#southeast native plants
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo
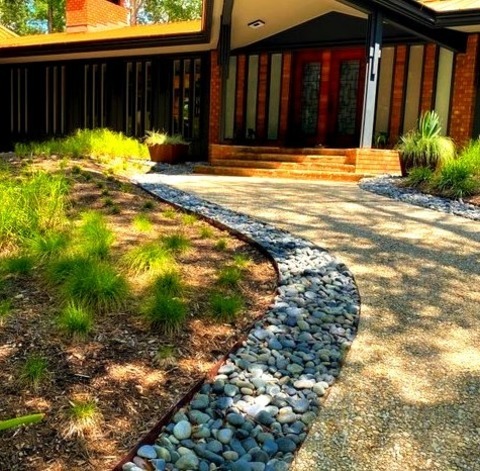

Landscape in Raleigh Design ideas for a large mid-century modern drought-tolerant and partial sun front yard river rock waterfall.
#low maintenance#sustainable landscape maintenance#mexican beach pebble#southeast native plants#waterfall#drought tolerant
6 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Waterfall Landscape (Raleigh)
#Ideas for a sizable#drought-tolerant#partially-shaded front yard river rock waterfall in the mid-century style. low maintenance#landscape#modern landscape#drought tolerant#mexican beach pebble#southeast native plants#sustainable landscape maintenance
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


dear monarda punctata,
i love you.
0 notes
Photo

Waterfall Landscape in Raleigh This is an illustration of a sizable, drought-tolerant, partial-sun front yard river rock waterfall from the mid-century modern era.
0 notes
Photo

Driveway Miami Design ideas for a contemporary full sun front yard concrete paver landscaping in spring.
0 notes
Photo

Landscape - Midcentury Landscape Design ideas for a large mid-century modern drought-tolerant and partial sun front yard river rock waterfall.
#sustainable landscape maintenance#southeast native plants#drought tolerant#modern landscape#landscape
0 notes
Text

May 2, 2024, 6:32pm: New growth on the Carolina Jessamine in the evening sunlight.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Meet the Alabama woman who is turning her farm into an indigenous food forest
Danny McArthur, Gulf States Newsroom

Angie Comeaux walks around her farm in Florala, Alabama. She calls it Hvrvnrvcukwv Ueki-honecv, or Hummingbird Springs, Farm.
It has its own water sources – like a spring that’s not too far from her house. She and a group of volunteers planted 2,000 trees that are all native species, as well as hundreds of plant species. It’s January, so at first glance, it just looks like overgrown grass and bushes.
“A lot of folks might come out here and they’ll look around and be like 2,000 trees where? But it’s because it’s winter time and they’re still small,” Comeaux said.

What’s actually there is the early stages of an indigenous food forest. To understand what that is, think about corn, beans, and squash. They’re known in some circles as the Three Sisters because they grow together, like family.
“So the corn is tall, and it gives a trellis for the beans to climb up. But the beans will put nitrogen into the soil and that will help both the corn and squash grow,” Comeaux said.
The story of the Three Sisters is a smaller version of what happens in a food forest. The plants here grow stronger, together.
“The squash leaves are very prickly and they’re big and cover a lot of the ground, so it’s giving moisture control to the soil,” Comeaux said. “It also gives pest control because bugs don’t like to walk on prickly little leaves.”
From extreme heat, to periods of drought, climate change is impacting farmers in the South. In response some farmers, like Comeaux, are leaning on regenerative practices. For her, that means returning to indigenous practices that focus on preserving the land for future generations – rather than depleting it now.

Comeaux’s journey to launching Hummingbird Springs Farm started in early 2020. She was originally born in New Orleans and raised in southeast Louisiana but she always had a goal of getting land and living off it once her children were out of the house. Then the COVID-19 pandemic hit, her son had to finish school online and she saw her chance to get started.
Comeaux, who said she’s Mvskoke, Cherokee and Chahta, came to Alabama to farm her ancestral lands. She found land from a family of multi-generational farmers looking to sell. But, when she first arrived, it was completely clear cut and hadn’t been farmed in seven years. For nearly a century before that, it had been a peanut farm. Comeaux said that kind of monoculture farming tends to leave the soil depleted.
“We definitely saw that as an opportunity to reclaim and reestablish a healthy ecosystem,” Comeaux said.
To do that, she’s using traditional ecological knowledge, or knowledge that has been passed down by generations of indigenous people based on their direct experience with the environment.
More at the link
503 notes
·
View notes
Text




