#transcriptome analysis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Python-Based Pipelines for Variant Calling in Genomic Research

In the rapidly evolving field of genomics, variant calling is a cornerstone of genomic research that enables scientists to identify genetic variations associated with diseases, traits, and evolutionary processes. With the exponential growth of high-throughput sequencing technologies, researchers are now faced with vast amounts of genomic data, necessitating efficient and robust tools for analysis. Python, a versatile programming language with a rich ecosystem of libraries, has become a popular choice for developing variant calling pipelines. In this article, we will explore how to create Python-based pipelines for variant calling, focusing on the process of handling VCF files, and illustrating how Python can transform genomic data into meaningful discoveries.
To know more, visit us at: https://edgenebiomed.com/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Data Analysis Online Training
🚀 Unlock the power of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) and elevate your bioinformatics skills with our upcoming training course! ⭐ Why join us? In today’s rapidly evolving world of life sciences, mastering NGS data analysis is essential for cutting-edge research. Our comprehensive training programs are designed to equip you with the skills needed to excel in bioinformatics, whether you’re a beginner or looking to advance your expertise. Registrations Open: ✅ Next-Generation Sequencing Data Analysis ✅ Python & Biopython for Bioinformatics 🗓 Dates NGS Data Analysis: September 17 - October 17, 2024 Python & Biopython: September 17 - October 03, 2024 ⏰ Time: 7:00 PM - 8:00 PM IST 🗓 Registration Closes: September 15, 2024 💻 Mode: Online 🎯 Ready to make a difference in your research? Don't miss out on this opportunity to enhance your bioinformatics skills and open new doors in your career. 👉 𝐒𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐘𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐒𝐩𝐨𝐭 𝐓𝐨𝐝𝐚𝐲: https://lnkd.in/grUEakiP For more details/queries, contact: [email protected] Feel free to reach out with any questions! #Bioinformatics#NGSDataAnalysis#Python hashtag#Biopython #TrainingCourses#CareerGrowth#BioinformaticsEducation#Students #OnlineCourses #BioinformaticsTools #ComputationalBiology #ScienceInnovation

#bioinformatics#next generation sequencing#ngs#genomics!#transcriptomics#omics#online courses#handsontraining#python#data analysis
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Immunotherapy#thymic epithelial tumors#bioinformatics#cancer research#precision medicine#transcriptomics#proteomics#immune biomarkers#cancer therapeutics#experimental analysis#tumor microenvironment#oncology innovation#therapeutic targets#immune evasion#TET research#molecular oncology#computational biology#immune checkpoint inhibitors#cancer genomics#personalized treatment.#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Global Europe, Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market: Insights and Market Forecast
The Europe, CIS & Africa spatial transcriptomics market was valued at approximately USD 93.9 million in 2023 and is expected to experience robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.57% from 2024 to 2030. Several key factors are contributing to this growth, including the increasing recognition of spatial omics analysis in cancer research, the introduction of fourth-generation sequencing technologies (such as in-situ sequencing), and a surge in funding and collaborative initiatives aimed at advancing spatial biology research.
A primary driver behind the market expansion is the rising prevalence of cancer. As cancer rates continue to climb, there is an increasing demand for more effective approaches to biomarker discovery, early detection, and precise diagnostics. These advancements are critical for better disease management and more targeted treatment options. Spatial omics analysis, particularly in the field of oncology, has shown considerable promise in addressing these needs. It offers a more nuanced understanding of tumor heterogeneity, supports the identification of potential biomarkers, and helps inform personalized treatment strategies that can be tailored to individual patients.
One of the major advantages of spatial omics technologies is their ability to map the spatial distribution of various cell types within a tumor. This feature is vital for studying the heterogeneity of tumors, which can significantly affect treatment outcomes. A relevant example of this is a study published in Nature in May 2024, where researchers employed both spatial and single-cell transcriptomics to explore the molecular interactions and tumor heterogeneity in colorectal cancer (CRC). By using these advanced techniques, the researchers were able to gain deeper insights into the underlying mechanisms driving CRC progression, showcasing the potential of spatial transcriptomics in improving our understanding of complex diseases like cancer.
