Text
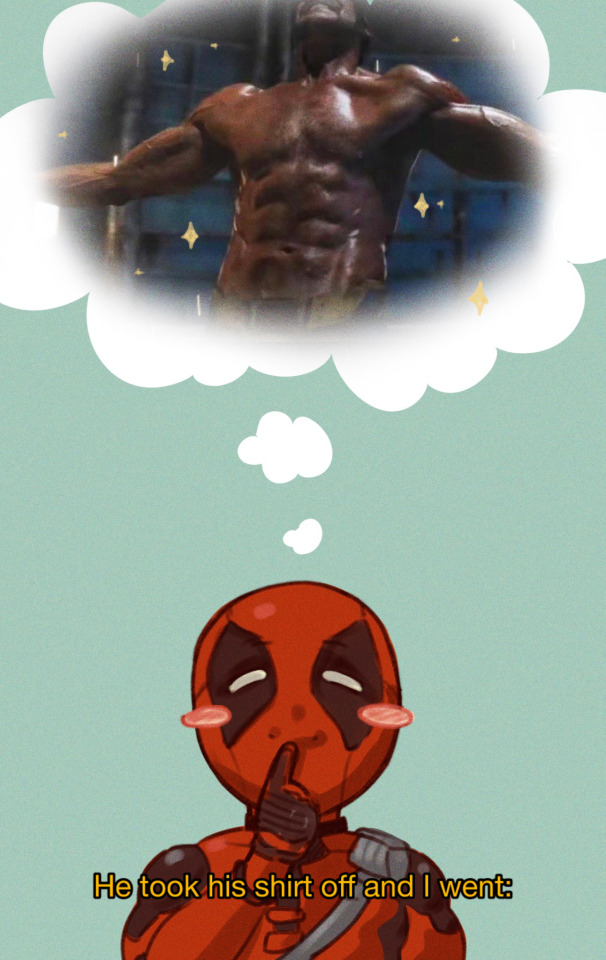
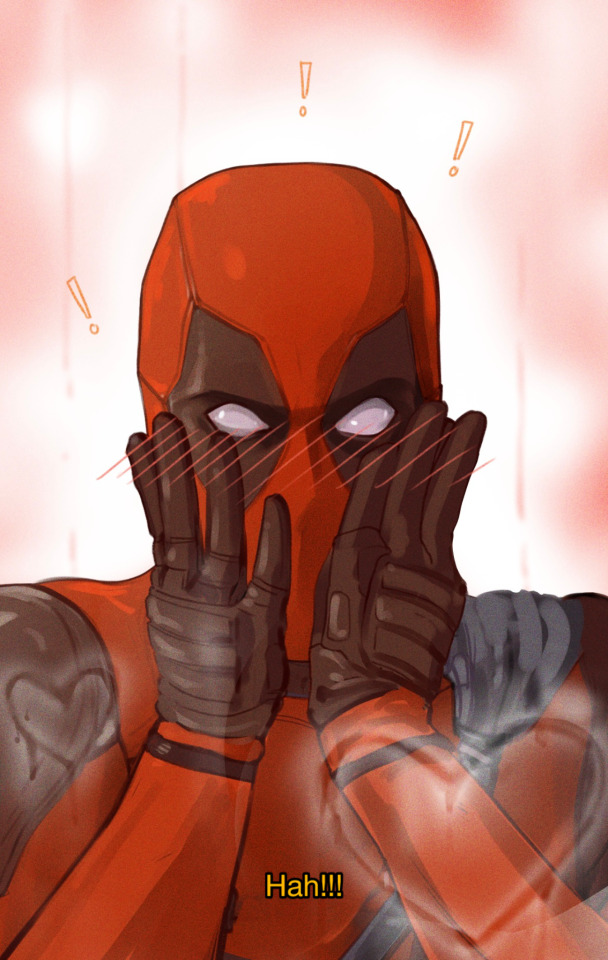
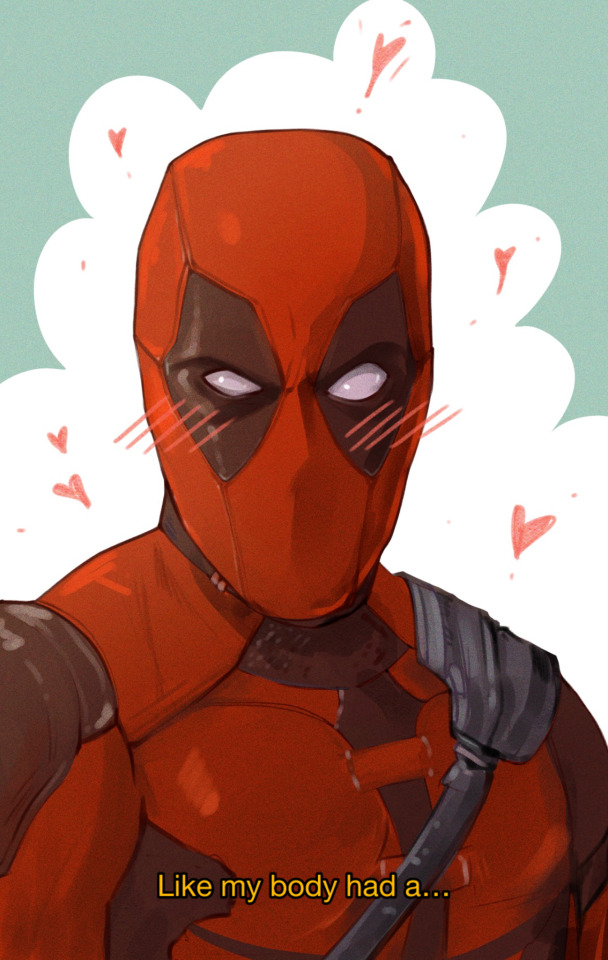
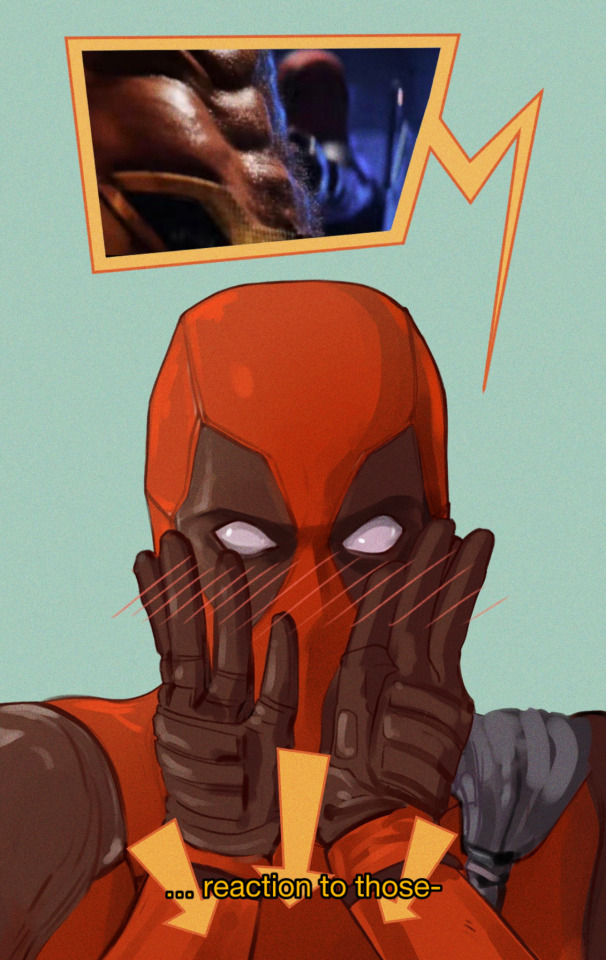
WOLFEY!! :D
wolfey con perish... :(
0 notes
Text
A layman's guide to olympic fencing—
for writers, artists, olympic fans, or the otherwise curious.

disclaimer: i say layman for a reason! i'm not at all a professional, or even good, but i have been fencing (very) recreationally at an amateur level for ~7 years. also, my exposure to sabre is extremely limited, and i am speaking from an american POV, so please feel free to correct me on any points you see necessary. :)
long post incoming...
So, what is "Olympic fencing?"
First and foremost, it is a sport. Not a fight, not a duel—a sport. One of five that have been permanent fixtures since the very first modern Olympic games, actually—hence the name! While other similar sword-wielding activities (such as historical European martial arts (HEMA), kendo, or wushu for example) may occasionally be referred to as "fencing," most people (me included) define fencing as this specific sport, and use other classifiers to categorize the rest.
Originally, fencing began as a form of military training in Germany and Italy, before spreading recreationally across more areas in Europe. Currently, the fencing scene is almost uncontestedly dominated by Italy, France, and Hungary, though both China/HK and the US have had some pretty stellar wins more recently.
