#prophet muhammad death
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Bible > Quran
youtube
Besides all the verses which contradict the Bible and teachings which sound not of God. There’s always something which sticks out with Islam. They say Christ didn’t get crucified, rather it was Judas Iscariot who took his place. How did the people get confide you wonder? Because God supposedly made an illusion to make it seem that Christ died. Where am I getting at? If Christ truly wasn’t God, and the supposed crucifying of him was merely an illusion? Why would God do this and knowingly allow many people to believe such a lie (Christ being God), which according to Islam, that Christ is not God. He makes an illusion, which by his hands makes people deceived. I ask you this, is God a deceiver? (Well according to the Quran he is). Would he ever make such a mistake like that which would last till today? The belief that Christ is God?
Mind you, Christ is indeed God, that is not even a question. However, this is a plot hole, if you will, which breaks Islam entirely. You want people to believe, and by doing so you make an action which causes people to believe something else which is not you? Is that even possible? Especially to our Lord? No, which is why the Quran will now and always be false.
“Who is a liar but he that denieth that Jesus is the Christ? He is antichrist, that denieth the Father and the Son. Whosoever denieth the Son, the same hath not the Father: (but) he that acknowledgeth the Son hath the Father also.” 1 John 2:22-23
#youtube#jesus christ#god#truth#bible verse#wisdom#christians#church#faith#body of christ#Quran false#without lies islam dies#islam is a death cult#the way the truth the life#king of kings#lord of lords#alpha and omega#yeshua messiah#One true lord Jesus Christ#Muhammad is a false prophet#1 John 2:22-23
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Premium Times
Published: Apr 11, 2025
The court declared Section 382(b) of the Kano State Sharia Penal Code Law (2000), which imposes the death penalty for insulting the Prophet Muhammad, as "excessive and disproportionate" in a democratic society.
The ECOWAS Court of Justice has ruled that the blasphemy laws in Nigeria violate freedom of expression protections guaranteed under regional and international human rights instruments.
A press release from the court on Friday said the court, in a landmark judgement delivered on 9 April (Wednesday), ruled that the existence of such laws is against Nigeria’s international human rights commitments.
Ruling on a case filed by a civil society organisation, the Expression Now Human Rights Initiative, specifically challenging Kano State’s version of the law, the court declared that section 210 of the state’s Penal Code and section 382(b) of its Sharia Penal Code Law (2000) criminalising blasphemy are incompatible with Nigeria’s obligations to protect freedom of expression.
The court’s three-member bench led by Rcardo Cláudio Monteiro Gonçalves struck down the two legal provisions in the Kano State laws, and ordered the Federal Republic of Nigeria to repeal or amend the identified legal provisions and similar laws in Nigeria to align with Article 9(2) of the African Charter.
The Nigeria’s federal government, sued as the sole defendant in the suit, does not have a role in the lawmaking process in states under Nigeria’s federal system, but can only push for necessary legal reforms at that level of government through political solutions.
The two other members of the panel of judges are Sengu Mohamed Koroma (member) and Dupe Atoki, the judge rapporteur, who delivered the court’s unanimous decision.
Blasphemy laws in Nigeria
The judgement highlights concerns over the violation of human rights in blasphemy cases in Nigeria, referencing international conventions and the Nigerian constitution, which guarantees freedom of religion and expression.
Blasphemy laws are deeply entrenched religious issues with social and political contexts in many of the states of the conservative northern Nigeria.
The laws are in force in at least 12 of the 19 northern states.
In Kano, like other states, the law criminalises words or expression, written or verbal, by means of gesture, which show or demonstrate any form of contempt or abuse against the Holy Qur’an or any Prophet shall.
Critics have said the laws pose a significant risk to religious freedom for Nigerians and those who express unpopular or dissenting beliefs, worldviews, or religious interpretations in the states where the laws are in place.
On many occasions, some people have been mobbed to death under vigilante justice for making blasphemous comments.
In 2022, Deborah Samuel, a student of Shehu Shagari College of Education, Sokoto State, was roasted alive by her fellow students on campus for making comments purported to be blasphemous in a class WhatsApp platform.
Others have been sentenced to death or are facing trials on blasphemy charges.
Yahaya Sharif-Aminu, a singer in his 20s, was sentenced to death by hanging by an Upper Sharia Court in Kano State in August 2020 for allegedly making derogatory remarks about Prophet Muhammad in a song.
But on appeal instituted by the convict, the Kano State High Court in January 2021 quashed his conviction and sentence because his trial at the Sharia court was characterised by procedural irregularities. On that basis, the court ordered his retrial.
Similarly, in August 2022, the Court of Appeal in Kano upheld the decision of the Kano State High Court by quashing Mr Sharif-Aminu’s conviction and ordering his retrial.
The case is currently pending before Nigeria’s Supreme Court, with Mr Sharif-Aminu still in detention under reportedly deteriorating health conditions.
Proponents of the blasphemy laws have argued that they prevent actions or speech that could incite religious tensions or violence and safeguard the dignity and sanctity of religious beliefs, ensuring that followers of various faiths feel respected and protected, thereby maintaining peace in a multi-religious society like Nigeria.
Although blasphemy laws are not enforced nationwide but only in specific states that have enacted them, Nigerian courts have on different occasions affirmed that these laws are consistent with the Nigerian constitution.
The Court of Appeal and the Supreme Court have validated the conviction of some blasphemy convicts on the legal basis that making of law for the maintenance of law and order is the joint responsibility of both the National and the State Houses of Assembly.
Recently, the Kano Division of the Court of Appeal affirmed the conviction of Abdulazeed Dauda by the Shariah Court, Rijiyar Lemo, Kano, for use of blasphemous words against Prophet Muhammad and inciting an uprising and arson.
However, the arguments in favour of blasphemy laws are often countered by concerns about freedom of expression guaranteed by the Nigerian constitution and international conventions and the potential misuse of such laws.
In February, the European Parliament passed a resolution calling on Nigerian authorities to immediately release Yahaya Sharif-Aminu, a musician sentenced to death for blasphemy in Kano State.
EU Parliament also demanded that the government repeal blasphemy laws that contradict the country’s constitutional and international human rights obligations.
Lead-up to ECOWAS Court judgement
The incorporated trustees of Expression Now Human Rights Initiative, a civil society group, filed its public interest case challenging blasphemy laws that have led to serious human rights concerns in Nigeria.
The organisation documented cases where individuals faced arbitrary arrest, detention, and death sentences merely for alleged blasphemous expression.
The application also highlighted incidents of vigilante justice, where accused persons were killed by mobs with apparent impunity.
The organisation contended that Nigeria failed in its obligation to protect citizens’ fundamental rights to life, religious freedom, and freedom of expression by maintaining these laws and failing to prevent related violence.
Why ECOWAS Court strikes down Kano blasphemy laws
Deciding on the case on merit, the ECOWAS Court struck down two key blasphemy provisions in Kano State law as violations of international human rights standards.
The Court specifically identified Section 210 of the Kano State Penal Code as vague, failing to provide clear guidance on what constitutes religious insult and therefore lacking the legal precision required under international human rights standards.
The Court further declared Section 382(b) of the Kano State Sharia Penal Code Law (2000), which imposes the death penalty for insulting the Prophet Muhammad, as “excessive and disproportionate” in a democratic society.
Though recognising states’ legitimate interest in maintaining public order and respecting religious beliefs, the court determined that these laws fail the established human rights tests of legality, necessity, and proportionality under both Article 9(2) of the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights and Article 19 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR).
Regarding allegations of state failure to prevent blasphemy-related mob violence, the court found insufficient evidence to support these claims, noting that media reports without additional corroboration did not meet the required standard of proof.
Earlier in its ruling on the preliminary objection against the suit by the Nigerian government, the ECOWAS Court confirmed its jurisdiction to hear the case under its established mandate in Article 9(4) of its Protocol to address human rights violations within member states.
While accepting jurisdiction, the court narrowed the scope of the challenge, permitting only the freedom of expression claims to proceed.
Claims regarding rights to life and religious freedom were deemed inadmissible as private rights that cannot be pursued through public interest litigation.
#Economic Community of West African States#Nigeria#ECOWAS#islam#blasphemy#blasphemy laws#religious freedom#Deborah Samuel#death sentence#islamic violence#prophet muhammad#muhammad#freedom of religion#human rights#religion#freedom of expression#religion of violence#religion is a mental illness
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
يَـٰعِبَادِىَ ٱلَّذِينَ ءَامَنُوٓا۟ إِنَّ أَرْضِى وَٰسِعَةٌۭ فَإِيَّـٰىَ فَٱعْبُدُونِ ٥٦ كُلُّ نَفْسٍۢ ذَآئِقَةُ ٱلْمَوْتِ ۖ ثُمَّ إِلَيْنَا تُرْجَعُونَ ٥٧
O My believing servants! My earth is truly spacious, so worship Me ˹alone˺. Every soul will taste death, then to Us you will ˹all˺ be returned.
[Quran 29:56-57]
Recitation: Abdur Rahman mossad
#muslim#quran#allah#hadith#prophet#dua#prophet muhammad#islam#hadees#islamicpost#death note#tw death
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
why do sunnis hate shi'as that much what the fuck is their problem?
Hatred towards Shi'a Muslims is not only a concurrent issue, it's a 1400 year old issue that started as a result of the political unrest that took place following the Prophet Muhammad's (pbuh&hf) death. It laid the foundation for the political schism of Islam. Initially, the Shi'as (or Alids) were just a group of partisans that would only develop their own theology a hundred years later. And then you had those who supported Abu Bakr rise to the caliphate. For Shi'as, we believe Abu Bakr usurped the caliphate due to various incidents, and thus, we rejected his ascent to power. These were the partisans of Ali (a). When Ali (a) eventually became the caliph, he was met with a lot of hardship and opposition by people who either hated him or sought political power. During the caliphate of Uthman, the Umayyads were given unrestrained power, and it was not until Ali (a) became the caliph that he removed them from power for their greed and nepotism. However, Muawiyah, a "companion" of the Prophet, who was intially opposed to him before his clan lost in the final battle of Mecca, was in control of Sham (Syria) and refused to go down, hence a renewed civil strife within the Islamic world. The Umayyads were vicious people who were renown for their corruption and hedonism, and their caliphate was founded on the blood of Imam Hussain (a), the son of Imam Ali (a). For Sunnis, these events aren't particularly important, and Islamic history is often neglected, promoting the idea that whatever happened in the past has no religious or theological significance to Islam as a religion. This is where we disagree because, as Shi'as, we simply can't accept certain religious doctrines on the basis of these people being unreliable. For example, Ayesha, having been the wife of the Prophet, is one thing, but she still waged an unjust war against Ali (a). There is no way we can accept her narrations because she's simply untrustworthy.
Because of the power that the Umayyads managed to consolidate for themselves, superseeding the Rashidun caliphate, there was a state-sponsored campaign with the purpose of supressing any Shi'i resistance against the rule, the Shi'as were among these groups and suffered severe persecution to such extent that even members of the Prophet's family were brutally oppressed. For Shi'as, the Prophet's family are a source of emulation and knowledge, and we have to adhere to their understanding of Islamic theology, this is why Islamic history is important, so we can highlight the root behind the resistance. However, dwindling in power and numbers, the Shi'as ultimately committed themselves to Taqiyyah (concealing one's religion) to ensure their survival. This is how we managed to survive for 1400 years. For Sunnis, the Umayyads and subsequent caliphs are a source of great pride, hence why Syria is considered an important heritage site for Sunnis who regard the Umayyads with great respect.
With that said, the reason there's so much sectarian animosity towards Shi'as is because with history in mind, our tradition of reviling these companions is considered an act of disbelief. Sunnis often retort that these companions are noble people and could not possibly be reviled because they had been in the companionship with the prophet, holding that despite the wars and atrocities committed by these people, we should respect them nevertheless. Either way, Shi'a Muslims have a doctrine called Tabarrah (dissociation), which is extended to those people who have caused harm towards the Prophet and his family. This includes "cursing" them, which is considered one of the most offensive acts and a reason why Sunnis get up in arms when we criticize the companions, especially the first caliph Abu Bakr and the second caliph Umar. Furthermore, our emphasis on the doctrine of intercession has caused much controversy because stricter muslims, such as Salafists consider these acts tantamous to idolatry, hence why it's easier for Shi'as to be considered heretics. The fact that we have shrines is considered blasphemous and there are many instances in which these shrines have been attacked. Shi'as are so reviled that for some Sunnis and Salafists, the difference between a Christian and a Shi'a is that Christians have rights as pertained to their status as "People of the Book", while Shi'as are considered heretics, and ultimately disbelievers. For such a reason, we do not have any rights; our blood becomes lawful to them.
In short, HTS, AS, ISIS, Al-Qaeda and all their Salafist sympathisers believe that the blood of a Shi'a is lawful because we are heretics. We are simply putting up a resistance against them. Shi'ism is not just a branch of Islam. It's one of the oldest resistance movements in the world.
519 notes
·
View notes
Text

