#pp discourse //
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
An Essay Exploring Psycho-Pass's Most Controversial Character
I know I’m opening a huge, slimy can of worms and potentially incurring the wrath of half the Psycho-Pass fandom, but I feel compelled to share my feelings on Mika Shimotsuki and how I believe she serves as a lightning rod for fan culture misogyny. Now, before I start, let me just say that this essay isn’t targeted at any one individual, and it’s just my personal opinion, which you are more than welcome to disagree with. I’d also like to stress that, despite my love for Mika’s character, I’m going to try my very best to approach this topic from an academic standpoint rather than an emotional one. I recently picked Parasocial Relationships and their effect on female celebrities and fictional characters as a thesis for my Gender and Media course, and it really got me thinking about this anime in particular, so here we go…
Let’s tackle the female side of things first, because it’s the one that shocks and disappoints me the most. Don’t get me wrong -- I think fandoms with a strong female presence are awesome, complex, uplifting, and oftentimes incredibly positive and inclusive spaces. I love being a female genre fan and interacting with other female genre fans. That said, I’ve noticed female fandom can sometimes fall prey to online bullying and misogynistic groupthink when it comes to (a) female characters they find arrogant, bossy, mean, etc. and (b) female characters who are positioned as potential love interests for their collective male "blorbos," "husbandos," "faves," whatever the term may be. These two things very often overlap, which I’ll touch on later, but for now, let’s talk about the first point.
There was a big movement online several years ago urging creators to, “Let women be mean. Let them be angry. Let them be petty and complex and difficult. Let them be messy.” I fully support this idea in both theory and practice and wish it were that simple, but unfortunately, it’s not, because uncomfortably large swaths of fandom don’t like/appreciate unapologetically mean female characters the way they do male characters. Men in fiction are allowed to be cutthroat, selfish, cruel, narcissistic, arrogant, and even evil without garnering a fraction of the judgement that female characters receive for simply being “difficult” or “unlikable.”
Take, for instance, Shougo Makishima. The Psycho-Pass fandom at large adores this character (myself included), despite the fact that he’s a remorseless sociopath who touts the importance of free will as a wholesale excuse for murder. He is a bad person, full-stop, and yet he garners love -- even sympathy -- in abundance. He’s the subject of fawning fan fiction, chibi art, thirst tweets, and endless Reddit analysis. Fans are capable of seeing him, murderous warts and all, as a product of the warped dystopian society Sibyl has created. But Mika? Nope. Just “a bitch, a whiner, an arrogant little girl who deserves to get slapped in the mouth.” (I am not making this up. These are the type of comments I see *female* fans making left and right about her character). She receives far more hate for giving up the location of Akane’s grandmother as a blackmailed, frightened teenager than Makishima does for slashing Yuki’s throat or blowing up Masaoka. Hell, she catches more heat for Akane’s grandmother than Sakuya Togane, the woman’s actual murderer and -- I can’t stress this enough -- a 41-year-old adult man.
Now, I know what some of you are thinking -- Makishima and Togane are villains, so their personality flaws (putting it lightly) and horrible actions are essential to the narrative and indicative of good storytelling. We’re meant to “love to hate them.” All correct, and yet this doesn’t change or excuse the fact that their standing in the fandom, when compared to the equally complex and emotionally fractured Mika, is textbook pernicious misogyny. But, for the sake of argument, let’s compare Mika to another character ostensibly on the side of good -- Nobuchika Ginoza. [Note: Ginoza is my favorite character in Psycho-Pass, and any commentary regarding his PP1 shittiness is made with pure love and appreciation for him and nuanced character growth in general.]
When we first meet Ginoza, he is rude, terse, unyielding, intellectually smug, and totally unforgiving of those closest to him. He’s a brilliant character, and his behavior, no matter how insufferable and seemingly cruel, is the result of compounded trauma -- the trauma of having his father ripped away when he was only nine, the trauma of being unfairly judged for the “sins” of said latent criminal father, the trauma of his mother numbing her pain with medication and eventually becoming something akin to a human corpse, the trauma of finding a new support system and best friend in Kougami only to once again be “abandoned” for the other side of the law. In many ways, he’s still a hurt child lashing out at the world, unwilling to see it for the complicated, morally gray place that it is, because being mad is easier. Telling himself that Enforcers are nothing more than dogs for him to guide and use as shields is easier. Blindly trusting the judgements handed down by Sibyl is easier.
In this way, he and Mika are remarkably similar. When she first joins the MWPSB, she’s a 17-year-old minor whose best friend (and probably first love) was dismembered by a latent criminal under the direction of a serial killer disguising himself as a teacher -- a trusted authority figure. She’s filled with guilt and self-loathing over her failure to act, and the easiest way for her to sort out her feelings and ensure the same thing doesn’t happen again is to harden herself to all latent criminals. Distrusting them, treating them as “other,” is her form of self-preservation. Yes, it makes her come across as mean, as closed-minded, as unlikable, but that’s not a bad thing. It’s good storytelling, and it presents her with plenty of potential for growth, which she is certainly given.

