#varanosuchus
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Fossil Crocs of 2024
Another year another list of new fossil crocodilians that greatly expand our knowledge of Pseudosuchia across deep time. Happy to say that this is my third time doing this now, so I'm not going to bog you down with the details and get right into it.
Benggwigwishingasuchus
Our first entry, sorted by geological age of course, is Benggwigwishingasuchus eremicarminis (desert song fishing crocodile) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Nevada. It was a member of the clade Poposauroidea, which some of you might recognize as also containing such bizarre early croc cousins like Arizonasaurus and Effigia. Also notable about Benggwigwishingasuchus is that it was found in the Fossil Hill Member of the Favret Formation. Why is that notable? Well the Fossil Hill Member preserves an environment deposited 10 km off the Triassic coastline and also yielded fossils of animals like Cymbospondylus, the giant ichthyosaur. Despite this however, Benggwigwishingasuchus shows no obvious signs of having been a swimmer or diver. Instead, its been hypothesized that it was simply foraging around the coast and might have been washed out to sea.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe (@knuppitalism-with-ue) and Jorge A. Gonzalez


Parvosuchus
Fast forward some 5 million years to the Ladinian - Carnian of Brazil, specifically the Santa Maria Formation. Here you'll find the one new genus on the list I did not write the wikipedia page for: Parvosuchus aurelioi (Aurélio's Small Crocodile). With only a meter in length, Parvosuchus is amongst the smallest pseudosuchians of the year and a member of the aptly named Gracilisuchidae. Santa Maria was actually home to multiple pseudosuchians, including the mighty Prestosuchus (and its possible juvenile form Decuriasuchus), the small erpetosuchid Archeopelta and larger Pagosvenator and one more...
Artwork by Matheus Fernandes and Joschua Knüppe


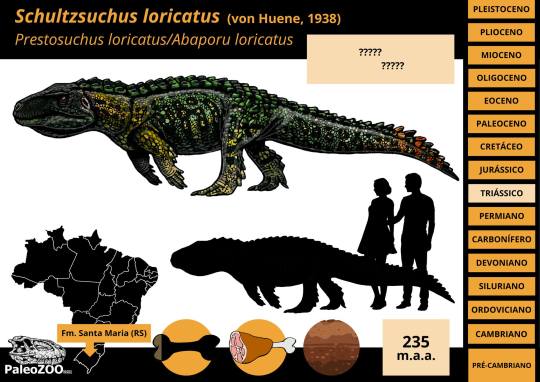
Schultzsuchus
Yup, Santa Maria has been eating good this year. Before the description of Parvosuchus, scientists coined the name Schultzsuchus loricatus (Schultz's Crocodile). Now this one's not entirely new and has long been known under the name Prestosuchus loricatus (by which I mean since 1938). What's interesting is that this new redescription suggests that rather than being a Loricatan, Schultzsuchus was actually an early member of Poposauroidea like Benggwigwishingasuchus. Even if it was no longer thought to be close to Prestosuchus, it was liekly still a formidable predator and among the larger pseudosuchians of the formation.
Artwork by Felipe Alves Elias
Garzapelta
Our last Triassic pseudosuchian and our only aetosaur of the year came to us in the form of Garzapelta muelleri (Mueller's Garza County Shield). It comes from the Late Triassic (Norian) Cooper Canyon Formation of, you guessed it, Garza County, Texas. As an aetosaur, the osteoderms are already regarded as diagnostic, tho unlike some other recent examples there is a little more material to go off from. It's still primarily osteoderms, but at least a good amount and even some ribs.
Artwork by Márcio L. Castro

Ophiussasuchus
Our only Jurassic newcommer is Ophiussasuchus paimogonectes (Paimogo Beach Swimmer Portuguese Crocodile), but arguably you couldn't find a better posterchild for Jurassic crocodyliforms. This new lad is a goniopholidid from the Kimmeridgian to Tithonian Lourinhã Formation, yup, Europe's Morrison. It's anatomy is perhaps not the most exciting, like other goniopholidids it had a flattened, very crocodilian-esque snout and was likely semi-aquatic like its relatives.
Artwork by @manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe

Enalioetes
Another quintessential group of Jurassic crocodyliforms are the metriorhynchoids, however, 2024's only new addition to this clade was actually Cretaceous, specifically from the earliest Cretaceous (Valanginian) of Germany. Like Schultzsuchus, Enalioetes schroederi (Schroeder's Sea Dweller) is new in name only, as fossil material has been found at the latest in 1918 and given the name Enaliosuchus "schroederi" in 1936. This kickstarted a whole series of taxonomic back and forth until the recent redescriptoin finally just gave it a new name and settled things (for now). Looking back I realize that I really need to take the time and fix up the Wikipedia page. Tho I've written its current status, I was kinda limited by being on vacation and never dived into the description section.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Jackosaurus
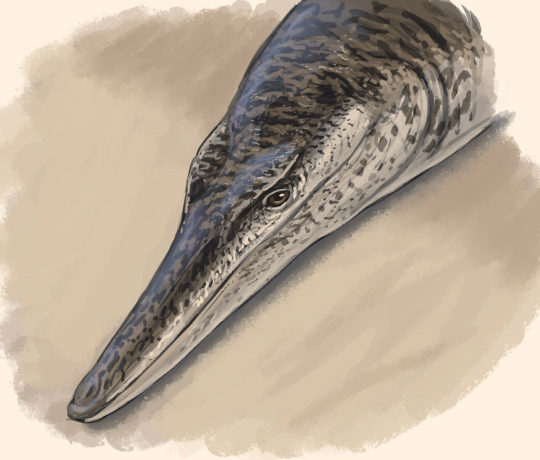


