#rf transmitter and receiver
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Low-Latency & High Fidelity Wireless Audio Module SA326
For consultation, please contact NiceRF (Email: [email protected])
1 note
·
View note
Text
IR (Infrared) transmitters and receivers use infrared light for communication. RF (Radio Frequency) transmitters and receivers use radio waves. Both transmit signals wirelessly over short or long distances.
0 notes
Text
Creating an ESPHome Remote Control Device with Infrared & Radio Frequency
#configuration#DIY#electronics#ESP8266#ESPHome#Home Assistant#infrared#IR#make#making#microcontroller#NodeMCU#radio frequency#receiver#remote#remote controll#RF#transmitter#YAML
0 notes
Text
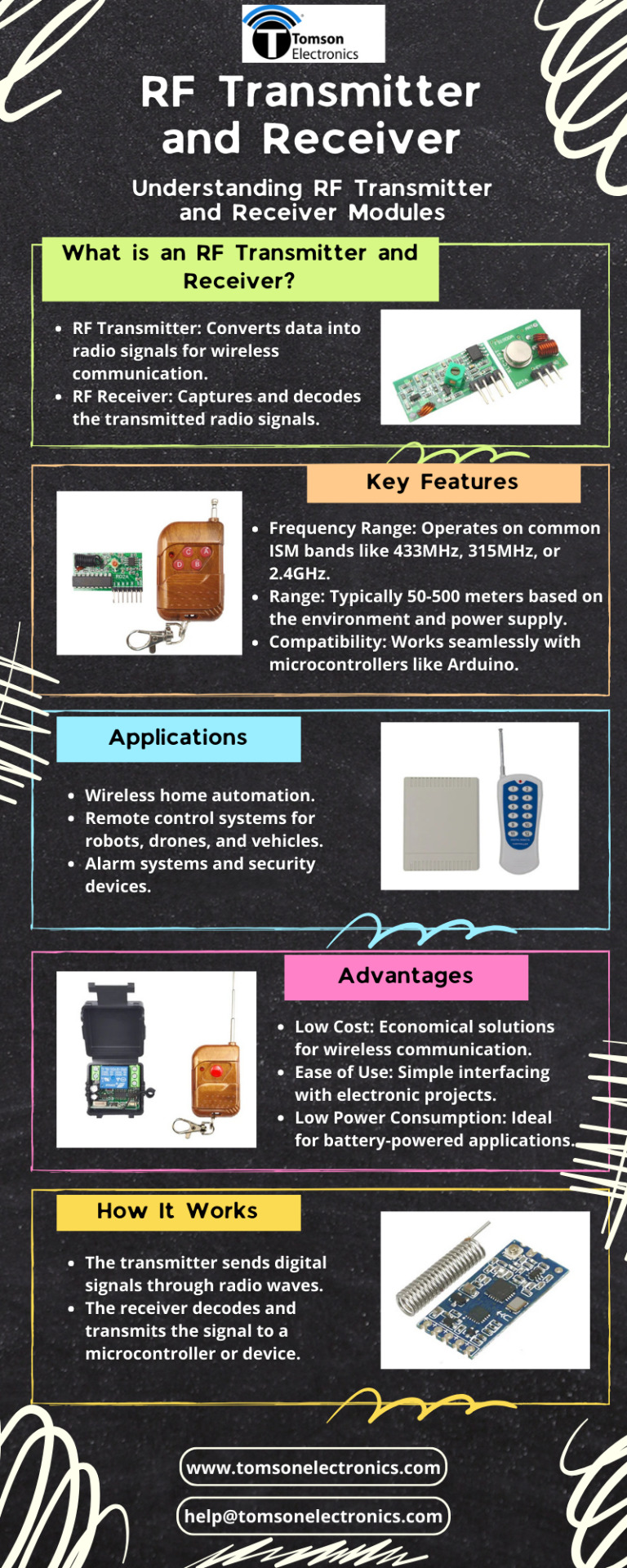
RF TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER online in India
Buy RF transmitter and receiver online from Tomson Electronic online store. Welcome to the world were quality meets discounts. Avail attractive discounts at Checkouts.
0 notes
Text

