#synagogue destruction
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

The tenth of Av
#I wanted to do a piece about synagogue destruction in Kuttenberg#specifically the day after the destruction#if I did smth wrong with tefillin I'm sorry#I googled how the correct way to wear them in Ashkenazi tradition looks like#but I'm not sure if I captured it right#he is not wearing a tallit cause he is not married yet#kcd 2 samuel#kcd2 samuel#samuel kcd2#kcd2 fanart#kingdom come#kingdom come 2#kingdom come deliverance#kingdom come deliverance 2#samuel kcd#my art
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
Praying for the Peace of Israel: A Call Beyond the Psalms
Introduction: A Longing for Peace When we open the Bible to the time of King David in the 10th century BC, we encounter a vision of peace that stirs the soul. In Psalms, we’re instructed to “pray for the peace of Jerusalem” (Psalm 122:6), a call rooted in David’s longing for a kingdom where God’s shalom—wholeness, rest, and righteousness—would reign. David dreamed of a land where “everyone would…
#AD 70 destruction#AntiChrist#biblical prophecy#church apostasy#Davidic kingdom#end times#fullness of Gentiles#Hosea 5:4-7#Israel apostasy#Jeremiah 7:16#Jesus peace#kingdom transfer#Matthew 21:43#Messianic Jews#prayer discernment#Psalm 122:6#rapture#shalom#spiritual temple#synagogue of Satan
0 notes
Text
“never let them convince you broken glass or property damage is violence”
the pogrom that kickstarted the Holocaust is literally named after the broken glass from the destruction of Jewish businesses, synagogues, and homes
even outside of literal pogroms, smashing windows & defacing people’s property during a protest or riot comes with an implicit threat of violence in the same way that someone punching a hole in the wall or smashing a chair in the middle of an argument does.
it may be less violent than if they physically hit your body, but it is still threatening, and is often a precursor to more extreme actions that do cause physical harm.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Gotta occasionally post about antisemitism like rent-lowering gunshots so here's a periodic reminder that:
1. No one is saying you shouldn't advocate for Palestine. I'm also upset about the treatment of Palestinians and I really hate war. But harassing random Jews is not going to help.
2. If you could accept the fact that random civilizations do not represent their nation's government for every other country except Israel, you're being antisemitic.
3. Even if every single Israeli was completely, 100% on board with Netanyahu's bullshit (which they're not), that does not justify antisemitism. That does not justify October 7th. That does not justify pogroms. That does not justify the intentional destruction of synagogues. That does not justify the mistreatment of Jews anywhere.
4. Too many leftists are preoccupied with finding someone acceptable to hate instead of standing up for marginalized communities. Work on this, please.
I'm tired. I want peace. And I want antisemites to not fucking follow me.
#antisemitism#current events#jumblr#<- tagging that for anyone who needs a rent-lowering antisemitism post#original post
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient Greek Women Mathematicians you didn't know about

Αίθρα - Aethra (10th - 9th century BC), daughter of the king of Troizina Pitthea and mother of Theseus, knew mathematics in another capacity unknown to many. So sacred to the beginnings of the most cerebral science, Aethra taught arithmetic to the children of Troizina, with that complex awe-inspiring method, since there was no zero… and the numbers were symbolically complex, as their symbols required many repetitions.
Πολυγνώτη - Polygnoti (7th - 6th century BC) The historian Lovon Argeios mentions Polygnotis as a companion and student of Thalis. A scholar of many geometric theorems, it is said in Vitruvius' testimony, that she contributed to the simplification of arithmetic symbols by introducing the principle of acrophony. She managed this by introducing alphabetic letters that corresponded to each in the initial letter of the name of the number. Thus, Δ, the initial of Δέκα (ΤΕΝ), represents the number 10. X, the initial of Χίλια (Thousand), represents the number 1000 etc. According to Vitruvius, Polygnoti formulated and first proved the proposition "Εν κύκλω η εν τω ημικυκλίω γωνία ορθή εστίν" - "In the circle the angle in the hemi-circle is right angle."
Θεμιστόκλεια - Themistoklia (6th century BC). Diogenes the Laertius scholar-writer mentions it as Αριστόκλεια - Aristoclia or Θεόκλεια - Theoclia. Pythagoras took most of his moral principles from the Delphic priestess Themistoclia, who at the same time introduced him to the principles of arithmetic and geometry. According to the philosopher Aristoxenos (4th century BC), Themistoclia taught mathematics to those of the visitors of Delphi who had the relevant appeal. Legend has it that Themistoclia decorated the altar of Apollo with geometric shapes. According to Aristoxenos, Pythagoras admired the knowledge and wisdom of Themistoclia, a fact that prompted him to accept women later in his School.
Μελίσσα - Melissa (6th century BC). Pupil of Pythagoras. She was involved in the construction of regular polygons. Lovon Argeios writes about an unknown work of hers: "Ο Κύκλος Φυσίν - η Μελίσσα - Των Εγγραφομένων Πολυγώνων Απάντων Εστί". (The title translates to "The circle is always the basis of the written polygons" or so.)
Τυμίχα - Tymicha (6th century BC). Thymiha, wife of Crotonian Millios, was (according to Diogenes Laertius) a Spartan, born in Croton. From a very early age, she became a member of the Pythagorean community. Iamblichus mentions a book about "friend numbers". After the destruction of the school by the Democrats of Croton, Tymicha took refuge in Syracuse. The tyrant of Syracuse, Dionysios, demanded that Tymicha reveal to him the secrets of the Pythagorean teaching for a great reward. She flatly refused and even cut her own tongue with her teeth and spat in Dionysius' face. This fact is reported by Hippobotus and Neanthis.
Βιτάλη - Vitali or Vistala (6th – 5th century BC). Vitali was the daughter of Damos and granddaughter of Pythagoras, and an expert in Pythagorean mathematics. Before Pythagoras died, he entrusted her with the "memoirs", that is, the philosophical texts of her father.
Πανδροσίων ή Πάνδροσος - Pandrosion or Pandrossos (4th century AD). Alexandrian geometer, probably a student of Pappos, who dedicates to her the third book of the "Synagogue". Pandrosion divides geometric problems into three categories:" Three genera are of the problems in Geometry and these, levels are called, and the other linear ones."
Πυθαΐς - Pythais (2nd century BC). Geometer, daughter of the mathematician Zenodoros.
