#the fact that Moses from the Bible
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
brain tired from Latin so have an appreciation post for humanity
#lol such a terrible way to begin that#anyways i think that humanity is so beautiful#my reason being the fact that bluegrass exists#two seemingly unrelated subjects lol#hear me out:#bluegrass lyrics are what they are because no matter what time on earth you lived they will be relatable#that's what makes bluegrass beautiful#it's vague enough with terms to not be time-specific#but it's also so so specific about emotions and stuff that doesn't change over the millenia#and this is where i connect the dots#the fact that Moses from the Bible#Alexander the Great#some peasant in the 1500s#a small-town duke in the middle of the 9th century#and you sitting here on your device#can all share emotions and anger and joy and thoughts and questions#is truly beautiful#Diogenes the Cynic probably made some people laugh a lot when he did the whole 'behold a man' thingy#just the same as you laugh at cat videos or funny mistakes every day (with no harm intended either)#it's so cool#and i love it so much#humanity's tools and views may have changed#but at the heart of it all lies the human heart#connecting us and bringing us in as a scoiety#if you read this you're amazing lol <333#the talkies tag
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Won't You Suffer for the Angels to Fly?
➔ Joel Miller x fem!Reader - 2k
➔ Joel finds religion in the last place he expected to--a preacher's daughter.
➔ Rated MA for pure blasphemy. a lot of religious imagery and defiling of holy places--please read at your own risk. unprotected p in v sex, creampie, squirting, fingering (f receiving), corruption kink, HEFTY age gap (r is early 20s [unspecified], joel is 56), reader uses feminine pronouns and has female anatomy [please let me know if i missed anything at all :)]
➔ this is for my mid to plus!sized readers :) you're beautiful and valid and i love you. this was written in basically one sitting after i binged mike flanagan's midnight mass in one night. thank you to my lovelies @ramblers-lets-get-ramblin and @shakespeareanwannabe for talking me through this <3 title is from "heaven only knows" by bob moses

The Bible teaches–at least according to what Joel was able to gleam from the Easter service–that everything happens for a reason. That every pelting raindrop in its descent from the sky, even before it lands heavy and dark in his hair or soaks the lush green landscape of Jackson, has a purpose.
He’s struggled a lot with purpose ever since hearing that existential crisis-inspiring sermon that Tommy had dragged him to.
In the preacher’s defense, it went over well with everyone else. So many people are lost nowadays, adrift in a world that doesn’t seem to have space for them. They need that hope, that reassurance that they’re here for a reason. That they’ve survived hell on earth not out of luck, but out of purpose. He pulled out the big gun that everyone needed to hear on one of the two days a year that everyone in Jackson has their ears open to him. It was tactful, and Joel has to acknowledge that. Your father is clever, if not cunning.
It’s a trait that you’ve learned directly from him, whether purposeful or not. But you sat right in the front row and nodded along to every word, accepting without thought or conflict that purpose is in every action, every reaction, every change of tide and every gust of wind.
And if everything has a purpose, your purpose must be to torture him.
You never have anything but a smile on your face for Joel. Joel, a man older than your own father, a man whose hands have broken every commandment that you hold so dear. A man that should know better than to let you get under his skin and infect his dreams.
He wonders what it would be like to hold someone so perfectly untainted in hands that have killed and destroyed and sinned. Hands that are strong, hands that are experienced, hands that are greedy. He’s certain he could teach you all about greed. He could make you beg, plead, sob for more and more and more until the only thought remaining in your pretty little head is how much you want to take from him. Until you become a glutton at the altar of his generosity.
And oh, how generous he could be once he had you begging. Minding your manners and asking nicely for what you need, of course, but he would never deny you anything you asked of him.
“Can I help you with that, Mr. Miller?” He hadn’t even noticed he was struggling–and he wouldn’t be, really, if he wasn’t so distracted. Putting new legs on a pew isn’t the issue after all; it’s the fact that you’re sitting there on the stairs that lead up to the altar and absentmindedly swinging your legs as if you’re taunting him. As if you understand that his resolve is slipping with every passing second he’s alone in this room with you.
“Joel.”
“Hmm?” You shift your posture to lean closer, and that skirt that’s already way too short to be worn by the pastor’s daughter, in a house of God of all places, rides just a little further up your deliciously full thighs.
How is he expected to work, to keep his mind on the job, when all he wants is to know what those thighs might feel like wrapped around his head?
He clears his throat and adjusts “You can call me Joel, sweetheart.”
He sees it, then. It’s so subtle, but it’s not imagined. You squirm at the pet name, at the raspy drawl of his voice, and it changes everything for him.
He sees in his mind the sweet girl, barely out of her teens, who sits in the front pew with a Bible in her lap. He sees the girl who sings so sweetly to the tune of every hymn. He sees the girl who’s so shy that she blushes every time she catches his gaze.
And then he sees everything underneath the act. He sees the girl who’s bold enough to wear a bright red dress to the Easter service. He sees the girl who makes eye contact with him across the dining hall every night to watch the way he reacts to her lips wrapped so tantalizingly smoothly around her spoon. He sees the girl who knew he would be alone in the chapel today–the girl who wore an easily accessible skirt just for the occasion.
You bookmark the page you’re on and set down the book you were reading, eyes fixated on him all the while. “Is there something I can help with, Joel?”
There certainly is, and it’s not the pew he’s supposed to be repairing.
He remembers, vaguely, hearing something about how God spares guilt from sinners when sin is necessary. It must be necessary to teach you a lesson, then–as you stride over and kneel beside him, your eyes heavy with anticipation and lashes fluttering, he doesn’t feel an ounce of guilt.
“Hasn’t your daddy taught you not to dress like this?” He takes the hem of your skirt idly in his hand, rubs the silky fabric between his thumb and forefinger. He’s not touching you, not really, but his hand is so achingly close. An inch or two, and he’d feel your warmth–those plush thighs that God created to rule over Joel Miller’s mind, body, and soul; ‘til death does he finally know peace, amen.
You shake your head and even manage to seem smug as you say, “No. He just teaches everyone else to resist temptation.”
“I’ve never been much good at that,” he murmurs.
He thinks that you know that. He thinks that you’re his crucible, his most important moral trial–that maybe, if he can turn you away now, he’s a good man.
Joel Miller is not a good man. His kiss is crushing. It’s hellfire, it’s brimstone, it’s everything you’ve been taught to fear your entire life. You melt into it so prettily, accepting your damnation with parted lips and eager eyes. A wanton moan gets caught in your throat when his hand slips further up your skirt.
No panties–in a place of worship, no less. He should bend you over his knee for this transgression, make sure you understand how filthy you are. But there’s hardly time for that now, not when he’s even more desperate than you are. And you are desperate–dripping down his fingers into the palm of his hand as your teeth leave perfect little indents in the plush skin of your bottom lip.
His free hand grips your chin firmly, guiding your eyes to his. He wants to see your depravity, the flickering embers of lust in your eyes as you come on his fingers and cry out for salvation from the all-consuming pleasure.
“Oh my God–”
His hand tightens around your jaw just the slightest bit in warning. “No, baby. You moan my name when I’m touchin’ you.”
And you do–thighs trembling, eyes watering, you cry out his name like a prayer as your cunt pulses and squeezes around his willing fingers.
There’s an unpracticed tremble to your hand as you reach to work open his belt, and it makes his cock throb under the confining material of his jeans.
You want every inch of his skin pressed against yours, so desperate for it that you’re nearly in tears when he pulls your fingers away from the buttons on his shirt. He’s not foolish–no one steps foot into this place during the week, but he knows better than to tempt God’s sense of humor. This has to be quick and contained, and you know it too; you picked your little skirt for exactly that reason.
He catches a glimpse of your glistening need as you settle over his thighs, and once again he battles to resist temptation. He whispers in your ear as you settle your chest against his and grind that fluttering, sensitive cunt along his length–promises himself more than you, really, that he’ll bury his face in your folds and drink from you next time. Next time–the promise makes you clench impossibly hard around nothing.
His eyes have never been quite as heavy as they are when you start to sink that dripping heat down his cock. Head tipped back, throat exposed, completely at your mercy. He has to force himself to look up at you–to worship the goddess enshrined on his altar, all his for the taking.
You bite into your lip nearly hard enough to draw blood as your hips settle against his, completely overwhelmed by the burning stretch of his size. He’s a challenge, certainly, but one that you are determined to overcome.
“Easy, baby girl,” he grumbles as you start to rock against him before you’re truly accommodated. His hands rest heavy on your hips–not anchoring, but encouraging. As wrong–as depraved–as this may be, he wants you to enjoy it without pain. “That’s right, nice and slow.”
It doesn’t stay that way, though; the desperation mounts to a boiling point until you’re bouncing fervently in his lap. It’s delicious, the way the thick head of him drags against something deep and sensitive within you. He guides you when your thighs start to burn, grip tightening enough to leave forbidden bruises in the soft flesh of your hips. His mouth presses to yours, breathing the oxygen straight from your lungs as he presses his hips up. There’s nothing you can do but take it, pliant in his hold, head rolling back to accommodate the wet drag of his mouth and the tickling scratch of his beard against your throat.
He feels it before you do–a subtle flutter as your cunt tries sucking him in even deeper. And maybe, if he was a good man, he’d lean away from it and have mercy on you. But he’s not a good man–he’s a greedy, wanton, desperate man. He angles his hips and thrusts as hard as he can, shoving you into your release with force.
You overflow with it; gushing over him like a flood, staining his hastily pushed down jeans and the floorboards beneath.
He pushes you onto your back like you’re weightless, adrenaline coursing as he starts to slam into you. It’s not polite or sweet or loving–he fucks into you and empties himself like an animal. He growls deep in his throat as his cock pulses within you, instructing you to “take it, baby girl” as if you’d consider anything less.
You don’t know where your release ends and his begins. All you know is his weight on top of you, his mouth on your jaw, the collective breathless pants that fill the room as you both come down together.
You’re not sure how long it is before he pulls out of your warmth with an actual whine, breath heavy against your neck where his face is so comfortably nestled.
And you start to laugh, because you wish you’d worn panties after all–you don’t know how you’re going to get home with the mess of cum that’s dripping down the curve of your ass.
He even chuckles with you, until he tears his eyes away from your blissed face and sees the cross hanging heavy on the far wall.
“Th-that…” he gulps. “That can’t happen again.”
“It can,” you assure him, and he supposes you’re right.
You keep your head down and your eyes to yourself on Sunday, even as you spot the barely-noticeable stain on the hardwood floor next to the newly-repaired pew on the right side of the aisle. It’s so faint that no one would notice it unless they were looking for it, but it’s glaringly obvious to you. You should be ashamed; you should be begging for forgiveness. But then you meet Joel’s watchful eyes, and the shame washes away. How can you feel guilty over an act of worship?
THE END
➔ Want to see more from me in the future? Follow @freelancearsonist-updates and turn on post notifications to be notified when I post new fics!
➔ Want to support me? Please reblog this fic! It helps boost it in the algorithm and gives it more circulation no matter what your follower count is :)
#joel miller#joel miller x reader#joel miller fanfiction#joel miller smut#joel miller one shot#the last of us#the last of us fanfiction#the last of us smut#the last of us one shot#joel tlou#cece writes
798 notes
·
View notes
Note
in that post about palestinians being descendants of the ancient canaanites, one of the additions claimed that jews founded an empire is that true?
No, that's not true. Jews and Palestinians share the same ancestry in that they all are descendants from the Ancient Canaanites. The idea that Jews are conquerors stems from the Biblical narrative that the B'net Yisrael or Children of Israel committed genocide against the indigenous people (or Amalekites) of the Holy Land following the Exodus upon Moses' (a) death. But even if one was to take that narrative, the Israelite nation started with Jacob (a), who at that time, lived in the Holy Land. None of these are supported by any archeological findings. The Bible may have some historicy to it, but claiming that the Bible is a primary source for Ancient Israelite history should be taken with intense scrutiny.
The matter of fact is that Jewish people have had a continuous presence in the Holy Land, and therefore the Palestinians have too. Like I've said, the Palestinians can trace their roots back to before the Arab expansion. They were arabized following the Arab conquest and assimilated to Arab culture, traditions, language and etc. This does not erase your indigeneity.
