#written records
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Towards the end of each year, as fireplaces are lit and hot cocoa is made, Americans have made it a tradition to revisit their favorite classic holiday books, movies and songs.
And though ghost stories may seem out of place in present-day American holiday celebrations, they were once a Christmas staple, reaching their peak of popularity in Victorian England.
A Dark, Spooky Time of Year

Like most longstanding cultural customs, the precise origin of telling ghost stories at the end of the year is unknown, largely because it began as an oral tradition without written records.
But, according to Sara Cleto, a folklorist specializing in British literature and co-founder of The Carterhaugh School of Folklore and the Fantastic, the season around winter solstice, has been one of transition and change.
“For a very, very, very long time, [the season] has provoked oral stories about spooky things in many different countries and cultures all over the world,” she says.
Furthermore, spooky storytelling gave people something to do during the long, dark evenings before electricity.
“The long midwinter nights meant folks had to stop working early, and they spent their leisure hours huddled close to the fire,” says Tara Moore, an assistant professor of English at Elizabethtown College, author of 'Victorian Christmas in Print' and editor of The Valancourt Book of Victorian Christmas Ghost Stories.
“Plus, you didn’t need to be literate to retell the local ghost story.”
Effects of the Industrialization Revolution
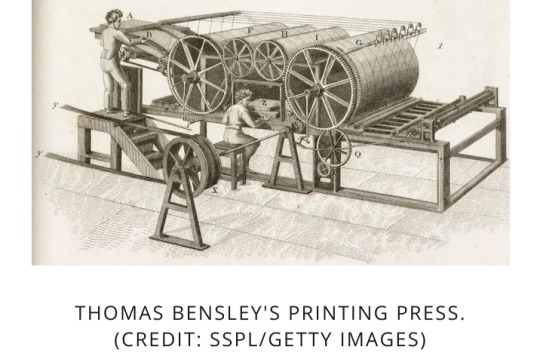
It was in Victorian England that telling supernatural tales at the end of the year — specifically, during the Christmas season — went from an oral tradition to a timely trend.
This was in part due to the development of the steam-powered printing press during the Industrial Revolution that made the written word more widely available.
This gave Victorians the opportunity to commercialize and commodify existing oral ghost stories, turning them into a version they could sell.
“Higher literacy rates, cheaper printing costs, and more periodicals meant that editors needed to fill pages,” Moore says.
“Around Christmas time, they figured they could convert the old storytelling tradition to a printed version.”
People who moved out of their towns and villages and into larger cities still wanted access to the supernatural sagas they heard around the fireplace growing up.
“Fortunately, Victorian authors like Elizabeth Gaskell, Margaret Oliphant, and Arthur Conan Doyle worked through the fall to cook up these stories and have them ready to print in time for Christmas,” Moore says.
Industrialization not only provided tools to distribute spooky stories, uncertainty during the era also fueled interest in the genre, says Brittany Warman, a folklorist specializing in Gothic literature and co-founder of The Carterhaugh School of Folklore and the Fantastic. She adds:
"Interest was driven by the rise of industrialization, the rise of science, and the looming fall of Victorian Britain as a superpower.
All of these things were in people's minds and made the world seem a little bit darker [and] a little bit scarier.”
Stories Find a Wide-Ranging Audience

Telling horror-filled holiday tales continued to be a family affair in England, even when they were read rather than recited.
“We know from illustrations and diaries that whole families read these periodicals together,” Moore says.
The popularity of Victorian Christmas ghost stories also transcended socioeconomic status, according to Moore.
They were available to read everywhere from cheap publications to expensive Christmas annuals that middle-class ladies would show off on their coffee tables.
Their broad audience was reflected in the stories themselves, which sometimes centered around working class characters and other times took place in haunted manor houses.
“These upper class settings were intended to invite readers from all classes into an idealized, upper-crust Christmas, the type todays’ fans of Downton Abbey still enjoy as entertainment,” Moore adds.

Charles Dickens’ 1843 novella A Christmas Carol has forever linked the British author with the holiday season, but his contributions to Christmas in Victorian England — including the tradition of telling and reading ghost stories — extend far beyond Jacob Marley’s visit to Scrooge.
In fact, Cleto says that Dickens played a “huge part” in popularizing the genre in England.
“He wrote a bunch of different Christmas novellas, several of which involved ghosts, specifically,” she says, “and then he started editing more and more Christmas ghost stories from other people, and working those into the magazines he was already editing. And that just caught like wildfire.”
Dickens also helped shape Christmas literature in general, Moore says, by formalizing expectations about themes like forgiveness and reunion during the holiday season.