Αξιόθεα - Axiothea (4th century BC). She is also a student, like Lasthenia, of Plato's academy. She came to Athens from the Peloponnesian city of Fliounda. She showed a special interest in mathematics and natural philosophy, and later taught these sciences in Corinth and Athens.
Περικτιόνη - Periktioni (5th century BC). Pythagorean philosopher, writer, and mathematician. Various sources identify her with Perictioni, Plato's mother and Critius' daughter. Plato owes his first acquaintance with mathematics and philosophy to Perictioni.
Διοτίμα - Diotima from Mantineia (6th-5th century BC). In Plato's "Symposium", Socrates refers to the Teacher of Diotima, a priestess in Mantineia, who was a Pythagorean and a connoisseur of Pythagorean numerology. According to Xenophon, Diotima had no difficulty in understanding the most complex geometric theorems.

Iamblichos, in his work "On Pythagorean Life", saved the names of Pythagorean women who were connoisseurs of Pythagorean philosophy and Pythagorean mathematics. We have already mentioned some of them. The rest:
Ρυνδακώ - Rynthako
Οκκελώ - Okkelo
Χειλωνίς - Chilonis
Κρατησίκλεια - Kratisiklia
Λασθένια - Lasthenia
Αβροτέλεια - Avrotelia
Εχεκράτεια - Ehekratia
Θεανώ - Theano
Τυρσηνίς - Tyrsinis
Πεισιρρόδη - Pisirrodi
Θεαδούσα - Theathousa
Βοιώ - Voio
Βαβέλυκα - Vavelyka
Κλεαίχμα - Cleaihma
Νισθαιαδούσα - Nistheathousa
Νικαρέτη - Nikareti from Corinth
There are so many women whose contribution to science remains hidden. We should strive to find out about more of them! For more information, check out the books of the Greek philologist, lecturer, and professor of ancient Greek history and language, Anna Tziropoulou-Eustathiou.
#I noted those names down from different sources and I copied a few more info from a comment under a video#international women's day#science#history#mathematics#pythagoras#greek women#greek history#hellas#women in stem#women in science#women in mathematics#Pythagorean mathematics#women's history
796 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is why I do not call for the destruction or dismantling of countries. This is why I am wary and judgmental of those of you who do.
You sound like my right-wing father. You sound like the worst of American society.
I grew up in the 90’s. I grew up during a military operation called “Desert Storm”. To most people, they know it as the Gulf War. I grew up with a military father. I grew up with right-wing rhetoric. I grew up with someone who called for the destruction of countries.
“Glass the Middle East and turn it into a parking lot” was a very common sentiment at the time, and not just from my father. By “glass”, people mean to bomb these countries (many of which are deserts) so brutally that the sand itself melts into glass.
It is a call for genocide. It is the call for the dismantling of entire countries because their governments were “too evil”.
(Of course, that’s just the line the public was fed. Behind the scenes, it was also largely about access to oil, and we all know that)
The Gulf War was specifically about Iraq, but let’s be clear: Americans did not give a fuck which country it was, “The Middle East” was talked about as a single entity that was evil because it was Muslim. The civilians of these countries were simultaneously evil guerrilla combatants (because they were Muslim) and victims needing “liberation” by Americans. American soldiers were described as bringing “freedom” to the poor oppressed ignorant people of the Middle East. My father still hates all Muslims to this day.
10 years later, 9/11 happened.
Time will never erase the stomach-clenching fear I felt. Not fear of Saudi Arabia. I was 17 by then and I knew better. No, I was afraid FOR them, because I knew what America would do, and I hated it. I saw the people all around me once again calling for the destruction of a country, a government, and deciding America had the right to do it. I watched people froth at the mouth and pound their chests the chance to attack another middle eastern country. Islamophobic propaganda was absolutely everywhere, and life in America for anyone even suspected of being Muslim was a living hell.
So do excuse me when I side-eye you as you call for Israel’s destruction. Excuse me if I roll my eyes when you claim Hamas are “freedom fighters”. Excuse me when I hear you spreading blatant antisemitic propaganda like it’s truth. Excuse me as I see you blocking Jewish students on campuses, attacking synagogues, and screaming antisemitic slurs at Jewish school children.
Because at the end of the day, all of you calling for Israel’s destruction sound like my father.. It doesn’t matter what your justification is. I just see the same hatred that has consumed Americans since the 90’s aimed at MENA countries. You’ve just moved on to the next target. I grew up with this hateful rhetoric and I REJECTED it.
Why have you embraced it?
“But this time the country we’ve chosen to hate and that we’re saying deserves to be glassed actually deserves it! This time the civilians really are evil!”
Yeah. Sure.
688 notes
·
View notes
Text
awful tweet warning:
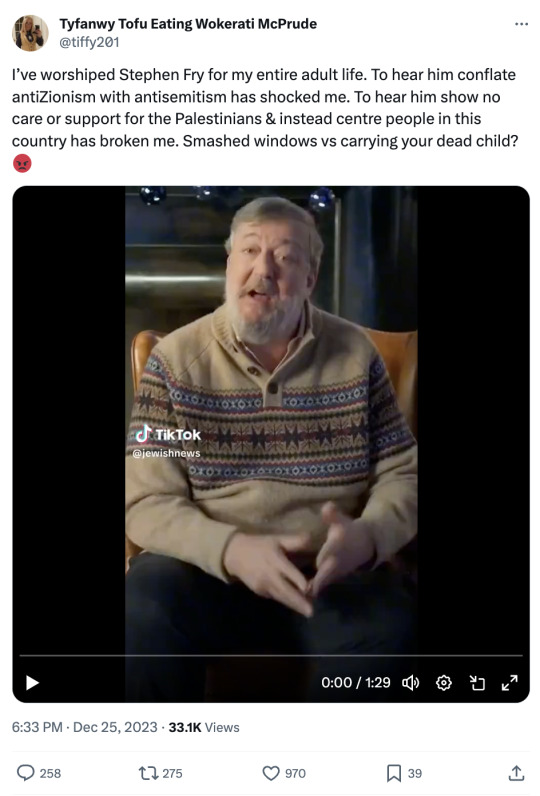
Before I describe everything that's wrong with this tweet, let me transcribe Stephen Fry's words:
I am Stephen Fry, and I am a Jew. The great Irish thinker and writer Conor Cruise O'Brien once said that antisemitism is a light sleeper. Well, it seems to have woken up of late. The horrendous events of October 7th, and the Israeli response, seem to have stirred up this ancient hatred. It's agonizing to see all violence and destruction that is unfolding, and the terrible loss of life on both sides brings me an overwhelming sadness and heartache. But whatever our opinions on what is happening, there can be no excuse for the behaviour of some of our citizens. Since October the 7th, there have been 50 separate reported incidents of antisemitism every single day in London alone, an increase of 1350%, according to the Metropolitan police. Shop windows smashed, stars of David and swastikas daubed on walls of Jewish properties, synagogues, and cemeteries. Jewish schools have been forced to close. There is real fear stalking the Jewish neighbourhoods of Britain. Jewish people here are becoming fearful of showing themselves, in Britain, in 2023.
