advantage of tax-saving opportunities and keep more of your hard-earned money. Click here to read the full article!
0 notes
Text
The Benefits Of Hiring A Tax Service For Truck Drivers With Multiple Income Sources

Truck drivers who manage multiple income sources face a unique set of challenges when it comes to tax preparation. Many drivers have income from different streams—such as long-haul trucking, local deliveries, side gigs, or even vehicle rentals—which can complicate the process of filing taxes. This is where a professional tax service can provide invaluable assistance. Hiring a tax service ensures drivers can manage their finances efficiently, reduce stress, and maximize tax benefits. Below are key benefits for truck drivers with multiple income sources when hiring experts offering tax service for truck drivers.
1. Expertise in Navigating Complex Tax Situations
A tax service specializes in understanding complex tax codes and can guide truck drivers through intricate rules regarding income reporting. Truck drivers with multiple income sources may face issues like determining which expenses are deductible, how to report income from various channels, and how to file accurately. Tax professionals have the expertise to navigate these complexities, ensuring compliance with the IRS and reducing the risk of costly mistakes.
2. Maximizing Tax Deductions
Truck drivers can take advantage of numerous tax deductions, such as vehicle expenses, maintenance, fuel costs, meals, lodging, and even truck-related technology. A tax service will know all the deductions available to drivers and help them maximize their savings. With multiple income sources, it’s easy to miss out on deductions unless someone with expertise is handling the filing.
3. Simplified Record Keeping
Managing multiple income streams means handling a variety of records, including pay stubs, receipts, and documentation for side gigs or business ventures. A tax service can organize and simplify record-keeping processes. They will help drivers track expenses, organize receipts, and store documents electronically, making tax season much easier to handle.
4. Accurate Filing Across Multiple Forms
Truck drivers with multiple income sources will likely need to file various forms, such as W-2s, 1099s, and Schedule C for self-employed income. A tax service ensures that these forms are filed correctly and on time, reducing the likelihood of missing deadlines or making errors that could result in penalties or audits.
5. Guidance for Estimated Tax Payments
Many truck drivers, especially those who are self-employed or working as independent contractors, may need to make estimated quarterly tax payments. A tax service can help drivers determine the right amount to pay based on their income and avoid underpayment penalties. This proactive approach ensures that drivers stay ahead of their tax obligations and avoid surprises come tax season.
6. Audit Protection and Peace of Mind
Tax filing can be stressful, especially when dealing with multiple income sources. Hiring a tax service provides peace of mind, knowing that a professional is handling your tax filings. In the event of an audit, tax professionals can provide representation and ensure everything is in order. They can offer valuable advice and handle the situation professionally, reducing stress and worry for the driver.
7. Long-Term Financial Planning
Beyond immediate tax filing, a tax service can offer long-term advice for truck drivers. They can help drivers plan for retirement, set up savings strategies, and offer insights on how to manage multiple streams of income. This kind of financial guidance can lead to better tax efficiency and overall financial health.
In conclusion, hiring a tax service for truck drivers with multiple income sources is an investment that can save time, reduce tax liabilities, and ensure compliance. With the support of tax professionals, truck drivers can focus on their work while maximizing their tax benefits and achieving long-term financial success.
0 notes
Text
1099 Filing: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
When tax season rolls around, one of the most important tasks for many self-employed individuals, freelancers, contractors, and businesses is 1099 filing. This form, specifically the 1099-NEC (Non-Employee Compensation), is used to report income earned outside of traditional employment. If you're unfamiliar with this process, it can seem daunting at first, but understanding the essentials of 1099 filing can make tax time a lot easier.

What is a 1099 Form?
The 1099 form is an IRS document used to report a variety of different types of income that don't fall under the standard W-2 category, which is typically for employees. The 1099-NEC is the most common form for freelancers, independent contractors, and anyone else receiving non-employee compensation. This form is also used to report other income, such as interest or dividends, depending on the type of 1099 form being filed.
The 1099-NEC is particularly important for anyone who works on a contract basis, providing services for a business or individual without being considered an employee. For example, if you're a freelance writer, graphic designer, or consultant, you'll likely receive a 1099-NEC if you earned $600 or more from a client during the year.
Who Needs to File a 1099?
Businesses that hire independent contractors or pay non-employee compensation typically need to file a 1099-NEC for any contractor or freelancer who earned $600 or more during the year. The responsibility to file the 1099 generally falls on the business or individual making the payment, not the contractor receiving the payment.