American Christmas Traditions: More Syrupy Than Spooky

Although countless trends made their way from England to America during the Victorian era, the telling of ghost stories during the Christmas season was not one that really caught on.
A Christmas Carol was an immediate best-seller in the United States, but at the time of its publication, Dickens was arguably the most famous writer in the world and already wildly popular.
The novella’s success in the U.S. likely had more to do with Dickens’ existing (massive) fan base than it did Americans’ interest in incorporating the supernatural into Christmas.
“American Christmas scenes and stories tended to be syrupy sweet,” Moore explains.
"There were a few American writers of the period trying to put Victorian-style Christmas ghost stories into American culture,” Warman says, including Nathaniel Hawthorne and Henry James.
Washington Irving made a similar and earlier attempt, slipping the supernatural into Christmas-themed short stories published in 1819 and 1820.
Warman theorizes that America’s reluctance to embrace the Christmas ghost story tradition had to do, at least in part, with the country’s attitudes towards things like magic and superstitions.
“In America, we generally had a bit of a resistance to the supernatural in a way that European countries didn't,” she explains.
“When you come to America, you come with a fresh start. You come with a secular mindset and the idea that you were leaving the past behind. And some of these spooky superstitions were thought of as being part of the past.”
Another reason telling spooky stories never took off as a Christmas tradition in the United States was because it became more firmly established as a Halloween tradition, thanks to Irish and Scottish immigrants.
“That really impacted culture here, because they brought with them a concept similar to Halloween and that became, for America, the time period for ghosts,” Warman explains.
Traces of the Tradition

Other than A Christmas Carol, there is another piece of pop culture that reflects the Victorian Christmas tradition: a single line from a song written and released in 1963 by American musicians.
First recorded by Andy Williams, the song “It’s the Most Wonderful Time of the Year” lists 'scary ghost stories' as one of the highlights of the holiday season.
Although it’s unclear why the writers of the song (Edward Pola and George Wyle) included the tradition, Cleto says that it’s possible that the lyric is a reference to Dickens’ A Christmas Carol.
“It's only the one text,” she notes, “but it's such a big deal here in the US and the UK, and is pretty much all that Americans know about Christmas ghost stories in isolation.”
#Christmas#Christmas Ghost Stories#Victorian Era#1800s#19th century#Victorian England#oral tradition#written records#Sara Cleto#winter solstice#folklore#British literature#spooky storytelling#Tara Moore#steam-powered printing press#Industrial Revolution#ghost stories#Brittany Warman#Victorian Christmas#Charles Dickens#A Christmas Carol#Jacob Marley#Scrooge#Halloween
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Seriously. Write down the recipe.
I remember as a kid, when The Internet first started becoming A Thing, I remember worrying "how will I find this ___ if the Internet goes down one day?" The reverse of that was "how will I find ___ if the paper copy burns up?"
(I worried about strange things as a child)
Point is, it never hurts to have both a physical and a digital copy, and considering how long things like papyrus and parchment have lasted...
Write down the recipe.
You should be starting a recipe book. I don't give a shit if you're only 20-years-old. The modern web is rotting away bit by bit before our very eyes. You have no idea when that indie mom blog is going down or when Pinterest will remove that recipe. Copy it down in a notebook, physically or digitally. Save it somewhere only you can remove it. Trust me, looking for a recipe only to find out it's been wiped off the internet is so fucking sad. I've learned my lesson one too many times.
82K notes
·
View notes
Text




"Not gonna lie, we're doing pretty well already But yes, oh my doctor said There's a lot of room left to grow"
seonghwa, matz (2023)
#ateez#atz#atzedit#atzsource#seonghwanet#park seonghwa#seonghwa#matz#*#actually i very much favour seonghwa in matz#i thought he would be out of his element#and i didn't really expect much#but learning that he was responsible for matz sounding the way it does#having written over 100 lines for his verses#having recorded 424 versions of the song#seonghwa has been the most delicious surprise so far#what an absolutely fascinating human being#his persona dichotomy on stage is so#it's layered. there are definitely layers to him#but like#the same way there are layers to the universe you know#such an amazing idol and professional
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Alright, so this is basically...an art dump for all the pics i drew when i was trying to draft the ending i wanted my Odile looping Au 'Like a Wheel Ever Turning' which...is not even SLIGHTLY how this fic is going to end now, but while figuring that out i still like draw all this and had to do SOMETHING with it.
So figured I'd post it and be like 'hey! fun Odile looping act 5 boss fight vibes not connected to anything else!' since like...that basic IS what they are at this point lol.
