#wildlife. conservation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

All of my friends that work at wildlife rehab centers have had to untangle animals from this stuff, or had animals brought in that died in it. This is especially nasty for small owl species.
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
When I was in vet school I went to this one lecture that I will never forget. Various clubs would have different guest lecturers come in to talk about relevant topics and since I was in the Wildlife Disease Association club I naturally attended all the wildlife and conservation discussions. Well on this particular occasion, the speakers started off telling us they had been working on a project involving the conservation of lemurs in Madagascar. Lemurs exist only in Madagascar, and they are in real trouble; they’re considered the most endangered group of mammals on Earth. This team of veterinarians was initially assembled to address threats to lemur health and work on conservation solutions to try and save as many lemur species from extinction as possible. As they explored the most present dangers to lemurs they found that although habitat loss was the primary problem for these vulnerable animals, predation by humans was a significant cause of losses as well. The vets realized it was crucial for the hunting of lemurs by native people to stop, but of course this is not so simple a problem.
The local Malagasy people are dealing with extreme poverty and food insecurity, with nearly half of children under five years old suffering from chronic malnutrition. The local people have always subsisted on hunting wildlife for food, and as Madagascar’s wildlife population declines, the people who rely on so-called bushmeat to survive are struggling more and more. People are literally starving.
Our conservation team thought about this a lot. They had initially intended to focus efforts on education but came to understand that this is not an issue arising from a lack of knowledge. For these people it is a question of survival. It doesn’t matter how many times a foreigner tells you not to eat an animal you’ve hunted your entire life, if your child is starving you are going to do everything in your power to keep your family alive.
So the vets changed course. Rather than focus efforts on simply teaching people about lemurs, they decided to try and use veterinary medicine to reduce the underlying issue of food insecurity. They supposed that if a reliable protein source could be introduced for the people who needed it, the dependence on meat from wildlife would greatly decrease. So they got to work establishing new flocks of chickens in the most at-risk communities, and also initiated an aggressive vaccination program for Newcastle disease (an infectious illness of poultry that is of particular concern in this area). They worked with over 600 households to ensure appropriate husbandry and vaccination for every flock, and soon found these communities were being transformed by the introduction of a steady protein source. Families with a healthy flock of chickens were far less likely to hunt wild animals like lemurs, and fewer kids went hungry. Thats what we call a win-win situation.
This chicken vaccine program became just one small part of an amazing conservation outreach initiative in Madagascar that puts local people at the center of everything they do. Helping these vulnerable communities of people helps similarly vulnerable wildlife, always. If we go into a country guns-blazing with that fire for conservation in our hearts and a plan to save native animals, we simply cannot ignore the humans who live around them. Doing so is counterintuitive to creating an effective plan because whether we recognize it or not, humans and animals are inextricably linked in many ways. A true conservation success story is one that doesn’t leave needy humans in its wake, and that is why I think this particular story has stuck with me for so long.
(Source 1)
(Source 2- cool video exploring this initiative from some folks involved)
(Source 3)
#we can save the world just maybe not in the way we’d planned#long post#scicomm#conservation#lemurs#wildlife#ecology#animals#vet med#veterinary medicine#One Health
33K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you aren't following the news here in the Pacific Northwest, this is a very, very big deal. Our native salmon numbers have been plummeting over the past century and change. First it was due to overfishing by commercial canneries, then the dams went in and slowed the rivers down and blocked the salmons' migratory paths. More recently climate change is warming the water even more than the slower river flows have, and salmon can easily die of overheating in temperatures we would consider comfortable.
Removing the dams will allow the Klamath River and its tributaries to return to their natural states, making them more hospitable to salmon and other native wildlife (the reservoirs created by the dams were full of non-native fish stocked there over the years.) Not only will this help the salmon thrive, but it makes the entire ecosystem in the region more resilient. The nutrients that salmon bring back from their years in the ocean, stored within their flesh and bones, works its way through the surrounding forest and can be traced in plants several miles from the river.
This is also a victory for the Yurok, Karuk, and other indigenous people who have relied on the Klamath for many generations. The salmon aren't just a crucial source of food, but also deeply ingrained in indigenous cultures. It's a small step toward righting one of the many wrongs that indigenous people in the Americas have suffered for centuries.