[Upon discovering that her best friend, fellow Oso Academy student Kagami Kawarazaki, has been murdered by Rikako Oryo, Mika breaks down in tears, blaming herself for the tragedy. This is the moment her distrust of latent criminals is solidified.]
But, unlike Ginoza (a 28-year-old adult man), over half the fandom decided that Mika was so awful, so totally unforgivable, such a “heinous cunt,” that they were unwilling to allow her the time and space to grow beyond her trauma and immaturity. But why? Is it because we’ve been taught to judge women, even fictional ones, based on a different set of criteria than men? I think the answer is obvious, and I urge fans who dislike Mika’s character with such intensity to seriously examine their reasoning. I don’t mean to say that she’s infallible (hardly) or that it’s wrong to dislike her. Everyone is entitled to their opinion, and no one person’s take is more valid than another’s, but it’s definitely something to think about in the larger conversation that is media analysis.
Which brings me to Akane Tsunemori, someone who fits all the abovementioned criteria for a “likeable” female character. [Another note: I love Akane, and none of this is meant to disparage her. I am simply trying to point out that she’s a more easily digestible female when viewed through the patriarchal lens of pop culture.] She’s smart but not arrogant about it, strong-willed but never disagreeable, empathetic but not easily led by her emotions, and most importantly, she’s always kind to the fandom’s male faves. She is, in almost every way, trademark "Best Girl" material, and Mika is her foil (at least in PP2). She’s set up to be the anti-Akane, both in personality and narrative function. If Akane trusts someone, Mika doesn’t. If Akane wants to bend the rules, Mika is rigid in upholding them. If Akane isn’t afraid of clouding her Hue, Mika is downright terrified.
Though it’s never stated outright, she probably hoped Akane would serve as a mentor figure, yet we see none of that from the senior Inspector, who often abandons Mika to chase down seemingly wild leads and appears to be stuck in the past, yearning for the original Division 01. (Mika even says as much to Ginoza in a novelization of the first film.) On top of that, I think it’s important to remember that we’re predisposed to side with Akane, as she is both our POV protagonist *and* the hero of the narrative. We have unprecedented access to her private moments, motivations, and methodology. We know she means well and trust that her unconventional strategy will pay off in the end. Mika does not. All she knows is that her direct superior is habitually breaking the rules, overloading her team with what feels like excessive busywork, and ignoring the more bureaucratic side of the job in favor of unconventional/unsanctioned detective work. If I’m being perfectly honest, I would also be submitting concerned reports to my boss.

[When Akane blatantly disregards Sibyl's judgement of bomber Akira Kitazawa, talking him down from a Crime Coefficient of 302 to 299, Mika confronts her for putting both their colleagues and nearby civilians in danger. This later proves to be the right call, as Kitazawa attacks Inspector Risa Aoyanagi and escapes police custody.]

[While investigating Kirito Kamui, Akane keeps her suspicions/theories close to the chest, leaving Mika and the rest of Division 01 in the dark as to her game plan.]

[Although Akane's decision to entrust Hinakawa with all 185 Halos proves to be the right one, it's understandable why Mika is taken aback by her placing so much responsibility on a single subordinate -- especially one with Hinakawa's history.]
Now, that’s not to say Mika’s feelings about Akane are purely altruistic. She’s definitely jealous of her fellow Inspector and resents her standing within the Bureau, which makes her behave in ways both petty and vindictive. But I’d argue that this, too, is understandable, if not wholly forgivable, when viewed through Mika’s eyes. Picture this: You’re the youngest-ever recruit to a highly coveted position. You follow protocol to a T, are deferential to your superiors, and show a genuine aptitude for the job. Even your callousness toward the Enforcers (again, your childhood best friend was butchered by a latent criminal) is in accordance with Sybil’s will. Shitty, yes, but standard for someone raised within the Orwellian hellscape of 2100s Japan. And yet, everyone around you prefers your senior Inspector. Your subordinates defer to her when you’re the officer in charge (Hinakawa) and even help her game the system (Ginoza). The Chief tells you you’re boring, but displays obvious favoritism toward her. This severely harms your self-esteem and colors the way you interact with everyone around you. After all, it’s hard to feel like a valued member of the team when you’re being undermined and lectured at every turn. This doesn’t excuse Mika’s behavior, and if she didn’t evolve, I might understand some of the hate, but she does evolve. Spectacularly. She’s just not Akane, and that’s okay.

