#sarugami
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo
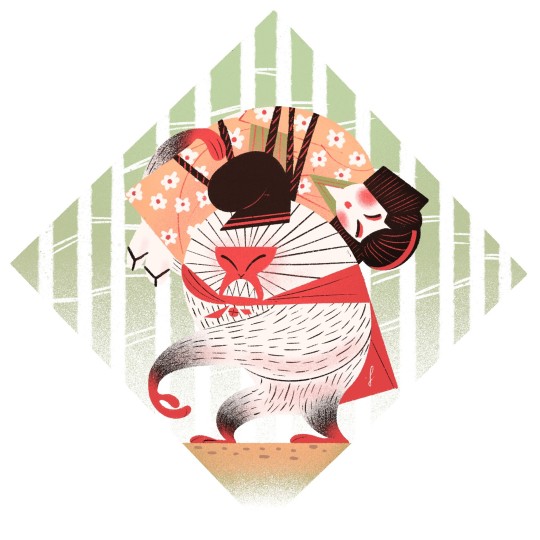









Yokai, by Lorenzo Colangeli.
#art#lorenzo colangeli#folklore#japan#yokai#tanuki#kappa#kitsune#rokuro-kubi#futakuchi-onna#sarugami#tengu#tsukumogami#karakasa-obake#chochin-obake#bakezori
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kitsune and the Pantheon
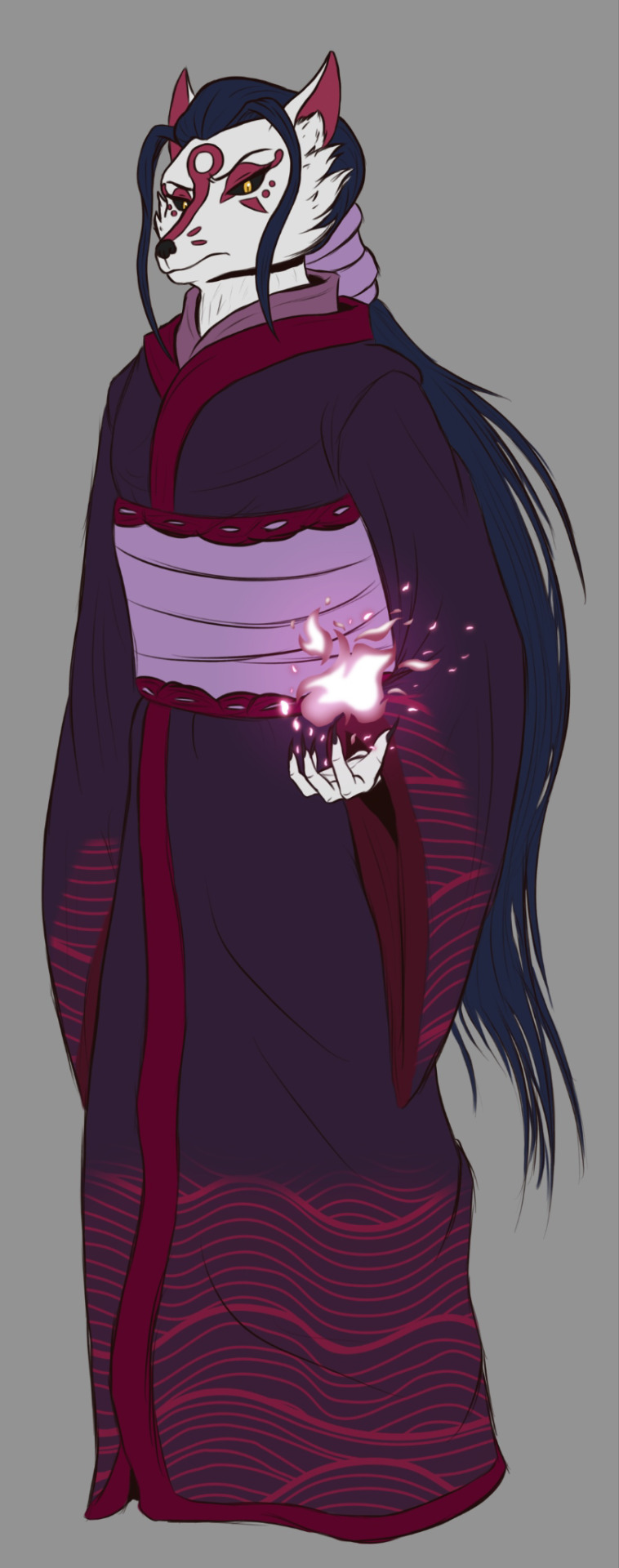
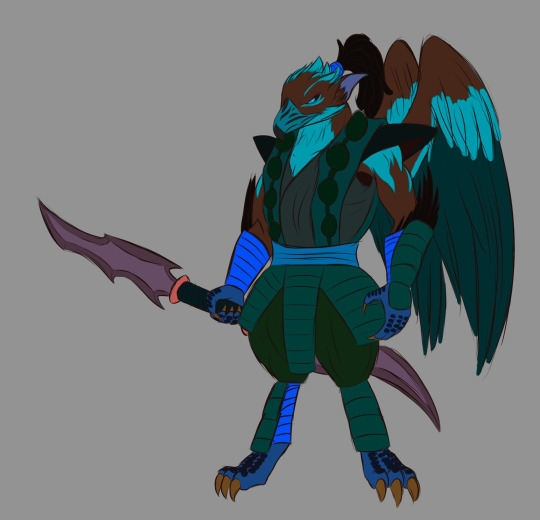
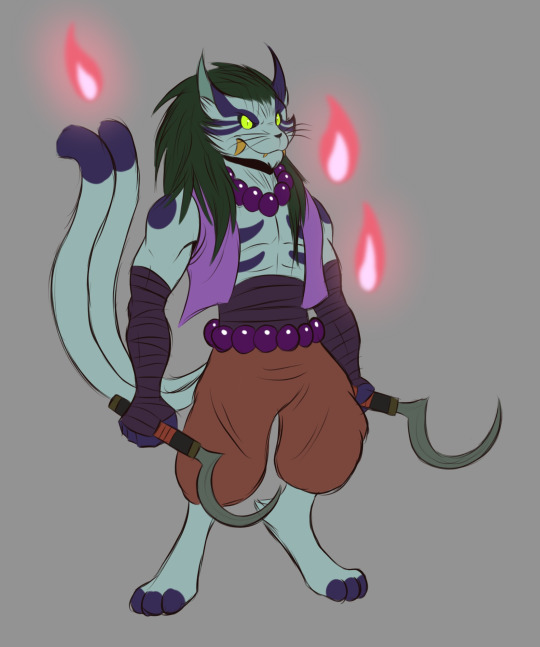
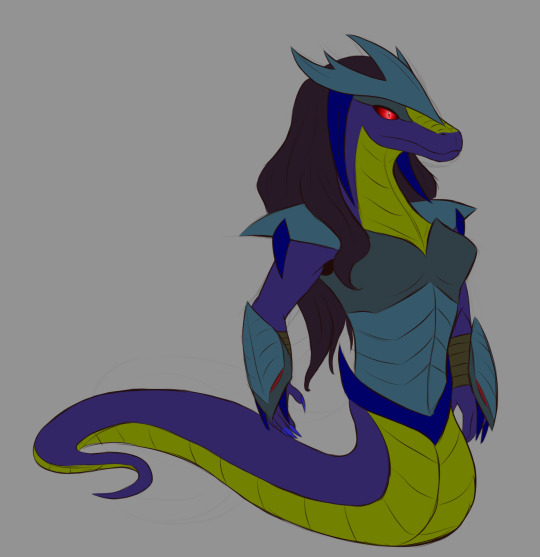