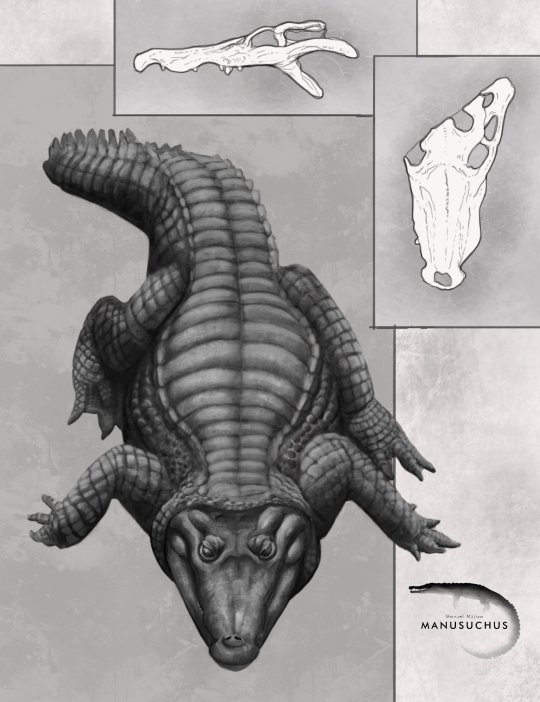
Varanosuchus
Another Early Cretaceous crocodyliform is Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis (Monitor Lizard Crocodile from the Sakon Nakhon Province), described from Thailand's Sao Khua Formation. It lived around the same time as Enalioetes, but otherwise couldn't have been more different. Where Enalioetes was fully marine, Varanosuchus was more a land dweller as evidenced by the deep skull and long, slender legs. At the same time, some other features, like its more robust limbs compared to its kin, might suggest that Varanosuchus could have still spent some time in the water like some modern lizards. Tho one might be reminded of Parvosuchus from earlier, Varanosuchus is a much more recent example of small terrestrial croc-relatives, the atoposaurids, which are much closer to todays crocodiles and alligators.
Artwork once again by Manusuchus

Araripesuchus manzanensis
Yet another example of a small, gracile land "crocodile" comes to us in the form of Araripesuchus manzanensis (Araripe Basin Crocodile from the El Manzano Farm). And once again, it belonged to a completely different group, this time the notosuchian family Uruguaysuchidae. Now Araripesuchus is well known as a genus, in part due to the work of Paul Sereno and Hans Larsson (who popularized the names "dog croc" and "rat croc" for two species). Tangent aside, A. manzanensis is known from the upper layers of Argentina's Candeleros Formation, corresponding to the Cenomanian (earliest Late Cretaceous). The same locality also yielded A. buitreraensis, from which A. manzanensis can be distinguished on account of its blunt molariform teeth in the back of its jaw. This dentition, which corresponds to a durophageous diet of hardshelled prey, could explain how it coexisted with the related A. buitrensis at the same locality, allowing the two to occupy different niches. There is a neat little animation done for this animal you can watch here.
Artwork by Gabriel Diaz Yantén

Caipirasuchus catanduvensis
We're staying in South America but moving to Brazil's Adamantina Formation for our next entry: Caipirasuchus catanduvensis (Caipiras Crocodile from Catanduva). This one is a little more recent, tho the age of the Adamantina Formation is a bit of a mess far as I can tell, ranging anywhere from the Turonian to the Maastrichtian. One could also argue that C. catanduvensis is part of the "lanky small croc club" that Parvosuchus, Varanosuchus and A. manzanensis belong to, but I feel that the very short snout helps it stand out from that bunch more easily. Anyhow, Caipirasuchus catanduvensis is a member of Sphagesauridae, related to Armadillosuchus, and herbivorous. What's really interesting tho is that the internal anatomy suggests the presence of resonance chambers not unlike that of hadrosaurs, possibly suggesting that these animals were quite vocal. This could also explain why baurusuchids appear to have had very keen hearing.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Guilherme Gehr


Epoidesuchus
We're staying in the Adamantina Formation for our last Mesozoic croc of the year, Epoidesuchus tavaresae (Tavares' Enchanted Crocodile). Tho also a Notosuchian like Araripesuchus and Caipirasuchus, this one belongs to the family Itasuchidae (or the subfamily Pepesuchinae depending on who you ask), which stand out as being rare examples of semi-aquatic members of this otherwise largely terrestrial group. Epoidesuchus was fairly large for its kin and had long, slender jaws. Like I said, Epoidesuchus and its relatives were likely more semi-aquatic than other notosuchians, something that might explain the relative lack of semi-aquatic neosuchians across Gondwana. They aren't absent mind you, but noticably rarer than they are in the northern hemisphere.
Artwork by Guilherme Gehr