[While dealing with the hostage situation in PP2, Mika notices Hinakawa working on something off to the side. When she confronts him about it, he admits that he's acting on Akane's orders, even though Mika is technically the officer in charge.]

[A similar incident occurs in Sinners of the System: Case. 1, when Ginoza shoots down Mika's (admittedly ridiculous) plan, which she interprets as him once again siding with Akane over her.]
Again, this is good storytelling at work, and you can acknowledge that these two women are diametrically opposed and still appreciate -- hell, even like -- both of them for the well-written characters they are. After all, most Psycho-Pass fans like both Kougami and Ginoza in PP1 despite their many differences, not to mention the fact that Ginoza is (and I say this with love) a giant asshole. Let’s not forget, he was *this close* to microwaving Kougami at Chief Kasei’s behest. You can tell yourself he wouldn’t have, but are you sure? Are you really sure? But we forgive him, because he’s a man. Anyway, back to Akane and Mika. For reasons I’ll never understand, many fans find it borderline impossible to love two women with beef, whether it’s one-sided or mutual. There can only be one Best Girl, and everyone better be on her team. It reminds me of the Sansa vs. Daenerys discourse that gripped the Game of Thrones fandom in its last few seasons. This is doubly ridiculous in Psycho-Pass’s case, because Akane and Mika come to trust, respect, and depend on each other. But people decided to hate this 19-year-old forever, so none of that matters.

[Notice how Ginoza's gaze narrows ominously in the last frame, suggesting he might actually have pulled the trigger, thereby killing his best friend, had Akane not intervened.]
Now, let’s return to my earlier point about certain fans irrationally hating any female character they deem unworthy of their blorbo, husbando, etc. This is where Parasocial Relationships become extremely interesting. As mentioned above, Ginoza is my favorite character in Psycho-Pass, which I think is pretty common. While I myself have never been one for self-insertion or creating OCs to pair with my favorite characters, I understand that it’s a popular trend, and if you enjoy it, more power to you. It becomes problematic, however, when those who engage in self-shipping/OC-shipping decide to collectively gang up on the female character creators have paired (or hinted at pairing) with the object of their affection. Enter GinoMika. Now, I know what you’re thinking -- “But Mika’s a lesbian!” I don’t necessarily agree. Do I think she was in love with her best friend at Oso Academy? Yes. Do I think she had a crush on Yayoi at the beginning of PP2? Yes. Do I also think it’s obvious she currently has feelings for Ginoza, which have been steadily growing since Sinners of the System? Absolutely. For this reason, I interpret her as being both bisexual and demisexual. But that’s beside the point --
The point is that many Ginoza fans who ship him with themselves, their OCs, or Akane (remember, she’s Best Girl) seem to enjoy trashing on Mika like it’s an Olympic sport. And when I say “trashing,” I don’t mean your normal yet still disappointing level of ship nonsense; I mean unhinged, violent rhetoric that makes me feel like the Internet is a place where women can never win. And why? Because she was mean to him when she first started working for the MWPSB? As if he was oh-so-kind to the Enforcers who worked under him. I seem to recall him screaming at his father and threatening to “make him pay” for visiting his sick wife without permission. Oh, and then there was the time he introduced Akane to her new colleagues by telling her, “Don’t think that the guys you’re about to meet are humans like us.” But yes, Mika once told him that she didn’t want his opinion as a latent criminal, which is so much worse. And before you can say that she’s still a bitch to him, let me point out that she is a textbook tsundere. That’s how she flirts, shows affection, etc. She can never come right out and say what she means, because that would make her vulnerable. But she can surreptitiously tell Ginoza he better come back alive by insisting he return her special Dominator. You know, because it would be a real hassle if she had to replace that thing.

[The language Ginoza uses when introducing Akane to the Enforcers, including his own best friend and father, is deeply dehumanizing.]