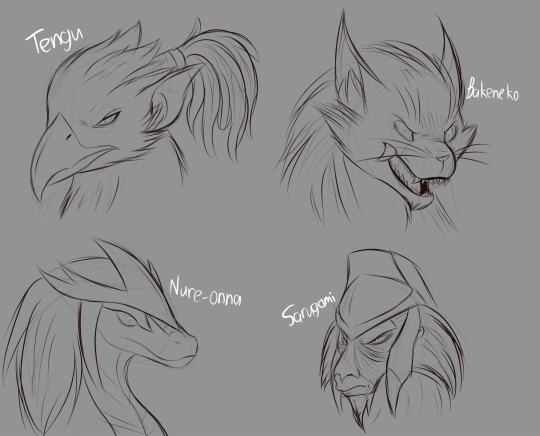




(I have yet to make a full design for Sarugami)
The Pantheon are a mysterious group of powerful yokai who claim themselves to be demigods, with their gift of immortality and immense mystic powers that differentiate them from the rest of yokaikind. It is even said that they were the first yokai to ever exist.
Kitsune: A fox yokai who is the eldest of the Pantheon. She is known for her variety of mystic powers and tricks. She is first seen in the Shredder Arc, where she is Shredder's right hand (other than Tatsu). She is then seen again in the Baron Draxum Arc, where she is Draxum's right hand.
Tengu: An eagle yokai who is the second eldest of the Pantheon. He is known for his mystic powers in powerful weather-like abilities (thunder, earthquakes, etc.). He takes his duties more seriously.
Bakeneko: A cat yokai who is the youngest of the Pantheon. They are known for shapeshifting and playing with fire. They are very mischievous.
Nure-onna: A snake yokai who is the second youngest of the Pantheon. She is known for her deadly poison and cataclysmic powers (yes this is based off of Cat Noir, shut up). She is very scary.
Sarugami: A monkey yokai who is the middle sibling of the Pantheon. He is known for his immense strength. He does not speak at all.
Hinoenma: ?
And they all share one goal:
To free their father, Ryujin, and destroy the world.
(Also, you may notice that, excluding Kitsune, the other Pantheon members may look familiar from a specific movie).
#my trashy art#kitty's tmnt-verse#tmnt au#tmnt kitsune#tmnt iteration#tmnt pantheon#tengu#bakeneko#nure-onna#sarugami
25 notes
·
View notes
Text