A Signal Processing Company in Defense and Aerospace
#Scenario Simulation#Modelling & Simulation#Signal Processing company in Hyderabad#Radar & EW Sensor Testing#Digital Signal Processing#Ansys STK AGI#Telemetry Receivers Manufacturers in hyderabad#radar target echo simulator#Digital Telemtry Receiver#EW Emitter simulator#Target simulator radar in hyderabad#Radar signal generator in hyderabad#Electronic warfare#sar simulator Hyderabad (synthetic aperture radar )#RF environment simulation#ELINT#comint#sigint simulator#THREAT simulator in hyderabad#Aerospace Signal processing company#Best Signal processing company in Hyderabad#Radar signal processing companies in india#Defense Equipment manufacturing companies#Communication systems IP in hyderabad#CRTK Applications#Telemetry manufacturers from Hyderabad#Digital Telemetry Transmitter#Radar Toolkit for Labview
0 notes
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--wireless-rf--transceiver-ics/sp4082een-l-tr-maxlinear-6164468
High speed data transmission, Bus Transceiver, USB RFreceiver
SP4082E Series 115 kbps 5 V RS-485 / RS-422 Transceiver - NSOIC-8
#MaxLinear#SP4082EEN-L/TR#Wireless & RF#Transceiver ICs#rf transceiver module#usb rf transmitter#High speed data transmission#Bus Transceiver#usb rf receiver#Replacement USB Receiver
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.futureelectronics.com/p/semiconductors--wireless-rf--transceiver-ics/sp3077een-l-maxlinear-2168612
RF Transceiver utilizes, WIFI transceiver, High speed data, wireless transmitter
SP3077E Series 16 Mbps ±15 kV ESD Protected RS-485/RS-422 Transceiver-NSOIC-8
#Wireless & RF#Transceiver ICs#SP3077EEN-L#MaxLinear#Wireless receiver#Bluetooth transceiver#RF Transceiver utilizes#WIFI transceiver#High speed data#wireless transmitter#Microwave transceiver#USB wireless transceiver#RF utilizes
1 note
·
View note
Text
Wireless Wonders: Unraveling the Magic of IR and RF Transmitter and Receivers

In a world where wires seem to be disappearing faster than a magician’s rabbit, the spotlight is shining brightly on the magic of wireless communication. If you’ve ever marveled at how your TV remote controls the channel or your car key unlocks the door from a distance, you’ve witnessed the enchanting performance of Infrared (IR) and Radio Frequency (RF) transmitters and receivers.
Let’s dive into the captivating world of these electronic wizards and discover how they make the seemingly impossible, possible.
IR Transmitters and Receivers: The Invisible Light Symphony
Imagine your TV remote as a maestro, conducting an orchestra of invisible light. This is precisely what happens with IR transmitters and receivers. IR technology uses light waves just below the visible spectrum to transmit information.
When you press a button on your remote, the corresponding command is translated into a unique pattern of infrared light pulses. The IR receiver on your TV picks up these pulses and decodes them, instructing your television to change the channel, adjust the volume, or perform other tasks.
IR technology is not just confined to the living room. It’s the wizard behind many gadgets, from air conditioners to digital cameras. However, there’s a catch — IR signals require a direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. That’s why you often find yourself pointing your remote at the TV for it to work its magic.
RF Transmitters and Receivers: The Wireless Symphony
Now, let’s step into the realm of RF technology, where the magic of wireless communication truly shines. Unlike IR, Radio Frequency doesn’t demand a visual connection. It dances through walls, ceilings, and even furniture to deliver its commands.
Your car key fob is a prime example of RF technology. When you press the unlock button, the RF transmitter in your key fob sends a signal to the RF receiver in your car, triggering the doors to unlock. This enchanting dance of signals happens through the air, making RF technology the go-to choice for applications that require a broader range.
One of the RF technology’s superpowers lies in its ability to operate at different frequencies. This flexibility allows various devices to communicate simultaneously without interference, creating a wireless symphony where each instrument plays its unique tune.
The Harmony of Everyday Applications
Now that we’ve peeked behind the curtain of IR and RF technology, it’s clear that these electronic maestros are orchestrating the harmony of our daily lives. From home entertainment systems to car security, they’re the unsung heroes making convenience and efficiency possible.
So, the next time you change the channel with your TV remote or unlock your car with a click of a button, take a moment to appreciate the invisible symphony of IR and RF transmitter and receivers working their magic behind the scenes.
In this era of wireless wonders, it’s these electronic wizards that remind us that the future is not just wireless; it’s enchantingly untethered.
0 notes
Text