Gather more insights about the market drivers, restrains and growth of the Europe, Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market
Country Insights
Europe led the spatial transcriptomics market in 2023, commanding a dominant share of 94.57%. This dominance can be attributed to the region's well-established biotechnology research and development (R&D) sector, its growing emphasis on spatial biology, and the presence of leading industry players. Additionally, substantial investments and funding from both public and private entities have significantly contributed to advancing spatial transcriptomics research and facilitating the commercialization of spatial omics products, further driving market growth.
United Kingdom (UK):
The spatial transcriptomics market in the UK is anticipated to experience significant growth in the coming years. This is largely due to the continuous technological advancements in spatial biology, which are increasingly being applied across various fields such as oncology, neurology, and personalized medicine. A key example of the UK's role in fostering innovation is the 12th Annual Single Cell & Spatial Analysis UK Congress, part of Next Gen Omics 2024, scheduled for October 23-25, 2024, in London. This prominent event will bring together leading experts from around the world to discuss the latest developments, cutting-edge technologies, and future prospects of spatial biology, underscoring the UK's position as a hub for research and innovation in the field.
Germany:
Germany's spatial transcriptomics market is experiencing significant growth, particularly within the broader multi-omics field. The country benefits from active engagement by renowned academic institutions, leading biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and substantial government-backed research funding. For example, in early 2024, the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) hosted a series of events and training courses, focusing on integrating and analyzing multiomics data, further enhancing the country's position in spatial transcriptomics and related fields.
France:
In France, the spatial transcriptomics market is also set to witness strong growth, driven by the increasing adoption of advanced genomic technologies and their expanding applications across diverse fields such as cancer research, drug discovery, and translational research. Moreover, the French government’s continued investment in genomic research initiatives is providing a solid foundation for the market’s development, fostering both innovation and collaboration in the space.
Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) Market Trends
The CIS region, which includes countries such as Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, and Kazakhstan, is expected to see growth in the spatial transcriptomics market. This growth is largely fueled by an increased adoption of advanced genomics and transcriptomics technologies, a growing focus on spatial biology research, and rising demand for more detailed insights into cellular function and organization. These CIS countries are home to several well-established research institutions and academic centers with deep expertise in molecular biology and biotechnology, providing a strong foundation for growth in spatial transcriptomics research and applications.
Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market Trends
South Africa is expected to experience significant growth in the spatial transcriptomics market, driven by an increased demand for improved diagnostic tools that support disease prevention and treatment. The country’s growing healthcare sector, combined with ongoing advancements in genomic technologies, creates a promising landscape for the adoption of spatial transcriptomics.
In contrast, the Nigerian market for spatial transcriptomics remains in its early stages. While there is potential for growth, the market faces challenges due to the high costs associated with specialized equipment and reagents. Additionally, the need for skilled labor to operate these advanced technologies represents another potential barrier to rapid market development. As such, significant investment in infrastructure, training, and research capacity will be necessary to accelerate market growth in Nigeria and other parts of West Africa.
Browse through Grand View Research's Biotechnology Industry Research Reports.
• The global exosomes market size was estimated at USD 177.4 million in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 28.73% from 2025 to 2030.
• The global cell culture media storage containers market size was estimated at USD 2.11 billion in 2024 and is projected to witness a CAGR of 12.55% from 2025 to 2030.
Key Europe, CIS & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Company Insights
Several key players in the spatial transcriptomics market are actively pursuing strategies to strengthen their market presence and expand the reach of their products and services. These strategies primarily include expansion activities and strategic partnerships aimed at advancing research, increasing the commercialization of spatial omics products, and enhancing collaborations between academia and industry. Through these initiatives, companies are not only boosting their market footprint but are also contributing to the broader advancement of spatial biology and transcriptomics technologies.
Key Europe, CIS & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Companies:
• Illumina, Inc.