WIP
#art wip#current wip#my wips#wip#work in progress#oc#oc art#oc artist#oc artwork#original character#japanese yokai#yokai oc#sarugami#monkey yokai#i am not sure how the hell this happened but i downed a bottle of wine and i drew him#didnt think i was capable of drawing this way#he looks too good to be my creation
1 note
·
View note
Text
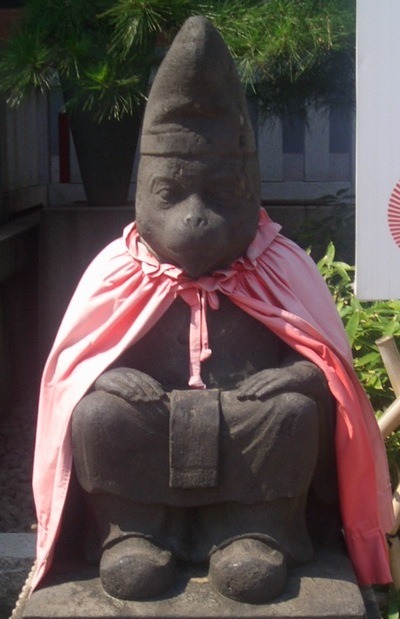
Sarugami
Sarugami (猿さる神がみ, "Monkey God") was a deity who protected a village. He inhabited an orb called the go-shintai from time to time that was housed in his shrine.
Please contribute, add more information, and share with friends!
1 note
·
View note
Text
doodling ;3

at first i wanna make gian like a sarugami but that doesnt really fit him so he ended up as your humble simple oni. suneo as kitsune that serves the inari okami, i made shizu chan to be like the crane wife folklore and then nobitanuki, and dksg is there as like a white snake descendant (hes smoking to keep his lower body temp regulated)

also doodled some of them in my own style. I really like how jaiko turned out but shizu chan is too gloomy so need workshopping
#my art#nobi nobita#dekisugi hidetoshi#doodle#rkgk#gouda takeshi#minamoto shizuka#honekawa suneo#gouda jaiko
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
The real life inspirations behind new characters in Touhou 19 (Unfinished Dream of All Living Ghost) While I haven’t been posting much about Touhou as of late, I felt obliged to put together the customary post about the inspirations behind the new characters. The new game genuinely renewed my interest. In contrast with similar write-ups pertaining to previous games the research is not entirely mine - some of the sections are a result of cooperation between me and @just9art. Without further ado, let’s delve into the secrets of the new cast. Find out if Biten is the first “Wukong impersonator” ever, when a tanuki is actually a badger, and why Hisami both is and isn’t an oni. Naturally, the post is full of spoilers. Also, fair warning, it's long.
1. Biten Son - sarugami + Sun Wukong

Sarugami means “monkey kami”, the monkey in mention being the Japanese macaque.To my best knowledge, the term is actually not used commonly in English - the results on jstor and De Gruyter are in the low single digits, Brill outright has nothing to offer. Translations are much more common.

Sarugami are particularly strongly associated with Mount Hiei. You might have heard of it because of its association with Matarajin, though in this case he’s not exactly relevant. Instead, it is believed the monkeys act as messengers of Sanno (the “mountain king”), Sekizan Myojin and Juzenji. Sanno himself could take the form of a monkey according to medieval texts, while Juzenji can be accompanied by a deity depicted as a man with a monkey’s head, Daigyoji, known from the Hie mandala. Sarutahiko is also associated with monkeys based on the similarity between his name and the word saru. Bernard Faure notes that despite the clearly positive portrayal of monkeys as semi-divine beings in service of these deities, their perception in folklore and mythology can nonetheless be considered ambivalent, because they could be viewed as aggressive. There are even examples of sarugami being portrayed as monstrous antagonists to be defeated by a hero. The best known tale of this variety is known simply as Sarugami taiji. It is preserved in the Konjaku monogatari. Here the sarugami is a fearsome monster who terrorizes a village and demands the offering of one young woman each year.
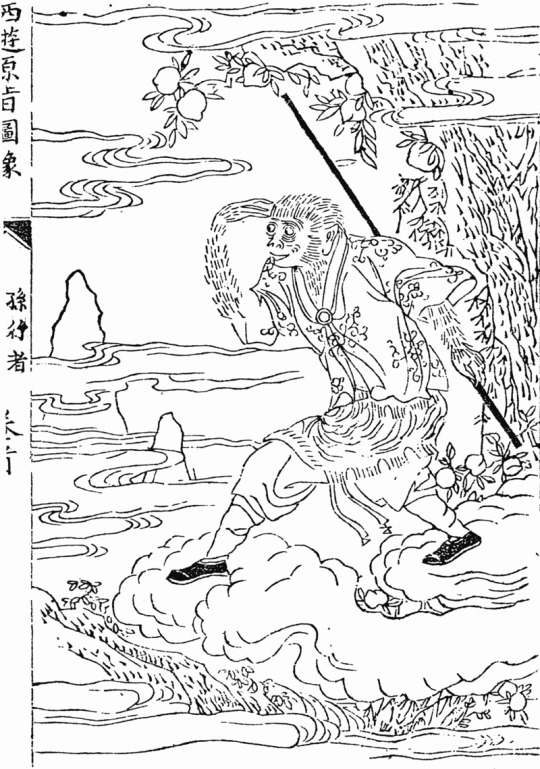

In contrast with the sarugami, I do not think Sun Wukong, one of the protagonists of the classic Chinese novel Journey to the West, needs much of an introduction. We reached the point where even in the west he is recognizable enough to warrant toys based on him (there’s a Lego Wukong on my desk right now). Biten's design has many callbacks to traditional portrayals of Wukong, including the staff (which in the novel is a pillar stolen from the undersea palace of a dragon emperor) and a very distinctive diadem (in the novel making it possible to pressure the unruly Wukong into obeying the monk he is meant to protect). As a curiosity it’s worth noting that “fake Wukong” is not a brand new idea - in the novel itself, one of the enemies of the heroes, Six-Eared Macaque, actually impersonates him for a time. Wukong is effectively himself a “divine monkey”, seeing as despite his origin as a literary character he actually came to be worshiped as a deity in mainland China, Taiwan and various areas with a large Chinese diaspora. The topic of Wukong worship itself came to be an inspiration for literature, starting with the excellent The Great Sage, Heaven’s Equal by Pu Songling, a writer active during the reign of the Qing dynasty, in the early eighteenth century.
2. Enoko Mitsugashira - “immortal yamainu” + Cerberus

Enoko gets the least coverage here, because there really isn’t much to say. Yamainu, “mountain dog”, isn’t really a supernatural creature, it’s an old term for either the extinct Japanese wolf, a type of feral dog, or a hybrid between these. It can also be used as a synonym of okuri-inu, a youkai wolf believed to accompany travelers at night.

