#uber profit
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
food stamp card arrived, god bless
#my diary#the sigh of relief I sighed when I heard the balance#that shit un-greyed a hair on me#I am also a grubhub driver now#I chickened out on uber anxiety won but food delivery? much less stressful#I did a test run delivering pizza to some kid on campus at the nearby college#minor stress trying to find the dorm's parking lot but we got there#making less than 5 dollars felt pretty demeaning lmao but it's $4.82 more than I had yesterday#not gonna do any more tonight but I think spending a couple days a week doing lunch deliveries could be profitable#and I hate to say it but the grubhub driver app sets it up so it's kinda like a game with a map and quest markers and like.... I enjoy that#if this paid like a real job I might do it in lieu of a real job honestly I like driving around doing little errands
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm done ordering uber eats. they forgot my queso 2 orders ago. my last order they double charged me for my tip. I noticed right away, contact them, "nah that was ur total it just took it later" I know this isn't the case because I looked at the total before I bought the shit. I talk to 3 guys. third guys name is pushkar and he just hangs up the conversation, I reconnect and get him again and he's just ignoring me so I'm talking shit to him. finally I'm all "okay when you're selling street meat again don't be surprised, pushkar." connect with another guy. "nah it's chill brody u just buy so much stuff" "can I see a receipt" very clearly double tip, and I send him pics of the receipt and my bank transactions. for like 4 dollars. it's wild that people pay all the money they do to get uber eats every day and I guarantee pushkar is doing the same shit to all of u.
#nobody is as petty as me to battle pushkar for $4 so they just make insane profits#obv uber eats didn't forget my queso but having been in the store when we get uber eats orders I know everybody is just mad as shit#like to just have the audacity to order uber eats fucking pisses them off in there#to be clear the total with tip was 31.97 with tip and tax and they charged me that and another $5#no this time we actually decided to make the tip a seperate charge even though it never was before#the totals not adding up is all in your head#time isn’t real but you believe in money?….. follow me @pushkarfast
0 notes
Text
I need someone smarter than me and whose done the research to do a podcast episode because I very much feel like a lot of stuff we see now in the crypto and AI space are related to earlier problems in the tech industry.
#when you look at what they want to do it’s basically the same as what Uber did to taxi drivers#price yourself as the lowest possible thing for people/companies. then once you’ve killed the market and have no competitors you jack the#prices up. because that’s literally the only way AI could turn a profit#it’s expensive to have these data centers use up all the power#they market themselves as a cheap alternative to humans but they 100% plan on raising the prices 100 fold once they get companies to sign#gwon
0 notes
Text
If anyone wants to know why every tech company in the world right now is clamoring for AI like drowned rats scrabbling to board a ship, I decided to make a post to explain what's happening.
(Disclaimer to start: I'm a software engineer who's been employed full time since 2018. I am not a historian nor an overconfident Youtube essayist, so this post is my working knowledge of what I see around me and the logical bridges between pieces.)
Okay anyway. The explanation starts further back than what's going on now. I'm gonna start with the year 2000. The Dot Com Bubble just spectacularly burst. The model of "we get the users first, we learn how to profit off them later" went out in a no-money-having bang (remember this, it will be relevant later). A lot of money was lost. A lot of people ended up out of a job. A lot of startup companies went under. Investors left with a sour taste in their mouth and, in general, investment in the internet stayed pretty cooled for that decade. This was, in my opinion, very good for the internet as it was an era not suffocating under the grip of mega-corporation oligarchs and was, instead, filled with Club Penguin and I Can Haz Cheezburger websites.
Then around the 2010-2012 years, a few things happened. Interest rates got low, and then lower. Facebook got huge. The iPhone took off. And suddenly there was a huge new potential market of internet users and phone-havers, and the cheap money was available to start backing new tech startup companies trying to hop on this opportunity. Companies like Uber, Netflix, and Amazon either started in this time, or hit their ramp-up in these years by shifting focus to the internet and apps.
Now, every start-up tech company dreaming of being the next big thing has one thing in common: they need to start off by getting themselves massively in debt. Because before you can turn a profit you need to first spend money on employees and spend money on equipment and spend money on data centers and spend money on advertising and spend money on scale and and and
But also, everyone wants to be on the ship for The Next Big Thing that takes off to the moon.
