#sdss
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text






Part 1
Mission success?? Maybe??
450 notes
·
View notes
Text


I have a mini dream. I really want Benjamin Walker and Mark Ferguson to meet on stage one day somewhere at the Magic Con / SDSS and shake hands, and all this to the accompaniment of thunderous applause from the audience
You just imagine 2 GG 🤩
#the rings of power#silmarillion#lord of the rings#silmarillion theory#lord elrond#high king gil galad#the hobbit#tolkien#gil galad#banjamin walker#Mark Ferguson#SDSS#Magic con#dream#hobbits#lotr books
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hazy Galaxy
157 notes
·
View notes
Text

#pretend you do not see the imperfections sdss#i was in hurry#whatever whatever i just miss her AND WINGDEER MADE A NEW HAIR#I OWE WINGDEER MY LIFE#I'VE DREAMT ABOUT THIS HAIR FOR MONTHS#cyberpunk 2077#fem v#val garcia#kleff vp
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
FASHION turn to the left FASHION turn to the right
Anyway I ADHD f'd with my bandage and ended up redoing the wound care with silver sulfadiazine and mom had me cut old (clean) pantyhose to put over the taped up gauze this time. Very cutesy.
#My way retired 70yr old ma's running a family Rite Aid at this point#Hey! I DID NOT INJURE MYSELF ON PURPOSE this time#haven't in years#I just am prone to accidents#every stupid job I have “Why would we need to be prepared for x y z or up to date on this or that first aid”#well first of all - law and second - safety preparedness and third - me#It's me#you wanna know why your knives should be sharp not dull and you should limit serrated knife use#and have burn treatments ready when you have a facility that has things that can burn?#You wanna know why slip resistant shoe requirements aren't enough and I suggest mats?#IT'S ME#Hello! I can tell you Everything Your Facility Is Missing#And if there's an AED I want to know where and you better have and tell me the location of the SDSs