(Then it cuts off.)
For those who still don't know why this tweet was ignorant and inane, let me explain.
"To hear him conflate antiZionism with antisemitism has shocked me."
Guess how many times Stephen Fry mentions zionism? Zero! Guess how many times he mentions the country of Israel? Zero! (Unless you count "the Israeli response" which is unrelated to the existence of the country, or Zionism at all.) What this person is saying, is that they consider the smashing of shop windows, and the vandalism and marking of Jewish property, to be anti-Zionism. Considering they are an anti-Zionist, by following their logic, we can conclude that they not only believe this destruction and harassment is acceptable, but they believe it is ethical.
Further, they accuse him of showing no care for the Palestinians, even though he explicitly states that the loss of life on both sides brings him overwhelming sadness.
Finally, they accuse him of "[Centring] people in this country". It is disturbing that this person believes one cannot be concerned over two issues at a time. It perpetuates the idea that we can only talk about the "worst oppression" and talking about anything else means you are complicit in "silencing" someone else. If this were true, we would not be allowed to talk about Gaza either, or Ukraine, or police brutality, racism, islamophobia, homophobia, transphobia, and so on and so on, because clearly there are other issues with hundreds of thousands more deaths, and millions more displacements, so why bring attention to it ever?
Unfortunately, people are not talking about those countries, like Syria, Yemen, Ethiopia, Congo, and more, and anyone who does is spammed with "free Palestine" comments. In fact, the most I've heard people talking about Sudan is when these TikTok geopolitical experts attempt to spam the Palestinian flag and get it wrong.
This is not new. This is obviously not new. I have seen tweets like these every single day in the hundreds for the last 80 days. It is not surprising that people think smashing windows is "anti-zionism", nor that they think it good. It is not surprising that they hear a Jew speak, and experience shock and disgust, regardless of what we say.
I do wonder if they would regard anything short of a second Holocaust as antisemitism.
#antisemitism#i/p#jumblr#israel#palestine#stephen fry#israel palestine conflict#leftist antisemitism#gaza#avi posts
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Jewish women visiting the Užupis cemetery in Vilna, Lithuania, 1917
In the 19th century the road from Vilna Old town through Užupis leading to the Jewish cemetery was occasionally called a death road. It received such a macabre name because of long funeral processions that were going through it. The cemetery was destroyed by the Soviet authorities in the 1960s following the destruction of the Great Synagogue of Vilna. Tombstones were used for staircases in various construction works around the city. Currently a memorial constructed of them marks the location of the former entrance to the cemetery.
217 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Casey Babb
While the outbreak of antisemitism throughout the West has been precipitous in virtually every country—the tenor, violence, and extremist nature of Jew-hatred in Canada has ratcheted up in a way few other places on Earth have experienced.
Consider the following—much of which has gotten scant media attention.
Targeting Jews in Their Backyards
In September 2024 protesters sympathetic to Hamas and the “resistance” jubilantly rallied outside a Jewish retirement facility in Ottawa where several Holocaust survivors live, and where 60 percent of the residents suffer from dementia. Chants of “Go back to Europe” and “We want bullets and missiles!” in Arabic could be heard from their bedrooms.
On Remembrance Day in 2024 at Sir Robert Borden public school in Ottawa, where there is a large Jewish student body, a Palestinian protest song was the only song played during an event to honor Canadian soldiers. When pressed on the choice of music, Principal Aaron Hobbs said it was chosen to add some diversity and inclusion to a day usually about “a white guy who has done something related to the military.”
There have been numerous instances where, in predominantly Jewish neighborhoods, protesters have dressed up like Palestinian terrorists, including the October 7 mastermind Yahya Sinwar.
Hundreds of pro-Palestinian protests surrounded the Holocaust Museum in Montreal in March 2024, where they shouted, “Death to Israel” and “Death to the Jews.”
At a softball game for teenage girls between Canada and Israel as part of last year’s Canada Cup Women’s International Softball Championship in Surrey, British Columbia, protesters stood on the sidelines wearing keffiyehs, holding signs that read “Israel is a genocidal state,” with another equating Israel with Nazi Germany.
In April, a pro-Hamas rally was staged in Winnipeg, just steps from a Jewish community center where children attend school and day care.
During Israel’s official day of remembrance for fallen soldiers and victims of terrorism on April 29, protesters stood in front of Beth Emeth Bais Yehuda Synagogue in Toronto waving Palestinian flags. One man wore a sweater that read “Palestinian Holocaust: Never Again Is Now.”
Earlier this month in Montreal, protesters were filmed chanting “All the Zionists are racists” through megaphones at a school for students ages 4 to 16 with intellectual disabilities and autism-spectrum disorders.
These activities aren’t normal protests. They aren’t in front of the Israeli embassy in Ottawa or the Israeli consulate in Toronto. They aren’t directed toward a specific Israeli policy, law, regulation, or act, and they certainly make no mention of Hamas, Hezbollah, or any other terrorist organization that has brought immense death and destruction upon the Palestinians. These are belligerent acts of aggression designed to intimidate Canada’s Jewish community, to coerce them into silence, and ultimately, to extinguish their public presence.Activists gather during the Stop The Genocide rally in Edmonton, Alberta, on April 13, 2025. (Artur Widak/NurPhoto via AP)
Open Antisemitism and Valorizing Terrorism
In October 2024, men masked with keffiyehs took to the streets of Ottawa, calling for Jews to “go back to Europe”—a phrase they’ve repeatedly used everywhere from flag-raising ceremonies to synagogues to university campuses.
