#prices
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The one weird monopoly trick that gave us Walmart and Amazon and killed Main Street

I'm coming to BURNING MAN! On TUESDAY (Aug 27) at 1PM, I'm giving a talk called "DISENSHITTIFY OR DIE!" at PALENQUE NORTE (7&E). On WEDNESDAY (Aug 28) at NOON, I'm doing a "Talking Caterpillar" Q&A at LIMINAL LABS (830&C).

Walmart didn't just happen. The rise of Walmart – and Amazon, its online successor – was the result of a specific policy choice, the decision by the Reagan administration not to enforce a key antitrust law. Walmart may have been founded by Sam Walton, but its success (and the demise of the American Main Street) are down to Reaganomics.
The law that Reagan neutered? The Robinson-Patman Act, a very boring-sounding law that makes it illegal for powerful companies (like Walmart) to demand preferential pricing from their suppliers (farmers, packaged goods makers, meat producers, etc). The idea here is straightforward. A company like Walmart is a powerful buyer (a "monopsonist" – compare with "monopolist," a powerful seller). That means that they can demand deep discounts from suppliers. Smaller stores – the mom and pop store on your Main Street – don't have the clout to demand those discounts. Worse, because those buyers are weak, the sellers – packaged goods companies, agribusiness cartels, Big Meat – can actually charge them more to make up for the losses they're taking in selling below cost to Walmart.
Reagan ordered his antitrust cops to stop enforcing Robinson-Patman, which was a huge giveaway to big business. Of course, that's not how Reagan framed it: He called Robinson-Patman a declaration of "war on low prices," because it prevented big companies from using their buying power to squeeze huge discounts. Reagan's court sorcerers/economists asserted that if Walmart could get goods at lower prices, they would sell goods at lower prices.
Which was true…up to a point. Because preferential discounting (offering better discounts to bigger customers) creates a structural advantage over smaller businesses, it meant that big box stores would eventually eliminate virtually all of their smaller competitors. That's exactly what happened: downtowns withered, suburban big boxes grew. Spending that would have formerly stayed in the community was whisked away to corporate headquarters. These corporate HQs were inevitably located in "onshore-offshore" tax haven states, meaning they were barely taxed at the state level. That left plenty of money in these big companies' coffers to spend on funny accountants who'd help them avoid federal taxes, too. That's another structural advantage the big box stores had over the mom-and-pops: not only did they get their inventory at below-cost discounts, they didn't have to pay tax on the profits, either.
MBA programs actually teach this as a strategy to pursue: they usually refer to Amazon's "flywheel" where lower prices bring in more customers which allows them to demand even lower prices:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BaSwWYemLek
You might have heard about rural and inner-city "food deserts," where all the independent grocery stores have shuttered, leaving behind nothing but dollar stores? These are the direct product of the decision not to enforce Robinson-Patman. Dollar stores target working class neighborhoods with functional, beloved local grocers. They open multiple dollar stores nearby (nearly all the dollar stores you see are owned by one of two conglomerates, no matter what the sign over the door says). They price goods below cost and pay for high levels of staffing, draining business off the community grocery store until it collapses. Then, all the dollar stores except one close and the remaining store fires most of its staff (working at a dollar store is incredibly dangerous, thanks to low staffing levels that make them easy targets for armed robbers). Then, they jack up prices, selling goods in "cheater" sizes that are smaller than the normal retail packaging, and which are only made available to large dollar store conglomerates:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/03/27/walmarts-jackals/#cheater-sizes
Writing in The American Prospect, Max M Miller and Bryce Tuttle1 – a current and a former staffer for FTC Commissioner Alvaro Bedoya – write about the long shadow cast by Reagan's decision to put Robinson-Patman in mothballs:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-08-13-stopping-excessive-market-power-monopoly/
They tell the story of Robinson-Patman's origins in 1936, when A&P was using preferential discounts to destroy the independent grocery sector and endanger the American food system. A&P didn't just demand preferential discounts from its suppliers; it also charged them a fortune to be displayed on its shelves, an early version of Amazon's $38b/year payola system:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
They point out that Robinson-Patman didn't really need to be enacted; America already had an antitrust law that banned this conduct: section 2 of the the Clayton Act, which was passed in 1914. But for decades, the US courts refused to interpret the Clayton Act according to its plain meaning, with judges tying themselves in knots to insist that the law couldn't possibly mean what it said. Robinson-Patman was one of a series of antitrust laws that Congress passed in a bid to explain in words so small even federal judges could understand them that the purpose of American antitrust law was to keep corporations weak:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/14/aiming-at-dollars/#not-men