So there is a mutual interest between new tech companies, and venture capitalists who are willing to invest $$$ into said new tech companies. Because if the venture capitalists can identify a prize pig and get in early, that money could come back to them 100-fold or 1,000-fold. In fact it hardly matters if they invest in 10 or 20 total bust projects along the way to find that unicorn.
But also, becoming profitable takes time. And that might mean being in debt for a long long time before that rocket ship takes off to make everyone onboard a gazzilionaire.
But luckily, for tech startup bros and venture capitalists, being in debt in the 2010's was cheap, and it only got cheaper between 2010 and 2020. If people could secure loans for ~3% or 4% annual interest, well then a $100,000 loan only really costs $3,000 of interest a year to keep afloat. And if inflation is higher than that or at least similar, you're still beating the system.
So from 2010 through early 2022, times were good for tech companies. Startups could take off with massive growth, showing massive potential for something, and venture capitalists would throw infinite money at them in the hopes of pegging just one winner who will take off. And supporting the struggling investments or the long-haulers remained pretty cheap to keep funding.
You hear constantly about "Such and such app has 10-bazillion users gained over the last 10 years and has never once been profitable", yet the thing keeps chugging along because the investors backing it aren't stressed about the immediate future, and are still banking on that "eventually" when it learns how to really monetize its users and turn that profit.
The pandemic in 2020 took a magnifying-glass-in-the-sun effect to this, as EVERYTHING was forcibly turned online which pumped a ton of money and workers into tech investment. Simultaneously, money got really REALLY cheap, bottoming out with historic lows for interest rates.
Then the tide changed with the massive inflation that struck late 2021. Because this all-gas no-brakes state of things was also contributing to off-the-rails inflation (along with your standard-fare greedflation and price gouging, given the extremely convenient excuses of pandemic hardships and supply chain issues). The federal reserve whipped out interest rate hikes to try to curb this huge inflation, which is like a fire extinguisher dousing and suffocating your really-cool, actively-on-fire party where everyone else is burning but you're in the pool. And then they did this more, and then more. And the financial climate followed suit. And suddenly money was not cheap anymore, and new loans became expensive, because loans that used to compound at 2% a year are now compounding at 7 or 8% which, in the language of compounding, is a HUGE difference. A $100,000 loan at a 2% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, accrues to $121,899. A $100,000 loan at an 8% interest rate, if not repaid a single cent in 10 years, more than doubles to $215,892.
Now it is scary and risky to throw money at "could eventually be profitable" tech companies. Now investors are watching companies burn through their current funding and, when the companies come back asking for more, investors are tightening their coin purses instead. The bill is coming due. The free money is drying up and companies are under compounding pressure to produce a profit for their waiting investors who are now done waiting.
You get enshittification. You get quality going down and price going up. You get "now that you're a captive audience here, we're forcing ads or we're forcing subscriptions on you." Don't get me wrong, the plan was ALWAYS to monetize the users. It's just that it's come earlier than expected, with way more feet-to-the-fire than these companies were expecting. ESPECIALLY with Wall Street as the other factor in funding (public) companies, where Wall Street exhibits roughly the same temperament as a baby screaming crying upset that it's soiled its own diaper (maybe that's too mean a comparison to babies), and now companies are being put through the wringer for anything LESS than infinite growth that Wall Street demands of them.
Internal to the tech industry, you get MASSIVE wide-spread layoffs. You get an industry that used to be easy to land multiple job offers shriveling up and leaving recent graduates in a desperately awful situation where no company is hiring and the market is flooded with laid-off workers trying to get back on their feet.
Because those coin-purse-clutching investors DO love virtue-signaling efforts from companies that say "See! We're not being frivolous with your money! We only spend on the essentials." And this is true even for MASSIVE, PROFITABLE companies, because those companies' value is based on the Rich Person Feeling Graph (their stock) rather than the literal profit money. A company making a genuine gazillion dollars a year still tears through layoffs and freezes hiring and removes the free batteries from the printer room (totally not speaking from experience, surely) because the investors LOVE when you cut costs and take away employee perks. The "beer on tap, ping pong table in the common area" era of tech is drying up. And we're still unionless.
Never mind that last part.
And then in early 2023, AI (more specifically, Chat-GPT which is OpenAI's Large Language Model creation) tears its way into the tech scene with a meteor's amount of momentum. Here's Microsoft's prize pig, which it invested heavily in and is galivanting around the pig-show with, to the desperate jealousy and rapture of every other tech company and investor wishing it had that pig. And for the first time since the interest rate hikes, investors have dollar signs in their eyes, both venture capital and Wall Street alike. They're willing to restart the hose of money (even with the new risk) because this feels big enough for them to take the risk.