And thus we move into the Cenozoic and towards the end our or little list. From here on out, say goodbye to Notosuchians or other weird crocodylomorphs and get ready for Crocodilia far as the eye can see.
Ahdeskatanka
The first Cenozoic croc we got is Ahdeskatanka russlanddeutsche (Russian-German Alligator), which despite its name comes from North Dakota, specifically the Early Eocene Golden Valley Formation. Ahdeskatanka is similar to many early alligatorines like Allognathosuchus in being small with rounded, globular teeth that suggest that it fed on hardshelled prey. This would have definitely helped avoid competition in the Golden Valley Formation, which also housed a second, similar form not yet named, a large generalist with a V-shaped snout similar to Borealosuchus and the generalized early caiman Chrysochampsa, also large but with a U-shaped snout.
Artwork by meeeeeeee

Asiatosuchus oenotriensis
We had an alligatoroid, so now its time for a crocodyloid. Asiatosuchus has been recognized from the Late Eocene Duero Basin of Spain for a while now, but now we have a name: Asiatosuchus oenotriensis (Asian Crocodile Belonging To The Land Of Wine). Asiatosuchus is a complex genus, most often not really forming a monophyletic clade and likely representing several distinct or at least successive taxa that form the "Asiatosuchus-like complex". Within this complex, A. oenotriensis is thought to have been close-ish to Germany's Asiatosuchus germanicus.
Artwork by Manusuchus

Sutekhsuchus
Rounding out the trio of major crocodilian clades is Sutekhsuchus dowsoni (Set's Crocodile/God of Deception Crocodile), representing our only gavialoid of the year. Originally described as Tomistoma dowsoni in 1920 based on fossil remains from the Miocene of Egypt, Sutekhsuchus has been at times regarded as distinct and at other times lumped into Tomistoma lusitanica. It was one of several early gavialoids to inhabit the coast of the Tethys during the Miocene and appears to have been most closely related to the genus Eogavialis, clading together just outside of the American and Asian gharials. A fun little personal anecdote, I prematurely learned about this one due to a friend highlighting the name in a study on Eogavialis. Never having heard of "Sutekhsuchus" I took to google scholar, where I found a single result: a reference to the then unpublished description, which naturally I ended up eagerly awaiting.
Artwork by Manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe

Paranacaiman
Two more and we're done. First, completely arbitrarily, Paranacaiman bravardi (Bravard's Caiman from Parana) from the Miocene Ituzaingo Formation of Argentina. Material of this genus has originally been referred to Caiman lutescens, described in 1912 but now considered a nomen dubium. Paranacaiman is known from limited material only, just the skull table, but that would indicate a "huge" animal. My personal scaling recovered a size of almost 5 meters in length, similar to large black caimans today.
Once again, credit to me

