Text
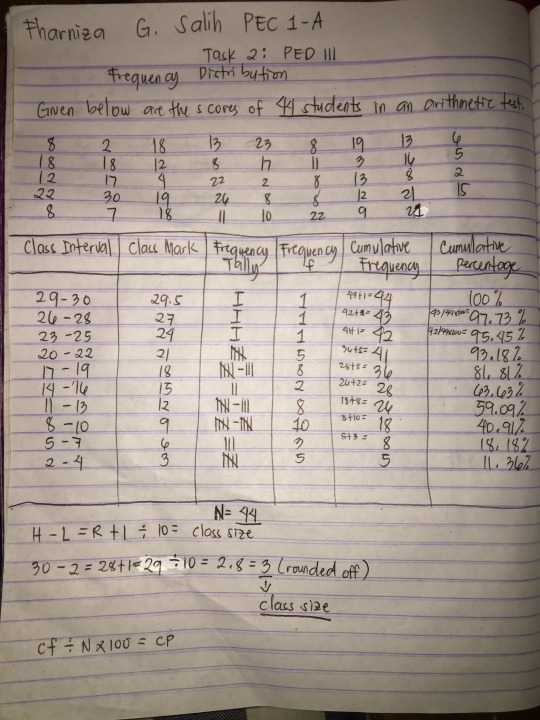
Task 2: Frequency Distribution Table

0 notes
Text
Item Analysis
Item analysisis a process of examining the student’s response to individual item in the
test. It consists of different procedures for assessing the quality of the test items given to the students. Through the use of item analysis we can identify which of the given are good and defective test items. Good items are to be retained and defective items are to be improved, to be revised or to be rejected.
Discrimination Index
It is the power of the item to discriminate the students who know the lesson and those
who do not know the lesson. It also refers to the number of students in the upper group who got an item correctly minus the number of students in the lower group who got an item correctly. Divide the difference by either the number of the students in the upper group or number of students in the lower group or get the higher number if they are not equal.
Discrimination index is the basis of measuring the validity of an item. This index can be interpreted as an indication of the
extent to which overall knowledge of the content area or mastery of the skills is related to the response on an item. The formula used to compute for the discrimination index is:
where: DI = discrimination index value; CUG= number of the students selecting the correct
answer in the upper group; CLG= number of students selecting the correct answer in the lower group; and D = the number of students in either the lower group or upper group.
Test Reliability
Reliabilityrefers to the consistency with which it yields the same rank for individuals who
take the test more than once (Kubiszyn and Borich, 2007). That is, how consistent test results or other assessment results from one measurement to another. A test is reliable when it can be used to predict practically the same scores when test administered twice to the same group of students and with a reliability index of 0.60 or above. The reliability of a test can be determined by means of Pearson Product Moment of Correlation, spearman-Brown Formula, Kuder-Richardson Formulas, Cronbach’s Alpha, etc.
Factors Affecting Reliability of a Test
1. Length of the test
2. Moderate item difficulty
3. Objective scoring
4. Heterogeneity of the student group
5. Limited time
Test Validity
Validity is concerned whether the information obtained from an assessment permits
the teacher to make a correct decision about a student’s learning. This means that
the appropriateness of score-based inferences or decisions made are based on the
students’ test results. Validity is the extent to which a test measures what it is
supposed to measure.
Types of Validity
1. Face Validity. It is the extent to which a measurement method appears “on its face” tomeasure the construct of interest. Face validity is at best a very weak kind of evidence that a measurement method is measuring what it is supposed to. One reason is that it is based on people’s intuitions about human behaviour, which are frequently wrong. It is also the case that many established measures in psychology work quite well despite lacking face validity.
2. Content Validity.
A type of validation that refers to the relationship between test and theinstructional objectives, establishes content so that the test measures what is supposed to measure. Things to remember about validity:
a. The evidence of the content validity of a test is found in the Table of specification.
b. This is the most important type of validity for a classroom teacher.
c. There is no coefficient for content validity. It is determined by experts judgmentally, not
empirically.
3. Criterion-related Validity.
A type of validation that refers to the extent to which scores from atest relate to theoretically similar measures. It is a measure of how accurately a student’s current test score can be used to estimate a score on a criterion measure, like performance in courses, classes or another measurement instrument. For example, the classroom reading grades should indicate similar levels of performance as Standardized Reading test scores.
a. Concurrent validity.