The one cool idea i loved that i think is now FIRMLY ditched is the act 5 boss fight starts when Odile uses wish craft to splinter herself into two halves.

The 'old/current' her that is meant to be her coldly logical side, and a younger 'copy' version, which is meant to be the childish irrational side...that is what's stopping her just shutting down the time loop because she can't figure out how to be happy with her friends leaving.

I mean, if you murder the part of you that WANTS the wish to come true, that's basically a 'get out of time loop free card' right? Right! Totally sound logic!

Yes the 'young' version of her firmly believes that she's real, and also also got memories going up to about age 21, and also that she ought to be in Ka Bue not HERE among these french weirdos.


Also yes again, a 'young' Odile is EXACTLY as unhinged about this as you'd expect a 21 year old to be upon finding out that apparently the 'real' her think murdering her is the correct solution to this problem!




The shift of the fight was meant to have the inverse 'colors' shift from one version to the other by the end, wrapping up with the point where the 'original' Odile is forced to have a heart to heart with the personification of her perceived 'worst' qualities.
Pretty sure the vibes for this ending was a lot more focused on the resolution of having deeply complex feeling about EXPRESSING emotion directly to other people. That along with a side helping of how isolating it is to be perceived as a 'real' adult such that you can't be weak enough to ask anyone for help. Because really if you can't even be that then why are you any different then when you were irritating mess of a youth?
Not saying any of that isn't still present in the story, but like...there is a LOT of other stuff going on, and those themes are now linked into many other ones too, and that's not even TOUCHING on how Loop's been...somewhat complicating my redrafting lol.
...Also I might have drawn/plotted this version before i knew about two-hats lol. THAT also is a factor.
Anyway! Still liked all of these enough to want to do SOMETHING with them, and figured this worked, so i could like map out my thoughts on them, even if i never got to write this.
#isat#in stars and time#isat odile#odile looping au#I might have written out like...way too many edgy and utterly disjointed notes for this fight too?#but none of THAT compelled enough for me to want to try and even reread it lol#drew all of this in fever state of creativity back in like september i think?#kept having the thought of 'oh i'll make SOME of it work in the main story'#HA no i didn't - that was the denial and wishful thinking talking#Like there was even a version where the 'young' odile had to do the whole final loop with the group#and that's what forced Loop to join them - to keep her alive no matter the 'other' her's attempts to kill her#while 'old' odile took the place of the king during that final run#'young' odile was DEEPLY weird at the rest of the group for the record - while they were also weirded out + low key endeared#Also before the even knew who the 'final battle' was against young odile HAD loudly declared she was willing to die for 'you weirdos' soooo#Ah to be young unhinged and realised people CAN love you despite that...and that apparently this is reason to commit a murder to AVOID#...if i had a nickle for everytime i wrote a odile looping au where she tried to murder herself#i'd have two nickles#which isn't a lot but ect ect#this one is WAY more serious with it tho lol#my art#like a wheel ever turning au
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
i love this bit SO MUCH. it's so fucking funny all of these jokes are fantastic to me and the delivery is perfect
#mike written all over it#my new non-stick cookware and psychic makeup. OKAY#con-stick nookware#🤨 are you really martha stewart? 🙁 yeah#we have a new record out!#YELL 000-MICK3Y#REALLY GOOD#1997 tv special#the monkees#peter tork#davy jones#micky dolenz#justus
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
( using written mediums like text/email is also a good safety measure when you have to communicate with abusers outside of work settings - if you don't have that un-editable transcript, it's much easier for them to forget, misremember, or actively lie about what they and you said )
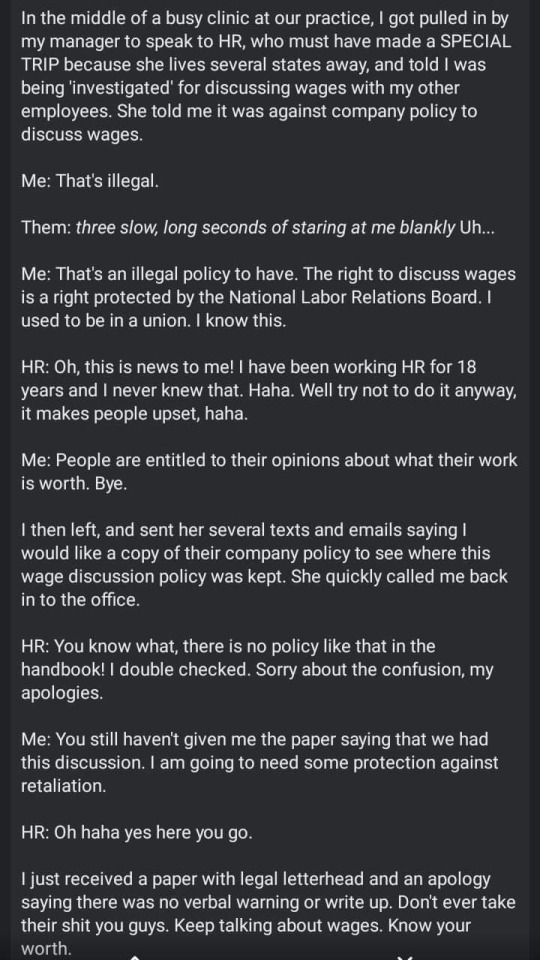
Do Not Let HR do this to you. It is not illegal to talk about wages in the work place. I did and got a 12% raise!