#salmon#dam removal#fish#animals#wildlife#dams#Klamath River#Klamath dams#restoration ecology#indigenous rights#Yurok Tribe#Karuk Tribe#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#PNW#Pacific Northwest
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
“People are inherently terrible” no!!! Have you ever seen a child wait for their friend while they tie their shoelaces? Have you ever known someone who would bring hurt squirrels and rabbits and mice to the nearest vet just so it doesn’t suffer? Have you seen someone grieve? Have you ever read something that hit your heart like a freight train? Have you looked at the stars and felt an unexplainable joy? Have you ever baked bread? Have you shared a meal with a friend? Have you not seen it? All the love? All the good? I know it’s hard to see sometimes, I know there’s pain everywhere. But look, there’s a child helping another up after a hard fall. Look, there’s someone giving their umbrella to a stranger. Look, there’s someone admiring the spring flowers. Look, there’s good, there’s good, there’s good. Look!!!!
#humans are good actually#humans are strange#hopecore#honey prose#respectfully do not fill my mentions w Christianity references this is NOT a capital G god friendly post#fuck the concept of original sin and also Thomas Hobbes#also for all the vet ppl in the tags saying don’t take a wild animal to the vet pls refer to ‘just so it doesn’t suffer’ IM A VET TECH.#THERE IS ONLY ONE THING WE CAN DO FOR A SMALL WILD ANIMAL THAT IS INJURED .#I’m talking about humane euthanasia for a creature that is clearly suffering when there’s no wildlife conservation for 60+ miles#I’ve actually never had a client that didn’t call to ask to bring it in that didn’t already know and understand euthanasia was all we’d be#able to do.#that’s the kindness part. that’s the love. ‘I can’t do anything except make sure you don’t suffer any longer than u already have since some#asshole ran over your back legs’
85K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Lower Ninth Ward of New Orleans has recently witnessed an incredible eco-renaissance following decades of damage and neglect.
Led by a local community development group, a 40-acre wetlands park has been restored to glories past with hundreds of local trees that attract over a hundred species of birds, plus joggers, picnickers, and nature lovers besides.
The story begins with Rashida Ferdinand, founder of Sankofa Community Development Corporation (CDC). Growing up in this historic part of New Orleans, where Black homeownership thrived, where Fats Domino was born, and where locals routinely went out into the wetlands to catch fish and crustaceans, she watched as it suffered from years of neglect.
Poor drainage, ruined roads, illegal trash dumping, and unmitigated damage from hurricanes slowly wasted the wetland away until it was a derelict eyesore.
In the name of restoring this wild heritage indicative of the culture in the Lower Ninth, and in order to protect her communities from flooding, Ferdinand founded the Sankofa CDC, and in 2014 entered into an agreement with the City of New Orleans for the restoration of Sankofa—a 40-acre section of neglected wetlands in the heart of the Lower Ninth.
The loss of Sankofa’s potential to dampen flooding from storms meant that over the years dozens of houses and properties were flooded and damaged beyond the ability of the inhabitants to recover. Forced out by a combination of nature’s fury and government failure, the cultural heritage of the community was receding along with the floodwaters.
Ferdinand knew that restoring natural flood barriers like Sankofa was key to protecting her community.
“Hurricane protection is a major concern in the community, but there’s a lack of trust in the infrastructure systems that are supposed to protect us,” Ferdinand told the Audubon Society.
Today, Sankofa Wetlands Park is a sight to behold. Hiking trails snake through a smattering of ponds and creeks, where bald cypresses and water tupelo trees continue to grow and cling to the ground even during storms. Picnic benches have appeared, wheelchair-accessible trails connect sections of the park to parts of the Lower Ninth, and local businesses are seeing more visitors.
It needed a lot of work though. Thousands of invasive tallow trees had to be uprooted. 27,000 cubic meters of illegally dumped trash compacted into the dirt had to be removed. A 60-year-old canal dug by the US Army Corps of Engineers had to be disconnected, and all new native flora had to be planted by hand.
Audubon says that Ferdinand routinely can’t believe her eyes when she looks at the transformation of Sankofa into its current state.
“Seeing butterflies, birds, and other pollinators in the park is a sign of a healthy ecosystem,” she says. “All we had to do was create the right conditions.”
Slated for official completion in 2025 with an outdoor amphitheater, interpretive signage, and additional trails, Ferdinand and the CDC have their eyes set on an even larger area of wetlands to the north of Sankofa.
Along the way, Ferdinand and the CDC attracted many helping hands, and entered into many partnerships, But the catalyst for change arose from the spirit and determination of one woman in the right place at the right time, for the benefit of hundreds in this historic heart of a historic city."
-via Good News Network, September 17, 2024
#new orleans#louisiana#nola#united states#wildlife#wetlands#ecology#ecological restoration#conservation#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