However, as an independent contractor, it’s essential to keep track of your income and ensure that you receive the necessary 1099 form from each client that paid you at least $600. If you don’t receive one, it’s important to reach out to the payer and ask for it. Without this form, reporting your income during tax season becomes more complicated.
Important Deadlines for 1099 Filing
The IRS has set clear deadlines for 1099 filing, and missing these deadlines can result in penalties. For 1099-NEC forms, the deadline for sending out the form to the recipients (i.e., the contractors or freelancers) is January 31st. This means that if you’ve earned at least $600 from a client, they are required to send you a 1099-NEC form by this date.
Additionally, businesses need to file the 1099-NEC with the IRS by January 31st as well, whether they’re submitting on paper or electronically. It’s critical to stay on top of these dates to avoid late fees or potential penalties.
How to File a 1099 Form
Filing a 1099 form might sound overwhelming, but it's relatively simple once you understand the steps. First, you'll need the payer's details, including their legal name, address, and Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), which is often a Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN). You'll also need to report the amount of money you were paid for services, as well as any applicable deductions.
Many business owners and contractors choose to file their 1099 forms electronically, using platforms like QuickBooks or TaxSlayer to simplify the process. The IRS also offers an online filing system called FIRE (Filing Information Returns Electronically) for businesses that file large numbers of 1099 forms.
For those with fewer forms, paper filing is still an option. You'll need to order 1099 forms from the IRS or purchase them through authorized vendors. It's important to note that you cannot print these forms yourself; they must be obtained through the proper channels to be accepted by the IRS.
Why 1099 Filing Matters
Properly filing your 1099 forms is crucial for both businesses and contractors. For businesses, failing to file these forms can result in penalties, which can add up quickly. For independent contractors, a missing or incorrect 1099 form can lead to issues with your tax return, especially if you miss out on income reporting.
In addition, filing your 1099 forms correctly helps the IRS ensure that all income is properly reported and taxed. It also gives you a solid record of the income you earned throughout the year, which can be helpful when filing your tax return or applying for loans.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in 1099 Filing
To make the process smoother, it’s important to avoid a few common mistakes during 1099 filing:
Incorrect or Missing Information: Double-check all details on the form, including the contractor’s name, TIN, and payment amount.
Missing Forms: Ensure that you send a 1099 form to every independent contractor you’ve paid $600 or more.
Late Filing: As mentioned, the IRS has strict deadlines for 1099 filing. Make sure you file on time to avoid penalties.
Final Thoughts on 1099 Filing
Whether you're a freelancer or a business owner, understanding the ins and outs of 1099 filing is key to a smooth tax season. By ensuring you receive your 1099 forms on time, keeping track of all income, and filing promptly, you’ll be in a good position to avoid penalties and remain compliant with IRS regulations. While tax filing can seem complex, the more informed you are, the easier it will be to stay organized and on top of deadlines.
By staying on top of your 1099 filing requirements and reaching out for help when necessary, you can navigate the process with confidence and ease.
1 note
·
View note
Text
tax return,
tax return,
Understanding Tax Returns: What You Need to Know
A tax return is a form submitted to the tax authorities that outlines an individual’s or business’s income, expenses, and other relevant financial information for a specific period, typically a year. It is a key document used to determine the amount of tax owed or the refund due.
Whether you’re filing as an individual or as a business, understanding how tax returns work can help you comply with tax laws and avoid penalties. Let’s break down what a tax return is, how it works, and why it’s important.
What is a Tax Return?
A tax return is a set of forms or documents filed with tax authorities that reports your financial information for a specific tax year. This includes details about your income (such as salary, wages, investments, and business earnings), deductions, credits, and taxes already paid. By completing and filing your tax return, you are essentially telling the government how much you earned and how much tax you owe or have already paid.
The most common types of tax returns include:
Individual Tax Returns: Filed by individual taxpayers, typically using forms like the 1040 in the United States.
Corporate Tax Returns: Filed by businesses to report profits, expenses, and taxes owed.
Partnership or LLC Tax Returns: Filed by businesses structured as partnerships or limited liability companies.
Why is a Tax Return Important?
Legal Compliance: Filing your tax return ensures you comply with your country’s tax laws. Failure to file a return can result in penalties, interest on overdue taxes, or even legal action in extreme cases.