#captioned#we said a thing#sy#exploitation#abuse#written records#written communication#text-based communication#gaslighting#hanging mention
73K notes
·
View notes
Note
please god i need to know what U think of the whole “jadebloods are all female!” thing because i got into homestuck in 2019 around the time of friendsim and (retching) Lanque so i always assumed they were explicitly intended to be an all-female caste. however, re-reading the comic this year, i couldnt find a mention of it other than virgo and the Space aspect being really feminine, but i think kanayas journey with motherhood is more kanaya-centric than All-Jadebloods centric??
on one hand, it makes sense given that alternia has very real gendered oppression, so what’s better for that than CATHOLICISM?? on the other hand, i always saw kanaya as being transfem coded, because it connects so well with roxy yknow.. homestuck fans love to insist that certain characters just have to be cis women (kanaya, jade, roxy)
(as an aside; was “long hair was butch on alternia” a one off joke? i like speculation about alternia’s fashion opposing earth, lol)
most all of our basis for explicitly gendered interpretation of Alternia comes from act 6 intermission 3, where Aranea tells us that "jade 8loods were also an almost exclusively female caste". so the door has always been open for there to be "some male jadebloods". but it's a mistake to view this as having anything to do with any kind of "biological sex". the whole idea of biological sex among trolls is a smoke screen. the jadebloods' assigned gender at birth is "jadeblood". this is what makes them a feminised caste.
Caliborn doesn't have a clue what biological sex is. Aranea will tell you that there are boy cherubs and girl cherubs, but for your own sanity you need to cast this idea out of your mind: cherub sex takes place between good and evil cherubs - which is determined by their blood - and anything else is just roleplay. Caliborn's attitude toward sexing is that the ones he likes are boys - that's all the thought that goes into it. and that's the mindset we need to be aware of when we delve into understanding troll gender. there are some trolls who have breast tissue and some who don't, but they aren't "mammaries" in any sense, so there's no reason to believe they're actually sexual characteristics of any kind; maybe this is what Lord English chose to base his gender schema on, but the idea that this means there must be "male trolls" and "female trolls" is completely imagined for the narrative convenience of the human reader.
when we read that there are "male-dominated" highblood castes and therefore by implication female-populated lowblood castes, it's not by some coincidence of biology: the highblood castes are male-dominated BECAUSE they are highblood castes. each caste has a role to play in Caliborn's Alternia, and just as the highblooded roles are those of patriarchal domination, the lower castes must take on roles of feminised submission; and in the case of the jades in particular, this means breeding duties. the fact that this also comes with the expectation to wear makeup and pretty clothes is just more roleplay.
so tl;dr what i think of "the all jadebloods are female thing" is that it is very obviously true but in a way more 5 dimensional gender studies way than anyone else tends to mean when they say it
my pet "long hair was butch on alternia" headcanon - which is a joke but in the way all headcanons about alternia should be jokes of some kind - actually kind of relates to this lol. bc i figure that if gendered expectations of female trolls includes working in disgusting underground caverns filled with genetic material, it's going to be practical to keep your hair close to your head where it won't get dirty, in much the same way the feminist image of the short-haired woman became popular in the west during and after world war 2, wherein a lot of women had to start wearing their hair close to their heads to avoid scalping themselves in the factory machinery they suddenly had to start working with. hence kanaya dedicated to her assigned feminine role and wearing her hair short vs. porrim rebelling against it for feminist reasons and thus wearing her hair at a length that would be totally impractical for wading through gene pools.