192 notes
·
View notes
Text
history of the hebrew bible
—1250-1000 bce israel emerges in the highlands of canaan, holding oral narratives of the pentateuch (abraham, if historical, ca. 1800, moses ca. 1250)
—1050 bce the united monarchy forms. saul's reign ca. 1050. david's ca. 1000. solomon's ca. 960. the latter erects the temple. the first former prophets are summoned
—ca 950 bce the oral narrative of the pentateuch is recorded in hebrew. some scholars name this earliest source the yahwist
—922 bce the kingdoms separate into israel in the north (capital samaria) and judah in the south (capital jerusalem). more former prophets are summoned, as well as the latter and the twelve
—ca 850 bce the so-called elohist source records oral narratives of the pentateuch. they may have access to the yahwist source
—722/21 bce assyria ruins samaria, exiles population. this exile affects prophets from the north such as amos and hosea
—621 bce josiah "finds" a scroll in the temple. this deuteronomist source reifies his reforms
—606 babylon and medes ruin nineveh
—597-596 bce babylon ruins jerusalem, namely, the temple. exiles population. this exile affects prophets from the south such as ezekiel and jeremiah
—ca 550 bce the priestly source, keen on re-membering in the midst of exile, records oral narratives of pentateuch. they made use of earlier written sources (so-called j, e, and d sources). some scholars suggest most, if not all, of the hebrew narrative is in fact recorded in this exile period
—539 bce persia ruins babylon, returns judean exiles, allows for temple to be rebuilt
—520-515 bce the temple rebuilt in jerusalem. this starts the 'second temple period'
—400 bce the torah section of the canon reaches its final form
—336-323 bce alexander the great ruins persia
—312-198 bce ptolemies of egypt reign over judah. the dead sea scrolls are composed ca. 300-100 bce. seleucids conquer jerusalem ca. 198
—200s bce LXX is composed in greek. the prophets section of the canon reaches its final form
—168/167 bce syria reigns over jerusalem. maccabean revolt
—33 ce a rabbi from nazareth with kind eyes hangs on a cross
—40s-60s ce a pharisee falls off a horse, sends letters to house churches (pauline epistles)
—66-70 ce the second temple is destroyed
—60s-110s the four gospels of the second testament are written. a fifth one, named q, may or may not be lost at this time
—100 ce the writings section of the canon reaches its final form
—300-400 ce codex vaticanus and codex sinaiticus composed
—600-900 ce the MT is rendered. hebrew is afforded vowels, finally. aleppo codex and cairo codex composed
#for anon#these are wellhausen's dates and for the record i dont subscribe wholly to any four source hypothesis but for the sake of our final exam#which i hope youre studying for#its good to know these#faq
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Islam was the second religion to emanate from Judaism, but as its founder was not a Jew and as it was not originally a Jewish sect, Islam's encounter with Judaism was significantly less bitter than Christianity's. As Salo Baron notes: "It was, therefore, from the beginning, a struggle between strangers, rather than an internecine strife among brethren." Largely because of this factor, Jews in the Islamic world were rarely persecuted as violently as their brethren in the Christian world. S. D. Goitein, perhaps the twentieth century's leading historian of Jewish life in the Arab world, concludes: "when the known facts are weighed, I believe it correct to say that as a whole the position of the non-Muslims [Christians and Jews under medieval Islamic rule] was far better than that of the Jews in medieval Christian Europe."
Goitein's assessment is valid, but it tells us much more about the Jews' condition under Christians than about their treatment by Muslims. For while the Jews of the Muslim world may have rarely experienced the tortures, pogroms, and expulsions that typified Jewish life under medieval Christian rule, their life under Islam was usually a life of degradation and insecurity. At the whim of a Muslim leader, a synagogue would be destroyed, Jewish orphans would be forcibly converted to Islam, or Jews would be forced to pay even more excessive taxes than usual.
Like Christianity's, Islam's anti-Judaism is deeply rooted. Islam too was born from the womb of Judaism; it too was rejected by the Jews whose validation was sought; and it too suffered an identity crisis vis-a-vis Judaism.
When Islam was born in the seventh century, there was a substantial Jewish population in Medina, where the first Muslim community arose. The Jews of pre-Islamic Arabia were active advocates of their religion, to such an extent that several kings of Himyar, now Yemen, converted to Judaism. Contemporary inscriptions described Dhu Nuwas As'ar, the last Jewish king of Himyar, as a believer in one deity whom the king called Rahman, the Merciful One, as called in Judaism and later in Islam.
During his early years, Muhammad related well to the Jews of Arabia, and their religious practices and ideas deeply influenced him. As Goitein noted: "The intrinsic values of the belief in one God, the creator of the world, the God of Justice and mercy, before whom everyone high and low bears responsibility came to Muhammad, as he never ceased to emphasized, from Israel."
The profound influence of the Jews, their Bible, and their laws on Muhammad is clearly expressed in the Koran, the Muslim bible, and in Muhammad's early religious legislation. Indeed, Muhammad saw himself as another Moses. In the Koran, he writes of his message (Sura 46, verse 12), "Before it the book of Moses was revealed....This Book confirms it. It is revealed in the Arabic tongue." Moses is a dominant figure on the Koran, in which he is mentioned over one hundred times.The Jewish doctrine that most deeply influenced Muhammad was monotheism: "There is no God but God." Muhammad's monotheism was so attuned to the uncompromising nature of Judaism's monotheism that though he had also been influenced by Christian teachers, he rejected the Christian trinity and the divinity of Jesus as not monotheistic: "Unbelievers are those that say, 'Allah is one of three.' There is but one God. If they do not desist from so saying, those of them that disbelieve shall be sternly punished" (5:71-73).
Jewish law also deeply influenced Muhammad. In the early days of Islam, Muslims prayed in the direction of the Jews' holy city, Jerusalem, and observed the most solemn Jewish holiday, Yom Kippur, the Day of Atonement. Only later, when Muhammad reluctantly concluded that the Jews would not embrace him as their prophet and convert to Islam, did he substitute Mecca for Jerusalem, and the fast of Ramadan for Yom Kippur. Similarly, Muhammad based Muslim dietary laws upon Judaism's laws of Kashrut: "You are forbidden carrion, blood, and the flesh of swine; also any flesh...of animals sacrificed to idols." The five daily prayers of Islam are likewise modeled on the three daily services of the Jews.
Second in importance only to his adoption of the Jews' God was Muhammad's adoption of the Jews' founding father, Abraham, as Islam's founder. In Sura 2, verse 125, Muhammad writes how Abraham and his son Ishmael converted the Kaaba, the holy rock of Arabian paganism, into the holy shrine of Islam.
Believing himself to be the final and greatest prophet of Mosaic monotheism, and having adopted so much of Jewish thought and practice, Muhammad appealed to the Jews of Arabia to recognize his role and to adopt Islam as the culmination of Judaism. "Even Luther," the late renowned philosopher Walter Kaufmann wrote, "expected the Jews to be converted by his version of Christianity, although he placed faith in Christ at the center of his teaching and firmly believed in the trinity. If even Luther...could expect that, how much more Muhammad, whose early revelations were so much closer to Judaism?" Muhammad's deep desire for Jewish recognition reflected the similar needs of Jesus and his followers. No group could validate Muhammad's religious claims as could the Jews, nor could any so seriously threaten to undermine them.
The Jews rejected Muhammad's claims as they had Jesus', holding in both cases that what was true in their messages was not new, and that what was new was not true. Islam may have served as a religious advance for Arabian pagans, but for the Jews it was merely another offshoot of Judaism.
One major factor that rendered Muhammad's prophetic claims untenable to Jews was his ignorance of the Bible. In large part because Muhammad never read the Bible, but only heard Bible stories, his references to the Jews' holy text were often erroneous. In Sura 28:38, for instance, he had Pharaoh (from Exodus) ask Haman (of the Book of Esther) to erect the Tower of Babel (which appears at the beginning of Genesis).
Another obstacle to Jewish acceptance of Muhammad was the moral quality of some of his teachings. They did not strike the Jews, or the Arabian Christians, as equaling, let alone superceding, the prophetic teachings of Judaism or Christianity. In 33:50, for example, Muhammad exempts himself from his own law limiting a man to four wives, and in 4:34 he instructs men to beat disobedient wives. Walter Kaufmann notes that "there is much more like this, especially in the 33rd Sura," and that "it must have struck the Jews as being a far cry from Amos and Jeremiah, and the Christians as rendering absurd the prophet's claim that he was superseding Jesus."
Finally, Muhammad's suspension of many Torah Laws invalidated him in the Jews' eyes.
For these and other reasons, the Jews rejected Muhammad's prophetic claims and refused to become Muslims. This alone infuriated Muhammad. But it was even more infuriating that the Jews publicly noted the errors in Muhammad's biblical teachings and may have even ridiculed his claims to prophecy. Goitein concludes, "it is only natural that Muhammad could not tolerate as a neighbor a large monotheistic community which categorically denied his claim as a prophet, and probably also ridiculed his inevitable blunders."
As a result Muhammad turned against the Jews and their religion, and never forgave them for not becoming his followers. And just as early Christian hostility to the Jews was canonized in the New Testament, so Muhammad's angry reactions to the Jews were recorded in the Koran. these writings gave Muslims throughout history a seemingly divinely-sanctioned antipathy to the Jews.
In the Koran, Muhammad attacked the Jews and attempted to invalidate Judaism in several ways. First, and most significantly, he changed Abraham from a Jew to a Muslim: "Abraham was neither Jew nor Christian. [He] surrendered himself to Allah....Surely the men who are nearest to Abraham are those who follow him, this Prophet" (3:67-68).
Second, he condemned the Jews and delegitimized their law by advancing a thesis similar to Paul's, that the many Torah laws had been given to the Jews as punishment for their sins: "Because of their iniquity we forbade the Jews good things which were formerly allowed them" (4:160).
Third, Muhammad charged the Jews with falsifying their Bible by deliberately omitting prophecies of his coming. For example, in the Koran (2:129), Muhammad has Abraham mouth a prophecy of his (Muhammad's) coming. Muhammad charged that the Jews "extinguish the light of Allah" (9:32) by having removed such prophecies from their Bible.
Fourth, Muhammad asserted that Jews, like Christians, were not true monotheists, a charge he substantiated by claiming that the Jews believed the prophet Ezra to be the Son of God. "And the Jews say: Ezra is the son of Allah...Allah fights against them. How perverse are they." (9:30).
These anti-Jewish fabrications, articulated by Muhammad as reactions to the Jews' rejection of him, have ever since been regarded by Muslims as God's word. Though originally directed against specific Jews of a specific time, these statements often have been understood by succeeding generations as referring to all Jews at all times, and thus form the basis of Islamic antisemitism.
One common example is 2:61: "And humiliation and wretchedness were stamped upon them and they were visited with wrath from Allah. That was because they disbelieved in Allah's revelations and slew the prophets wrongfully.j That was for their disobedience and transgression." This Koranic description of the Jews of seventh-century Arabia has often been cited by Muslims to describe Jews to this day. *
(* In a speech before his army officers on April 25, 1972, the late Egyptian President Anwar as-Sadat cited this Koranic verse, and then added: "The most splendid thing our prophet Muhammad, God's peace and blessing on him, did was to evict them [the Jews] from the entire Arabian peninsula...I pledge to you that we will celebrate on the next anniversary, God willing and on this place with God's help, not only the liberation of our land but also the defeat of the Israeli conceit and arrogance so that they must once again return to the condition decreed in our holy book: 'humiliation and wretchedness were stamped upon them'...We will not renounce this.")
Muhammad and the Koran thus laid the basis for subsequent antisemitism just as the early Christians had - and for basically the same reason: Jews remaining Jewish constituted a living refutation of Islamic beliefs. Thus, under Islam, just as under Christianity, Jew-hatred was ultimately Judaism-hatred. Any Jew who converted to Islam was accepted as an equal.
Christians under Muslim rule fared little better. Muslims and their laws generally dealt harshly with both Christians and Jews.
As long as Christian communities survived in the Muslim world, discriminatory legislation also applied to them as well. However, whereas Jewish communities often flourished as vibrant Jewish communities, Christian communities for the most part did not survive the intense Muslim hostility. Under the yoke of MUslim laws against Jews and Christians, hundreds of thousands of people in some of the oldest and strongest Christian communities in the world converted to Islam.
No fact better underscores the intensity of Muslim persecution of dhimmis (non-Muslim monotheists) than this disappearance of so many Christian communities under Islam. The fact that under similar conditions many Jewish communities flourished bears witness to the Jews' tenacious commitment to Judaism, not to Muslim benevolence toward them. This is often lost sight of when favorably comparing Muslim antisemitism with Christian antisemitism. Yet the conversion to Islam of nearly every pre-Islamic Christian community in the Muslim world (the Copts of Egypt constituting the most notable exception) eloquently testifies to what Jews had to endure in their long sojourn through the Muslim world.
The two guiding principles of Islam's treatment of Jews and Christians are that Islam dominates and is not dominated, and that Jews and Christians are to be subservient and degraded. Nonmonotheists were usually given the choice of conversion to Islam or death.
The Muslim legal code that prescribed the treatment of Jews and Christians, or dhimmis as they are both referred to in Islam, was the Pact of Umar, attributed to Muhammad's second successor, but assumed to date from about 720. Its key characteristic was the requirement that dhimmis always acknowledge their subservient position to Muslims. Jews and Christians had to pledge, for example, "We shall not manifest our religion publicly nor convert anyone to it. We shall not prevent any of our kin from entering Islam if they wish it." The subservience that dhimmis were required to show publicly to Muslims is analogous to the behavior once expected of Blacks in the Jim Crow American South: "We shall show respect...and we shall rise from our seats when they [Muslims] wish to sit." They also had to pledge "not to mount saddles," since riding a horse, or, according to some Muslims, any animal, was considered incompatible with the low status of a dhimmi. The dhimmis also had to vow "We shall not display our crosses or our books in the roads or markets of the Muslims nor shall we raise our voices when following our dead."
Anti-dhimmi legislation did not end with the Pact of Umar. In the Koran, Muhammad had urged Muslims, "Fight against such of those who have been given the Scripture...and follow not the religion of truth, until they pay the tribute readily, being brought low" (9:29). Accordingly, Muslim officials often insisted that when paying tribute, dhimmis must be "brought low," that is, humiliated.
An early Muslim regulation precisely prescribed how to humiliate Jews and Christians when they pay tribute: "The dhimmi, Christian or Jew, goes on a fixed day in person to the emir, appointed to receive the poll tax, who occupies a high throne-like seat. The dhimmi stands before him, offering the poll tax on his open palm. The emir takes it so that his hand is on top and the dhimmi's underneath. Then the emir gives him a blow on the neck, and a guard, standing upright before the emir, drives him roughly away The same procedure is followed with the second, third, and the following taxpayers. The public is admitted to enjoy this show." The public was not merely "admitted" to this humiliating spectacle, but as Baron observes, "Public participation was, indeed, essential for the purpose of demonstrating, according to the Shafi'ite school, the political superiority of Islam."
In the course of time Muslim rulers developed additional ways to humiliate dhimmis. Baron describes one of them: "Equally vexatious was the tax receipt, which in accordance with an old Babylonian custom, was sometimes stamped upon the neck of the 'unbelieving' taxpayer. This ancient mark of slavery...expressly prohibited in the Talmud under the sanction of the slave's forcible emancipation, occasionally reappeared here as a degrading stamp of 'infidelity.'"