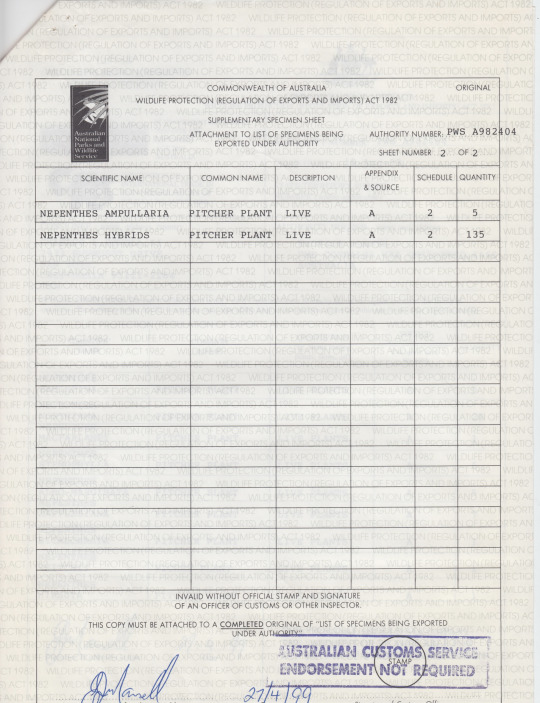
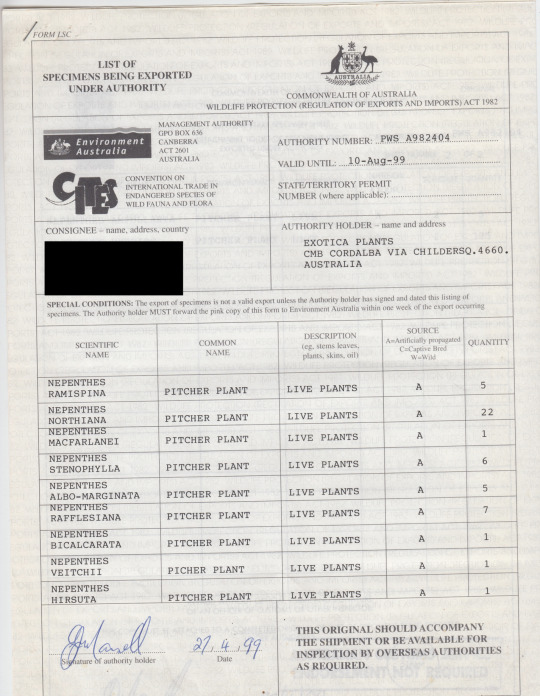


ok INCREDIBLY old content originally meant for this blog but in 2018 when i was just a wee lad with a little spinner propeller hat and big rainbow lollipop i went to a carnivorous plant convention in california and met a bunch of people who breed/collect/study these guys. one person was this collector who was slowly working on leaving the hobby or at least no longer growing plants, and he had a bunch of carnivorous plant related files he was charging like 50 cents for or something, and so i came into possession of these, which are examples of the kind of paperwork you have to have done to legally ship/trade endangered species of both plants and animals. functionally very boring paperwork, but something i found like, incredibly fascinating. i blacked out the personal id of the person and then immediately forgot to ever upload them, lmao.
these plants were bred and raised in a greenhouse and sold abroad, not taken from the wild, but because the species are endangered and often protected in their native countries (most of these are nepenthes, asian pitcher plants, a huge family spread throughout oceania and southeast asia), there's a lot more documentation that needs to be done regardless of their origin, both on the end of the seller and on the end of the buyer.
the rabbit hole on carnivorous plant trade is deep and kind of wild. there's plenty of common, non-threatened, greenhouse-grown pitcher plants on the market that people buy all the time, even non-collectors, but there's a whole debate to be had on if it's morally okay to be collecting the more endangered/rare of these plants in the first place. the big argument for breeding is that breeding them in captivity means there's more supply that's not poached from the wild, meaning poachers have less of an incentive to take the risk of taking adult plants from their habitats; from what i've heard, sometimes countries will issue permits for breeders to collect some wild seeds just to create a non-wild breeding pool to drive down the price. predictably, however, you also get people who are very much willing to pay a lot of money to get as rare of a plant as possible.
anyone familiar with the allure valuable plants have had over people throughout history can imagine the rest, but here's an article about a guy who started buying poached plants to enrich his private nepenthes collection, who then got busted by a fish and wildlife service agent embedded in his carvirorous plant circle. the plants this guy was buying were being sold to him without any CITES paperwork or declarations like the ones above; it was literally just a guy in indonesia taking rare plants from the woods around where he lived, selling them over facebook marketplace and ebay, and mailing them overseas as an undeclared 'gift' to get around customs. frighteningly small steps to take on all sides, to be honest.
(also, fun fact: another example of carnivorous plants that get poached are wild venus fly traps, which are only native to north and south carolina in the US. from what i understand it's a mix of people who genuinely did not know it's a native species and people who really are just going out into the woods and digging up plants to sell online. sometimes poaching is closer to home than you'd think!)
anyway. wild and interesting times in the land of plants recovered from a hard drive lmao
#nepenthes#annual 'plant poaching happens and it doesnt always look like the movies' post i suppose but also i think its really interesting#also the CITES system could do with an overhaul in how it approaches plants as well from what i understand but thats another thing#ive heard that like many systems like this they do not have the same urgency for plants as they do for animals#mostly because people just!! they dont get plants man!! they just say whatever its a plant!!#and poaching in general is only ever talked about like its with taking elephants for their tusks and stuff#also important conservation work but sometimes poaching really is just a guy with a shovel and that shit is WILD#carnivorous plants
525 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the NC State Extension plant database page for river cane:

my brain is permanently haunted by Arundinaria gigantea and the Canebrakes
American bamboo is disappearing and almost nobody knows about it, and most of the pictures labeled as A. gigantea online are actually invasive bamboo from Asia
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
September 2023 witch guide
SEPTEMBER 2024:
September 2023 witch guide
Full moon: September 29th
New moon: September 14th
Sabbats: Mabon September 23rd
September Harvest Moon
Also known as: Autumn moon, falling leaves moon, song moon, leaves turning moon, moon of brown leaves, yellow leaf moon, wine moon & Full corn moon
Element: Earth
Zodiac: Virgon& Libra
Animal spirits: Trooping Faeries
Deities: Brigid, Ceres, Ch'ang-o, Demeter, Freya, Isis & Vesta
Animals: Jackal & snake
Birds: Ibis & sparrow
Trees: Bay, hawthorn, hazel & larch
Herbs/plants: Copal, fennel, rye, skullcap, valerian, wheat & witch hazel
Flowers: Lily & Narcissus
Scents: Bergamot, gardenia, mastic & storax
Stones: Bloodstone, chrysolite, citrine, olivine, peridot & sapphire
Colors: Browns, dark blue, greens & yellows ( Earth tones)
Energy: Balance of light & dark, dietary matters, employment, health, intellectual pursuits, prosperity, psychism, rest, spirituality, success & work environments. Also cleaning & straightening mentally, physically & spiritually.
Technically, the Harvest Moon is the Full Moon closest to the September equinox around September 21st. The Harvest Moon is the only Full Moon name determined by the equinox rather than a month. Most years, it’s in September, but around every three years, it falls in October.
In September, the Full Moon is the Corn Moon from the Native American tribes harvesting their corn. It can also be the Harvest Moon, which corresponds with the Anglo-Saxon name, while Celtic and Old English names are Wine Moon, Song Moon, and Barley Moon.
Mabon
Also known as: Autumn Equinox, Cornucopia, Witch's Thanksgiving & Alban Elved
Season: Fall
Symbols: Acorns, apples, autumn leaves, berries, corn, cornucopia (horn of plenty), dried seeds, gourds, grains, grapes, ivy, pine cones, pomegranates, vines, wheat, white roses & wine
Colors: Blue brown, drk red, deep gold, gold, indigo, lead green, maroon, orange, red, russet, violet & yellow
Oils/incense: Apple, apple blossom, benzoin, black pepper, hay/straw, myrrh, passion flower, patchouli, pine, red poppy & sage
Animals: Dog, goose, hawk, swan, swallow & wolf
Stones: Agate, amethyst, carnelian, lapis lazuli, sapphire, yellow Agate & yellow topaz
Foods: Apples, blackberries, blackberry wine, bread, carrots, cider, corn, cornbread, grapes, heather wine, nuts, onions, pomegranates, potatoes, squash, vegetables, wheat & winw
Herbs/plants: Acorn, benzoin, cedar, corn, cypress, ferns, grains, hazel, hops, ivy, myrrh, oak, pine, sage, sassafras, Salomon's seal, thistle, tobacco & wheat
Flowers: Aster, heather, honeysuckle, marigold, milkweed, mum,passion flower& rose
Goddesses: Danu, Epona, Modron, Morrigan, Muses, Pomona, Persephone, Sophia & Sura
Gods: Esus, Green Man, Hermes, Mabon, Mannanan, Toth & Thor
Issues, Intentions & Powers: Accomplishment, agriculture, balance, goals, gratitude & grounding
Spellworks: Balance, harmony, protection, prosperity, security & self confidence
Related festivals:
• Sukkot- is a Torah-commanded holiday celebrated for seven days, beginning on the 15th day of the month of Tishrei. It is one of the Three Pilgrimage Festivals (Hebrew: שלוש רגלים, shalosh regalim) on which those Israelites who could were commanded to make a pilgrimage to the Temple in Jerusalem. In addition to its harvest roots, the holiday also holds spiritual importance with regard to its abandonment of materialism to focus on nationhood, spirituality, and hospitality, this principle underlying the construction of a temporary, almost nomadic, structure of a sukkah.
• Mid-Autumn festival- also known as the Moon Festival or Mooncake Festival, is a traditional festival celebrated in Chinese culture. Similar holidays are celebrated by other cultures in East & Southeast Asia. It is one of the most important holidays in Chinese culture; its popularity is on par with that of Chinese New Year. The history of the Mid-Autumn Festival dates back over 3,000 years. The festival is held on the 15th day of the 8th month of the Chinese lunisolar lunisolar calendar with a full moon at night, corresponding to mid-September to early October of the Gregorian calendar. On this day, the Chinese believe that the Moon is at its brightest and fullest size, coinciding with harvest time in the middle of Autumn.