Paranasuchus
Last but not least, Paranasuchus gasparinae (Gasparini's Crocodile from Parana). Coming from the same deposits as Paranacaiman, this one too has been known as a species of Caiman for some time before being assigned its own genus, though it at least got to retain its old species name. Alas, I have not scaled it myself, tho its material is at least more extensive than that of Paranacaiman, including even parts of the snout. A little nitpick because I don't have much to say, but I personally think the name was ill conceived. On its own both Paranacaiman and Paranasuchus are fine names don't get me wrong, but together, coined by the same authors in the same study no less, they strike me as needlessly confusing to non experts. Both are caimans, both are from Parana, so the distinction between "Parana Caiman" and "Parana Crocodile" is entirely arbitrary and doesn't really distinguish them. Not helped by the fact that they are even closely related in the original description. Other than that tho another good addition to our understanding of fossil crocs.
No artwork on this one, but fossil material from Bona et al. 2024
And that wraps up 2024. I hope This post, or my posts throughout the year or even my work on Wikipedia has helped to make these fascinating animals just a little bit more approachable and a massive thanks to all the artists who took their time to create fantastic pieces featuring these incredible animals. Special shout outs to Manusuchus, who diligently illustrated a lot of the featured animals and Joschua Knüppe, who had to listen to me suggest Ahdeskatanka every Sunday for about two months straight now.
Fossil Crocs of 2023
Fossil Crocs of 2022
#paranasuchus#paranacaiman#ahdeskatanka#sutekhsuchus#ophiussasuchus#epoidesuchus#caipirasuchus#araripesuchus#enalioetes#parvosuchus#benggwigwishingasuchus#schultzsuchus#garzapelta#varanosuchus#paleontology#prehistory#palaeoblr#long post#fossil crocs of 2024#paleo#paleonotlogy#crocodilia#crocodylomorpha#pseudosuchia#fossils#2024
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pseudosuchians described in 2024 #1 Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis
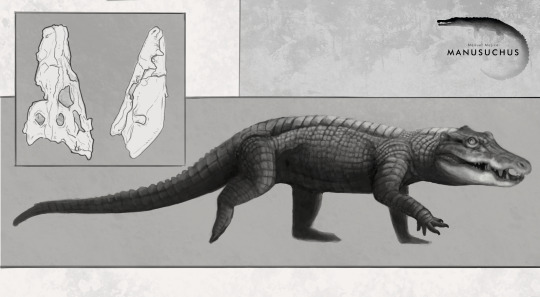
First of a series of quick sketches that I´ll try to do for each pseudosuchian that will be published throughout 2024 (I don't promise that I'll do all of them). I will give priority to everything that is closer to the crown group of the current crocodilians, although if I get too motivated I might even include phytosaurs, although I doubt it extremely. And yes, Im informed about Garzapelta, and I take this opportunity to say that I am sorry to all the aetosaurs´s fans, but these are totally excluded from the series because they are, objectively speaking, not only the most tedious tetrapod group to draw, but also the most boring looking (The truth hurts, I know). Now I could give a description of what Varanosuchus is and all that, but as usual, Armin has done it faster and better, so go and read his instead
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
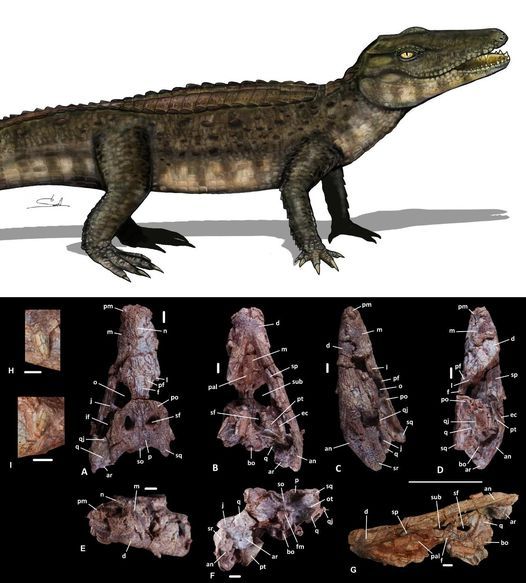
New Cretaceous neosuchians (Crocodylomorpha) from Thailand bridge the evolutionary history of atoposaurids and paralligatorids
Yohan Pochat-Cottilloux, Komsorn Lauprasert, Phornphen Chanthasit, Sita Manitkoon, Jérôme Adrien, Joël Lachambre, Romain Amiot, Jeremy E Martin
Abstract
The origin of modern crocodylians is rooted in the Cretaceous, but their evolutionary history is obscure because the relationships of outgroups and transitional forms are poorly resolved. Here, we describe a new form, Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis gen. nov., sp. nov., from the Early Cretaceous of Thailand that fills an evolutionary gap between Paralligatoridae and Atoposauridae, two derived neosuchian lineages with previously unsettled phylogenetic relationships. Three individuals, including a complete skull and associated postcranial remains, allow for a detailed description and phylogenetic analysis. The new taxon is distinguished from all other crocodylomorphs by an association of features, including a narrow altirostral morphology, a dorsal part of the postorbital with an anterolaterally facing edge, a depression on the posterolateral surface of the maxilla, and fully pterygoid-bound choanae. A phylogenetic analysis confirms the monophyly and taxonomic content of Atoposauridae and Paralligatoridae, and we underline the difficulty in reaching a robust definition of Eusuchia. Furthermore, we put forward further arguments related to the putative terrestrial ecology with semi-aquatic affinities of atoposaurids based on their altirostral snout morphology and osteoderm ornamentation.
Read the paper here:
https://academic.oup.com/zoolinnean/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlad195/7513556
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
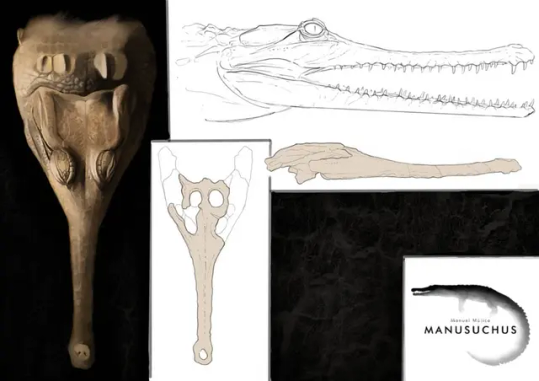
Varanosuchus: First Fossil Croc of 2024
We are two weeks into the year and we already had a bunch of big croc papers, so today I'll cover the first of the two new genera named so far. Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis (Monitor lizard crocodile from Sakon Nakhon) is a small atoposaurid neosuchian from the Early Cretaceous of Thailand, a country that has seen a virtual boom in croc papers this past year between the description of Alligator munensis and Antecrocodylus.
Varanosuchus was a small animal, maybe a meter in length if a little longer with a notably short and deep skull and long slender limbs revealing it to have been at least somewhat terrestrial. We actually have a decent amount of material of this guy. The holotype consists of a 3 dimensionally preserved skull as well as assorted postcranial remains (vertebrae, ribs, osteoderms and limbs), there is a second skull of whats likely to be a differently aged individual also showing a 3D skull and well the third ones just a skull table but 2/3 is still great.
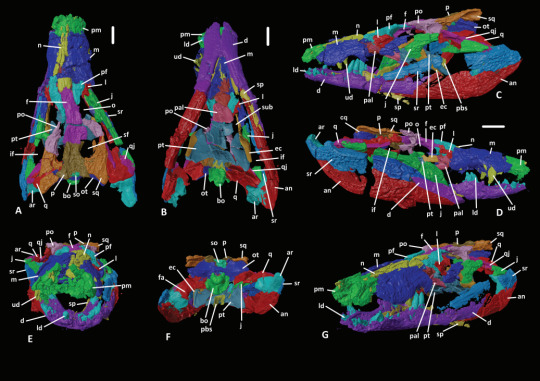
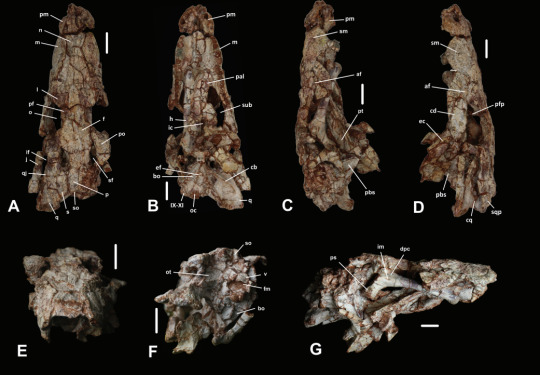
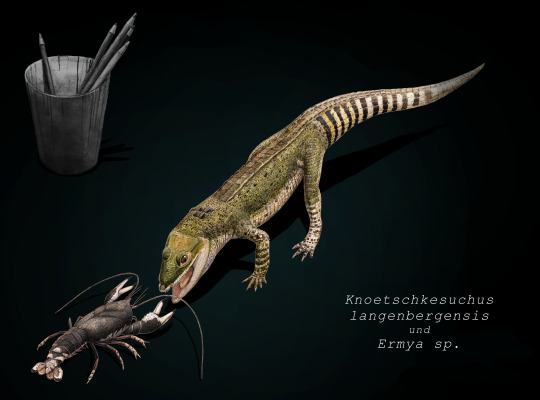
Now this guy was an atoposaurid, which is a group of crocodylomorphs that lived from the Jurassic to the end of the Cretaceous, their last members existing on the island of Hateg some 66 million years ago. Atopsaurids were generally small animals with short snouts and longish legs. Some examples of atoposaurids include Knoetschkesuchus from Germany, Aprosuchus from Romania and Alligatorellus from France and Germany, all three pictured below, art by @knuppitalism-with-ue