In addition, French has a pretty large influence on fencing terminology and language, at least in the West. Be prepared!
The Basics
Three Weapons
Fencing is divided into three disciplines, each with their own equipment, strategies, and ruleset. They are as follows:
Épée: The classic. The heaviest and most defensive of the three blades, épée's simple ruleset allows for more elaborate strategy and really lives up to fencing's moniker of "physical chess." In épée, the entirety of your opponents body (including face, toes, etc!) counts as valid target area and all hits must be scored with the tip of the blade. In case of a double-touch (relatively simultaneous hits from both opponents), both opponents score points.
Because there's no need for specific target areas, épéeists enjoy minimal equipment, forgoing lamés (electric jackets, pronounced luh-may) and mask cords in exchange for a larger bell guard to protect the hand (that big bit of metal at the end of the blade). Épéeists can use pistol grips for more point control (molded to fit a hand), or a french grip to get a little bit of extra distance (red stick grip).
Épée bouts are stereotypically known for being slow and boring, since the absence of right-of-way (explained later) allows more freedom in trying to sus out opponent reactions and strategize, and the whole-body target + double-touch system means there's more benefit to fencing slowly in comparison to sabre or foil. It's not uncommon for épée bouts to begin with both fencers being carded for passivity! There's a lot of bouncing back and forth in the middle.

Saber (Sabre): Fast, slashing, and aggressive. The fencing you see in movies? Sabre. It's the only cutting weapon, where the entire length of the blade is able to register contact with the opponent. In sabre, the target area is the upper half of the body (including the face, but excluding the hand) and their lamés reflect that. Sabre also employs what is known as right-of-way/priority/advantage (from here on abbreviated as RoW) which, in the case of a double-touch, essentially gives RoW—and therefore the point—to the "aggressing" fencer at the referee's discretion. RoW is pretty complicated, but is very influential in how both sabre and foil play out.
In their ready (en garde) position, sabreists also hold their blade vertically to protect the face (as opposed to foil and épée, where the blade is held horizontally to keep the point towards the opponent). Sabreists also need special masks to register hits, as well as a mask cord to connect it to the rest of the electric circuit. Sabre bell guards are kinda swoopy and extend downward (think pirates) and are always "french grips" (aka just a stick).
Sabreists are generally known for being (respectfully) batshit insane and dramatic as hell. Bouts are extremely fast (rarely more than a few seconds) and look simple, and rely much more on pure athleticism and fast reaction times than épée. Most bouts consist of the two fencers running towards each other, maybe a parry or two, then both fencers scoring hits with a fair bit of screaming and angrily pointing at the ref. Oh wait, did I say running? Sorry, I meant advancing, since sabre is also the only discipline where crossing-over with your legs got banned because people just started sprinting towards the middle instead of actually fencing. Love them for that.

Foil (Fleuret, rarely): Oh, foil. The artistic middleman. Originating as a practice weapon, foil tends to sit in the middle of épée's careful point-control and elaborate strategy and sabre's split-second reactions and fuck-it-we-ball energy. Yet somehow, it ends up being more nit-picky and complicated than both. It has the smallest target area of the three, only covering the torso, as well as the lightest blade. Touches are only registered from the tip.
RoW's influence is noticeably large, since, compared to sabre, the longer bout times actually allow for opportunity for RoW to be traded between you and your opponent. Foil can almost be thought of as turn-based combat. Fencer A initiates the attack first, now has RoW, lunges and misses, which gives RoW to Fencer B. Fencer B attacks, gets parried (back to Fencer A), A extends, B counterattacks, A gets the point.
Foil stereotypes aren't as strong as épée or sabre stereotypes, but foilists are generally known for either being super pedantic and arguing w/ the ref about RoW or whipping their blade around constantly & being flowery (hence, "fleuret"). Because of how bendy the foil is, foilists can also do cool stuff like flicks (snapping your wrist so that the blade bends around, oftentimes to hit your opponents back) and can also get into pretty funny in-fighting situations a bit more often than sabre/épée (since corps-a-corps contact isn't allowed in fencing, and stepping back means you lose RoW, there's a lot of awkward up-close poking).

Some Positions
En garde: the basic fencing position. In essence, a squat, with one foot facing forward and the other turned out, roughly one and a half foot-lengths apart. This is the basis from which all other movements—the lunge, the advance, the retreat—should be executed, and the position fencers return to once an action is completed.
