#yumiko igarashi manga
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
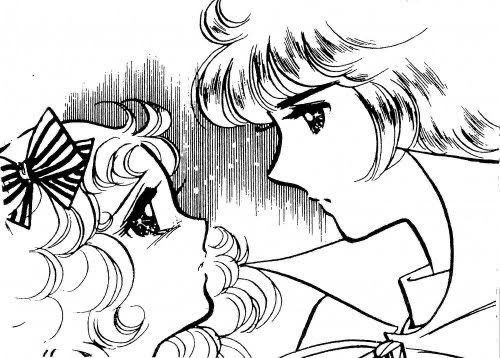
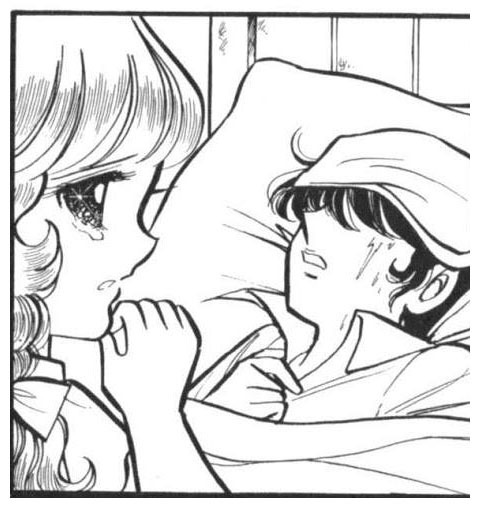
Candice "Candy" Andrew White Ardlay and Terence "Terry" Graham Grandchester from the manga "Candy Candy" (1975) by Yumiko Igarashi
#candice andrew white ardlay#candice andrew#alistair cornwell#candice ardlay#candice#candy candy#candy#candice white#stear#archie#archibald cornwell#terrius graham grandchester#terrius grandchester#terence grandchester#terence#terry#terrius graham#terence graham grandchester#terence graham#annie brighton#anthony brown#patricia o'brien#patty#neil leagan#eliza leagan#yumiko igarashi manga#igarashi yumiko#yumiko igarashi#shoujo#shoujo manga
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
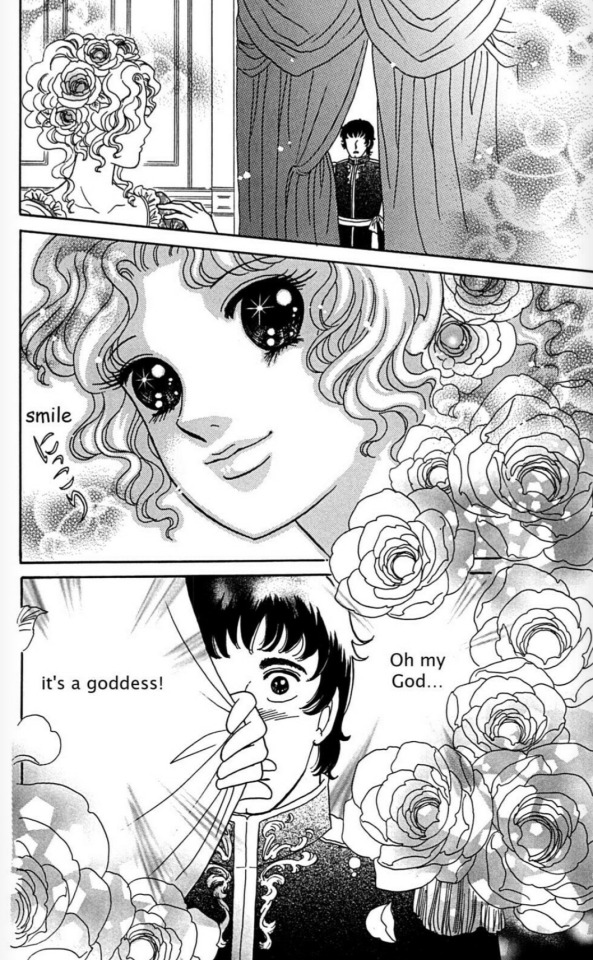
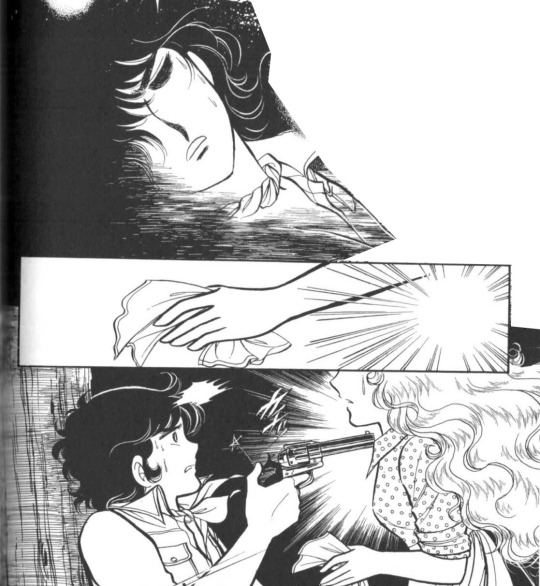
Their first meeting❤️🥹... this manga is too underrated. It's "Bara no Josephine"/ "Josephine the French Rose" by Yumiko Igarashi. Youn can read it on Manga Fire.



#shojo manga#manga#shojo#shoujo manga#shoujo#igarashi yumiko#yumiko igarashi manga#yumiko igarashi#bara no josephine#josephine the french rose#napoleon#napoleon bonaparte#josephine de beauharnais#french revolution#empire#emperor#empress
33 notes
·
View notes
Text

Candy Candy (1975) by Yumiko Igarashi
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The whole story of the illegal sale of Candy Candy products by Yumiko Igarashi

What is Candy Candy?
Candy Candy is shojo manga that was published between 1975 and 1981 in Nakayoshi magazine. It was written by Kyoko Mizuki (Keiko Nagita) and illustrated by Yumiko Igarashi. It was adapted to anime between 1976 and 1979 with a total of 115 episodes by Toei Animation.
The dramatic story of the sweet and optimistic Candy was an international success and is today an icon of shojo manga and one of the best sellers.
Evidently, the copyright holders are both Mizuki and Igarashi, and the trademark rights holder is Toei Animation.