#433 mhz antenna#rf antenna#rf antenna manufacturer#wireless rf#rf antenna types#rf connector for tv#rf booster antenna#rf antenna booster#solid rf signal booster#rf to antenna connector#433mhz rf antenna#433mhz rf module range#433mhz transmitter antenna#433mhz rf transmitter and receiver antenna#433 mhz rf module antenna#rf connector antenna#outdoor rf antenna#rf radio antenna#lmr400 coaxial#433mhz remote control arduino#antenna for rf module 433mhz#mmcx connector antenna#helical rf antenna#rf antenna suppliers#rf antenna cables
0 notes
Note
Ah yes very cool! My realm is ships 🥰 Same team tho! 🥰
With the title "anarcho electrificationism", it may be of interest for you to know that I actually work within the field of electrification. You're right for what you believe in and I'm rooting for you to join the fight when you start your career 💯 🥰💪
Well that is Specifically referring to Traction Electrification for Railroads, Streetcars, and Trolleybuses which is infact related to what I hope to do as I want to work in engineering
#I work on ship-to-shore communication#using RF transmitters#receivers#and associated control systems#to make sure big-ol girls can charge
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
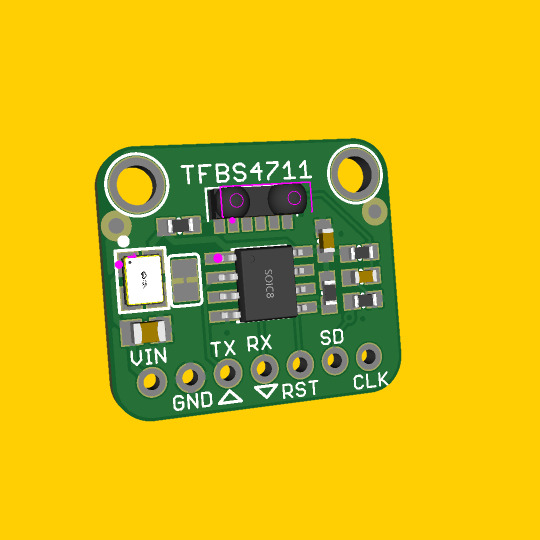
IrDA codec board 🔧📡🕰️
We've been designing all sorts of IR transmitters and receivers for the Adafruit shop lately, and a chance discussion got us thinking about IrDA - an old wireless protocol used in some PDAs, watches, laptops and toys. its not used anymore - bluetooth LE does a way better job - but there's probably some cases where IrDA hacking could be useful such as communicating with retro devices or if you want an RF-less wireless link. here's a board that combines a TFBS4711 transceiver (https://www.digikey.com/short/jn43cz31) with a MCP2112 codec (https://www.digikey.com/short/m8tp3708). you can communicate at 115.2kbps with RX and TX lines just like any UART. 115.2kbps is the standard baudrate. or, provide your own CLK for something like 9600 baud.
#adafruit#irda#ir#wirelessprotocol#retrotech#uartcommunication#electronicsdiy#communicationspeed#tfbs4711#mcp2112#hackoldtech#nostalgiatech#rfcommunication
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Scenario Simulation#Modelling & Simulation#Signal Processing company in Hyderabad#Radar & EW Sensor Testing#Digital Signal Processing#Ansys STK AGI#Telemetry Receivers Manufacturers in hyderabad#radar target echo simulator#Digital Telemtry Receiver#EW Emitter simulator#Target simulator radar in hyderabad#Radar signal generator in hyderabad#Electronic warfare#sar simulator Hyderabad (synthetic aperture radar )#RF environment simulation#ELINT#comint#sigint simulator#THREAT simulator in hyderabad#Aerospace Signal processing company#Best Signal processing company in Hyderabad#Radar signal processing companies in india#Defense Equipment manufacturing companies#Communication systems IP in hyderabad#CRTK Applications#Telemetry manufacturers from Hyderabad#Digital Telemetry Transmitter#Radar Toolkit for Labview
0 notes
Text