These humiliating and painful procedures had a terrible effect on the Jews: "An Arab poet rightly spoke of entering the door with bent heads 'as if we were Jews.'"
Another law designed to humiliate dhimmis required them to wear different clothing. The purposes of this law were to enable Muslims to recognize Jews and Christians at all times, and to make them appear foolish. In 807, the Abbasid Caliph Haroun al-Raschid, legislated that Jews must wear a yellow belt and a tall conical cap. This Muslim decree provided the model for the yellow badge associated with the degradation of Jews in Christian Europe and most recently imposed by the Nazis.
A Jew living in Baghdad in the days of Al-Muqtadir (1075-96) described additional measures passed by the vizier, Abu Shuja, to humiliate Jews: "each Jew had to have a stamp of lead...hang from his neck, on which the word dhimmi was inscribed. On women he likewise imposed two distinguishing marks: the shoes worn by each woman had to be one red and one black. She also had to carry on her neck or attached to her shoe a small brass bell...And the Gentiles used to ridicule Jews, the mob and children often assaulting Jews in all the streets of Baghdad.
During the same century in Egypt, the Fatimid Caliph Hakim ordered Christians to wear a cross with arms two feet long, while Jews were ordered to wear around their necks balls weighing five pounds, to commemorate the calf's head that their ancestors had once worshiped.
These clothing regulations were not only enforced in the Middle Ages. Until their departure from Yemen in 1948, all Jews, men and women alike, were compelled to dress like beggars.
In fact, Yemen offers us a unique opportunity to understand Muslim attitudes toward the Jews. For it was the one Muslim country with a non-Muslim minority (Jews) that was never ruled by a European power. It was therefore able to treat its Jews in the "purest" Muslim manner, uninfluenced by non-Muslim domination.
In 1679, Jews in most of Yemen were expelled from their cities and villages. When allowed to come back a year later, they were not allowed to return to their homes, but were forced to settle in Jewish settlements outside of the cities. During their expulsion the synagogue of San'a, the capital, was converted into a mosque, which still exists under the name Masjid al-Jala (the Mosque of the Expulsion).
Among the many indignities to which the Jews of Yemen were constantly subjected was the throwing of stones at them by Muslim children, a practice that was religiously sanctioned. When Turkish officials (the Turks occupied Yemen in 1872) asked an assembly of Muslim leaders to see that this practice be stopped, an elderly Muslim scholar responded that throwing rocks at Jews was an Ada, an old religious custom, and thus it was unlawful to forbid it.
The greatest recurrent suffering that Yemenite Jews experienced was th e forced conversion to Islam of Jewish children whose fathers had died. This was practiced until the Jews fled Yemen in 1948, and was also based upon Islamic doctrine. Muhammad was believed to have said, "Everyone is born in a state of natural religion [Islam]. It is only his parents who make a Jew or Christian out of him." Accordingly, a person should grow up in the "natural religion" of Islam.
When a Jewish father died, there was often a "race" between Jewish communal leaders who sought to place the man's children with Jewish parents and the Muslim authorities who wanted to convert the children to Islam and place them in Muslim homes (in the Yemenite Islamic culture it would appear that the surviving mother was regarded as irrelevant). The Jews often lost. Goitein reports that "many families arrived in Israel with one or more of their children lost to them, and I have heard of some widows who have been bereaved in this way of all their offspring."
Yet as persecuted as the Yemenite Jews were, they were also denied the right to leave the country.
By the nineteenth century, the Jews' situation under Islam went from degradation to being recurrent victims of violence - as these examples from Jewish life in Egypt, Syria, and Palestine illustrate.
Egypt
In his authoritative book, An Account of the Manners and Customs of the Modern Egyyptisns, Edward Lane wrote that, at the time of his study (1833-35), the Jews were living "under a less oppressive government in Egypt than in any other country of the Turkish Empire." He added, however, that the Jews "are held in the utmost contempt and abhorrence by the Muslims in general." Lane explained: "Not long ago, they used often to be jostled in the streets of Cairo, and sometimes beaten merely for passing on the right hand of a Muslim. At present, they are less oppressed; but still they scarcely ever dare to utter a word of abuse when reviled or beaten unjustly by the meanest Arab or Turk; for many a Jew has been put to death upon a false and malicious accusation of uttering idsrespectful words against the Kuran (sic] or the Prophet. It is common to hear an Arab abuse his jaded ass, and after applying to him various opprobrious epithets, end by calling the beast a Jew.
That this was the Jewish situation in Egypt, "a less oppressive government" than elsewhere in the Muslim Arab world, tells us a great deal about Muslim antisemitism in the nineteenth century - prior to the Zionist movement.
Syria
In 1840, some French Catholics introduced the blood libel into the Arab world. After a Capuchin monk in Damascus vanished, Ratti-Mention, the local French consul, told police authorities that the Jews probably had murdered him to procure his blood for a religious ritual. Several Damascus Jews were then arrested, and under torture, oneo f them "confessed" that leaders of the Jewish community had planned the monk's murder. Many other Jews were then arrested, and under torture more such confessions were obtained. French officials pressured Syria'sruler, Muhammad Ali, to try the arrested men, and it was only after an international protest organized by Jewish communities throughout the world that the Jews who survived their tortures were released.
The blood libel immediately became popular among Muslims, who attacked Jews as drinkers of Muslim blood in Aleppo, Syria, in 1853, Damascus again, in 1848 and 1890, Cairo in 1844 and 1901-2, and Alexandria in 1870 and 1881.
The blood libel played a decisive role in unsettling the lives of nineteenth-century Syrian Jews, and since then it has been repeatedly utilized in Arab anti-Jewish writings.
Palestine
Jews have lived continuously as a community in Palestine since approximately 1200 BCE. The only independent states ever to exist in Palestine have been Jewish. After the destruction of the second Jewish state in 70 CE and the suppression of the Bar Kochba revolt in 135 CE, Jews always maintained a presence in Palestine, awaiting the reestablishment of the Jewish state. But these Jews often had to live under degrading conditions.
In nineteenth-century Palestine, which was under Ottoman Muslim rule, Jews had to walk past Muslims on their left, as the left is identified with Satan, and they always had to yield the right of way to a Muslim, by "stepping into the street and letting him pass." Failure to abide by these degrading customs often provoked a violent response.
In Palestine as elsewhere, Jews had to avoid anything that could remind Arabs of Judaism; therefore, synagogues could be located only in hidden, remote areas, and Jews could pray only in muted voices. In addition, despite the widespread poverty among Palestinian Jews, they had to pay a host of special protection taxes (in actuality, a form of extortion). For example, Jews paid one hundred pounds a year to the Muslim villagers of Siloam (just outside Jerusalem) not to disturb the graves at the Jewish cemetery on the Mount of Olives, and fifty pounds a year to the Ta'amra Arabs not to deface the Tomb of Rachel on the road to Bethlehem. They also had to pay ten pounds annually to Sheik Abu Gosh to to molest Jewish travelers on the road to Jerusalem, even though the Turkish authorities were already paying him to maintain order on that road.
These anti-Jewish laws, taxes, and practices had a rather intimidating effect on the Jews. The British consul James Finn, who lived in Jerusalem in the 1850s, described in his book Stirring Times how "Arab merchants would dump their unsold wares on their Jewish neighbors and bill them, safe in the knowledge that the Jews so feared them that they would not dare return the items or deny their purchase."
Muslim antisemitism continued to be brutally expressed through the twentieth century. Albert Memmi, the noted French-Jewish novelist, who grew up in North Africa, cites a few examples:
"In Morocco in 1907, a huge massacre of Jews took place in Casablanca, along with the usual embellishments - rape, women carried away into the mountains, hundreds of homes and shops burned, etc....In 1912 a big massacre in Fez...In Algeria in 1934, massacre in Constantine, twenty-four people killed, dozens and dozens of others seriously wounded....In Aden in 1946...over one hundred people dead and seventy-six wounded, and two-thirds of the stores sacked and burned....In June, 1941, in Iraq, six hundred people killed, one thousand seriously wounded, looting, rapes, arson, one thousand houses destroyed, six hundred stores looted....[In Libya]: November 4th and 5th, 1945, massacre in Tripoli; November 6th and 7th in Zanzour, Zaouia, Foussaber, Ziltain, etc: girls and women raped in front of their families, the stomachs of pregnant women slashed open, the infants ripped out of them, children smashed with crowbars....All this can be found in the newspapers of the time, including the local Arab papers."
Memmi summarizes the Jewish status under Islam in the twentieth century: "Roughly speaking and in the best of cases, the Jew is protected like a dog which is part of man's property, but if he raises his head or acts like a man, then he must be beaten so that he will always remember his status."
It is the Jews' refusal to accept an unequal, inferior status that lies at the heart of the Arab-Muslim hatred for Israel. (It is this, not the Palestinian refugee issue, that has been the basis of Muslim antisemitism. Without minimizing the personal difficulties of the Palestinians, as Memmi notes [on page 35 of his book Jews and Arabs]: "The Palestinian Arabs' misfortune is having been moved about thirty miles within one vast Arab nation.") As Yehoshafat Harkabi, a leading scholar of the Arab world's attitude toward Israel, put it: "The existence of the Jews was not a provocation to Islam...as long as Jews were subordinate or degraded. But a Jewish state is incompatible with the view of Jews as humiliated or wretched." The call for a Palestinian Arab state in place of Israel is for a state in which once again 'Islam dominates and is not dominated."
This hatred of Jewish nationalism was so intense that during World War II, most Arab leaders were pro-Nazi. Among them was the head of the Muslims in Palestine, the mufti Haj Amin el-Husseini (who in 1929 had helped organize the large-scale murders of the ultra-Orthodox, non-Zionist Jews of Hebron).
An ardent supporter of Hitler, the mufti spent much of the war in Nazi Germany; on November 2, 1943, at a time when the Nazis were murdering thousands of Jews daily, the mufti declared in a speech: "The overwhelming egoism which lies in the character of Jews, their unworthy belief that they are God's chosen nation and their assertion that all was created for them and that other peoples are animals...[makes them] in capable of being trusted. They cannot mix with any other nation but live as parasites among the nations, suck out their blood, embezzle their property, corrupt their morals....The divine anger and curse that the Holy Koran mentions with reference to the Jews is because of this unique character of the Jews."
Though many Arab nations formally declared war against Germany in 1945, when German defeat was imminent, in order to be eligible for entry into the United Nations, extensive Arab sympathy with the Nazis continued even after Germany's surrender. The Egyptians and Syrians long welcomed Nazis to their countries, offering them the opportunity to further implement the "Final Solution," by assisting in their efforts to destroy Israel and wipe out the Jewish community living there.
Among many Arabs the Holocaust has come to be regarded with nostalgia. On August 17, 1956, the French newspaper Le Mongde quoted the government-controlled Damascus daily Al-Manar as observing, "One should not forget that, in contrast to Europe, Hitler occupied an honored place in the Arab world....[Journalists} are mistaken if they think that by calling Nasser Hitler, they are hurting us. On the contrary, his name makes us proud. Long live Hitler, the Nazi who struck at the heart of our enemies. Long live the Hitler [i.e., Nasser] of the Arab world."
On June 9, 1960, after Israeli agents captured Adolf Eichmann, the Nazi official who had supervised the murder of six million Jews, the Beirut daily Al-Anwar carried a cartoon depicting Eichmann speaking with Israeli Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion. Said Ben-Gurion: "You deserve the death penalty because you killed six million Jews." Responded Eichmann: "There are many who say I deserve the death penalty because I didn't manage to kill the rest."
On April 24, 1961, the Jordanian English-language daily Jerusalem Times published an "Open Letter to Eichmann," which concluded, "But be brave, Eichmann, find solace in the fact that this trial will one day culminate in the liquidation of the remaining six million to avenge your blood." At the UN sponsored "Conference Against Racism" in September 2001, an Arab pamphlet displayed at the Durban Exhibition Center featured a picture of Adolf Hitler with the caption, "If I had won the war there would be no...Palestinian blood lost."
Arab Jew-hatred also has brought about the resurrection of the blood libel. In 1962, the Egyptian Ministry of Education reissued Talmudic Sacrifices by Habib Faris, a book originally published in Cairo in 1890. The editor notes in his introduction that the book constitutes "an explicit documentation of indictment, based upon clear-cut evidence that the Jewish people permitted the shedding of blood as a religious duty enjoined in the Talmud."
On April 24, 1970, Fatah radio, under the leadership of Yasir Arafat, broadcast, "Reports from the captured homeland tell that the Zionist enemy has begun to kidnap small children from the streets. Afterwards the occupying forces take the blood of the children and throw away their empty bodies. The inhabitants of Gaza have seen this with their own eyes."
Even more disturbing, the blood libel accusations have been made by the most prominent figures within the Arab world. In November 1973, the late King Faisal of Saudi Arabia said that it was necessary to understand the Jewish religious obligation to obtain non-Jewish blood in order to comprehend the crimes of Zionism. A decade later, in 1984, the Saudi Arabian delegate to the UN Human Rights Commission Conference on religious tolerance, Marouf al-Dawalibi, told the commission, "The Talmud says that if a Jew does not drink every year the blood of a non-Jewish man, he will be damned for eternity." In The Matzah of Zion, a book that has remained in print since its publication in 1983, Mustafa Tlas, the Syrian Defense Minister since 1972, wrote, "The Jew can kill you and take your blood in order to make his Zionist bread." A 2000 article about Tlas's book in Al-Ahram, Egypt's largest, and government-controlled, newspaper, reported, "The Bestial drive to knead Passover matzahs with the blood of non-Jews is [confirmed] in the records of the Palestinian police where there are many recorded cases of the bodies of Arab children who had disappeared without being found, torn to pieces, without a single drop of blood. The most reasonable explanation is that the blood was taken to be used in matzahs to be devoured during Passover." As one American journalist commented: "If this is 'the most reasonable explanation," can you imagine an unreasonable one?" The Al-Ahram article went on to report that an Egyptian movie company is planning to shoot a multimillion dollar film version of The Matzah of Zion, which will retell, as truth, the story of the Damascus blood libel.
