#yani a
Text

Yani A
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

5K notes
·
View notes
Text






#posting this while listening to not like us#i feel blessed#lol#ts4#ts4 simblr#sims 4 screenshots#ts4 gameplay#sims 4#sim: ran#sim: yanis#bye mt komorebi for now#and yeah this is 🔞!!!!#apricot save
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Podcasting “Capitalists Hate Capitalism”

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

This week on my podcast, I read "Capitalists Hate Capitalism," my latest column for Locus Magazine:
https://locusmag.com/2024/03/cory-doctorow-capitalists-hate-capitalism/
What do I mean by "capitalists hate capitalism?" It all comes down to the difference between "profits" and "rents." A capitalist takes capital (money, or the things you can buy with it) and combines it with employees' labor, and generates profits (the capitalist's share) and wages (the workers' share).
Rents, meanwhile, come from owning an asset that capitalists need to generate profits. For example, a landlord who rents a storefront to a coffee shop extracts rent from the capitalist who owns the coffee shop. Meanwhile, the capitalist who owns the cafe extracts profits from the baristas' labor.
Capitalists' founding philosophers like Adam Smith hated rents. Worse: rents were the most important source of income at the time of capitalism's founding. Feudal lords owned great swathes of land, and there were armies of serfs who were bound to that land – it was illegal for them to leave it. The serfs owed rent to lords, and so they worked the land in order grow crops and raise livestock that they handed over the to lord as rent for the land they weren't allowed to leave.
Capitalists, meanwhile, wanted to turn that land into grazing territory for sheep as a source of wool for the "dark, Satanic mills" of the industrial revolution. They wanted the serfs to be kicked off their land so that they would become "free labor" that could be hired to work in those factories.
For the founders of capitalism, a "free market" wasn't free from regulation, it was free from rents, and "free labor" came from workers who were free to leave the estates where they were born – but also free to starve unless they took a job with the capitalists.
For capitalism's philosophers, free markets and free labor weren't just a source of profits, they were also a source of virtue. Capitalists – unlike lords – had to worry about competition from one another. They had to make better goods at lower prices, lest their customers take their business elsewhere; and they had to offer higher pay and better conditions, lest their "free labor" take a job elsewhere.
This means that capitalists are haunted by the fear of losing everything, and that fear acts as a goad, driving them to find ways to make everything better for everyone: better, cheaper products that benefit shoppers; and better-paid, safer jobs that benefit workers. For Smith, capitalism is alchemy, a philosopher's stone that transforms the base metal of greed into the gold of public spiritedness.
By contrast, rentiers are insulated from competition. Their workers are bound to the land, and must toil to pay the rent no matter whether they are treated well or abused. The rent rolls in reliably, without the lord having to invest in new, better ways to bring in the harvest. It's a good life (for the lord).
Think of that coffee-shop again: if a better cafe opens across the street, the owner can lose it all, as their customers and workers switch allegiance. But for the landlord, the failure of his capitalist tenant is a feature, not a bug. Once the cafe goes bust, the landlord gets a newly vacant storefront on the same block as the hot new coffee shop that can be rented out at even higher rates to another capitalist who tries his luck.
The industrial revolution wasn't just the triumph of automation over craft processes, nor the triumph of factory owners over weavers. It was also the triumph of profits over rents. The transformation of hereditary estates worked by serfs into part of the supply chain for textile mills was attended by – and contributed to – the political ascendancy of capitalists over rentiers.
Now, obviously, capitalism didn't end rents – just as feudalism didn't require the total absence of profits. Under feudalism, capitalists still extracted profits from capital and labor; and under capitalism, rentiers still extracted rents from assets that capitalists and workers paid them to use.
The difference comes in the way that conflicts between profits and rents were resolved. Feudalism is a system where rents triumph over profits, and capitalism is a system where profits triumph over rents.
It's conflict that tells you what really matters. You love your family, but they drive you crazy. If you side with your family over your friends – even when your friends might be right and your family's probably wrong – then you value your family more than your friends. That doesn't mean you don't value your friends – it means that you value them less than your family.
Conflict is a reliable way to know whether or not you're a leftist. As Steven Brust says, the way to distinguish a leftist is to ask "What's more important, human rights, or property rights?" If you answer "Property rights are human right," you're not a leftist. Leftists don't necessarily oppose all property rights – they just think they're less important than human rights.
Think of conflicts between property rights and human rights: the grocer who deliberately renders leftover food inedible before putting it in the dumpster to ensure that hungry people can't eat it, or the landlord who keeps an apartment empty while a homeless person freezes to death on its doorstep. You don't have to say "No one can own food or a home" to say, "in these cases, property rights are interfering with human rights, so they should be overridden." For leftists property rights can be a means to human rights (like revolutionary land reformers who give peasants title to the lands they work), but where property rights interfere with human rights, they are set aside.