In Vancouver, British Columbia, protesters gathered on the one-year anniversary of the October 7, 2023 massacre and declared “We are Hezbollah, and we are Hamas” while burning the Canadian flag.
Protesters have also gathered outside hospitals, such as Toronto’s Mount Sinai—a hospital founded by Jews—where patients could hear screams for an “intifada” from inside the building.
Last March, in downtown Ottawa—on the same streets where former prime minister Justin Trudeau invoked the Emergencies Act in response to the trucker convoy in 2022— a young man dressed as a Hamas terrorist taunted shocked onlookers, the flags of Lebanon and Palestine blowing in the wind behind him.
In November 2024, an estimated 50,000 students, as well as faculty, from universities including Concordia, McGill, and Dawson College took to the streets and campuses, where they overran buildings, destroyed property, and led schools to close. Chants of “Long live the intifada” could be heard, with one protester saying on camera, “The final solution is coming your way.”
In April, a man wearing a keffiyeh in downtown Toronto climbed onto scaffolding, lit an Israeli flag on fire, and doused it with gasoline, while chants of “All Zionists are racists; all Zionists are degenerates” could be heard in the background.
Violent Attacks
Since October 7, 2023, there have also been nearly a dozen terrorism-related incidents in Canada or abroad involving Canadians. These include:
A father-son duo, who had been planning a violent attack in Toronto, were arrested in July 2024.
Two Ottawa youths, plotting to attack the city’s Jewish community, were arrested in February 2024.
The September 2024 arrest of a Pakistani man studying in Toronto who was planning an ISIS-inspired attack against Jews in Brooklyn, New York.
The April arrest of a Yemeni man in Canada planning to join a terrorist organization in the Middle East.
An attack on Edmonton City Hall in January 2024.
A Canadian who traveled to Israel in July 2024 to attack Israeli soldiers.
And this list does not include the Jewish girls school in Toronto that was hit with gunfire on three separate occasions, the multiple shootings at a Jewish school in Montreal, the firebombing of a synagogue in Montreal, the firebombing of a synagogue near Montreal, the endless vandalism of Jewish-owned businesses, the vandalism of homes with swastikas, and the destruction of campaign signs for Jewish politicians running in the 2025 federal election.
Nor does it capture the anti-Israel indoctrination occurring at public schools, universities, and unions across the country, among many other things.
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Jewish youth carries the Star of David from the synagogue in Munich following its destruction on Kristallnacht in 1938.
Never again.
303 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's honestly a bit scary dating again as a jew.
I've come across so many people with "free Palestine" somewhere on their dating app profiles.
And whilst under normal circumstances, whilst I do have a bit of a visceral reaction to the slogan due to antisemites using it to be antisemitic, I like to be optimistic and assume that a person isn't inherently antisemitic as not everyone uses it to be antisemitic. I've met people who don't want the destruction of Israel and jews who say free Palestine. So I never want to assume.
However, what comes into play is that you typically put any politics you strongly agree with on a dating app so people who disagree with that see it and swipe left. An automatic weeding out. Any politics that you don't even want to entertain a person who disagrees with you on, you put in your profile.
So when someone is wanting to weed out anyone who disagrees with them about Palestine, I imagine doesn't want a peaceful one state solution or land for all, they want israel destroyed and jews to suffer.
Which has led to me the realization of "holy shit I may accidentally end up going on a date with an antisemite"
I've also had the wonderful experience of seeing someone who works at a different company but same office floor who has free Palestine in their profile, who I now genuinely feel unsafe being around. Like yeah there is a chance they will be normal about me being jewish and having family in Israel. But also, idk that as a fact and their bio seems to be leaning the other way from that. So now I make sure to avoid them in the elevator or bathroom as much as possible.
What has been a positive is my lesbian ass went on a first date with a woman and she asked me what I did this morning and I said I went to synagogue and she actually had a normal response. Later on in the date we were talking about family we had overseas and I mentioned I had family in Israel and again she was normal about it! She even kissed me a fee minutes later! This does give me some hope.
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
When Hamas themselves compares the student protests to the October 7th massacre by calling it the “Student Flood” (referencing their name for the massacre, “Al-Aqsa Flood”), and sees in them the destruction of Israel and its people, you don’t get to tell Jews we are imagining it when we see that they are violently antisemitic in nature.
We fully understand that the majority of students are not personally assaulting anyone, so you can stop waving that piece of rhetoric around like it means anything. Every single student at every single protest could be perfectly “peaceful” in the sense that they personally never lay a finger on another person, and the rhetoric & narratives being spun out of them would still be steeped in deeply antisemitic rhetoric & tropes that provide & launder justification for violence that make it considerably more likely that someone else will.
We understand this when the right wing does it. Most QAnon posters & members of right wing activist groups like Moms For Liberty or Gays Against Groomers aren’t actively assaulting Jews & queer people, or even directly saying they think all Jews & queer people are inherently evil (it’s just “the Cabal” & “groomers”). Hell, even most January 6th protesters weren’t actively committing felonies.
That doesn’t change the fact that their conspiratorial thinking is steeped in anti-queer, antisemitic, and anti-democratic narratives which provide motive for violence. When right wing “lone wolf” shooters shoot up schools & synagogues & mosques, we understand how the extreme rhetoric of their political spaces have led them to seeing their violence as completely justified & necessary. That is what stochastic terrorism is.
When calls for Global Intifada, more October 7ths, and Palestine “from the River to the Sea” are so ubiquitous that hardly a single protest can go by without them; when imagery of fighters with AK-47s keeps getting plastered around college campuses; when so many of the groups organizing these protests are spreading Khazar Theory, Blood Libel, and the like (and even those who don’t are linked arm-in-arm with those who do); when the core narratives at the root of the infographics shared in the movement erase Jewish history, monolithize Israelis, & misrepresent Zionism as something from the Protocols of the Elders of Zion; when their rhetoric provides justification for discrimination on the basis of religion, ethnicity, or nationality against Jews or Israelis; when Hamas sees these protests as not only advantageous to their regime, but a key part of its strategy, giving it the same branding as their massacre—you do not get to tell us they are not making us unsafe.