And still the blood libel goes on. A 2001 cartoon in the Jordanian newspaper Al-Dustour depicts an Israeli soldier presenting his mother with a Mother's Day gift of a bottle containing the blood of a Palestinian child. At about the same time (November 2001), Abu Dhabi Television depicted a caricature of Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon preparing to drink a cup of blood taken from a Palestinian. A March 10, 2002, article in Saudi Arabia's Al-Riyadh, the government-controlled newspaper, by Dr. Umayma Ahmad Al-Jalahma of King Faisal University, creates a new twist to this ancient libel, claiming that Jews use blood for Purim pastry and not just for Passover matzo: "Let us now examine how the victims' blood is spilled. For this, a needle-studded barrel is used; this is a kind of barrel, about the size of the human body, with extremely sharp needles set in it on all sides. [These needles] pierce the victim's body, from the moment he is placed in the barrel. These needles do the job, and the victim's blood drips from him very slowly. Thus, the victim suffers dreadful torment - torment that affords the Jewish vampires great delight as they carefully monitor every detail of the blood-shedding with pleasure and love that are difficult to comprehend."
Arab Muslims have also reached back to classical themes of Islamic antisemitism to attack the Jews and Israel. Many Arab speakers and publications echo Muhammad's charge in the Koran (5:82) that the Jews are the greatest enemies of humankind. For example, an Egyptian textbook, published in 1966 for use in teachers' seminars, taught that Jews (not only Israelis) are the "monsters of mankind [and] a nation of beasts."
Perhaps the favorite antisemitic publication in the Arab world for over fifty years has been The Protocols of the Elders of Zion.. In an interview with the editor of the Indian magazine Blitz, on October 4, 1958, President Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt praised the Protocols: "I wonder if you have read a book called 'Protocols of the Learned Elders of Zion.' It is very important that you should read it. I will give you an English copy. It proves clearly, to quote from the Protocols, that 'three hundred Zionists, each of whom knows all the others, govern the fate of the European continents and they elect their successors from their entourage."
The late King Faisal of Saudi Arabia gave copies of the Protocols to the guests of his regime. When he presented the Protocols, along with an anthology of antisemitic writings, to French journalists who accompanied French Foreign Minister Michel Jobert on his visit to Saudi Arabia in January 1974, "Saudi officials noted that these were the king's favorite books."
Article 32 of the 1988 Palestinian Hamas (the Islamic Resistance Movement) Covenant claims that the Zionist "scheme" foe takeover of the Arab world "has been laid out in The Protocols of the Elders of Zion, and their present [conduct] is the best proof of what is said there." Hamas literature repeatedly accuses Jews of controlling the world's wealth and its most important media, and using them to promote Jewish and Zionist interests, even of having established the League of Nations in the 1920s "in order to rule the world."
Al-Hayat Al-Jadida, the official newspaper of the Palestinian Authority (and therefore supposedly less extreme than Hamas), regularly contains references to the Protocols. Thus, even during the height of the Oslo peace process the paper published the following: "It is important to conduct the conflict according to the foundations which both are leaning on...particularly the Jews...such as the Torah, the Talmud, and the Protocols...This conflict resembles the conflict between men and Satan." At about the same time in Egypt, Al-Ahram, the country's largest newspaper, reported, "A compilation of the investigative' work of four reporters on Jewish control of the world states that Jews have become the political decision-makers and control the media in most capitals of the world (Washington, Paris, London, Berlin, Athens, Ankara)." As the journalist Andrew Sullivan comments, "It is worth noting that every word Al Ahram prints is vetted and approved by the Egyptian government, a regime to which the United States - i.e., you and I - contributed $2 billion a year."
It is perhaps no surprise that, as of 2002, over sixty editions of the Protocols are being sold throughout the Arab world, and this libelous "warrant for genocide" is probably more widely distributed today than at any other time in its history. In 2002, the New York Times, in a front-page story, reported that a major Egyptian television station was about to launch a forty-one-episode TV series based on the Protocols (complete with Jewish villains dressed in black hats, side curls, and beards) to run before and during the Muslim holy month of Ramadan.
The Islamic world today has combined antisemitic motifs from Nazism and medieval Christendom, as well as from its own tradition. This potent combination has made the Arabs the major source of antisemitic publications in the world today. And as in other forms of antisemitism, in the words of Yehoshafat Harkabi, "the evil in the Jews is ascribed not to race or blood, but to their spiritual character and religion." Thus, when Pakistani Islamic terrorists kidnapped Wall Street Journal reporter Daniel Pearl in January 2002, they forced Pearl to say, "I am a Jew," (and videotaped him doing so) before slitting his throat.
Only through an understanding of the deep theological roots of Muslim antisemitism and an awareness of its continuous history can present-day Muslim hatred of Israel be understood. Only then does one recognize how false are the claims of Israel's enemies that prior to Zionism, Jews and Muslims lived in harmony and that neither Islam nor Muslims have ever harbored Jew-hatred. The creation of the Jewish state in no way created Muslim Jew-hatred; it merely intensified it and gave it a new focus.
So long as the Jews acknowledged their inferior status among Muslims, they were humiliated but allowed to exist. But once the Jews decided to reject their inferior status, to become sovereign after centuries of servitude, and worst of all, to now govern some Muslims in a land where the Jews had so long been governed, their existence was no longer tolerable. Hence the passionate Arab Muslim hatred of Israel and Zionism, a hatred that entirely transcends political antagonisms. Hence the widespread Muslim call not merely for a military defeat of Israel, but for its annihilation.
As so often in Jewish history, it is the Jewish nation's existence that arouses hatred and needs to be ended. Despite peace treaties between Israel and Egypt (1979) and Jordan (1994), for most Muslims the source of their hatred remains the Jewish sate's existence, not its policies, nor even its borders.
The Muslim and Arab claim that the issue is anti-Zionism rather than antisemitism really means that so long as the Jews adhere to their dhimmi status in Arab Muslim nations, their existence as individuals is acceptable. But for a Jew to aspire to equality among Muslims, for a Jew to aspire to a status higher than "humiliation and wretchedness," is to aspire too high."
- Why the Jews? The Reason for Antisemitism, Dennis Prager and Joseph Telushkin, chapter nine
#joseph telushkin#rabbit joseph telushkin#dennis prager#antisemitism#history#jewish history#jumblr#why the jews the reason for antisemitism
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
the Daode JIng benefits from having a legendary author. everyone knows that it was a redaction of many poets into one text, and that there was not really a single author, but a mythical saint to whom the text was attributed in antiquity. all the same, even academic writing about the DDJ say that Laozi said this and that. there's an unspoken 'you know what i mean' going on. and while there are a few dissenters, most people agree that the text says something which you can read and interpret. in fact, paleographical challenges are not burdensome in DDJ scholarship.
the Bible is similar; we know that not only is it a collation of texts, but each text is itself a collation of texts, and so forth. it was written by this or that person, with this or that material (in the case of Genesis, the entire text is internally duplicated, narrating two incompatible stories from two incompatible sources). but it's not troubling, and for most discussions, we can act as if it really was written by Moses and not worry about those things until they come up.
perhaps for Dark Souls we should promote the false idea of Miyazaki as the master author, who wrote every line of code and composed every challenge in the game, and planned for every experience and interpretation players can come up with. only then we could talk start talking about it again...
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
I hear you like biblical characters who are also sad/tragic little men
Have you considered:
Abraham, one of the most depressing main characters in the Bible?
Consider, people historically misread this character to make him more exemplary, but according to the text:
1. Early in his arc we see some big wins for him; he gets God on his side, he learns to be confident in himself and in his internal sense of justice, so much so that at the crucial moment before Sodom and Gomorrah, God tests whether Abraham's loyalty is stronger than his sense of justice, and Abraham passes with flying colors. He castigates God's plan as despicable, profane, a gross miscarriage of justice from an apparently unjust being who deigns to call themself the judge of the universe—and does not become an Abrahamakebab (seriously it's like Odysseus challenging Athena levels of chutzpah)
2. God promises him everything including that he'll inherit the promised land and see his children fill the land
3. God tests him again and tells him to sacrifice Isaac, and Abraham absolutely beefs it. If you read the text closely, it really emphasizes how close Abraham and Isaac are, and God is really careful to emphasize and remind Abraham of this fact. What happens? Abraham and Isaac go up the mountain together. And then at the climactic moment? It's not God who intervenes, but an angel (before this point it's always God, always personal). And then Abraham (alone) descends the mountain. Not Abraham and Isaac, just Abraham. We never again see Abraham and Isaac in the same place until Abraham's funeral (not even to set up Isaac and Rivka; he sends a servant for that! Also the funniest part of the bible; Isaac's so hot Rivka falls off her camel). Sarah leaves him and returns to her ancestral land (we know this because Abraham has to travel to her land when she dies, while Isaac lives in the same region as Sarah). And God never again speaks to Abraham, and in fact doesn't speak directly to anyone ever again until Moses kills the overseer and then comes upon the burning bush, 400 years later. Abraham certainly doesn't live to inherit the promised land or see his children fill it.
Man rises to the highest of highs, and then through his own doing, loses his son, his wife, his God, his legacy, and his pride.
May I propose instead: King Saul
#wolfy tedtalks#anon#sorry i would like abraham more but my church ruined him for me#HAHA#king saul my original tortured bbg#wolfy religious tedtalks
286 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Peter Clarke
Published: Jun 20, 2024
Today, the governor of Louisiana signed a law requiring classrooms in the state to display the Ten Commandments. According to the Republican governor, Jeff Landry, “If you want to respect the rule of law, you gotta start from the original law given which was Moses. … He got his commandments from God.”
Apparently, Governor Landry never bothered to learn that the scholarly consensus is that Moses, if he existed at all, was “largely mythical.” The governor also apparently never reflected on the fact that America is founded on the separation of church and state. The ACLU, the Freedom from Religion Foundation, and others have already come out with a statement, observing that the new law results in “unconstitutional religious coercion of students.” The statement adds, “Politicians have no business imposing their preferred religious doctrine on students and families in public schools.”
Furthermore, Governor Landry apparently never took a moment to actually read the Ten Commandments. Because if he had, he may have noticed that they’re utterly unimpressive as far as moral commandments go. As Sam Harris wrote in Letter to a Christian Nation:
“If you think that it would be impossible to improve upon the Ten Commandments as a statement of morality, you really owe it to yourself to read some other scriptures. Once again, we need look no further than the Jains: Mahavira, the Jain patriarch, surpassed the morality of the Bible with a single sentence: ‘Do not injure, abuse, oppress, enslave, insult, torment, torture, or kill any creature or living being.’ Imagine how different our world might be if the Bible contained this as its central precept. Christians have abused, oppressed, enslaved, insulted, tormented, tortured, and killed people in the name of God for centuries, on the basis of a theologically defensible reading of the Bible.”
In fact, you don’t even have to look at other religious groups to find improvements to the Ten Commandments. There are countless secular alternatives to the Ten Commandments, any one of which would be more appropriate for the classroom.
Consider the Ten Commandments by blogger Adam Lee, which Richard Dawkins included in his book The God Delusion:
Do not do to others what you would not want them to do to you.
In all things, strive to cause no harm.
Treat your fellow human beings, your fellow living things, and the world in general with love, honesty, faithfulness and respect.
Do not overlook evil or shrink from administering justice, but always be ready to forgive wrongdoing freely admitted and honestly regretted.
Live life with a sense of joy and wonder.
Always seek to be learning something new.
Test all things; always check your ideas against the facts, and be ready to discard even a cherished belief if it does not conform to them.
Never seek to censor or cut yourself off from dissent; always respect the right of others to disagree with you.
Form independent opinions on the basis of your own reason and experience; do not allow yourself to be led blindly by others.
Question everything.
Or consider the crowdsourced Atheists’ New Ten Commandments from the 2015 Rethink Prize:
Be open-minded and be willing to alter your beliefs with new evidence.
Strive to understand what is most likely to be true, not to believe what you wish to be true.
The scientific method is the most reliable way of understanding the natural world.
Every person has the right to control of their body.
God is not necessary to be a good person or to live a full and meaningful life.
Be mindful of the consequences of all your actions and recognize that you must take responsibility for them.
Treat others as you would want them to treat you, and can reasonably expect them to want to be treated. Think about their perspective.
We have the responsibility to consider others, including future generations.
There is no one right way to live.
Leave the world a better place than you found it.
Or even consider the Seven Tenets from The Satanic Temple:
One should strive to act with compassion and empathy toward all creatures in accordance with reason.
The struggle for justice is an ongoing and necessary pursuit that should prevail over laws and institutions.
One’s body is inviolable, subject to one’s own will alone.
The freedoms of others should be respected, including the freedom to offend. To willfully and unjustly encroach upon the freedoms of another is to forgo one’s own.
Beliefs should conform to one’s best scientific understanding of the world. One should take care never to distort scientific facts to fit one’s beliefs.
People are fallible. If one makes a mistake, one should do one’s best to rectify it and resolve any harm that might have been caused.
Every tenet is a guiding principle designed to inspire nobility in action and thought. The spirit of compassion, wisdom, and justice should always prevail over the written or spoken word.
Finally, here’s ChatGPT, in response to the prompt, “Write 10 original secular commandments that are an improvement to the 10 commandments in the bible”:
Value and Respect All Human Life: Recognize and uphold the dignity, rights, and worth of every individual, regardless of their background or beliefs.