In his 2023 book Technofeudalism, Yanis Varoufakis claims that capitalism has given way to a new feudalism – that capitalism was a transitional phase between feudalism…and feudalism:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
Varoufakis's point isn't that capitalists have gone extinct. Rather, it's that today, conflicts between capital and assets – between rents and profits – reliably end with a victory of rent over profit.
Think of Amazon: the "everything store" appears to be a vast bazaar, a flea-market whose stalls are all operated by independent capitalists who decide what to sell, how to price it, and then compete to tempt shoppers. In reality, though, the whole system is owned by a single feudalist, who extracts 51% from every dollar those merchants take in, and decides who can sell, and what they can sell, and at what price, and whether anyone can even see it:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/01/managerial-discretion/#junk-fees
Or consider the patent trolls of the Eastern District of Texas. These "companies" are invisible and produce nothing. They consist solely of a serviced mailbox in a dusty, uninhabited office-building, and an overbroad patent (say, a patent on "tapping on a screen with your finger") issued by the US Patent and Trademark Office. These companies extract hundreds of millions of dollars from Apple, Google, Samsung for violating these patents. In other words, the government steps in and takes vast profits generated through productive activity by companies that make phones, and turns that money over as rent paid to unproductive companies whose sole "product" is lawsuits. It's the triumph of rent over profit.
Capitalists hate capitalism. All capitalists would rather extract rents than profits, because rents are insulated from competition. The merchants who sell on Jeff Bezos's Amazon (or open a cafe in a landlord's storefront, or license a foolish smartphone patent) bear all the risk. The landlords – of Amazon, the storefront, or the patent – get paid whether or not that risk pays off.
This is why Google, Apple and Samsung also have vast digital estates that they rent out to capitalists – everything from app stores to patent portfolios. They would much rather be in the business of renting things out to capitalists than competing with capitalists.
Hence that famous Adam Smith quote: "People of the same trade seldom meet together, even for merriment and diversion, but the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the public, or in some contrivance to raise prices." This is literally what Google and Meta do:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jedi_Blue
And it's what Apple and Google do:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/10/27/23934961/google-antitrust-trial-defaults-search-deal-26-3-billion
Why compete with one another when you can collude, like feudal lords with adjacent estates who trust one another to return any serf they catch trying to sneak away in the dead of night?
Because of course, it's not just "free markets" that have been captured by rents ("Competition is for losers" -P. Thiel) – it's also "free labor." For years, the largest tech and entertainment companies in America illegally colluded on a "no poach" agreement not to hire one-anothers' employees:
https://techcrunch.com/2015/09/03/apple-google-other-silicon-valley-tech-giants-ordered-to-pay-415m-in-no-poaching-suit/
These companies were bitter competitors – as were these sectors. Even as Big Content was lobbying for farcical copyright law expansions and vowing to capture Big Tech, all these companies on both sides were able to set aside their differences and collude to bind their free workers to their estates and end the "wasteful competition" to secure their labor.
Of course, this is even more pronounced at the bottom of the labor market, where noncompete "agreements" are the norm. The median American worker bound by a noncompete is a fast-food worker whose employer can wield the power of the state to prevent that worker from leaving behind the Wendy's cash-register to make $0.25/hour more at the McDonald's fry trap across the street:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/02/its-the-economy-stupid/#neofeudal
Employers defend this as necessary to secure their investment in training their workers and to ensure the integrity of their trade secrets. But why should their investments be protected? Capitalism is about risk, and the fear that accompanies risk – fear that drives capitalists to innovate, which creates the public benefit that is the moral justification for capitalism.
Capitalists hate capitalism. They don't want free labor – they want labor bound to the land. Capitalists benefit from free labor: if you have a better company, you can tempt away the best workers and cause your inferior rival to fail. But feudalists benefit from un-free labor, from tricks like "bondage fees" that force workers to pay in order to quit their jobs:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/21/bondage-fees/#doorman-building
Companies like Petsmart use "training repayment agreement provisions" (TRAPs) to keep low-waged workers from leaving for better employers. Petsmart says it costs $5,500 to train a pet-groomer, and if that worker is fired, laid off, or quits less than two years, they have to pay that amount to Petsmart:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/08/04/its-a-trap/#a-little-on-the-nose
Now, Petsmart is full of shit here. The "four-week training course" Petsmart claims is worth $5,500 actually only lasts for three weeks. What's more, the "training" consists of sweeping the floor and doing other low-level chores for three weeks, without pay.
But even if Petsmart were to give $5,500 worth of training to every pet-groomer, this would still be bullshit. Why should the worker bear the risk of Petsmart making a bad investment in their training? Under capitalism, risks justify rewards. Petsmart's argument for charging $50 to groom your dog and paying the groomer $15 for the job is that they took $35 worth of risk. But some of that risk is being borne by the worker – they're the ones footing the bill for the training.
