#🇲🇳
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text




Altan Uul (алтан уул) the Golden Mountain
Khövsgöl Province (Хөвсгөл)
Mongolia
NOMAD Science Bioarchaeology
4th to 7th (5th) of July 2023
5th of July after storms had rolled in during the afternoon. The sunset that night was amazing and still one of the best of the 3 weeks in the field.
#camping#road trip#photography#landscape#nature#mountains#scenery#geology#Mongolia#mongolia camping#🇲🇳#overseas camping#Archaeology#tent
34 notes
·
View notes
Photo

本日 白鵬引退 宮城野襲名 披露大相撲 . . . . . 📷2023.1.28 📍両国国技館 . . . . . ↓↓↓ . . . #白鵬引退 #白鵬 #HAKUHO #間垣親方 #宮城野部屋 #宮城野親方 #白鵬引退宮城野襲名披露大相撲 #白鵬翔 #白鵬関 #落合 #🇯🇵 #炎鵬 #石浦 #北青鵬 #🇲🇳 #mongolia . . . . #sumo #grandsumo3 #japan #rikishi #お相撲さん #力士 #大相撲 #相撲 #相撲好きと繋がりたい は #両国国技館 #両国 #墨田区 #日本橋 #20230128 @grandsumo3 @sumokyokai (両国国技館) https://www.instagram.com/p/Cn8B2AcPEA3/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#白鵬引退#白鵬#hakuho#間垣親方#宮城野部屋#宮城野親方#白鵬引退宮城野襲名披露大相撲#白鵬翔#白鵬関#落合#🇯🇵#炎鵬#石浦#北青鵬#🇲🇳#mongolia#sumo#grandsumo3#japan#rikishi#お相撲さん#力士#大相撲#���撲#相撲好きと繋がりたい#両国国技館#両国#墨田区#日本橋#20230128
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

I LOVE MONGOLIA🇲🇳
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Нээх сайхан нэмэх градус руугаа орж байхад дөрвөн сарын сүүлээр цас орно ч гэх шиг. Таарч дээ.
0 notes
Text

A Male Saiga Antelope in Russia's Black Land National Park. These highly social antelope live in herds. Photograph By Valeriy Malee/Nature Picture Library
This Floppy-Nosed Antelope Was Nearly Gone. 20 Years Later, It’s Thriving.
Less than a decade ago, more than half of the world’s saiga antelope were lost to a mysterious disease. Its comeback is a rare and phenomenal conservation success.
— By Jason Bittel | December 14, 2023
Just two decades ago, it seemed as if we might need to write a eulogy for the saiga antelope.
Cut down by widespread poaching and waves of disease, by 2003, just 6 percent of the floppy-nosed ungulates remained in Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Russia, and Uzbekistan.
But today, scientists are rejoicing at the saiga’s unlikely rebound.
There are now 1.9 million saiga antelope across Eurasia, according to the most recent estimates released this week. So many saiga, in fact, that the International Union for Conservation of Nature is upgrading the Red List status for the species from critically endangered to near threatened.
“There's a lot of conservation doom and gloom, and there isn't very much attention paid to conservation successes,” says E.J. Milner-Gulland, a conservation scientist at the University of Oxford and co-founder of the U.K-based Saiga Conservation Alliance. “It’s quite a vindication of 20 years of hard work by lots of people.”
To get a sense of just how far this species has come, in 2015, more than half of the worldwide population of saiga antelope were lost to a mysterious blood disease.
“This is phenomenal news,” says Joel Berger, an ecologist at Colorado State University and a senior scientist at the Wildlife Conservation Society, in an email.
“At a time when so many species and populations are in deep swan dives, to witness the recovery of saiga—a species deserving of more recognition in its own right—is something we all need to celebrate,” he says.