• Thanksgiving- This is a secular holiday which is similar to the cell of Mabon; A day to give thanks for the food & blessings of the previous year. The American Thanksgiving is the last Thursday of November while the Canadian Thanksgiving is celebrated in October
• Festival of Dionysus- There were several festivals that honored Dionysus, the God of wine. It was a time of fun, games, feasting & drinking wine.
Activities:
•Scatter offerings in a harvested fields, Offer libations to trees
• Decorate your home and/or altar space for fall
• Bake bread
• Perform a ritual to restore balance and harmony to your life
• Cleanse your home of negative energies
• Pick apples
• Have a dinner or feast with your family and/or friends
• Set intentions for the upcoming year
• Purge what is no longer serving you
•Take a walk in the woods
• Enjoy a pumpkin spice latte
• Donate to your local food bank
• Gather dried herbs, plants, seeds & pods
• Learn something new
• Make wine
• Brew an apple cinnamon simmer pot
• Create an outdoor Mabon altar
•Adorn burial sites with leaves, acorns, & pinecones to honor those who have passed over & visit their graves
Many cultures see the second harvest (after the first harvest Lammas) and equinox as a time for giving thanks. This time of year is when farmers know how well their summer crops did, and how well fed their animals have become. This determines whether you and your family would have enough food for the winter. That is why people used to give thanks around this time, thanks for their crops, and animals, and food.
The name Mabon comes from the Welsh God, who was the son of the Earth Mother Goddess. However, there is evidence that the name was adopted in the 1970s, and the holiday was not originally a Celtic celebration.
Some believe Night and day are of equal legth and the God's energy & strength are nearly gone . The Goddess begins to mourn the loss she knows is coming, but knows he will return when he reborn at Yule.
Sources:
Farmersalmanac .com
Wikipedia
Llewellyn's Complete Book of Correspondences by Sandra Kines
A Witch's Book of Correspondences by Viktorija Briggs
Mabon: Rituals, Recipes & Lore for the Autumn Equinox Llewellyn's Sabbat Essentials
#witchcraft#wheel of the year#sabbat#mabon#Corn moon#Harvest moon#witchblr#wiccablr#paganblr#pagan#Wicca#grimoire#spellbook#book of shadows#witches of tumblr#tumblr witch#moon magic#witch tips#witch guide#traditional witchcraft#witch community#witch society#witchy things#witches#witch friends#greenwitchcrafts#All witches#correspondence#witchyvibes#witchcore
729 notes
·
View notes
Note
I always hear about the ecosystems that are more biodiverse than expected, like grasslands, deserts, rivers. What ecosystems are less biodiverse that most people expect? Or do all ecosystems have a lot going on?
forests!!!!! i don’t wanna shit on them lol but it’s kinda funny—you go from rainforests, which are a hotbed of biodiversity, to places like the redwood forest or northern coniferous woods which are just…. strangely silent.
in the case of northern coniferous woods (like in parts of alaska), the geology contributes to it. only certain species can survive in geologically active areas with poor soil quality—conifers (pine, spruce, larch) LOVE that shit. in the case of the redwoods and other more southern but still northern forests (loll!! think oregon coast), there’s only so many species that can survive in those poor-quality soils that are constantly wet thru the year. again, wooo conifers!!
the redwoods though are specifically interesting… dense canopy leads to fewer plant species able to grow, which means there’s less food for other animals. if you ever get the chance to visit redwood national park, be silent and listen for a bit. there’s a noticeable lack of insects and birds. all of that goes together!!
that being said—there are some studies being done on the redwood canopies. there are specific fern and moss ecosystems that ONLY grow on those trees, and due to habitat fragmentation it’s pretty hard to gather info on them. these things grow on a scale of hundreds of years, so many of them just don’t exist anymore.
also, though, on the other side of the scale—the southeast US is STAGGERINGLY biodiverse. that part of north america mirrors southeast asia, both are considered rainforests (in parts lol). interestingly, too, there are a lot of species that are very similar despite being separated by the pacific ocean.