For Petsmart – as for all feudalists – a worker (with all the attendant risks) can be turned into an asset, something that isn't subject to competition. Petsmart doesn't have to retain workers through superior pay and conditions – they can use the state's contract-enforcement mechanism instead.
Capitalists hate capitalism, but they love feudalism. Sure, they dress this up by claiming that governmental de-risking spurs investment: "Who would pay to train a pet-groomer if that worker could walk out the next day and shave dogs for some competing shop?"
But this is obvious nonsense. Think of Silicon Valley: high tech is the most "IP-intensive" of all industries, the sector that has had to compete most fiercely for skilled labor. And yet, Silicon Valley is in California, where noncompetes are illegal. Every single successful Silicon Valley company has thrived in an environment in which their skilled workers can walk out the door at any time and take a job with a rival company.
There's no indication that the risk of free labor prevents investment. Think of AI, the biggest investment bubble in human history. All the major AI companies are in jurisdictions where noncompetes are illegal. Anthropic – OpenAI's most serious competitor – was founded by a sister/brother team who quit senior roles at OpenAI and founded a direct competitor. No one can claim with a straight face that OpenAI is now unable to raise capital on favorable terms.
What's more, when OpenAI founder Sam Altman was forced out by his board, Microsoft offered to hire him – and 700 other OpenAI personnel – to found an OpenAI competitor. When Altman returned to the company, Microsoft invested more money in OpenAI, despite their intimate understanding that anyone could hire away the company's founder and all of its top technical staff at any time.
The idea that the departure of the Burger King trade secrets locked up in its workers' heads constitute more of a risk to the ability to operate a hamburger restaurant than the departure of the entire technical staff of OpenAI is obvious nonsense. Noncompetes aren't a way to make it possible to run a business – they're a way to make it easy to run a business, by eliminating competition and pushing the risk onto employees.
Because capitalists hate capitalism. And who can blame them? Who wouldn't prefer a life with less risk to one where you have to constantly look over your shoulder for competitors who've found a way to make a superior offer to your customers and workers?
This is why businesses are so excited about securing "IP" – that is, a government-backed right to control your workers, customers, competitors or critics:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
The argument for every IP right expansion is the same: "Who would invest in creating something new without the assurance that someone else wouldn’t copy and improve on it and put them out of business?"
That was the argument raised five years ago, during the (mercifully brief) mania for genre writers seeking trademarks on common tropes. There was the romance writer who got a trademark on the word "cocky" in book titles:
https://www.theverge.com/2018/7/16/17566276/cockygate-amazon-kindle-unlimited-algorithm-self-published-romance-novel-cabal
And the fantasy writer who wanted a trademark on "dragon slayer" in fantasy novel titles:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/06/14/son-of-cocky-a-writer-is-trying-to-trademark-dragon-slayer-for-fantasy-novels/
Who subsequently sought a trademark on any book cover featuring a person holding a weapon:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/07/19/trademark-troll-who-claims-to-own-dragon-slayer-now-wants-exclusive-rights-to-book-covers-where-someone-is-holding-a-weapon/
For these would-be rentiers, the logic was the same: "Why would I write a book about a dragon-slayer if I could lose readers to someone else who writes a book about dragon-slayers?"
In these cases, the USPTO denied or rescinded its trademarks. Profits triumphed over rents. But increasingly, rents are triumphing over profits, and rent-extraction is celebrated as "smart business," while profits are for suckers, only slightly preferable to "wages" (the worst way to get paid under both capitalism and feudalism).
That's what's behind all the talk about "passive income" – that's just a euphemism for "rent." It's what Douglas Rushkoff is referring to in Survival of the Richest when he talks about the wealthy wanting to "go meta":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/09/13/collapse-porn/#collapse-porn
Don't drive a cab – go meta and buy a medallion. Don't buy a medallion, go meta and found Uber. Don't found Uber, go meta and invest in Uber. Don't invest in Uber, go meta and buy options on Uber stock. Don't buy Uber stock options, go meta and buy derivatives of options on Uber stock.
"Going meta" means distancing yourself from capitalism – from income derived from profits, from competition, from risk – and cozying up to feudalism.
Capitalists have always hated capitalism. The owners of the dark Satanic mills wanted peasants turned off the land and converted into "free labor" – but they also kidnapped Napoleonic war-orphans and indentured them to ten-year terms of service, which was all you could get out of a child's body before it was ruined for further work:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/26/enochs-hammer/#thats-fronkonsteen
When Varoufakis says we've entered a new feudal age, he doesn't mean that we've abolished capitalism. He means that – for the first time in centuries – when rents go to war against profits – the rents almost always emerge victorious.
Here's the podcast episode:
https://craphound.com/news/2024/04/14/capitalists-hate-capitalism/
Here's a direct link to the MP3 (hosting courtesy of the Internet Archive; they'll host your stuff for free, forever):
https://archive.org/download/Cory_Doctorow_Podcast_465/Cory_Doctorow_Podcast_465_-_Capitalists_Hate_Capitalism.mp3
And here's the RSS feed for my podcast:
http://feeds.feedburner.com/doctorow_podcast