RF TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER online in India
Buy RF transmitter and receiver online from Tomson Electronic online store. Welcome to the world were quality meets discounts. Avail attractive discounts at Checkouts.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
This RF Transmitter and Receiver module can be used with 433Mhz RF Radio modules for better communication and to avoid cross-connection with other transmitters and receiver modules working at the same radio frequency. This RF Transmitter Module uses the HT12E IC for encoding the message and the RF Receiver Module uses the HT12D IC for decoding.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the main characteristic parameters of the antenna?

Fundamental Antenna Parameters
To grasp the concept of how an antenna interacts with signals and its efficiency in transmitting or receiving them, understanding these fundamentals is crucial.
Antenna Gain (dBi)
Antenna gain is a metric that assesses the antenna's capacity to transmit or receive power in a direction when compared to an isotropic antenna, showcasing its effectiveness in focusing input power and effectively radiating it outwards.
Antenna gain in dBi (decibels relative to an isotropic radiator) is calculated using the following formula:

Pradiated is the Power radiated by the antenna (in watts) and Pinput is the Input power supplied to the antenna (in watts).
Directivity
Antenna directivity indicates how well an antenna can concentrate its signal in a direction, calculated by dividing the maximum radiated power in one direction by the average power radiated in all directions.
It can be also defined as the ratio of the radiation intensity (RI) of the antenna in a given direction and the RI of an isotropic radiator fed by the same amount of power:

Bandwidth and Range of Operation
The bandwidth refers to the span of frequencies within which an antenna can function optimally. The effectiveness of an antenna tends to diminish as the frequency moves away, from its frequency in real-world scenarios.
Separate bandwidths may be introduced: impedance bandwidth, pattern bandwidth, etc.

Polarization of Antenna Waves (Angle)
The antennas polarization refers to how the electric field's positioned around it. It can either be linear, with the electric field moving in a single plane (either horizontally or vertically), or circular or elliptical, with the electric field rotating.
It is important to have receiving and transmitting antennas with matched polarization, or some of the power of the signal will be lost due to the polarization mismatch. This is known as the polarization loss factor (PLF), which can be described with the equation:

Radiation Pattern and its Representation
An antenna's radiation pattern serves as a depiction of how it emits radiation, illustrating the distribution of power in various directions from the antenna's location.
VSWR and Impedance Matching (Typ.)
The Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (known as VSWR) quantifies the efficiency of power conversion into radiation by showing the level of impedance harmony between the antenna and the transmission line.
Any imperfection in the antenna design or antenna port/feed that results in an impedance mismatch leads to a degraded VSWR where some of the RF energy is reflected from the antenna port and the transmitter/receiver ports.