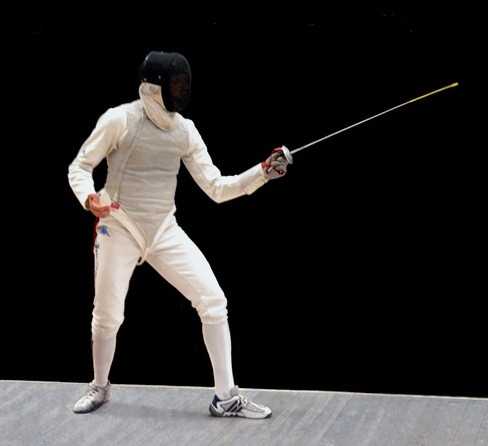

Lunge: the quintessential fencing attack. From en garde, extend your dominant arm, kick out your front foot, land forward, and extend your back arm for balance. To recover, bend your back leg and return to en garde.

Parry: the most basic piece of defensive bladework that every fencer learns, with the "beat" serving as its offensive counterpart. Consists of hitting your opponents blade to prevent a touch. There are nine different parries in classical fencing, but the most common (in foil/épée) are the four and six, which defend the inside and outside lines respectively.

Ettiquette & Other Fun Facts
All fencers must salute their opponent, referee, and audience (if there is one) before and after the bout. Usually just consists of "nodding" at the salutee with your blade before the mask is donned. At the end of bouts, a handshake with your opponent using your non-dominant hand is also expected. Many people substitute/add on to the handshake by tapping blades instead.
Unlike in tennis, seeing a fencer hold up a one on their hand after a touch is an acknowledgement of the opponent's point, whereas a closed fist is a claim of theirs.
When fencing without a ref, many people will slap their thigh to indicate the start of a bout.
Fencers may not speak while the mask is on.
Fencing clubs are also sometimes called salles.
While electrical equipment can vary between disciplines, all fencers are required to wear knickers, a plastron (under-arm protector), a body cord, a jacket, a glove, and a mask. For women, a plastic chest protector is also required. In sabre and foil, fencers also wear a mask cord and lamé.
The first safety rule most fencers learn is to never raise your blade towards someone without a mask on, and it's taken pretty seriously. Because the back of a mask is exposed, its also a big big no-no to turn your back to your opponent during a bout or otherwise lower your head.
Common Terminology
En garde, prez, allez! - On guard, ready, fence! Used to signal the start of a bout.
Halt! - Said by referees to. halt the bout.
Strip/piste - The surface on which fencers fence. Usually around 2m wide and 14m long, the lines on the piste also dictate where fencers must move to to begin bouts, and where they're considered out-of-bounds. Sometimes, they're on raised platforms. Yes, people have fallen off, yes, it's extremely funny.
Feint - Probably what you think it is.
Disengage - Moving your blade in a little circle to avoid contact with what is usually an incoming parry/beat. On a very basic level, straight attacks beat disengages, disengages beat parries, and parries beat straight attacks.
Fleche - An explosive running attack. Due to not being able to cross-over, sabreists use "flunges" instead, a mix between a fleche and a lunge that essentially entails flinging yourself at your opponent in a flying lunge.
Balestra - hop :)
Riposte - An immediate attack done after a defender's parry. Usually heard as "parry-riposte."
Tempo - A kind of nebulous concept, but very similar to the musical definition of the word. The pace of a bout, sorta. Often used when someone is advised to break tempo or if one fencer is controlling the tempo of a bout.
FAQ
Why are the blades bendy? To keep us from dying, mainly. What, you want the metal pole people can throw at each other at the same speed as a bullet (literally) to be solid? Also, blades break a lot already, especially in the hands of the inexperienced—they'd snap a hell of a lot more if they weren't flexible. Ouch.
Does it hurt? About as much as getting poked really hard with a steel stick would. Leaves bruises often, but cuts very rarely. You get used to it. The real kicker is staying in en garde for that long. Trust me, your quads will be screaming.
Is it- No, it's not dangerous. If you follow the rules, fencing is actually extremely safe, especially compared to contact sports.
Does a red light mean no touch? No. One fencer is assigned a red light that lights up whenever a touch is made, and the other is given green. In sabre and foil, yellow (sometimes white) means whatever the fencer hit was off-target, and should not be counted as a point. Épée doesn't have an off-target light, since épéeists don't wear lamés.