hunting Jews: the truth about Hamas
SEPTEMBER 15, 2024
Islam is a religion.
Islamism is a political ideology.
Recently rescued Israeli hostage, Qaid Farhan Alkadi, an Israeli Bedouin Muslim, gave the following testimony:
Farhan’s testimony, along with a plethora of other evidence, only makes what we’ve been saying all along abundantly clear: Hamas is not a “resistance” group against oppression. Hamas is a genocidal antisemitic terrorist group that targets Jews.

ISLAMISM IS AN INHERENTLY ANTISEMITIC IDEOLOGY
Hamas is an Islamist terrorist group. What does this mean?
Islamists believe that the doctrines of Islam should be congruent with those of the state. Islamists work to implement nation-states governed under Islamic Law (Sharia), emphasize pan-Islamic unity (in most cases, hoping for an eventual worldwide Islamic Caliphate, or empire), support the creation of Islamic theocracies, and reject all non-Muslim influences. For this reason, Islamists tend to portray themselves as “anti-imperialist,” while in truth they are striving to swap western imperialism with Islamic imperialism.
Islamist ideology can be traced back to Hassan al-Banna and the Muslim Brotherhood, founded in 1928. Al-Banna viewed the 1924 dissolution of the last Islamic Caliphate, the Ottoman Empire, and the European colonization of the Middle East, beginning with France’s 1830 occupation of Algeria, as an affront to Islam. The early 20th century was a period of rapid secularization in the Middle East, when Arab nationalism threatened to replace pan-Islamic identity with a pan-Arab identity. Al-Banna opposed all of this, hoping to return to “authentic” Islamic practice through the (re)establishment of the Islamic Caliphate.
Islamism is an antisemitic ideology. Islamists hate Jews -- and by extension, the Jewish state -- because of the Prophet Muhammad’s conflict with the Jewish tribes of the Arabian Peninsula in the 7th century. Islamistsbelieve that the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is rooted in a struggle between Muslims and their “eternal enemies,” the Jews.
Hassan Al-Banna, the founder of the Muslim Brotherhood, viewed the dissolution of the last Islamic Caliphate (empire) and the secularization of the Muslim world as an affront to Islam.
ISLAMISM, DHIMMITUDE, AND THE JEWS
Islamists seek to revive “authentic Islamic practice,” by which they mean, essentially, that they wish to go back in time. This desire to turn back the clock puts them in conflict with Jews for two reasons:
During his earliest conquests, the Prophet Muhammad and his army came into fierce conflict with a number of Jewish tribes that had settled in Arabia, some of which had refused to convert to Islam and even accused Muhammad and his followers of appropriating figures from the Torah. For Islamists, this initial conflict between Jews and the earliest Muslims is “proof” that Jews are “eternal enemies” of Islam.
Following Muhammad’s death in 632, the Arab Islamic empires conquered lands exponentially quickly. As a result of this rapid colonization, the Muslim authorities were faced with the “problem” of how to handle the conquered Indigenous peoples that resisted conversion to Islam. This “problem” was solved with a treaty known as the Pact of Umar. This so-called treaty allowed select religious and cultural minorities, known as dhimmis, or “People of the Book,” to practice their beliefs so long as they paid the “jizya” tax and abided by a set of restrictive, second-class citizenship laws.
Under Islamist regimes, such as the Islamic Republic of Iran, Jews are, to this day, still treated as dhimmis.
THE GENOCIDAL ANTISEMITISM OF THE MUSLIM BROTHERHOOD
Hamas emerged as the Palestinian branch of the Muslim Brotherhood. Hassan al-Banna, the founder of the Muslim Brotherhood, worshipped Adolf Hitler.
Like Hitler, al-Banna sought to exterminate all Jews…in his case, from the Middle East.
According to German documents from the period, in the 1940s, the Nazis trained some 700 members of the Muslim Brotherhood. Nazi Germany heavily funded the Brotherhood, which contributed to its massive growth. In 1938, the Brotherhood had some 800 members. By the end of World War II, it had grown to a million members.
In 1939, Germany “transferred to al-Banna some E£1000 per month, a substantial sum at the time. In comparison, the Muslim Brotherhood fundraising for the cause of Palestine yielded E£500 for that entire year.”
Naturally, Nazism deeply influenced the Muslim Brotherhood’s ideology.
The father of Palestinian nationalism, Haj Amin al-Husseini, was a prominent member of the Muslim Brotherhood. Yasser Arafat, the most influential Palestinian leader of all time, began his “career” fighting for the Muslim Brotherhood. Which brings us to Hamas. Hamas’s founder, Sheikh Ahmed Ismail Hassan Yassin, was a member of the Muslim Brotherhood and was responsible for establishing the Brotherhood’s Palestinian branch. In 1987, he founded Hamas.
The Muslim Brotherhood’s hatred for Jews goes far beyond its original Nazi affiliations. During the 1936-1939 Arab Revolt in Mandatory Palestine, during which Palestinian Arabs revolted against Jewish immigration and carried out a number of antisemitic massacres, the Muslim Brotherhood began disseminating antisemitic rhetoric, often targeting the Egyptian Jewish community.
Al-Nadhir, the Muslim Brotherhood’s magazine, published openly antisemitic articles, peddling conspiracy theories and demonizing the Egyptian Jewish community for its success in various industries. Notably, Al-Nadhir even called for the expulsion of Jews from Egypt, accusing Jews of “corrupting” Egypt and calling Jews a “societal cancer.” Al-Nadhir made boycott lists of Jewish businesses.
Unfortunately, the Muslim Brotherhood’s antisemitism is not a relic of the past. Mohammed Badie, the Muslim Brotherhood’s present day “Supreme Guide,” believes Jews “spread corruption on earth” and calls for “holy jihad” as an antidote.