Advanced Antenna Characteristics
You can adjust these settings to customize antenna selection according to your performance requirements.
Front-to-Back Ratio in Directional Antennas
The front-to-back ratio (referred to as the F/B ratio) measures the strength of the signal emitted in the intended direction (front) and compares it with the signal emitted in the opposite direction (back). This comparison is usually quantified in decibels (dB), providing insight into the extent of radiation that an antenna produces and aiding in assessing its performance relative to interference from behind—particularly critical in scenarios like point-to-point communication setups.
Half Power Beam Width (HPBW) and Antenna Coverage
The Half-Power Beam Width (HPBW) refers to the angle encompassing the half-power points of the lobe. Basically where the power is 3dB lower than the peak gain level at two distinct points. The HPBW serves as a measure of how broad the antenna beam offers insight, into its coverage area.
Antenna Efficiency and Total Performance
The efficiency of an antenna is determined by comparing the power emitted by the antenna with the power provided at its input point. Considers all losses leading up to the antenna's opening. This encompasses losses from reflections caused by mismatches in transmission lines, as well as losses from conductors and dielectrics.

RFecho: Your Reliable Antenna Partner
RFecho is known for its ability to address a range of requirements in various sectors, such as telecommunications and research fields.
RFecho's Expertise in Antenna Design and Manufacturing
RFecho is dedicated to creating and crafting premium antennas that cover a range of frequencies from low to THz frequencies. They provide a variety of products such as gain horns and reflector antennas along with more specialized options for specific uses.
High-Performance Antenna Solutions from RFecho
RFechos antenna solutions find applications in fields such as remote control operations, telemetry systems, electronic countermeasures, and data communication processes. To illustrate, their cavity-backed spiral antennas are well suited for tasks like satellite communication and GPS tracking systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, grasping essential antenna characteristics such as gain, directionality and effectiveness aids in enhancing antenna efficiency for uses guaranteeing dependable communication and signal strength.
References:
[1]AgileAdmin. 2024. What Are the Fundamental Parameters of Antennas? https://www.seimw.com/blog/what-are-the-fundamental-parameters-of-antennas/
[2]Steven Petten. 2021. Basic Antenna Parameters. https://aemantennas.com/antenna-terms/
[3] Antenna-Experts. 2023. Different Types of Antennas & Characteristics of Antenna. https://antennaexperts.co/blog/different-types-of-antennas-characteristics-of-antenna
[4]2023. LECTURE 4: Fundamental Antenna Parameters. https://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/faculty/nikolova/antenna_dload/current_lectures/L04_Param.pdf
[5]A.H. Systems, inc. Practical Overview of Antenna Parameters. https://www.ahsystems.com/articles/Practical-overview-of-antenna-parameters.php
Title: What are the main characteristic parameters of the antenna?
Meta Description: Discover key antenna parameters, including gain, directivity, bandwidth, polarization, and efficiency, to optimize performance in communication and research applications.
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] the availability of the rtl-sdr device for less than $20 brings software defined radio (SDR) to the home and work desktops of EE students, professional engineers and the maker community. The rtl-sdr can be used to acquire and Sample RF (radio frequency) signals transmitted in the frequency range 25Mhz to 1.75Ghz, and the MATLAB and Simulink environment can be used to develop receivers using first principles DSP (digital signal processing) algorithms. Signals that the rtl-sdr hardware can receive include: FM radio, uhf band signals, ISM signals, GSM, 3G and LTE mobile radio, GPS and satellite signals, and any that the reader can (legally) transmit of course! In this book we introduce readers to SDR methods by reviewing and analysing downconverted RF signals in the time and frequency domains, and then provide extensive DSP enabled SDR design exercises which the reader can learn from. The hands-on SDR design examples begin with simple am and FM receivers, and move on to the more challenging aspects of Phy layer DSP, where receive filter chains, real-time channelisers, and Advanced concepts such as carrier synchronisers, digital PLL designs and QPSK timing and Phase synchronisers are implemented. In the book we will also show how the rtl-sdr can be used with SDR transmitters to develop complete communication systems, capable of transmitting payloads such as simple text strings, images and audio across the lab desktop. . Publisher : Zaccheus Entertainment (1 January 2015) Language : English Paperback : 670 pages ISBN-10 : 0992978718 ISBN-13 : 978-0992978716 Item Weight : 1 kg 50 g Dimensions : 21.59 x 3.43 x 27.94 cm Country of Origin : United Kingdom [ad_2]
0 notes