Now all these companies, who were in varying stages of sweating as their bill came due, or wringing their hands as their stock prices tanked, see a single glorious gold-plated rocket up out of here, the likes of which haven't been seen since the free money days. It's their ticket to buy time, and buy investors, and say "see THIS is what will wring money forth, finally, we promise, just let us show you."
To be clear, AI is NOT profitable yet. It's a money-sink. Perhaps a money-black-hole. But everyone in the space is so wowed by it that there is a wide-spread and powerful conviction that it will become profitable and earn its keep. (Let's be real, half of that profit "potential" is the promise of automating away jobs of pesky employees who peskily cost money.) It's a tech-space industrial revolution that will automate away skilled jobs, and getting in on the ground floor is the absolute best thing you can do to get your pie slice's worth.
It's the thing that will win investors back. It's the thing that will get the investment money coming in again (or, get it second-hand if the company can be the PROVIDER of something needed for AI, which other companies with venture-back will pay handsomely for). It's the thing companies are terrified of missing out on, lest it leave them utterly irrelevant in a future where not having AI-integration is like not having a mobile phone app for your company or not having a website.
So I guess to reiterate on my earlier point:
Drowned rats. Swimming to the one ship in sight.
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
We Dug Into Uber's Finances. What We Found Will Shock You.
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text

Revolutionize dining and elevate your earnings! Alphacodez UberEats clone script isn't just a platform – it's a high-revenue business opportunity. Start your own food delivery empire, capitalize on the booming market, and watch your profits soar. 🚀💰🍽️
Refer : https://bit.ly/ubereats-clone-script
Contact us via email: [email protected] Contact us : +91 8122957365
#entrepreneurship#clone app development company#startup ideas#business ideas#ubereatsclonescript#profitable business#cloneapp#uber eats#food delivery clone script
0 notes
Text
How Does Uber Make Money? Uber Business Model
Introduction: In just a few short years, Uber has revolutionized the way we think about transportation. With its innovative use of technology and disruptive business model, Uber has transformed the way people move around cities worldwide. From its humble beginnings as a ride-hailing service, Uber has become a global phenomenon, challenging traditional taxi services and establishing itself as a…

View On WordPress
#business model for uber#How does Uber make money#How Uber generates revenue#how uber make money#Uber Business Model#uber business model canvas#Uber Business Strategy#uber businesses#Uber monetization strategies#Uber profitability#Uber Revenue Model#Uber revenue sources
0 notes
Text
Something very interesting about the framing of self-driving cars between the US and China.
In the US, companies like Uber, Lyft, or whoever, push self-driving cars with the objective of increasing their profit (but decreasing their rate of profit) by removing drivers from their cars, effectively shifting a large part of their labour costs from the driver seat to the factory.
In China, self-driving busses are designed, built, and tested with the goal of reducing the workload on bus-drivers - who, while remaining in the driver seat, now don't have to micromanage the route at all times, like using a cruise control. It is explicitly framed as a labour-saving device.
If you're interested in the socialist position on automation, there it is in practice.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Nurses whose shitty boss is a shitty app
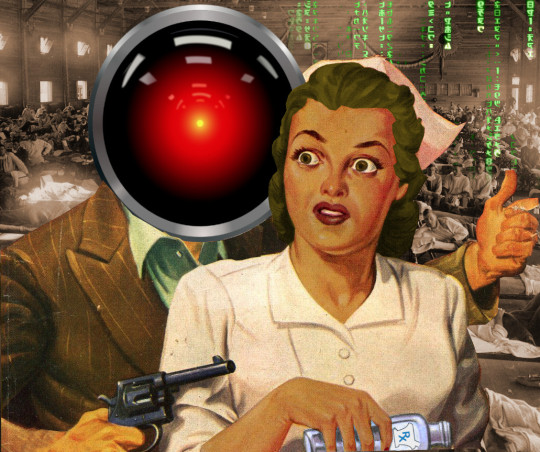
If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/12/17/loose-flapping-ends/#luigi-has-a-point

Operating a business is risky: you can't ever be sure how many customers you'll have, or what they'll show up looking for. If you guess wrong, you'll either have too few workers to serve the crowd, or you'll pay workers to stand around and wait for customers. This is true even when your "business" is a "hospital."