THE ORIGINAL HAMAS CHARTER: EXPLICITLY GENOCIDAL
Hamas’s founding 1988 charter is explicitly antisemitic and genocidal. Below are some excerpts:
“Our struggle against the Jews is very great and very serious.” -- Introduction
“The Day of Judgement will not come about until Moslems fight the Jews (killing the Jews), when the Jew will hide behind stones and trees. The stones and trees will say O Moslems, O Abdulla, there is a Jew behind me, come and kill him. Only the Gharkad tree, (evidently a certain kind of tree) would not do that because it is one of the trees of the Jews." -- Article 7
“In face of the Jews' usurpation of Palestine, it is compulsory that the banner of Jihad be raised.” -- Aritcle 15
“With their money, they took control of the world media, news agencies, the press, publishing houses, broadcasting stations, and others. With their money they stirred revolutions in various parts of the world with the purpose of achieving their interests and reaping the fruit therein. They were behind the French Revolution, the Communist revolution and most of the revolutions we heard and hear about, here and there. With their money they formed secret societies, such as Freemasons, Rotary Clubs, the Lions and others in different parts of the world for the purpose of sabotaging societies and achieving Zionist interests. With their money they were able to control imperialistic countries and instigate them to colonize many countries in order to enable them to exploit their resources and spread corruption there.” -- Article 22
“Israel, Judaism and Jews challenge Islam and the Moslem people.” -- Article 28
BUT...HAMAS CHANGED THEIR CHARTER!
Some Hamas apologists will tell you that Hamas no longer intends to exterminate all Jews, because in 2017, they “replaced their [openly genocidal] charter.” Well, lucky for you, Hamas is here to set the record straight. See, after releasing their “new” charter, Hamas co-founder Mahmoud al-Zahar assured the media that the 2017 document did not replace their original 1988 charter.
The 2017 document was thus not a “new” charter from a “reformed” Hamas, but rather, a propaganda document aimed at redeeming Hamas’s image to the west.
Since 2017, Hamas has made openly genocidal calls toward Jews. For example:
In 2018, Hamas’s Al-Aqsa TV media channel predicted “the cleansing of Palestine of the filth of the Jews.”
In 2019, Hamas Political Bureau member Fathi Hammad said, “You seven million Palestinians abroad, enough warming up! There are Jews everywhere! We must attack every Jew on planet Earth –- we must slaughter and kill them, with Allah’s help.” In 2021, Hammad called, via Al-Aqsa TV, for the Palestinians in Jerusalem to “cut off the heads of the Jews.”
In May of 2021, the leader of Hamas, Yahya Sinwar, led a rally in which the crowd was encouraged to chant, "We will trample on the heads of the Jews in front of everyone..."
ISLAMIST INFLUENCE ON PALESTINIAN NATIONALISM
The earliest Arab nationalists in Palestine were not necessarily Islamists. Falastin, an influential anti-Zionist, Arab nationalist newspaper, was founded by two Palestinian Christians in 1911. Khalil Beidas, who was the first Arab to identify as Palestinian, in 1898, was a Christian. Nevertheless, the Palestinian nationalist movement soon fell under the influence of the Muslim Brotherhood.
Initially, Palestinian Arab nationalists advocated for a unified Arab state in Greater Syria. In 1920, Haj Amin al-Husseini began advocating for an independent Palestinian Arab state. To draw people to his cause, which was not yet well-known to the average population, he began emphasizing the importance of Palestine to Islam, and particularly the importance of Jerusalem and Al-Aqsa Mosque. Soon, he began disseminating the libel that the Jews intended to destroy Al-Aqsa Mosque. This libel has cost thousands of Jewish lives and is spread widely to this day.
Early on, the Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt adopted the Palestinian cause. After World War II, Haj Amin al-Husseini, who had spent the war working as a propagandist for the Nazis in Berlin, escaped to Egypt with the help of the Muslim Brotherhood.
The Muslim Brotherhood fought against the State of Israel in 1948, along with other Islamist militias, such as the Army of the Holy War. Among its fighters were Yasser Arafat. In the 1960s, Arafat came under the influence of the Soviet Union and shifted his image to that of a communist counterrevolutionary, as opposed to an Islamist, though his rhetoric in Arabic continued emphasizing the importance of jihad and Al-Aqsa Mosque to the Palestinian movement. Nevertheless, after Islamic Revolution in Iran, after which the Islamic Republic adopted the Palestinian movement, and with the establishment of Hamas and groups such as Palestinian Islamic Jihad, Palestinian nationalism has once again been undergone an Islamization.
rootsmetals
as always: this post is not an endorsement of any given Israeli policy or politician. You can be highly critical of Israel’s handling of the situation without obfuscating or whitewashing the origins and goals of this ideology. It always, always came down to antisemitism. I won’t engage with straw man arguments in the comments 😗
MAIN SOURCES on Instagram
149 notes
·
View notes
Note
"I don't believe there's such a thing as Islamophobia" says the Islamophobic piece of shit.


Prophet Mohammed was a serial r*pist. He justified his actions by saying how his alter-ego Allah permitted him to do that. Then, hundreds of years later his dysgenic followers, called the Mohammedans, started whitewashing him and decapitating anyone who brought forward the truth.
See, anon, the more you come with such drivel to my inbox, the more I will expose this fella MoMo. :)
#asks#anon ask#anon#why do i get asks like this?#islam critique#islam is a death cult#prophet muhammad#piss be upon him
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
A striking account on the Russian Army from Saïd Ismagilov, Ukraine’s supreme mufti who has been fighting for Ukraine for the last three years.