• Bruker
• 10X Genomics
• EdenRoc Sciences (Cantata Bio, LLC)
• Shimadzu Corporation
• Waters Corporation
• Bio-Techne
• Vizgen Inc.
• Spatial Genomics
• Akoya Biosciences, Inc
Order a free sample PDF of the Europe, Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
#Europe#Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market#Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market Analysis#Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market Report#Cis & Africa Spatial Transcriptomics Market Regional Insights
0 notes
Text
GEO Datasets for Transcriptomics Meta-Analysis: Unlocking Hidden Insights
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical method that enables researchers to combine and analyze data from multiple studies, providing a broader perspective and more robust findings. In transcriptomics research, where the focus is on studying gene expression patterns, meta-analysis plays a crucial role in uncovering molecular signatures that may not be apparent in single studies due to limited sample sizes or variability.
This blog aims to empower transcriptomics researchers by providing insights into effective meta-analysis techniques. By leveraging available transcriptomics databases like GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus), ArrayExpress, and SRA, researchers can enhance their investigations and contribute to scientific progress. Polly, a tool designed to enhance data usability, helps make this data actionable, enabling researchers to streamline their analyses and gain deeper insights.
GEO Datasets for Impactful Meta-Analysis
The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) is an invaluable resource for transcriptomics, offering a vast array of publicly available gene expression data, including microarrays, RNA sequencing, etc. GEO facilitates global data sharing, enabling researchers to explore gene expression patterns, uncover molecular mechanisms, and investigate links to diseases. This collaborative platform encourages data reuse, scientific discovery, and open sharing within the genomics community.
Original Publish
0 notes
Text
RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market Partnering Deals of Key Players 2024 – 2031
The Insight Partners market research RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market Size and Share Report | 2031 is now available for purchase. This report offers an exclusive evaluation of a range of business environment factors impacting market participants. The market information included in this report is assimilated and reliant on a few strategies, for example, PESTLE, Porter's Five, SWOT examination, and market dynamics
RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market is evaluated based on current scenarios and future projections are added keeping the projected period in consideration. This report integrates the valuation of RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market size for esteem (million USD) and volume (K Units). Research analysts have used top-down, bottom-up, primary, and secondary research approaches to evaluate and approve the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market estimation.
Detailed scrutiny of market shares, optional sources, and basic essential sources has been done to integrate only valid facts. This research further reveals strategies to help companies grow in the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market.
Key objectives of this research are:
To contemporary market dynamics including drivers, challenges, threats, and opportunities in the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market.
To analyze the sum and market estimation of the worldwide RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market
Based on key facets, market segments are added.
The competitive analysis covers key market players and their business strategies.
To examine the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market for business probable and strategic outlook.
To review the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market size, key regions and countries, end-users, and statistical details.
To offer strategic recommendations based on the latest market developments, and RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market trends.
Perks of The Insight Partners’ RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market Research
Market Trends: Our report reveals developing RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market trends that are poised to reshape the market preparing businesses with the foresight to retain their competitive edge. This Market research report presents market trends, supply chain analysis, leading participants, and business growth strategies. This research covers technological progress and key developments covering various aspects of the inclusive market. It is valuable market research for existing key players as well as new entrants in the RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market. Through inputs derived from experts, this research attempts to guide future investors about market details and potential returns on investment.
Competitive Landscape: This research reveals key market players, their strategies, and possible areas for differentiation.
Analysts Viewpoint: We have industry-specific experts who add credibility to this report with their exclusive viewpoints based on market understanding and expertise. This report goes further into details of entire business processes and doesn’t restrict to only operational aspects. These insights cover venture economics and include tactics for capital investment, investor funding, and projections of ROIs. Net income and profit loss financial stats are crucial metrics of this RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market report. With these meticulous insights companies can reduce their risks and increase the success rate in the coming decade.
RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics Market Report Coverage:
Report Attributes
Details
Segmental Coverage
Product
Consumables
Instruments
Software Services
Technology
Microarray
Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sequencing Technologies
Application
Diagnostics Disease Profiling
Drug Discovery Others
End User
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
South Central America
and Geography
Regional and Country Coverage
North America (US, Canada, Mexico)
Europe (UK, Germany, France, Russia, Italy, Rest of Europe)
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia, Rest of APAC)
South / South & Central America (Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South/South & Central America)
Middle East & Africa (South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA)
Market Leaders and Key Company Profiles
BioRad Laboratories Inc.
Illumina Inc.
GE Healthcare
F. HoffmannLa Roche Ltd.
Agilent Technologies Inc.
Thermofisher Scientific Inc.
Sigma Aldrich
Qiagen N.V.
Affymetrix Inc.
Fluidigm Corporation
Other key companies
What all adds up to the credibility of this research?
A comprehensive summary of the contemporary RNA Analysis/Transcriptomics market scenario
Precise estimations on market revenue forecasts and CAGR to rationalize resources
Regional coverage to uncover new markets for business
Rivalry analysis aims to help corporations at a modest edge
Facts-based crystal-clear insights for business success
The research can be customized as per business necessities
Access to PDF, and PPT formats of this research
About Us:
The Insight Partners is a one-stop industry research provider of actionable intelligence. We help our clients in getting solutions to their research requirements through our syndicated and consulting research services. We specialize in industries such as Semiconductor and Electronics, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Biotechnology, Healthcare IT, Manufacturing and Construction, Medical Devices, Technology, Media and Telecommunications, Chemicals and Materials.
Contact Us: www.theinsightpartners.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market size#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market share#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market trends#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market analysis#Spatial Genomics & Transcriptomics Market forecast
0 notes
Text
Global Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Increasing Adoption of Spatial Genomics Technologies
Market Overview: Spatial genomics transcriptomics combines the technologies of spatial transcriptomics and genomics to analyze gene expression within the context of tissue architecture. This innovative approach allows researchers to study the spatial organization of gene expression within individual cells, leading to a better understanding of various biological processes and disease mechanisms. The market for spatial genomics transcriptomics is driven by the increasing adoption of these technologies in various research applications, including cancer research, neurobiology, developmental biology, and immunology. The ability to analyze gene expression within the context of tissue architecture provides valuable insights into cell-to-cell interactions, cellular heterogeneity, and spatial relationships, making it a powerful tool for biomedical research. The global Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Size is estimated to be valued at US$ 262.7 million in 2023 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 13% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights. Market Key Trends: One key trend driving the growth of the spatial genomics transcriptomics market is the increasing demand for single-cell analysis. Single-cell analysis allows researchers to study individual cells rather than bulk population samples, providing a deeper understanding of cellular heterogeneity and development. Spatial genomics transcriptomics takes single-cell analysis a step further by incorporating spatial information, enabling researchers to study gene expression within the context of tissue architecture. This integrated approach allows for a more comprehensive analysis of complex biological systems and has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of cellular processes and disease mechanisms. For example, 10x Genomics, one of the key players in the spatial genomics transcriptomics market, offers the Visium Spatial Gene Expression Solution, which enables researchers to analyze gene expression in intact tissue sections. This technology allows for the identification of cell types, mapping of gene expression, and analysis of the spatial relationships between cells. By combining single-cell analysis with spatial information, researchers can gain valuable insights into the role of gene expression in tissue development and disease progression. PEST Analysis: Political: The spatial genomics transcriptomics market is influenced by government regulations and policies regarding genomics research and healthcare. Government funding and support for research initiatives can drive market growth. Economic: The market is driven by increasing investment in genomics research and the growing demand for personalized medicine. The economic factors, such as GDP growth, healthcare expenditure, and disposable income, also impact the adoption of spatial genomics transcriptomics technologies. Social: The growing prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for better diagnostic and treatment options are driving the demand for spatial genomics transcriptomics technologies. The increasing awareness and acceptance of personalized medicine among patients and healthcare professionals are also contributing to market growth. In conclusion, the spatial genomics transcriptomics market is poised for significant growth due to the increasing adoption of these technologies in various research applications. The integration of spatial information with gene expression data provides valuable insights into cellular processes and disease mechanisms, driving the demand for spatial genomics transcriptomics technologies. With advancements in genomics research and technological innovation, this market is set to revolutionize our understanding of biology and contribute to the development of personalized medicine.