Capitalists hate capitalism. Capitalism is defined by risk – like the risk of competitors poaching your customers and workers. Capitalists all secretly dream of a "command economy" in which other people have to arrange their affairs to suit the capitalists' preferences, taking the risk off their shoulders. Capitalists love anti-competitive exclusivity deals with suppliers, and they really love noncompete "agreements" that ban their workers from taking better jobs:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/21/bondage-fees/#doorman-building
One of the sleaziest, most common ways for capitalists to shed risk is by shifting it onto their workers' shoulders, for example, by sending workers home on slow days and refusing to pay them for the rest of their shifts. This is easy for capitalists to do because workers have a collective action problem: for workers to force their bosses not to do this, they all have to agree to go on strike, and other workers have to honor their picket-lines. That's a lot of chivvying and bargaining and group-forming, and it's very hard. Meanwhile, the only person the boss needs to convince to screw you this way is themself.
Libertarians will insist that this is impossible, of course, because workers will just quit and go work for someone else when this happens, and so bosses will be disciplined by the competition to find workers willing to put up with their bullshit. Of course, these same libertarians will tell you that it should be legal for your boss to require you to sign a noncompete "agreement" so you can't quit and get a job elsewhere in your field. They'll also tell you that we don't need antitrust enforcement to prevent your boss from buying up all the businesses you might work for if you do manage to quit.
In practice, the only way workers have successfully resisted being burdened with their bosses' risks is by a) forming a union, and then b) using the union to lobby for strong labor laws. Labor laws aren't a substitute for a union, but they are an important backstop, and of course, if you're not unionized, labor law is all you've got.
Enter the tech-bro, app in hand. The tech-bro's most absurd (and successful) ruse is "it's not a crime, I did it with an app." As in "it's not money-laundering, I did it with an app." Or "it's not a privacy violation, I did it with an app." Or "it's not securities fraud, I did it with an app." Or "it's not price-gouging, I did it with an app," or, importantly, "it's not a labor-law violation, I did it with an app."
The point of the "gig economy" is to use the "did it with an app" trick to avoid labor laws, so that bosses can shift risks onto workers, because capitalists hate capitalism. These apps were first used to immiserate taxi-drivers, and this was so successful that it spawned a whole universe of "Uber for __________" apps that took away labor rights from other kinds of workers, from dog-groomers to carpenters.
One group of workers whose rights are being devoured by gig-work apps is nurses, which is bad news, because without nurses, I would be dead by now.
A new report from the Roosevelt Institute goes deep on the way that nurses' lives are being destroyed by gig work apps that let bosses in America's wildly dysfunctional for-profit health care industry shift risk from bosses to the hardest-working group of health care professionals:
https://rooseveltinstitute.org/publications/uber-for-nursing/
The report's authors interviewed nurses who were employed through three apps: Shiftkey, Shiftmed and Carerev, and reveal a host of risk-shifting, worker-abusing practices that has nurses working for so little that they can't afford medical insurance themselves.
Take Shiftkey: nurses are required to log into Shiftkey and indicate which shifts they are available for, and if they are assigned any of those shifts later but can't take them, their app-based score declines and they risk not being offered shifts in the future. But Shiftkey doesn't guarantee that you'll get work on any of those shifts – in other words, nurses have to pledge not to take any work during the times when Shiftkey might need them, but they only get paid for those hours where Shiftkey calls them out. Nurses assume all the risk that there won't be enough demand for their services.
Each Shiftkey nurse is offered a different pay-scale for each shift. Apps use commercially available financial data – purchased on the cheap from the chaotic, unregulated data broker sector – to predict how desperate each nurse is. The less money you have in your bank accounts and the more you owe on your credit cards, the lower the wage the app will offer you. This is a classic example of what the legal scholar Veena Dubal calls "algorithmic wage discrimination" – a form of wage theft that's supposedly legal because it's done with an app:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Shiftkey workers also have to bid against one another for shifts, with the job going to the worker who accepts the lowest wage. Shiftkey pays nominal wages that sound reasonable – one nurse's topline rate is $23/hour. But by payday, Shiftkey has used junk fees to scrape that rate down to the bone. Workers have to pay a daily $3.67 "safety fee" to pay for background checks, drug screening, etc. Nevermind that these tasks are only performed once per nurse, not every day – and nevermind that this is another way to force workers to assume the boss's risks. Nurses also pay daily fees for accident insurance ($2.14) and malpractice insurance ($0.21) – more employer risk being shifted onto workers. Workers also pay $2 per shift if they want to get paid on the same day – a payday lending-style usury levied against workers whose wages are priced based on their desperation. Then there's a $6/shift fee nurses pay as a finders' fee to the app, a fee that's up to $7/shift next year. All told, that $23/hour rate cashes out to $13/hour.