#i had someone get mad at me once for saying this bc it implied vriska was butch or whatever.#which idgaf about. any further interpretations you make about the other girl trolls based on this are out of my hands#anyway i wont apologise for making this so long bc im sure at this point it's what you all want out of me when you ask this stuff LOL#homestuck#for tha record. i have written articles about each caste on the mspa wiki. all my sources r there you dont ALWAYS need to do your own rsrch
289 notes
·
View notes
Text





#tvedit#filmedit#dcedit#thepenguinedit#the penguin hbo#oz cobb#thebatmanedit#colin farrell#gifs#*#the way he pats her hand!!!!!!!!!!#i've written how he loves his parents old records!!!!!!!!!! kill me!!!!
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
waitt wait wait sirius finds a tape recorder he left behind in grimmauld place decades ago and a box of tapes hidden and realises regulus had started to use them as a diary after sirius left
#you could do some fun things#w a mix of podfic and written fic#this would so just be angst#like regulus’ life recorded in his voice#and then it gets stopped by sirius needing to process#because why did he never know any of this#marauders#regulus black#sirius black#marauders era#posting day and night#marauders fic idea
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
DONT ASK ME WHAT THIS IS I'M SPEED RUNNING THIS BEFORE I PASS TF OUT TW COERSION I GUESS??? TW STANCEST TW SMIDGE OF IMPLIED/REFERENCED SA TW A/B/O DYNAMICS
Ford's long fingers curled tightly into the blankets as he tried to swaddle himself even smaller. He almost threw the blanket when it didnt bring the relief he wanted.
Ford had read about the omegan estrous cycle - he had to, when he turned fifteen and it became clear Stanley was growing broader but he was not. He knew if he was just held by familiar people it would calm the knashing pain in his stomach and the pulsing in his head.
But instead he was alone, because Ma had locked the door and told him not to let anyone in except her. It was day three, the most optimistic estimate was he still had another two full days of trying to figure out how to hold himself the way someone else would hold him - touch himself the way someone else would touch him.
Then there were three quick knocks before the door was shoved open. Ma looked pale. "You and Stanley stay in here until you don't see your Pa's car on the road, capiche? Don't open this door for anything until then, there's money on the counter, leftovers in the fridge, Stanford you call my sister when it's safe, I love you both, goodbye." She said in a whirlwind that barely made it through Ford's cloudy thoughts. Then Stanley was shoved in the room and the door was slammed behind him.
Ford stared at Stanley for a second with wide eyes. Ma hadn't allowed him in their room since Ford had presented, acting cagey whenever he asked before eventually just saying that Stanley looked like an alpha and alphas couldn't control themselves. That was why Pa wasn't allowed in. Ford knew it was factually incorrect - alphas were capable of resisting urges, they simply chose not to in many cases. Part of him wondered if Stanley would be so forceful once he presented. He certainly had the build for it.
Then a wimper drew Ford's gaze away from his indimidating form and up to his face. His face was a deep pink, tears rolling down his cheeks and trembling where he stood.
Then the scent cut through his own. Oh.
Stanley had presented.
Ford slowly drew away from his blankets - the open air was suffocating, but Stanley could help that - Stanley was just another omega, he could help, wrap those big arms around him, press that heavy weight into his ribs until he didn't have to feel anything anymore.
"Stanley. Why are you crying?" His voice dragged as he got closer - he was only wearing his boxers, he couldn't find it in him to care.
"I wa-was s'posed to be - be an alpha. That-That's what Ma said." He babbled. "How can I prote-ct us if I'm an omega?" He whimpered, digging his heels into his eyes. "I'm sor-ry." He hiccuped.
Ford felt a rush of something wash over him. In the next second he had Stan's face in his hands - so warm, he fit perfectly between 12 fingers. "You're still a great boxer, Stanley. But now - now you can help me. Don't you want that?" Stanley looked up at him with those big brown eyes, hopeful. It made Ford's stomach roll in a new way.
"H-How?" Stanley asked, laying his own smaller hands over Ford's with such ease, as if the contact Ford had needed was just so easy to give.
Ford pulled Stanley closer. "Physical contact. Familial omegan contact can bring smaller amounts of the endorphins released during copulation. You want it too, don't you?" Stanley nodded quickly. "The come here." He purred, and Stanley curled around him in a tight hug. Stanford shivered, clinging back to his twin. For a moment, they stood there, similar scents intertwining, both making small pleased huffs as they gripped eachother tighter.
But like an addiction, he started itching for more. "Stanley." He muttered into his brother's ear. "We should go back to the bed. I tried building a nest it--" Stan's nose touched the gland on his neck and he made a quiet keening noise. "--it isn't great, but omegan behavioral studies were very vague with how they're made."