Beginning of the conflict: Cancellation of the contract with Kodansha
According to Igarashi, her subsequent works at Kodansha didn't achieve significant sales, so the publisher abandoned her.
Candy Candy's views were decreasing over time and Kodansha did nothing. So Igarashi asked Mizuki to cancel her contract with Kodansha, Mizuki chose her friend and they did so on February 26, 1995.
Toei Animation also had a contract with Kodansha for Candy Candy, which automatically expired when Mizuki and Igarashi canceled their contract. To broadcast Candy Candy, Toei Animation had to sign a new contract with Igarashi and Mizuki. Toei Animation and Mizuki tried to contact Igarashi many times for this but were unsuccessful.
Meanwhile, Igarashi was working with Fuji Sankei (now Qualus), through which she was able to offer licenses to many companies to sell Candy Candy products without asking permission from Mizuki or Toei.
The unmasking: Banpresto's purikura
One of these companies was Banpresto Co., Ltd., which develops video games and makes collectible figures. Igarashi lied about creating a new (fictitious) company in Hong Kong with Mizuki and Toei called "Candy Corporation." Igarashi and Banpresto made a "purikura" (Japanese photo booths) contract. Banpresto asked Igarashi many times if Mizuki was aware of this contract, Igarashi always confirmed it. Banpresto considered it rude to ask Mizuki herself to confirm, so they agreed.
So how did they find out what Igarashi was doing? Candy Candy's purikura was set up at the Tokyo Gulliver Store in Matsudo, Chiba Prefecture, which was a large gaming center managed by Banpresto.

Banpresto intended to install its purikura machines throughout the country, including Candy Candy.

Igarashi stated that she accepted the purikura because it was only "a test case" and that she would have no compensation. She said that she was worried that Mizuki would reject the offer because Mizuki didn't like games at all (which Mizuki never said), so she planned to talk to Mizuki later if the test was successful. News of Candy Candy's purikura spread through the media and reached Mizuki in May 1997. Igarashi says that Mizuki told her over the phone that if she had known she wouldn't have refused, and that Igarashi was trying to keep the profits for herself. She said that Mizuki forced her to cancel the purikura event and that she hired a lawyer to sue Igarashi. Mizuki refuted this on her official website. Igarashi stated that she didn't receive any benefit from the purikura because it was only a prototype. Even if it were, purikura isn't free, so benefits were generated.
The problem is that the idea of creating a purikura was Igarashi's, not Banpresto's. Banpresto, upon realizing that they hadn't received permission from Mizuki, removed the purikura and wouldn't move it until the copyright issue was resolved. That's why Mizuki didn't sue Banpresto. Still, Banpresto apologized profusely for being involved in the scam.
Mizuki comments that she wasn't sure about canceling the contract with Kodansha, her husband didn't recommend it, but she still did it and regrets it. Her husband asked the legal advisor who had drawn up the contract, the legal advisor didn't know. Worried, Mizuki and her husband wanted to talk to Igarashi to discuss what they would do with Candy Candy from then on, but Igarashi kept putting off her request, saying that she was busy and for her to wait until the next month, and so on.
Mizuki became suspicious and finally they found out about the purikura issue, they even went to Banpresto to ask for explanations, to which Banpresto responded that they received the copyright to do it from the (fictitious) company that Igarashi created without Mizuki or Toei. They also told her how Igarashi confirmed to them several times that she had Mizuki's permission. Although purikura was considered a test, they received benefits for it.
As a result of this, everything that Igarashi had been doing in Hong Kong was discovered: she published manga products without authorization through Jade Dynasty Publishing. When this publisher found out that they didn't have Mizuki's permission either, they canceled the contract with Candy Corporation.
So far it was discovered what Igarashi had been doing without Mizuki's permission:
Original reproductions by Fuji Sankei and others.
Candy Candy reprint by Fusosha Publishing.
Fuji Sankei CD-ROM.
Postcards and cards manufactured by Jade Dynasty Publishing.
The Banpresto purikura.
Legal CD-ROM Manga.

Illegal CD-ROM Manga.

To all this, Igarashi insisted that 80% of Candy Candy belongs to her, and that only 20% belongs to Mizuki.
The case of fake original illustrations
In August 1997, the sale of original illustrations (again, without Mizuki's permission) was announced in the Sankei Shimbun. Finally, in September 1997, Fuji Sankei was sued for its lack of sincerity. These illustrations were actually prints made by a printer, they went on sale in February 1998 as a high quality print, but people in the art world warned that it wasn't a high quality print. That is, they were selling reprints at a high price as if they were high quality but they weren't.

An expert commented that these fakes have a real value of 30 to 200 yen ($0.19-1.27). If they were originals, it would be between 8,000 and 20,000 yen ($50.73-126.84) (and framed); but Igarashi and Fuji Sankei sold them for between 40,000 and 140,000 yen ($253.67-887.85). The deceived fans were deeply hurt, if they had known that they were buying it without Mizuki's permission and at a higher price than the real one, they wouldn't have bought it.