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/18/in-extremis-veritas/#the-winnah
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

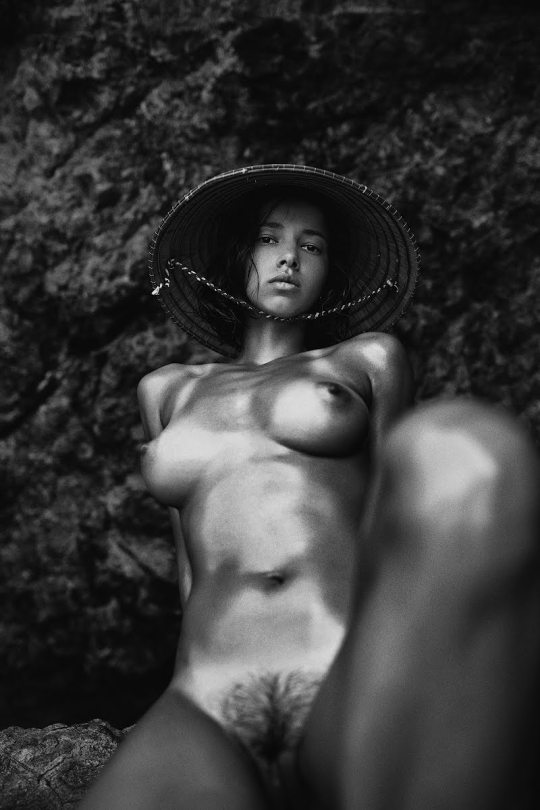
Galina Berezovskaya by Yanis Gusak
#galina berezovskaya#stunning beauty#charming babe#amazing goddess#awesome body#seductive girl#attractive woman#so cute and gorgeous#so hot and sexy#kinky chick#naughty content#slim and sexy#so fucking sexy#so fucking hot#beautiful model#nipplicous#boobilicious#yanis gusak#great bewbs#lovely breasts#perfect breast#artistic nude
734 notes
·
View notes
Text