On top of that, gig nurses have to pay for their own uniforms, licenses, equipment and equipment, including different colored scrubs and even shoes for each hospital. And because these nurses are "their own bosses" they have to deduct their own payroll taxes from that final figure. As "self-employed" workers, they aren't entitled to overtime or worker's comp, they get no retirement plan, health insurance, sick days or vacation.
The apps sell themselves to bosses as a way to get vetted, qualified nurses, but the entire vetting process is automated. Nurses upload a laundry list of documents related to their qualifications and undergo a background check, but are never interviewed by a human. They are assessed through automated means – for example, they have to run a location-tracking app en route to callouts and their reliability scores decline if they lose mobile data service while stuck in traffic.
Shiftmed docks nurses who cancel shifts after agreeing to take them, but bosses who cancel on nurses, even at the last minute, get away at most a small penalty (having to pay for the first two hours of a canceled shift), or, more often, nothing at all. For example, bosses who book nurses through the Carerev app can cancel without penalty on a mere two hours' notice. One nurse quoted in the study describes getting up at 5AM for a 7AM shift, only to discover that the shift was canceled while she slept, leaving her without any work or pay for the day, after having made arrangements for her kid to get childcare. The nurse assumes all the risk again: blocking out a day's work, paying for childcare, altering her sleep schedule. If she cancels on Carerev, her score goes down and she will get fewer shifts in the future. But if the boss cancels, he faces no consequences.
Carerev also lets bosses send nurses home early without paying them for the whole day – and they don't pay overtime if a nurse stays after her shift ends in order to ensure that their patients are cared for. The librarian scholar Fobazi Ettarh coined the term "vocational awe" to describe how workers in caring professions will endure abusive conditions and put in unpaid overtime because of their commitment to the patrons, patients, and pupils who depend on them:
https://www.inthelibrarywiththeleadpipe.org/2018/vocational-awe/
Many of the nurses in the study report having shifts canceled on them as they pull into the hospital parking lot. Needless to say, when your shift is canceled just as it was supposed to start, it's unlikely you'll be able to book a shift at another facility.
The American healthcare industry is dominated by monopolies. First came the pharma monopolies, when pharma companies merged and merged and merged, allowing them to screw hospitals with sky-high prices. Then the hospitals gobbled each other up, merging until most regions were dominated by one or two hospital chains, who could use buyer power to get a better deal on pharma prices – but also use seller power to screw the insurers with outrageous prices for care. So the insurers merged, too, until they could fight hospital price-gouging.
Everywhere you turn in the healthcare industry, you find another monopolist: pharmacists and pharmacy benefit managers, group purchasing organizations, medical beds, saline and supplies. Monopoly begets monopoly.
(Unitedhealthcare is extraordinary in that its divisions are among the most powerful players in all of these sectors, making it a monopolist among monopolists – for example, UHC is the nation's largest employer of physicians:)
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/its-time-to-break-up-big-medicine
But there two key stakeholders in American health-care who can't monopolize: patients and health-care workers. We are the disorganized, loose, flapping ends at the beginning and end of the healthcare supply-chain. We are easy pickings for the monopolists in the middle, which is why patients pay more for worse care every year, and why healthcare workers get paid less for worse working conditions every year.
This is the one area where the Biden administration indisputably took action, bringing cases, making rules, and freaking out investment bankers and billionaires by repeatedly announcing that crimes were still crimes, even if you used an app to commit them.
The kind of treatment these apps mete out to nurses is illegal, app or no. In an important speech just last month, FTC commissioner Alvaro Bedoya explained how the FTC Act empowered the agency to shut down this kind of bossware because it is an "unfair and deceptive" form of competition:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/11/26/hawtch-hawtch/#you-treasure-what-you-measure
This is the kind of thing the FTC could be doing. Will Trump's FTC actually do it? The Trump campaign called the FTC "politicized" – but Trump's pick for the next FTC chair has vowed to politicize it even more:
https://theintercept.com/2024/12/18/trump-ftc-andrew-ferguson-ticket-fees/
Like Biden's FTC, Trump's FTC will have a target-rich environment if it wants to bring enforcement actions on behalf of workers. But Biden's trustbusters chose their targets by giving priority to the crooked companies that were doing the most harm to Americans, while Trump's trustbusters are more likely to give priority to the crooked companies that Trump personally dislikes:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/11/12/the-enemy-of-your-enemy/#is-your-enemy
So if one of these nursing apps pisses off Trump or one of his cronies, then yeah, maybe those nurses will get justice.