Now the matter of ecology for atoposaurids in general and Varanosuchus in particular is not clear. Altirostral skulls such as that of Varanosuchus are generally associated with terrestrial crocodylomorphs as best examplified by notosuchians. Their teeth and size both obviously speak against being shoreline ambush predators like modern crocs and their legs are straight and slender, suggesting they had an erect posture and not the more sprawling one seen in semi-aquatic forms. Though they could have still had some aquatic affinities. The authors for instance argue that the osteoderms, having plenty of pits, are more like those of an animal that spends time in the water and would thus use them in thermoregulation. So maybe they did enter water from time to time, somewhat like some modern lizards, tho I think its fairly certain that they spend a decent amount of time on land. The artwork below is the reconstruction from the paper itself.

Another matter discussed in the paper is phylogeny, more precisely the relationship of Neosuchians and how Eusuchia is defined. On the first front, its worth noting that the paper recovered both atoposaurids and paralligatorids as monophyletic groups and had them be each others closest relatives, a notion that has been recovered before. More interesting perhaps is the fact that the next closest relatives to these two were hylaeochampsids and Bernissartia, which are typically recovered closer to modern crocs. Which in fact form a separate branch that is the sister group to all the afforementioned clades and taxa. And then you got goniopholids, dyrosaurs and pholidosaurs which are all more basal than the paralligatorid+atoposaurid+crocodilian group, which is back to the ordinary really. The second thing is the definition of Eusuchia. So for the longest time Eusuchia has been defined to include those Neosuchians that have choanae that are fully enclosed by the pterygoid bones (I know I know a bunch of anatomy stuff bear with me). So if the choanae was surrounded by the pterygoid, its an Eusuchian, if not, its more basal. Well, atoposaurids don't have that....BUT VARANOSUCHUS DOES. This, coupled with hylaeochampsids also having this feature and being recovered closer to atoposaurids than to Crocodilians basically suggests that the feature is not diagnostic for Eusuchia and instead appeared multiple times independently.
Moving away from anatomy and phylogeny and all that stuff, I think its very cool that croc research in Thailand has kinda picked up this last year. And fittingly enough some people have even worked on a short documentary covering the known diversity of pseudosuchians from Thailand, giving an overview over the named forms from the Jurassic to today, from titans like Chalawan to even these newest dwarf forms. While the narration is obviously in Thai, there are English subs and I highly recommend looking into it (even if I disagree with their depiction of Varanosuchus as arboreal, its perhaps overshooting the goal a little bit).
youtube
Finally here's the paper itself (tho paywalled) New Cretaceous neosuchians (Crocodylomorpha) from Thailand bridge the evolutionary history of atoposaurids and paralligatorids | Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society | Oxford Academic (oup.com) and the wikipedia page I've been working on Varanosuchus - Wikipedia
I'll try to write up a post on the other new genus, Garzapelta, later this weekend so stay tuned for that.
#varanosuchus#atoposauridae#crocodylomorpha#neosuchia#thailand#cretaeous#pseudosuchia#croc#crocodile#land crocodile#prehistory#paleontology#palaeblr#long post#Youtube
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
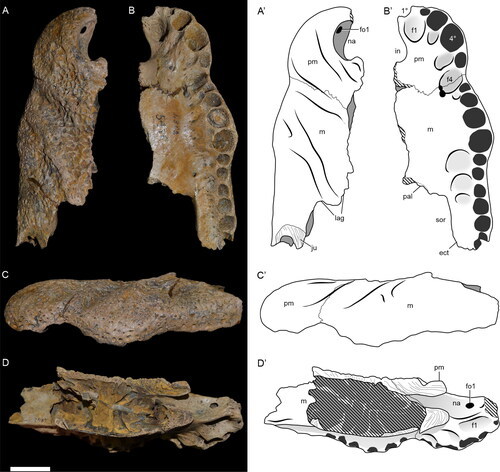
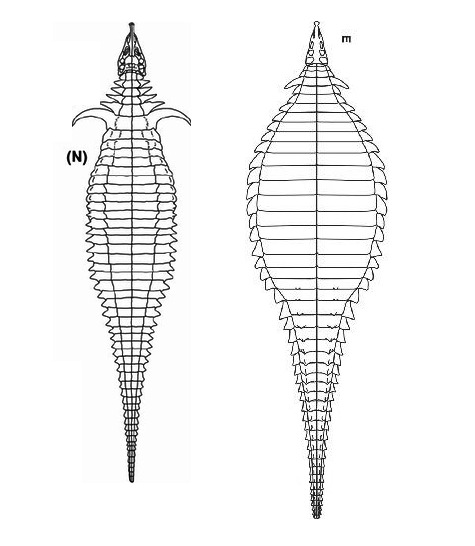
Garzapelta: The Convergent Aetosaur
Our second pseudosuchian of 2024 couldn't be any more different from the first. While the first genus named this year was Varanosuchus, a small, agile atoposaurid from the Cretaceous, our second genus is Garzapelta (Garza County Shield), a large lumbering aetosaur, basically the ankylosaur of the Triassic.
If you remember the two posts on aetosaurs I did last year, you probably remember how osteoderms are super diagnostic for these guys and how the material doesn't need to be all that exciting to represent a new genus. In the case of Garzapelta its kind of an intermediate. It's better than the handfull of osteoderms we got for Venkatasuchus and Kryphioparma but its still mostly just osteoderms and some ribs (and a single toe bone).