chen yiwen and chang yani win gold in women's synchronized 3m springboard (jul 27, 2024)
#chen yiwen#chang yani#温文尔雅#paris 2024#*#i'm SORRYYYYY i just needed to get one proper gifset out of my system 😭 and couldn't find any to reblog....#summer break has me going down unspeakable xhs rabbitholes...................#(points at gay couple) who says shit like 我很高兴和你在一起 to her gf's face on camera and who gets flustered and covers her mouth
406 notes
·
View notes
Text
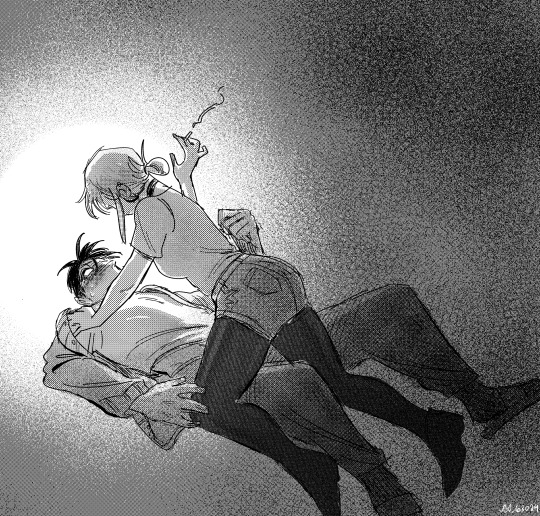

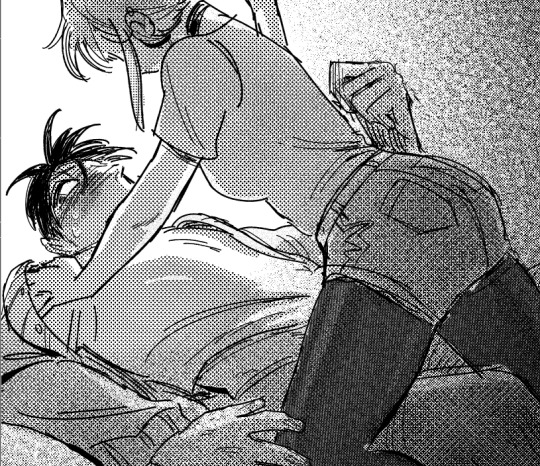
read a manga and went a little bonkers
#and by bonkers I mean kind of lost my shit a little bitmfghg#ugly wheezing sounds hELP#manga is Super no Ura de Yani Suu Futari#crawls out of the abyss to post a suggestive drawing once every 5 years aKFHJFJH#sketchbook stuff#still trying to get the hang of tones/trying to pay attention a little more when reading manga#I swear I'll get to the asks later today >:'D#my break time went from reading manga to furiously drawing lmao#-squints- jhmmmg actually I think if I showed the girl's right shoulder more/arm stretched out#would work better#also the guy's left arm is a wee wonky but eh#anywaYS
436 notes
·
View notes
Text

you got this rookie
#artists on tumblr#chris redfield#leon kennedy#chreon#resident evil#fanart#doodle#I sat down to paint Joe bc of FF trailer but it looked so...#anyway so i went and thought of chreon instead#i finally FINISHED ALL THE MATHS SUBJECTS#i need to study some geometry though im thinking of not studying on everything#tbh idk#N E WAY....#ill keep posting stuff like this if i pick up the digital tablet#osmanlı duraklama dönemi yaşıyorum şu an#gerçekten bir daha anladım çizime ara vermemin haklılığını çünkü 💩 gibi oldu#benim işim değilmiş yani olmayınca olmuyor arkadaş
919 notes
·
View notes
Text

2K notes
·
View notes
Text
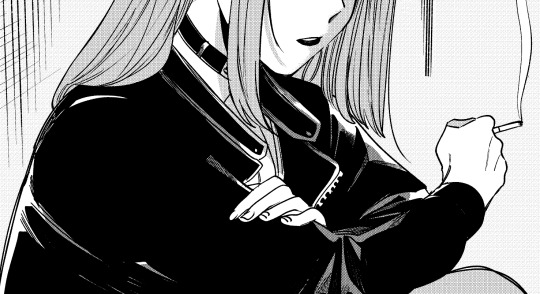
#Suupaa no Ura de Yani Suu Hanashi#A Story About Smoking At The Back Of The Supermarket#Jinushi#manga cap#mangacap#manga
499 notes
·
View notes
Text




435 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yanis Varoufakis’s “Technofeudalism: What Killed Capitalism?”