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#nursing#labor#algorithmic wage discrimination#uber for nurses#wage theft#gig economy#accountability sinks#precaratization#health#health care#usausausa#guillotine watch#monopolies#ai#roosevelt institute#shiftkey#shiftmed#carerev
414 notes
·
View notes
Text

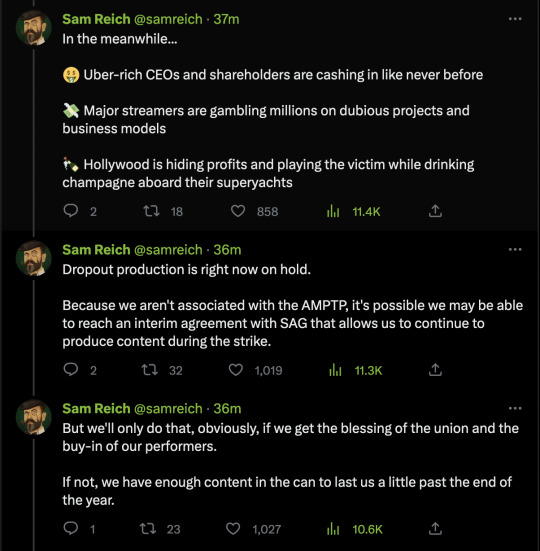



Full thread from Sam on the SAG strike and Dropout!
[ID: A thread from Sam on twitter, as follows: "A thread about the strike and Dropout production: 👇✊. I stand in complete and utter solidarity with our striking performers. I myself am SAG-AFTRA, as are others on our executive team, having come from the world of working actors. I am nothing but sympathetic to their cause and outraged by the mafia-like behavior of the major streamers and AMPTP. It is harder than ever to make a living in this industry, and that goes even for the lucky few of us who get to work on meaningful projects.
In the meanwhile… 🤑 Uber-rich CEOs and shareholders are cashing in like never before 💸 Major streamers are gambling millions on dubious projects and business models 🍾 Hollywood is hiding profits and playing the victim while drinking champagne aboard their superyachts
Dropout production is right now on hold. Because we aren't associated with the AMPTP, it's possible we may be able to reach an interim agreement with SAG that allows us to continue to produce content during the strike.
But we'll only do that, obviously, if we get the blessing of the union and the buy-in of our performers. If not, we have enough content in the can to last us a little past the end of the year.
I pride myself in that Dropout has always paid above SAG minimums. As the years go on and the company is healthier, we will strive to do even better, and then even better still. Without the talent of our performers, we are zilch. Zero. Nothing."
Attached is an instagram post from an actor reading: "The Netflix show in question is shorter than a traditional half hour. But @ collegehumor and @ dropouttv paid me MORE than that for one of their scripted series. Dropout was a brand new online platform at the time and they still managed to pay their actors more than NETFLIX for scripted short form content."
Thread continues: "Public companies don't do this for the very simple reason that they feel more indebted to their executives and shareholders than they do their workforce. It's why corporations are so often exploitative. Our industry, because our jobs are so desirable, is especially vulnerable to exploitation. Hollywood takes advantage of that by making us feel generally commoditized, cheap, and replaceable …which is ironic given just how personal our work so often is. That's why unions - and the power of collective bargaining - is so important: because public companies often won't pay their workforce any more than they're forced to.
As for me, I intend to honor my union's position that I not promote SAG productions as a performer -- even if they are produced by me. That means that I won't personally be promoting any of our shows for the time being.
Attached is a screenshot of Sam on Discord responding to the question "given the strike… what picket line chant will you be rockin'?" with "i'm a talent / CEO! me says me has got to go!"