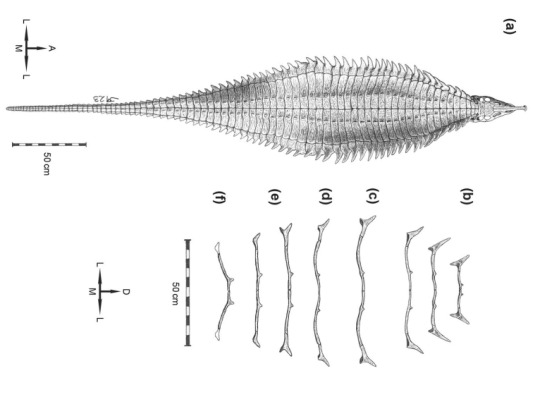
Now the thing that stands out about Garzapelta is the specific combination of characters displayed by the osteoderms. So if you take a step back and look at aetosaurs as a whole, you'll see two big groups that split off from one another. The stagonolepoids, which eventually gave rise to the overly spiky desmatosuchines, and the aetosaurines, which gave rise to some really wide paratypothoracines. Shown below Desmatosuchus and Paratypothorax (not to scale), taken from Martz et al. 2013 and Heckert et al. 2010
But this doesn't yet say why Garzapelta is special. Well you see. We got both the paramedian osteoderms (the central two rows) and the lateral osteoderms (those spikes on the side). Now, the lateral osteoderms are morphologically really similar to those of desmatosuchines, HOWEVER, the paramedian osteoderms more closely resemble those of paratypothoracines. This is so extreme that when writing the paper, Reyes and colleagues did separate phylogenetic analysis for both osteoderm types. And as you might have guessed, when just looking at the laterals it was recovered as a desmatosuchine, but when looking at the paramedians it was recovered as a paratypothoracine (or rather something close to said groups). And when looking at both at the same time....well still a desmatosuchine.
Ironically, despite this, the authors don't think it was a desmatosuchine. Instead, the way the lateral and paramedian osteoderms connect is way more similar to paratypothoracines and ultimately the authors argue that its way more likely that the shape of the lateral osteoderms is the thing that evolved convergently. This whole situation does however highlight a major thing. Current datasets aren't really ready to deal with convergence like this.
And thats all I got to say about this one. Not as extensive as little Varanosuchus I know, but its surprisingly much given its just a bunch of osteoderms and not much in terms of skull remains or anything like that.
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fascinating!
Fossil Crocs of 2024
Another year another list of new fossil crocodilians that greatly expand our knowledge of Pseudosuchia across deep time. Happy to say that this is my third time doing this now, so I'm not going to bog you down with the details and get right into it.
Benggwigwishingasuchus
Our first entry, sorted by geological age of course, is Benggwigwishingasuchus eremicarminis (desert song fishing crocodile) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Nevada. It was a member of the clade Poposauroidea, which some of you might recognize as also containing such bizarre early croc cousins like Arizonasaurus and Effigia. Also notable about Benggwigwishingasuchus is that it was found in the Fossil Hill Member of the Favret Formation. Why is that notable? Well the Fossil Hill Member preserves an environment deposited 10 km off the Triassic coastline and also yielded fossils of animals like Cymbospondylus, the giant ichthyosaur. Despite this however, Benggwigwishingasuchus shows no obvious signs of having been a swimmer or diver. Instead, its been hypothesized that it was simply foraging around the coast and might have been washed out to sea.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe (@knuppitalism-with-ue) and Jorge A. Gonzalez


Parvosuchus
Fast forward some 5 million years to the Ladinian - Carnian of Brazil, specifically the Santa Maria Formation. Here you'll find the one new genus on the list I did not write the wikipedia page for: Parvosuchus aurelioi (Aurélio's Small Crocodile). With only a meter in length, Parvosuchus is amongst the smallest pseudosuchians of the year and a member of the aptly named Gracilisuchidae. Santa Maria was actually home to multiple pseudosuchians, including the mighty Prestosuchus (and its possible juvenile form Decuriasuchus), the small erpetosuchid Archeopelta and larger Pagosvenator and one more...
Artwork by Matheus Fernandes and Joschua Knüppe