Male Saiga Antelope Battle in Black Lands National Park. Males and their horns are a specific target of poachers. Photograph By Valeriy Malee/Nature Picture Library
The Saiga’s Downward Spiral
Those who have been paying attention to the saiga’s saga know that it’s been a wild ride.
“Twenty years ago, it had the fastest increase in threat status of any mammal,” says Milner-Gulland. “The population had plummeted by more than 90 percent over a really short time of a few years, so it went straight in at critically endangered.”
As for what happened, Milner-Gulland explains that the saiga’s downfall can be attributed to several factors. For starters, saiga horn has great value in China, Singapore, Vietnam, and Malaysia as a component in traditional medicine. And this demand, coupled with the breakup of the Soviet Union, led to a dramatic rise in hunting.
It’s a Symbol of the Wild Steppe, of Independence and Freedom.
— E.J. Milner-Gulland, Conservation Scientist at the University of Oxford
“The economies of these countries basically collapsed,” she says. “And they were living in very harsh conditions on the steppe. So they turned to poaching.”
Fencing along the border between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan also put a barrier in the middle of the saiga’s migratory route, while infrastructure development cut into saiga habitat. Finally, an unknown trigger turned a naturally occurring microbe in the saiga’s characteristic nose into a virulent pathogen, leading to the mass die-offs.
It’s for all these reasons that the IUCN has chosen not to de-list the saiga completely.
“The near threatened category is right for the saiga, because we know that at any time, we could just get large numbers of them dropping dead again,” says Milner-Gulland. “They are very vulnerable.”

A Path to Recovery
Just as the threats to the saiga were multi-faceted, so too have been the efforts to protect the species, which are important seed dispersers and grazers that contribute to plant biodiversity.
For instance, an international collaboration between countries where saigas roam, countries that traditionally consume saiga products, and other stakeholder nations, including the United States, led to a memorandum of understanding in 2006 to conserve the species, restore its habitat, and restrict harvest to a sustainable level.
For its part, Kazakhstan’s government focused on stronger anti-poaching measures, including law enforcement to prevent saiga hunting. The Saiga Conservation Alliance supplied financing for gasoline, uniforms, motorbikes, and shelters for those rangers, who live in the harsh, windswept grasslands. Customs agents also improved detection of saiga products leaving the country as part of the illicit wildlife trade. Lastly, the country designated multiple protected areas totaling more than 12 million acres of saiga antelope habitat.
Now that economic conditions have leveled out and local people don’t have to choose between their own survival and saving saiga, there has also been a dramatic shift in support for the species.
“The thing about saiga is the local people really love it,” says Milner-Gulland. “It’s a symbol of the wild steppe, of independence and freedom.”

Saiga (Drinking on Southern Russia's Astrakhan Steppe) can migrate up to 600 miles over summer and winter. Photograph By Valeriy Malee/Nature Picture Library
#Animals 🦓 🦒 🐘#Floppy Nosed Antelope#Kazakhstan 🇰🇿 | Mongolia 🇲🇳 | Russia 🇷🇺 | Uzbekistan 🇺🇿#University of Oxford#Saiga Antelope#China 🇨🇳 | Singapore 🇸🇬 | Vietnam 🇻🇳 | Malaysia 🇲🇾#E.J. Milner-Gulland | Conservation Scientist | University of Oxford
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello everyone ,,Please don't let my words pass like this.
I am Ilham from Gaza, a mother of three beautiful children, Ayser, Tia and Tila... I lost everything I owned: my home, my job, my future, my dreams and part of my family.Every day I struggle to save my children's lives. I stand in a long queue to get water and food... Please help me and donate to save the lives of my three children... My baby Tila needs milk and diapers...
Please do not abandon me 😭😭🇵🇸🍉
https://gofund.me/7895f76f
#free gaza#gaza strip#gaza under attack#American#Muslims in the whole world#🇹🇨🇹🇦🇹🇰🇵🇷🇬🇧🇺🇸🇹🇻🇻🇬🇱🇷🇵🇾🇲🇳🇹🇫
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Shoutout to “Yellow Dreams Youth Art Contest” by the Mongolian Culture and Heritage Center of Colorado deadline April 15, 2023. http://www.mongolianchcc.org #yellowdreamsartcontest2023 #mchcc #mongolianculturecenter🇲🇳 #youthartcontest #aapi #aapiheritage https://www.instagram.com/p/CqVpU_sL69-/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Text
OK uh HERE YOU GO
Ok girlies (gender neutral) I am curious about something. Reblog and tell me in the tags if you had your favorite bias (or biases) in your contact list, what would be their contact name? (Bonus points if you tell me who that bias is)
#Joshua Hong: My one and only Gentledeer🦌#Chuu: MAKE WAY FOR QUEEN CHUU👑#Lee Heeseung: Bambiby Maknae💕💕💕#Yang Jeongin: Bobbybubbywubbybub#Felix Lee: PILIKMATA CHONKYCHONK CHUBBACHUPS🥴#Song Mingi: MINGI🐺MANGO🥭MONGO 🇲🇳MUNGGO🐄#Seonghwa: Hubbybubbybubs💍#Steven Kim: Universe 🌌🌠🌙#Choi Beomgyu: Wuvvy bonneh🐇#Lee Chan: Schnookiepookie🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪🍪#Cha Eunwoo/Lee Dongmin: Beloved 💕#Moon Bin: Binniby 💕🌙#Sorn: MY PRECIOUS 💞💞💞💞
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
★ . . . 𝐂𝐑𝐀𝐙𝐘 𝐑𝐈𝐂𝐇 𝐀𝐒𝐈𝐀𝐍𝐒 , 𝐅𝟏 𝐆𝐑𝐈𝐃
summary , a series where asian readers, from all over, are showcased and appreciated because they deserve to be loved, respected, and treated like queens
inspired by , amar x100pre by @f1version
status , ongoing
main masterlist | f1 masterlist | f1 grid masterlist