Mail order advertisements in newspapers ceased, but they were still distributed and sold in art galleries, for example Atelier Beauty and Prince Gallery.
The problem of selling products without the Mizuki's name
A friend of Igarashi spread the false rumor that Mizuki sued Igarashi without talking to her first. In fact, the decision to report a friend of 20 years wasn't easy for Mizuki, but she had to do it AFTER talking to her. But she and Fuji Sankei refused to have a conversation with her about what happened. Several people told Mizuki to be careful with Igarashi, but Mizuki always defended her.
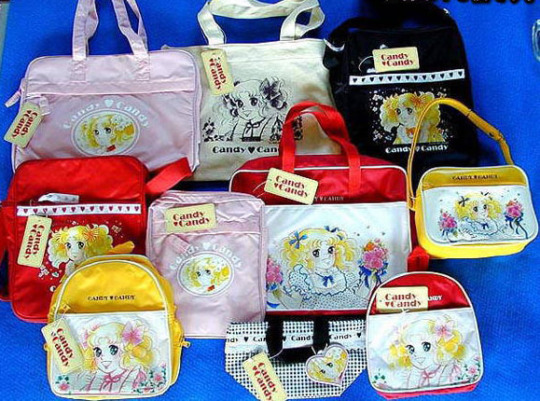
In the indication © on products, the names of all copyright holders must be added and never omitted without their consent. In the following images you can see which are the official products and which are the Igarashi products.
In this bag we see that the three names are included, it is original.


This backpack is also an official product, it contains the names of Mizuki and Igarashi.


Let's now look at the illegal merchandise. In this product we can see only the Igarashi's name.


This other one used Mizuki's name without her permission.


The impossible broadcast of Candy Candy
In 2001 all broadcasting rights granted to foreign companies expired. So the later copies are pirated copies disguised as official products. This was done, for example, by Power International Multimedia Inc., Igarashi's business partner in Taiwan. Even after Igarashi lost her lawsuit in 2008, Power International released this DVD box set unlicensed from Toei Animation.

When it was discovered what Igarashi had been doing, Toei and Mizuko planned to resolve the situation by ratifying the illegal goods (confirming the counterfeit products and rebirthing them as an official product) if the Igarashi side appealed and didn't fight further after the court's ruling, with the intention to help scammed companies. But the matter reached the Supreme Court. The products spread so much around the world that nothing could be done about it.
On August 23, 1999, Mizuki and Toei signed an agreement stating that Toei Animation could register "Candy Candy" as a trademark so that it can broadcast the anime.
Currently, Toei Animation is wary of digitally remastering all 115 episodes (which would cost a considerable amount of money) only to have it eventually canceled due to the ongoing copyright dispute.
Mizuki allowed the anime to be broadcast. But there are many factors why it cannot be broadcast, even abroad:
The contract with Toei Animation hasn't been renewed.
The copyright dispute.
The problem of infringement of trademark rights by Igarashi.
Igarashi sent Toei Animation to court to invalidate its trademark on July 10, 2001, but this was dismissed.
Igarashi filed a lawsuit against Mizuki requesting consent to remake it.
In short, if both creators don't recognize the copyright and give their consent, the anime cannot be broadcast. But Igarashi didn't want to, she even wanted the trademark rights for herself, but Mizuki didn't allow it. Anyway, it's not fair because the anime version is also the work of Toei staff and voice actors. Igarashi gave Toei permission to rebroadcast it, but without acknowledging Mizuki's copyright, it became a vicious cycle.
Japan Manga Society against Kyoko Mizuki
Igarashi has publicly stated on many sites that Kyoko Mizuki isn't the original author. This is quite questionable because the story was written by Mizuki, Igarashi drew it. The Japan Manga Society doesn't offer Mizuki's presence and instead allows Igarashi to present convenient arguments and dismiss the Supreme Court's ruling. The Copyright Subcommittee of the Japan Manga Society declared that Mizuki's blocking the sale of products produced by Igarashi without permission from Mizuki and Toei was an abuse of rights without justifiable reason, even suggesting that Igarashi file a lawsuit against Mizuki.