Act with Compassion and Kindness: Treat others with empathy, understanding, and kindness, striving to alleviate suffering and promote happiness.
Seek and Promote Truth: Commit to the pursuit of knowledge and truth, encouraging critical thinking, honesty, and transparency in all interactions.
Protect and Preserve the Environment: Take responsibility for the well-being of our planet, ensuring sustainable practices and the protection of natural resources for future generations.
Support Equality and Justice: Advocate for fair treatment and equal opportunities for all, working to eliminate discrimination, prejudice, and injustice in society.
Respect Personal Autonomy: Honor the right of individuals to make their own choices and live their lives according to their values and beliefs, as long as they do not harm others.
Cultivate Peace and Non-Violence: Strive to resolve conflicts through dialogue, understanding, and non-violent means, promoting peaceful coexistence.
Encourage Community and Solidarity: Foster a sense of community and mutual support, working together to address common challenges and enhance collective well-being.
Pursue Lifelong Learning and Growth: Embrace continuous personal development and education, seeking to improve oneself and contribute positively to society.
Practice Gratitude and Humility: Recognize and appreciate the contributions and perspectives of others, remaining humble and open to learning from diverse experiences and viewpoints.
Why not put that in Louisiana classrooms, governor?
Oh…right. Because you don’t actually care about promoting ethical behavior that would improve the wellbeing of your community. You just care about virtue signaling to your mythical deity from the Bronze Age.
#Peter Clarke#Atheists for Liberty#Ten Commandments#The Ten Commandments#secularism#ethical behavior#ethics#morality#secular morality#atheism#First Amendment#religion#freedom of religion#freedom from religion#religion is a mental illness
21 notes
·
View notes
Text







stained glass windows I can't get enough of.
1/ Sainte-Chapelle, Paris
The stained glass windows in Sainte-Chapelle form a drenched masterpiece of stained glass with 15 immense bays of vibrant colors and intricate biblical scenes. These 13th-century windows document the scenes of the Bible, from Creation to Apocalypse.
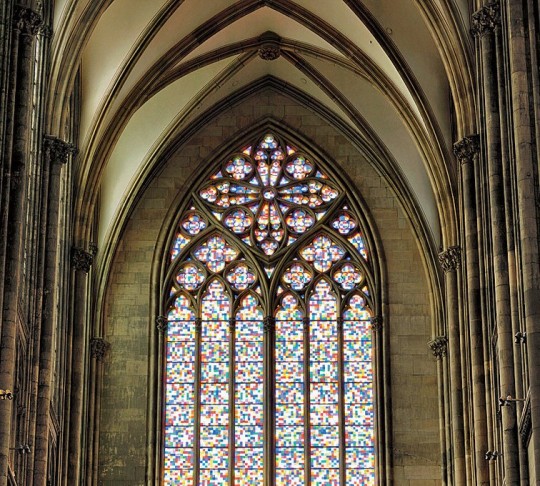
2/ Cologne Cathedral, Germany:
The stained glass windows of Cologne Cathedral were done in a number of periods, such as the 14th and 16th centuries, when some windows, including the St. Peter window and the Tree of Jesse Window, date from 1509. The design for the window of the south transept of the cathedral was done by Gerhard Richter, finished in 2007, with 11,263 glass squares in 72 colors.
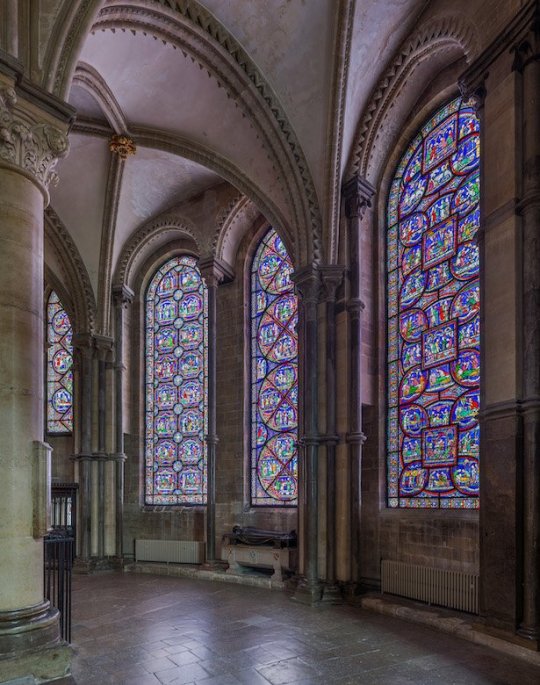
3/ Canterbury Cathedral, England:
The stained glass of Canterbury Cathedral dates back to the 12th century, with some panels thought to be among the oldest in the world. In fact, the oldest glass within the building is over 840 years old, showing biblical figures and their genealogies. A range of the Ancestors of Christ series, dating from the mid-1100s, possibly constitutes the oldest surviving stained glass windows in England.
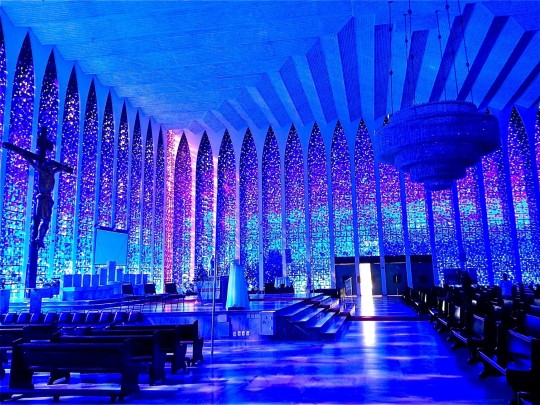
4/ Santurio Dom Bosco, Brazil
The stained glass of Santuário Dom Bosco in Brasilia was designed by architect Cláudio Naves with Hubert Van Doorne in the 1960s, it contains giant walls in stained blue glass with rosé glass at each corner, creating a really dramatic interior illumination.
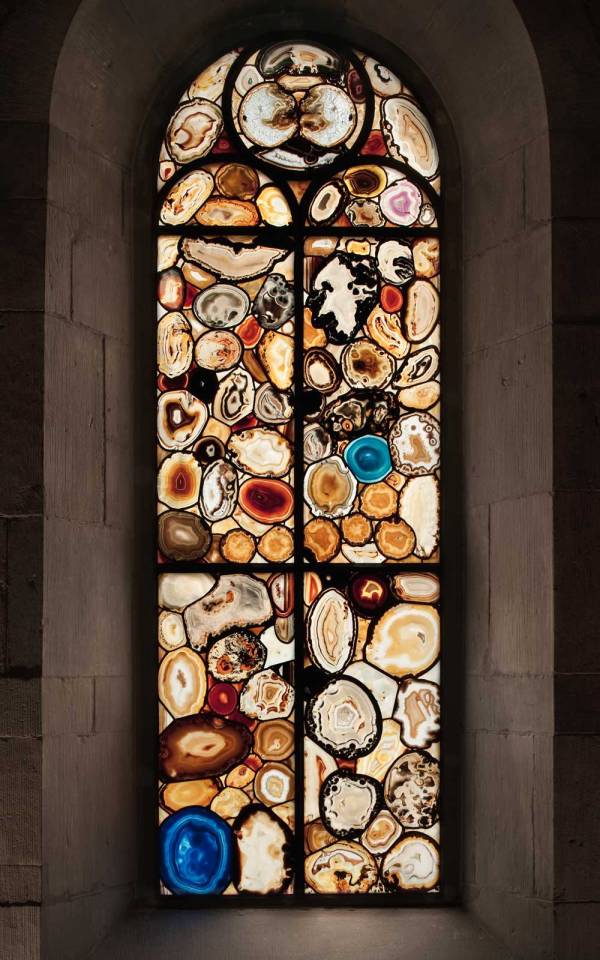
5/ Grossmunster Zurich, Germany
The stained glass windows of Grossmünster Zurich were designed by Sigmar Polke and installed in 2009. The windows feature seven windows in the nave made from agate, which were cut into thin slices through which light was passed to create a brightly glowing effect. Five further figurative windows, depicting Old Testament figures leading towards the chancel window created by Augusto Giacometti in 1933.
6/ Metropolitan Cathedral of St. Sebastian, Brazil
The stained glass windows of the Metropolitan Cathedral of St. Sebastian were designed in an intricate symbolism in the city of Rio de Janeiro. The windows, from the 1960s, stand as a symbol of the unity, sanctity, mission, and hierarchy of the Catholic Church. They are part of the unique architecture that boasts a Greek cross and a round base drawing inspiration from Mayan pyramids to mean closeness to God.
7/ Augsburg Cathedral, Germany
The oldest of these stained glass windows are found in Augsburg Cathedral and date back to approximately 1065. Five Old Testament figures—Moses, David, Daniel, Hosea, and Jonah—are depicted in the Prophet Windows of the nave in monumental Romanesque style. Biblical scenes and stories of the Virgin also appear in later medieval windows.
#stained glass#cathedrals#sainte chapelle#cologne cathedral#canterbury cathedral#santurio dom bosco#grossmunster zurich#Brazil#metropolitan cathedral of st Sebastian#Augsburg Cathedral
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Evidence of Exodus
Many often wonder if there is any factual evidence proving the Bible being true. What if I told you that not only can I point you to strong evidence of the old testament Exodus being real, I can point you to a person in Exodus who has a real life replica of himself. Being possibly the only person mentioned in the Bible that we can truly see how they appeared. (With the exception of Vladimir Putin's recent 2024 claim that he has an original painting of Jesus Christ that has been in Russia).
bNow, if you're not familiar with the book of Exodus (chapters 1-14), I suggest you taking a moment to read it. Otherwise, what I'm about to say may not make much Sense. Or, read this and then read Exodus, and things might make more sense to you as it's being read. Either way, I highly recommend reading it.
Archeologically, we're able to prove many things within the Bible, however, Exodus is not one of them. Matter of fact, some of the things are extremely questionable. For example, where are all these Israelites coming from mentioned? There are no records of a man named Moses in Egypt. Many movies depict the enslaved Israelites were building the pyramids, however, The pyramids were built long before the Israelites were enslaved. There are many things that people question in the book of Exodus, you might as well. Maybe I can help with any doubt that you may have. In hopes to open your eyes as to the possibility that these things really could have, and did indeed happen.
Let's go back to the story of Joseph. Joseph is one of the 12 sons of Jacob, also named Israel. (Remember God changed his name to Israel because of his faith in willing to sacrifice his son). They fell into a Great famine Aunt resources grew very slim, so they went searching for a better life elsewhere. Can you guess where they ended up? That's right, Egypt! This is where we get "The children of Israel", also known as, the Israelites.
Joseph's gift from God was the ability to interpret dreams. In doing so, he was able to interpret the Pharaoh's dream which ultimately helped save Egypt from a great famine. So how did his people, his family, end up in bondage? Answer is, the Israelites were living and the delta and we're living a pretty prosperous existence. Up until the moment a new pharaoh becomes in charge. This Pharaoh knows nothing about Joseph. For none other than narcissistic reasons, the new pharaoh is upset that the Israelites are living such a lavish life. He ordered task masters to watch over them, which is when they became enslaved. This Pharaoh is historically documented saying to his midwives, "watch the two stones." Meaning, Egyptian women often give birth while sitting straight up to let gravity help them with the birthing process. Often, they would sit on two stones to help assist them during labor. This correlates with the Bible when pharaoh ordered the death of all the Israelite males that were being born. This is around the time that Moses was born. With Moses's mom afraid of him being murdered, she sent him away, down the river, for a chance at life.
Another questionable biblical text says that the pharaohs daughter finds Moses and the river and takes him in as her own. An Egyptian naming their child Moses, which is Hebrew is not very likely. Leaving some skepticism. Let me push that skepticism aside.
Remember, Moses is sent down river, so when he's found, he's found in the reeds. Now the Hebrew word massa (משא) means brought out. However Moses, Moses is actually a pure Egyptian name, which means Born. Just think about Ra-Moses, Ra means God and Moses means birth in Egyptian, God is Born. Another common Egyptian term is Toth-Moses. So therefore, just because the name Moses doesn't appear as someone's name being an actual person, it does not mean he did not exist. Moses literally means birth and Egyptian. Something someone would say or call a newborn baby.
Moses later has an encounter with God through a burning bush. God tells Moses that he is going to be the one to help set the Israelites free and lead them into the promised land. Moses, brings his brother Aaron with him to go speak to the pharaoh. Moses performs many miraculous wonders and so do the pharaohs magic wielders. So it's like they're in competition for a moment. Moses has a staff and he throws it down and it turns into a snake. Then Pharaoh has his people throw a staff and they also turn into snakes. It was almost like this was something that they've seen before, and we're unimpressed. Now you can take it exactly how it was written and think that a staff was thrown down and turned into a snake and both parties were able to do so. What I think happened is, the staff happened to be a cobra snake that was stiff like a staff with the head as the handle. When you throw the snake down onto the ground it then is able to slither away. This is a known practice and Egypt then and even today which would explain why people wouldn't be impressed. Moses and Aaron came back time and time again with 9 different plagues. Trying to convince Pharaoh to let his people go. Pharaoh gets annoyed and Now orders that the Israelites are no longer going to be given prepared straw to mix with their bricks. Leaving them to cut their own straw to mix with clay in order to make their own bricks. Giving double work with the same deadline. None of the plagues presented so far didn't seem to phase the Egyptians whatsoever. By this point, God says enough is enough and lets the pharaoh know that if he does not cooperate, he will take all the firstborns of families who do not have a blood sacrifice over their door frame. Of course Pharaoh did not take this threat seriously, so there was no blood sacrifice and he ended up losing his son. This is what makes pharaoh say okay, You can have your freedom, you can go.