🇦🇫 YOU HATE CUZ YOU AIN'T , oscar piastri
����🇲 DOWN SOUTH , lando norris
🇦🇿 KILLER COOKIES , charles leclerc
🇧🇭 STALKER! , max verstappen
🇧🇩 ONLINE LOVE , max verstappen
🇧🇹 THE MOTHERLAND , lewis hamilton
🇧🇳 SULTAN'S SON IN LAW , alex albon
🇲🇲 MEET THE FAM , carlos sainz
🇰🇭 WEDDING OF DREAMS , lando norris
🇨🇳 SO HAWT , f1 grid
🇬🇪 WINNING DRIVE , f1 grid
🇭🇰 THE ART OF CURSING IN CANTONESE , max verstappen
🇮🇳 MAIN TERA BOYFRIEND , logan sargent x fem! gf! reader
🇮🇩 NEW YEARS KISS , lando norris
🇮🇷 VELOCITY OF LOVE , lewis hamilton
🇮🇶 SPICES OF LIFE , yuki tsunoda
🇯🇵 BOW DOWN , winter break in full swing and lewis takes a trip to the land of the rising sun and leaves with the heart of there darling princess
🇯🇴 TOUR LIFE , logan sargent
🇰🇿 JUST DANCE THE KARA ZHORGA , daniel ricciardo
🇰🇼 SUGAR BABY , lando norris
🇱🇧 10 YEARS IN THE MAKING , pierre gasly
🇲🇾 PRESIDENTIAL ANNOUCEMENT , a secret that has been hidden for 2 years finally is revealed and the people couldn't be happier with the out come
🇲🇳 QUICK LERNER , lando norris
🇳🇵I THINK THEY KNOW , charles leclerc
🇴🇲 NOBODY BETTER , lance stroll
🇵🇰 LOVE AT FIRST ROTI , max verstappen
🇵🇸 PROUD OF MY HERITAGE , a fast passed romance has the world captivated as secrets are shared and kept but they eventually all come out in the end
🇵🇬 UNDER THE BAR LIGHTS , carlos sainz
🇵🇭 MY PERFECT PERSON , charles leclerc
🇶🇦 HEATED , charles leclerc
🇸🇦 DAD DOSEN'T APPROVE , toto wolff
🇸🇬 CAN'T BEAT THEM BUY THEM , mick schumacher
🇰🇷 DISPARCH WATCH , the princess of kpop is on hiatus japan with a special someone but people are in denial until they publicly confirm it
🇱🇰 BAD B FROM , lando norris
🇸🇾 EXCUSE MOI , charles leclerc
🇹🇼 NEVER TRUST THE AMERICAN , oscar piastri
🇹🇭 LIGHTS, CAMERA, SPEED! , max verstappen
🇹🇷 SCENE FROM A MOVIE , sebastian vettle
🇦🇪 RULERS OF THE WORLD , max verstappen
🇺🇿 THE BRAID SITUATION , liam lawson
🇻🇳 CULTURE THE WHITE MAN , f1 grid
🇾🇪 FORCED WINTER BONDING , charles leclerc
#꒰꒰ ‧₊˚📁 ─ lola's masterlist's ˚₊· ꒱꒱#formula one x reader#formula 1 x reader#lewis hamilton x reader#max verstappen x reader#george russell x reader#daniel riccardo x reader#lando norris x reader#charles leclerc x reader#carlos sainz x reader#mick schumacher x reader#pierre gasly x reader#yuki tsunoda x reader#esteban ocon x reader#f1 fic#f1 fanfic#f1 fanfiction#f1 fandom#f1 instagram au#sebastian vettel x reader#f1#f1 x reader
409 notes
·
View notes
Text
HERE is the list of the 134 countries that are NOT supporting South Africa's 🇿🇦 claims of genocide against Israel 🇮🇱:
🇦🇩 Andorra
🇦🇴 Angola
🇦🇬 Antigua and Barbuda
🇦🇷 Argentina
🇦🇲 Armenia
🇦🇺 Australia
🇦🇹 Austria
🇧🇸 Bahamas
🇧🇧 Barbados
🇧🇾 Belarus
🇧🇿 Belize
🇧🇹 Bhutan
🇧🇦 Bosnia and Herzegovina
🇧🇼 Botswana
🇧🇬 Bulgaria
🇧🇮 Burundi
🇨🇻 Cabo Verde
🇰🇭 Cambodia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇫 Central African Republic
🇨🇱 Chile
🇨🇳 China
🇰🇲 Comoros
🇨🇬 Congo
🇨🇷 Costa Rica
🇭🇷 Croatia
🇨🇺 Cuba
🇨🇾 Cyprus
🇨🇿 Czech Republic
🇨🇩 Democratic Republic of the Congo
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇩🇲 Dominica
🇩🇴 Dominican Republic
🇹🇱 East Timor (Timor-Leste)
🇪🇨 Ecuador
🇸🇻 El Salvador
🇬🇶 Equatorial Guinea
🇪🇷 Eritrea
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇸🇿 Eswatini
🇪🇹 Ethiopia
🇫🇯 Fiji
🇫🇮 Finland
🇫🇷 France
🇬🇪 Georgia
🇩🇪 Germany
🇬🇭 Ghana
🇬🇷 Greece
🇬🇩 Grenada
🇬🇹 Guatemala
🇭🇹 Haiti
🇭🇳 Honduras
🇭🇺 Hungary
🇮🇸 Iceland
🇮🇳 India
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇲 Jamaica
🇯🇵 Japan
🇰🇪 Kenya
🇰🇮 Kiribati
🇰🇵 Korea, North (North Korea)
🇰🇷 Korea, South (South Korea)
🇽🇰 Kosovo
🇱🇦 Laos
🇱🇻 Latvia
🇱🇸 Lesotho
🇱🇷 Liberia
🇱🇮 Liechtenstein
🇱🇹 Lithuania
🇱🇺 Luxembourg
🇲🇬 Madagascar
🇲🇼 Malawi
🇲🇹 Malta
🇲🇭 Marshall Islands
🇲🇺 Mauritius
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇫🇲 Micronesia
🇲🇩 Moldova
🇲🇨 Monaco
🇲🇳 Mongolia
🇲🇪 Montenegro
🇲🇲 Myanmar (Burma)
🇳🇷 Nauru
🇳🇵 Nepal
🇳🇱 Netherlands
🇳🇿 New Zealand
🇳🇮 Nicaragua
🇲🇰 North Macedonia (Macedonia)
🇳🇴 Norway
🇵🇼 Palau
🇵🇦 Panama
🇵🇬 Papua New Guinea
🇵🇾 Paraguay
🇵🇪 Peru
🇵🇭 Philippines
🇵🇱 Poland
🇵🇹 Portugal
🇷🇴 Romania
🇷🇺 Russia
🇷🇼 Rwanda
🇰🇳 Saint Kitts and Nevis
🇱🇨 Saint Lucia
🇻🇨 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
🇼🇸 Samoa
🇸🇲 San Marino
🇸🇹 Sao Tome and Principe
🇷🇸 Serbia
🇸🇨 Seychelles
🇸🇱 Sierra Leone
🇸🇬 Singapore
🇸🇰 Slovakia
🇸🇮 Slovenia
🇸🇧 Solomon Islands
🇪🇸 Spain
🇱🇰 Sri Lanka
🇸🇪 Sweden
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇹🇼 Taiwan
🇹🇿 Tanzania
🇹🇭 Thailand
🇹🇴 Tonga
🇹🇹 Trinidad and Tobago
🇹🇳 Tunisia
🇹🇲 Turkmenistan
🇹🇻 Tuvalu
🇺🇦 Ukraine
🇬🇧 United Kingdom (UK)
🇺🇸 United States of America (USA)
🇺🇾 Uruguay
🇻🇺 Vanuatu
🇻🇦 Vatican City
🇻🇳 Vietnam
🇿🇲 Zambia
🇿🇼 Zimbabwe
448 notes
·
View notes
Photo