#green memes for ecological fiends#zoology#ecology#bird#hawks#environmental science#biodiversity#conservation biology#conservation#wildlife
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
EEEEEEEE EEEEEEEEE EEEEEEE

That's right! It's International Bat Appreciation Day! We share our planet with over 1400 species of bat, making the second most abundant mammal order, and they perform a wide variety of ecological roles, from dispersing seeds to pollinating flowers to eating thousands of insects in a single night! Over 200 bat species are listed as Threatened by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature--that is over 14 percent of all bats!
YOU can help endangered bats today by donating to Pennsylvania Bat Rescue at this link. This PA-based organization rehabilitates sick or injured bats and helps educate people like you and me in how we can create more bat-friendly environments.
If you want to learn about particularly-cool bat species native to New Zealand, check out this Consider Nature article on the Pekapeka, the bat that walks:
For the rest of the day, Consider Nature will be bat-bombing Tumblr with some of our favorite bat species to share them with the world!
Alt text: a small brown bat stretching its wings with the kind of fabulous flourish that would impress Ryan Evans.
#animals#nature#science#biology#wildlife#conservation#environment#bats#international bat appreciation day#batbombing
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
And away they go!
seven_seas_explorer
#Heron Island#Queensland#Australia#hatchlings#baby turtles#heading home#wildlife#ocean life#conservation#cute animals#good luck little ones!#curators on tumblr
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - June 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $Kaybarr1735! And if you tip me and give me a way to contact you, at the end of the month I'll send you a link to all of the articles I found but didn't use each week!
1. Victory for Same-Sex Marriage in Thailand
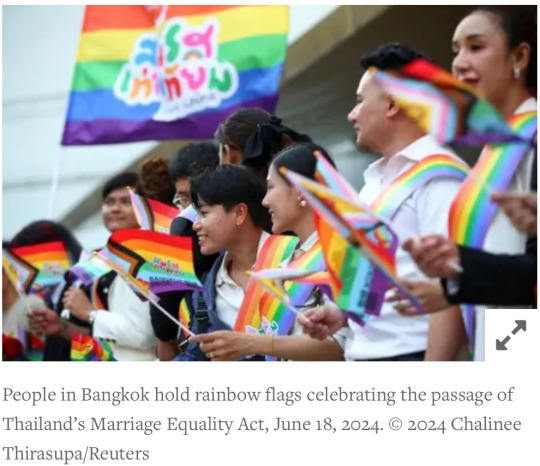
“Thailand’s Senate voted 130-4 today to pass a same-sex marriage bill that the lower house had approved by an overwhelming majority in March. This makes Thailand the first country in Southeast Asia, and the second in Asia, to recognize same-sex relationships. […] The Thai Marriage Equality Act […] will come into force 120 days after publication in the Royal Gazette. It will stand as an example of LGBT rights progress across the Asia-Pacific region and the world.”
2. One of world’s rarest cats no longer endangered