Tax Refunds: If you’ve overpaid on your taxes, filing a return allows you to claim a refund. For instance, if you had taxes withheld from your paycheck, you might have paid more than required, and the government will return the excess.
Deductions and Credits: Your tax return is where you can claim deductions or credits to lower your tax liability. This could include deductions for medical expenses, mortgage interest, charitable donations, and child tax credits.
Record Keeping: Filing a tax return creates a formal record of your financial activity. This can be useful for future reference, whether you’re applying for a loan, seeking government benefits, or proving income.
How to File a Tax Return
Gather Documents: Collect all relevant financial documents, such as income statements (e.g., W-2, 1099), proof of expenses, receipts for deductions, and any other records of financial transactions during the tax year.
Choose the Right Form: The form you need to fill out depends on your income type, filing status, and other factors. For individuals in the United States, the most common form is the Form 1040. Some may need additional schedules for more complex situations.
Fill Out the Form: Accurately complete your form by listing all of your income and expenses. You can either do this manually or use tax preparation software, which simplifies the process and reduces the likelihood of mistakes.
File the Return: Once completed, you can file your return electronically through online platforms, such as the IRS e-file system (for U.S. residents), or submit a paper return by mail.
Pay Any Taxes Owed: If you owe additional taxes beyond what you’ve already paid, you must remit payment by the tax filing deadline. Failure to do so may result in penalties and interest charges.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Underreporting Income: Always report all sources of income, even if they seem small. Not reporting income can lead to audits or penalties.
Missed Deductions: Failing to claim eligible deductions is another common mistake. Ensure you take advantage of every credit or deduction you qualify for, such as child tax credits, student loan interest deductions, or retirement savings contributions.
Late Filing: Always file on time to avoid penalties. If you need more time, consider filing for an extension (note that this only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline).
Errors in Tax Software: While tax software can be a helpful tool, it’s crucial to double-check all the information entered, as errors in data can lead to inaccurate filings.
When to File a Tax Return
In many countries, tax returns must be filed by a specific deadline. For example, in the United States, the deadline for individual tax returns is typically April 15 each year (unless extended). However, businesses or individuals with special circumstances might have different deadlines, so it's important to stay informed.
Tax Professionals vs. Self-Filing
While some individuals prefer to file their own tax returns using software or manual methods, others may choose to hire a tax professional. Tax preparers can be especially helpful for complex financial situations, such as owning a business, having international income, or claiming a large number of deductions.
Hiring a professional can also save time and ensure accuracy, but it's important to choose someone trustworthy and knowledgeable.
Conclusion
Filing a tax return is an essential part of managing your finances and complying with tax laws. Whether you’re filing as an individual or a business, understanding the process helps ensure you are not overpaying or underpaying taxes, and that you are taking full advantage of any deductions or credits available to you. Always make sure to file your return on time, and consult a tax professional if needed to avoid costly mistakes.
4o mini
O
0 notes
Video
youtube
How To Get Your SETC Self-Employed Tax Credit in Record Time
The FFCRA Sick and Family Leave Credit is a government-backed program designed to reimburse you for wages lost due to COVID-related illness, caregiving, or quarantine. If you were impacted, this credit helps cover the income you missed. It’s your money—specifically set aside to support those who kept our economy moving during the pandemic.
Find out how much you are eligible for
The deadline to claim your SETC Self-Employed Tax Credit is fast approaching - April 15th. United Business Solutions has direct integration with the IRS so there is no need to search for past tax forms and records.
The self-employed tax credit is for individuals who file a 1099 and Schedule C for their business. Includes sole proprietors, 1099 contractors, Self-Employed, Single Member LLC’s, Freelancers, Gig-Workers, Self-Employed Couples who file jointly, anyone who files a Schedule C or SE.
Just some of the many who may qualify: entrepreneurs, business owners, Uber drivers, real estate agents, hair stylists, plumbers, painters, freelancers, Construction workers, Insurance agents, doctors and dentists, and anyone who is self-employed.
Find out how much you may qualify for in 5 minutes or less (with no commitment)
#youtube#FFCRA#Sick and Family Leave Credit#setc#self-employed tax credit#tax refunds#how to file for the self-employed tax credit#do I qualify for the setc self-employed tax credit#how to get your SETC self-employed tax credit in record time
1 note
·
View note
Text
Getting Ready for Taxes: Essential Guidelines for 2024
Tax season can feel overwhelming, but being prepared makes all the difference. Here’s a detailed guide to essential tax considerations for 2024 to help you navigate the process smoothly.