大相撲大阪場所 . . 15日目は 千秋楽 本割りでは 霧馬山が大栄翔に勝ちました。 優勝決定戦でも 霧馬山が大栄翔に勝ちました。 12勝3敗 大栄翔 霧馬山 . . 十両は14勝1敗 逸ノ城 13勝2敗 朝乃山 . . 📷2022.06 ↓↓↓ share #霧馬山優勝 #陸奥部屋 #🇲🇳 #Mongolia #大相撲大阪場所 #大相撲春場所 #大相撲3月場所 #翠富士 #金峰山 #大栄翔 #豊昇龍 #若元春 #宇良 #朝乃山 #逸ノ城 #霧馬山 #sumo #grandsumo3 #tokyo #japan #sumoday #followme #rikishi #おすもうさん #力士 #大相撲 #相撲 #大相撲好きな人と繋がりたい #両国 #エディオンアリーナ大阪 @grandsumo3 @sumokyokai (荒汐部屋) https://www.instagram.com/p/CqPv-forw8g/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#霧馬山優勝#陸奥部屋#🇲🇳#mongolia#大相撲大阪場所#大相撲春場所#大相撲3月場所#翠富士#金峰山#大栄翔#豊昇龍#若元春#宇良#朝乃山#逸ノ城#霧馬山#sumo#grandsumo3#tokyo#japan#sumoday#followme#rikishi#おすもうさん#力士#大相撲#相撲#大相撲好きな人と繋がりたい#両国#エディオンアリーナ大阪
0 notes
Text
Mongolian Miku 🇲🇳✨