“This society is a swarm of locusts. Their purpose is to push forward no matter what, seizing new territories. Every day in Vovchansk, they advance in small groups of 3-5, climbing over the corpses of those who, hours earlier, stormed the same position. No sense, no reason, no success — just piling bodies against us.
This differs from Soviet Marshal Zhukov’s meat grinder assaults only in that they now attack in smaller groups, not to capture kilometers, but to take a single position of a few square meters. Day after day, methodically—wave after wave, if lose ground, they fall back, if anyone’s left to fall back.
But with some insane persistence. The individual dissolves, becoming part of the swarm, where the death of a few doesn’t even register. I can’t explain why they keep coming, even knowing we’ll kill them.
My philosophical education stops me from seeing this routine through a mathematician’s eyes, simply noting: minus one, minus five, minus forty. My philosophical and theological training pushes my mind to make sense of why this conditional Homo erectus (“upright man,” because I can’t organically call them Homo sapiens, seeing no rationality in their actions) climbs over the corpses of their swarm to certain death, amid ruins resembling a Martian landscape. For what? What’s the motivation? What do they hope to gain?
When I spoke to 🇷🇺 PoWs, they all said they wanted money from Putin’s regime to improve their financial situation. Not one mentioned ideological motives, belief in higher values, or a lofty goal. Just loans, debts, mortgages, poverty, the need to raise kids.
You came to kill our children to raise yours? Silence. Eyes down. But that’s the reality. They’d calmly kill us and our children, take our homes, sleep in our beds, even wear our clothes. They don’t see it as repulsive or wrong. Their authorities gave them permission, so it’s fine. Without hesitation, they’d wear your dress and eat from your plate because their czar and church blessed it.
They come to take and devour our resources, to populate our land with themselves. While the swarm’s leaders try to explain why they attack & kill us, the lower ranks just want to enrich themselves by murdering & looting.
The Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him!) gave an interesting take on human stupidity and greed: “The Day of Judgment won’t come until the Euphrates parts, revealing a mountain of gold. People will fight over it, and out of every hundred, ninety-nine will die. Yet each will think: Maybe I’ll be the one to survive!”
Watching them, I wonder if each one charges into the assault thinking they’ll be the one to survive and get rich. But then our guys hit them, and the stats report: another five down, dead.”
#ukraine#russia is a terrorist state#russian invasion of ukraine#україна#укртумбочка#укртумба#укртамблер#war crimes#russia#russian culture#genocide#war crime
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Rant of Truth
The reason Islamists, Atheists, and Progressives try so hard to disparage, defame, change, and mock Christ (and Christianity) is because He is the Truth.
The onslaught against Christ, and the Kingdom and Love of God, is not because it's random, nor that it's overly theologically "complex", nor that the Bible and Christianity is "pious", "contradictory", and "inaccurate", but because there's always been an onslaught against Truth, specifically Truth that goes against what is commonly desired, praised, and normalized.
Truth is not subjective, but rather objective, and truth is not proven by how many people follow it, or how many people claim it, but Truth is proven by what it produces.
Islam, atheism, and progressivism, have all attempted, decade after decade, failed theologians after false prophets, to convince others that the "truth" of Christ is not based in God, it is not based on historical accounts and evidence, nor in genealogy, but their "truth" is "evidenced" by man-made suffering, man-made religion, and man-paid wickedness. Yes, man is inherently flawed, and weak, and prideful, and sinful, these are true because none of us can say we are wholeheartedly good without mentioning we have committed a lie, a gossip, a vulgar word, opinion, action, or thought. Satan is real, and uses his legion of demons and spirits to take advantage of our God-image to defile, degrade, and kill us because we are spiritually and eternally valuable, power-filled, and loved.
Islam denies the divinity of Christ and the Trinity, yet it is not the prophet Muhammad who comes back to judge the world, it is Christ. If Christ is not the Son of God, how was He was born of a virgin; if He is not God humbled in the state of flesh, why is there no account that He committed sin in the flesh, like man does. If He is not the Word, and the Word who became flesh, and was Crucified and pierced for our transgressions, why are there so many eye-witnesses accounts of the Crucifixion - not just Christians, but non-christians (Romans and Samaritans) - and there's preserved texts and archaeological remains that prove these accounts and Christ's crucifixion: all from written, and oral traditions. If Christ did not die for our sins, and resurrect, why is He returning for Judgement in the final days? Would it not have been better to judge man at the time the prophet Muhammed stated? Would Allah not have shown judgement in famine, war, and death, and prepared way for the Judgement of Jesus Christ like He did with the other prophets when they spoke? Why would Allah not want to reveal the immediate Judgment that his prophet Muhammad calls to happen? Why rely on Jesus Christ, who is not divine in any Islamic way, to come judge the world, when Muhammed is clearly the prophet worth worshipping and venerating? If Jesus is just as mortal as Muhammed, why is it not Muhammed coming back?
Atheism denies the existence of an omnipotent, good Christian God, not because that God has done anything evil or wicked or unfair against man, but because man commits evil, and wickedness, and unfairness against one another, and therefore it is not man's fault for his failures, and wickedness, and actions, but the Christian God's. Atheism blames the Christian God for all that is wrong in the world, yet they believe all the other gods of this world are fair-game to believe in and praise and in no way blame for temptation, death, evil, slaughter, rape, molestation, starvation... Those gods who have been praised historically and traditionally for using humans as sacrifices, used humans for sex and humiliation and entertainment, gods who rely on the elements of man's body and creativity, to receive power and glory and authority and need a statue made of wood, silver, or gold to behold their existence as god; they are in no way partially responsible for the destruction, harm, and misguidance of man. Man does all the wrong, and little of good, but none of the good and all of the wrong is God's fault. So if we are not born good, yet we are taught to do good, be good, and reinforced the idea that we should treat others with goodness, why do we do more wrong than good, and if the good is not of ourselves or our worldly influences, where does goodness come from? If goodness comes from within, but we are born without it, how is that so? And why can we dictate what is goodness and what is wrong? Surely there isn't a divine, preconceived nature that influences and distinguishes the difference? We create so much media and art about good versus evil, and if we believe in an ultimate evil, why can't we believe in an ultimate good that is void of ever committing evil?
Progressivism, is not about leading the nation forward toward acceptance and love and peace, because if we truly were to follow radical acceptance, why would we deny the scriptures, from the same book of scriptures we use in gay churches, that speaks about fornication, homosexuality, prostitution, lying, murdering, blaspheming, cowardliness, and pride, being sins and we should repent from them, and not accept what is evil, but overcome evil with good? If we were really to follow radical love, would we not want to love one another regardless of sex, religion, race, disability, stag of human life, and social status, and be good in respecting differences and treat everyone as an equal by allowing fair criticism and redirected guidance for each other's health, and safe and fair living? If we were really to follow radical peace, would we not want to see eye-to-eye and allow for disagreements, change of introspection and boundaries, and care for all human life, and be able to forgive in due time without holding onto past shame, rejection, hypocrisy or spite? Would we not want to set boundaries on what we read, watch, listen to, teach, tolerate, and wear as a society, so we may uplift one another to have peaceable communities, well-developed children and adults, stable self-image, and mental wellness?
Jesus Christ lived out and taught us these laws that exalted these kinds of fulfillments of love, faith, hope, purity, justice, sanctity of human life, and forgiveness, from God. But those laws are wrong to progressives, not because the law is faulty and problematic, no, it is because the law goes against their feelings. Because feelings are not facts, but facts are truth, because they have been consistently proven to be true without distortion or compromise.
Many man-made beliefs desire to triumph over God, and deny Christ, because they believe if they deny Him long enough, He will go away and cease to exist. But God the Father, Jesus Christ, and the Holy Spirit, are not flawed, intellectually limited, physically depraved, sinful, human beings - they are One, they are Holy, they are Everlasting, and every denial and blasphemy and mockery of this nature of Goodness, Mercy, and Grace, is leading to the opposite nature of wickedness, unforgiving wrath, and death.
So Islam, Atheism, and Progressivism can continue to lie through their teeth, distort scripture, cherry-pick morals, deny Christ, and persecute Christians, because there is grace for them to turn away from such... Yet no matter how hard, and how many times you exact war, change ideologies, create pseudo-sciences, code-switch, and equivocate, and preach death against Truth-sayers: Truth will not be erased, Truth will not be fear-mongered, and Truth will not die, and Truth will win in The End. It is only your choice to accept the Truth and live in opposition of it, or live in accordance to it. Truth will not change because you demand it to, Truth demands you change because your human nature will always be in opposition to it; unless you surrender by your subjective choice to the infallible objectivity of Truth's nature. That is what Christ proved. That is what Christ lived by. That is what Christ fulfilled in the good, perfect, objective law of God. None of these theologians, false prophets, fake pastors, and deniers can change, erase, and convolute enough false religions and proclamations to counteract the power and authority of Christ in Heaven, on Earth, and over Hell.
Jesus Christ is The Way, The Truth, and The Life. No amount of heresies, conspiracies, and cults made against Him, will succeed, because all these things have been conquered once, and they will be conquered again, by Jesus Christ, who is of the Father, and aided by the Holy Spirit.
Amen. Amen. Amen.
#christianity#christian#christian faith#christian bible#christian blog#christian girl#faith in jesus#jesus christ#I only came back to make this post#bye <3
44 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why is it so hard to get into Al Jannah?
Hard!!
The Prophet Mohammad ﷺ said, 'Whoever prays the two cool prayers will enter Paradise.'" Fajr (dawn) and Asr (afternoon) prayers
He ﷺ also said, "Whoever asks Allah for Paradise three times, Paradise(Al-Jannah) will say, 'Ya Allah, admit him into Paradise.' And whoever seeks protection from Hellfire three times, Hellfire will say, 'Ya Allah, protect him from Hellfire.'"
And He ﷺ said: "There is none of you who performs ablution (wudu) and does it well, then says: 'I bear witness that there is no god but Allah, alone with no partner, and I bear witness that Muhammad is His servant and Messenger,' except that the eight gates of Paradise are opened for him, and he may enter through whichever one he wishes."
And He ﷺ also said "Whoever’s last words are 'There is no god but Allah' will enter Paradise."
And He ﷺ said "Whoever recites Ayat al-Kursi after every obligatory prayer will have nothing standing between him and entering Paradise except death."
And He ﷺ also said "Allah has ninety-nine names.Whoever enumerates them (knows and acts upon them) will enter Paradise."
#jannah#islamic#islam#islamdaily#islampost#ummah#reminder#deenoverdunya#duaa#art#hadith#haqq#dawah#daily duaa#allah#muslim#reading#religion#صلى الله على سيدنا محمدﷺ❤#صلوا على النبي محمدﷺ#prophet#prophet mohammed#تمبلريات#photography#qoutes#quran kareem#quraan#quotes#quran#ask
108 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, do you have any tips on how to be comfortable being a Muslim while being queer?
I've been trying to do that for a very long time, focusing on my faith in Allah, but it's a bit hard and I always get demotivated randomly :(
Hey! Salam! Sorry for the kind of late response, moving houses has been hectic. This will be a long response (sorry), so I will put it under the cut.
I want to preface this by saying every queer person is different. I don't know the specifics of your identity so I am going to cover both sexual queerness and gender queerness.
My biggest obstacle in nurturing my relationship with Allah was believing that the way I am was haram, and even that I was cursed by Allah. I no longer believe this, but it was a long road.
Sexuality
I don't believe that homosexuality is haram. The common claim that the story of Lut is about homosexuality is full of holes and inconsistencies and it's largely based on the Christian religious tradition, even if the grammar of the Qur'an doesn't align with the Christian tradition (eg. the Qur'an uses the word "banaat" for Prophet Lut's (as) daughters. Bannat is plural, meaning 3 or more daughters, and in the traditional telling Lut (as) has 2 daughters).
Here is a really good study by Nahida Nisa:
I recommend reading all of Nahida's things because she's an amazing writer.
And a video from Dr. Shehnaz Haqaani's (PhD, Islamic Studies) podcast "What The Patriarchy":
youtube
and you can find her blog here
These articles from the blog, Lamp of Islam are also pretty good. He is a hardcore Qur'anist with some strange opinions, so peruse his blog with caution.
Letting go of the belief that the way I am was haram and that Allah had cursed me was the most critical part of fixing my iman and overall nurturing my relationship with Allah.
Also, it doesn't make any sense that The All-Merciful, Allah would make someone with an innate attraction to the same gender and then forbid them from "acting on it".
The Prophet (salla Allahu alayhi wa salam) never punished anyone for homosexuality, after his death, his companions debated whether or not to punish homosexuals and they could not come to a conclusion.
Gender
The Qur'an seems to acknowledge the differences between sex and gender. For example, the word for 'man' in the Qur'an is rijal and the word for 'male' is dhukran. And the word for 'woman' is nisa, but the word for 'female' is untsa. You can read Lamp of Islam's article on the meanings of these words here.
There also may be a vague reference to intersex and/or gender non-conforming people in verse 42:50.
There are also some hadith that seem to imply that gender non-conforming people were accepted around Prophet Muhammad (salla Allahu alayhi wa salam). Prophet Muhammad's (Salla Allahu alayhi wa salam) wife Umm Salama (Radi Allahu anha) had a seemingly close friend who was then called a 'mukhanath', named Hit, who was described as a 'male who exhibited effeminate traits' was was welcome into the private women's section of the Prophet's (Salla Allahu alayhi wa salam) home. Today this person might have been a gay man (who displayed effeminate traits by accepting the "woman's role" (🙄) in relationships), or, more likely IMO, this person would be considered a trans woman today.
Hit was punished by the Prophet (salla Allahu alayhi wa salam), but not for their sexuality/gender expression, they were punished for describing a woman's body to a man, which was possible because they were allowed into both men's and women's spaces. The punishment of Hit is often used as 'evidence' to support homophobia and transphobia, but they neglect to mention the specific reason that Hit was punished.
You can read more about queerness in Islamic history here.
The link above takes you to Muslims For Progressive Values, they also offer marriage services for queer Muslims and interfaith couples, specifically for Muslim women seeking to marry non-Muslim men.
Here is a link to MPV's video series, but massive trigger warning for the comment section.
And a second MPV video series.
And another article from MPV.
More Tips
As I said, learning about LGBTQ Islamic History helped me a lot.
Keep your relationship with Allah between you and Him. Only share it with people who you 100% trust, because religion is extremely personal.
Find your people. Whether online or in-person, a community of people like you is important.
Know that Allah knows you, your identity, and the way you feel. Ultimately, Allah is your creator and we will only return to him. And we, as queer people KNOW that this is the way we were created. Nobody can tell you that who you are is false because they have no way to know that.
Block. Block. Block. Block. Block anyone who is being a problem, who might become a problem in the future. Block them all. Block Islamophobic queers, block queerphobic Muslims. Protect your peace and your relationship with Allah at all costs.
Here are people that I block quickly: anyone who has outwardly queerphobic or Islamophobic things posted on their page. Salafis and Wahabis. The black flag freaks: those with black flags in their user names/bios. I block people for the comments they leave all the time. Generally, I don't wait for them to do something, I block them on sight.
You mentioned that you struggle with low imaan sometimes. It's important to know that fluctuations of imaan are normal and completely natural. But I'm assuming since you've sent this ask, you always come back, which is what's important.
Here is another video from Dr. Shehnaz Haqaani's (PhD Islamic Studies) Podcast for Muslims who struggle to practice.
And a TikTok from @/soundous.boualam:
My biggest tip for building faith is to start slow.
Pray one prayer a day at first, and wait until that prayer is deeply ingrained into your habits, then add another. I recommend starting with Isha before bed. Don't try to do everything at once. You'll burn yourself out.
Build up the fard actions. Your prayers, primarily.
If you can take on more, add in the dhikr after prayer (subhanallah 33x, alhamdullilah 33x, and allahu akbar 34x). Or add dhikr in throughout your day. I use an app called Azkar that I set to send notifications to remind me to do various worship activities.
When I braid my hair I say alhamdullilah every time I cross a piece over another.
If you can, it might also help to put a poster or picture on your wall with your favorite Qur'an verse, hadith, or Islamic quote on your wall, or make your screensaver a reminder to remember Allah.
You can also buy or make a beaded tasbih bracelet, sometimes having something on your wrist can make it easier to remember.
I also like to spend 20-30 minutes every morning after Fajr to just spend time with Allah, talk to Him, and read the Qur'an.
But also remember that you don't only get rewarded for outright acts of worship. You get rewarded for caring for your body, taking a nap when you're tired, eating food, drinking water, caring for pets, and spending time with family. All of that stuff is worship.
Be easy with yourself. Allah does not want hardship for you (2:185).
And I'll leave you with a Qur'an verse.
It was We Who created man, and We know what his soul whispers to him, and We are closer to him that [his] jugular vein. (50:16)
I hope this helps you some. I love you. Allah loves you. May Allah bless you with peace, imaan, and His abundant guidance and mercy, Allahumma Ameen.
You can ask questions in the comments or in asks if you want.
193 notes
·
View notes
Text