When the Israelites leave, the Egyptians are all mourning the deaths of their firstborns. So, when the Israelites asked for gold and silver upon leaving, they just handed it over with no issues. So the Israelites are able to leave rich with gold and silver. Rightfully so in my opinion. They just spent approximately 430 years, in slavery and are now heading to the promised lands.
As the Israelites were on their way, Pharaoh quickly changed his mind and decided to go after the Israelites and bring them back. This is when the famous part of Exodus happens that most people are familiar with. Did the Israelites really cross the Red Sea on dry land? While the Egyptians get swallowed whole by the water? There is a lot of skepticism about rather or not they truly did part the Red Sea.
Here the Israelites are leaving on foot with all this gold and silver. We know that they lived in the Delta part of Egypt so we can kind of figure out the route that they took. They don't take the Philistine route because Palestine is highly guarded with watchtowers. So what they do is go through the marsh. Now the misconception lies with where exactly they crossed at. Which they actually crossed through the Sea of Reeds and not the Red Sea. Now in the Bible it says that Pharaoh's chariots were clogged. Sounds like they were going through mud. If you ask me. Which if I'm on foot I can get through but if I'm in a chariot I cannot. So Pharaoh's men ended up perishing while God helped the Israelites make it through safely.
In playing devil's advocate, if this story is true then why is there no record other than what is mentioned in the Bible of this particular situation? The answer is Egyptians were horrible at record keeping in general. Their record keeping is mainly made up of what is written in tombs or on Stella's. Which never mentioned anything about any of their defeats. Egyptians only kept records of victories. Honestly, this entire situation only really mattered to the Israelites. No one else really cared. But this was the beginning of their entire religion.
Biblically they never say who the pharaoh actually was. Historically, Egypt didn't even have a pharaoh at this time. Who ever was in charge would technically be a king. So where does the Bible get Pharaoh from? It's actually a conjunction of 2 Egyptian words, that meant house, great. Which Pharaoh meant the one who lived in a great house. Fitting for someone living in a palace.
A clue in the Bible as to who this pharaoh may be is when they speak of the Israelites building the store cities with bricks. Is it a coincidence that one of the cities names is Pi-Ramess? They are using bricks, which historically we can narrow down the time frame in which bricks began being used to build the storehouse in these 2 cities mentioned.
i'm going to agree with Bob Brier, an egyptologist who suggested the Pharaoh in the book of Exodus is...... Ramesses the Great. Why?
Ramesses' built his capitol right beside the Delta, which would be close enough to the Israelites. Especially during the times Moses and Aaron were traveling back and forth trying to convince him to let his people go. The Israelite slaves built the city of Ramesses out of brick and he was the one who built these cities. There is a sentence written on a Papyrus that explains grain ratios to be handed out to the soldiers and apperu (now I know I butchered inthe spelling of this word, but I spelled it the way it sounded). Which The translation is thought to mean Hebrew. Many scholars believe that this is our Israelites. Other scholars believe that Merneptah was the ruler over The Exodus. They believe this because the first time Israel is mentioned is during the reign of Merneptah, which is Rameses 13th son and his successor. However, when Merneptah mentions Israel on his Stella. It is referred to as a people and not a country or a foreign land. Meaning around this time the Israelites were still wondering. Therefore, if they are wandering at this time, that means they must have left right before he began his reign. Biblical scholars believe The Exodus happened in year 20 of rameses reign. Guess what else happens right around this time? Ramesses loses his firstborn son, Amonhirkhopshef.
In the Egyptian museum, you can now see the mummy of Ramesses the Great. Which very well may be the only face you can look upon that is a real biblical figure. I love it when science, history and the Bible correlate.
References:
Brier, Bob. The history of ancient Egypt. (2013). The great courses.
Exodus 1+14
#reading#my writing#spilled ink#books#writing#writeblr#exodus#bible#science#history#ancient egypt#moss#pj masks pharaoh boy
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
My complete and unhinged Metatron analysis
Hello, I have seen that many people are theorizing about Metatron, so I'm here presenting an analysis of who Metatron is, rather his biblical role and how he may be more connected to the Aziraphale and Crowley than we might believe.
-Also, English is not my first language, so please be patient with me-
ANALYSIS OF METATRON AS A FIGURE WITHIN CHRISTIANITY:
Metatron, has always been a controversial figure in Christianity, full of dualisms.
Let's start with its etymologically. The term Metatron has two completely different translations: one comes from the Greek metradromos meaning "he who pursues with vengeance"; or it is also possible that its origin is from the term meta ton thronon which means "closer to the throne". There are many doubts about his true origin, since it is mentioned in non-canonical versions of the Bible, during Genesis*. However, in the most current and official versions of the Bible, it never appears.
While there is nothing official, the most accepted version is that he is actually the prophet Enoch, Noah's grandfather. Enoch -who used to have his own book of the Bible in earlier versions- was a prophet who had the God-given gift of visiting Heaven through different visions. In his 1st vision, Enoch has the mission to intercede with God on behalf of the fallen angels. In another vision, he sees the Cherubim in Heaven, whom he describes as beings of fire. Later, he is taken by the archangel Michael to the highest heaven. Enoch also travels in his visions or dreams to the tree of knowledge. He is supposed to have lived 365 years and, at the end of his visions, Enoch is chosen by God to become the archangel Metatron, a powerful archangel who is also called the little Yahweh.
There is another explanation for his origin: he is the first being of creation, seated at the left hand of the father, which in tradition is associated with Satan.
The Zohar also describes Metatron as "the king of angels" who reigns over the tree of the knowledge of good and evil.
When Enoch was on Earth, he devoted himself to writing a book containing the secrets of wisdom until he was taken to Heaven to become an angel. God allowed Enoch to continue this same ministry in Heaven** .

FUN FACTS:
Metatron was the one who led the Israelites to the Promised Land (Moses).
Metatron is the patron angel of children.
Metatron transmits God's daily orders to the angels Gabriel and Raphael.
Not being an angel from his origin, Metatron is associated with the angels in charge of Death, he supervises them when they help the souls to make their transition from the physical to the spiritual plane.
He is canonically the most powerful archangel in the entire celestial realm, second only to God. His role is similar to Lucifer's original rol, the right hand of God.
The archangel Metatron is in charge of directing the ascension and activation of the human being's light body. Having been human, he knows the path of enlightenment. He represents the potential for transformation and purification of the soul when it sets out to transcend matter to unite with the pure spirit of the Divine. Metatron is in charge of guiding the souls towards the light, towards purity (insert the fact that he asks for coffee with almonds, which in Christianity is related to purification).

METATRON IN THE LORE OF GOOD OMENS
It is worth mentioning that in the original Good Omens book, Metatron is the only angel that appears besides Aziraphale. While other angels are mentioned, Metatron is the only one who appears, firstly when Zira wants to talk to God, and secondly when Beelzebub and Metatron make presence at the Tadfield airbase to try to convince Adam to restart the end of the world (it is not Gabriel who appears in the book).
And, considering that the 3rd season is based on the sequel to the book that never came out, it makes sense that Metatron would have had a bigger role because he was always a present character.

HIS RELATIONSHIP WITH CROWLEY AND ZIRA:
So, from all this information, I would like to point out that Metatron not only used to be human and knows the "true path of purification," but he is also in charge of caring the tree of knowledge.
You know, that tree?

Aziraphale and Crowley represent the two things that oppose his very existence: an angel that is becoming more and more human with each passing day and the Serpent of Temptation that keeps doubting and questioning the edges and the difference between good and evil. These two not only were they not punished, but together they are two extremely powerful entities, perhaps as powerful as he is.
They are a threat… but only together.

Metatron can see in Aziraphale the very opposite of what he represents, someone who needs to return to the path of divinity:
Aziraphale, the supposed guardian of Eden, who started out as an angel, who gradually transformed into someone with more and more human habits, falling into almost all the deadly sins, in love with the Serpent who tempted humans to eat from the forbidden fruit of the tree of knowledge. Someone who loves forbidden books and bibles, with a hedonistic and condescending personality who managed to deceive his brother angels for millennia to protect humanity and his earthly life***.

It would also explain his disdain towards Crowley, why he looked at him with that face: Metatron is the protector of the tree that Crowley managed to corrupt.

To all this we can add that Metatron/Enoch renounced his humanity to become something superior, while Crowley and Aziraphale consider humanity to be something superior worth defending and loving. They see in humans what Enoch could not see behind his judgment of false celestial purity. They are two supernatural entities who managed to love humanity more than he, a human, ever could.
These parallels are not only born out of my obsession, no. The fact that Metatron has separated them has a much more possible and deep significance.
Narratively, this can only mean one thing: Metatron is the villain, the perfect antagonist to Aziracrow.

CLARIFICATIONS *Genesis is where the Adam and Eve story is found, the Garden of Eden, the moment that changes Zira and Crowley forever…. **That "book that contained the secrets of wisdom"… is it the book of life? Is Metatron the only one who has access to it? ***I would like to clarify, that for me the real main character of Good Omens is Aziraphale, that's why I find more comparisons with him, followed by Crowley as co-protagonist, but I will continue this theory another day.
#good omens#ineffable husbands#aziracrow#did i just also make a whole bible analysis? Look what you made me do gaiman#can this be tagged as a bible study?#bible study#every time i see a catholic metatron figure i want to throw up#neil gaiman#terry pratchett#good omen season 2#good omens theory#good omens metatron#go2#aziraphale#crowley#good omen 2 spoilers
158 notes
·
View notes
Note
this is a rant that spirals im warning you on incoherence
hi. I think theres something in the fact that marisol is a shortening of “our lady of solitude” in spanish. (if i am asked why it is spanish i WILL go into a rant abt the colonization of the Philippines)
Like, shes one of the first characters mentioned and was THE first to notice elijah who, also i think elijah was chosen VERY specifically as the prophet to name him after the prophet elijah from the bible as opposed to say, moses, enoch or joshua (WOW joshua is a biblical name i wish i was lying) (i feel like its obvious he wouldnt be named after enoch, his main book isnt even biblical canon) Why? the sheer amount of just- godly smiting Elijah causes, but also the fact that he resurrected a woman's son. speaking of a woman’s son, cut the baby in half. (i was raised w this story, so i wish everyone would know it, but obv some wont) Essentially two women bring king solomon a baby and say one is the mother, he says cut the baby in half and only the real mother cares. Which, weird. Anyway another one of king solomon’s names was JEDIDIAH. King Solomon said to kill a child, Elijah resurrected one, but not before causing the mother a lot of grief. Elijah also got taken into heaven by a golden chariot of fire and horses which I THINK mirrors the pyre. Also Sydney is one of the few non-biblical name of the main characters, it coming from old english and meaning “of the wide meadow”. which, huh theres a lot of nature names in chnt. Soren, as a name is derived from a CATHOLIC SAINT who is the patron against bad luck a drought, thats weird but if in soren’s head makes sense that he’d believe that.
uuhhhh will come back w more rambling once i unlock anymore core catholic memories™
WOAAHH
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi all,
Welcome to the last part of my 2024 altar tour! 4/4
What a year it has been! I have learned so much and made so many new friends! My altar has always been a reflection of my psyche, seeing it’s beauty reminds me of the beauty that exists within me. :)



So this is my final little work space where I do pendulum magick and tarot readings. There is a devotional mug to Lord Lucifer which I use for our morning coffee chats. There is also Lucifer’s devotional dragon statue, as well as the dual scrying mirror for him and Faviel.
There is a normal mirror and a statue of a pharaoh’s tomb. The board which the flowers and offerings are placed on dawns Faviel’s sigil and candle. To Faviel I have offered a palm stone, flowers, an acorn, smoky quartz, some black earrings, and some grubs.
Beside him is my pendulum in a selenite charging bowl along with my pendulum mat.
The black and white image you see was a piece of art I made for Archangel Jophiel after he gifted me a vision a year or so ago. I use it whenever I’m reaching out to him.

Beneath my altar is some space for storage where I keep my larger cauldron, mortar and pestle, larger candles, etc. There is also my stand where I keep my broom, fire poker, and shovel. My witch broom is wrapped in a protective seal. I use it to sweep ash from my prayer mat.


And finally, here are a few of the books I have in my collection that have greatly greatly aided me in my craft. Remember to do your research my dears!
The Arbatel of Magick- First English edition 1633, new edition 2013, edited by Earl Marwick
Healing with Form, Energy, and Light- Tenzin Wangyal Rinpoche
Gods and Goddesses- Hallam, Elizabeth
The Lesser Key of Solomon- S.L MacGregor Mathers and Aleister Crowley
The Dictionary of Alchemy- Diana Fernando
The Art of Angels- Howard Loxton
Backland’s Book of Spirit Communications- Raymond Buckland
Transcendental Magick- Éliphas Lévi
The Greater Key of Solomon- S.L MacGregor Mathers
A History of God- Karen Armstrong
A Dictionary of Angels, Including Fallen Angels- Gustav Davidson
Making Talismans- Nick Farrell
The Sixth and Seventh Books of Moses- Johann Scheibel
The Egyptian Book of the Dead
The Rise and Fall of the Nephilim- Scott Alan Roberts
Buckland’s Complete Book of Witchcraft- Raymond Buckland
Candle Burning Rituals- Raymond Buckland
The Complete Book of Black Magick and Witchcraft
Green Witchcraft, Folk Magick, Fairy Lore & Herb Craft- Ann Moura
The Book of Forbidden Knowledge, Black Magick, Superstition, Charms and Divination- First Edition 1910s Johnson Smith & co. New Edition 2016 edited by Earl Marwick
Three Books of Occult Philosophy- Henry Cornelius Agrippa
and of course, The Holy Bible- New Living Translation.