Saw at least three of other Mongolian Mikus, so I wanted to put my own spin on it :3
(Aka, I made her too much like my cousins)
#vocaloid hatsune#hatsune fanart#hatsune miku#brazilian hatsune miku#Brazilian Miku#< these tags are here to show you what trend I’m doing lol#Mongolian Miku#Mongolian Hatsune Miku#hatsune miku fanart#vocaloid miku#miku fanart#alr I think that’s all#woah i draw 🤯
195 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mongolian Miku and a khalkh version! 🇲🇳 by mantoupan
114 notes
·
View notes
Text

It was ‘Draw Miku in Your Culture’, so as someone who’s Native and Mongolian🇲🇳I just had to represent her in my cultural attire!🏹🪶🛖 I was originally planning to combine elements from both cultures, but it got a bit too complicated 😭
#native american#native#vocaloid miku#hatsune miku#hatsune fanart#vocaloid hatsune#miku hatsune icons#native art#mongolia#mongolian#mix breed#anime art#anime fanart#fanart#digital artist#artist on tumblr#blue character#mikuhatsune#miku fanart#miku#anime#draw miku in your culture#art#navajo
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Archaeology: How Asia’s First Nomadic Empire Broke the Rules of Imperial Expansion
Ancient China’s mobile neighbors built an empire that’s attracting scientific scrutiny