Monday (October 2), I'll be in Boise to host an event with VE Schwab. On October 7–8, I'm in Milan to keynote Wired Nextfest.

Socialists have been hotly anticipating the end of capitalism since at least 1848, when Marx and Engels published The Communist Manifesto - but the Manifesto also reminds us that capitalism is only too happy to reinvent itself during its crises, coming back in new forms, over and over again:
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/10/31/books/review/a-spectre-haunting-china-mieville.html
Now, in Technofeudalism: What Killed Capitalism, Yanis Varoufakis - the "libertarian Marxist" former finance minister of Greece - makes an excellent case that capitalism died a decade ago, turning into a new form of feudalism: technofeudalism:
https://www.penguin.co.uk/books/451795/technofeudalism-by-varoufakis-yanis/9781847927279
To understand where Varoufakis is coming from, you need to go beyond the colloquial meanings of "capitalism" and "feudalism." Capitalism isn't just "a system where we buy and sell things." It's a system where capital rules the roost: the richest, most powerful people are those who coerce workers into using their capital (factories, tools, vehicles, etc) to create income in the form of profits.
By contrast, a feudal society is one organized around people who own things, charging others to use them to produce goods and services. In a feudal society, the most important form of income isn't profit, it's rent. To quote Varoufakis: "rent flows from privileged access to things in fixed supply" (land, fossil fuels, etc). Profit comes from "entrepreneurial people who have invested in things that wouldn't have otherwise existed."
This distinction is subtle, but important: "Profit is vulnerable to market competition, rent is not." If you have a coffee shop, then every other coffee shop that opens on your block is a competitive threat that could erode your margins. But if you own the building the coffee shop owner rents, then every other coffee shop that opens on the block raises the property values and the amount of rent you can charge.
The capitalist revolution - extolled and condemned in the Manifesto - was led by people who valorized profits as the heroic returns for making something new in this world, and who condemned rents as a parasitic drain on the true producers whose entrepreneurial spirits would enrich us all. The "free markets" extolled by Adam Smith weren't free from regulation - they were free from rents:
https://locusmag.com/2021/03/cory-doctorow-free-markets/
But rents, Varoufakis writes, "survived only parasitically on, and in the shadows of, profit." That is, rentiers (people whose wealth comes from rents) were a small rump of the economy, slightly suspect and on the periphery of any consideration of how to organize our society. But all that changed in 2008, when the world's central banks addressed the Great Financial Crisis by bailing out not just the banks, but the bankers, funneling trillions to the people whose reckless behavior brought the world to the brink of economic ruin.
Suddenly, these wealthy people, and their banks, experienced enormous wealth-gains without profits. Their businesses lost billions in profits (the cost of offering the business's products and services vastly exceeded the money people spent on those products and services). But the business still had billions more at the end of the year than they'd had at the start: billions in public money, funneled to them by central banks.
This kicked off the "everything rally" in which every kind of asset - real estate, art, stocks, bonds, even monkey JPEGs - ballooned in value. That's exactly what you'd expect from an economy where rents dominate over profits. Feudal rentiers don't need to invest to keep making money - remember, their wealth comes from owning things that other people invest in to make money.
Rents are not vulnerable to competition, so rentiers don't need to plow their rents into new technology to keep the money coming in. The capitalist that leases the oil field needs to invest in new pumps and refining to stay competitive with other oil companies. But the rentier of the oil field doesn't have to do anything: either the capitalist tenant will invest in more capital and make the field more valuable, or they will lose out to another capitalist who'll replace them. Either way, the rentier gets more rent.
So when capitalists get richer, they spend some of that money on new capital, but when rentiers get richer, them spend money on more assets they can rent to capitalists. The "everything rally" made all kinds of capital more valuable, and companies that were transitioning to a feudal footing turned around and handed that money to their investors in stock buybacks and dividends, rather than spending the money on R&D, or new plants, or new technology.