Both the Clayton Act and Robinson-Patman reject the argument that it's OK to let monopolies form and come to dominate critical sectors of the American economy based on the theoretical possibility that this will lead to lower prices. They reject this idea first as a legal matter. We don't let giant corporations victimize small businesses and their suppliers just because that might help someone else.
Beyond this, there's the realpolitik of monopoly. Yes, companies could pass lower costs on to customers, but will they? Look at Amazon: the company takes $0.45-$0.51 out of every dollar that its sellers earn, and requires them to offer their lowest price on Amazon. No one has a 45-51% margin, so every seller jacks up their prices on Amazon, but you don't notice it, because Amazon forces them to jack up prices everywhere else:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/01/managerial-discretion/#junk-fees
The Robinson-Patman Act did important work, and its absence led to many of the horribles we're living through today. This week on his Peoples & Things podcast, Lee Vinsel talked with Benjamin Waterhouse about his new book, One Day I’ll Work for Myself: The Dream and Delusion That Conquered America:
https://athenaeum.vt.domains/peoplesandthings/2024/08/12/78-benjamin-c-waterhouse-on-one-day-ill-work-for-myself-the-dream-and-delusion-that-conquered-america/
Towards the end of the discussion, Vinsel and Waterhouse turn to Robinson-Patman, its author, Wright Patman, and the politics of small business in America. They point out – correctly – that Wright Patman was something of a creep, a "Dixiecrat" (southern Democrat) who was either an ideological segregationist or someone who didn't mind supporting segregation irrespective of his beliefs.
That's a valid critique of Wright Patman, but it's got little bearing on the substance and history of the law that bears his name, the Robinson-Patman Act. Vinsel and Waterhouse get into that as well, and while they made some good points that I wholeheartedly agreed with, I fiercely disagree with the conclusion they drew from these points.
Vinsel and Waterhouse point out (again, correctly) that small businesses have a long history of supporting reactionary causes and attacking workers' rights – associations of small businesses, small women-owned business, and small minority-owned businesses were all in on opposition to minimum wages and other key labor causes.
But while this is all true, that doesn't make Robinson-Patman a reactionary law, or bad for workers. The point of protecting small businesses from the predatory practices of large firms is to maintain an American economy where business can't trump workers or government. Large companies are literally ungovernable: they have gigantic war-chests they can spend lobbying governments and corrupting the political process, and concentrated sectors find it comparatively easy to come together to decide on a single lobbying position and then make it reality.
As Vinsel and Waterhouse discuss, US big business has traditionally hated small business. They recount a notorious and telling anaecdote about the editor of the Chamber of Commerce magazine asking his boss if he could include coverage of small businesses, given the many small business owners who belonged to the Chamber, only to be told, "Over my dead body." Why did – why does – big business hate small business so much? Because small businesses wreck the game. If they are included in hearings, notices of inquiry, or just given a vote on what the Chamber of Commerce will lobby for with their membership dollars, they will ask for things that break with the big business lobbying consensus.
That's why we should like small business. Not because small business owners are incapable of being petty tyrants, but because whatever else, they will be petty. They won't be able to hire million-dollar-a-month union-busting law-firms, they won't be able to bribe Congress to pass favorable laws, they can't capture their regulators with juicy offers of sweet jobs after their government service ends.
Vinsel and Waterhouse point out that many large firms emerged during the era in which Robinson-Patman was in force, but that misunderstands the purpose of Robinson-Patman: it wasn't designed to prevent any large businesses from emerging. There are some capital-intensive sectors (say, chip fabrication) where the minimum size for doing anything is pretty damned big.
As Miller and Tuttle write:
The goal of RPA was not to create a permanent Jeffersonian agrarian republic of exclusively small businesses. It was to preserve a diverse economy of big and small businesses. Congress recognized that the needs of communities and people—whether in their role as consumers, business owners, or workers—are varied and diverse. A handful of large chains would never be able to meet all those needs in every community, especially if they are granted pricing power.
The fight against monopoly is only secondarily a fight between small businesses and giant ones. It's foundationally a fight about whether corporations should have so much power that they are too big to fail, too big to jail, and too big to care.