Stan hummed. "Nest. Yeah. That - that sounds so good." He said, before picking Ford up. Ford took the chance to wrap his legs around him. When Stan finally pressed him into the mattress Ford whined loudly, a purr still filled with the cracklings of puberty rumbling in his chest. Stan shoved his face into Ford's whispy chest hairs, whining right back at him.
"You're - You're right, your nest is crap." Stanley teased breathlessly. Ford jabbed him in the back with the sole of his foot and Stanley giggled, eyes still red-rimmed but smiling, now. Ford couldn't help smiling back.
"Fix it then." Ford replied, and Stan pulled away very slightly before dropping back down.
"Nah." Stan said simply, clinging to Ford.
The cramps were still there - but with Stanley they were barely a nuiscence. Just a low presence to match the feeling of his wet boxers.
Then he noticed Stan's slight shifting.
He still looked completely distracted, blissed-out and clinging to Ford like a piece of driftwood in the ocean. But lower down his hips were twitching into the mattress just a little. Ford traced the tiny erratic rolling of Stan's hips in a trance. Did Stanley even notice?
Then Stanley made a little groaning, huffing noise and Ford's own hips twitched. Except any movement on his own part resulted in directly jutting into his brother's stomach.
Stanley's eyes snapped open. He looked up at Ford slowly. Before he could say a word Ford had pushed up his glasses. "it's perfectly normal to have the same physical symptoms of arousal during an estrous cycle, Stanley." He said almost defensively, but Stanley's relief seemed to be directed inward. He rolled his hips more brazenly against the mattress.
Then Stan's whole body froze, and he started pulling away. Ford tried to follow him, but Stanley looked close to crying again. "Whats the matter? I promise it's normal, Stanley - what's wrong?"
"I gotta go." Stan said stiffly.
"You can't go, Stanley - Pa isn't gone yet." He said, sitting up and reaching for him.
"I don't care about Pa, I'll just punch him again if I gotta." His voice wavered with a little bit of fear.
Ford stood again. "Don't be ridiculous Stanley - why do you have to leave?"
Stan looked away.
"Stanley."
"I think I peed myself."
Ford stared at him. Then down at his perfectly dry jeans. Then he snorted.
Stan's face twisted angrily, though his eyes were glassy again. "Shut up."
"You didn't pee yourself, Stanley - did you even read the omegan biology book I lent you? Or were you too busy drawing Lil' Stanley in the margins?" Stan shrank in on himself a little. Ford sighed fondly. "Here - it's happening to me, too, it's just discharge." He wiped some from his inner thigh onto his finger for Stan to see. "The pH is within the acidic range, though, so you should probably get out of your good jeans before you bleach them." He said, and Stan just kept staring at his two damp fingers.
Ford would have let Stan indulge his curiosity, but the lack of contact was getting to Ford. "Stanley?"
His brother nodded, clearing his throat and unbuckling his belt. Ford watched his hands make quick work of the leather, before he slid the denim down over his tight boxers and his large, chubby thighs. There was a small wet spot on the inside of his jeans. Ford wondered if he would add it to their nest.
Stan threw his shirt over his head and then they were both in similar attire. Ford pulled Stanley closer to him again - he just couldn't stand the itch of not touching his twin for long. "Now that that's established..." He dragged Stan back into his bed. They laid facing eachother, legs tangled and arms clinging.
Stan was just so perfect as an omega - so pliant. Ford wondered how he ever could have thought Stan would be an alpha, even with his build. He was so perfect, so trusting, he fit just perfectly in Ford's arms, held into every word despite the physical advantage and the primal mindset an estrous cycle brought to the forefront. Watching Stan happily nuzzle into his smaller chest made Ford almost understand the gaze of an alpha. Stan would just be so easy to take and claim for himself - not because Stanley was weak but because he was Stanford Pines and Stanley was pliant for him and him alone.
He curled a little further towards his brother, when his thightouched something warm and wet. Stanley didn't move away, his nose just scrunched a little and he whined softly. Ford studied every subtle change in his expression.
Then Stan's hips rolled against his thigh. His dick was solid, pressing into his stomach, but Stan was more interested in the new sensations his hole brought, grinding it against Ford's thigh with tiny huffing whines, getting his leg wet while Stan lost himself with his nose still pressed into Ford's ribcage. Ford was like this, too, the first day. It was so cute on Stanley, though. Ford pushed his leg a little harder upward and Stanley moaned quietly, like he thought he was being subtle.
Stan's whines got a little more desperate the longer he went without orgasm, chasing an end that wouldn't come just from a bit of frotting. Ford let him get frustrated, felt his thick thighs quiver under the blanket while he tried to grind harder. Ford felt a drip of hot discharge run off his knee and he snapped.