I have many other books in my collection on tarot and astrology in my living room, but these are the books that have had the greatest impact on my craft. Here are a few of those other ones:

Love Potions- Tatania Hardie
The Book of Destinies- Jane Struthers
The Crystal Bible 2- Judy Hall
The Tarot Bible- Sarah Barlett
The Wicca Bible- Ann Marie Gallagher
Cunningham’s Encyclopedia of Magical Herbs- Scott Cunningham
Magic and Medicine of Plants- Reader’s Digest
The Power of Birthdays Stars and Numbers- Saffi Crawford and Geraldine Sullivan
The Witches’ Goddess- Janet and Stewart Farrar
The Witches’ God- Janet and Stewart Farrar
•••
I wanted to end this tour off with my reading material because I want to emphasize how important it is to understand that “magick” is not just “stuff”.
I really enjoy all of my magical tools and there’s absolutely nothing wrong with having and wanting pretty things or an aesthetically pleasing altar. In fact I believe aesthetic and care are acts of love in themselves. Don’t ever let someone shame you for wanting to decorate and indulge in the aesthetics of your craft.
But please do remember that our greatest magical tool is our minds, our senses, and our experiences- our brains. Remember to read read read lots of material from many different sources. Contemplate honestly on everything you read, hear and experience. Do not take everything you believe today as a fact, do not box yourself in to anything. (Maybe that’s the Luciferian in me speaking lol)
Learn how to do magick alone, without any tools. My magick is not my stuff, although my stuff greatly aids me in my magick. Does that make sense?
Thank you so much for reading! I look forward to growing and learning so much more this year! :)
Blessed be!
#magick#witchcraft#occultism#witch community#demonology#pagan#paganism#witch aesthetic#witchblr#grimoire#altar#altar tour#spell work#spellcraft#divination#pagan witch#deity work#deity worship#daily devotion#devotee
81 notes
·
View notes
Photo
The world of Abraham, 18th century BC.
via cartesdhistoire
Source: « Histoire universelle des Juifs », Élie Barnavi, Hachette, 1992
Abraham, the father of monotheism, is with Isaac and Jacob one of the three patriarchs who founded the Jewish people. The biblical story of Genesis describes the wanderings of the Patriarchs across the Fertile Crescent, from the mouth of the Euphrates to the land of Canaan. The Bible places the Patriarchs in space but not in time, even if we can assume that Abraham lived in the 18th century. av. AD
Judaism constitutes the first expression of monotheism, but this appearance, far from being sudden, was the result of a slow evolution. Already in Mesopotamia, each state favored one deity among the many that populated its pantheon. In Egypt, the pharaoh Akhenaten (1353-1337 BC) had decided to worship only the god Aten and to do so had launched a vast iconoclastic campaign intended to eradicate all traces of worship of the god Amon. Here we see the outline of a shift towards henotheism, namely the idea that if there are several divinities, one of them is superior to the others.
From henotheism comes monolatry, namely the fact of worshiping only one god without denying that there are others. The development of henotheism stems from a form of nationalization of the gods which was notably encouraged by the Achaemenid Persians within their empire. In the biblical story of the Exodus, the alliance that the prophet Moses concluded with Yahweh was conditioned by the latter on the fact that the people of Israel made him their sole and exclusive god and renounced honoring others, which clearly shows that the existence of other gods is then recognized.
It was only around the 6th century. av. BC that Judaism asserts itself as a monotheism, that is to say that it postulates the existence of a single and universal god and therefore considers any other religious belief to be false. The true innovation introduced by monotheism is not so much the idea of divine unity as that of exclusivity and, with it, of truth.
97 notes
·
View notes
Note
This may be a bit of a dump question but I've always wondered about this and I thought I could ask this from you since you seem to know more about it. I hope that's okay! Are the translations of the bible and their differences very important? Are the messages that the writings send us that different from each other depending on the translation?
it's very important. translation is an art, like anything else. from a semitic language like hebrew or arabic, it's difficult and often impossible to fully capture the meaning of a word in the original text using english (or any other language). in judaism every stroke of every letter is thought to be an emanation of God: he is the words themselves. the quran is the word of God exactly as it was transmitted to the prophet. so abrahamic religions, bar christianity, place extraordinary important in literal meaning, because you encounter God not only in the meaning of the words but in their very essence, their form and shape.
scriptural translation has always, always been fraught with problems. for instance jerome, developing the vulgate, encountered exodus 34, where moses encounters God face to face and is transformed with rays of light. the hebrew word for this transformation is קָרַ֛ן, and jerome translate it to "cornuta," horns: for centuries afterward moses is depicted in art as having horns, like a goat, because of this mistranslation. it may be that jerome meant "glorified" rather than "horned," based off his later commentaries and use of the term by previous exegetes, but the fact remains that outside of the theological sphere this single word, translated to a western language, stripped back meaning tragically. even to the extent that it propagated harmful stereotypes about jews.
or consider the use of the word "atonement" in english translations of the new testament: katallage, used in romans 5:11, is translated as atonement, but it actually means "reconciliation" or "restitution." in fact, jesus never speaks of atonement. in the old testament the word translated to atonement is כָּפַר, "kaphar", which means "covering." in 1 peter 4:8 we are told, "love covers over a great number of sins." how different would christian understandings of atonement be if we translated "kaphar" as "covering" and not atonement? forgiveness for wrongdoing becomes not something we offer to or beg from God, but something to which we submit, because the action is removed from us, humble as we are, to the great forgiver- the great lover.
i say all this to contextualize the difficulty of translation to begin with. but in the sense of critical pedagogy, every translation of any religious text is subject to the bias of the translator. a good translator is conscious of their bias and seeks to remove it from their work. but christian scripture has an agenda. it is not only something we read for a personal relationship to God but something that is used to dictate right behaviour, as a means of social control, something that develops culture. if a person translating a text has this in mind, they can construct the meaning of the text towards what version of a society or culture they feel is "right," based on their personal and invariably biased understanding of a text. this is why i dislike the kjv translation and never recommend it. the kjv is a product of its time. it is not a good translation of the bible: it is old, but it is not the oldest english translation, and its meaning is absolutely skewed. this is difficult, because many evangelical christians believe the kjv is the absolute word of God, and they are already wrong, because no translation will ever be absolute truth: it is only translation.
words are a limiting system. when we try to capture the essence of something like a god, we are limiting him to our vocabulary.
i always recommend the nrsv because it is version i use for scholarly work. it isn't beautiful but it is as close to a "correct" translation as you can get. but i always supplement my reading with other tools: the jewish annotated new testament is wonderful, for instance, and biblehub has detailed interlinear translations of different translations and the original text. but i am also aware i will never be able to fully comprehend the depth and beautiful of scripture until i learn hebrew and greek, at minimum. but this should not discourage anyone: scripture is meant to be read. but it has to be read actively, critically. God wants you to swallow his words, but he needs you to chew them first.
40 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi curious anon here. You mentioned in one of your posts (I think the sennek one? If I’m spelling it right) that the exodus from Egypt was metaphorical as the enslavement in Egypt didn’t happen, but I thought it did? Can you explain? (If you’re happy to of course)
Hi Anon! Thanks for your question. My response is looong lol (you got me going about a special interest), so buckle up!
Sooo I’m going to make a few guesses here, based on the way you’ve phrased your question. Judging from the fact that you’ve written Sukkot as “sennek” (I've looked through recent posts, and I think this is the post you're referring to), I’m going to guess that you’re not Jewish.
And judging from the fact that you think that Shemot, or “Names” (commonly written in Christian bibles as Exodus), is a literal historical account of Jewish history, I’m guessing that you have a Christian background.
You’re not alone in this. And I’m not saying this to pick on you. Many Christians have a literalist interpretation of the Bible, and most have zero knowledge of Jewish history (aside from maybe knowing some facts about the Holocaust). And so, what knowledge of Jewish history you have mostly comes from the Tanakh (what you call the Old Testament).
Tanakh is an acronym. It stands for Torah (the Five Books of Moses), Nevi’im (Prophets), Ketuvim (Writings). Also, the Tanakh and the “Old Testament” are not the same. The Tanakh has its own internal organization that makes sense for Jewish practice. The various Christian movements took the Tanakh, cut it up, reordered it, and then often mistranslated it as a way to justify the persecution of various groups of people — I’m looking at you, King James Bible.
But back to Shemot, the “Exodus” story. The story of Moshe leading the Israelites out of Egypt is more of a Canaanite cultural memory of the Late Bronze Age Collapse between around 1200 – 1150 BCE, which was preserved in oral history and passed down through the ages until it was written down in the form that we know it in the 6th century BCE by Jewish leaders from the Southern Kingdom of Judah.
Since the text is influenced by Babylonian culture and mythology, just as Bereshit is (which you know as Genesis), it is likely that some of the writing and editing of Shemot took place during and after the Babylonian exile in the 500s BCE.
Now, I’m guessing that what I’ve just written in these two paragraphs above sounds very strange to you.
Wait, you might say, didn’t the Israelites conquer the land of Canaan?
Wasn’t the "Exodus" written by Moses’s own hand during the 13th century BCE?
And wasn’t the Pharaoh in the Exodus Ramesses II (aka Ramesses the Great), who ruled in the 13th century BCE?
Actually, no. None of that happened.
The Israelites didn’t conquer Canaan. The Israelites were the same people as the Canaanites, and these are the same peoples as who later became the Jews, as I will explain. The Semitic peoples who would become the Jewish people have been in this area of the Levant since the Bronze Age.
Moshe was not a historical figure and did not write the Torah.
The “Pharaoh” in Exodus is not any specific Egyptian ruler (Ramesses the Great as the “Pharaoh” is mostly a pop culture theory from the 20th century).
Okay, now that I’ve said all that, let’s dive in.
The first ever mention of Israel was inscribed in the Merneptah Stele, somewhere between 1213 to 1203 BCE. Pharaoh Merneptah, who was the Pharaoh after Ramesses the Great, describes a campaign in Canaan to subdue a people called Israel. But there is no mention of plagues or an exodus because those things didn’t happen. The Canaanites were not slaves in Egypt. Canaan was a vassal state of Egypt.
In fact, the events that occurred during the reign of a later Pharaoh, Ramesses III, relate more to Jewish history. Ramesses III won a pyrrhic victory over the Peleset and other “Sea Peoples” who came to Egypt fighting for resources during a time of famine, earthquakes, and extreme societal turmoil. And Ramesses III would witness the beginning of the end of the Bronze Age.
The Canaanites, who were a Semitic people in the Levant, gradually evolved into the people who would become the Northern Kingdom of Israel and the Southern Kingdom of Judah (i.e., Jewish people), but during the 13th Century BCE, they were Canaanites, not Jews.
The Canaanites were polytheistic, worshiping a complex pantheon of gods; they didn’t follow the later Jewish dietary laws (i.e., they ate pork); and their religious practice bore little to no resemblance to the Jewish people of the Second Temple Period.
So, to reiterate, the people in Canaan who called themselves Israel during the Bronze Age were a Semitic people, but they were not recognizably Jewish, at least not to us Jews today. Canaan was a vassal state of Egypt, just as Ugarit and the Hittite Empire were.
Canaan was part of the vast trading alliance that allowed the Bronze Age to produce the metal that historians have named it for: bronze.
Bronze is a mixture of copper and tin (about 90% copper and 10% tin), and in order to make it, the kingdoms of the Bronze Age had to coordinate the mining, transportation, and smelting of these metals from all over the known world. This trading network allowed for the exchange of all sorts of goods, from grain to textiles to gold. Canaan was just one of these trading partners.
Well, between 1200 BCE and 1150 BCE, this entire trading alliance that allowed Bronze Age society to function went (pardon the expression) completely tits up. This is likely due to a large array of events, including famine and earthquakes, which led to an overall societal disarray.
Some of the people who were hardest hit by the famine, people from Sardinia and Sicily to Mycenae and Crete, came together in a loose organization of peoples, looking for greener pastures. These were all peoples who were known to Egypt, and many of them had either served Egypt directly or had traded with Egypt during better days. According to ancient records, this loose grouping of peoples would arrive at various cities, consume resources there, and then leave for the next city (sacking the city in the process).
Just to be clear, these people were just as much the victims of famine as the cities they sacked. There were no “good guys” or “bad guys” in this equation, just people trying as best as they could to survive in a world that was going to shit.
Well, these “Sea Peoples” (as they were much later dubbed in the 19th century CE) eventually made their way to Egypt, but Ramesses III defeated them in battle around 1175 BCE. He had the battle immortalized on his mortuary temple at Medinet Habu.
We don’t know much about these Sea Peoples, but we do know what the Egyptians called them. And from those names, we can figure out some of their origins. Peoples such as the Ekwesh and the Denyen. These were likely the Achaeans and the Danaans.
If you’re familiar with Homer’s Iliad, you’ll recognize these as some of the names that Homer gives to the Greek tribes. Many of the Sea Peoples were from city states that are now part of Greece and Italy.
Yes, the Late Bronze Age Collapse of the 12th Century BCE didn’t just get handed down as a cultural memory of the “Exodus” to the people who would centuries later become the Jews. That cataclysm also inspired the stories that “Homer” would later canonize as the Trojan War in the Iliad and the Odyssey. The Exodus and the Trojan War are both ancient cultural memories of the same societal collapse.
And neither the Trojan War nor the Exodus are factual. However, despite having little to no historicity, they both capture a similar feeling of the world being turned upside down.
Well, back to the Sea Peoples. Remember the Peleset that I mentioned a few paragraphs ago? They were one of these “Sea Peoples” that Ramesses III defeated. They were likely Mycenaean in origin, and possibly originated from Crete. After Ramesses III defeated them, he needed a place to relocate them along with several other tribes, including the Denyen and Tjeker. It was a “you don’t have to go home, but you can’t stay here” situation.
So, Egypt rounded up the surviving Peleset and sent them north to settle — to the land of Canaan.
Now, if you have some Biblical background, let me ask you this. What does “Peleset” sound like? What if we start it with an aspirated consonant, more of a “Ph” instead of a “P”?