Community voting for SXSW is live! If you wanna hear RIDA QADRI and me talk about how GIG WORKERS can DISENSHITTIFY their jobs with INTEROPERABILITY, VOTE FOR THIS ONE!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/14/the-price-is-wright/#enforcement-priorities
#pluralistic#Robinson-Patman Act#ftc#alvaro bedoya#monopoly#monopsony#main street#too big to jail#too big to care#impunity#regulatory capture#prices#the american prospect#Max M Miller#Bryce Tuttle#a and p#wright patman
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Virgins treated gently, spinsters satisfied, widows a specialty! @official-penis-posts @differentcatcat
527 notes
·
View notes
Text




I've reopened a couple spots for Doodle comms, and there's still a couple other things left on the ko-fi! Please check em out if you'd like!
https://ko-fi.com/blushily/commissions
149 notes
·
View notes
Photo
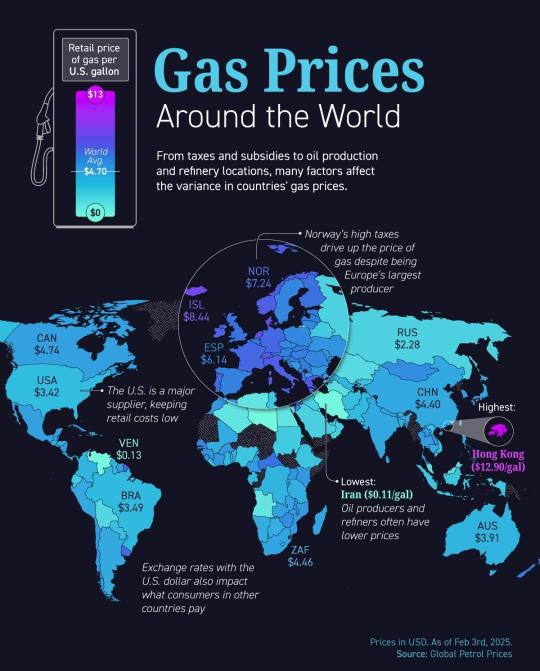
Gas prices of Feb 2025
123 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's somewhat unfortunate that it took Switch 2 to remind gamers that yes, politics does, in fact, affect you whether you like it or not.
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, so my art commissions are open because of an emergency. My examples of my art are below, including my prices.
Prices:
Headshot: 10$-$50
Halfbody: 30$-$100
Full body:$100-$200
My cashapp is $yycarmy just in case if you want to donate or tip. Every ounce counts.







#art commisions#commissions open#commission#commisions#art commissions open#art comms open#art community#art commission info#art#my art#artists on tumblr#roblox#roblox dandys world#dandys world#anime#illustration#emergency#prices#art prices#ultrakill#madness combat#madcom#fandom#fandoms
160 notes
·
View notes
Text

Trump: "The golden age of America begins..."
Reality: Natural Gas prices jump from $3.50 under Biden to $4.01 under Trump
134 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finding Home: A Chiss Ascendancy Zine Price Announcement
With preorders opening on MONDAY, MARCH 17th, we are proud to announce our bundle prices!
All purchases of a physical zine will also come with a PDF download of the digital zine. For a preview of the zine, click here!
Digital Merch includes: - Computer Desktop Background - Phone Wallpaper - Discord Emojis - (stretch goal: Digital sketch artbook "making of" for much of the art of the zine) - (stretch goal: audiobook recordings of some of the stories from the zine)
Physical Merch includes: - 4x6 prints of various art from the zine - stickers of Captains and their first officers - bookmarks based on the Ascendancy book covers - "Visit Csilla" postcard - (stretch goal: Keychains) - (stretch goal: "Visit Csilla" as a poster) Add-on: Supporter Tier - For an extra $30, your name will be added into the zine as a "Supporter"! Thank you for helping make this project happen! - Supporter Tier will only be available through Monday, April 14th. Then the zine will be finalized and sent to be printed.
Stretch goals will be determined as being affordable or not based on how well our sales do at Indiana ComicCon and the first week of preorders.