example: american beautyberry vs asian beautyberry!!
also, shout out to central texas for being a biodiversity hotspot <333 i will forever maintain that the hill country is one of the most special places in the country!!! old oaks, sycamores, pecans, and bald cypress (best tree) lining the rivers—cliffsides covered in trees, amazing diversity of insects and reptiles, riverside flood plains, native tall grass prairies—it’s amazing!! i’m biased though obviously lol!!
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
BALİKTURLERİ - MEGA+ (3)

Molly Fish is a popular freshwater aquarium fish that is easy to care for and comes in a variety of types. These fish are known for their peaceful nature and are suitable for community tanks. They can grow up to 4 inches in length and have a lifespan of up to 5 years. Molly Fish are omnivorous and require a balanced diet of both plant-based and protein-based foods. They are also known to be hardy and can tolerate a wide range of water conditions. When it comes to tank mates, Molly Fish are compatible with other peaceful community fish of similar size and temperament. Vampire Crab is a unique and fascinating semi-terrestrial aquarium species that is easy to care for and has a relatively long lifespan. These crabs are native to the mangrove swamps of Southeast Asia and require a mix of both land and water in their habitat. They are omnivorous and can eat a range of foods, including commercial crab food, vegetables, and small insects. Vampire Crabs are known for their sociable nature and can be kept in pairs or small groups. However, they are territorial and can exhibit aggressive behavior towards other crab species. Therefore, it is best to keep them with other peaceful community fish. Rainbow Shark is a popular freshwater aquarium fish that is known for its unique appearance and territorial behavior. These fish are native to the rivers of Thailand and can grow up to 6 inches in length. Rainbow Sharks are omnivorous and require a balanced diet of both plant-based and protein-based foods. They are also known to be hardy and can tolerate a wide range of water conditions. However, they are territorial and can exhibit aggressive behavior towards other fish species, particularly those of similar appearance or size. Therefore, it is best to keep them with other peaceful community fish that are not too similar in appearance.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
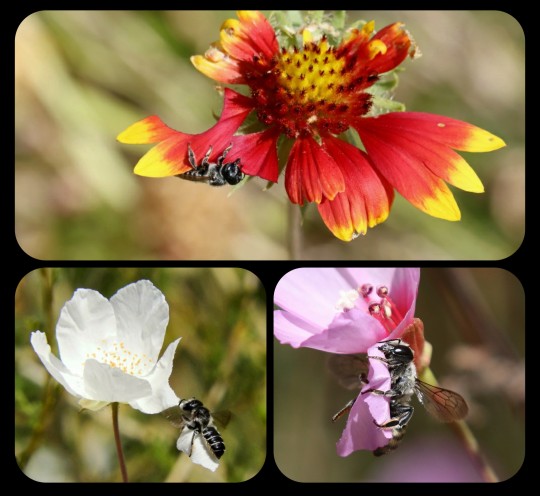
Leafcutter Bees: these bees snip off bits of foliage and/or flower petals and then weave the pieces together to build their nests
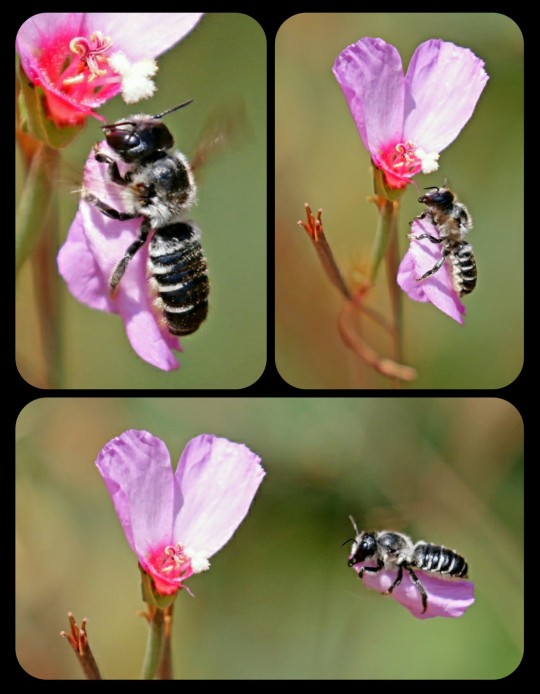