#antisemitism#antisemitic flood#i/p#edited:#couple very obvious typos in the original including swapped letters & double instances of words
975 notes
·
View notes
Text
Helpful lists of questions for goyim when it comes to engaging with the Israel-Hamas war 🙂
QUESTIONS TO ASK YOURSELF WHEN A POST ABOUT THE ISRAEL-HAMAS WAR CROSSES YOUR DASH AND YOU WANT TO REBLOG IT:
Does this post link to a source?
If the post does link to a source, is it a credible one?
If the post does not link to a source, is there one screenshotted in the post that you can find? If so, please search out that source and read the entire thing in context. And make sure the source is credible. Ideally, if you decide to reblog it, add a link to the source.
Is the post just screenshots of tweets? If so, you probably should not reblog this. Posts that are just screenshots of tweets are a massive red flag. Do not believe something because it's a twitter screenshot. Frankly this rule is for everyone about everything all the time.
What is the tone of the post? Does it make you angry? If yes, this is a red flag. Exercise caution reblogging.
Does the post frame Israel as a uniquely evil country in need of destruction? Does the post treat Israel with different standards than those that are applied to every other country that has done horrible, horrible things, such as Russia, the UK, or United States? This is a red flag. If the government of Israel falls without some sort of transition plan, there will be Jewish genocide. Anyone advocating for a one-state solution either way is advocating for one group to get genocided. A two-state solution is the only possible peaceful end to this conflict (technically my opinion but I feel comfy stating it as fact).
Does the post treat Hamas as anything other than a terrorist organization? Do not reblog.
Is the post promoting Jewish Voice for Peace/JVP? Do not reblog. That organization is not Jewish and is antisemitic.
What is the focus of the content of the post? Is the post discussing reasonable paths to a ceasefire/peace? Is the post criticizing Israel's actions without using antisemitic stereotypes? Netanyahu is a disgusting fascist who I hate, but even though he is a terrible person you are not allowed to portray him as an antisemitic caricature. Similar to how you don't get to misgender shitty trans people, you don't get to be antisemitic towards shitty Jewish people (even if he's really, really shitty).
How does the post use the word "zionist?" Does the word have any coherent meaning in the post besides "person (often Jew) that I hate?" Does it treat zionists as a group of people who are disgusting and deserve to be murdered and/or raped? Does the use of the word "zionist" completely dehumanize the person/people the label is applied to into nothing more than evil that the Earth must be rid of? This is antisemitic. Do not reblog.
QUESTIONS TO ASK YOURSELF WHEN YOU'RE AT A PRO-PALESTINE PROTEST:
Are people chanting antisemitic slogans such as "globalize the intifada" and/or "from the river to the sea" (these are both antisemitic you cannot remove the antisemitic meaning from them, they are both advocating for the murder of Jewish people, sorry, stop using them.)?
Are people comparing themselves to Palestinians in Gaza? (this is not a joke, I saw a video of a Columbia student who compared Columbia sending out fliers to leave or be suspended to the IDF dropping flyers in Gaza saying "the army is coming in 24 hours.") If so, they care more about fetishizing Palestinian pain and making themselves feel like noble victims than the Israel-Palestine conflict.
Are people harassing Jews? This includes: preventing them from getting to class, yelling things at them like "go back to Poland," and/or physically assaulting them.
Are people defacing Jewish property/monuments? Are people defacing synagogues? Businesses with known Jewish owners? Statues and/or memorials of/for Jews?
What is the purpose of this protest? Would you feel comfortable sharing opinions that differ from the majority? Would you feel comfortable engaging in a conversation about this issue with fellow protesters? Are any of you actually educated on the complicated and lengthy history of the Israel-Palestine conflict? Is the protest about a peaceful solution, or is it just making you angrier and/or more upset? Does the protest/your fellow protestors care more about freeing Palestine so that Palestinians and Israelis can live in peace, or about hating Israel and treating it like a uniquely evil country?
If people are chanting antisemitic slogans, harassing Jews, and/or defacing Jewish things, then this is an antisemitic protest. Do you want to be associated with these people and this protest? If your answer is yes, you are an antisemite-sympathizer, which is basically an antisemite.
MORAL OF THE STORY: antisemitism is all over this issue and it's easy to get more antisemitic and spread antisemitism because bad actors use this issue to indoctrinate people who start off just genuinely caring about the issue but are not educated at all about it or what antisemitism actually looks like. BE CAREFUL. All Jews want, all we've ever wanted, is to be left alone to do our thing. Random Jews are not at fault for the horrific actions taken by the Israeli government since the terrorist attack on October 7th. We support the existence of Israel, but we do not support all of the current government's actions. We are just trying to live. We want there to be a ceasefire now. If you actually read this whole thing, thank you. It means a lot to be listened to.
For those of you that made it to the end, I'll offer one last reminder and one last gentle suggestion.
My last reminder is: "it is not your job to finish the work by neither are you free to ignore it" is a Jewish passage I really like. I think in times like these, it is important to focus on the first half. It is not your job to finish the work. The fate of Palestine does not rest on your shoulders. It's ok. Take time to decompress and log off.
My last suggestion is: one of the biggest Jewish values is "tikkun olam," which means "repairing the world." I think all action when it comes to this conflict (and life in general) should be done with tikkun olam in mind. It doesn't hurt to ask yourself "is this action repairing the world, or further tearing it apart?" no matter what you're doing. Thank you for reading.
263 notes
·
View notes
Text
Golems and Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy
I did a writeup about how a character based on the Jewish folkloric golem might work in Eureka: Investigative Urban Fantasy! It includes a short essay about the thematic implications of the golem, and a set of custom rules for living dolls made of unfired clay.
If you don't know what Eureka is, it's the first tabletop RPG by @anim-ttrpgs, an up-and-coming indie studio making carefully designed and rigorously playtested tabletop games outside of the D&D 5e ecosystem. Eureka is a system for stories where amateur investigators look into intricate and (sometimes deadly) mysteries, trying to get to the bottom of whatever conspiracy is at hand. It also has robust rules for a variety of supernatural phenomena that may or may not exist, letting players explore the thematic and logistical implications of people who are vampires, man-eating alien shapeshifters, supernaturally animated dolls, or a variety of other strange creatures. It's one of the best RPGs I've ever played or read, so if you're interested in finely crafted tabletop games, mystery and detective stories, social commentary on the rights of "unsavory" marginalized people, or just supernatural creatures that eat people, I'd recommend checking it out.
My writing under the cut!