Posts like these do nothing to combat bigotry against Muslims. People will not take you seriously if they can tell you are being dishonest.
It is dishonest to pretend that all of European concerns about Muslim conquest were “fearmongering,” when different Muslim empires did conquer significant portions of Europe.
Perhaps the most famous example would be the defeat of the Byzantine Empire by Mehmet the Conquerer in 1452.
(Hadiths compiled in the centuries after Muhammad’s death contain his prediction that a Muslim army would take Constantinople.)
And guess what? Still not an excuse to dehumanize Muslims.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Who was Allah before Islam?, with Ahmad Al-Jallad

A conversation with Ahmad Al-Jallad about the languages and inscriptions of pre-Islamic Arabia, our main contemporary source for life, death, and worship before the time of the Prophet Muhammad. We talk about field surveys in search of inscriptions and what they tell us about Allah and other Arabian deities in the early centuries of the first millennium.
Click here to listen
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
🧵𝐍𝐨, 𝐈𝐭 𝐃𝐢𝐝𝐧’𝐭 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐨𝐧 𝐎𝐜𝐭𝐨𝐛𝐞𝐫 𝟕𝐭𝐡: 𝐂𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐟 𝐉𝐞𝐰𝐢𝐬𝐡 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐢𝐧 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐌𝐢𝐝𝐝𝐥𝐞 𝐄𝐚𝐬𝐭.🧵
Thread: The idea that Arabs loved Jews until the creation of Israel is a widespread and untrue myth. Many believe that Jews were welcomed and lived peacefully among Arabs until the establishment of the modern state of Israel in 1948. This view is not only historically inaccurate but dangerously overlooks the long and painful history of Jewish suffering in the Middle East. Long before Zionism, Jews faced massacres, forced conversions, and expulsions in regions once ruled by the Arabs. In fact, Jews in the Arab world endured centuries of persecution under both Muslim and Ottoman rulers. Here’s a look at some of the most significant massacres and pogroms throughout this period, revealing the true story of Jewish life in the Middle East.

1. The Massacre of the Banu Qurayza (627 CE).
Long before Zionism, Jewish communities in the Middle East endured persecution, including one of the earliest and most harrowing incidents: the massacre of the Banu Qurayza in Medina during the time of the Prophet Muhammad.
The Banu Qurayza, a Jewish tribe in Medina, had entered into a pact with Muhammad under the Constitution of Medina, which allowed Muslims and Jews to coexist. However, during the Battle of the Trench, the tribe was accused of conspiring with Muhammad’s enemies, the Quraysh. After the Muslim victory, Muhammad and his forces besieged the Banu Qurayza’s fortress, forcing their surrender.
What followed was brutal. A tribunal led by Sa’d ibn Mu’adh sentenced all adult males of the tribe to death and enslaved the women and children. To determine who qualified as an “adult male,” boys were subjected to inspections for signs of puberty, specifically the presence of pubic hair. Those deemed adults were executed alongside the men. Historical sources, such as Ibn Ishaq and al-Tabari, report that between 600 and 900 men and boys were killed, their bodies dumped into trenches.
The Banu Qurayza’s women and children were sold into slavery, marking the total destruction of the tribe. This event illustrates the precarious and often deadly position of Jewish communities in the early Islamic period, long before the creation of Israel or the modern conflict in the region.