[When Aoyanagi takes Masaoka to visit his estranged wife, Ginoza reacts with explosive anger, reprimanding his father in front of their colleagues and threatening to retaliate should he do it again.]
Which brings us, at long last, to the male portion of the fandom. While many female fans like to call Mika out for her more negative character traits, completely ignoring any and all growth she’s experienced since PP2, male fans tend to direct their anger, dislike, etc. in a much more aggressive manner. I wish I was exaggerating when I say that I’ve seen multiple posts praying for Mika’s rape and subsequent murder. You can’t dive into a single “Season 4 Wish List” thread without finding at least one person wishing extreme ill on Mika Shimotsuki. It's pure misogyny, classic “I’ll fuck the bitch right out of her” rhetoric, and it has no place in this fandom or any other. You would never see a male character being talked about in these terms. Consider this: There’s more fan fiction featuring Mika being raped or coerced into sex by her tormentor, Sakuya Togane, than her having a positive, consensual experience with any other character. Love her or hate her, that is extremely fucked up. We as a fandom need to do better, because once this type of misogyny can be weaponized against fictional characters, it becomes much easier to use against real people. Fan culture, though it might seem trivial, says a lot about us and our values.

[This is just a sampling of the comments you'll find on Twitter, Tumblr, Reddit, and other social media sites.]
That said, I’d like to end this essay on a more positive note, so let’s take a look at all the ways in which Mika has become a better, more compassionate human being over the course of the series...
By PP3, she shows obvious concern for her Enforcers, values their opinions, and treats them like integral members of her team. In an especially cute scene, she even fist-bumps Tenma Todoroki after they work seamlessly to defeat Koichi Azusawa’s henchmen. She also makes a point to attend the party thrown in the Enforcers’ quarters, as she now longs to be part of the gang -- a gang she would have actively shunned in PP2.
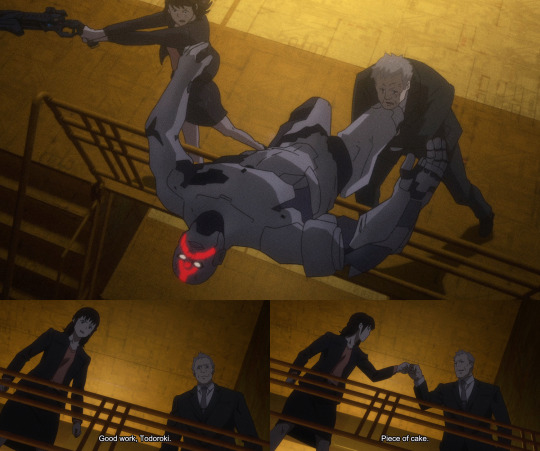

[During First Inspector, Mika shows time and again that she's willing to work with and for her Enforcers.]

[As Chief, Mika realizes that Enforcers deserve respect and gratitude from their superiors. They are no longer dogs to her.]

[In PP2, Mika tells Ginoza she doesn't care what the Enforcers think of her. By PP3, however, we see her display concern that her team might find her dull. She wants to be liked and accepted by them.]
She becomes far more flexible with her co-workers, allowing Inspectors Arata Shindo and Kei Mikhail Ignatov plenty of freedom to conduct investigations as they see fit. Yes, she consistently scolds them (textbook tsundere behavior), but this is done in a manner far more humorous than anything else. We know she actually trusts them and has their best interests at heart; she just can’t bring herself to say it aloud. She also repeatedly takes heat from Chief Hosorogi on their behalf and is genuinely worried for Arata when it seems like Sibyl might “eliminate” him. The palpable relief on her face when she finds out he’s allowed to remain an Inspector speaks volumes.
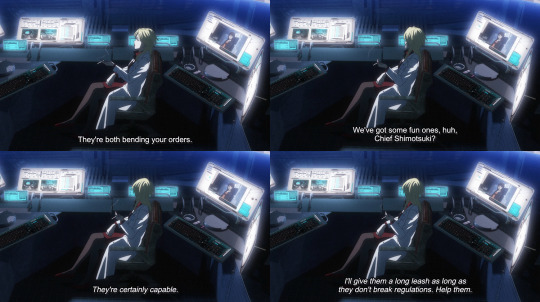
[Throughout PP3, Mika allows Kei and Arata to play to their individual strengths, even if it means bending the rules -- something she would never have done in PP2 or the first film.]