(I wouldn't normally post my own long-form writing here, but I felt good about this and also couldn't pass up an opportunity to talk about Eureka. This isn't very polished, so ignore any typos or awkward wording, but feel free to check it out and give your own thoughts. Enjoy!)
Thoughts on golems in Eureka (Essay – Rules below!)
Contrary to how the word is usually used in English-language fantasy media, a golem in its original context is not just a generic term for any supernaturally animated artificial creature. (If it were, then it would be more or less synonymous with Eureka’s use of the term “living doll” to begin with!) Rather, it refers to a specific creature in Jewish folklore: a facsimile of the human form made out of clay, animated by various words of power placed in or on its body, acting as a source of protection and power for the impoverished and oppressed communities which created it. It is a servant which exists to meet a need of its community, animated by the power of God as channeled through the expertise of a meticulous member of the Jewish community. (Arguably the most notable difference from the genre fiction definition is this inherently Jewish perspective. The creation of a golem is a closed-practice, specifically Jewish tradition, and also, the tradition of Jewish mysticism implies high degrees of specialized knowledge – some written down in studied texts, and others discovered by training under a mentor or interacting with other Jewish leaders. In this way, the golem implies a degree of studiousness and community engagement on the part of its creator, both of which are heavily emphasized values in Jewish spheres.)
My analysis of the thematic role played by the golem is probably best represented in the best-known folkloric golem, the golem of Prague. In this story, a 16th century rabbi of the Prague synagogue creates a humanoid form from clay with the purpose of protecting the ghetto (in this context, the dedicated Jewish quarter of the city) from pogroms and other antisemitic attacks, animating it into a golem by inscribing holy words on its head or placing a scroll of those words in its mouth. Things go wrong in ways which vary from telling to telling, with a common version of the story stating that the golem becomes too dangerous and destructive, and the rabbi removes the inscription of the holy name to render the golem dormant (although rather than destroying his creation, he preserves it in the synagogue’s attic to be reanimated if it’s ever needed). In a fun bit of wordplay, some tellings describe the holy inscription as being the Hebrew word “emet” (“truth”), which is only one letter away from the word “met” (“dead”), with the idea that the rabbi deactivates the golem by erasing a single letter. More traditional interpretations would describe a formula consisting of various divine epithets, either instead of or alongside the previous method. In the Jewish mystical tradition, names of God are thought to be emanations of God’s own glory, and invoking their power in specific ways is seen as a way of causing things beyond the bounds of normal reality.
A few thematic points jump out at me about the golem, both from the story of the Prague golem and from the broader characteristics of the golem. One is the fact that a golem is implicitly lacking in personal identity. Golems are almost never named, and they have very little agency in their own stories – in almost every version of the golem of Prague, for instance, it is deactivated because it has gained too much autonomy. It fights the wrong people, uses too much force defending its community, or even just falls in love, and so it is too dangerous to keep around. Even the terminology being used implies this lack of identity, as it etymologically derives from a Biblical Hebrew term, used only once in the Tanakh, which describes the unfinished form of a human before God breathes life into them. A golem is not perceived as a fully formed individual, but rather as an extension of its creator, built by someone else’s will and discarded whenever it isn’t needed. To me, this has a high degree of relevance to the themes associated with Eureka’s living dolls, who often also grapple with defining their own identity and purpose in the absence of their original context. Their unique struggles evoke concepts of alienation and depersonalization, and I think a golem without a master would have to deal with all of the same issues on that front as they navigate life as a newly independent person.
Golems as a whole, and especially the story of the Prague ghetto, also raise another problem that can create thematic conflict for a character: in their attempts to defend vulnerable people in their community, they can end up making situations more dangerous, rather than helping to defuse them. When the golem of Prague rampages, in many tellings, it doesn’t fully stem the tide of antisemitic antagonism. Instead, it destroys more of the ghetto and allows the gentile population to create a post-hoc justification for their hatred of the Jewish community. In the context of Eureka, I think that this can be a powerful metaphor for how the fear of oppression can lead people to become paranoid, closed off, and destructive to themselves and others. A golem whose purpose is to protect and serve the people around them might want to do just that, but if they find themselves in a situation where superhuman strength and stamina can’t solve a problem, they may be in way over their depth, and they might accidentally harm other people when they try to navigate that. (My use of the phrase “protect and serve” here is no accident – one of many inspirations for this thematic element is people who call for increased police presence in their neighborhoods, even when those communities are more harmed by over-policing than they are by crime. Being afraid and wanting to support their community spurs them to action, but it also blinds them to approaches that don’t use force.) For example, one golem character I’ve come up with has had to flee her home and change her name because she saw someone being harassed, didn’t know her own strength, and intervened in the first way she could think of: violently. She was lucky not to be arrested.
To get a little bit more specific, this theme is most specifically inspired by my own experiences in discussions among members of the Jewish community, as the scars from millennia of marginalization, expulsion, and murder don’t fade quickly. Paranoia is a veritable norm even within our households and places of worship. In our homes, many of us keep passports readily available if there’s a need to escape or show identification, and during any prayer service at a synagogue, there will likely be armed security guards standing at the door. Many of us laugh about it, but there’s a degree of genuine fear that we can’t shake. Often, that fear is harmless, but it can get exhausting to live with, to say little of how it affects other people or how it can be weaponized by bad actors. One look at how the Israeli government seeks to justify its violence in propaganda makes clear that the generational trauma of Jewish communities can be exploited and warped as a means to justify some pretty awful things. The figure of the golem is, in a sense our communal power fantasy – it’s comforting to think that with a bit of ingenuity and some elbow grease we can design our own hero to protect us and help us thrive – but even that fantasy is not free of the reality that, like a superhero, a golem’s innate abilities just aren’t always enough to save everyone. (Indeed, this tension is part of what inspired the Jewish creators of Superman: he has superhuman abilities that he uses to protect vulnerable people, but not every problem can be solved by punching it, and with all his strength he has to be very careful not to destroy everything he loves. This has been noticed by a lot of people, and I’m far from the first to bring it up, but in particular I’d say this observation is borrowed from the excellent video essay “The Golem and the Jewish Superhero” by Jacob Geller on YouTube.) A golem being fleshed out as a character can really lean into that tension.