Thread continues: "This year, instead of running a FYC campaign for Game Changer, we donated $10k to the Entertainment Community Fund in solidarity with the WGA. Today, in solidarity with SAG-AFTRA, I'm personally matching that donation with another $10,000. If you have any disposable income, I encourage you to donate as well: https://entertainmentcommunity.org. And as soon as I test negative for COVID, I'll see you on the picket line. ✊"]
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
These hurricanes are not an "act of God", they are not even "biblical". They are the direct result of sacrificing plants, animals, natural resources, and human lives on the altar of bottom-line profit. The uber-wealthy and influential mine the earth the exhaustion and pump the oceans full of poison and destroy the atmosphere, then have the audacity to act surprised when it results in loss of life.
I am scared for Florida and my heart is in pieces over what Helene already did to the South. But prayers and donations and even infrastructure, as essential as they are, wont change the fact that those who hold the reins of industry, politics, economics, and trade are actively killing the world.
I hope their billion dollar bunkers flood.
278 notes
·
View notes
Text

So, I don't want to give away too much of what I do for an actual job, but I can tell you how much of a disaster this would be because of how borked so many city's vital underground infrastructure like gas, water, and wastewater lines are.
Like, imagining a private for-profit company like Uber (which have such good track records of not trying to cut corners at every possible turn) trying to maintain underground pipe infrastructure sends fucking shivers down my spine.
One of these is going to hit an unmarked gas line trying to express deliver someone's Chipotle order and it's going to end poorly.
660 notes
·
View notes
Text
crimes of the elite: a deep dive
voted on here. (other editions) bold = favourite
corporate harms
behind the smiles at amazon
the long, dark shadow of bhopal (bhopal gas disaster)
how lobbying blocked european safety checks for dangerous medical implants
7-eleven revealed
who controls the world's food supply?
the true cost of tuna: marine observers dying at sea
how a big pharma company stalled a potentially lifesaving vaccine in pursuit of bigger profits
24 years after, some victims not compensated and still can't live normal lives (pfizer's nigeria vaccine trials)
the corporate crime of the century
uber broke laws, duped police and secretly lobbied governments, leak reveals (the uber files)
the baby killer (nestle infant formula scandal)
2 paths of bayer drug in 80's: riskier one steered overseas (hiv-risk contaminated blood product scandal)
global banks defy u.s. crackdowns by serving oligarchs, criminals and terrorists (fincen files)
the ultra-rich
eliminalia: a reputation laundromat for criminals
the fall of the god of cars (international fugitive carlos ghosn)
a u.s. billionaire took over a tropical island pension fund. then hundreds of millions of dollars allegedly went missing (cyprus confidential)
the trial of sam bankman-fried, explained (ftx crypto fraud)
how the wealthiest avoid income tax (the irs files)
the haves and the have-yachts
madoff and his models (madoff ponzi scheme)
the imposter (blockchain terminal fraud)
the ultra-rich: (allegedly) stolen antiquities
crime of the centuries
stolen treasure traders
a hunt for cambodia's looted heritage leads to top museums (pandora papers)
an art crime for the ages
#studyblr#studyspo#student#university#productivity#reading lists#literature#criminology#crime#mydeepdives#i'm working on the lists for state crime and online crime rn!! coming soon hopefully#i will get to all the poll options eventually
530 notes
·
View notes
Text
Arson is forbidden. I refuse to deal with more paperwork because you had a momentary psychotic episode. Also, what new toxic concoction did you eat this time?
It is three twelve in the sage forsaken morning I have not slept I have a stomach ache and a bizarre amount of energy. Possibly the urge to commit arson as well. I genuinely cannot tell what I want in this moment.
#crazy ANBU#I was just thinking Uber ANBU sounds like a profitable endeavor#Get your Hokage coffee?#Something stronger?#whotookmysenbon
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quick FAQ on Tumblr, "Value", and the Proposed Crab Day
Motivation: I see a lot of misinformation circulating on the dash re the proposed crab day and I wanted to offer a simplified and judgement free perspective using core principles of finance.
Q: We keep being told that tumblr's been making nothing but a loss for years, and yet, if it is so unprofitable, then why is no one is shutting the website down? Is it really in need of our money if it's already owned by a multi-billion dollar corporation?
This is in fact not as much of a paradox as it appears to be because "value" in corporate finance terms is a function of present and expected future profits (adjusting for the fact that profits you expect to be earn in the near future are worth a lot more than equivalent profits expected to be earned much later in time).
This means that you can have a company or a product that is currently making a loss (i.e. costing a lot more to run than the income it generates) and it might still be worth some (or a lot of) money as long as you expect it to generate enough profits going forward. Uber for example has been making a loss for years and is still valued at billions of dollars because people think it will eventually generate a lot of profit.