[Just look at that excited face. No caption necessary.]
She goes out of her way to make sure the immigrant prostitutes saved by religious leader Joseph Auma are protected following his death. This is an especially big deal, since many of these individuals are latent criminals, and Mika is forced to ask her newfound nemesis, Frederica Hanashiro, for a favor in order to secure their safety. When she tries to pretend it’s no big deal, Frederica calls her bluff by pointing out that no one would stoop to asking someone they hate for help in order to protect people whose fates they don’t care about.
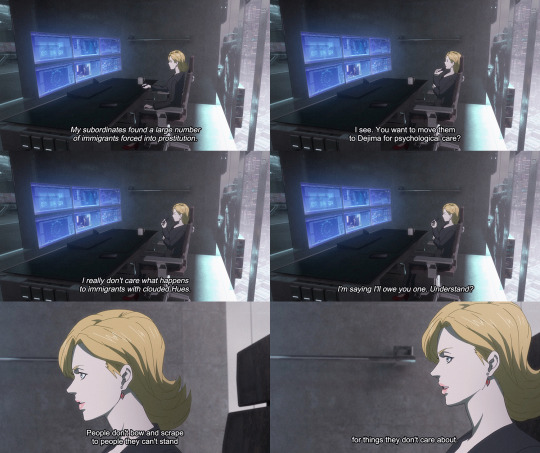
[Even though Mika detests Frederica, she puts the well-being of the immigrants before her own pride.]
In Sinners of the System: Case. 1, her distrust of latent criminals is permanently altered after dealing with Izumi Yasaka, whom she works tirelessly to rescue and comes to view as brave, capable, and worthy of reintegration into society. She also displays genuine concern for and lack of discrimination toward Takeya Kukuri, the young son of a latent criminal, and is horrified to discover that the latent criminal inmates at Sanctuary are being used as disposable tools to move nuclear waste canisters.

[Sinners of the System: Case. 1 marks a decided shift in the way Mika views latent criminals. Instead of lumping them all together, she begins to see them as individuals who deserve basic human rights.]

[Even though Mika is unable to save all the latent criminals at Sanctuary, she does everything in her power to ensure Yasaka and Takeya walk away clean.]
When Enforcer Mao Kisaragi turns out to be the “fox within the CID,” Mika and the rest of Division 01 are united in supporting her claim of innocence. Mika trusts (without concrete proof, mind you) that she’s telling the truth about being an unwitting accomplice, something she never would have done in PP2 or even the first film.

[While the old Mika would have been the first person to distrust Kisaragi, here we see her standing up for the beleaguered Enforcer.]
She comes to respect Division 01 (Akane, Ginoza, Sugo, Hinakawa, Kunizuka, and Shion), views them as a surrogate family, and misses them once their unit is disbanded. In Sinners of the System: Case. 3, Frederica Hanashiro, who temporarily worked as part of their unit, says, “CID Division 01… They’re not just capable; they have a rare teamwork that overcomes the barrier between Inspectors and Enforcers.” Yes, this is mostly due to Akane’s guiding influence, but it’s clear Frederica is talking about the whole team. It’s taken Mika years to get there, but she is now definitely part of the group, not a jealous outsider looking in. In fact, even Mika’s obvious dislike of Frederica in PP3 is a clear result of this affection. After finally finding a place to belong, she feels as though Frederica swooped in and stole her found family, leaving her right back where she started -- on the outside.

[Though she'll never admit it, Mika views Ginoza as both a mentor and a friend. When he leaves the PSB to join SAD/MOFA, she misses having him around.]
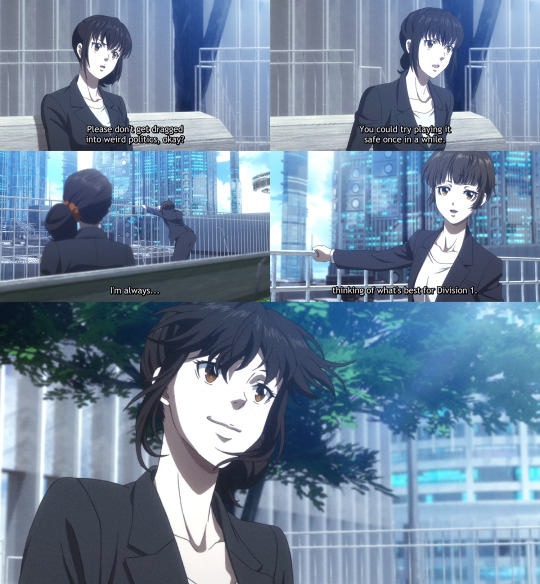

[During her lowest moment in PP2, a jealous Mika actually hopes that Akane's Hue will darken. In Sinners of the System: Case. 2, she pleads with her to take her own safety more seriously. It's clear a big change has occurred in the intervening years.]