Schultzsuchus
Yup, Santa Maria has been eating good this year. Before the description of Parvosuchus, scientists coined the name Schultzsuchus loricatus (Schultz's Crocodile). Now this one's not entirely new and has long been known under the name Prestosuchus loricatus (by which I mean since 1938). What's interesting is that this new redescription suggests that rather than being a Loricatan, Schultzsuchus was actually an early member of Poposauroidea like Benggwigwishingasuchus. Even if it was no longer thought to be close to Prestosuchus, it was liekly still a formidable predator and among the larger pseudosuchians of the formation.
Artwork by Felipe Alves Elias

Garzapelta
Our last Triassic pseudosuchian and our only aetosaur of the year came to us in the form of Garzapelta muelleri (Mueller's Garza County Shield). It comes from the Late Triassic (Norian) Cooper Canyon Formation of, you guessed it, Garza County, Texas. As an aetosaur, the osteoderms are already regarded as diagnostic, tho unlike some other recent examples there is a little more material to go off from. It's still primarily osteoderms, but at least a good amount and even some ribs.
Artwork by Márcio L. Castro

Ophiussasuchus
Our only Jurassic newcommer is Ophiussasuchus paimogonectes (Paimogo Beach Swimmer Portuguese Crocodile), but arguably you couldn't find a better posterchild for Jurassic crocodyliforms. This new lad is a goniopholidid from the Kimmeridgian to Tithonian Lourinhã Formation, yup, Europe's Morrison. It's anatomy is perhaps not the most exciting, like other goniopholidids it had a flattened, very crocodilian-esque snout and was likely semi-aquatic like its relatives.
Artwork by @manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe


Enalioetes
Another quintessential group of Jurassic crocodyliforms are the metriorhynchoids, however, 2024's only new addition to this clade was actually Cretaceous, specifically from the earliest Cretaceous (Valanginian) of Germany. Like Schultzsuchus, Enalioetes schroederi (Schroeder's Sea Dweller) is new in name only, as fossil material has been found at the latest in 1918 and given the name Enaliosuchus "schroederi" in 1936. This kickstarted a whole series of taxonomic back and forth until the recent redescriptoin finally just gave it a new name and settled things (for now). Looking back I realize that I really need to take the time and fix up the Wikipedia page. Tho I've written its current status, I was kinda limited by being on vacation and never dived into the description section.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Jackosaurus


Varanosuchus
Another Early Cretaceous crocodyliform is Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis (Monitor Lizard Crocodile from the Sakon Nakhon Province), described from Thailand's Sao Khua Formation. It lived around the same time as Enalioetes, but otherwise couldn't have been more different. Where Enalioetes was fully marine, Varanosuchus was more a land dweller as evidenced by the deep skull and long, slender legs. At the same time, some other features, like its more robust limbs compared to its kin, might suggest that Varanosuchus could have still spent some time in the water like some modern lizards. Tho one might be reminded of Parvosuchus from earlier, Varanosuchus is a much more recent example of small terrestrial croc-relatives, the atoposaurids, which are much closer to todays crocodiles and alligators.
Artwork once again by Manusuchus

Araripesuchus manzanensis
Yet another example of a small, gracile land "crocodile" comes to us in the form of Araripesuchus manzanensis (Araripe Basin Crocodile from the El Manzano Farm). And once again, it belonged to a completely different group, this time the notosuchian family Uruguaysuchidae. Now Araripesuchus is well known as a genus, in part due to the work of Paul Sereno and Hans Larsson (who popularized the names "dog croc" and "rat croc" for two species). Tangent aside, A. manzanensis is known from the upper layers of Argentina's Candeleros Formation, corresponding to the Cenomanian (earliest Late Cretaceous). The same locality also yielded A. buitreraensis, from which A. manzanensis can be distinguished on account of its blunt molariform teeth in the back of its jaw. This dentition, which corresponds to a durophageous diet of hardshelled prey, could explain how it coexisted with the related A. buitrensis at the same locality, allowing the two to occupy different niches. There is a neat little animation done for this animal you can watch here.
Artwork by Gabriel Diaz Yantén

Caipirasuchus catanduvensis
We're staying in South America but moving to Brazil's Adamantina Formation for our next entry: Caipirasuchus catanduvensis (Caipiras Crocodile from Catanduva). This one is a little more recent, tho the age of the Adamantina Formation is a bit of a mess far as I can tell, ranging anywhere from the Turonian to the Maastrichtian. One could also argue that C. catanduvensis is part of the "lanky small croc club" that Parvosuchus, Varanosuchus and A. manzanensis belong to, but I feel that the very short snout helps it stand out from that bunch more easily. Anyhow, Caipirasuchus catanduvensis is a member of Sphagesauridae, related to Armadillosuchus, and herbivorous. What's really interesting tho is that the internal anatomy suggests the presence of resonance chambers not unlike that of hadrosaurs, possibly suggesting that these animals were quite vocal. This could also explain why baurusuchids appear to have had very keen hearing.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Guilherme Gehr