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
#taleblr#taleblr pie#maxwell acachalla#taleblr aimee#cardboard friend#the toilet toucher#billy acachalla#taleblr headcanons#winner gets a doodle post marking their strengths and weaknesses in the style of toast’s book?#if I’m missing one lmk but sdss; Jimmy Casket; the housekeeper; and Prince Fang get their own post
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sicilia, recuperato un altro rostro della Battaglia delle Egadi del 241 a.C. [FOTO / VIDEO]
ARCHEOLOGIA | Sicilia, recuperato un altro rostro della Battaglia delle Egadi del 241 a.C. [FOTO / VIDEO] I dettagli e il videoservizio su Storie & Archeostorie
Elena Percivaldi Guarda il videoservizio Il mare siciliano continua a restituire importanti tesori archeologici. La campagna di ricerche di agosto ha, infatti, consentito di recuperare un altro rostro in bronzo, rimasto adagiato per oltre 2.200 anni a circa 80 metri di profondità sul fondale a nord-ovest dell’isola di Lèvanzo. Era infatti il 10 marzo del 241 a.C. quando Romani e Cartaginesi si…
#archeologia#Battaglia delle Egadi#Cartagine#Isole Egadi#notizie#Regione Siciliana#Roma antica#rostri#scavi#scavi archeologici#scoperte#Sdss - Society for documentation of submerged sites#Soprintendenza del Mare
0 notes
Text
Sundar Dhoka Saathi Sewa (SDSS) Vacancy 2081 at Finance and Admin Officer
Sundar Dhoka Saathi Sewa (SDSS) Vacancy 2081 at Finance and Admin Officer. Interested and Qualified candidates are invited to apply by 15th July 2024,5:00 p.m. CAREER OPPORTUNITY Sundar Dhoka Saathi Sewa (SDSS) Vacancy 2081 at Finance and Admin Officer Sundar Dhoka Saathi Sewa (SDSS) is a registered Non-Government Organization in Lalitpur district that aims to make positive changes in the life…
0 notes
Text
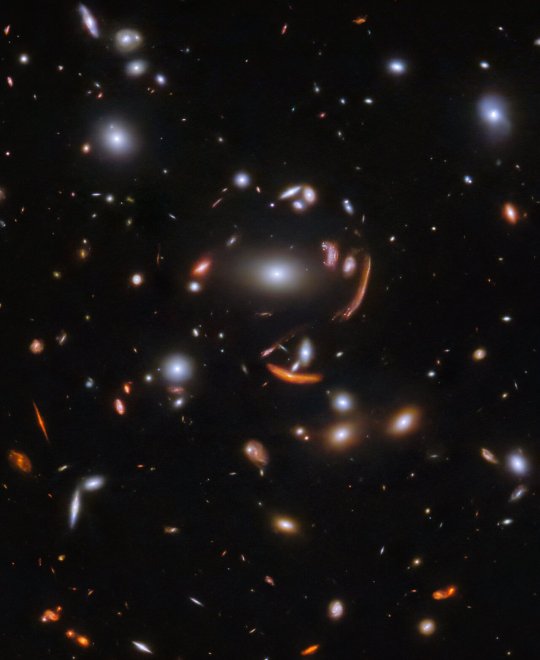
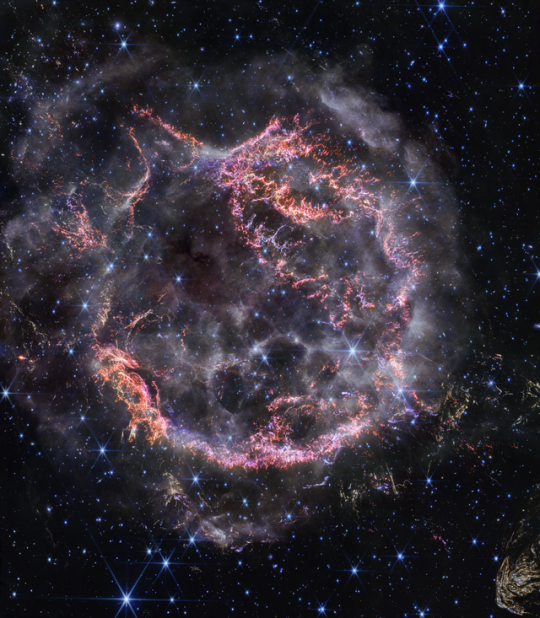
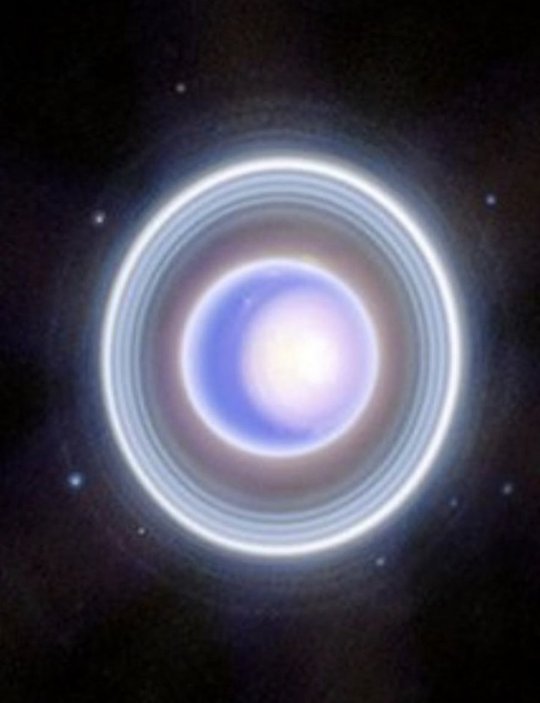