The tech companies, though, were the exception. They invested in "cloud capital" - the servers, lines, and services that everyone else would have to pay rent on in order to practice capitalism.
Think of Amazon: Varoufakis likens shopping on Amazon to visiting a bustling city center filled with shops run by independent capitalists. However, all of those capitalists are subservient to a feudal lord: Jeff Bezos, who takes 51 cents out of every dollar they bring in, and furthermore gets to decide which products they can sell and how those products must be displayed:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
The postcapitalist, technofeudal world isn't a world without capitalism, then. It's a world where capitalists are subservient to feudalists ("cloudalists" in Varoufakis's thesis), as are the rest of us the cloud peons, from the social media users and performers who fill the technofuedalists' siloes with "content" to the regular users whose media diet is dictated by the cloudalists' recommendation systems:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
A defining feature of cloudalism is the ability of the rentier lord to destroy any capitalist vassal's business with the click of a mouse. If Google kicks your business out of the search index, or if Facebook blocks your publication, or if Twitter shadowbans mentions of your product, or if Apple pulls your app from the store, you're toast.
Capitalists "still have the power to command labor from the majority who are reliant on wages," but they are still mere vassals to the cloudalists. Even the most energetic capitalist can't escape paying rent, thanks in large part to "IP," which I claim is best understood as "laws that let a company reach beyond its walls to dictate the conduct of competitors, critics and customers":
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Varoufakis points to ways that the cloudalists can cement their gains: for example, "green" energy doesn't rely on land-leases (like fossil fuels), but it does rely on networked grids and data-protocols that can be loaded up with IP, either or both of which can be turned into chokepoints for feudal rent-extraction. To make things worse, Varoufakis argues that cloudalists won't be able to muster the degree of coordination and patience needed to actually resolve the climate emergency - they'll not only extract rent from every source of renewables, but they'll also silo them in ways that make them incapable of doing the things we need them to do.
Energy is just one of the technofeudal implications that Varoufakis explores in this book: there are also lengthy and fascinating sections on geopolitics, monetary policy, and the New Cold War. Technofeudalism - and the struggle to produce a dominant fiefdom - is a very useful lens for understanding US/Chinese tech wars.
Though Varoufakis is laying out a technical and even esoteric argument here, he takes great pains to make it accessible. The book is structured as a long open letter to his father, a chemical engineer and leftist who was a political prisoner during the fascist takeover of Greece. The framing device works very well, especially if you've read Talking To My Daughter About the Economy, Varoufakis's 2018 radical economics primer in the form of a letter to his young daughter:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9780374538491/talkingtomydaughterabouttheeconomy
At the very end of the book, Varoufakis calls for "a cloud rebellion to overthrow technofeudalism." This section is very short - and short on details. That's not a knock against the book: there are plenty of very good books that consist primarily or entirely of analysis of the problems with a system, without having to lay out a detailed program for solving those problems.
But for what it's worth, I think there is a way to plan and execute a "cloud rebellion" - a way to use laws, technology, reverse-engineering and human rights frameworks to shatter the platforms and seize the means of computation. I lay out that program in The Internet Con: How the Seize the Means of Computation, a book I published with Verso Books a couple weeks ago:
https://www.versobooks.com/products/3035-the-internet-con

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/28/cloudalists/#cloud-capital
#pluralistic#yanis varoufakis#socialism#communism#technofeudalism#economics#postcapitalism#political science#rent-seeking#rentiers#books#reviews#gift guide
735 notes
·
View notes
Text

Galina Berezovskaya by Yanis Gusak
#galina berezovskaya#seductive girl#amazing goddess#attractive woman#charming babe#slim and sexy#awesome body#kinky chick#stunning beauty#so cute and gorgeous#nipplicous#so hot and sexy#boobilicious#magnificent rack#yanis gusak#so fucking sexy#so fucking hot#naughty content#great bewbs#artistic nude
321 notes
·
View notes