The criterion and the predictor data are collected at the same time. This type of validity is appropriate for tests designed to assess a student’s criterion status or when you want to diagnose student’s status; it is a good diagnostic screening test. It is established by correlating the criterion and the predictor using Pearson
Product Correlation Coefficient and other statistical tools correlations.
b. Predictive validity.
A type of validation that refers to a measure of the extent to which student’s current test result can be used to estimate accurately the outcome of the student’s performance at later time. It is appropriate for tests designed to assess students’ future status on a criterion. Regression analysis can be sued to predict the criterion of a single predictor or multiple predictors.
4. Construct Validity.
A type of validation that refers to the measure of the extent to which a test measures a theoretical and unobservable variable qualities such as intelligence, math achievement, performance anxiety, and the like, over a period of time on the basis of gathering evidence. It is established through intensive study of the test or measurement instrument using convergent/divergent validation and factor analysis. There are other ways of assessing construct validity like test’s internal consistency, developmental change and experimental
intervention.
a. Convergent validity is a type of construct validation wherein a test has a high correlation with another test that measures the same construct.
b. Divergent validity is type of construct validation wherein a test has low correlation with a test that measures a different construct. In this case, a high validity occurs only when there is a low correlation coefficient between the tests that measure different
traits.
c. Factor analysis assesses the construct validity of a test using complex statistical procedures conducted with different procedures.
#Assessment Tools Development
#Assessment development cycle
#Test item formulation
#Item analysis
#Reliability
#Measurements of relationship
#Index of discrimination
#Inter-rater Reliability
#Validity
Fharniza G. Salih PEC 1-A
0 notes
Text
IV. Assessment Tools Development
Assessment Development Cycle
1. Planning Stage
Determine who will use the assessment results and how they will use them.
Identify the learning targets to be assessed.
Select the appropriate assessment method or methods.
Determine the sample size.
2. Development Stage
Develop or select items, exercises, tasks, and scoring procedures.
Review and critique the overall assessment for quality before use.
3. Use Stage
Conduct and score the assessment.
Revise as needed for future use.
Steps in Developing Assessment Tools
1. Examine the instructional objectives of the topics previously discussed. The first step in
developing a test is to examine and go back to the instructional objectives so that you can
match with the test items to be constructed.
2. Make a table of specification (TOS). TOS ensures that the assessment is based from the intended learning outcomes.
3. Construct the test items. In constructing test items, it is necessary to follow the general
guidelines for constructing test items. Kubiszyn and Borich (2007) suggested some guidelines for writing test items to help classroom teachers improve the quality of test items to write.
Begin writing items far enough or in advance so that you will have time to revise them.
Match items to intended outcomes at appropriate level of difficulty to provide valid measure of instructional objectives. Limit the question to the skill being assessed.
Be sure each item deals with an important aspect of the content area and not with trivia.
Be sure the problem posed is clear and unambiguous.
Be sure that the item is independent with all other items. The answer to one item should not be required as a condition in answering the next item. A hint to one answer should not be embedded to another item.
Be sure the item has one or best answer on which experts would agree.
Prevent unintended clues to an answer in the statement or question. Grammaticalinconsistencies such as “a” or “an” give clues to the correct answer to those students who are not well prepared for the test.
Avoid replication of the textbook in writing test items; do not quote directly from the textual materials. You are usually not interested in how well students memorize the text. Besides, taken out of context, direct quotes from the text are often ambiguous.
Avoid trick or catch questions in an achievement test. Do not waste time testing how well the students can interpret your intentions.
Try to write items that require higher-order thinking skills.
4. Assemble the test items
After constructing the test items following the different principles of constructing test item, the next step to consider is to assemble the test items. There are two steps in assembling the test: (1) packaging the test; and (2) reproducing the test. In
assembling the test, consider the following guidelines:
Group all test items with similar format.
Arrange test items from easy to difficult.
Space the test items for easy reading.
Keep items and option in the same page.
Place the illustrations near the description
Check the answer key.
Decide where to record the answer.
5. Check the assembled test items
Before reproducing the test, it is very important to proofread first the test items for typographical and grammatical errors and make necessary corrections if any. If possible, let others examine the test to validate its content. This can save time during the examination and avoid destruction of the concentration of the students.