One more theme I want to bring up is not something I’ve come to any particular conclusions about – it’s really just a few spare thoughts I’ve had rattling around, and an invitation to look into this concept more. It comes out of my research on the development of the word “golem” in Hebrew and Yiddish, as the term has developed beyond just the connotation of a humanoid clay form. It can be a pejorative term like “fool”, but more interesting to me is its use in reference to embryos and pupas. This made me consider the transitory nature of the golem as a representative of change, which I haven’t seen explored very much in any stories out there. Not only has the word gained those connotations, but also, looking at the characteristics of the golem as a creature gives some more fuel to that fire. The fact that it’s generally made out of specifically unfired clay gives it the sense of being unfinished. Its nature of being created in its adult form from the very beginning means that it can display a childish outlook as a seeming adult learning about the world outside of its creator’s life. The story of the golem of Prague even has an ending hook entirely centered around the idea of the golem being temporarily disabled but capable of being reanimated if need be. This idea of a golem as a character with a unique capacity to adapt and change hasn’t been explored very much, but I think it could be interesting to consider.
The last thing I’ll leave here is thoughts on character creation beyond themes. In this document, I’ve included a custom set of rules to play a living doll made of unfired clay, which is the traditional material for a golem. This isn’t playtested in any way, but since Eureka doesn’t try too hard to be balanced around physical attributes, I think it should probably work fine – it’s more thematic than anything. To make a golem, the doll’s purpose should be external in some way, pushing them to help and support other people in their community, especially the most disadvantaged of them. In terms of backstory, the details of a golem’s past can be left fairly foggy if you’d like, but the one thing that can’t be skipped is that they were intentionally created by a Jewish creator invoking Jewish traditions. It’s fine to make a living doll that was animated in some other way, but the character would not be a golem in that case. It’s similar to how Eureka vampires must have some association with Christianity, not because non-Christian undead monsters can’t exist, but because outside of that context, the specific vampire mythos lacks any meaning. (Honestly, also, if you don’t have background information about Jewish life and culture, I would recommend asking someone who does to help with your portrayal.) Finally, in terms of giving a golem a hook to investigate a mystery, it could of course be anything, but there’s one aspect in particular that I would consider: in some versions of the Prague golem’s story, it protected the ghetto by looking into cases where Jews were accused of murder and finding the true culprits, thus clearing the names of the accused. Which is to say, there’s genuine historical precedent for golems investigating mysteries, and it often happens as a means of helping people who are falsely accused of a crime. That’s not mandatory, but it could be fun to keep in mind. Have fun, and if anyone ends up playing a golem investigator using these guidelines, please let me know!
Wet Clay Living Doll – Rules
A living doll made from earthenware materials that have not been hardened by firing. This variant was originally designed to represent the golem of Jewish mythology, but it could also be used to portray, for example, an unfinished art project or a proof of concept for another piece. Depending on their construction and the flexibility of the clay they are made from, they may be treated as jointed or unjointed.
Wet clay living dolls weigh more than twice as much as an average person of their size would. They cannot swim or float, and will sink to the bottom of any body of water immediately.
These living dolls take half damage from all weapons while they have at least 1 point of Superficial HP remaining. Damage from falling is unaffected. Wet clay living dolls are immune to electrical damage.
When a wet clay living doll encounters fire or high heat (in excess of about 500 ºC), their outer layer of clay is fired and becomes hard and brittle. When this happens, this living doll should be mechanically treated as an unjointed living stone statue. If another character has access to tools to chip away the outer layer and a large supply of wet clay to replace it, they can reverse this process with a Full Success on a Technology roll. Regardless of the result, this process will take 1 Tick of time and cause 1 Superficial Damage to the living doll.
Wet clay living dolls are easier to repair. Do not apply the -3 Technology penalty when restoring Penetrative HP.
Wet clay living dolls generally possess superhuman strength, but when they are hurt, they may lose chunks of clay that would otherwise generate weight and power. They have a +5 Contextual Bonus to Athletics and Close Combat, but for each point of sustained Penetrative Damage, this bonus is reduced by 1 point.
Given 1 Tick of time, appropriate tools, and a supply of clay, a wet clay living doll can alter their physical appearance and proportions. They cannot precisely change specific details such as facial features, but can make themselves larger or smaller, change their perceived distribution of fat and muscle, and change the shape of their body enough to be recognizably different. When a wet clay living doll attempts to alter their body, roll Technology.
Full Success: The living doll successfully alters their body to exact specifications. They are able to completely alter their facial features and/or specify a new height and body type, and even on close scrutiny they will not appear out of the ordinary.
Partial Success: The living doll mostly succeeds in altering their body, but they get sloppy. They take 1 Superficial Damage, and close inspection reveals that parts of their skin have abnormal marks and blemishes, but they are still able to make the changes that they hoped for.
Failure: The living doll struggles with even the most basic alterations, doing a messy and imprecise job. They take 1 Superficial Damage, and cuts and blemishes are visible across their skin. They also don't convincingly make the correct changes to their bodies, doing either too much or too little to differentiate themselves from their previous form.
#eureka: investigative urban fantasy#eureka#ttrpg design#ttrpg#indie ttrpg#homebrew#jewish#judaism#golem#game design#jacob geller#essay#my work#queer art#living doll#doll#jew stuff#urban fantasy#detective#investigation#noir#neo noir
79 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is it true that during the founding of Israel, to persuade Arab Jewish peoples to emigrate from their countries to Israeli settlements, European zionists would stage false flag attacks on Arab Jewish communities and bomb synagogues and community centers to stoke tensions and fear? Are there any resources like books where I can read about this?
I'm so sorry, I just saw this now and it's past 3AM over here so I'm running on fumes 😣 sorry if this is confusing or doesn't make sense
Look up the 1950–1951 Baghdad bombings, where Iraqi Zionists and the Mossad staged terrorist attacks against Jews in Iraq to literally scare them into moving to Israel. And also the Levon affair and Operation Susannah; more terrorists attacks this time for geopolitical reasons (the US' growing support of Egypt at the time).
Off the top of my head I can't remember the exact titles of the books I read (I read them in another language and I really don't want to mess up and give you titles that don't exist in English), but pretty much anything written by Ilan Pappé is a must. He's an Israeli historian and political scientist, and also an anti-Zionist activist who left Israel.