How do the masks know when a point is scored? Often asked upon seeing the little lights on the side of masks light up upon touches. Unless you're "dry fencing" (no electricity), you're typically hooked up to a circuit. If you fence épée or foil, there's a little button on the end of your blade that registers when pressure is added onto it. When a hit is scored, the signal goes through the wire in your blade, up your body cord, and eventually to "the box" (and your mask if you're fancy), and the corresponding light is flashed.
Why hold your hand behind your back? Most people don't! Some beginners do it to prevent themselves from reflexively moving their non-gloved hand in front of them when being attacked (which is against the rules), but most fencers either keep their hand relaxed at their side, raised in a t-rex pose, or occasionally above the head.
Helmet? Mask.
Sword? If you want.
Touché? Often "touche," actually. No accent.
Paralympics? On (stationary) wheelchairs. Extremely cool, actually, and very hard. Check it out!
Expensive? To get all your own stuff? Yes. But most clubs will rent you equipment, or sometimes lend it for free! But yes, more expensive than, like, soccer. :(.
Is it fun? Absolutely. To quote some random internet user, "it's like chess, at 90 miles an hour, oh and there's swords!" I would 100% recommend it to everyone, especially if you're on the older side (fencing isn't super age-restricted at all—seeing a 12 y/o and a 70 y/o facing off on a club piste isn't uncommon!) It is exhausting, exhilarating, and super, super fun. Give it a shot!
.
Please feel free to send any and all questions, corrections, or musings my way. Thanks for reading—I hope this was interesting and/or useful!
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
whodunnit but the mc dies first and is trying to solve the mystery from beyond the grave
0 notes
Text
Not sure how many people are gonna get this

Edit: this blew up on twitter so Incase you saw it there I am the same person
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing tips for labs/scientists
for biology wet labs, but possibly applicable elsewhere:
there is a hierarchy, but not a harsh one. undergrads/hs interns < grad/phd students (in order of seniority, ie 1st year, 2nd year...) < postdocs < PI (principal investigator, the big boss). each higher "level" generally advises and mentors the level below them, with the PI directing and advising research for all lab members. the mentor/mentee relationship is very important, and "younger" lab members will often spend a lot of time just shadowing/assisting their mentors.
"publish or perish" is the system that funds labs and motivates ppl. for this reason, confidentiality is also important, and its not uncommon for researchers to pull long hours to graduate on time or get a paper out before someone else does.
labs are/should be collaborative environments! everyone knows what project everyone else is working on, and its very common for people to approach you asking for advice or protocols.
labs aren't just white! they're typically very colorful. neon tip boxes everywhere, multicolored tape, random post-its, memes, cutesy nerdy science merch. also cardboard. cardboard everywhere. also, usually people don't just work exclusively in the lab—they have normal offices too.
yes people wear lab coats. gloves are usually blue or black, and come in S/M/L.
almost every lab comes with a "hood," which is essentially a workspace connected to a big metal vacuum. the purpose of the hood is sterility—everything that goes in should be sprayed with ethanol (including hands!), and once you take something out, it's generally considered non-sterile and potentially contaminated. often connected/serves another purpose as a cell culture room. cells are usually stored in flasks laid on their side, and depending on the color of cell media used, usually range from yellow-ish clear to red.
it's generally bad practice to talk about in vivo stuff to non-scientists (pictures are 100% banned). DM me if you're curious and i'd be happy to give you more insight!