During and after losing the case, Igarashi continued her illegal business saying that she had reached a deal with Mizuki (a lie).
Yumiko Igarashi on trial
Kodansha itself attempted to persuade Igarashi to apologize and reconcile with Mizuki by submitting a total of 3 statements to the district court in 1998 by Mitsuro Shimizu, the editor in charge of Candy Candy at Kodansha. Still, Japan Manga Society said Kodansha didn't testify. Mitsuro Shimizu explained that the editorial department selected Mizuki as the original author, the concept of Candy was discussed between Igarashi, Mizuki and Shimizu. Igarashi expressed her wishes and opinions but in the end it was Mizuki who made the final decision as the writer. Kunio Hase, the director of the Japan Manga Society said that these statements were false. Yukio Shindo, director of copyright business promotion at Kodansha, stated in court in October 1998 that manga works written from the original work are always subject to the original copyright of the original author, which to use a work for secondary use, permission must be obtained from the original author and the manga artist whatever it may be (even if they're illustrations) and that Kodansha always considered Kyoko Mizuko as the original author during the 20-year contract. The Japan Manga Society said that the Supreme Court's decision to position Mizuki as the original author is an absurd ruling that doesn't reflect the real situation of the manga industry. Kodansha has always maintained with legal opinions that Kyoko Mizuki is the original author and the manga work is a derivative, the work of the original manuscript. Yumiko Igarashi commented that the Supreme Court ruling naming Mizuko as the original author was unfair and doesn't accept that the person who wrote "just the words" has the copyright. In this situation, neither Kodansha can reprint the manga, nor can Toei broadcast the anime.
List of court cases related to “Candy Candy”
February 25, 1999: "Candy Candy" Case (Fuji Sankei)
Mizuki denounces the sale without her permission of false "high quality" illustrations by Igarashi and Fuji Kasei. The court recognized Mizuki as the owner of the copyright and ordered Igarashi to stop publication. Characters can't be used without Mizuki's permission. In November 1995 they signed a contract that established that their consent was required for the use of the characters, but Igarashi breached it.
April 8, 1999: "Candy Candy" Incident (Yumiko Igarashi Museum)
Mizuki denounces that products with Candy Candy's image continue to be sold without her permission, even after winning the first trial. The Yumiko Igarashi Museum had been conducting mail-order sales of Candy Candy products on the official Yumiko Igarashi website.
March 17, 2000: Candy Candy Illustration Sales Case (Shizuka Art)
Mizuki sues Shizuka Art for selling Candy Candy's image without her permission. An interim injunction was granted against Shizuka Art to prohibit sales. Shizuka Art was exhibiting and selling new paintings by Yumiko Igarashi as original paintings.
March 30, 2000: "Candy Candy" Case (Fuji Sankei)
The judge noted that in manga, the illustrations and the development of the story are inseparable and integral. You can't sell the illustrations.
May 25, 2000: "Candy Candy" Case (Kabaya Foods)
Between 1998 and 1999, Kabaya Foods, with only Igarashi's consent, manufactured and sold candy bags featuring the Candy Candy characters. The judge stated that the original author can exercise copyright even if only images are used. The Tokyo District Court ordered the defendant to pay approximately 3 million yen ($19,029.75).
October 17, 2000: Candy Candy Paintings Sales Case (Shizuka Art)
The "Hello Candy Candy" exhibition displayed and sold paintings of Candy Candy, again without Mizuki's consent.
December 26, 2000: Candy Candy Commercialization Case
Mizuki demands Fuji Sankei and Yumiko Igarashi.
March 2001: Japanese anime remake test
Igarashi filed a lawsuit against Mizuki demanding a remake of Candy Candy with Nippon Animation.
August 7-September 28, 2001: Toei trademark invalidation trial
Igarashi filed a trademark invalidation suit against Toei Animation on July 10 but it was dismissed because in 1999 Mizuki and Toei signed an agreement establishing that Toei Animation would register Candy Candy as a trademark.
October 25, 2001: "Candy Candy" Case (Fuji Sankei)
For the third time, the judge explains to her that copyright can't be enforced without the consent of the original author and the manga artist. They granted the copyright to the original author, Mizuki.
February 23, 2002: "Candy Candy" Incident (Lucky Corporation, Osaka)
Lucky Corporation sues Igarashi because it suffered damages of approximately 45 million yen ($285,446.25) from the manufacture and sale of "Candy Candy" products, a right granted by Igarashi but not by Mizuki. Igarashi paid about 10 million yen ($63,432.50) and a settlement fee.
April 2002: Otaru Art Museum Exhibition Test
Yumiko sued Mizuki over the exhibition at the Otaru Art Museum.
May 30, 2002: Candy Candy Clothing Sale (Tanii, Dan Enterprises, Sunbright, Earth Project)
Mizuki sues several clothing sales companies for commercializing Candy Candy characters without permission. The damage claim was for 55 million yen ($348,878.75), but the Tokyo District Court ordered her to pay approximately 29 million yen ($183,954.25).
September 10, 2003: "Candy Candy" merchandise breach of contract case
Toymaker Apple One made Candy Candy puzzles, again, only with Igarashi's permission, not Mizuki's. So they sued Igarashi and other companies that claimed to own the copyrights they granted them to make the puzzles.
July 21, 2004: "Candy Candy" merchandise breach of contract case
The Tokyo District Court of First Instance sentenced Igarashi to pay approximately 1.75 million yen ($11,100.69).
September 2005: Kurashiki Art Museum Exhibition Test
Mizuki against the Kurashiki Art Museum, which held an exhibition of Candy Candy with only the permission of Igarashi, who said "I don't need permission to show it."
甜甜 Lady Lady: The Taiwanese Candy
You may have ever used an image mistakenly thinking it was Candy. That's because Igarashi created a "new original work" called "Lady Lady" in Taiwan that curiously resembles "Candy Candy" (the difference is in the bangs and that she doesn't have freckles). The other two characters also look like Anthony and Terry.

In this way, Igarashi challenges Toei Animation by infringing (again) Toei's trademark rights. As if that were not enough, "Lady Lady" is the title of the animated version of "Lady!!" by Yoko Hide and trademark of Toei Animation. Also, Candy Candy's title in Chinese is "小甜甜" (Xiǎo tián tián), literally "Little Candy Candy". I mean, it's a shameless mix between Candy Candy and Lady Lady. 甜甜 is the Chinese name of Yumiko Igarashi's Lady Lady.

Current situation
Since as of today they have not reached an agreement, the anime cannot be broadcast nor the manga can be published either in Japan or abroad. The authors continued with their professional careers. Igarashi can't create or sell any products related to Candy Candy, something Mizuki can do, without using Igarashi's illustrations.
To date, Igarashi has't expressed any apology to Mizuki or Toei Animation. In fact, she is suspected of still producing illegal goods on the foreign market. Mizuki feels sad, not only because of everything that happened, but also because of the malicious mentality that Igarashi had about her, thinking that she was her friend.
Please, be careful with the products you buy of Candy Candy, try to make sure they're original and not illegal products. Do not contribute to Igarashi's illegal business.