[Instead of feeling constant competition with Akane, by PP3, Mika is finally able to give her her due. It's clear they trust and respect each other despite their many differences.]
She’s grown from an immature young woman who couldn’t bring herself to take responsibility for her failures -- most notably her involvement in Akane’s grandmother’s murder -- to a responsible PSB Chief who holds herself accountable for anything that goes wrong with her Inspectors and Enforcers. This is most evident in her reaction to Koichi Azusawa taking control of Nona Tower and subsequently endangering the lives of MWPSB faculty and agents. We first see inklings of this change near the end of PP2, when Kunizuka tells Mika she’ll never forgive the person who gave up Aoi Tsunemori’s location, and Mika responds in kind. It’s clear that she’s not merely parroting a response to save her own skin but is deeply troubled and filled with regret over her own actions.

[In PP2, Mika is constantly blaming others for her mistakes. By First Inspector, she's owning mistakes she didn't even make.]

[Mika trusts her team so much, she's willing to put her job on the line.]

[Although Mika doesn't come clean to Kunizuka about her role in Aoi Tsunemori's death, it's clear she’s haunted by it. Later, when she confesses the truth to Ginoza, he admits to feeling a similar guilt over the way he treated his late father, telling Mika they'll have to bear their respective shame silently for the rest of their lives.]
And lastly, I believe the biggest example of Mika's growth can be found in what is arguably her most important relationship -- the one she shares with Ginoza. Whether you view them as mentor/mentee, begrudging friends, potential love interests, or all three, you can't deny that they have one of the most interesting and entertaining dynamics in the series. As mentioned above, when Mika first meets Ginoza, she views him as a cautionary tale. His demotion from Inspector to Enforcer is her worst nightmare, something that could conceivably happen to her, though she'll never admit it. Because of this, she treats him with hostility, disregarding his opinions and shunning his advice. But the longer they work together, the more we realize that Ginoza brings out the best in Mika -- and vice-versa. His calm, cool demeanor tempers her fiery spirit, and her enthusiasm makes him feel like he still has a purpose. By the time PP3 rolls around, he's become her #1 confidant, the person she calls whenever she has intel to share, grievances to air, etc. And you can't deny that Mika is the one person who makes Ginoza funny. Their flirtatious banter is genuinely charming and shows the softer, more human side of both their characters.

[Given her history with latent criminals, Mika refuses to listen to Ginoza, even when he's coming from a place of experience and genuinely trying to help her.]

[After working together for several years, Mika learns to value Ginoza's opinion and even feels proud when he compliments her.]

[During the Sanctuary case, Ginoza admits to both Akane and himself that being an Enforcer isn't so bad, as long as Mika is the one calling the shots. He knows she has a good heart, and working for her reminds him why he joined the MWPSB in the first place.]