hope this was interesting and/or useful :)
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
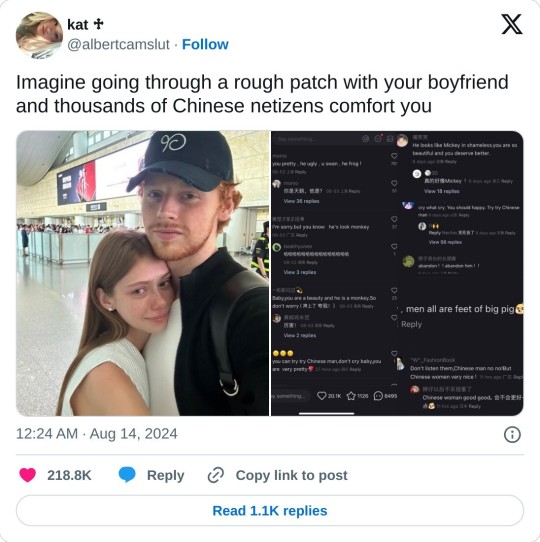
View on Twitter
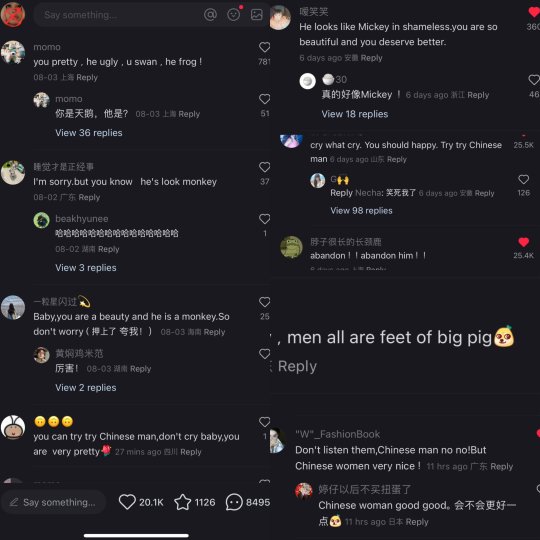
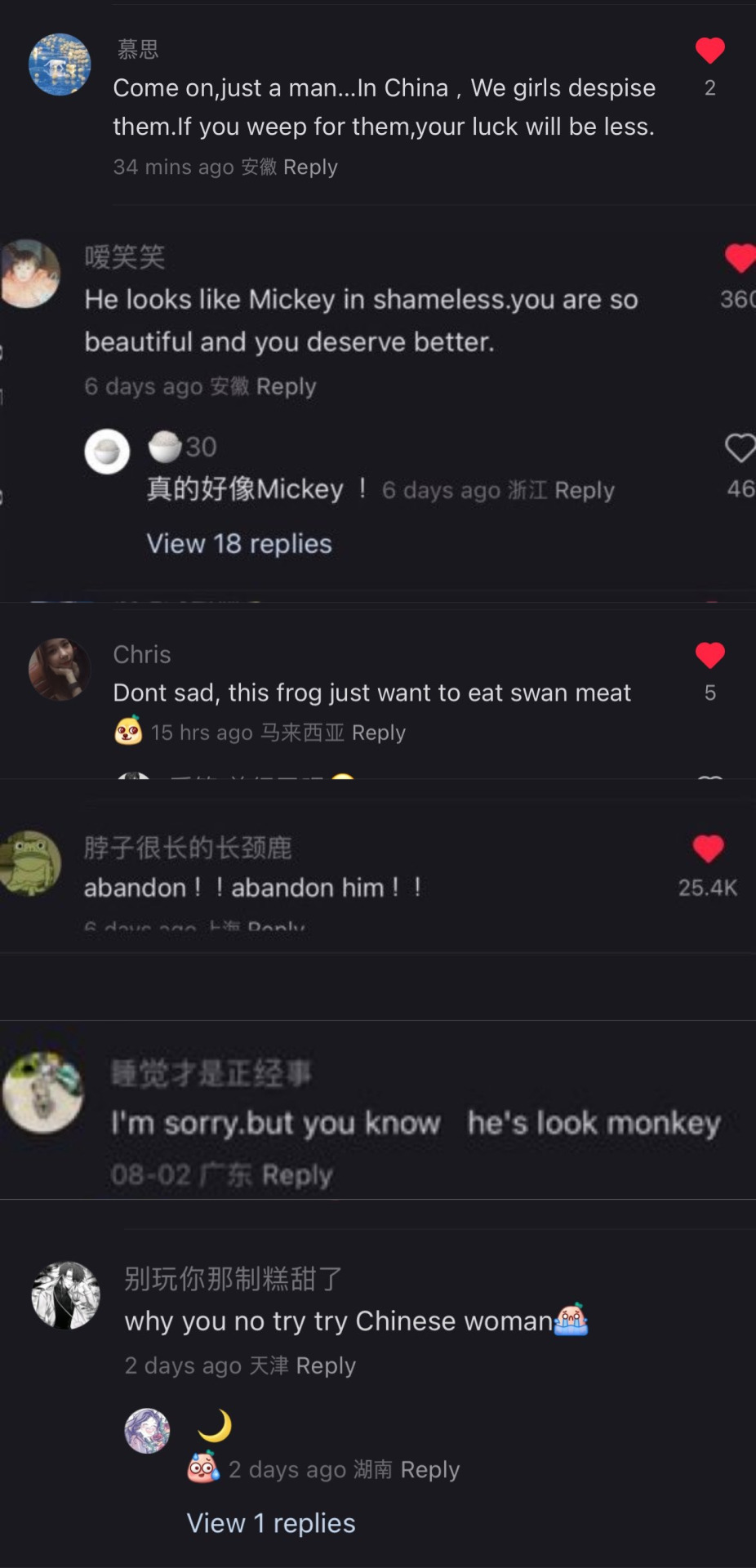
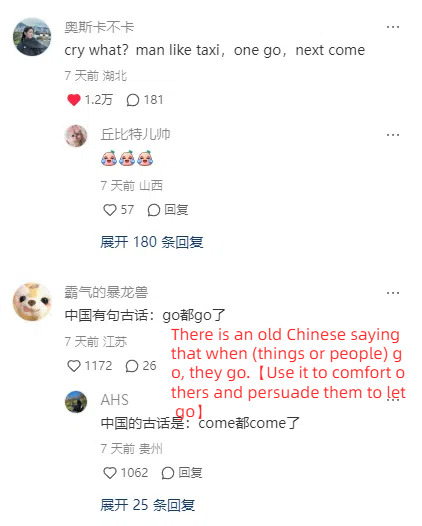
This is so fucking funny omg
And I go through the model’s acount on xhs and it’s getting even funnier XD
Also cnetizens can be really impatient with love-struck people especially young people who are lovesick and simp for someone who don’t love them. They call this type a lian-ai-nao恋爱脑 lit. love brain, so it’s funny how they reacted in the comments when the girl tends to be a love brain.