Sources:
#candy candy#yumiko igarashi#toei animation#anime#manga#shojo#shoujo#shoujo anime#shoujo manga#shojo anime#shojo manga#old shojo#old shoujo#kyoko mizuki
259 notes
·
View notes
Text


なかよし (Nakayoshi) November 1976 issue's cover and back cover featuring Candy Candy by Igarashi Yumiko.
#いがらしゆみこ#yumiko igarashi#candy candy#70s manga#retro shoujo#vintage shoujo#nakayoshi#shoujo magazine#vintage manga#キャンディキャンディ#70s
99 notes
·
View notes
Text

candy candy (yumiko igarashi, 1975)
39 notes
·
View notes
Text

Candy Candy
Follow me on:
deviantART [♥] twitter [♥] Instagram [♥]
Please,re-blog don’t re-post my works! ♥
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Manga#Lucy Maud Montgomery#Yumiko Igarashi#Akage no Anne#Anne of Green Gables#Anne Shirley#Matthew Cuthbert#Marilla Cuthbert#Diana Barry
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Candace the lil' darlin that u are





#Kyoko Mizuki#candy candy#Keiko Nagita#candy white#⛈️#cutie patootie yargh#shojō manga#yumiko igarashi
16 notes
·
View notes
Text





Georgie! by Izawa Man and Igarashi Yumiko
65 notes
·
View notes
Text

Whumptober 2023 No. 13 'Cold Compress'
Yumiko Igarashi's “Mayme Angel” manga.
Johnny gets injured a lot during the manga and he often ends laying feverish with a cold compress on his forehead.

Armand also ends laying the same way...



The time that Johnny hasn't got the cold compress...

LAST MINUTE ADD:
Tsukasa Hojo’s “City Hunter” manga, chapter 171.
Ryo Saeba is feverish and taken care of with cold compresses all night.
@whumptober @whumptober-archive

#whumptober2023#no.13#Cold Compress#Mayme Angel#gif#Johnny Hardley#Yumiko Igarashi#whumpslist gifs#manga#manga whump#whumpedit#feverish#injured#Armand Rockfield#Tsukasa Hojo#City Hunter#Ryo Saeba
55 notes
·
View notes
Text

Candice "Candy" Andrew White Ardlay and Terence "Terry" Graham Grandchester from the manga "Candy Candy" (1975-1979) by Yumiko Igarashi
#yumiko igarashi manga#igarashi yumiko#yumiko igarashi#candice andrew white ardlay#candice andrew#candice ardlay#alistair cornwell#candy candy#candy#candice#archibald cornwell#archie#stear#terence graham grandchester#terrius graham grandchester#terence#terence grandchester#terry#terrius grandchester#annie brighton#patricia o'brien#patty#anthony brown#sister lane#sister pony#neil leagan#eliza leagan#shojo#shoujo#shojo manga
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love them so much in this manga❤️... they're so sweet and they look so cute and good together there🥹🫶🏻 I would really love to see an anime based on this manga❤️


Manga: Josephine the French Rose/ Bara no Josephine- Yumiko Igarashi
Characters: Napoleon Bonaparte and Josephine de Beauharnais
#shojo manga#manga#shojo#shoujo manga#shoujo#yumiko igarashi#yumiko igarashi manga#rose#napoleon#napoleon bonaparte#josephine#bara no josephine#josephine the french rose#josephine de beauharnais#history#historical manga
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

Magical Mami (1983) by Yumiko Igarashi
174 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shoujo Manga's Golden Decade (Part 3)
Shoujo manga, comics for girls, played a pivotal role in shaping Japanese girls’ culture, and its dynamic evolution mirrors the prevailing trends and aspirations of the era. For many, this genre peaked in the 1970s. But why?
Part 1
Part 2
Follow the Trend
Before we move on to the third movement of the '70s, let's take a quick look at an essential characteristic of shoujo manga: its sensitivity to trends.
The early '70s were a confusing time for the industry. There was extreme freedom in certain corners, with Yukari Ichijo, Machiko Satonaka, and other prominent artists drawing very adult-like drama in shoujo magazines for very young girls. In contrast, there was also a lot of moralism. The fact manga wasn't taken very seriously meant magazines could get away with a lot since adults considered them terrible influences anyway. But, at the same time, since manga wasn't a respected medium, they were also prone to hysteria. Nothing illustrates this scenario better than the controversies surrounding "Harenchi Gakuen," the first full-length series by Go Nagai, who went on to become one of the most celebrated manga artists of the '70s.


Shameless! The nudity and erotic jokes in Go Nagai''s "Harenchi Gakuen" were a hit with kids and teens, scandalized parents and teachers, and made the shoujo industry chase after their own erotic hits.
Nagai, already a respected yet fledgling name in the industry, was recruited by Shueisha to be part of Shonen Jump's inaugural team in the late '60s. Jump, as any manga fan knows, is by far the biggest success story in manga's editorial history. However, back then, it was just a newcomer in a field dominated by Kodansha's Weekly Shonen Magazine and Shogakukan's Shonen Sunday. Go Nagai's series, whose translated name meant "Shameless High School," is Jump's initial smash hit and one of the titles behind its extraordinary ascent.
But "Harenchi Gakuen," a gag manga with erotic jokes, scandalized adults across the nation. The Japanese Parents and Teachers Association successfully led a Shonen Jump boycott, getting the magazine banned in several shops across the country and triggering a media circus. At the time, agitated journalists often accosted Go Nagai at airports and public events, aggressively pointing their mics at him, a consequence of manga-kas celebrity-like notoriety during that era.
Meanwhile, the reaction around "Harenchi Gakuen" did not intimidate other manga magazines. In fact, all of them were pursuing their own "harenchi"-like phenomenon and publishing stories with erotic dirty jokes. And yes, that included the manga magazines for little girls. In Ribon, male manga-ka Hikaru Yuzuki was responsible for the "dirty" manga series. At Weekly Margaret, Yuzuki also had a considerable hit with the high school comedy "Elite Kyousoukyoku," which, while not precisely "ecchi," had a tone reminiscent of Nagai's work. At Nakayoshi, the artist in charge of this type of content was none other than a pre-"Candy Candy" Yumiko Igarashi.