Epoidesuchus
We're staying in the Adamantina Formation for our last Mesozoic croc of the year, Epoidesuchus tavaresae (Tavares' Enchanted Crocodile). Tho also a Notosuchian like Araripesuchus and Caipirasuchus, this one belongs to the family Itasuchidae (or the subfamily Pepesuchinae depending on who you ask), which stand out as being rare examples of semi-aquatic members of this otherwise largely terrestrial group. Epoidesuchus was fairly large for its kin and had long, slender jaws. Like I said, Epoidesuchus and its relatives were likely more semi-aquatic than other notosuchians, something that might explain the relative lack of semi-aquatic neosuchians across Gondwana. They aren't absent mind you, but noticably rarer than they are in the northern hemisphere.
Artwork by Guilherme Gehr

And thus we move into the Cenozoic and towards the end our or little list. From here on out, say goodbye to Notosuchians or other weird crocodylomorphs and get ready for Crocodilia far as the eye can see.
Ahdeskatanka
The first Cenozoic croc we got is Ahdeskatanka russlanddeutsche (Russian-German Alligator), which despite its name comes from North Dakota, specifically the Early Eocene Golden Valley Formation. Ahdeskatanka is similar to many early alligatorines like Allognathosuchus in being small with rounded, globular teeth that suggest that it fed on hardshelled prey. This would have definitely helped avoid competition in the Golden Valley Formation, which also housed a second, similar form not yet named, a large generalist with a V-shaped snout similar to Borealosuchus and the generalized early caiman Chrysochampsa, also large but with a U-shaped snout.
Artwork by meeeeeeee

Asiatosuchus oenotriensis
We had an alligatoroid, so now its time for a crocodyloid. Asiatosuchus has been recognized from the Late Eocene Duero Basin of Spain for a while now, but now we have a name: Asiatosuchus oenotriensis (Asian Crocodile Belonging To The Land Of Wine). Asiatosuchus is a complex genus, most often not really forming a monophyletic clade and likely representing several distinct or at least successive taxa that form the "Asiatosuchus-like complex". Within this complex, A. oenotriensis is thought to have been close-ish to Germany's Asiatosuchus germanicus.
Artwork by Manusuchus

Sutekhsuchus
Rounding out the trio of major crocodilian clades is Sutekhsuchus dowsoni (Set's Crocodile/God of Deception Crocodile), representing our only gavialoid of the year. Originally described as Tomistoma dowsoni in 1920 based on fossil remains from the Miocene of Egypt, Sutekhsuchus has been at times regarded as distinct and at other times lumped into Tomistoma lusitanica. It was one of several early gavialoids to inhabit the coast of the Tethys during the Miocene and appears to have been most closely related to the genus Eogavialis, clading together just outside of the American and Asian gharials. A fun little personal anecdote, I prematurely learned about this one due to a friend highlighting the name in a study on Eogavialis. Never having heard of "Sutekhsuchus" I took to google scholar, where I found a single result: a reference to the then unpublished description, which naturally I ended up eagerly awaiting.
Artwork by Manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe


Paranacaiman
Two more and we're done. First, completely arbitrarily, Paranacaiman bravardi (Bravard's Caiman from Parana) from the Miocene Ituzaingo Formation of Argentina. Material of this genus has originally been referred to Caiman lutescens, described in 1912 but now considered a nomen dubium. Paranacaiman is known from limited material only, just the skull table, but that would indicate a "huge" animal. My personal scaling recovered a size of almost 5 meters in length, similar to large black caimans today.
Once again, credit to me

Paranasuchus
Last but not least, Paranasuchus gasparinae (Gasparini's Crocodile from Parana). Coming from the same deposits as Paranacaiman, this one too has been known as a species of Caiman for some time before being assigned its own genus, though it at least got to retain its old species name. Alas, I have not scaled it myself, tho its material is at least more extensive than that of Paranacaiman, including even parts of the snout. A little nitpick because I don't have much to say, but I personally think the name was ill conceived. On its own both Paranacaiman and Paranasuchus are fine names don't get me wrong, but together, coined by the same authors in the same study no less, they strike me as needlessly confusing to non experts. Both are caimans, both are from Parana, so the distinction between "Parana Caiman" and "Parana Crocodile" is entirely arbitrary and doesn't really distinguish them. Not helped by the fact that they are even closely related in the original description. Other than that tho another good addition to our understanding of fossil crocs.
No artwork on this one, but fossil material from Bona et al. 2024

And that wraps up 2024. I hope This post, or my posts throughout the year or even my work on Wikipedia has helped to make these fascinating animals just a little bit more approachable and a massive thanks to all the artists who took their time to create fantastic pieces featuring these incredible animals. Special shout outs to Manusuchus, who diligently illustrated a lot of the featured animals and Joschua Knüppe, who had to listen to me suggest Ahdeskatanka every Sunday for about two months straight now.
Fossil Crocs of 2023
Fossil Crocs of 2022
#paranasuchus#paranacaiman#ahdeskatanka#sutekhsuchus#epoidesuchus#enalioetes#parvosuchus#benggwigwishingasuchus#araripesuchus#varanosuchus#garzapelta#schultzsuchus#paleontology#caipirasuchus#ophiussasuchus#fossil crocs of 2024#long post#prehistory#paleonotlogy#crocodylomorpha#pseudosuchia#2024#crocodilia#palaeoblr#Always a paleontology adventure#science communication#sci comm
260 notes
·
View notes