Gifts from Webb l Dec. 2023
The vast galaxy cluster SDSS J1226+2152 l Center of Star cluster IC 348 l Supernova Remnant Cassiopeia A l Ice giant Uranus & its moons
#space#nasa#webb#galaxy#astrophotography#astronomy#stars#sky#solar system#uranus#cassiopeia A#supernova remnant#planets#universe#james webb telescope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

An article published in the journal "Nature" reports the discovery of a pair of merging galaxies cataloged as SDSS J0749+2255 which has the peculiarity of hosting a double quasar. A team of researchers led by the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign used various ground-based and space telescopes to study SDSS J0749+2255 to obtain observations detailed enough to resolve the two quasars, both of which are extremely bright. The difficulty in these observations is also given by the fact that this pair is very distant and we see it as it was when the universe was about three billion years old and the distance between the two supermassive black holes that power their respective quasars is only about ten thousand light-years.
0 notes
Text

Galactic Gathering © JWST
Galaxy Cluster SDSS J1226+2152: its immense mass distorts and magnifies the light from more distant galaxies behind it - a spectacular example of gravitational lensing
#galaxy cluster#nasa#webb#JWST#space#astrophotography#stars#night sky#galaxy#universe#planet#solar system#astronomy#cosmos#james webb space telescope
528 notes
·
View notes
Text






Self-Doubt ; Self-Sacrifice
-
Ghost can’t even give a gift right poor guy
188 notes
·
View notes
Text

Wide field Hubble view of extremely red quasar SDSS J165202.64+172852.3 by European Space Agency
218 notes
·
View notes
Text
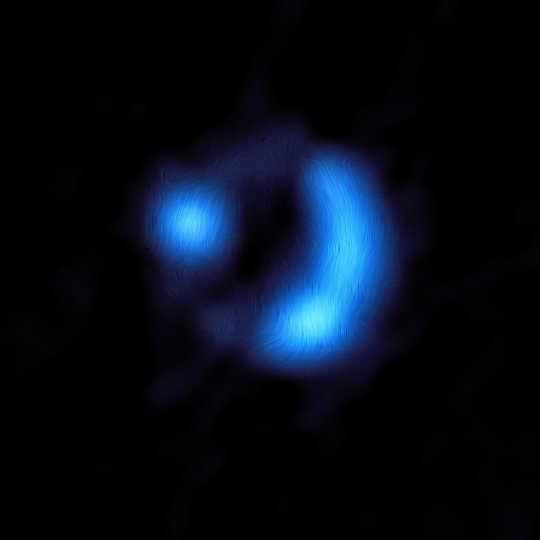
Early Galactic Magnetic Field
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ancient Warship’s Bronze Battering Ram Sunk During a Battle Between Rome and Carthage Found
Found near the Aegadian Islands, just west of Sicily, the bronze rostrum played a role in the last battle of the First Punic War, which ended in 241 B.C.E.
In 241 B.C.E., two empires faced off in a naval clash off the coast of Sicily. By then, Rome and Carthage had been fighting for more than two decades. Rome’s victory in the skirmish, officially called the Battle of the Aegates, brought an end to the First Punic War, the initial conflict in a series of wars between the two ancient powers.
Now, explorers have recovered a piece of that final battle: the bronze battering ram of an ancient warship. According to a statement from Sicily’s Superintendence of the Sea, the ram was found on the seafloor off the western coast of the Mediterranean island, at a depth of around 260 feet. To retrieve the artifact, the team used deep-water submarines from the Society for Documentation of Submerged Sites (SDSS) and the oceanographic research vessel Hercules.
The seabed off the Aegadian Islands “is always a valuable source of information to add further knowledge about the naval battle between the Roman and Carthaginian fleets,” Regional Councilor for Cultural Heritage Francesco Paolo Scarpinato tells Finestre sull’Arte. He adds that the find is yet another confirmation of the work of the late archaeologist Sebastiano Tusa, who spearheaded exploration of the seabed as the site of the 241 battle after a separate ram, also known as a rostrum, was first found there in the early 2000s. In the two decades since, researchers have recovered at least 25 rams from the seabed.
At the time of the Battle of the Aegates, Rome and Carthage had been at war for 23 years, fighting for dominance in the Mediterranean. As the Greek historian Polybius later wrote, the Romans sank 50 Carthaginian ships and captured another 70 along with their crews, taking nearly 10,000 sailors prisoner during the naval battle. Rome forced Carthage to surrender. But the fragile peace was short-lived: Over the next century, Rome would go on to fight a second and third war against the Punic people, winning each time.
“It was very costly, both in terms of human life and economically,” Francesca Oliveri, an archaeologist at the superintendence, told BBC News’ Alessia Franco and David Robson in 2022. “In the last phase, Rome even had to ask for a loan from the most well-to-do families to arm the fleet and build new boats.”




The recently discovered ram has been brought to Favignana, one of the Aegadian Islands, for further study. Though its features are difficult to make out because the object is covered in marine life, researchers have been able to discern a decoration on its front: a relief depicting a Montefortino-style Roman helmet decorated with three feathers.
The battering ram adds to the wealth of war relics found on the seabed, which also include 30 Roman soldiers’ Montefortino helmets, two swords, coins and many clay amphorae (large storage jars).
According to the SDSS, rams were the most important naval weapons of their time. They were placed on the bows of warships at water level so that sailors could crash their boats into enemy vessels, damaging and sinking them. The plethora of rams scattered on the seabed are testaments to the weapons’ effectiveness in ancient battle.
“We are finding so many things that help to illustrate a little better the world of the third century [B.C.E.],” Oliveri told BBC News in 2022. “It’s the first site of a naval battle, in the world, that has been scientifically documented like this, and it will continue to be documented—because the area of interest is very large. … It will take at least another 20 years to explore it fully.”
By Sonja Anderson.