Xiongnu Herders in what’s now Mongolia, portrayed in this painting, followed their own rules in building a multiethnic empire and advancing iron-making technology starting around 2,200 years ago, new studies indicate. Flickr (CC0 1.0)
— By Bruce Bower | July 2, 2023
In an age that spawned the ancient Roman and Egyptian Empires, Mongolia’s Xiongnu Empire broke the rules of imperial expansion.
Long before the Mongol Empire arose, Asia’s first nomadic empire, horse-riding Xiongnu people, conquered ethnic groups across the continent’s northeastern and central expanses (SN: 1/29/10). A common political system headed by Xiongnu imperial rulers formed about 209 B.C. and lasted for roughly 300 years. Unlike in Rome or Egypt, mobile groups of Xiongnu animal herders accomplished this feat without building cities, forming central bureaucracies, devising a writing system or mobilizing masses of farmers to produce food.
Today, remnants of Xiongnu culture largely consist of more than 7,000 tombs, some heavily looted and many yet to be excavated, in Mongolia and nearby parts of China and Russia. In the last decade, geneticists and archaeologists have ramped up efforts to study these sites and ancient records to decipher the Xiongnu Empire’s political organization and technological achievements.

Starting from a heartland in what’s now central Mongolia, the Xiongnu Empire (brown) spread across a large part of northern Asia, taking hold around 2,200 years ago. Naturalearthdata.Com/Wikipedia (CC0 1.0)
A few ancient Chinese chronicles include descriptions of the Xiongnu political system. These accounts portray the Xiongnu as predatory raiders who belonged to a “simple” confederation of herding groups run by a few nomadic alpha males. Even so, warfare with mounted Xiongnu warriors equipped with bows, arrows and metal weapons had inspired Imperial Chinese leaders to construct their Great Wall.
Some researchers have argued that Xiongnu people formed a lesser, “shadow empire” alongside Imperial China. But that view is giving way to a picture of the Xiongnu Empire as a different, not lesser, type of ancient state, says Yale University archaeologist William Honeychurch.
In this view, nomadic Xiongnu elites developed a flexible system of political power that connected mobile groups with different genetic and cultural ancestries spread across extensive grasslands and forests. “Elite lineages were not only an important part of a multiethnic Xiongnu state, but members of these lineages were sent to peripheral areas as part of state integration,” Honeychurch says. One new study, for example, indicates that Xiongnu women from elite lineages in central Mongolia served as “princess” emissaries to the empire’s frontier, assuming political power in distant territories populated by various ethnic groups.
“This must have been an empire organized around moving populations,” says archaeologist Bryan Miller of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Xiongnu elites were savvy politicians who delegated power to keep the empire together.”
In another recent development, excavations in Central Mongolia point to Xiongnu people as early ironworking innovators whose advances spread to their regional neighbors. These discoveries, and others, highlight the unappreciated complexity and the ongoing mystery of how Xiongnu society worked, researchers say.
The Xiongnu Dispatched Frontier ‘Princesses’
Initial insights into the Xiongnu people’s diverse genetic origins were first published in 2020. DNA extracted from remains of 60 individuals excavated at 27 Xiongnu sites indicated that two genetically distinct populations of Mongolian herders had coalesced to become the Xiongnu people around 2,200 years ago. One population descended from several western Mongolian cultures and the other from a couple of eastern Mongolian cultures.
Additional genetic contributions to the Xiongnu mix then came from farther away, most likely a culture near present-day Ukraine as well as Imperial China, reported archaeogeneticist Choongwon Jeong of Seoul National University in South Korea and colleagues.
Building on those findings, Jeong’s team then examined DNA of 17 individuals from elite and low-status graves at two Mongolian cemeteries on the Xiongnu Empire’s western frontier. Central Mongolia’s Xiongnu heartland lay around 1,200 kilometers to the east.
The six largest and richest tombs contained women whose genetic ancestry traced back to central Mongolia, the scientists reported in April in Science Advances. These women rested in wooden coffins placed in square tombs. Items found in these tombs included gold sun and moon emblems of Xiongnu imperial power, glass beads, silk clothes and Chinese mirrors.