Before finding success with the smash hit "Candy Candy" manga, Yumiko Igarashi was the Nakayoshi artist in charge of recreating the "harenchi" phenomenon in the pages of the magazine. Above, in a good display of how public manga artists were in the '70s, Yumiko describes her panties as part of a Nakayoshi feature.
The "harenchi" phenomenon hinted at a shoujo field that wasn't yet wholly solidified and, therefore, was taking cues straight from the shonen segment, which would later become uncommon. But it also illustrates how the genre projects readers' dreams and preferences.
An example of this is one of Ribon's most popular series during the '70s, Yukko Yamamoto's "Miki to Apple Pie." Serialized between 1973 and 1976, this gag high school manga was full of absurd humor and nudity in the "Harenchi" vein. The twist is that it also had everything girls dreamed of.
The "apple pie" in the title was a reference to the lead character's favorite dessert during the time the American apple pie had just arrived in Japan and was considered the trendiest sweet. Miki Miyazawa, a popular and beautiful girl who served as the proxy for readers and was loosely modeled after talento Aki Aizawa, also loved astrology and the horoscope, and the romantic lead was a transfer student named Hideki Nanjo, who was a carbon copy of Hideki Saijo, the biggest popstar heartthrob of the '70s. Basically, "Miki to Apple Pie"'s central premise was "What if the popstars girls go crazy for was your silly gorgeous classmate?".
In fact, a testament to Saijo's popularity was how many shoujo manga romantic partners of the era used him as a model. Besides "Miki to Apple Pie," inserts of him were present in Satonaka Machiko's "Spotlight," Shigeko Maehara's "Kimi Iro no Hibi," Mayumi Yoshida's "Lemon Hakusho," among others.


With nudity, slapstick humor, and numerous references to trends and pop culture, "Miki to Apple Pie" became a sensation in the pages of '70s Ribon. The romantic lead, Hideki Nanjo, modeled after heartthrob Hideki Saiji, frequently performed impromptu renditions of popular hits from stars like Agnes Chan, Finger Five, Momoe Yamaguchi, Junko Sakurada, and, of course, Hideki Saiji himself. Full of shockingly offensive and scatological jokes, very little was considered off-limits, making "Miki to Apple Pie" a quintessential example of the distinctive '70s shoujo manga published during the peak of the "Harenchi" boom. It also serves as a perfect time capsule of its era, satirizing and commenting on everything popular at the time—from iconic products like the Panasonic Quintrix television and memorable TV commercials to celebrities, the toilet paper shortage during the Oil Shock, the Discover Japan campaign, and the widespread teenage girls' fascination with horoscopes. This manga elevated shoujo manga's trend obsession to unprecedented heights and mixed it with absurdity.
Saijo is a relic of the past, but shoujo echoing the trends of its time is a timeless characteristic of the genre. That's why most shoujo artists are women who are close in age to their readers: this sensibility to girls' desires is a vital component of the market. From the way the characters look to how they dress to even the shape of their eyebrows, everything is supposed to reflect its time. Therefore, to successfully create shoujo, one has to understand how girls perceive themselves and also how they want to be perceived. How they dress and look, but also how and what they dream of looking and wearing. What they aspire to and, above all, what they find attractive in the opposite sex.
It was precisely that sensitivity and this unique sense of what girls want and dream of that led to the creation of what is now the number 1 shoujo manga trope: the high school romance starring an unassuming, ordinary heroine. Leading the way was another group of artists that, while not as internationally celebrated as the Year 24 Group, are definitely equally as crucial to shoujo history.
The Otometique Fervor


An "otometique" girl by Mutsu A-ko and some of the artist's popular furoku.
Yoshiko Nishitani, another of Shueisha's top shoujo artists of that era, is often credited as being the first to create a series around ordinary high school love. She did that in 1965's "Marie Lou," published in Weekly Margaret. "Marie Lou" was set in an American high school and had a very fashionable white girl as its lead. On her next manga, "Lemon to Sakuranbo" (Lemon and Cherries), she'd once again achieve immense success by bringing the teen romance closer to reality, using an ordinary Japanese high school as a backdrop.
While Nishitani pioneered this narrative style, the rise of more realistic, everyday stories gained momentum about a decade later. One catalyst for this was the "Otometique boom," a phenomenon that unfolded in the pages of Shueisha's Ribon magazine in the latter half of the '70s.
The term "Otometique" combines "otome," meaning "maiden" or a pure young girl, with the "-tique" (tikku in Japanese) suffix. A-ko Mutsu was the artist who spearheaded this movement.
A-ko made her debut in Ribon in 1971 at the age of 18. Her popularity skyrocketed four years later when her first short stories, led by "Tasogaredoki ni mitsuketa no" (What I Found at Twilight), were compiled into a tankobon that became a best-seller. This success elevated her status in Ribon, and soon her "otometique" style became the talk of the town.

Mutsu A-ko's art.
In contrast to the dramatic narratives of the "Satonaka-domain" faction, "otometique" stories adopted a more straightforward structure devoid of major plot twists and intense drama. Instead, they focused on modest love stories where the exhilarating moments were ordinary occurrences, like spotting a cute boy on the street or touching a crush's hand for the first time. While some stories included sad or supernatural elements, readers were captivated by the uncomplicated, heartwarming moments.
Ako's heroines were ordinary, unassuming schoolgirls, often characterized by shyness and insecurity. Different from extraordinary characters like Lady Oscar from "BeruBara" or the iconic Madame Butterfly tennis star in "Ace wo Nerae," Ako's protagonists were life-sized.
"Otometique" manga often incorporated romantic comedy tropes, such as chance encounters with cute guys on the way to school or the transformation into beauty after removing glasses. The happy endings typically featured a boy reciprocating the girl's love by accepting her as perfect and beautiful just as she was.