The nests are built and used only by the female leafcutter bees (family Megachilidae). Unlike honey bees, leafcutters do not form colonies or live together in hives, meaning that each nest belongs to a single, solitary bee.
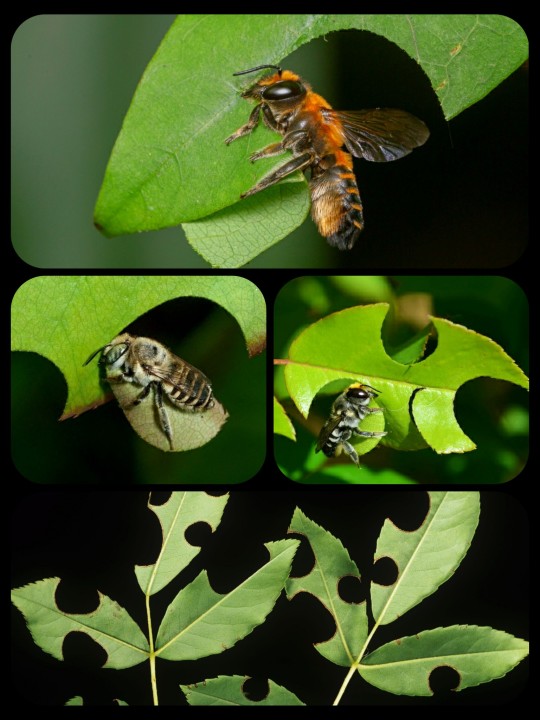

The females use their mandibles to cut out pieces of foliage, carefully snipping off rounded segments and then carrying them back to an existing cavity/burrow (which may be located in a plant stem, a piece of wood, the side of a tree, etc.), where the pieces are used to construct a series of brood cells along the inner walls of the cavity.
Most leafcutter bees build their nests out of leaves, but there are some species that are more accurately described as "petalcutters," because they use flower petals instead.

The Silver-Tailed Petalcutter Bee (M. montivaga): this species uses flower petals to build its nest; it is one of the few Megachilid bees to do so
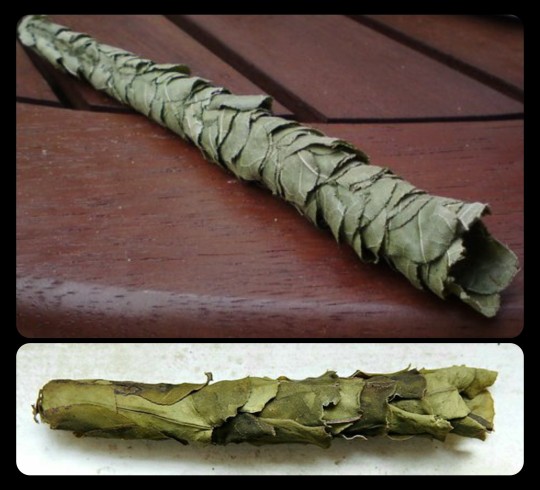
The leaves and/or flower petals are then folded together along the inner walls of the chamber, forming a long, cigar-shaped nest that contains multiple brood cells.