2/ Granada Massacre (1066) - Al-Andalus (Muslim Spain).
The first well-documented massacre of Jews in the Middle East dates back to 1066 in Granada, part of the Muslim-ruled Al-Andalus (Muslim Spain). After a Jewish vizier, Joseph Ibn Naghrela, was blamed for the death of the Muslim king, the situation escalated. A mob of Muslims, inspired by rumors and political tension, attacked the Jewish population of Granada. Over 4,000 Jews were slaughtered in a brutal pogrom that saw entire families butchered, their homes looted, and their properties destroyed. This massacre was part of a larger pattern of Jewish scapegoating across Muslim-ruled territories during periods of political instability. The massacre marked a turning point for Jews in the Iberian Peninsula, with many fleeing to other parts of the Muslim world for safety.

3/ The Persecution of Jews in Yemen: 1165 to 1679
The Jewish community in Yemen endured centuries of brutal persecution, systemic discrimination, and forced displacement, with two particularly devastating events defining their history before modern Zionism.
In 1165, during the reign of the Muslim leader Abd-al-Nabi ibn Mahdi, Yemen’s Jews faces an ultimatum: convert to Islam or face death. This period marked one of the earliest recorded instances of mass violence against Yemeni Jews. Synagogues were destroyed, and Jewish religious practices were outlawed. While some Jews fled or were forcibly converted, others were massacred for refusing to abandon their faith. This event signified the precarious existence of Jews in Yemen, where tolerance depended on the ruler’s whims.
Centuries later, in 1679, the Yemeni Jewish community faced an even more catastrophic event known as the Mawza Exile. Under the rule of Imam Al-Mahdi Ahmad, all Jews were expelled from their homes and forced into the barren Mawza desert. The journey itself claimed thousands of lives due to starvation and disease. Those who survived the desert exile were not allowed to return to their homes for several years, and when they did, they found their properties confiscated and their communities decimated. This period permanently weakened the Jewish presence in Yemen.
Throughout these centuries, Yemeni Jews were subjected to the degrading status of dhimmi under Islamic law, requiring them to pay exorbitant taxes, wear distinctive clothing, and accept legal and social inferiority. Forced conversions, kidnappings, and violent riots were regular occurrences. Despite these challenges, the community persisted, holding on to their traditions and faith until most were ultimately forced to leave Yemen in the mid-20th century.


4/ The Safed Attacks (1517).
In 1517, following the Ottoman conquest of the Levant from the Mamluks, chaos erupted in the city of Safed, one of the holiest cities in Judaism. The transition of power unleashed lawlessness, and Jewish communities became an easy target for violence.
Led by rogue Ottoman soldiers and local mobs, the attacks on Safed’s Jews were devastating. Homes and synagogues were looted and burned, and many Jews were brutally murdered. The violence displaced much of Safed’s Jewish population, forcing survivors to flee to neighboring areas.
Safed had been a center of Jewish learning and spirituality, with a thriving community. The attacks disrupted this flourishing cultural hub and instilled fear among Jews living in Ottoman-controlled lands. This event was one of the earliest indications that even under the Ottomans, Jewish communities would face intermittent violence and persecution, often fueled by local unrest and anti-Jewish sentiment.
The Safed Attacks of 1517 were a sad reminder of how quickly Jewish communities could become scapegoats during periods of political upheaval, long before modern Zionism or the establishment of Israel.

5/ The Tripoli Pogrom (1785).
In 1785, the Jewish community of Tripoli, Libya, endured a catastrophic pogrom instigated by Ali Burghul, an Ottoman officer who temporarily seized power in the region. After overthrowing the ruling pasha, Burghul wanted to consolidate his rule by targeting the city’s vulnerable minorities, particularly Jews.
The violence against Jews was brutal and systematic. Jewish homes and businesses were looted, synagogues were desecrated, and many Jews were tortured or killed. The pogrom decimated the Jewish quarter of Tripoli, leaving countless families homeless and destitute.
While Burghul’s regime lasted less than a year, the damage to the Jewish community was profound and long-lasting. Survivors faced the daunting task of rebuilding their lives amidst persistent discrimination and insecurity. This pogrom was a stark reminder of the precarious existence of Jews in North Africa, where they were often targeted during periods of political upheaval.
The Tripoli Pogrom of 1785 shows you again, the centuries-long persecution faced by Jews in Arab lands, well before the emergence of modern Zionism or the creation of Israel.

6/ The Baghdad Pogrom (1828).
In 1828, the Jewish community in Baghdad, Iraq, was subjected to one of the most devastating anti-Jewish pogroms in Ottoman-controlled Iraq. Tensions between Jews and Muslims had been rising due to a combination of economic envy, political instability, and increasing religious intolerance.
The pogrom began when a prominent Muslim figure, incited by local political and economic disputes, spread false accusations against the Jews of Baghdad. Jews were blamed for a series of issues, including alleged economic exploitation and religious violations, though no evidence supported these claims.
A violent mob quickly assembled, attacking Jewish homes, shops, and synagogues. Many Jews were beaten, and several were killed in the streets. Property was looted, and entire neighborhoods were set on fire. The violence lasted for several days, and it is estimated that several dozen Jews were killed, with many more injured or left destitute.
The pogrom also resulted in mass destruction of Jewish religious and cultural landmarks in Baghdad, severely damaging the local Jewish community’s infrastructure. This event left lasting scars on the Jewish population, contributing to a growing sense of insecurity and vulnerability. While the situation temporarily improved, the event remained a painful chapter in the history of Jewish life in Iraq.
The Baghdad Pogrom of 1828 showed how easily Jews were targeted and scapegoated in times of political and religious tension, long before the rise of modern Zionism or the establishment of Israel.

7/ The 1838 Safed Pogrom.
The second major pogrom in Safed, occurring in 1838, further demonstrated the uncertain position of Jews in the region during Ottoman rule. This wave of violence took place during the Egyptian-Ottoman War, as Ibrahim Pasha’s Egyptian forces temporarily controlled Israel. When Ibrahim’s forces retreated from Safed, local Arab mobs, emboldened by the chaos and lack of authority, turned their fury on the city’s Jewish population.
Over several days, armed bands ransacked Jewish homes, robbed businesses, and desecrated synagogues. Entire families were beaten and humiliated, while women and children were subjected to horrifying abuse. Many Jews fled to the surrounding hills for safety, living in caves or shelters with little food or water, while those who remained in the city faced murder or severe physical violence.
The Ottoman authorities did little to restore order or protect the Jewish residents. The aftermath of the pogrom left the Jewish quarter of Safed devastated, with entire families displaced and ancient synagogues reduced to ruins. Survivors recounted harrowing stories of betrayal by neighbors who joined in the looting and violence. The 1838 pogrom was a traumatic event that further destabilized the already struggling Jewish community in Safed, leading many to consider emigration.
The recurring violence in Safed was a reminder of the vulnerability of Jewish communities in Israel long before the modern Zionist movement emerged.

8/ The 1840 Damascus Affair
The Damascus Affair of 1840 was a horrifying example of the blood libel myth, a baseless and antisemitic accusation that Jews murder non-Jews to use their blood for religious rituals. This particular incident unfolded in Ottoman-controlled Damascus and left a deep scar on Jewish communities across the region and beyond.
The tragedy began when Father Thomas, a Catholic monk, and his Muslim servant mysteriously disappeared. Almost immediately local Christian leaders accused the Jewish community of abducting and murdering them for their blood, supposedly to bake matzot for Passover. The accusation, entirely unfounded, unleashed a torrent of violence and state-backed persecution against Damascus’s Jews.
Under pressure from local Christian clergy, the Ottoman authorities arrested several prominent Jewish figures, including rabbis and community leaders. These men were subjected to brutal torture to extract confessions to a crime they did not commit. Torture methods included floggings, burning, and deprivation of food and water. One man, Isaac Harari, died from the torture, and another, Aaron Monshe Rehama, succumbed to his injuries shortly after being released. The torture yielded forced confessions that only fueled further hysteria.
As rumors spread, mobs looted Jewish homes and desecrated synagogues. The community lived in terror, with many families hiding in fear of further arrests or violence. The situation worsened when the Ottoman authorities imprisoned dozens more Jews, including children, in an attempt to pressure the community into “confessing” to collective guilt.
The Damascus Affair also had international implications. Initially, France supported the blood libel accusations due to the influence of local Catholic leaders. However, prominent Jews in Europe, including Sir Moses Montefiore, Adolphe Crémieux, and Salomon Munk, mobilized a vigorous diplomatic campaign to challenge the lies. They traveled to Alexandria and Constantinople, lobbying influential leaders like Muhammad Ali of Egypt and Sultan Abdülmecid I of the Ottoman Empire to stop the persecution.
Eventually, after months of pressure and mounting evidence of the absurdity of the charges, the surviving Jewish prisoners were released. Still, the community was left in ruins. The aftermath of the affair saw Damascus’s Jewish population diminished and traumatized. Many families fled, and those who remained lived under the shadow of renewed accusations.
The Damascus Affair exposed yet again the fragility of Jewish life under Ottoman rule and the enduring danger of antisemitic myths, this as well happened long before the creation of modern Zionism.