#ascendancy zine#chiss#chiss ascendancy#thrawn#star wars fanart#star wars zine#star wars fanfiction#fanzine#thrawn books#grand admiral thrawn#thrawn ascendancy#thrawn trilogy#prices#orders
55 notes
·
View notes
Text

70 notes
·
View notes
Text


Opening more slots! I would love to do some mixed media artworks and painted portraits! If you are interested, please fill the commission inquiry form :3 I also do commercial comms, email me at annyiva0020[at]gmail.com if interested!
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
By the way, my new kofi commission slots are open!
Looking to fill up slots for January/February. A couple new things this time around such as expression sheets and small animations.
Also, after being gone for a while, Half Body (full renders) are back!
Please take a look if you 're interested! thanks so much for the support!




120 notes
·
View notes
Text
The health industry’s invisible hand is a fist

On June 21, I'm doing an ONLINE READING for the LOCUS AWARDS at 16hPT. On June 22, I'll be in OAKLAND, CA for a panel and a keynote at the LOCUS AWARDS.

The US has the rich world's most expensive health care system, and that system delivers the worst health outcomes of any country in the rich world. Also, the US is unique in relying on market forces as the primary regulator of its health care system. All of these facts are related!
Capitalism's most dogmatic zealots have a mystical belief in the power of markets to "efficiently allocate" goods and services. For them, the process by which goods and services are offered and purchased performs a kind of vast, distributed computation that "discovers the price" of everything. Our decisions to accept or refuse prices are the data that feeds this distributed computer, and the signals these decisions send about our desires triggers investment decisions by sellers, which guides the whole system to "equilibrium" in which we are all better off.
There's some truth to this: when demand for something exceeds the supply, prices tend to go up. These higher prices tempt new sellers into the market, until demand is met and prices fall and production is stabilized at the level that meets demand.
But this elegant, self-regulating system rarely survives contact with reality. It's the kind of simplified model that works when we're hypothesizing about perfectly spherical cows of uniform density on a frictionless surface, but ceases to be useful when it encounters a messy world of imperfect rationality, imperfect information, monopolization, regulatory capture, and other unavoidable properties of reality.
For members of the "efficient market" cult, reality's stubborn refusal to behave the way it does in their thought experiments is a personal affront. Panged by cognitive dissonance, the cult members insist that any market failures in the real world are illusions caused by not doing capitalism hard enough. When deregulation and markets fail, the answer is always more deregulation and more markets.
That's the story of the American health industry in a nutshell. Rather than accepting that people won't shop for the best emergency room while unconscious in an ambulance, or that the "clearing price" of "not dying of cancer" is "infinity," the cult insists that America's worst-in-class, most expensive health system just needs more capitalism to turn it into a world leader.
In the 1980s, Reagan's court sorcerers decreed that they could fix health care with something called "Prospective Payment Systems," which would pay hospitals a lump sum for treating conditions, rather than reimbursing them for each procedure, using competition and profit motives to drive "efficiency." The hospital system responded by "upcoding' patients: if you showed up with a broken leg and a history of coronary disease, they would code you as a heart patient and someone who needed a cast. They'd collect both lump sums, slap a cast on you, and wheel you out the door:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4195137/
As Robert Kuttner writes for The American Prospect, this kind of abuse was predictable from the outset, especially since Health and Human Services is starved of budget for auditors and can only hand out "slaps on the wrist" when they catch a hospital ripping off the system:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-06-13-fantasyland-general/
Upcoding isn't limited to Medicare fraud, either. Hospitals and insurers are locked in a death-battle over payments, and hospitals' favorite scam is sending everyone to the ER, even when they don't have emergencies (some hospitals literally lock all the doors except for the ER entrance). That way, a normal, uncomplicated childbirth can be transformed into a "Level 5" emergency treatment (the highest severity of emergency) and generate a surprise bill of over $2,700:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/10/27/crossing-a-line/#zero-fucks-given
The US health industry is bad enough to generate a constant degree of political will for change, but the industry (and its captured politicians and regulators) is also canny enough to dream up an endless procession of useless gimmicks designed to temporarily bleed off the pressure for change. In 2018, HHS passed a rule requiring hospitals to publish their prices.