He grabbed Stan by the hips and Stan stopped dead. "Proper orgasm during an estrous cycle is nearly impossible to achieve by one's self because of the lack of physical contact. This is enough to get rid of the cramps, but if you want to come then you have to ask." His voice was rough from the sight of Stanley, he felt his own slick running down his thighs.
"P-Please." Stanley whimpered. Ford immediately surged forwards, bracketing Stan's larger form under him and pressing their lips together for a searing moment. When he pulled back, Stan tried to follow.
"You want something in your hole, don't you?"
Stan nodded quickly, back arched just a little, neck exposed obscenely.
"Gorgeous - god, Stan, you're so pretty, you know that?" He mumbled into Stan's jaw between short, soft kisses. "You probably want some big alpha to stretch you out, don't you? Fill you up while you take it so perfectly?"
"No." Stan whispered. "Jus-Just you. Please, I want - need you, please." Ford shivered at the words.
"Perfect, Stanley, you're so perfect." Ford purred into Stan's skin while six fingers dipped under Stan's waistband. Stanley was a mess, sopping wet for him and Ford would spend hours licking it all up if Stan hadn't asked to be filled.
Two of his fingers grazed Stanley's soaked enterance and Stanley keened. "M' ready, m'ready - please, Stanford--" Ford pulled his own boxers down and rubbed Stan's slick onto his skin before grabbing Stan's legs to put on his shoulders.
Stanford put his thumbs on either side of Stanley's hole to watch it stretch, watch a little bit of clear fluid burble out. Stan whined under him. "It's gonna hurt, Stanley, I'm telling you."
"Then hurt me." Stanley demanded.
Ford lined himself up and pushed into Stan's feverish warmth. He keened, feeling Stan all around him, slick dripping down into two puddles under them, close enough to merge. He took a breath while Stanley shivered and moaned.
"Move - damn it Sixer gimme all of it--" Ford pulled out and thrust back in again, the smack sounded in the room and both omegas groaned.
"Perfect - g-god Stanley, my perfect little omega - fuck. Gon-gonna full you up, fill you up with my pups - gotta - god - gotta let the world know they lost the perfect omega to an-another fucking omega." Stanley yelped when Ford found his prostate, grinding against if for all he was worth.
"S-Six - gotta - gonna--" Stan sobbed.
"I've gotcha, I've - Stanley." Ford whined, taking one of his hands off Stan's hips to run over his own hole, wetting his fingers in his own sopping mess. "I'm close."
"Please - please--!" Ford shoved two fingers in alongside his dick as his orgasm peaked, and Stan squealed on his pseudo-knot while he came himself. Ford kissed the fresh tears from Stan's face and waited for Stan to come down before gently easing his fingers out.
Stanley's arms wrapped fully around him in a crushing embrace the second Ford was out of him, and his own more practiced purr rumbled them both out of consciousness.
#stancest#Don't ask what allegory for sexism this is I don't know either#I've written 3 ficlets in 24 hours I think that's a new record for me#If you see typos just know I was writing part of this with my eyes closed because I'm so tired rn#a/b/o dynamics#drafts
72 notes
·
View notes
Text





Yeah we're all totally normal about minsung.
#guys i SCREAMED#I've been playing non stop while freaking out on youtube#honestly god bless youtube music#best tool for a stay when a skz record drops#minsung#!!!!!!!!!!!#gays keep winning#idc what u have to say#the cheesiest sweetest cutest love song written by han sung by minsung#it's EVERYTHING#lee know#han jisung#han#skz record#want so bad#skz#stray kids
481 notes
·
View notes
Note
I always though Mal's mom was meant to be like "Eleanor" but they stuck an M at the start honestly, Sobbing Emoji. But "Maleanor" also makes me feel less insane since in that scene where she's just handed egg Malleus to Lilia and went to battle, it sounds more like Lilia is saying "Maleanor" than "Meleanor" (Japanese accent pending). Mayhaps they went more with what it sounded like the characters were saying :0 (we don't talk about Doodle Suit to Paint The Roses)
the transliteration of her name is Marenoa (マレノア), which is what all the voice lines are saying! all the Draconias' names start with マレ (Malleus' grandma is Maleficia/マレフィシア) as a nod to Maleficent. :D it's almost certainly a take on Eleanor, which is Erenoa (エレノア), but her name is written in English at a couple points, and I was pretty surprised to see it was Mel instead of Mal!