A title I do remember (because it's on my nightstand right now lol) is "Jewish Terrorism in Israel (Columbia Studies in Terrorism and Irregular Warfare)" which describes various acts of Israeli terrorists, from their attacks against British soldiers and the Arabs, to the assassination of the last Israeli Prime Minister that tried to sign a 2-State solution with Palestine (Yitzhak Rabin, who was about to sign the Oslo Accords; the Israeli right wing created such a climate of fear and violence around him and the Accords, that a Jewish extremist killed him in the streets of Tel Aviv, during a peaceful demonstration in support of the Accords; to this day, some members of the Knesset openly accuse Netanyahu of being behind the assassination).
If you want quicker access to information, I've recently found 2 Jewish activists that I suggest you check out: one is Sim Kern, author and journalist (Sim_bookstagrams_badly on Instagram, simkern on TikTok), they have some great books suggestions, both for fiction and historical/educational purposes. Their latest suggestion is:
"The Hundred Years' War on Palestine: A History of Settler Colonialism and Resistance, 1917-2017"
By Rashid Khalidi
They also have some GREAT videos explaining how the perception of Jews changes in the eye of the global Western superpowers depending on the situation (how they treat Jewish people in their own countries as people of color, while at the same time seeing the Israelis as white because they are an extension of their power, basically); how Israelis cannot be considered indigenous of Palestine (the first European Jews openly called themselves colonizers, they brought violence, death and destruction to the people and the environment of Palestine, and have dispossessed indigenous people who have continuously lived in Palestine for millennia; ). Basically how Israelis continuously enact white supremacy, racism, ethic cleansing on the Palestinians (and now genocide). Israel is founded on acts of terrorism.
The other activist is Katherine W. Bogen (k.w.bogen on Instagram and sexyalityscholar on TikTok). She makes easy to comprehend, straight-to-the-point videos about the history of Zionism, Israel being an apartheid state, how Israel does not represent Judaism, etc.
Norman Finkelstein is also a famous anti-Zionist activist, who wrote "The Holocaust Industry: Reflections on the Exploitation of Jewish Suffering". You might have seen a famous video where he absolutely demolishes an Israeli sympathizer for using the Holocaust to justify the oppression of Palestinians, and how their "crocodile tears" don't move him.
Another book I suggest is "Theft of a Nation", by William W. Baker.
Edward Said was a Christian Palestinian-American activist and academic, check out his work. I've recently seen an old video of him: he was invited on a television interview to debate the at-the-time Israeli ambassador Netanyahu. Netanyahu not only refused to be in the same room as him, but wanted to be in a different building altogether. When the moderator asked why, Netanyahu answered "Because he wants to kill me!" and started talking about how all Palestinians want to kill the Israelis 🙄 (obviously, the moderator didn't care for it lol)
If you feel like going for a deep dive, you might want to check out the website and Publications archives of B'TSELEM. They are an Israeli, non-governmental, non-profit organization whose goal is to document the human rights violations committed by Israel in the West Bank.
Try to find videos of ex Israeli soldiers that have left the army and Israel because they couldn't stand their policy of violence any more. What the Israeli army and police do in the West Bank and at the time in Gaza on a DAILY basis can't be described in any other way. Kidnappings, beatings, dispossession, "administrative detention" aka imprisonment without charge or trial, which can be extended every 6 months, indefinitely. There are Palestinians who have been imprisoned without cause for years, even children as young as 11, kept in solitary confinement. Over 800,000 Palestinians have been imprisoned without charge or trial since 1967 (after the war that Israel started by bombing Egypt).
IF one is "lucky" enough to get a trial, it's in front of a military court. A judge even admitted that he gets ALL the information on the case from the military and doesn't doubt what they say. Independent organizations have estimated that 10,000 Palestinians are currently imprisoned in Israel.
(I always suggest to check out Israelis who speak out against Israel not because I want to center their perspective, but because Zionists will dismiss any opinion that comes from other sources)
Lastly, know that Menachem Begin, founder of the Likud party (that currently governs Israel) and 6th Prime Minister of Israel, was internationally recognized as a terrorist. He was the leader of the terrorist organization Irgun, that committed such atrocities against Palestinians that Einstein (yes, that Einstein) and Hannah Arendt compared it to the Nazis.
That's the foundation of Israel. Israel is a terrorist state.
Edit:
.
And check out a book called "Zionism in the age of dictators" written by journalist Lenni Brenner. It talks about how Zionists collaborated with fascists and Nazis to establish Israel.
Also google the Lehi militant group, a Jewish terrorist organization.
From Wikipedia:
"[...] often known pejoratively as the Stern Gang, [Lehi] was a Zionist paramilitary militant organization founded by Avraham ("Yair") Stern in Mandatory Palestine. Its avowed aim was to evict the British authorities from Palestine by use of violence, allowing unrestricted immigration of Jews and the formation of a Jewish state. It was initially called the National Military Organization in Israel, upon being founded in August 1940, but was renamed Lehi one month later. The group referred to its members as terrorists and admitted to having carried out terrorist attacks.
Lehi split from the Irgun militant group in 1940 in order to continue fighting the British during World War II. It initially sought an alliance with Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany. Believing that Nazi Germany was a lesser enemy of the Jews than Britain, Lehi twice attempted to form an alliance with the Nazis, proposing a Jewish state based on "nationalist and totalitarian principles, and linked to the German Reich by an alliance"
Lehi assassinated Lord Moyne, British Minister Resident in the Middle East, and made many other attacks on the British in Palestine."
Israel is a terrorist state.
463 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Golden Rose Synagogue is one of the oldest synagogue in what is today Ukraine. Its builder between 1580 and 1595 was Yitzhak ben Nachman (or Izak Nachmanowicz), the local Jewish counselor of Stephen Báthory, Prince of Transylvania and King of Poland, and its master the Italian Paulus Fortunatus, who raised a large number of Renaissance buildings all over Poland and was known by his guild nickname Paweł Szczęśliwy (Paul the Fortunate). The synagogue was named after the wife of Nahman, Rosa.
In 1941 it was closed down and in 1943, at the liquidation of the ghetto, blown up by the German invaders. Its ruins have lain untouched ever since. After the downtown of Lviv was declared World Heritage (1998), the city authorities gave permission to a private investor to build a hotel on the property, which would have meant the final destruction of the remains. On an international protest, however, the permission was withdrawn. The site has since been waiting for a positive turn of its destiny behind a metal construction plank.

195 notes
·
View notes