1. Charitable Contributions
If you’ve donated to charity, only out-of-pocket expenses are deductible. This includes costs incurred for volunteering, such as mileage or supplies purchased for a charitable cause. Ensure you keep proper receipts or documentation for all donations and expenses to claim deductions. Remember, contributions must be made to qualified organizations, and cash donations over $250 require a written acknowledgment.
2. 1099 Forms
If you’ve paid $600 or more to independent contractors, freelancers, or other non-employees, you’re required to issue a Form 1099-NEC by January 31, 2025. This ensures that both you and the recipient report the payment accurately to the IRS. Keep records of all payments throughout the year to avoid last-minute scrambles.
3. Estimated Tax Payments
For income not subject to withholding, such as self-employment earnings, rental income, or investment income, you need to make quarterly estimated tax payments. Deadlines are typically in April, June, September, and January. Missing payments or underpaying can result in penalties, so calculate your payments based on expected income and keep track of due dates.
4. Retirement Contributions
SEP IRAs: If you’re self-employed, you can contribute to a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA up until March 15, 2025, if you file an extension.
Traditional IRAs: Contributions for the 2024 tax year must be made by April 15, 2025. Maximize your retirement contributions to take advantage of tax-deferred growth and reduce your taxable income.
5. Capital Gains and Losses
When selling investments like stocks or property, keep these tax rules in mind:
You can offset up to $3,000 of capital losses against your ordinary income.
Long-term capital gains (investments held for more than a year) are taxed at preferential rates of 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income level. Document all transactions, and work with a tax professional to determine the best strategies for reducing tax liability.
6. Home Office Deductions
If you’re self-employed and use part of your home exclusively and regularly for business, you may qualify for home office deductions. Deductible expenses include a portion of your rent or mortgage interest, utilities, and maintenance. Use the simplified method (deduct $5 per square foot, up to 300 square feet) or calculate actual expenses for the most accurate deduction.
7. FBAR and FATCA Compliance
FBAR (Foreign Bank Account Report): If the balance of your foreign bank accounts exceeded $10,000 at any time during the year, you must file an FBAR using FinCEN Form 114 by April 15, 2025.
FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act): If you hold foreign financial assets above the threshold ($50,000 for individuals in the U.S.), report them on Form 8938 along with your tax return. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties, so ensure all foreign assets are reported accurately.
8. Rental Income
If you own rental properties, you must report all rental income on your tax return. Deductible expenses include mortgage interest, property taxes, repairs, insurance, and maintenance. Keep detailed records of all income and expenses to substantiate your claims. If you’re renting part of your home, only expenses related to the rental portion can be deducted.
9. Gift Taxes
For 2024, gifts exceeding $18,000 per recipient require you to file a gift tax return (Form 709). The annual exclusion amount increases to $19,000 in 2025. However, most taxpayers won’t owe any taxes due to the unified estate and gift tax exemption, which allows up to $13.61 million in lifetime exclusions in 2024.
10. Estate and Inheritance Taxes
The estate tax exemption for 2024 is $13.61 million per individual. Any inheritance below this amount is not subject to federal estate taxes. If inherited assets are sold immediately, beneficiaries may avoid capital gains taxes, as the cost basis typically steps up to the fair market value at the time of death. Work with an estate planning expert to make the most of these benefits.
Seek Professional Guidance
Tax rules can be complex, and every taxpayer’s situation is unique. To ensure you maximize deductions and comply with IRS requirements, consult a tax professional. Early preparation helps reduce stress and increases your chances of filing an accurate return.
Prepare now and stay ahead of the game for 2024!
For more Information Contact Us: https://www.saicpaservices.com/ or (908) 380-6876
https://www.facebook.com/AjayKCPA
https://www.instagram.com/sai_cpa_services/
https://twitter.com/SaiCPA
https://www.linkedin.com/in/saicpaservices/
https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Va9qWRI60eBg1dRfEa1I
0 notes
Text
Avoid These Common Tax Preparation Mistakes
Tax season can be overwhelming, but avoiding common pitfalls can save you money, reduce stress, and prevent costly penalties. Whether you’re filing as an individual or for your business, here are the most frequent tax preparation mistakes and how to steer clear of them.