9/ The 1920 Nebi Musa Riots.
The Nebi Musa Riots, which took place during Easter week in April 1920, were among the first major instances of anti-Jewish violence in British-controlled Israel, occurring long before the establishment of modern Israel. The riots shattered the myth of peaceful coexistence between Jews and Arabs in the region and exposed the hostility Arab leaders harbored toward the growing Jewish community.
Nebi Musa was a Muslim religious festival traditionally marked by processions to a shrine near Jericho. In 1920, the festival coincided with Easter and Passover, bringing an unusually large number of Muslims, Christians, and Jews to Jerusalem. Arab leaders, including Haj Amin al-Husseini (later notorious for his collaboration with the Nazis), used the occasion to incite the crowds against the Jewish community. They spread false claims that Jews were threatening the Al-Aqsa Mosque and seeking to take over Muslim holy sites, a tactic that would recur in later decades.
The inflammatory rhetoric worked. On April 4, 1920, Arab mobs began attacking Jewish neighborhoods in Jerusalem. Armed with knives, clubs, and stones, they looted Jewish homes and businesses, burned property, and assaulted Jewish residents. Reports described horrific acts of violence, including the brutal killing of five Jews and the injury of over 200 others. Jewish women were targeted for sexual violence, adding to the community’s trauma.
The British authorities, unprepared for the scale of the violence, initially failed to contain the riots. British soldiers were criticized for their slow response, and some were even accused of sympathizing with the rioters. Jewish self-defense groups, including the Haganah’s predecessors, stepped in to protect their communities, marking one of the first organized efforts by Jews to defend themselves in modern Israel.
The aftermath of the riots further deepened tensions. Haj Amin al-Husseini, though implicated in inciting the violence, received a relatively light punishment and would later be appointed the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, a decision with disastrous consequences. Meanwhile, the Jewish community, already shaken from European pogroms, began to view self-defense as essential for survival in the face of local hostility.
The 1920 Nebi Musa Riots are a powerful reminder that violence against Jews in the Middle East was not a product of Zionism but a reflection of deep hostility toward Jewish communities.

10/ The 1929 Hebron Massacre.
In August 1929, one of the darkest chapters in Jewish history under the British Mandate unfolded in the ancient city of Hebron, where a long established Jewish community had lived for thousands of years. Hebron, considered one of Judaism’s four holy cities, was home to a mix of Sephardi and Ashkenazi Jews, many of whom lived peacefully alongside their Arab neighbors, until incitement turned deadly.
Tensions had been brewing for months, fueled by false rumors spread by Arab leaders and the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, Amin al-Husseini. Claims circulated that Jews were planning to take over the Temple Mount and destroy the al-Aqsa Mosque. These fabrications were spread intentionally to inflame anti-Jewish sentiment and provoke violence.
On the 23rd and 24th of August, Arab mobs descended upon the Jewish community of Hebron, armed with knives, clubs, and firearms. The British authorities, overwhelmed and unprepared, failed to intervene effectively. Over the course of two days, 67 Jews were brutally murdered, men, women, and children alike. Victims were tortured, mutilated, and dismembered. Entire families were wiped out in their homes.
One of the most horrific aspects of the massacre was the betrayal by neighbors. Some Arabs, with whom the Jews had coexisted peacefully for years, turned on them.
The aftermath was devastating. The Jewish quarter was looted and ransacked. Synagogues were desecrated, Torah scrolls destroyed. Survivors were forcibly evacuated by the British, ending a Jewish presence in Hebron that had lasted centuries. The city, once a symbol of coexistence, became a stark reminder of how quickly incitement and hatred could shatter fragile relations.
The massacre was part of a larger wave of violence that also targeted Jews in Jerusalem, Safed, and other areas of Israel during the same period. It was not an isolated event but a symptom of escalating hostility toward the Jewish community, years before the establishment of modern Israel.

11/ The 1941 Farhud Massacre.
The Farhud, which took place on June 1-2, 1941, was a brutal pogrom against the Jewish community in Baghdad, Iraq. The violence erupted during the Jewish holiday of Shavuot, fueled by Nazi propaganda and growing political instability. The Iraqi government, under the pro-Nazi Rashid Ali al-Gaylani, had recently been overthrown by the British, leaving the country in chaos.
Pro-Nazi mobs, fueled by years of antisemitic rhetoric, attacked Jews with brutal force. Over 180 Jews were murdered, and hundreds more were injured. Mobs looted Jewish homes, destroyed businesses, and desecrated synagogues. Women were raped, and many victims were tortured and mutilated.
The British and Iraqi authorities intervened after two days of unchecked violence, but the damage was done. The Farhud shattered the Iraqi Jewish community, marking the beginning of a mass exodus. By the 1950s, most of Iraq’s 150,000 Jews had fled, many of them to Israel.
The Farhud remains a tragic reminder of how quickly a Jewish community, with a history in the region spanning over 2,600 years, could be destroyed by hatred and incitement. It underscored the urgent need for Jewish self-determination, which Zionism sought to provide.

12/ Palestinian Collaboration with Nazi Germany.
During the 1930s and 40s, the Palestinian Arab leadership, particularly the Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Amin al-Husseini, formed an alliance with Nazi Germany. Husseini, who opposed Jewish immigration to Israel, wanted Nazi support for his goal of preventing a Jewish homeland. In 1941, he met with Adolf Hitler, where he expressed his admiration for the Nazis’ anti-Semitic policies and urged them to support the Arab cause against the Jews. Husseini also played a role in recruiting Muslim soldiers to fight for the Axis powers, including the notorious Waffen-SS. His collaboration with Nazi Germany, which included attempts to organize massacres of Jews in Israel, contributed to deepening the hostility and violence toward Jewish communities in the region.

Conclusion.
When I started studying and looking up these events, I was shocked by the crazy number of them. I had to choose from hundreds, if not thousands, of such atrocities throughout history. And knowing that each of these incidents means real people, Jewish men, women, and children, lost their lives or endured unimaginable torture, it broke my heart. It’s heartbreaking that, even today, we continue to prove, over and over again, how badly Jews have been treated, and how, in some corners of the world, there are still those who want us to endure even more suffering. The existence of Israel today is a direct result of all these painful events—a nation born out of the ashes of centuries of persecution. Israel stands as a shield, ensuring that Jews will never again face the horrors of those dark days. This history is not just a series of events, it’s a painful reminder of the resilience required to survive and the urgency of remembering so we can prevent such horrors from happening again.


Although not all of the events happened in the Middle east per se, all of them happened under Muslim rule.
@AP_from_NY
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
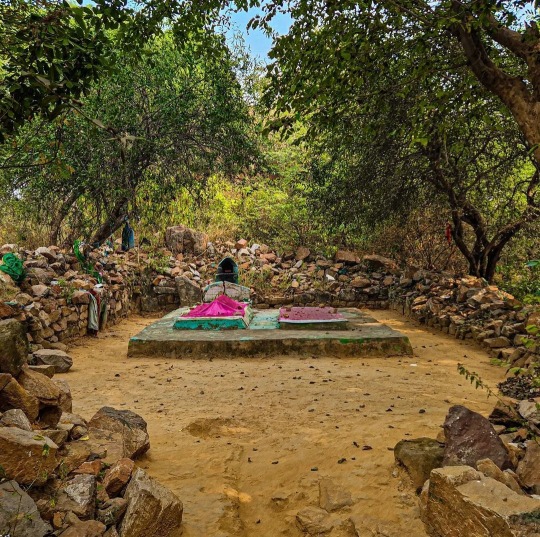
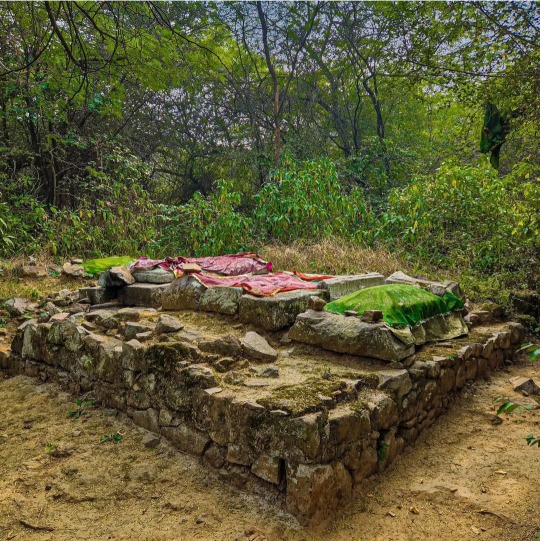