There’s actually a distinctly Journey to the West-esque component to Enoko’s backstory, but I have no clue if this is intentional. In the aforementioned novel, many of the antagonists, who are generally demonic animals, are motivated by the desire to devour the flesh of the protagonist, the Buddhist monk Tang Sanzang, because it is said to grant immortality. Granted, given the obscurity of the figure Zanmu is based on - more on that later - perhaps this is an allusion to something else we have yet to uncover. Cerberus, being probably one of the most famous mythical monsters in the world, does not really need to be discussed here. The illustration is included mostly because I like Edmund Dulac and any opportunity is suitable for sharing his illustrations. I do not think it needs to be pointed out that Enoko's bear trap weapons are meant to evoke Cerberus' extra heads.

3. Chiyari Tenkajin - tenkaijin (+ mujina) + chupacabra

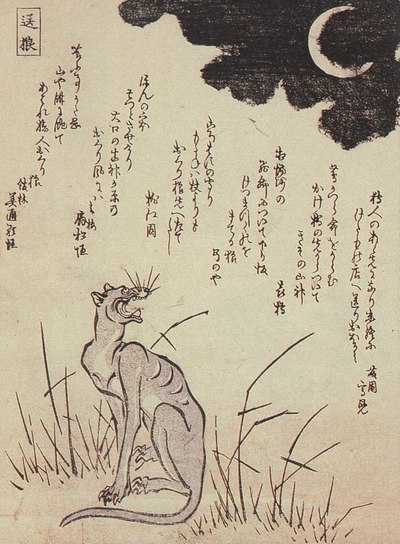
While my favorite animal youkai not yet featured in Touhou is easily the kawauso (otter), I was very pleased to learn we sort of got a mujina since I wanted to cover this topic since forever, but never got much of a chance. Technically Chiyari is actually meant to be a tenkaijin, which is not a mujina but a slightly different youkai (a will-o-wisp or St. Elmo’s fire-like creature, specifically) who in the single tale dealing with it takes the form of a mujina after dying, but as there is not much to say about it beyond that you will get a crash course in mujina folklore instead.

Today the word mujina is pretty firmly a synonym of anaguma - in other words, the Japanese badger. The animal does not substantially differ from other badgers, so I do not think much needs to be said about its ecology. However, historically the term could be used to refer to the tanuki regionally, or interchangeably to both animals, so in some cases if insufficient detail is provided it is hard to tell which one is meant. This ambiguity extends to the folklore surrounding them, and generally if you know what to expect from tanuki tales, which I’m sure most people reading this do, you will instantly recognize many of the plot elements typical for mujina ones. In other words, it is yet another yokai which typically takes the role of a shapeshifting trickster. Some supernatural phenomena could be basically interchangeably attributed to mujina, tanuki, kitsune or kawauso. Mujina are commonly described taking the form of Buddhist monks, which is one of the many similarities between them and tanuki.

The most famous depiction of a shapeshifting mujina comes from Toriyama Sekien’s Konjaku Gazu Zoku Hyakki (The Illustrated One Hundred Demons from the Present and the Past). The accompanying text compares the creature to the supernatural versions of kitsune and tanuki, and states that the artist relied on a tale according to which a mujina was able to successfully impersonate a Buddhist monk until accidentally revealing its tail.
What makes the mujina special is that it is actually the oldest recorded example of a youkai of this sort. A mujina tale already appears in the early Japanese chronicle Nihon Shoki, dated to 627. It reports an incident of a mujina transforming into a human and singing somewhere in the Michinoku Province. I feel like this alone is a good example of why you should be wary of people who seek to present Nihon Shoki or Kojiki as historical truth. Western audiences as far as I know were first introduced to mujina by Lafcadio Hearn. To my best knowledge, the fabulous shapeshifting badgers however failed to gain the popcultural recognition enjoyed by tanuki and kitsune. They did appear in Shigeru Mizuki's stories every now and then, and I found a mascot character based on them, but overall there isn't all that much beyond that.
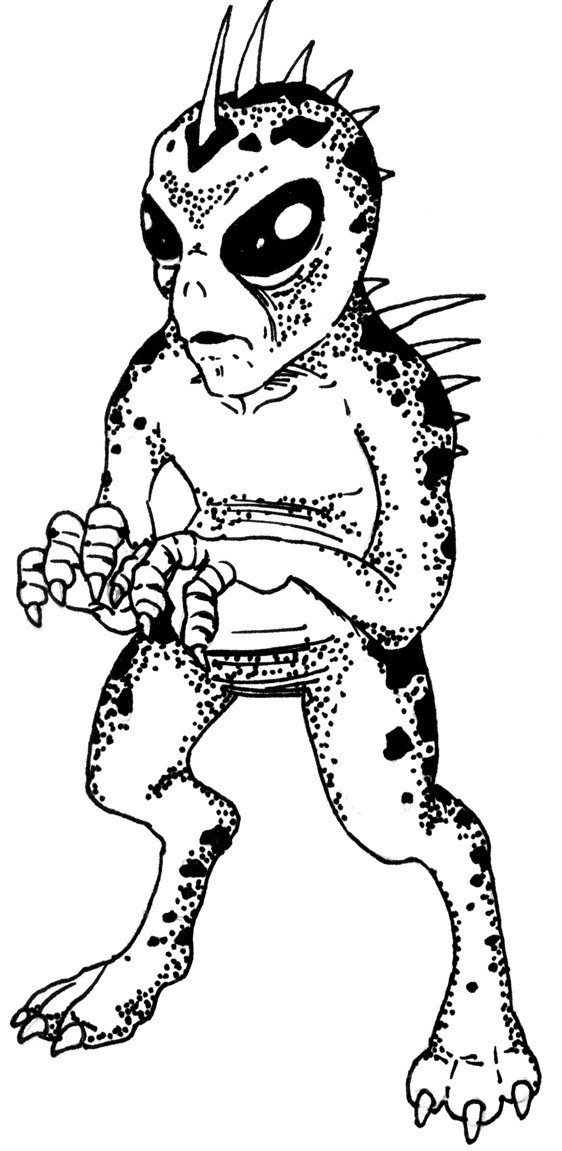