As this article explains:
Leafcutter bees may nest in many different spaces, such as existing holes in timber or masonry, hollow stems, gaps in door/window frames, old folded towels left outside, rock walls and outdoor furniture.
Each female builds her own nest. The cut leaves are used to make a tube as a nest for the eggs or to line an existing hole with it. The leaves are cut in various shapes, round and elongated, to suit the construction of the cell for the eggs. The cell is then stocked with a mixture of nectar and pollen in which the leafcutter bee lays her eggs.
There are multiple brood cells built into the internal structure of the nest, but they are all separate from one another. Each cell contains a single egg, along with just enough pollen and nectar to sustain the larva until it reaches maturity.
When the eggs hatch, tiny larvae eat the provisions and, when fully grown, they spin silky cocoons and then develop into pupae, finally emerging as adult bees.
Leafcutter bees come in a wide variety of colors, shapes, and sizes. These are just a few other examples:
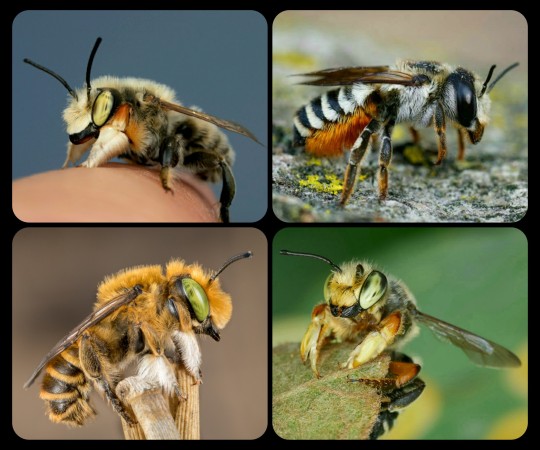

Top Row (left-to-right): Megachile latimanus and Megachile octosignata; Bottom Row: Megachiloides sp. and Megachile poeyi
Sources & More Info:
University of Colorado's Museum of Natural History: Leafcutting Bee
Florida Wildflower Foundation: Getting to Know your Native Pollinators - Leafcutter Bees
University of Nebraska: Facts about the Leafcutter Bee
Land for Wildlife (Southeast Queensland): Leafcutter Bees
What's that Bug?: Leafcutter Bee Life Cycle - a Fascinating Journey Revealed
Entomology Today: Beyond the Honey Bee - How Pesticides Affect Solitary, Cavity-Nesting Bees
#entomology#insects#nature#hymenoptera#arthropods#megachile#megachilidae#leafcutter bees#petalcutter bees#animals#biology#flowers#cute bugs#bees#solitary bees#gardening#plants#cute animals#bugs that like to pick flowers#to decorate their homes
60 notes
·
View notes
Note
What would be the main differences between a template forest and a tropical jungle for fantasy? I guess that things like iron armor pieces would never become a thing since historically they weren't popular in other hot climates, winters without snow might be less feared but summers with big floods might be more worrisome? I guess that cuisine and farming would also be massively different although I don't know exactly how.
Out of the top of my head:
Equatorial climates are notoriously stable, since it's always the same day lenght there are no seasons, especially if you live near the ocean which estabilizes the temperature. You will get dry and wet seasons (and sometimes even hurricane seasons) depending on particular geographic conditions
Tropical/subtropical climates often have harsher seasons the farther away from the ocean they are, but never snow (that's the difference actually; temperate climates can get snow, subtropical can get frost but not snow, tropical neither). So yes, in general in a tropical or subtropical the main difference between seasons is rain, and perhaps frost which does play a role in some plants like citrics. Rainforests, of course, get it all year, subtropical forests have dry and rainy seasons. You can see a mixture of both: in my home (Northern Argentina) we do get marked winters with ocassional frost, but the main fact is that they're dry compared to summer.
ANYWAYS. Cultural stuff! Yes, one of the main differences you will find is clothing. It's difficult to make generalizations, but overall, tropical cultures just wear less, if there is armor at all. Don't get mistaken and say that it's because they don't have metallurgy, though, it's just that metal armor is indeed heavy, hot, and not much use if the opponet isn't wearing anything either. At most, you would see padded cloth armor (cotton mostly) or hide/leather at most. If you look at soldiers from, for example, Mesoamerica or Southeast Asia, you will find little armor.
Similarily, while you can go wild with noble clothing and colors, and the preferred materials are indeed cotton or silk, you will find very simple clothes among the general population. To give you an idea, here's a sample of Aztec clothes (including armor!)