Hospitals responded to this with a shrewd gambit: they simply ignored the rule. So in 2021, HHS made another rule, creating penalties for ignoring the first rule:
https://www.cms.gov/priorities/key-initiatives/hospital-price-transparency/hospitals
The theory here was that publishing prices would create "market discipline." Again, this isn't wholly nonsensical. To the extent that patients have nonurgent conditions and the free time to shop around, being able to access prices will help them. Indeed, if the prices are in a standards-defined, machine-readable form, patients and their advocates could automatically import them, create price-comparison sites, leaderboards, etc. None of this addresses the core problem that health-care is a) a human right and b) not a discretionary expense, but it could help at the margins.
But there's another wrinkle here. The same people who claim that prices can solve all of our problems also insist that monopolies are impossible. They've presided over a decades-long assault on antitrust law that has seen hospitals, pharma companies, insurers, and a menagerie of obscure middlemen merge into gigantic companies that are too big to fail and too big to jail. When a single hospital system is responsible for the majority of care in a city or even a county, how much punishment can regulators realistically subject it to?
Not much, as it turns out. Kuttner describes how Mass Gen Brigham cornered the market on health-care in Boston, allowing it to flout the rules on pricing. In addition to standard tricks – like charging self-pay patients vastly more than insured payments (because individuals don't have the bargaining power of insurers), Mass Gen Brigham's price data is a sick joke.
See for yourself! The portal will send you giant, unstructured, ZIPped text files filled with cryptic garbage like:
ADJUSTABLE C TAPER NECK PLUS|1|UNITED HEALTHCARE [1016]|HB CH UNITED HMO / PPO / INDEMNITY [34]|UNITED HEALTHCARE HMO [101604]|75|Inv Loc: 1004203; from OR location 1004203|52.02|Inpatient PAF; 69.36% Billed|75|Inv Loc: 1004203; from OR location 1004203|56.87|Outpatient PAF; 75.83% Billed
https://www.massgeneralbrigham.org/en/patient-care/patient-visitor-information/billing/cms-required-hospital-charge-data
These files have tens of thousands of rows. As a patient, you are meant to parse through these in order to decide whether you're getting ripped off on that HIP STEM 16X203MM SIZE 4 FEMORAL PRESS FIT NEUTRAL REVISION TITANIUM you're in the market for (as it happens, I have two of these in my body).
Kuttner describes the surreal lengths he had to go through to prevent his mother from getting ripped off by Mass Gen through an upcoding hustle. By coding her as "admitted for observation," Mass Gen was able to turn her into an outpatient, with a 20% co-pay (this is down to a GW Bush policy that punishes hospitals that charge Medicare for inpatient care when they could be treated as outpatients – hospitals reflexively game the system to make every patient an outpatient, even if they have overnight hospital stays).
Kuttner's an expert on this: he was national policy correspondent for the New England Journal of Medicine and covers the health beat for the Prospect. Even so, it took him ten hours of phone calls to two doctors' offices and Blue Cross to resolve the discrepancy. The average person is not qualified to do this – indeed, the average person won't even know they've been upcoded.
Needless to say that people in other countries – countries where health care is cheaper and the outcomes are better – are baffled by this. Canadians, Britons, Australians, Germans, Finns, etc do not have to price-shop for their care. They don't have to hawkishly monitor their admission paperwork for sneaky upcodes. They don't have to spend ten hours on the phone arguing about esoteric billing practices.
In a rational world, we'd compare the American system to the rest of the world and say, "Well, they've figured it out, we should do what they're doing." But in good old U-S-A! U-S-A! U-S-A!, the answer to this is more prices, more commercialization, more market forces. Just rub some capitalism on it!
That's where companies like Multiplan come in: this is a middleman that serves other middlemen. Multiplan negotiates prices on behalf of insurers, and splits the difference between the list price and the negotiated price with them:
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/04/07/us/health-insurance-medical-bills.html
But – as the Arm and a Leg podcast points out – this provides the perverse incentive for Multiplan to drive list prices up. If the list price quintuples, and then Multiplan drives it back down to, say, double the old price, they collect more money. Meanwhile, your insurer sticks you with the bill, over and above your deductible and co-pay:
https://armandalegshow.com/episode/multiplan/