Gold Sun and Moon Emblems of Imperial Xiongnu power were found among other elite items in a woman’s tomb on the western edge of the ancient nomadic empire. DNA evidence indicates the woman was related to ruling families in the empire’s Mongolian heartland. © J. Bayarsaikhan
One woman was buried with horse-riding equipment, a gilded iron belt clasp and a Chinese lacquer cup. These objects have previously been found in graves of male horse-mounted warriors. But such items signal that a deceased person had been powerful, not necessarily a warrior, says Miller, a study coauthor.
Miller and his colleagues suggest that the women had been sent to the frontier to maintain Xiongnu traditions and nurture contacts with Silk Road trade networks (SN: 3/8/17). Preliminary signs of genetic relatedness among individuals interred at one of the cemeteries suggest that some elite Xiongnu “princesses” also cemented power by marrying into local families.
The elite women’s graves were flanked by simple graves of adult men, and of girls and boys ranging from babies to adolescents. These commoners possessed greater genetic diversity than the female big shots. If the men were retainers or servants of female elites, they had come from distant parts of the Xiongnu Empire or possibly beyond, the researchers say.
Male Rulers Were Homebody ‘Princes’
Like these female elites, premier Xiongnu rulers had common roots in central Mongolia while their followers had diverse geographic origins, another team reports in the June Archaeological Research in Asia. But rather than being sent to the far reaches of the empire, these rulers stayed close to home.
Three male nobles interred in large underground tombs at one of the largest Xiongnu cemeteries, Gol Mod 2, spent most or possibly all their lives in the Khanuy Valley where they were buried, say archaeologist Ligang Zhou of Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology in Zhengzhou, China and colleagues.
Meanwhile, at least four of eight individuals buried in some of the many small satellite graves situated near the nobles’ tombs had spent much of their lives in distant places before settling in or near the Khanuy Valley, measurements of different forms of the element strontium in individuals’ teeth and bones indicate. Diet-related strontium signatures, which vary from one region to another, signal where a person spent early and later parts of their lives.
The identities of those in satellite graves, who were apparently killed to form entourages of followers that accompanied deceased nobles, are unclear. They include children and adults, Zhou says. Some were buried with metal weapons or luxury objects such as jewelry.
Genetic and strontium findings suggest that “Xiongnu political organization in central and western Mongolia was highly similar,” Zhou says. Then, as the empire expanded, rulers in the Xiongnu heartland sent select members of their extended families, such as high-ranking women, to new territories in order to replicate the imperial power structure.
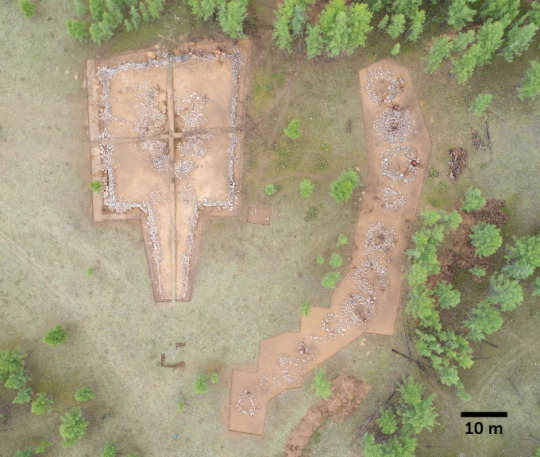