That’s right. The Peleset settled in Canaan and became the Philistines.
This is where the real story of the people who would become the Jews begins.
As the Mycenaean (aka Greek) Peleset settled in their new home, they clashed with the Semitic Israelite people of Canaan. Some of these Canaanites fought back. These Canaanites also organized themselves into different groups, or “tribes.” (See where this is going?) Some of these tribes were in the Northern area of Canaan, and some were in the South, but there was a delineation between North and South — aka they did not start out as one people and then split in two. They started as two separate groups.
If you’re following me so far, you’ll know that I’m now talking about what would in time become the Northern Kingdom of Israel and the Southern Kingdom of Judah.
Well, backtracking a bit. The Bronze Age was ending, and the Iron Age was about to begin. The Peleset/Philistines were experts at smelting iron, which was harder to work with than bronze due to it having a much higher smelting temperature. When the Peleset settled in Canaan, they brought this iron smelting knowledge with them, and they used it to make weapons to subdue the local Canaanite peoples. The Canaanites therefore had to fight back “with sticks and stones.”
Hmm. Does that sound familiar? Who is one of the most famous Philistines you can think of from the Tanakh (the Old Testament)? I’ll give you a guess. It’s in the Book of Samuel (in the Tanakh, that’s in the Nevi’im — The Prophets).
That’s right. Goliath.
The story of “David and Goliath” is likely a Jewish cultural memory that was transmitted orally from the time of the Canaanite struggles against the Peleset.
The man who would become King David used a well-slinged stone to fell the much greater Goliath, and then he used Goliath’s own iron sword to cut off Goliath’s head.
In this metaphor, we can see the struggle between the Canaanite tribes and the Peleset, as the Canaanites fought to hold off the Peleset’s greater military might.
Historically, the Peleset eventually intermarried with the Canaanites, and within several generations, they were all one people. Likewise, the Mycenaean Denyen tribe may have settled in the Northern Kingdom of Israel, intermarried with the Canaanites, and become the Tribe of Dan.
The Book of Samuel, containing the story of David and Goliath, was written down in the form we would recognize today in the 500s BCE during the Babylonian Exile. It is a cultural memory of the time that the Canaanites were unable to wield iron weapons against a much more technologically advanced society, and it would have resonated with the Jews held captive in Babylon.
And with this mention of the Babylonian Exile, I come to the question that remains. And I think the question that you are asking. Where did the story of Shemot, the “Exodus,” the “Going Out,” come from?
And more importantly, why was that story so important to canonize in the Torah — the Jewish people’s “Instruction”?
The Shemot was likely written down and edited in a form that we would recognize today during and after the Babylonian Exile.
So, what was the Babylonian Exile? And what was its impact on Judaism?
To answer that, I need to start this part of the story about 130 years before the Babylonian Exile, in around 730 BCE. We’re now about 450 years after the Late Bronze Age Collapse, when the Canaanites were fighting the Peleset tribe.
Between about 730 and 720 BCE, the Neo-Assyrian Empire conquered the Northern Kingdom of Israel.
Now, you may know this as the time when the “Ten Tribes of Israel were lost.”
In reality, the Assyrians didn’t capture the entire population of Israel. They did capture the Israelite elite and force them to relocate to Mesopotamia, but there were many people from the Israelite tribes left behind. The Ten Tribes were never “lost” because many of the remaining people in the Northern Kingdom migrated south to the Kingdom of Judah.
One such group of people from the Northern Kingdom of Israel maintained their distinct identity and still exist today: the Samaritans. These are the people who today are the Samaritan Israelites. They have their own Torah and their own Temple on Mount Gerizim, where they continue the tradition of animal sacrifice, as the Jews did in Jerusalem before the Romans destroyed the Second Temple in 70 CE. The Samaritans keep the Sabbath, they observe Kashrut laws (i.e., they keep kosher), and they hold sacrifices on Yom Kippur and Pesach. In short, they have maintained religious practices that are similar to Judaism during the Second Temple period.
This mass migration into the Kingdom of Judah in the late 700s and early 600s BCE is where Judaism as we know it today really started to take shape.
At that time, the people of the Northern Kingdom of Israel were polytheistic. They ate pork. They did many of the things that the writers of the Torah tell the Jews not to do.
This is where many of these commandments began, when the priests of Judah needed to define what it was to be a Jew (a member of the Tribe of Judah), in the face of this mass migration from the Kingdom of Israel.
You see, the Ancient Jews didn’t know about germ theory or recognize that trichinosis was caused by eating undercooked pork. That’s not why pigs are treyf. Pigs are treyf because eating pork began as a societal taboo. In short, pigs take a lot of resources to care for, and they eat people food, not grass (i.e. they don’t chew a cud). So if you kept pigs, you would be taking away resources from other people. When you are living in a precarious society that is constantly being raided and conquered by outsiders, you have to make sure that your people are fed, and if you’re competing with a particular livestock over food, that livestock has to be outlawed.
This time period is also likely when the Kingdom of Judah started to practice monolatry (worshiping one God without explicitly denying the existence of other Gods). The people of Judah worshiped YHWH (Adonai) as their God, and the Northern Kingdom of Israel worshiped El as the head of their polytheistic pantheon. The Jews put both of them together as the same G-d. That is why the Bereshit (Genesis) begins:
When Elohim (G-d) began to shape heaven and earth, and the earth then was welter and waste, and darkness over Tehom (the Deep), and the breath of Elohim (G-d) hovering over the waters
NOTE: This is a modification to Robert Alter’s translation of the first two lines of Bereshit (Genesis) in the Tanakh. In a few paragraphs, I will explain the modification I’ve made of transliterating the Hebrew word “Tehom,” instead of (mis)translating this word as “the Deep” as in nearly every translation of Genesis.
Then over the next two hundred years, monolatry would gradually become monotheism. One of the Northern Kingdom’s gods, Baal, was especially popular, so the Judean leadership had to expressly forbid the worship of this god during the writing of the Tanakh.
The message was clear: If we’re going to be one people, we need to worship one G-d. And the importance of the Babylonian Exile cannot be overstated in this shift from monolatry to monotheism. The period during and after the Babylonian Exile is when most of the Tanakh was edited into a form that we would recognize today.
So, I come back to the question, what was the Babylonian Exile? It began, as many wars do, as a conflict over monetary tribute.
Around 598 BCE, the Judean King Jehoiakim refused to continue paying tribute to the Babylonian King Nebuchadnezzar II. And so in around 597 BCE, Nebuchadnezzar II’s troops besieged Jerusalem, killed King Jehoiakim, and captured much of the Judean leadership, holding them captive in Babylon. Over the next ten years, Nebuchadnezzar II continued his siege of Jerusalem, and in 587, he destroyed the First Temple, looted it for its treasures, and took more of the Jews captive. The deportation of the Jewish people to Babylon continued throughout the 580s BCE.
So, by the 570s BCE, the majority of the Jews were captives in a strange land. They were second-class citizens with few rights. The Jews feared that their people would start to assimilate into Babylonian society, intermarry so that they could secure greater freedom for their descendants, and then ultimately disappear as a unique people.
The Jewish leadership knew that this assimilation would begin by the Jews worshiping Babylonian gods.
So the Jewish leadership had a brilliant idea. They said, “We are not in danger of our people drifting into polytheism, assimilation, and cultural death, because we declare that the Babylonian gods do not exist. There is only one G-d, Adonai.”
Now we have left monolatry, and we are fully in monotheism.
And so, the Jews in captivity took Babylonian stories that their children heard around them, and they made these stories Jewish.
That is why the opening lines of Genesis sound so much like the opening lines of the Babylonian creation story, the Enuma Elish.
And remember when I mentioned that I had transliterated “Tehom” in the first two lines of Bereshit (Genesis) above, instead of using the standard translation of “the Deep”? That is because Tehom is a Hebrew cognate for the Babylonian sea goddess Tiamat, who the Babylonian god Marduk defeated and used to shape the heavens and the earth, just as Elohim shaped the heavens and the earth.
When you read the Enuma Elish, you can see the parallels to Genesis:
When the heavens above did not exist, And earth beneath had not come into being — There was Apsû, the first in order, their begetter, And demiurge Tiamat, who gave birth to them all; They had mingled their waters together Before meadow-land had coalesced and reed-bed was to be found — When not one of the gods had been formed Or had come into being, when no destinies had been decreed, The gods were created within them
That is also why the flood story of Noah and the Ark sounds so much like the flood story from the Epic of Gilgamesh.
That is why the story of Moshe’s mother saving him by placing him in a basket on the Nile River parallels the story of King Sargon of Akkad’s mother saving him by placing him in a basket on the Euphrates River.
In order to survive as a people, the Jews consolidated all gods into one G-d. Adonai. Shema Yisrael Adonai eloheinu Adonai ehad. "Hear O Israel, the Lord is our God, the Lord is One."
The Jews said, yes, we acknowledge that we are hearing these polytheistic Babylonian stories in our captivity, but we will make them our own so that we can continue to exist as a people.
But back to your question. What about the story told in Shemot, the “Exodus” from the Land of Egypt?
I think by now you can see the parallels between the Jewish people held as captives in Babylon and the story that they told, of the Israelites held as slaves in Egypt.
And so, the Exodus story, which had been told and retold in various ways as a means to process the cataclysmic trauma of the Late Bronze Age Collapse (similar to the oral retellings of the Trojan War epic before they were written down by “Homer”), now took on a new meaning.
The Exodus story now represented the Jewish people’s hope for escape from Babylon. It represented the Jewish people’s desire to rebuild the Temple in Jerusalem that Nebuchadnezzar II had destroyed. It represented the acceptance that it would take at least a generation before the Jews would be able to return to Jerusalem.
And it represented a cautionary tale about leaders who become too powerful, no matter how beloved they may be.
At a Torah study this Sukkot, the Rabbi discussed why the writers of Devarim (Deuteronomy) said that Moshe couldn’t enter Canaan, even though he'd led the Israelites out of Egypt (which, again, didn't literally happen). And one interpretation is because the Jewish leaders were writing and editing the Exodus during and shortly after the Babylonian Exile, and after seeing the Kingdom of Judah fall because of bad leadership. And they were saying, “It doesn't matter how beloved a leader is. If they start becoming a demagogue, and start behaving as someone who is drunk on their own power, you can't trust them as a leader. And you need to find new leadership.” And damn if that isn't a lesson that we could all stand to learn from!
So, was the Exodus story historically true? No. But does it matter that the Exodus story isn’t historically true? No, it does not. It was and is and will continue to be deeply meaningful to the Jewish people. The Shemot, the Exodus, the breaking of chains, the escape from the “Pharaohs” that enslave us — these are still deeply meaningful to us as Jews.
Was Moshe a historical figure? No, he was not. Is he one of the most fascinating, inspiring, and deeply human figures in Jewish tradition, and in literature in general? Yes, he is. Moshe was an emergent leader, an everyman, a stutterer, and yet he was chosen to lead and speak for his people. He was chosen to write the Torah, the “Instruction,” that has guided us for thousands of years. It doesn't matter that he was not a historical person. What matters is what he stands for. He is the one who directed us in what it is to be Jewish.
Now, fast forward to 538 BCE, around 60 years after the Jews were first taken as captives to Babylon. The Jewish people’s prayers were answered when Persian King Cyrus the Great defeated Babylon in battle, and allowed the Jews to return to Jerusalem, where they began construction on the Second Temple, which was completed around 515 BCE.
The Persian Zoroastrians were henotheistic (they worshiped one God, Ahura Mazda, but they recognized other gods as well). They also had a chief adversarial deity, Angra Mainyu, who was in direct opposition to Ahura Mazda.
Just as the Jews had incorporated Babylonian stories into their texts as a way to preserve their identity as a Jewish people, the Jews now incorporated this idea of “good versus evil” (i.e., It’s better to assimilate the foreign god to us, than to assimilate us to the foreign god).
This shift can be seen in the later story of the Book of Job, which is in the Ketuvim (Writings). Jews have no devil and no hell. There is no “eternal afterlife damnation," and there is no “original sin.” Jews believe in living a good life, right here on earth, and being buried in Jewish soil. Some Jews believe that we go to Sheol when we die, which is a shadowy place of peaceful rest, similar to the Greek realm of Hades. In the Book of Job, the Hebrew word “hassatan” (which Christians transliterate as “Satan”) is just a lawyerly adversary, like a “devil’s advocate” who debates for the other side of the argument. It’s certainly not anything akin to a Christian “devil.”
However, throughout the Second Temple period, various apocalyptic Jewish sects would arise in response to Greek and then Roman persecution, inspired by the Zoroastrian idea of a battle between “the light and the dark.”
In the 1st and 2nd centuries CE, this would lead to a search for the Moshiach: a human leader (not divine) who was descended from the line of King David, and who would restore Jerusalem. And that would not culminate in Jesus (Jews don’t recognize Jesus as Moshiach — for us, he's a really cool dude who said some very profound things, but he's not That Guy).
Rather, the search for Moshiach would stem from the events leading up to the Jewish War, which concluded in 70 CE with the Romans destroying the Second Temple and sacking Jerusalem, and it would culminate in the Bar Kochba revolt between 132 and 135 CE. The Bar Kochba revolt resulted in a Roman campaign of systematic Jewish slaughter and “ethnic cleansing” that nearly destroyed the Jewish people a second time. But that’s a story for another day!
In closing, I encourage you to learn more about Jewish history. And don’t just learn about us from the Holocaust, our darkest hour. Learn about our full history. I highly recommend Sam Aronow’s excellent series on YouTube, which is an ongoing Jewish history project. The YouTube channel Useful Charts also provides excellent overviews of Jewish history.
#tfw a simple ask compels you to write 4000 words#i hope i've answered your question anon!#jewish history#jewish studies#judaism tag
106 notes
·
View notes