Naturally, there isn't much mujina in Chiyari's design, and she instead most likely owes her distinctly spiky appearance to the other inspiration behind her character, the chupacabra. Mujina are not really portrayed as bloodthirsty, but the poorly documented tenkajin apparently is, which is presumably why ZUN decided to connect Chiyari with the chupacabra, the best known modern blood-drinking creature, who first appeared in tall tales from 1995 and subsequently took popculture by storm after spreading from Puerto Rico to mainland USA and Mexico. I am not a chupacabra aficionado so I have little to offer here, sadly.
4. Hisami Yomotsu - yomotsu-shikome
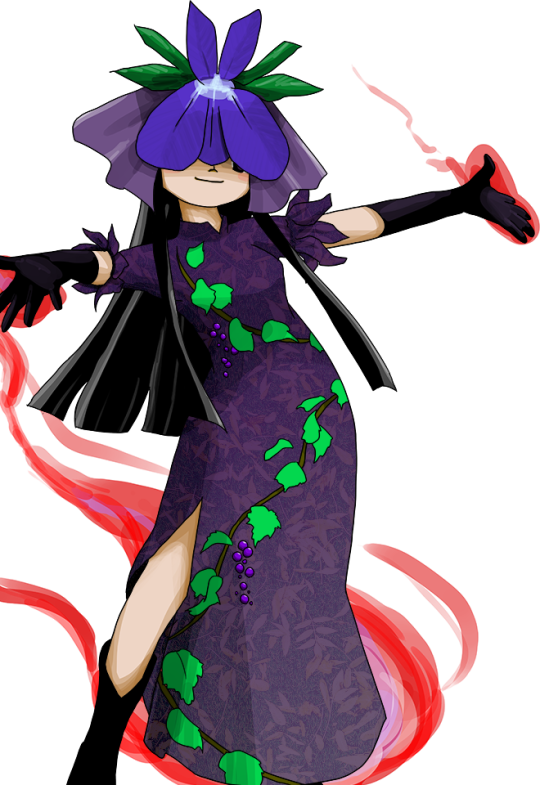

Judging from what I’ve seen on social media and on pixiv, Hisami is shaping up to be one of the most popular new characters (she’s my fave too). In sharp contrast with that, her basis is pretty obscure. So obscure that there isn’t even any historical art to showcase, as far as I can tell (note that this blog claims night parade scrolls might have something to offer, though - I was unable to verify this claim for now, sadly). As we learn from her bio, she is supposed to be a yomotsu-shikome. They’re called the “hags of Yomi” of Yomi in Donald L. Philippi’s Kojiki translation. The term shikome can be literally translated as “ugly woman”. Nothing about them really implies femme fatale leanings we are evidently seeing in Touhou but I’m not going to complain about that. Yomotsu-shikome appear only in the Kojiki and the Nihon Shoki, and in both of these early chronicles they are portrayed as servants of Izanami after she died and came to reside in Yomi, the land of the dead. Nihon Shoki states there are only eight of them. The distinct grape vine motif present on Hisami’s clothes seems like an obvious reference to Izanagi’s escape from Yomi following his meeting with Izanami, portrayed in the myth recorded in both of these sources. When the yomotsu-shikome started to pursue him, he threw a vine he used to hold his hair at them. The plant instantly bore fruit, which the entities started to eat. They later resumed the chase, but were once again held back, this time by a bamboo shot. According to the Nihon Shoki, they eventually give up after he creates a river from his piss (sic) to keep them away.