#Ancient Warship’s Bronze Battering Ram Sunk During a Battle Between Rome and Carthage Found#roman rostrum#bronze#bronze rostrum#bronze battering ram#Battle of the Aegates#First Punic War#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
IN THE EARLY UNIVERSE TIME WAS SLOWER??
Blog#312
Saturday, July 8th, 2023
Welcome back,
Time has been observed passing more slowly in quasars in the early universe.
The observed time dilation comes as a consequence of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity combined with the expansion of space. "At its heart, this is another 'Einstein is right again' story," Geraint Lewis, a cosmologist at the University of Sydney, told Space.com.

Lewis and Brendon Brewer of the University of Auckland are co-authors on a new paper describing the long-sought after confirmation of time dilation effects in the variability of quasars. A quasar is powered by an accreting supermassive black hole at the heart of an extremely active galaxy. Because the accretion disk around the black hole is relatively small, fluctuations in the light emitted by the quasar can take place in just days. This makes them easier to track.

However, in the time since the light, and its fluctuations, was emitted from the 12 billion-year-old quasars, the universe has expanded greatly. This means that we are seeing the quasars as they existed over 12 billion years ago.
"We expected quasars to also exhibit this behavior, but previous searches had failed to find it," said Lewis.

A new sample of 190 high-redshift quasars observed over 20 years by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), Pan-STARRS and the Dark Energy Survey, has provided Lewis and Brewer with the tools to finally detect time dilation in the variability of quasar light. The long period of observations coupled with telescopic sensitivity to the quasar fluctuations reveals the time dilation effect.
Based on how slowly the fluctuations seem to be occurring, time in these quasars appears to run five times slower than it does for us in our frame of reference on Earth.

"We can pin-down the characteristics of their variability and show that quasars truly play ball with the cosmos," said Lewis.
To be clear, time didn't really run slow in those quasars relative to everything around them — in their frame of reference, time ran normally. Einstein's theory of relativity and how he described the passage of time is based on the concept of frames of reference, and that these frames can be distinguished by their velocity relative to each other.

"The motion of distant galaxies is due to expanding space," said Lewis. Consider that the Hubble constant describes how fast a volume of space 3.26 million light-years across is expanding per second. This is an incremental effect, where the expanding volumes of space add up. The farther a galaxy is from us, the more space has expanded between the galaxy and us, and the faster that galaxy seems to be moving away from us.
"Some of these quasars were moving faster than the speed of light, relative to us, when the photons were emitted," said Lewis.

As Einstein showed, strange things happen when you approach the speed of light. One of these strange things is time dilation. A stationary observer on Earth would observe a clock traveling faster than them, whether on a spacecraft or in a quasar, appear to slow down. The faster the clock is moving, the greater the effect. At velocities approaching the speed of light, the effect is dramatically pronounced, resulting in peculiarities such as the twin paradox.

Time dilation is not just theoretical. It has been observed, albeit in tiny amounts, in satellites orbiting the Earth — the Global Positioning System has to take this into account. Cosmologically, time dilation has been observed in supernovae that exploded 6 to 7 billion years ago, but never in objects more distant than that until now.
Besides being another successful test of Einstein's theory of relativity, the time dilation observed in the quasars is also further evidence that we do indeed live in a universe that is expanding as a result of the Big Bang.

If the universe were not expanding, the quasars would not appear to be moving at relativistic speeds relative to us. Lewis described the findings as "putting to bed some of the more extreme ideas that had been proposed, including that cosmologists have it all wrong, due to the previous failure to see quasar time dilation."
Originally published on space.com
COMING UP!!
(Wednesday, July 12th, 2023)
"WHAT IS A QUANTUM COMPUTER ??"
#astronomy#outer space#alternate universe#astrophysics#universe#spacecraft#white universe#space#parallel universe#astrophotography
239 notes
·
View notes