1. Failing to Keep Accurate Records
Disorganized or incomplete financial records can lead to errors, missed deductions, and filing delays.
Solution: Use reliable accounting software or apps to track income, expenses, and deductions year-round. Organize your receipts and documents for easy access. For personalized tax planning support, check out Lodestar Tax Planning Services.
2. Overlooking Deductions and Credits
Missing out on eligible deductions and credits can significantly increase your tax liability.
Solution: Familiarize yourself with deductions like education expenses, home office costs, and retirement contributions. A tax professional can ensure you claim all benefits. Learn more at Lodestar Tax Preparation Services.
3. Incorrect Income Reporting
Failing to report all income sources, including freelance or investment earnings, can lead to penalties.
Solution: Gather all income-related documents, such as W-2s and 1099s, before filing. Double-check your entries to ensure accuracy.
4. Missing Filing Deadlines
Late tax filings result in penalties and interest, increasing your financial burden.
Solution: Mark tax deadlines on your calendar and set reminders. If you need more time, file for an extension, but remember to pay any taxes owed by the original deadline.
5. Ignoring Tax Law Updates
Tax laws change frequently, and staying unaware can lead to errors or missed opportunities.
Solution: Stay informed about updates by consulting trusted sources or professionals. For expert advice on adapting to tax law changes, visit Lodestar Tax Planning Excellence.
6. Choosing the Wrong Filing Status
Selecting an incorrect filing status can result in higher taxes or lost benefits.
Solution: Review the eligibility requirements for each filing status. Choose the one that best fits your circumstances, such as single, married filing jointly, or head of household.
7. Skipping a Final Review
Errors in calculations or typos can delay your refund or cause complications with the IRS.
Solution: Carefully review your tax return for accuracy before submitting it. Verify calculations, personal information, and deductions.
8. Not Seeking Professional Assistance
Relying solely on tax software or self-preparation can result in mistakes, especially with complex returns.
Solution: Consider hiring a tax professional for expert guidance and accurate filing. Explore how Lodestar can help with complex cases at Lodestar Tax IRS Resolutions Services.
9. Overlooking State and Local Taxes
Federal taxes often take center stage, but neglecting state and local obligations can lead to non-compliance.
Solution: Familiarize yourself with state and local tax requirements, deadlines, and forms. Ensure compliance at all levels.
10. Missing Retirement Contributions
Failing to contribute to retirement accounts can mean losing valuable tax benefits.
Solution: Maximize contributions to IRAs or 401(k)s before the tax deadline to reduce taxable income and grow long-term savings.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common tax preparation mistakes can simplify your filing process, reduce stress, and maximize your financial benefits. Staying organized, understanding tax laws, and seeking professional assistance when needed can make tax season a breeze.
For expert guidance and support, partner with Lodestar Taxes. Their experienced team can help you avoid errors, maximize deductions, and stay compliant. Visit Lodestar Tax Planning Services to get started today.
0 notes
Text
How To Simplify Tax Compliance With An HR Payroll And Accounting System

Managing tax compliance can be a daunting task for businesses of all sizes. The complexities of staying up-to-date with tax regulations, ensuring accurate deductions, and filing timely returns can become overwhelming. However, with the right HR Payroll and Accounting System in place, these challenges can be significantly simplified. At Ignite HCM, we specialize in providing innovative solutions that streamline your business operations, including tax compliance.
In this blog, we’ll explore how an HR Payroll and Accounting System can make tax compliance more efficient and stress-free while improving overall business performance.
The Challenges of Tax Compliance
Before diving into the solution, let’s look at some common challenges businesses face with tax compliance:
Complex Regulations: Tax laws frequently change, and keeping up with federal, state, and local requirements can be difficult.
Human Errors: Manual payroll processing increases the risk of miscalculations and missed deadlines.
Time-Consuming Processes: Filing taxes involves gathering data, cross-checking records, and ensuring every deduction is accounted for.
Penalties and Fines: Non-compliance due to errors or delays can result in costly penalties.
These challenges emphasize the need for an efficient, automated system to handle tax compliance seamlessly.
What is an HR Payroll and Accounting System?
An HR Payroll and Accounting System is a technology solution that integrates payroll, HR management, and accounting functions into one platform. This system ensures accurate employee compensation, tracks financial data, and simplifies tax reporting processes. At Ignite HCM, we offer tailored HR Payroll and Accounting Systems designed to meet the unique needs of businesses in various industries.