Yomotsu-shikome are sometimes compared to oni by modern researchers. Noriko T. Reider in her monograph about oni argues that alongside hashihime and yamanba (pictured above) they can be effectively grouped with them. Another researcher, Michael D. Foster, is more cautious, and states that despite clear similarities it’s best to avoid conflating oni-like female demons with female oni proper, especially since the latter have a distinct iconography and a distinct set of traits. Norinaga Motoori, the founder of kokugaku or “national learning”, a nationalist intellectual movement in Edo and Meiji period Japan, claimed that oni were based on yomotsu-shikome, which is a pretty dubious claim. It is ultimately not certain when the term oni started to be used, but it is safe to say it has continental origin. And, of course, oni permeate Japanese culture in a way yomotsu-shikome do not.
5. Zanmu Nippaku - Zanmu
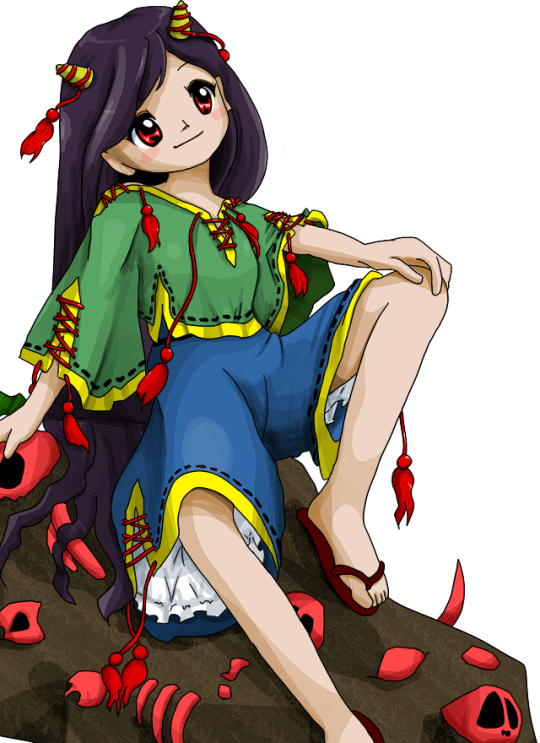

This was the toughest mystery to solve, and I am fully indebted to 9 here, since they figured it out, I am merely depending on what they directed me to. Research is still ongoing, and it feels like we just started to untangle this mystery, so you can safely expect further updates. Zanmu appears to be based on the Buddhist monk… well, Zanmu. You can learn a bit about him here or on Japanese wikipedia; it seems there are quite literally 0 sources pertaining to him in English, and even in Japanese there is actually very little. Their names are not written the same, ZUN swapped the sign for “dream” from the original name for one which can be read as “nothingness”. If the unsourced quote on wikipedia is genuine, the reason might be tied to the personal views of the irl Zanmu. What little we’ve been able to gather about him is that he was active in the Sengoku period, and apparently was regarded as unorthodox and eccentric. This lines up with Zanmu’s omake bio pretty well. Seems the real Zanmu was also unusually long lived, and was able to recall events from distant past in great detail, though obviously the figure of 139 years attributed to him in a few places online has to be an exaggeration.