Note how simple and lightweight they are, even for rulers. They are colorful too (the artist, Daniel Parada, has more pictures like this for other cultures based on historical records) but although tropical enviroments might seem to have greater access to dyes, medieval european did also have dyes, often not as vibrant as carmine though.
Farming, of course, affects cuisine. I think that instead of thinking about a "pan-tropical" farming, we could analyze this by centers of origin of crops:
From Southeast Asia we got soy, several types of beans (or Fabaceae if you wanna get technical), all citrics, mango, banana, pear, cherry,, but this pales in comparison to rice, of course. Rice defines the tropical and subtropical diet of Asia, being what wheat is to the Mediterranean. Rice cultivation is particular in that is labor extensive, much more productive by area compared to other crops (so smaller plots) and requires extensive irrigation, resulting in complex managed enviroments.
From tropical America we got manioc, squashes (all sorts of curcubita actually), beans, peppers, pineapples, papaya, so much more, but it's especifically from Mesoamerica we got corn, and from the Andes we got potatoes. Potatoes are key in cold climates. Meanwhile, the corn-beans-squash trio, that is known in North America as "three sisters" and in Latin America as "milpa" is spread all over the continent. These three kinds of plants are very adaptable to tropical and subtropical conditions, and combined are very productive.
I will admit that my knowledge about tropical Africa is less than ideal. There are native species of rice that can be found in Western Africa, Ethiopia has traditionally grown barley and sorghum (and is the home of coffee), and millet, like corn for the Americas, seem to be widespread.
As for spices, tropical areas do seem to be blessed with spices, this is true. I recommend this guy to tell you about it. Hell, I recommend his channel in general.
What IS a common theme, regardless, is that jungles are NOT pristine enviroments or wild enviroments untouched by human activity. Jungles have been managed, in overt ways (like for example, rice cultivation) or more subtle ways (planting domesticated species inside the forest) for thousands of years. This is also done by controlled burns, conscious planting, or even accidental things, like, for example, peoples settling in a place and bringing domesticated plants to that place that then grow semi-wildly.
THIS IS SO FRUSTRATING TO TALK ABOUT BECAUSE EVEN IF I STUDY THIS EXACT THING, I HAVE NO REAL DEFINITION OF IT YOU CAN SEARCH. You can find about this phenomenon of "humans managing and changing forest enviroments" by lots of terms, like agroforestry, silviculture, and so many more. The term I use is "landscape management" (no, not "landscaping") where a "landscape" is a term for an enviroment were both humans and natural factors build it (like I said, there is no thing as "pristine nature" ALL natural enviroments have been managed and modified by humans, and you can find evidence of that in tropical America, Asia, and Africa).
In fact, the reason why those enviroments seem "natural" and unchanged to Western views is precisely, because tropical cultures often use wood and adobe to build structures (if they have them at all), which don'r preserve well at all. But also, jungles are fast growing and often eat everything, remaining, interestingly, these subtle domestication and managment efforts in what once were thriving settlements.
Which doesn't mean you haven't tropical cultures to study. THERE ARE PLENTY. You got, like I said, the whole of tropical America, tropical Africa, and tropical Asia and Oceania. It is getting very difficult to me to generalize, and yet, one can see some similarities.
Since this post is general enough, I encourage you to ask more about what you want. What would you like me to focus on?
oh, and you can throw me a tip, if you want! Sorry for selling out, but I'm living under an insane libertarian president right now, so every bit helps!
#worldbuilding#sorry this is such a rant#but I hope it might be useful for you to get questions I can answer better!#biotipo worldbuilding
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

秋の野芥子[Akinonogeshi] Lactuca indica
秋[Aki] : Autumn
の[No] : Of
野芥子[Nogeshi] : Sonchus oleraceus
Native to Southeast Asia, it is believed to have been introduced with rice cultivation. There are various theories about rice cultivation, but this plant probably arrived in the the Yayoi period(about 10th to 3rd century BC) or earlier. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yayoi_period
It grows in sunny fields, and the larger ones are up to about two meters tall. Nogeshi(S. oleraceus) is also known as 春の野芥子[Harunonogeshi] because it blooms yellow flowers resemble those of the 蒲公英[Tanpopo](Dandelion) in spring. 春 means spring. And, this is so named because its leaf resembles that of a 芥子|罌粟[Keshi](Poppy) and produce a white latex like the poppy when the stems and leaves are broken. Akinonogeshi also produces the latex as well, but the shape of the leaf resembles that of an 薊[Azami](Thistle).
The yellowish cream flower is quite beautiful.
21 notes
·
View notes