How an HR Payroll and Accounting System Simplifies Tax Compliance
Automated Tax Calculations One of the most significant advantages of using an HR Payroll and Accounting System is its ability to automate tax calculations. These systems are programmed to:
Calculate federal, state, and local taxes based on current regulations.
Automatically adjust tax rates for employees in different locations.
Apply the correct deductions for Social Security, Medicare, and other contributions.
By automating these processes, businesses eliminate manual errors and ensure precise calculations every pay period.
2. Real-Time Updates on Tax Regulations Tax laws and regulations can change frequently. Keeping track of these updates manually can be both time-consuming and risky. HR Payroll and Accounting Systems from Ignite HCM are equipped to handle these changes in real-time.
The system automatically updates tax rates and compliance requirements.
Alerts notify HR and accounting teams of upcoming changes or deadlines.
This ensures your business always stays compliant without the need for constant manual monitoring.
3. Seamless Integration of Payroll and Accounting Integrating payroll with accounting is critical for accurate tax reporting. An HR Payroll and Accounting System streamlines this integration by:
Automatically transferring payroll data to accounting ledgers.
Ensuring deductions, bonuses, and benefits are accurately recorded.
Simplifying financial audits with centralized data storage.
This level of integration reduces the chances of discrepancies and makes tax filing more straightforward.
4. Comprehensive Reporting and Documentation Tax compliance requires thorough documentation. With an HR Payroll and Accounting System, generating and organizing these documents is effortless.
Generate W-2s, 1099s, and other tax forms with just a few clicks.
Access historical payroll data for audits or tax filing purposes.
Create custom reports to analyze payroll and tax trends.
At Ignite HCM, our systems provide robust reporting tools to ensure you have all the necessary information for tax compliance at your fingertips.
5. Ensuring Timely Tax Filings Missing tax deadlines can result in hefty fines and penalties. HR Payroll and Accounting Systems help businesses stay on track by:
Setting up automated reminders for tax deadlines.
Scheduling payroll runs to align with tax filing schedules.
Filing taxes directly through the system in some cases.
This reduces stress for HR and accounting teams and ensures compliance with minimal effort.
6. Enhanced Security for Sensitive Data Tax data includes sensitive employee and financial information. HR Payroll and Accounting Systems are designed with robust security features to protect this data.
Encryption ensures secure storage and transmission of information.
Role-based access controls limit data visibility to authorized personnel.
Regular backups protect against data loss.
With Ignite HCM, your tax data is safeguarded, giving you peace of mind during tax season.
Why Choose Ignite HCM for Your HR Payroll and Accounting System?
At Ignite HCM, we understand the unique challenges businesses face when managing payroll, accounting, and tax compliance. Our solutions are:
Customizable: Tailored to your specific business needs.
User-Friendly: Intuitive interfaces that simplify complex processes.
Scalable: Designed to grow with your business.
Supportive: Backed by a dedicated support team to assist you every step of the way.
Our HR Payroll and Accounting Systems empower businesses to focus on growth while we handle the complexities of tax compliance.
Additional Benefits of an HR Payroll and Accounting System
Apart from simplifying tax compliance, these systems offer numerous other benefits:
Improved Employee Satisfaction: Accurate and timely payroll processing leads to happier employees.
Cost Savings: Automation reduces the need for extensive manual labor and minimizes errors.
Better Decision-Making: Centralized data provides valuable insights into workforce and financial trends.
Regulatory Compliance: Beyond taxes, these systems help businesses adhere to labor laws and other regulations.
Conclusion
Tax compliance doesn’t have to be a source of stress for your business. By leveraging an advanced HR Payroll and Accounting System from Ignite HCM, you can simplify tax calculations, ensure timely filings, and maintain compliance with ease.
With the right tools in place, your business can save time, reduce errors, and avoid penalties, allowing you to focus on achieving your organizational goals. Let Ignite HCM be your trusted partner in streamlining HR, payroll, and accounting processes.
Are you ready to take the next step toward hassle-free tax compliance? Contact Ignite HCM today to learn more about our solutions and how they can transform your business operations.
Website : https://www.ignitehcm.com/
Email : [email protected]
Phone : +1 301-674-8033
#HR Payroll System#Accounting And Payroll#Payroll Software Solutions#HR And Accounting Integration#Tax Compliance Solutions#Business Payroll Management
0 notes