6. Write directions
Check the test directions for each item format to be sure that it is clear for the students to understand. The test direction should contain the numbers of items to which they apply; how to record their answers; the basis of which they select answer; and the criteria for scoring or the scoring system.
7. Make the answer key
Be sure to check your answer key so that the correct answers follow a fairly random sequence.
8. Analyze and improve the test items
Analyzing and improving the test items should be done after checking, scoring and recording the test.
#D. Assessment Tools Development#Assessment Development cycle#Test item formulation#Item analysis#Reliability#Measures of relationship#Index of determination#Inter-raterReliability#Validity
0 notes
Text
III. Learning Target and Assessment Method Match
Table of Specifications (TOS)
is a chart or table that details the content and level of cognitive domain assessed on a test as well as the types and emphases of test items (Gareis and Grant, 2008).
TOSis very important in addressing the validity and reliability of the test items. The
validity of the test means that the assessment can be used to draw appropriate result
from the assessment because the assessment guarded against any systematic error. TOS provides the test constructor a way to ensure that the assessment is based from the intended learning outcomes. It is also a way of ensuring that the number of questions on the test is adequate to ensure dependable results that are not likely caused by I chance.It is also a useful guide in constructing a test and in determining the type of test items that
you need to construct.
#C. Learning Target and Assessment Method Match: Table of Specifications
0 notes
Text
II. Types of Teacher-made Tests
There are different types of assessing the performance of the students like objective test, subjective test, performance based assessment, oral questioning, portfolio assessment, self-assessment and checklist. Each of this has their own function and use. The type of assessment tools should always be appropriate with the objectives of the lesson. There are two general types of test item to use in achievement test using paper and pencil test. It is classified as selection-
type items and supply-type items.
0 notes
Text
I. Characteristics of Quality Assessment Tools
Assessment tools are used to measure a student’s academic abilities, skills and/or fluency in a given subject or to measure one’s progress toward academic proficiency in a specific subject area. It is the instrument that used to collect data for each outcome. The actual product that is handed out to students for the purpose of assessing whether they have achieved a particular learning outcomes.
Assessments can be either formal or informal.
Informal assessments are often inferences an educator draws as a function of unsystematic observations of a student’s performance in the subject matter under consideration.
Formal assessments are objective measurements of a students’ abilities, skills, and fluency using screening, progress, monitoring, diagnosis, or evaluation. Both types of assessments are important; however, only formal assessments are research, or evidence-based.
Educators use assessment tools to make informed decisions regarding strategies to enhance student learning.
The type of test used should match the instructional objective or learning outcomes of the subject matter posed during the delivery of the instruction. The following are the types of assessment tools:
1. Objective Test
It requires student to select the correct response or to supply a word or shortphrase to answer a question or complete statement. It includes true-false, matching type, and multiple-choice questions. The word objective refers to the scoring, it indicates that there is only one correct answer.
2. Subjective Test
It permits the student to organize and present an original answer. It includeseither short answer questions or long general questions. This type of test has no specific
answer. Hence, it is usually scored on an opinion basis, although there will be certain facts and understanding expected in the answer.
3. Performance Assessment
Is an assessment in which students are asked to perform real-world tasks that demonstrate meaningful application of essential knowledge and skills. It can appropriately measure learning objectives which focus on the ability of the students to demonstrate skills or knowledge in real-lifer situations.
4. Portfolio Assessment
It is an assessment that is based on the systematic, longitudinal collection of student work created in response to specific, known instructional objectives and
evaluated in relation to the same criteria. Portfolio is a purposeful collection of students’ work that exhibits the students’ efforts, progress and achievements in one or more areas over a period of time. It measures the growth and development of students.
5. Oral Questioning
This method is used to collect assessment data by asking oral questions.
The most commonly used of all forms of assessment in class, assuming that the learner hears and shares the use of common language with the teacher during instruction. The ability of the students to communicate orally is very relevant to this type of assessment. This is also a form of formative assessment.
6. Observation Technique
This is a method of collecting assessment data. The teacher will
observe how students carry our certain activities either observing the process or product.
There are two types of observation techniques: formal and informal observations.
Formal observations are planned in advance like when the teacher assess oral report or presentation in class while informal observationis done spontaneously, during instruction like observing the working behavior of students while performing a laboratory experiment.
7. Self-report
The responses of the students may be used to evaluate both performance and attitude. Assessment tools could include sentence completion, Likert scales, checklists, or holistic scales.