In otometique manga, girls were often in cute plaid and gingham check dresses and skirts, while boys were impeccably dressed in Ivy style, as seen in Mutsu Ako's art above.
While the stories may have seemed mundane, their distinctiveness lay in the meticulous attention to detail. As significant as the exploration of falling in love and discovering inner strength were all the visual details in "otometique" art. Girls had braids or long wavy hair and wore adorable clothes with plaids and gingham-check, as well as cute accessories. At a time when most Japanese girls still had Japanese-style rooms, "otometique" heroines had gorgeous Western-style rooms. They hung out in cozy cafes, made handmade goods, and ate tasty-looking sweets. Houses had French windows and balconies. Boys were tall, lean, with fluffy hair, and were always dressed impeccably in Ivy-style clothes. The "otometique" artists created an atmosphere that perfectly matched girls' aspirations at the time.

Girls often dreamed with having Western-style bedrooms like the ones in Otometique manga.
While Mutsu A-ko was the trailblazer, she was soon joined at the top by two other iconic artists, Yumiko Tabuchi, and Hideko Tachikake. Each of them had their quirks. Tabuchi, for example, often had college girls as her heroines, mirroring herself as a student at the elite, trendy Waseda University. While Tabuchi and A-ko preferred short stories, Tachikake had a penchant for longer series with a bit more drama. But they all had a similar aesthetic and relied on the charm of ordinary love.
The "otometique" phenomenon reflected the trends of the time and foreshadowed the emerging consumer culture that would swallow the country in the next decade. The sophisticated visuals attracted people of all ages, from elementary school-aged girls to highly educated women and men. Both the top public and private universities in Japan, Tokyo University and Waseda, respectively, had famous "otometique" clubs full of students who loved the genre and the style. The mangas were so trendy that they were often referred to as "Ivy mangas," in reference to the iconic Ivy style that was the catalyst of Japan's youth fashion, which was going through a second revival around that time.
While projecting an atmosphere that girls dreamed of, "otometique" also showcases '70s youth and girls' culture. Melancholic, simple love stories among young people were also the theme of the big folk hits of the time. Ivy or country fashion and long hair for men were the top fashion trends. Western-inspired ideals- in decoration, fashion, and musical taste- were pervasive. And creating subcultures and hobbies around consumption was the path society was taking. Simple life-sized stories as a narrative preference echoed the reality of Japan, which was stabilizing itself after decades of turbulence. These stories brought what the country was craving: comfort.


Above, a Mutsu A-ko's bedroom that lived in girls' imagination. Below, the room is recreated in a 2021 exhibition of Ako's art.
Meanwhile, the rise of consumer culture among young girls led to a "fancy goods" boom, with stores selling cute stationery, stickers, and small items popping up everywhere around the country. Illustrators and companies, eager to capitalize, spared no time in creating appealing mascots and drawings to adorn these goods, and it was in that period that Sanrio created Hello Kitty.
Ribon and Nakayoshi, which were "furoku" magazines, also benefitted. Furoku are extra gifts that come with the purchase of the magazines. And the "otometique" boom meant Ribon could include "fancy goods" -- like notebooks, stickers, letter sets, and small paper goods readers could assemble -- with the illustration of these highly sought-after artists. Most girls around Japan could only dream of Western-style rooms, a closet full of cute Ivy fashion, trips to trendy cafes, and homes with French windows. But they could recreate a bit of this sophisticated atmosphere by having letter sets, notebooks, stickers, and small accessories with A-ko Mutsu, Hideko Tachikake, and Yumiko Tabuchi's art. These popular furokus and the "otometique" stories were critical for Ribon magazine to surpass 1 million copies in circulation.
Girls admired A-ko, Tabuchi, and Tachikake not only as artists creating heartfelt stories with attractive atmospheres but as personalities. The trio, who were in their late teens and early 20s, closely resonated with their fans due to their proximity in age and shared interests. The readers were moved when Ribon featured an article in which A-ko Mutsu had the opportunity to meet and interview her favorite singer, the rock star Kenji Sawada, a prominent teen idol of that era. The positive response was so overwhelming that, a few issues later, Hideko Tachikake, an avid folk music enthusiast, also had the chance to interview her idol, Kosetsu Minami, the lead singer of Kaguyahime.


An otometique girl by Yumiko Tabuchi (left) and a collection of furoku illustrated by her as seen on a 2021 exhibition on her art.
The popularity of "otometique" peaked in 1977. By 1981, the boom had almost faded, and A-ko, Tabuchi, and Tachikake published their last works on Ribon in 1985. Tabuchi and Tachikake married and semi-retired, while A-ko successfully transitioned to manga for adult women.
Despite the end of the style, "otometique" permeated every corner of Japanese society. Its furoku and atmosphere were one of the bases for the almighty "kawaii" culture which now rules the country. The life-sized heroines and focus on mundane love stories and everyday emotions went on to become one of the main characteristics of the shoujo manga industry.
The Iwadate Domain
For years, the influence of "otometique" has been downplayed, one of the reasons why the movement is almost undiscussed in the West. However, in the last few years, best-selling books reminiscing the style were published, and exhibitions of A-ko Mutsu and Yumiko Tabuchi's works were big hits across Japan. A-ko, who moved back from Tokyo to her hometown in Fukuoka and never stopped creating manga, was recognized by the local prefecture as an honorary citizen and gained a permanent museum in the area, signaling her importance to the industry.
But while the "otometique" phenomenon happened on the pages of Ribon magazine, Mutsu, Tabuchi, and Tachikake weren't the only three attracting a massive audience to this type of real-life love story.