“[The Iberian lynx’s] population grew from 62 mature individuals in 2001 to 648 in 2022. While young and mature lynx combined now have an estimated population of more than 2,000, the IUCN reports. The increase is largely thanks to conservation efforts that have focused on increasing the abundance of its main food source - the also endangered wild rabbit, known as European rabbit. Programmes to free hundreds of captive lynxes and restoring scrublands and forests have also played an important role in ensuring the lynx is no longer endangered.”
3. Planning parenthood for incarcerated men
��[M]any incarcerated young men missed [sex-ed] classroom lessons due to truancy or incarceration. Their lack of knowledge about sexual health puts them at a lifelong disadvantage. De La Cruz [a health educator] will guide [incarcerated youths] in lessons about anatomy and pregnancy, birth control and sexually transmitted infections. He also explores healthy relationships and the pitfalls of toxic masculinity. […] Workshops cover healthy relationships, gender and sexuality, and sex trafficking.”
4. Peru puts endemic fog oasis under protection

“Lomas are unique ecosystems relying on marine fog that host rare and endemic plants and animal species. […] The Peruvian government has formally granted conservation status to the 6,449-hectare (16,000-acre) desert oasis site[….] The site, the first of its kind to become protected after more than 15 years of scientific and advocacy efforts, will help scientists understand climatic and marine cycles in the area[, … and] will be protected for future research and exploration for at least three decades.”
5. Religious groups are protecting Pride events — upending the LGBTQ+ vs. faith narrative

“In some cases, de-escalation teams stand as a physical barrier between protesters and event attendees. In other instances, they try to talk with protesters. The goal is generally to keep everyone safe. Leigh was learning that sometimes this didn’t mean acting as security, but doing actual outreach. That might mean making time and space to listen to hate speech. It might mean offering food or water. […] After undergoing Zoom trainings this spring, the members of some 120 faith organizations will fan out across more than 50 Pride events in 16 states to de-escalate the actions of extremist anti-LGBTQ+ hate groups.”
6. 25 years of research shows how to restore damaged rainforest
“For the first time, results from 25 years of work to rehabilitate fire-damaged and heavily logged rainforest are now being presented. The study fills a knowledge gap about the long-term effects of restoration and may become an important guide for future efforts to restore damaged ecosystems.”
7. Audubon and Grassroots Carbon Announce First-of-its-Kind Partnership to Reward Landowners for Improving Habitats for Birds while Building Healthy Soils

“Participating landowners can profit from additional soil carbon storage created through their regenerative land management practices. These practices restore grasslands, improve bird habits, build soil health and drive nature-based soil organic carbon drawdown through the healthy soils of farms and ranches. […] Additionally, regenerative land management practices improve habitats for birds. […] This partnership exemplifies how sustainable practices can drive positive environmental change while providing tangible economic benefits for landowners.”
8. Circular food systems found to dramatically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, require much less agricultural land
“Redesigning the European food system will reduce agricultural land by 44% while dramatically reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture by 70%. This reduction is possible with the current consumption of animal protein. “Moreover, animals are recyclers in the system. They can recycle nutrients from human-inedible parts of the organic waste and by-products in the food system and convert them to valuable animal products," Simon says.”
9. Could Treating Injured Raptors Help Lift a Population? Researchers found the work of rehabbers can have long-lasting benefits

“[“Wildlife professionals”] tend to have a dismissive attitude toward addressing individual animal welfare,” [… but f]or most raptor species, they found, birds released after rehabilitation were about as likely to survive as wild birds. Those released birds can have even broader impacts on the population. Back in the wild, the birds mate and breed, raising hatchlings that grow up to mate and breed, too. When the researchers modeled the effects, they found most species would see at least some population-level benefits from returning raptors to the wild.”
10. Indigenous people in the Amazon are helping to build bridges & save primates