The Multiplan layer doesn't just allow insurers to rip you off (though boy does it allow insurers to rip you off), it also makes it literally impossible to know what the price is going to be before you get your procedure. As with any proposition bet, the added complexity is there to make it impossible for you to calculate the odds and figure out if you're getting robbed:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/04/house-always-wins/#are-you-on-drugs
Multiplan is the purest expression of market dynamics brainworms I've yet encountered: solving the inefficiencies created by the complexity of a system with too many middlemen by adding another middle-man who is even more complex.
No matter what the problem is with America's health industry, the answer is always the same: more markets! Are older voters getting pissed off at politicians for slashing Medicare? No problem: just create Medicare Advantage, where old people can surrender their right to government care and place themselves in the loving hands of a giant corporation that makes more money by denying them care.
The US health industry is a perfect parable about the dangers of trusting shareholder accountable markets to do the work of democratically accountable governments. Shareholders love monopolies, so they drove monopolization throughout the health supply chain. As David Dayen writes in his 2020 book Monopolized the pharma industry monopolized first, and put the screws to hospitals:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/29/fractal-bullshit/#dayenu
Hospitals formed regional monopolies to counter the seller power of consolidated Big Pharma. That's Mass Gen's story: tapping the capital markets to buy other hospitals in the region until it became too big to fail and too big to jail (and too big to care). Consolidated hospitals, in turn, put the screws to insurers, so they also consolidated, fighting Big Hospital's pricing power.
Monopoly at any point in a supply chain leads to monopoly throughout the supply chain. But patients can't consolidate (that's what governments are for – representing the diffuse interests of people). Neither can health workers (that's what unions are for). So the system screwed everyone: patients paid more for worse care. Health workers put in longer hours under worse conditions and got paid less.
Kuttner describes how his eye doctor races from patient to patient "as if he was on roller skates." When Kuttner wrote him a letter questioning the quality of care, the eye doctor answered that he understood that he was giving his patients short shrift, but explained that he had to, because his pay was half what he needed, relegating him to a small apartment and an old car. The hospital – which skims the payments he gets for care – sets his caseload, and he can't turn down patients.
The answers to this are obvious: get markets out of health care. Unionize health workers. Give regulators the budgets and power to hold health corporations to account.
But for market cultists, all of that can't work. Instead, we have to create more esoteric middlemen like "pharmacy benefit managers" and Multiplan. We need more prices to shovel into the market computer's data-hopper. If we just capitalism hard enough, surely the system will finally work…someday.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/13/a-punch-in-the-guts/#hayek-pilled
#billing codes#health#corruption#ripoffs#arm and a leg podcast#robert kuttner#prices#austrian economics#Prospective Payment Systems#the invisible hand#shop around#a market for lemons#monopoly#monopolization#upcoding
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
Looking to order some custom content or just wanna see more pics/vids? Shoot me a DM and let's talk about it! I accept payments directly to my venmo! Wanna see me model any specific lingerie or just wanna help a girl out? You can find my Throne wishlist here!


55 notes
·
View notes
Text

Commission prices starting Jan-2024:
-Comms come with standard 3 sketches and 3 edit moments. -General due date of 30 days after full payment. -If you have questions feel free to DM me for more info.
Commissions are currently on a wait list basis! Hit me up if you'd like to be on either the:
ASAP list: I'll get to you as soon as I finish up the current batch
-Specific month list: If you have a month in mind I'll write you in for then and I'll get to you by that time.
I look forward to working with you
265 notes
·
View notes
Text
COMMISSIONS OPEN!






So, yeah... times are terrible for me, and even if I'll be very slow with them, I am opening commissions! I really can draw a lot of stuff, so these are some of the things I usually do. I wanted to add comic pages (both sketched or refined) but let's see how these work first.
Send your requests to: ✨[email protected]✨ with the title "COMMISSION :)"
I will accept ✨PayPal✨ as payment, sent to the same email address above.
We'll talk about your request and see how it can work. If you want OCs, please send references. If you want a specific scene, I might ask about the whole story behind it to better illustrate it.
I will take half the payment beforehand and the rest when I send the finished piece.
Thanks to everyone who will commission me or even share the post around to let it be seen. 🙏🙏🙏
79 notes
·
View notes