Q: What does all of that mean for tumblr, specifically?
Given how unprofitable tumblr has been historically it's actually a pretty good sign that management has a plan to try and make it profitable because it means they haven't thrown in the towel yet!
But if they fail or if they decide that no matter what they do tumblr will remain unprofitable, then they wouldn't have much business incentive to keep running it. This is why participating in crab day or spending some money on tumblr in general is a good idea, if you can afford it and if tumblr is a service you would like to keep enjoying into the future. And if the answer is no to either of those questions, that's ok too--don't let anyone guilt you on this.
Even more questions-and-answers under the cut! My inbox is also open for any (good faith) questions you might have.
Q: But we all use tumblr religiously--isn't that enough?
Not quite. Tumblr's current state means that the existing userbase is not enough to make the site profitable. For that to change, either the existing userbase needs to become more profitable, or tumblr needs to get a lot more new users--or have a combination of both.
Q: Can crab day really solve all this?
Once again, not quite. A one time cash-injection is not equal to sustainable income, which is what tumblr ultimately needs. This means tumblr will still need to court potential new users and that entails some change to the design and/or the perception of the site. (I love tumblr but guys, if we are real for a second, last time I told my coworkers that, they asked me if I also had a myspace account.)
Q: So why participate then?
Because it will still help. While some change is inevitable and necessary, if we the existing users put our money where our mouth is, it would send a strong signal to management that we value the service they offer and that they should take our preferences into account in designing the site's future also. Also some cash, even if it is a one time deal,
Q: I heard people who came up with the idea are transphobic Christian fundies--do you really want to associate with people like that?
I don't. But who the blogs behind this idea, as people, are has no bearing on the merits of the idea itself.
#crab day#save this hellsite#im gonna say something i never explicitly have#and ask that you rb this if you agree with it#finance is confusing! and the more we get the message across#the better i think#for keeping tumblr around for a long time
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
After nearly 15 years, Uber claims it’s finally turned an annual profit. Between 2014 and 2023, the company set over $31 billion on fire in its quest to drive taxi companies out of business and build a global monopoly. It failed on both fronts, but in the meantime it built an organization that can wield significant power over transportation — and that’s exactly how it got to last week’s milestone. Uber turned a net profit of nearly $1.9 billion in 2023, but what few of the headlines will tell you is that over $1.6 billion of it came from unrealized gains from its holdings in companies like Aurora and Didi. Basically, the value of those shares are up, so on paper it looks like Uber’s core business made a lot more money than it actually did. Whether the companies are really worth that much is another question entirely — but that doesn’t matter to Uber. At least it’s not using the much more deceptive “adjusted EBITDA” metric it spent years getting the media to treat as an accurate picture of its finances. Don’t be fooled into thinking the supposed innovation Uber was meant to deliver is finally bearing fruit. The profit it’s reporting is purely due to exploitative business practices where the worker and consumer are squeezed to serve investors — and technology is the tool to do it. This is the moment CEO Dara Khosrowshahi has been working toward for years, and the plan he’s trying to implement to cement the company’s position should have us all concerned about the future of how we get around and how we work.
[...]
Uber didn’t become a global player in transportation because it wielded technology to more efficiently deliver services to the public. The tens of billions of dollars it lost over the past decade went into undercutting taxis on price and drawing drivers to its service — including some taxi drivers — by promising good wages, only to cut them once the competition posed by taxis had been eroded and consumers had gotten used to turning to the Uber app instead of calling or hailing a cab. As transport analyst Hubert Horan outlined, for-hire rides are not a service that can take advantage of economies of scale like a software or logistics company, meaning just because you deliver more rides doesn’t mean the per-ride cost gets significantly cheaper. Uber actually created a less cost-efficient model because it forces drivers to use their own vehicles and buy their own insurance instead of having a fleet of similar vehicles covered by fleet insurance. Plus, it has a ton of costs your average taxi company doesn’t: a high-paid tech workforce, expensive headquarters scattered around the world, and outrageously compensated executive management like Khosrowshahi, just to name a few. How did Uber cut costs then? By systematically going after the workers that deliver its service. More recently, it took advantage of the cost-of-living crisis to keep them on board in the same way it exploited workers left behind by the financial crisis in the years after its initial launch. Its only real innovation is finding new ways to exploit labor.
387 notes
·
View notes