“Working together, the Reconecta Project and the Waimiri-Atroari Indigenous people build bridges that connect the forest canopy over the BR-174 road[….] In the first 10 months of monitoring, eight different species were documented — not only monkeys such as the golden-handed tamarin and the common squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus), but also kinkajous (Potos flavus), mouse opossums (Marmosops sp.), and opossums (Didelphis sp.).”
Bonus: A rare maneless zebra was born in the UK
June 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#lgbtq#gay rights#gay marriage#same sex marriage#thailand#lynx#big cats#cats#endangered species#endangered#sex education#prison#peru#conservation#habitat#religion#pride#faith#pride month#lgbt pride#compassion#rainforest#birds#nature#climate change#wildlife rehab#wildlife#indigenous
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Yesterday I was birding in a wildlife refuge and this huge dog without a leash and no owner in sight ran up to me and started barking at me, and getting closer and closer. Literally thought it was going to pounce. It had a collar, but no owner in sight. I'm not afraid of dogs, but I am afraid of any large animal that's angry and has the capacity to knock me over. After about five minutes of this dog growling at me and me trying to calm it down, its owner finally showed up, and was like......"oh haha I thought he was yelling at an animal." As if it would have been normal and fine for the dog to attack the wildlife.
It's a wildlife refuge. There are endangered species that live there. Dogs are required to be leashed at the park...you know why?? Precisely because dogs like to go after birds and other small creatures.
This isn't even the first time I've dealt with unleashed dogs....
I was at a beach, collecting seashells and birding, when a huge pitbull ran up to me growling. Thankfully it didn't attack and just sniffed my bag, but the owner was just a speck in the horizon, didn't care that their dog was running around doing god knows what. The dog could have gone after the wildlife, too.
People letting their cats roam free outdoors 🤝 People that let their dogs run around without a leash:
Endangering their pet, the environment, and other people with their stupid choices
Keep your dog on a fucking leash
7K notes
·
View notes
Note
hi
what's this one cause I have questions

1; is it edible
2: fun facts about it
THAMK YOU
That is a flying gurnard (Dactylopterus volitans)!

To answer your first question, they are edible! They're steadily becoming a more popular food choice because they have a relatively low oil content.


The first thing you might notice about this species is their very large pectoral fins. It's believed that their primary use is to scare off predators. Often the fish rest on the seafloor with the large fins tucked in, only displaying them when threatened. Additionally, they have finger-like segments of their pectoral fins which they use to walk across the sea floor.
These fish can also make noises! Using their swim bladder and jaw, they can make a grunt-like sound believed be used to scare off predators or communicate with each other.
#marine biology#science#animal facts#wildlife#biology#marine life#animals#marine ecology#ocean#fun facts#fish#weird fish#fishblr#cool fish#marine ecosystem#marine animals#aquatic#sea creatures#sea life#environment#environmental science#ecology#conservation#environmentalism#flying gurnard#cool animals
504 notes
·
View notes
Text