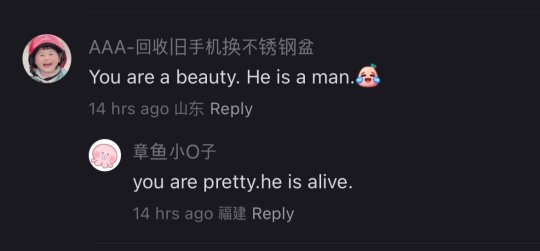
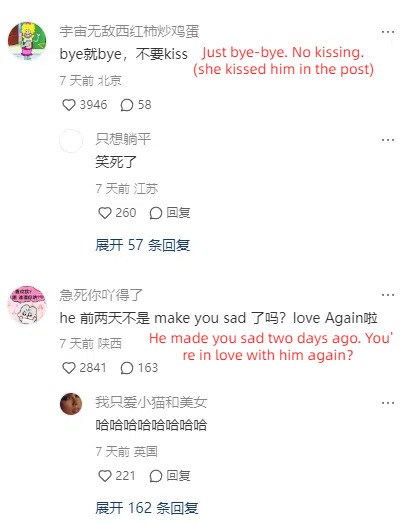
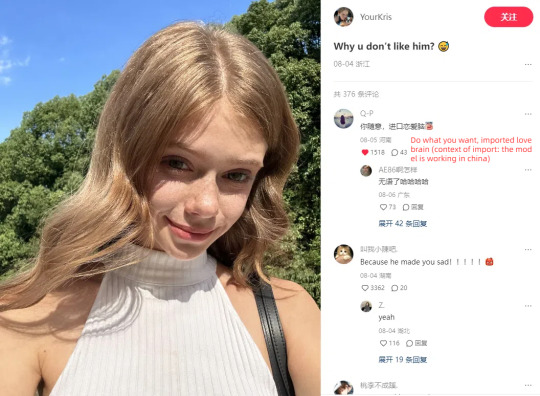

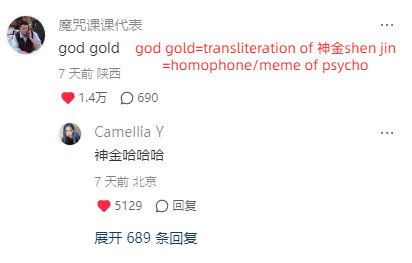
3K notes
·
View notes
Text




House drugged that coffee btw
114K notes
·
View notes
Text
the problem with reading and writing leading to a strong vocabulary is that you tend to know the vibe of words instead of their meanings.
if I used this word in a sentence, would it make sense? absolutely. if you asked me what it meant, could I tell you? absolutely not.
170K notes
·
View notes
