Yet more puzzling is the reference to Zanmu’s familiarity with Ikkyo you might spot in the linked article. Whether the famous Ikkyo who you may know from the tale of Jigoku Dayu is meant is difficult to determine. The chronology does not really add up; on the other hand the logic behind associating one eccentric semi-legendary monk with another in later legends isn’t particularly convoluted. As 9 pointed out to me, if ZUN was aware of this link, and the same Ikkyo really was meant, it is not impossible the connection between Zanmu and Hisami is meant to in some way mirror that between Ikkyo and Jigoku Dayu. As you can easily notice, it’s pretty clear the historical Zanmu was male. It does not seem his Touhou counterpart is, obviously. I would say we should wait for more info until declaring that we have a second Miko situation on our hands, with a male historical figure directly reimagined as a female character without any indication we are dealing with a relative rather than the real deal. There’s still relatively little info to go by so I would remain cautious (though naturally this is not meant to discourage you from having headcanons).
Neither me nor 9 were able to find any connection between the historical Zanmu and oni… so far, at least. Therefore, what motivated ZUN to make Zanmu an oni remains to be discovered. As a final curiosity, on a semi-related note it might be worth pointing out that while not as common as their male peers, female oni are not a modern invention, and already appear in setsuwa from the 13th century. A particularly common motif are tales describing a woman turning into oni due to jealousy or anger. Further reading:
Jason Colavito, The Secret Prehistory of El Chupacabra (2011)
Bernard Faure, Gods of Medieval Japan vol. 1-3 (2015-2022)
Michael Daniel Foster, The Book of Yokai. Mysterious Creatures of Japanese Folklore (2015)
John Knight, Waiting for Wolves in Japan. An Anthropological Study of People-wildlife Relations (2003)
Noriko T. Reider, Japanese Demon Lore (2010)
276 notes
·
View notes
Text
Japanese Monkey God
User @red-lights-burning asked if there was a connection between Sun Wukong and the monkey gods of Japan. They provided lovely info, which was split between two asks, but I decided to put everything together into a single post.
@red-lights-burning asked: Japan has their own monkey protector named Masaru AKA Sannō Gongen, who was created back in the early 9th century by Tendai Buddhist sect founder Saichō shortly after he returned from China. So it makes me think if Monkey King was already a thing in the 800’s and if he was one of the inspirations for Masaru. A description from onmarkproductions (a really great site for anyone curious about Japanese Buddhism and Shintō) MASARU 神猿 Literally “Kami Monkey.” Masaru is the sacred monkey and protector of the Hie Shrine (aka Hie Jinja 日吉神社, Hiyoshi Taisha 日吉大社). The term “Masura” is often translated as “excel,” reflecting the belief that this sacred monkey can overcome all obstacles and prevail against all evil. Masaru is thus considered a demon queller par excellence (魔が去る・何よりも勝る). In the Heian era, Masaru (also translated “Great Monkey”) was invoked in Kōshin rituals to stop the three worms from escaping the body. Masaru also appears in Japanese scrolls used in Koushin rites. Here’s a couple other descriptions SANNŌ GONGEN 山王 権現 SARUGAMI 猿神 Fertility, Childbirth & Marriage Monkeys are patrons of harmonious marriage and safe childbirth at some of the 3,800 Hie Jinja shrines in Japan. These shrines are often dedicated to Sannō Gongen 山王権現 (lit. = mountain king avatar), who is a monkey. Sannō is the central deity of Japan’s Tendai Shinto-Buddhist multiplex on Mt. Hiei (Shiga Prefecture, near Kyoto). The monkey is Sannou’s Shinto messenger (tsukai 使い) and Buddhist avatar (gongen 権現). The monkey messenger is also known as Sarugami (猿神; literally “monkey kami”). Sarugami is the Shinto deity to whom the three monkeys (hear, speak, see no evil) are reportedly faithful. The monkey shrine at Nakayama Shrine 中山神社 in Tsuyama City, Okayama Prefecture, is dedicated to a red monkey named Sarugami, who blesses couples with children. According to shrine legends, the local people at one time offered human sacrifices (using females) to this deity. The shrine is mentioned in the Konjaku Monogatari-shu (今昔物語集), a collection of over 1000 tales from India, China, and Japan written during the late Heian Period (794-1192 AD). Sarugami, like Sannou Gongen, is also worshipped as the deity of easy delivery and child rearing. At such shrines, statues of the monkey deity are often decked in red bibs -- a color closely associated with fertility, children, and protection against evil forces and diseases like smallpox.
My answer:
I've read only a little bit about Japanese monkey gods. I previously referenced Sarugami in my article about the possible shamanic origins of primate-based boxing in China. Part of footnote #14 reads:
In Japan, monkeys were also associated with horses and healing via the warding of evil. Apart from monkeys being kept in stables like their Chinese counterparts, their fur was applied to the harnesses and quivers of Samurai because the warriors believed it gave them more control over their mounts. Furthermore, monkey body parts have been consumed for centuries as curative medicines, and their hides have even been stuffed to make protective amulets (kukurizaru) to ward off illness. Likewise, a genre of painting depicts divine monkeys (saru gami), messengers of the mountain deity, performing Da Nuo-like dances to ensure a good rice harvest (Ohnuki-Tierney, 1987, pp. 43-50)
The aforementioned article suggests a connection between monkeys and the Shang-Zhou Da Nuo (大儺 / 難; Jp: Tsuina, 追儺) ritual, an ancient, war-like, shamanic animal dance designed to drive away demonic illness and influences. The pertinent section reads:
It’s possible that the “twelve animals” of the Da Nuo exorcism refer to some precursor of the Chinese zodiacal animals (rat, ox, tiger, rabbit, dragon, snake, horse, goat, monkey, rooster, dog, and pig). If true, monkey fur could have been among the animal products worn by the ritual army. After all, monkeys have long been associated with curing illness and expelling evil in East Asia. [14] A modern example of exorcists who don monkey fur are the shamans of the Qiang ethnic group of Sichuan. The Qiang worship monkeys as the source and savior of their sacred knowledge, as well as the progenitor of their people, the latter being a myth cycle common among ethnic groups of Tibet and southwestern China.
This is the only relevant info that comes to mind. But based on what I know, I would guess that Sun Wukong and the monkey gods of Japan draw upon the same cultural sources. I hope this helps.
Source:
Ohnuki-Tierney, E. (1987). The Monkey as Mirror: Symbolic Transformations in Japanese History and Ritual. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
#asks#Sun Wukong#Monkey King#Journey to the West#JTTW#Japanese Buddhism#Shinto#Buddhism#monkey god#shamanism#Lego Monkie Kid#LMK
76 notes
·
View notes
Text




Sarugami Armour - Ghost of Tsushima
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sarugami, Kijigami, Inugami from Momo Kyun Sword
Today's AniAnimal are Sarugami, Inugami, and Kijigami from "Momo Kyun Sword". So many anime have characters based on the Peach Boy story. 今日のアニアニマルは『モモキュンソード』の猿神、犬神、雉神です。桃太郎の物語に基づいたキャラクターが登場するアニメはたくさんありますね。
1 note
·
View note
Text