#relatable#weather#oklahoma department of wildlife conservation#meme#memes#tweet#tweets#twitter#funny#lol
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
A study that just came out demonstrates that outdoor cats are known to prey on over two thousands species of wild animal, from mammals to birds to insects. That includes 347 species that are endangered, threatened or otherwise of concern, and they've been a key factor of the permanent extinction of over 60 species. And while cats may not always bring home what they catch, chances are if your cat is allowed to roam unsupervised outside, they're killing your local wildlife.
Why is this so important? Worldwide, wild animal populations have decreased in number by 69% in the past fifty years; that means that in my lifetime (born in 1978), the sheer number of wild animals in the world has been decreased by over half. Even "common" wild species are less numerous than before. While habitat population is the single biggest cause of species endangerment and extinction overall, outdoor and indoor/outdoor cats are a significant cause as well. In fact, they are the single biggest cause of human-caused mortality in wild birds.
Most importantly, it's very, very simple to fix this problem: keep your cats indoors, and spay and neuter them. If your cat is bored, they need more enrichment, and there are plenty of ways to make your home more exciting for them, from bringing home cardboard boxes for them to explore, to playing with them more often. If you want your cat to get some outdoor enrichment, leash train them (yes, it can be done!) If you have the space and resources, build them a catio where they can be safe from outdoor dangers like predators and cars, while also keeping local wildlife safe from them.
If you just give into their whining and pawing at the door, then they know that that's what they have to do to get their way; I know it's a tough transition, but it's worth it in the end for everyone involved. Cats are domesticated, which means they are not native anywhere in the world; there are exactly zero ecosystems in which they belong, save for the safety of your home. It is your responsibility to give them an enriching environment without taking the shortcut of letting them go wreak havoc outside.
#cats#outdoor cats#feral cats#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#birds#endangered species#extinction#domesticated animals#domestication#biology#animal behavior#animal welfare
8K notes
·
View notes
Text

It’s World Orangutan Day! Weighing up to 200 lbs (90.1 kg), the orangutan (genus Pongo) is the largest arboreal animal on the planet! This tree-dweller is also Asia’s only great ape. The critically endangered primate is mostly herbivorous, with a diet that consists of flowers, nuts, and fruit. This species’ historic range in Southeast Asia has shrunk down to just two islands—Borneo and Sumatra—and their population has dipped sharply in the last century. Because they live in lush tropical forests, orangutans are especially vulnerable to deforestation, an ongoing threat as agriculture encroaches on their habitat.
Photo: Eric Kilby, CC BY-SA 2.0, flickr
#science#nature#natural history#animals#fact of the day#did you know#endangered species#orangutan#world orangutan day#animal facts#biodiversity#primates#great apes#mammalogy#conservation#wildlife
444 notes
·
View notes
Text
Camera-trapping data revealed in a new study show a steady recovery of tigers in Thailand’s Western Forest Complex over the past two decades.
The tiger recovery has been mirrored by a simultaneous increase in the numbers of the tigers’ prey animals, such as sambar deer and types of wild cattle.
The authors attribute the recovery of the tigers and their prey to long-term efforts to strengthen systematic ranger patrols to control poaching as well as efforts to restore key habitats and water sources.
Experts say the lessons learnt can be applied to support tiger recovery in other parts of Thailand and underscore the importance of the core WEFCOM population as a vital source of tigers repopulating adjacent landscapes.
The tiger population density in a series of protected areas in western Thailand has more than doubled over the past two decades, according to new survey data.
Thailand is the final stronghold of the Indochinese tiger (Panthera tigris corbetti), the subspecies having been extirpated from neighboring Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam over the past decade due to poaching, habitat loss and indiscriminate snaring...
Fewer than 200 tigers are thought to remain in Thailand’s national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, only a handful of which are sufficiently undisturbed and well-protected to preserve breeding tigers.
The most important of these protected areas for tigers is the Huai Kha Khaeng Thung Yai (HKK-TY) UNESCO World Heritage Site, which comprises three distinct reserves out of the 17 that make up Thailand’s Western Forest Complex (WEFCOM). Together, these three reserves — Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary, Thungyai Naresuan West and Thungyai Naresuan East — account for more than a third of the entire WEFCOM landscape.
Now, a new study published in Global Ecology and Conservation documents a steady recovery of tigers within the HKK-TY reserves since camera trap surveys began in 2007. The most recent year of surveys, which concluded in November 2023, photographed 94 individual tigers, up from 75 individuals in the previous year, and from fewer than 40 in 2007.
Healthy tiger families
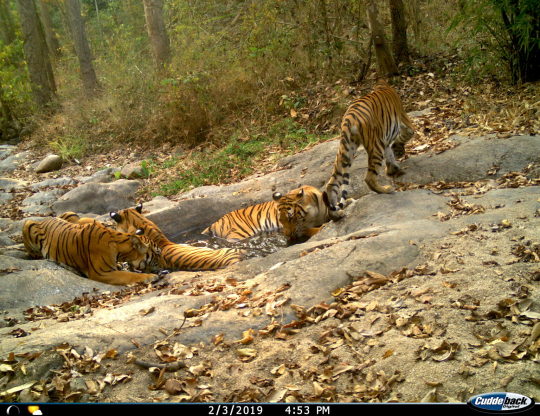