[Notice how Mika's body language changes from PP2 to Sinners of the System. She now looks at Ginoza with appreciation and, in certain instances, affection. The fact that he views her the same way speaks volumes about how far their relationship has come.]
If you made it to the end of this mammoth post, thank you for sticking with me. Hopefully, we can all treat Mika with a little more patience, kindness, and respect when PP4 arrives.
#psycho pass#psycho-pass#pp#shimotsuki mika#tsunemori akane#ginoza nobuchika#ginomika#ginoza x mika#anime#animanga#anime meta#women in anime#women in media#feminism#tsundere#my meta#text post#fandom discourse#did i really write a 4000 word essay defending an anime character?#you fucking bet i did#and i brought receipts
151 notes
·
View notes
Note
Will Marianne's actual in-game characterization ever be represented again in Heroes, or is she doomed to be flanderized into "Momo suffered so much sad uwu" for the rest of the game's timespan?
Mean me wants to say she has no characterisation to give anything substantial to FEH to work around, but it's me being mean.
I guess that anything relating to her Relic, and Relics in general, will be flanderised and the truth will never be revealed because tea bags, and even if FEH tried, last year, with F!F!Billy (was it last year?) to give more meat to that subplot by saying Sothis from Nopes was pissed and wants revenge because her kin were slaughtered, even FEH can't craft stuff KT/IS left purposedly hanging in their games.
Sobbing about Momo though, give the impression that the devs care about the "lore" of Fodlan and give another, imo, more interesting angle to Marianne even if it comes as the cost of woobifying Momo but hey, since it's a given that no one gives a fuck about Nabateans, it's alright, poor Momo was a victim of his curse uwu, let's just not/never talk about what that curse is.
#anon#replies#back in the days i had hopes for a WoH game or material but#it will never see the day#unless IS decides to not give a fuck about Fodlan and the potential dollars it can bring#and release material/notes that will reveal that the uwu relics had names back when they were living people#and how some humans were perfectly aware that Seiros'n'co were giant lizards but didn't want to slaughter them bcs their ears were pointy#or ban them from 'having power over the people' because their ears were pointy#I'm not talking about dev notes like the leaked GF stuff with a man using his pp on an octillery#but notes saying that 'back then' humans weren't that opposed to befriend the pointy ears#and maybe have hybrids together or something#but we know if something like this is revealed#I men look at how they tried to retcon Supreme Leader's crust discourse in nopes#or how the lolcalisation tried to erase the 'race' mention in Dimitri's convo with Zelestia in Engage#imo it's telling enough that since Fodlan still sells its characters have to be revamped to continue selling even if they don't have#anything to do with the characters they were in their base game anymore#I mean look at the travesty that is FEH!Lyon
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Who up giving Tacitus gender envy.
#valeria messallina#[Joshel S. R. (1997). “Female Desire and the Discourse of Empire: Tacitus' Messalina”#In Roman Sexualities (pp. p. 221-254) Ed. by J. Hallett and M. Skinner.]#tacitus
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
hey guys not to get too into it but would anyone be in favour of a weird tag specifically for scott stuff? I usually don't maintag my art of him anyway so if you've got that blocked it won't help. or do we simply not care enough lol
#delete later#discourse#<-- i guess#i dont rlly make art For the ccs anyway so idc too much eitherway#but if one of u doesnt wanna see content of him at all on ur feed thats an easy fix on my end#it would be like. shmajhor or smth dumb lol#cw shcott shmajor 😭😭#i usually just tag it as 'scott' which. i can understand if pp don't wanna block that lmao
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Anyone making fun of this shot either never took a 1st aid class or never paid attention in them and it fucking shows. Stfu please <3
#she passed out#it's clearly been at least a few minutes#this is not fainting#she fell slam hard onto the ground#they obviously moved locations since then#there is protocol to this which is actually. Almost entirely accurate to a real-life scenario here.#u can't expect them to exactly coddle her also#esp while they're all trying to reevaluate exactly wtf is going on and where to go#she passed out after she found out one of her best friends died after everything they tried and I know I sure as hell#would not want 4 other ppl over me while in that position#this is one of the only times I will pick v9 discourse but please kindly stfu if you're one of those “BuT They JUSt LeFT hEr TheRe haha” pp#ok I'm done now#riin rewatches v9#9x1
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
neurodivergence IS a disability and not acknowledging that is ableist
some autistic people need caretakers, are they not disabled? some people with panic disorders or agoraphobia physically cannot go outside, are they not disabled? people with severe social phobias cannot hold a job or support themselves, are they not disabled? people with addictions physically cannot go without their substance and are often discriminated against because of it, are they not disabled? plenty of people with mental illness have physical pain and symptoms to the point where it is indistinguishable from a chronic illness, are they not disabled? what about people with amnesia?
do you think being neurodivergent means theyre "just sad" and not actually sick in the literal brain? do you think theyre "pretending to be disabled"? is that not what abled people say to you all the time? do you enjoy turning that on your own community? are you proud of that?
on the flip side, plenty of people with chronic illness arent disabled. plenty of them go their entire lives without even noticing or knowing or even think its normal. many even recover. if you try to lump everyone into the neat box of "physically ill and disabled" and "mentally ill and able-bodied" you are going to get nowhere real quick.