and, like, that's fine, it wouldn't be first Twst romanization that's tripped me up (like Keito for Cater, I know that's something to do with the loanword specific to playing cards(?) but it's just not how my brain wants to read it). but now Eng has given us Maleanor! and someone else said it was spelled inconsistently between Maleanor and Maeleanor??????? so WHO KNOWS it's a SPELLING FREE-FOR-ALL
I AM torn on which I want to use, because Mel just sounds so cute to me (and is what I'm used to now), but...the Mal consistency is kinda too good to pass up. alas, alas, truly these are the most difficult conundrums of our times. 😔
#twisted wonderland#twisted wonderland spoilers#i...am unsure if maleficia's name gets mentioned pre-part 6 so i'm gonna go overboard on the spoiler tags just in case#i-i just want to be careful okay#twisted wonderland episode 7 spoilers#twisted wonderland book 7 spoilers#twisted wonderland episode 7 part 6 spoilers#twisted wonderland book 7 part 6 spoilers#well if nothing else i'm happy i can stop calling him revaan. that was getting too silly.#and seeing baur finally twigged the reference for me (somewhat embarrassingly late)#me: (looking at a crocodile man whose name is literally written bauru) HMM I JUST DON'T KNOW#(i assume they went with 'baur' instead of 'bauru' to make it more of a reference and less...literally the name of a municipality)#(and also a sandwich according to wikipedia?)#(no actually he should have been bauru that would've been incredible) (sandwich grandpa)#i might call artistic license and use something like 'the briarlands' instead of 'briarland' though if it ever comes up#(it looks like we're going to be leaving the pre-valley timeline soon so it probably won't) (but i just want it on record)#i actually do like it being more unique than just 'briar country/kingdom' but i think the plural adds more of that ~fantasy flair~#...also this is how i find out that trey's magic name is different in eng?#(wow i really do not pay attention huh)#'paint the roses' IS the actual translation of his magic (薔薇を塗ろう) so it's not...COMPLETELY different at least?#i...guess they went for the more immediately obvious reference...? weird
355 notes
·
View notes
Text
just read this snippet in a vanilla fic where character A sneezes and character B unthinkingly lends them their jacket. only, A realizes after the jacket is on that it's feverishly warm, and they lean over and feel B's forehead... 😵💫
what lack of self preservation would you need to have to lend someone your jacket so unthinkingly when you're the one with a fever?! also to feel someone's fever through the residual warmth of a clothing article?? the scene will not leave my mind
#for the record the fic is not a sickfic and this goes unacknowledged and unexplained for the rest of the fic#why did the author write that in?????????? what purpose did the mention of his fever serve narratively??????#idk but it's very very hot to me 😭#(...if anyone read my latest fic yes a is ti//ll and b is i//van in the fic i'm referencing. which i hesitate to link outside of dms bc#it is written by a vanilla 😭 but i fell asleep thinking about it and now i'm awake thinking about it again)
117 notes
·
View notes
Text

made a weird dog
#oc#monochrome#me when there's a creature that exists between two states and watches beyond more than that:#its cool with this for the record its having a lot of fun#based super loosely off the concept of coyote from gunnerkrigg court. friend of mine wanted me to read it and i. dont like it that much but#i wanted to give it a shot bc i hate all the other webcomics they like ;-; unfortunately i still dont like it that much. it is badly writte#like materially. the reason i dislike it is because it is not well written and unlike them i came up in an era where i could read stories#like that in webcomic format that were well written#a couple ideas bit me though. as you can see#dog#sort of a fox? i guess?#also obviously goes without saying but Extremely Derivative Obviously Not My Own Original Ideas]#favorite
157 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you need a serotonin boost today, picture this: iii and iv hearing Euclid for the first time and seeing how it all ties together and how the song has callbacks to TNDNBTG and the absolute geniusness of the whole thing. Them in complete awe just like us fans were when we first heard it, knowing Vessel and ii cooked with this song. They were probably even more excited as they are musicians and part of the band
#whether they found out while it was being written or recorded or when the entire album was finished#anyway hope this helps :)#worshitposting#sleep token#sleep token vessel#sleep token ii#sleep token iii#sleep token iv
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
fanfic idea: While building the portal, Stan makes audio logs every day for 30 years to track and record his process on re-building the portal. When Ford eventually returns through the rebuilt portal, he finds and listens to them.
#idea came to me because it would be useful for him to have notes and stuff saved right? track his progress#but he's not the type to keep a written journal or notes like Ford would#hence audio recordings#free to use!! tag me if you do ^^#gravity falls#ford pines#stan pines#stanford pines#stanley pines#tbob#the book of bill
85 notes
·
View notes