Mariko Iwadate's work was extremely popular from the late '70s to the mid-2000s. Above, a collection of her work from her Margaret era.
Going back to the research of sociologist Shinji Miyadai, three domains divided '70s shoujo. There was the "Moto Hagio domain," which included the Year 24 artists. The Hagio domain was more highbrow and intellectually challenging, and many considered it an equivalent to literature, attracting the intellectual elite that sniffed at manga in general. It is by far the most discussed and debated '70s shoujo movement, as well as the most famous in the West, but it was the least commercially successful at the time. Then there was the "Machiko Satonaka domain," with emotionally driven stories full of drama, plot twists, and larger-than-life heroines. Most of the '70s best-selling shoujo series fall under this category, which includes the work of Yukari Ichijo and Ryoko Ikeda and sports manga like "Ace wo Nerae," among others.
Finally, there's the domain in which the "otometique" stories were created. And Miyadai doesn't name it after any of the Ribon artists, calling it the "Mariko Iwadate domain" instead.
In the Satonaka domain, the heroine served as a proxy for the reader in a fantastical world, while in the Iwadate domain, the heroine represented the reader in the real world. But, after all, who is the influential Iwadate?
Mariko Iwadate, who made her debut in 1973 at the age of 16, rose to prominence by embracing the "otometique" style during its peak in the late '70s. Similar to Ribon artists, Iwadate, who mostly worked for Weekly Margaret, captivated readers with her elegant and stylish art, featuring cute clothes, accessories, and intricate details.
Miyadai's choice to name the category after Iwadate rather than the genre pioneer A-ko Mutsu may be attributed to Iwadate's sustained success. After leaving Ribon in 1985, A-ko remained prolific and had a dedicated audience, but she couldn't replicate her peak. Iwadate's popularity, on the other hand, continued unabated even after she transitioned to adult women's manga. Iwadate's work, recognized for its emotional depth, became a significant inspiration for trailblazers like best-selling novelist Banana Yoshimoto and avant-garde manga artist Kyoko Okazaki. In 1993, when Miyadai wrote his book, Iwadate's fame and respect probably made her a more recognizable figure for readers to associate with the category.

Iwadate's soft girly art and story-telling made her extremely popular and influential.
Mariko Iwadate's narrative, especially her post-80s work, has a more psychological and mature element to it when compared to Ribon's artists. She, as an artist, bridged the gap between "otometique" and another highly influential "Iwadate domain" artist, Fusako Kuramochi.
Fusako Kuramochi, debuting while still a teen in the early '70s at Bessatsu Margaret (Betsuma), initially emulated her favorite artists, Moto Hagio and Keiko Takemiya, before finding her style—a realistic portrayal of romance with a substantial psychological element. Her success contributed to shaping Betsuma, alongside Ribon, as arguably the most influential and commercially thriving shoujo title -- the go-to magazine for high school rom-com.
Like the otometique artists, Fusako Kuramochi first gained prominence with short stories and one-shots. In 1979, she wrote her first series, "Oshiaberi Kaidan," in which each chapter depicted the life of a young girl from junior high to her graduation day. In 1980, she published "Itsumo poketto ni Chopin," a classical music manga that also dealt with growing up as a teenager in the city. From then on, she'd publish about two hit series every year in Betsuma before graduating successfully to adult women's manga in 1994.
Kuramochi's success was due to her great skill in portraying girls going through crushes, heartbreaks, and jealousy. The psychological elements struck a chord with readers and helped her create male romantic leads that were extremely popular.
Another component of Kuramochi's work was her sophistication, a result of her upbringing. Her father was the chairman of one of Japan's biggest printing companies, and she was raised in Shibuya, in the center of Tokyo, while attending an exclusive all-female institution. The fact she spent her youth in the middle of Tokyo's hustle and bustle meant she knew the capital well, and her works were full of references to trendy cafes, restaurants, nightspots, and neighborhoods. Her Betsuma work was published right before and during Japan's ostentatious Bubble years, so many chasing an exciting city life referred to her work.
While her stories reflected the reality and aspirations of the Bubble years, Kuramochi's true gift lay in providing readers with a realistic depiction of growing up and falling in love, making her work immensely popular. In general, consumerism -- displayed through clothes, accessories, and decor -- isn't as crucial to her success as the three Ribon "otometique" artists.
While Fusako Kuramochi is part of the "Iwadate domain," you can argue that Kuramochi evolved into her own category, which was vital for the development of real-life love stories in shoujo in the '80s and '90s and the rise of other highly-influential artists like Ryo Ikuemi.
But going back to the three '70s movements, "otometique"/"Iwadate domain" was definitely the most influential one in steering shoujo manga in its current direction. On the other hand, all of these domains co-existed together and fed from each other. In 1977, during the "otometique" boom, Yukari Ichijo remained untouched as one of Ribon's most popular artists with her emotionally charged dramas. It was the success of Ichijo and other "Satonaka domain" artists that allowed the "Hagio domain" to debut and take risks. In turn, it was the "Hagio domain" that showed there were rewards for young risk-taking shoujo artists.

Yumiko Oshima, known for her girly art and sensitive story-telling, is the inspiration behind the otometique boom.
When asked which artist inspired them the most, both A-ko Mutsu and Mariko Iwadate gave the same answer: Yumiko Oshima. Oshima, known for her quirky love stories and girly art, is an artist who trained alongside Hagio and Takemiya at the Oizumi salon and rose as part of the "Year 24 group," publishing risk-taking manga in Shogakukan and Hakusensha's magazine after a brief stint in Weekly Margaret. In other words, despite the striking differences, the origin of the "Iwadate domain" is the "Hagio domain."
While the influence of the idealized real-life romance is the one we can better observe today, contemporary shoujo would not exist if not for all these three styles meshing together and creating something new. And from that, things kept evolving and changing and gaining new forms. Because, once again, manga, and especially shoujo manga, is about reflecting the girly ideals of its time.
#ribon#margaret#go nagai#miki to apple pie#yumiko tabuchi#otometique#otometique manga#mutsu a-ko#mutsu ako#hideko tabuchi#70s japan#fusako kuramochi#betsuma#shoujo manga#vintage shoujo#vintage manga#harenchi gakuen#yumiko igarashi#nakayoshi#yumiko oshima
51 notes
·
View notes