#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Size#Coherent Market Insights#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Demand#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Growth#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Trends#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Analysis#Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Forecast
0 notes
Note

The duality of (wo)man
If you're on this blog you're getting both with no brakes. It's what you signed up for.
Now if you'll excuse me, I need to scroll through scantily clad tgirl selfies in between runs of my transcriptomic analysis pipeline.
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reference saved in our archive
An interesting pilot study showing a probable biomarker for long covid.
Abstract
Introduction: Long COVID is a debilitating condition that lasts for more than three months post-infection by SARS–CoV–2. On average, one in ten individuals infected with SARS CoV- 2 develops Long COVID worldwide. A knowledge gap exists in our understanding of the mechanisms, genetic risk factors, and biomarkers that could be associated with Long COVID.
Methods: In this pilot study we used RNA-Seq to quantify the transcriptomes of peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from COVID-recovered individuals, seven with and seven without Long COVID symptoms (age- and sex-matched individuals), on average 6 months after infection.
Results: Seventy genes were identified as significantly up- or down-regulated in Long COVID samples, and the vast majority were downregulated. The most significantly up- or downregulated genes fell into two main categories, either associated with cell survival or with inflammation. This included genes such as ICOS (FDR p = 0.024) and S1PR1 (FDR p = 0.019) that were both up-regulated, indicating that a pro-inflammatory state is sustained in Long COVID PBMCs compared with COVID recovered PBMCs. Functional enrichment analysis identified that immune-related functions were expectedly predominant among the up- or down-regulated genes. The most frequently downregulated genes in significantly altered functional categories were two leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptors LILRB1 (FDR p = 0.005) and LILRB2 (FDR p = 0.027). PCA analysis demonstrated that LILRB1 and LILRB2 expression discriminated all of the Long COVID samples from COVID recovered samples.
Discussion: Downregulation of these inhibitory receptors similarly indicates a sustained pro-inflammatory state in Long COVID PBMCs. LILRB1 and LILRB2 should be validated as prospective biomarkers of Long COVID in larger cohorts, over time and against clinically overlapping conditions.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid is not over
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

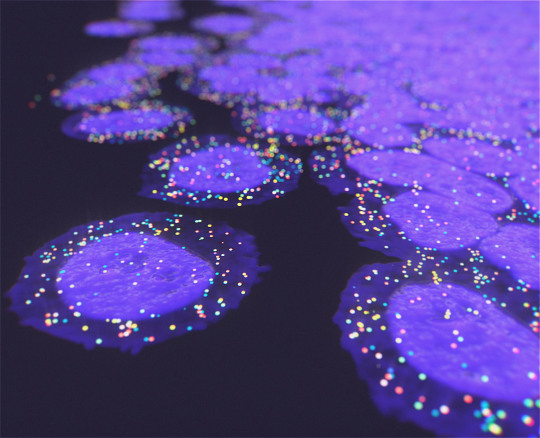
Abreast with Cells
Characterisation of the 12 cell types that make up the human breast by profiling their gene activity (transcriptome). This analysis provides a resource which both distinguishes them and reveals the biological processes in which they participate
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Katelyn Del Toro and Rosalyn Sayaman, and colleagues
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in PLOS Biology, November 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
6 notes
·
View notes
Link
RNA sequencing is currently a useful tool for studying the dynamic transcriptional mechanisms that control the operation of eukaryotic cells. Nevertheless, complicated experimental designs with various biological variables and multiple analysis time points cannot be automatically analyzed by the tools that are currently on the market for the analysis of raw sequencing data. Multiple programs are combined into a single framework by the MultiRNAflow suite by researchers from the University of Lorraine, France, enabling supervised and exploratory statistical analysis of temporal data for various biological situations. Nuclear DNA genes in eukaryotic cells are translated into messenger RNA molecules prior to being translated into proteins that maintain normal cellular activities. Stochastic events that impact transcription during cell dormancy cause a transcriptional noise within the cell. Thousands of genes are triggered upon changes to the cellular environment (such as receptor activation or cellular stress), which causes a dynamic, transient transcriptional response that enables the cells to adjust to the initial environmental disturbance.