The oldest Sufi shrine in Delhi has been demolished.
"The earliest Sufi Shrine in Delhi - belonging to a relative of Prithviraj Chauhan and dating from BEFORE the Turkish conquest - has been Demolished by the Delhi Development Authority in an "anti encroachment" drive.
In the late 12th century, a group of Afghan pastoralists, suddenly burst onto the world stage. In a matter of years, they toppled their rulers of Ghazni and seized major Persian cities like Herat, and then established the major Indian sultanate in Delhi.
We often think of this "Islamic invasion" as the start of the Muslim presence in India. Yet recent scholarship has shown that by the time of Ghori's conquest of Delhi, Muslims were already a central part of Indian society
Some of the earliest mosques are found in Kerala, dating from a few decades after the prophet Muhammad's death. Tamil Pallava, Chola and Pandya kings all built sizeable mosques
Delhi also had a single sufi shrine before the Afghan conquest - this one.
Until 31 January, when it was demolished, the shrine of Baba Haji Rozbih had been located by the Fateh Burj, or Victory Gate of Lal Kot. The grave next to it under a reddish Chador belongs to his female disciple Bibi. Bibi was said to be a close relative of Prithviraj Chauhan who embraced Islam under the aegis of Haji Rozbih.
This demolition is an UTTERLY MINDLESS LOSS and complete cultural desecration.
What's more the "anti encroachment" drive is apparently scheduled to include the Aashiq Allah Dargah dated to 1317AD which is where the great Punjabi Saint Baba Farid used to meditate, and his small 'chillagah' is still visible here.
Please do share and write about this so we can save what remains! "
- from the historian Sam Dalrymple .
...
This is the third Islamic structure to be demolished in Delhi this month. Isn't it funny how only certain structures are the victim of anti- encroachment drives? This is part of a planned programme by the current right-wing government of India that is violently islamophobic and wants to create a hindu ethnostate modeled after Israel.
#india#desi tumblr#desiblr#south asia#punjab#sufi#sufism#islam#delhi#new delhi#anti-hindutva#anti-bjp#islamophobia#anti hindutva#anti bjp
172 notes
·
View notes
Text

Allah calls Himself Al-Quddoos— The Most Pure, The All-Perfect— on two occasions in the Quran. He is the One who is the absolutely pure in essence and attributes. Al-Quddoos is free from and far above any worldly imperfection, and He is beyond all human understanding of purity and perfection!
The Most Pure, the All-Perfect
Quddoos comes from the root qaaf-daal-seen, which points to three main meanings. The first main meaning is to be pure and clean. The second is to be far removed from impurity or imperfection, and the third main meaning is to be sacred or blessed.
This root appears ten times in the Quran in five derived forms. Examples of these forms are al-qudusi (“the Holy [spirit]”) and al-muqadasi (“the sacred”).
Linguistically, quddoos is on the intense structure of the attribute of quds, which refers to cleanliness or tahaarah and comes from the verb qadasa. Al-Quddoos is ‘clean’ or free from any partner, spouse, or child, from death, from injustice, lying, forgetfulness, error, poverty, and stinginess. Laa ilaaha illa huwa– there is no God but He.
Al-Quddoos Himself says: He is Allah , other than whom there is no deity, the Sovereign, the Pure … [Quran, 59:23] Whatever is in the heavens and whatever is on the earth is exalting Allah, the Sovereign, the Pure, the Exalted in Might, the Wise. [Quran, 62:1]
Subhanallah and alhamdulillah
They said, ‘Will You place upon it one who causes corruption therein and sheds blood, while we declare Your praise and sanctify You?’ [Quran, 2:30]. The angels glorify and praise Allah al-Quddoos continuously and so does the whole universe. Al-Quddoos created us human beings to worship, glorify, and praise Him as He gave us something different: our hearts.
Using the human heart to reflect on His creations, His perfection and greatness, it realizes that glorification and praise of the Creator is inevitable. So we praise and thank Al-Quddoos (alhamdulillah) and glorify Him (subhanAllah) as He is high above anything that does not befit Him. Isn’t it a blessing to have such a perfect lord, and aren’t we blessed to be able to praise Him?
How can you live by this name?
1.Have a pure belief in Al-Quddoos.
Believe in the oneness of Al-Quddoos and make sure your creed (or aqeedah) is pure by studying the types of tawheed and their practical meanings in your daily life from trustworthy sources, like Kitaab ut -Tawheed (The Book of Tawheed) by ibn Abd Al-Wahhab.
2. Praise Al-Quddoos.
Say alhamdulilah and subhanAllah from the bottom of your heart. The Prophet salallahu ‘alayhi wa sallam used to say in his prayer while in the bowing position (ruku): subboohun quddoosun Rabbul-malaa’ikati war-rooh (praise and Holiness be to You, Lord of the angels and the Soul). [Muslim] You can add this beautiful invocation to enhance your prayer.
3. Purify yourself through prayer.
The Prophet salallahu ‘alayhi wa sallam asked the companions: If someone bathes in a river outside of his house five times a day, will there be any impurity left on him? [Muslim] Visualize your prayer as cleansing your body and soul. Your prayer also protects you: indeed the prayer prevents from the indecency and evil. [Quran, 29:45]
4. Give the best sadaqah.
Give zakah (obligatory) and sadaqah (charity) to “purify” and increase your wealth. Take, [O, Muhammad], from their wealth a charity by which you purify them and cause them increase. [Quran 9:103] Remind yourself when you give sadaqah to give the best, as Allah is Al-Quddoos and He deserves the best to be given for His sake. Aishah radiyalahu anha used to perfume the charity she gave!
5. Don’t be unjust.
Allah does not wrong a person even to the amount of an atom’s weight [Quran 4:40]. Even if people do dhulm (injustice) to Him, Al-Quddoos never does injustice to people. Allah ‘azza wa jall also made injustice and oppression forbidden for you; so don’t be unjust to anyone, family or stranger, child, adult or even to animals.
6. Be clean.
Be clean inside and out and strive to purify and keep renewing your intentions when you do a good deed. Be thoughtful with your wudu; do your best to not only keep your belongings and house clean, but also your environment by not throwing litter and by removing harmful objects. Consume healthy and permissable food and drink— bought with halaal earnings— and teach children this way of living.
7. Let the Quran purify you.
And who is more truthful than Allah in speech? [Quran, 4:122] The speech of Al-Quddoos is pure and is a cure, healing, and guidance for you to purify yourself. So turn to the Quran to seek cure from the diseases of your heart, let the ayaat help you to improve your character, and recite the Quran daily to clean your heart and bring tranquillity to your body.
8. Ask Al-Quddoos.
The Prophet salallahu’ alayhi wa sallam used to ask Al-Quddoos at the beginning of prayer:
اللهم باعد بيني وبين خطاياي كما باعدت بين المشرق والمغرب اللهم نقني من خطاياي كما ينقى الثوب الأبيض من الدنس اللهم اغسلني من خطاياي بالثلج والماء والب
O Allah, distance me from my sins just as You have distanced The East from The West, O Allah, purify me of my sins as a white robe is purified of filth, O Allah, cleanse me of my sins with snow, water, and ice. [Al-Bukharee, Muslim] Use and reflect on this supplication as it contains all forms of purification: distancing (moving far away from dirt and deficiencies), removing dirt or filth, and washing or cleansing, so no impurity remains at the end.
O Allah, Al-Quddoos, we know that You are the absolutely pure beyond imagination. Lead us to a sound belief in Your oneness, help us in purifying our hearts, deeds, and intentions, and guide us to purify our bodies and keep our environment clean. Aid us in performing the best salah, giving the best charity, and helping us to turn to the Quran so we can come to You with a pure heart, ameen!
#allah#islam#revert help team#asma al husna#muslim#revert help#ayat#dua#allah’s name#daily#pray#prayer#reminder#religion#salah#god#help#revert#revert islam#converthelp#convert islam#new convert#convert#new revert#reevrt help#convert help#welcome to islam#how to convert islam#how to convert to islam
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
O' Ummah of Muhammad (صَلَّى اللّٰهُ عَلَيْهِ وَسَلَّمَ) wake up, wake up from the sleep of heedlessness. Your Prophet (صَلَّى اللّٰهُ عَلَيْهِ وَسَلَّمَ) is being insulted. What are you doing? You forgot about your meeting with Allah? How could your worship be accepted when there is no Muhammad (صَلَّى اللّٰهُ عَلَيْهِ وَسَلَّمَ) in your heart?
Boycotting has become a difficult task for you? They are insulting Allah and you are still asleep? Fighting muslims and cursing them. By Allah, if you become sincere, victory is yours. Our love for kuffar is increasing ! Our pfp's are filled with the pictures of kuffar.
Wake up O' Ummah of Muhammad (صَلَّى اللّٰهُ عَلَيْهِ وَسَلَّمَ). Learn Islam and stop wasting your time. Stop being disobedient to Allah. You don't know which missile will come rushing at you. There is no return after death. There is a meeting with Allah. Imagine a sun above your head while you naked afraid and waiting for your turn.
Islam is being attacked from every cornor. Defend it ya Abd-Allah. Muslims are being slaughtered! Wake up! And leave the desires of this world and turn to your Lord in complete submission.
Ya Abd-Allah "enjoin good and forbid evil".
Lower your gaze, wear a beard, keep your lowers above your knees, wear the hijab, leave haraam relationships, leave music and naked women. Marry and defend Islam.
Ya Abd-Allah this message has reached you and you shall be asked!
#islamdaily#quranandsunnah#islam#islam help#islamic#quranquotes#islamicpost#islamislove#al quran#convert to islam
14 notes
·
View notes