And they almost did
#my trashy art#tmnt#memes i made#tmnt au#kitty's tmnt-verse#tmnt iteration#bakeneko#sarugami#tmnt donatello#tmnt donnie
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Options sourced from Ghost of Tsushima Fandom Wiki.
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
Ghost of Tsushima Iki Island genişletmesi, Jin için yeni bir zırh seti içeriyor Jin bu yeni zırh setini The Eagle Tribe...
0 notes
Text
Genshin Verse
Much like Heizou, Gohan is a Catalyst user and a Catalyst user who uses melee combat. His punches and kicks are covered in a fire so hot it oscillates between a blue or gold coloration.
Unlike Heizou, Gohan is Half-Yokai on his father's side. Goku was a powerful Sarugami yokai who, years after meeting Chi-Chi near Fire Mountain, married her and had Gohan.
Gohan is a Pyro vision holder, his own martial arts style being an adaptation of his father's own off-shoot developed after he learned from Master Roshi. Master Roshi was a hermit from Natlan, a talented Shadow Boxer who travelled to Inazuma where he further refined Natlan's Shadow Boxing into the sorta official "Kame Ryu" which he later taught Grandpa Gohan and Ox-King (Chi-Chi's father), later on, Gohan Senior would pass that onto Goku who went even further beyond and developed his own off-shoot style which he THEN taught Gohan.
Much like Itto, Gohan can, under specific circumstances, unleash his inner Sarugami Yokai power granting him even more strength and speed, at the cost of going slightly feral.
#( Verse Tag Pending )#WELL HERE IT IS!#After months of smacking my head against the wall#I finally put this together#It's still VERY WIP since I know next to nothing abt g.enshin
1 note
·
View note
Note
How many Buddhist characters are there in Touhou, and which branch of Buddhism do they represent?
Putting aside the explicitly Buddhist Byakuren and the other Myouren-adjacent characters, who are presumably either Shingon or Tendai (I'm fairly sure I've seen both claims made regarding the semi-historical Myouren; I cannot check this right now, I'm sorry), the characters at the very least based on something Buddhism-related include: Yuyuko: her name is an allusion to Saigyo, who was a Buddhist monk, based on his reverence for Kukai’s teachings belonging to the Shingon school. Keine: hakutaku is hardly Buddhist, but her school is a terakoya, which is ultimately a (derivative of a) Buddhist institution, hence the frequent use of “temple school” in translations. I do not think ZUN ever addressed if there is a Buddhist temple in the village though, let alone what Keine has to do with it. Akyuu: while we know nothing about the personal beliefs of the semi-historical Hieda no Are, the term referring to Akyuu’s ability in Touhou, gumonji, is actually a real Buddhist ceremony belonging to the Shingon tradition. Ashiyama’s “officially unofficial” Gensokyo of Humans went all out with this. Eiki: while not exclusively Buddhist, the concept of kings of hell and related imagery did enter Japan in a Buddhist context. And her backstory is pretty explicitly based on the Buddhist notion of equivalence between Enma (Yama) and Jizou. Neither of these is exclusive to a specific school. Tengu, collectively: while the matter of tengu origin is complex, the notion of tengu living in an organized society, publishing own literature, etc. is rooted in so-called tengu scrolls from the Kamakura period, which are best understood as Buddhist political cartoons of the “I drew myself as the Chad and you as the tengu” sort. Arose due to rivalry between old establishment schools, Tendai and Shingon, with new ones like Nichiren in the Kamakura period. Tojiko: while nothing in the game really points at Tojiko herself being a Buddhist, I feel like it’s worth mentioning the Soga clan was the most firmly pro-Buddhist in the period when this was still a novelty not yet firmly rooted in Japan. The first schools established in Japan by Korean and Chinse missionaries are known collectively as Nanto Rokoshu. Miko: as we learn from the game itself, the semi-historical crown prince Shotoku was very much invested in spreading Buddhism, Miko's professed Taoist beliefs notwithstanding. I’m pretty sure ZUN’s idea is partially based on the Honchou Shinsenden, where Shotoku is presented as the Buddhist version of a Taoist immortal. Narumi: while Narumi’s in-universe status is sort of its own unique thing, Jizou is a firmly Buddhist figure as already discussed above, and she keeps the distinct iconography. Once again, not really tied to a specific school. Mai and Satono: directly based on Matarajin’s attendant deities, Chōreita Dōji and Nishita Dōji. Exclusively Tendai, and limited to genshi kimyodan rites at that, basically one of the deepest cuts in ZUN’s repertoire so far. Okina: based on Matarajin, probably the single most Buddhist character in Touhou in that her inclusion opened many doors (heh) for adapting irl materials for Touhou wholesale. Pretty firmly Tendai. Eika: the Ebisu theme is certainly there, and I do wish more was done with it, but her whole gimmick is largely based on Sai no Kawara, which is pretty explicitly Buddhist and ties into the Jizou and ten kings-related beliefs. Not really connected to a specific denomination though. Megumu: at the very least named after Iizuna Gongen, who is a Buddhist deity - not exclusively, but still. Ultimately associated with Shugendo more closely than any Buddhist school. Tsukasa is based on a youkai associated with practicioners of shugendo too. Bitten: sarugami are associated with multiple strictly Tendai deities like Sekizan Myojin and Sanno. Zanmu: based on legendary Zen monk Zanmu Nichihaku who according to a legend was actually a different, earlier Tendai monk, Kaison Hitachibo. Zun seems to focus on the Zen connection.
PC-98 only has the dubiously Buddhist example of Konngara, who is clearly named after Kongara-douji, but I frankly do not see much of a reason to assume the name isn’t used randomly in this context.
All around, Touhou pretty heavily skews towards Heian and Kamakura Buddhism, ie. more towards a time period rather than a specific school. I do think it is notable Zanmu is pretty clear Zen though. We'll see if that will lead to introduction of Nichiren and Pure Land characters eventually.
71 notes
·
View notes
Text


“Sarugami” digital illustration,character design contest entry, 2020
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sarugami
Omnipotent. Isn’t that what kami are supposed to be? Sacred and omnipotent? Apparently that depends on the familiars that serve you, because in Sarugami’s case, he is neither sacred nor omnipotent. No. Thanks to his pupils, he is a monkey god stuck as a pickling stone.

5 notes
·
View notes