Continue Reading
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Antarctic moss proves cold weather isnt just for penguins
Antarctic moss proves cold weather isn’t just for penguins https://ift.tt/LciIb3E Mosses, which often go unnoticed in gardens and forests, have demonstrated an outstanding ability to adapt to extreme environments. Among them, Antarctic mosses are particularly interesting due to their resilience in one of the most challenging climates on Earth. Despite the freezing temperatures, prolonged drought, and intense ultraviolet radiation, these plants not only survive but also exhibit active growth during a brief summer season. Now, new research published in AoB PLANTS, shows that some Antarctic mosses adapt to these conditions by increasing the expression of genes related to lipid metabolism and the accumulation of unsaturated fatty acids. In this new study, the research team from Niigata University in Japan, focused on Bryum pseudotriquetrum, one of the more common mosses found in Antarctica. By employing transcriptome analyses, they explored how this species adapts to its challenging surroundings, particularly in comparison to controlled artificial conditions at 15°C. The research generated 88,205 contigs through de novo assembly, which represent the diverse array of genes expressed by this moss species. The analysis unveiled that under natural Antarctic field conditions 1,377 genes were upregulated, while 435 were downregulated when compared to those grown in more temperate, artificially controlled settings. But what does this mean for the moss’s survival? The upregulated genes included several related to lipid metabolism and the formation of oil bodies, two critical components that play a vital role in plants’ ability to cope with stress. Lipid metabolism is crucial for plants, especially in extreme environments where maintaining cellular integrity is essential. The study found that the expression levels of these lipid-related genes increased significantly in response to various artificial stress treatments, including low temperatures, salt exposure, and osmotic stress. This suggests that Bryum pseudotriquetrum has evolved mechanisms to change its lipid profiles in response to environmental challenges. Interestingly, the researchers observed that mosses grown in Antarctic conditions contained elevated levels of fatty acids, particularly α-linolenic acid, linolenic acid, and arachidonic acid and a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids. These fatty acids play a key role in maintaining membrane fluidity, and thus support cellular function in cold environments where membranes might otherwise become rigid. In the present study, RNA-seq analysis was carried out in the common moss Bryum pseudotriquetrum and genes related to lipid metabolism and oil body formation were found to be highly expressed in field samples. In plant cells, lipid accumulation and changes in fatty acid composition are important mechanisms for acquiring environmental stress tolerance. Thus, these genes may be involved in multiple stress tolerance in Bryum pseudotriquetrum growing in Antarctica. This study marks a significant advance in our understanding of how some plants respond to the extreme conditions of their native habitats. By providing the first gene expression profiles for mosses grown directly under Antarctic field conditions, it highlights the role of lipid metabolism and fatty acid composition in stress tolerance. The results also highlight the importance of in situ studies for understanding the mechanisms of plant resilience in stressed environments. READ THE ARTICLE Otani N., Kitamura H., Kudoh S., Imura S. and Nakano M. (2024) “Transcriptome analysis of the common moss Bryum pseudotriquetrum grown under Antarctic field condition” AoB PLANTS. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plae043 Cover image by HermannSchachner – Own work, CC0, Link The post Antarctic moss proves cold weather isn’t just for penguins appeared first on Botany One. via Botany One https://botany.one/ October 23, 2024 at 03:30PM
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Continuous presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, particularly antisense ORF1ab RNA, suggests the virus may remain active long after initial infection. This could explain some of the persistent symptoms of long COVID
If you would like an analysis of this study please read the twitter thread below.

3 notes
·
View notes