Seen from above, a Xiongnu noble’s tomb, left, lies near a set of small tombs that contained his followers to the afterlife. Xiao Ren, Henan Provincial Institute of Culture Heritage an Archaeology
Iron Innovations Bolstered the Xiongnu Empire
From the start, Xiongnu imperial power depended on a ready supply of iron weapons and other gear that enabled horse-mounted warfare. Researchers who view the Xiongnu Empire as a faint version of Imperial China argue that the nomads’ power depended on importing crops and borrowing iron-making techniques, or simply trading for iron products, from the Chinese.
But new findings suggest that Central Mongolian metallurgists launched a regional boom in iron production around the time the Xiongnu Empire originated, says archaeologist Ursula Brosseder of the University of Bonn in Germany.
At a riverbank site, Brosseder and colleagues have excavated five iron smelting installations that contain by-products of iron making and burned wood. Radiocarbon dates of that material extend to as early as around 2,200 years ago, when the Xiongnu Empire arose.
That makes these finds, each of which consists of two pits connected by a tunnel, the oldest Xiongnu iron smelting kilns by at least 100 years, the researchers reported in March in Asian Archaeology.
Earlier research had established that people living just north of Xiongnu territory in southern Siberia started producing iron as early as around 2,800 years ago. Based on comparisons of finds in the two regions, Xiongnu metallurgists not only learned about iron making from their neighbors but also invented tunnel furnaces, the investigators say. Eastern Asian groups outside the Xiongnu sphere began making and using tunnel furnaces over the next couple of centuries.
Discoveries by Brosseder’s group “show that metallurgy reached the Xiongnu in Mongolia from southern Siberia, not China,” says archaeologist Nikolay Kradin, director of the Institute of History, Archaeology and Ethnology at the Far-Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Vladivostok. Craftspeople at several iron-making centers, some slightly younger than Brosseder’s discoveries and others yet to be found, must have managed that technological transition, hypothesizes Kradin, who did not participate in the new research.
Brosseder suspects the Mongolian site she’s studied hosted a major iron-making operation. Four iron-making furnaces excavated near the other five have not yet been dated. And ground-based remote sensing equipment has revealed signs of at least 15, and possibly 26, more iron smelting kilns still covered by sediment.
“We can expect more findings of Xiongnu iron smelting centers considering the demand for iron horse gear, arrowheads, carts and other material by the empire’s large army,” Brosseder says.
No reliable estimates exist for the size of that army, or for the overall number of Xiongnu people, says Michigan’s Miller. Xiongnu herders, who also occasionally cultivated a grain called millet, moved across the landscape in relatively small groups that must have been greatly outnumbered by Imperial China’s estimated 60 million citizens.
The Capital Was a Seasonal Seat of Power
In the same valley where Brosseder’s group discovered the oldest known Xiongnu iron smelting kilns, Mongolian researchers have uncovered remains of what was probably a Xiongnu political center, or perhaps even its capital, called Longcheng in 2020. Consistent with everything else about the Xiongnu Empire, “this was a capital of a different kind,” says Miller.
Longcheng excavations so far have focused on a large building that may have hosted important gatherings.
Roof tiles on that structure bear an inscription in ancient Chinese characters that reads “Son of Heaven Chanyu.” Chinese records refer to the supreme Xiongnu ruler as “chanyu.” That royal inscription, the only one found within the Xiongnu realm, identifies Longcheng as a seat of power, Miller says.
Rather than a permanent site, Longcheng, like several excavated Xiongnu villages and walled compounds in central Mongolia, served as a seasonal stopover or temporary meeting place, Miller suspects (SN: 11/15/17). “We don’t know if those other sites were separate political capitals for the Xiongnu,” he says. Top Xiongnu honchos gathered for part of the year at Longcheng before packing up and moving elsewhere, he speculates. Xiongnu herders, regardless of political status, navigated animals to seasonal grazing spots. Staying in one place throughout the year was not an option.
Having a flexible, mobile system of rule appears to have kept the nomadic realm rolling for a few hundred years before the Xiongnu Empire rapidly disintegrated about 1,900 years ago. Why it did so is an enduring mystery. Perhaps the empire succumbed to combined attacks by Imperial China and other groups or, in true nomadic fashion, Xiongnu people reorganized on a smaller scale and moved to safer areas.
Still, “the Xiongnu had created a massive imperial network in Asia,” Miller says. “Their ways of life didn’t go away overnight.” For instance, Xiongnu-mediated trading by groups situated along Central Asia’s Silk Road routes continued despite military defeats in the empire’s central Mongolian heartland. Only further archaeological and genetic discoveries can clarify how Xiongnu people in the imperial core responded to those setbacks.
Whatever happened, Asia’s first nomadic empire can likely be counted on for a few more surprises.
— Science New, July 02, 2023, By Bruce Bower
#Archaeology#Nomedic Empire#Bruce Bower#Xiongnu Herders#Mongolia 🇲🇳#Roman and Egyptian Empires#Xiongnu Empire and Empirial Rulers#Xiongnu Warriors#Chinese Imperial Leaders#Great Wall#Yale University Archaeologist William Honeychurch#Bryan Miller of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor#Science Advances#Glass Beads Silk Clothes and Chinese Mirrors#Wooden Coffins ⚰️#Square Tombs#Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology in Zhengzhou China 🇨🇳#Princesses#Nikolay Kradin#Institute of History Archaeology and Ethnology at the Far-Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Vladivostok#Siberia#Brosseder’s Group#Archaeologist Ursula Brosseder of the University of Bonn Germany 🇩🇪
2 notes
·
View notes