The study findings reveal that the tiger population grew on average 4% per year in Hua Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary, the largest and longest-protected of the reserves, corresponding to an increase in tiger density from 1.3 tigers per 100 square kilometers, to 2.9 tigers/100 km2.
“Tiger recoveries in Southeast Asia are few, and examples such as these highlight that recoveries can be supported outside of South Asia, where most of the good news [about tigers] appears to come from,” said Abishek Harihar, tiger program director for Panthera, the global wildcat conservation organization, who was not involved in the study.
Among the camera trap footage gathered in HKK-TY over the years were encouraging scenes of healthy tiger families, including one instance of a mother tiger and her three grownup cubs lapping water and lounging in a jacuzzi-sized watering hole. The tiger family stayed by the water source for five days during the height of the dry season.
The team of researchers from Thailand’s Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation, the Wildlife Conservation Society, Kasetsart University, and India’s Center for Wildlife Studies deployed camera traps at more than 270 separate locations throughout the HKK-TY reserves, amassing 98,305 days’ worth of camera-trap data over the 19-year study period.
Using software that identifies individual tigers by their unique stripe patterns, they built a reference database of all known tigers frequenting the three reserves. A total of 291 individual tigers older than 1 year were recorded, as well as 67 cubs younger than 1 year [over the course of the study].
Ten of the tigers were photographed in more than one of the reserves, indicating their territories straddled the reserve boundaries. The authors conclude that each of the three reserves has a solid breeding tiger population and that, taken together, the HKK-TY landscape is a vital source of tigers that could potentially repopulate surrounding areas where they’ve been lost. This is supported by cases of known HKK-TY tigers dispersing into neighboring parts of WEFCOM and even across the border into Myanmar.
Conservation efforts pay off
Anak Pattanavibool, study co-author and Thailand country director at the Wildlife Conservation Society, told Mongabay that population models that take into account the full extent of suitable habitat available to tigers within the reserves and the likelihood that some tigers inevitably go undetected by camera surveys indicate there could be up to 140 tigers within the HKK-YT landscape.
Anak told Mongabay the tiger recovery is a clear indication that conservation efforts are starting to pay off. In particular, long-term action to strengthen systematic ranger patrols to control poaching as well as efforts to boost the tigers’ prey populations seem to be working, he said.
“Conservation success takes time. At the beginning we didn’t have much confidence that it would be possible [to recover tiger numbers], but we’ve been patient,” Anak said. For him, the turning point came in 2012, when authorities arrested and — with the aid of tiger stripe recognition software — prosecuted several tiger-poaching gangs operating in Huai Kha Khaeng. “These cases sent a strong message to poaching gangs and they stopped coming to these forests,” he said."
...ranger teams have detected no tiger poaching in the HKK-TY part of WEFCOM since 2013.
-via Mongabay News, July 17, 2024
#tigers#thailand#thai#endangered species#big cats#conservation#wildlife#wildlife conservation#wildlife photography#poaching#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
yeah facebook is terrible but sometimes you stumble across pure gold. there are dream animals i want to see in the wild and there will be posts like

ma'am that is the critically endangered regent honeyeater. There are less than 300 of them left in the wild
#the anklet indicates captive breed and released BUT STILL#i want to see one so bad this is so funny to me#birds#regent honeyeater#Anthochaera phrygia#bird#honeyeater#australian animals#fauna#conservation#wildlife
20K notes
·
View notes