Different Qualities of Assessment Tools
Validity- refers to appropriateness of score- based inferences; or decisions made based on the students’ test results. The assessment measures what it is intended to measure for its intended purpose.
Reliability- refers to the consistency of measurement; that is how, consistent test results or other assessments results form one measurement to another.
Fairness- means the test item should not have any biases. It should not be offensive to any examinee subgroup. A test can only be good if it is fair to all the examinees.
Objectivity- refers to the two or more raters or test administrators concerning the score of a student.
Scorability- means that the test should be easy to score, direction for scoring should be clearly stated in tge instruction. Provide the students an answer sheet and the answer key for the one who will check the test.
Adequacy- means that the test should contain a wide range of sampling of items determine tge educational outcomes or abilities so that the resulting scores are representatives of the total performance in the areas measured.
Administrability- means the test should be administered uniformly to all students so that the scores obtained will not vary due to factors other than differences of the students’ knowledge and skills.
Practicality and Efficiency- refers to the teachers familiarity with the method used, time required for the assessment, complexity of the administration, ease of scoring, ease of interpretation of the test results and the materials used must be at the lowest cost.
#A.Characteristics of Quality Assessment tools
0 notes
Text
Task 1: Designing and Developing Assessments
Assessments literacy involves understanding how assesstments are made, what type of assessments answer what questions, and how the data from assessments can be used to hell teachers, students, parents, and other stakeholders make decision about teaching and learning.
In this blog, we’ll know the characteristics of quality assessment tools and the different types of teacher-made tests. This also includes the learning target, assessment methods and assessment tools development.
#Task 1 - Designing and Developing Assessments
#Introduction of Topic
Fharniza G. Salih PEC 1-A
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text

#OBJECTIVE TYPE OF TEST#TRUE OR FALSE#SENTENCE COMPLETION#MATCHING TYPE#MULTIPLE CHOICE#MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
0 notes
Text
What do we mean by Assessment, Testing, Measurement and Evaluation? What’s the difference?
In educational setting, assessment, evaluation, and testing are all used to measure the learning capabilities, different learning style of the students and how well they meet the stated goals and objective and as well as the facilitator with regards on how their instructional learning materials is useful and effective.
To make you really understand the differences, here are sime definitions;
Assessment is a systematic process of documenting and using emphirical data to measure knowledge, skills, attitudes and beliefs. While Testing or teat is used to examine someone’s knowledge of something to determine what person know or has learned.
The Measurement refers to the set of procedures and the principles on how to use the procedures in educational tests and assessments and Evaluation is a systematic process of collectinf, analysing and interpreting.
To simplify things, assessment focuses on improving the learning process of the learners. A Test us described to measure the performance of the learners in relation to what knowledge they have been reached. And Measurement is a set of procedures in educational evaluations such as raw score, percentile ranks and etc. While Evaluation focuses on grades and may reflect classroom components.
Overall, assessments,test, measurement and evaluation plays a vital role in developing the learning process of the learners and also imrpoving the learning instructional startegies of the teachers.
0 notes
Text
PED 111 ASSESSMENT IN STUDENTS LEARNING 1
Discovering and Learning is a helpful way to improve and expand our ability and learning skills.
This course focuses on the principles development and utilization to conventional assessment tools to improve the teaching and learning process.
Assessment is the process on determining the learning process of the learners. It has a vital role in the process of learning and motivation. It also aims to identify and provide data or information about the progress of the learners. Assessment is an integral part of instruction because it determines wether or not the goals of education are being met.
Principles of assessment also serves as a guidelines that helps students to ensure that the teaching mode or strategies is effective, useful and appropriate.
By assessing the learners using the 3 Types of assessment is a great way to be to able identify and measure the effectiveness of teaching methods. The 3 Types of Assessment is The Assesment as Learning, The Assessment of Learning and Assessment for Learning.
Applying this 3 types of assessment and by the guidance of principles of educational assessment, Teachers will able to know on what students have learned in their lessons and also on what particular subjects and what reasons that the students haven’t met the standard grade or get a low grade. Teachers determine the weaknesses and strengths of their students in their learning process. Also Teachers may ask themselves if they really teach what the students supposed to be learned.
So, in this matter, teachers begin to understand and provide the efficient and effective teaching strategies to help the learners enhanced their learning skills and produced a quality education.
FHARNIZA G. SALIH PEC-1A
1 note
·
View note