because dis/abled are medical terms used by the government to describe how you (dont) function in a capitalist society, and not an indicator of the pain you go through. you arent disabled because you have an illness: youre disabled because you cant support yourself. thats it.
invisible and neurological disabilities belong in your disability rights movement, always
#💿 red#NO fucking cr*pp*nks on this post or on my blog or in my line of sight. get banished to the shadow realm dipshit#methinks yall are determined on gatekeeping your Disabled Dick Measuring Contest#<- which btw. if this were literal it would be awesome. mines huge id win. but its not literal its a metaphor. you get it.#disabled#unitypunk#tw discourse#<- ?#cripls
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi mx witch, I’ve been debating whether to send this in for a bit but I am curious what you think. I’ve been going back and forth on the ongoing “can you read at least one singular book by a Black woman” discussion bc there is a thing where especially white readers (I am also white, non american but also somewhere with significant Black diaspora) hold up Black authors as somehow being the pinnacle of diversity and ending the conversation there. I don’t think you are doing this btw but this is the reading comprehension site. I just worry it doesn’t prompt people to think about more general issues of diversity in publishing when E/SE/S Asian authors also get screwed over in the industry (especially Asian women who don’t want to write about being Oppressed by their Traditional Culture) and there are just shamefully few published Indigenous authors from any continent.
HOWEVER. then I see some of the more tar pit responses to your book posts and to the rap discourse (oh my god the rap discourse) and I am like. hmmm maybe we should stay focussed on prompting people to challenge their anti-blackness for a bit when so many people are clearly incapable of the baby step of reading more widely. Much to consider.
📚
ps if you post this and anyone reads it and goes “oh wow this is so right, I guess I don’t need to read books by Black women”: no
pps SORRY for spam if this is a second anon, I asked this morning with dodgy signal and have no idea if it went through or if you are just swamped/don’t want to reply. no pressure.
hi anon,
I think it's a really good and thoughtful question, and I appreciate the good faith engagement with this question a lot! your concern reminds me a lot of something Yaa Gyasi (an author who's come up a lot in discussion about Black women writers!) said in this interview a few years ago:
Representation isn’t enough. It’s not enough to see people as representatives, and not actually engage with what they’re trying to say. I guess I’ve been feeling dispirited about the way that my work gets read, as it allows people to pat themselves on the back and feel like they’ve done something. Is literature enough? That’s frankly the question I’ve been asking this past year. I used to be the kind of person who would say this is making us more empathetic. But I’m not sure anymore if that’s what’s happening. Are you reading, or are you reading?
and I definitely agree with her, and think that a lot of people have a tendency to reduce authors who aren't white, heterosexual men to tokens whose work they're morally obligated to read to be Good Allies, rather than because the work genuinely speaks to them, entertains them, moves them, challenges them, or does anything else that literature is capable of. it doesn't help that the publishing industry itself has an awful tendency of tokenzing authors, as you alluded to.
this is one of the reasons why I never include spaces pertaining to an author's personal identity on the reading bingo sheets that I design. I know that prompts like "read a book by a Native author" or "read a book by a trans author" and so on are quite popular in many book bingo spaces, but to me they run the risk of tokenizing those authors and make it seem as if it's fine if, for instance, no Native or trans authors are found anywhere else on the sheet, since they have a designated space. which isn't a perfect solution, to be sure - without a specific prompt, it's just as likely that there will be zero authors who are Native or trans or whatever other marginalized identity one can come up with on the bingo sheet. I'll be honest: as much as I love seeing the bingo sheets my followers are filling out, I'm a little stunned and disheartened to see how starkly white many of them are!
in this conversation, where people are being challenged to name even a single author who's a Black woman and coming up short, I think many people, especially hobby readers, are maybe realizing for the first time that they way they read doesn't quite live up to the ideas of equity that they personally hold and they're interested in changing that now. I've received a lot of feedback that does boil down to people excitedly reporting that they're now deliberately rushing to the library to seek out books by Black woman, and I can easily see how, pessimistically, that could be seen as further tokenizing those authors.
as much as I've rolled my eyes at the people who loudly insist that they couldn't possibly know what gender, race, ethnicity, etc, any author is because they only care about the story (with the implication being that knowing anything about the author would somehow cheapen the story - lmao), I do somewhat understand where they're coming from. while colorblindness is certainly not the solution, it would be ideal if nobody had to think much about hitting any kind of quota in regards to their reading habits. and I'm certainly not advocating for anything that strictly structured! but if so many people can't name a single Black woman who's written a book, then we need to acknowledge that there's a reason for that, and that not all authors are being read equally, and that it takes an active effort to course correct something like that.
my hope is that, with time, readers broadening their horizons enough that they don't have to actively seek out Black women authors (or Black authors in general, or Asian authors, or Latine authors, or trans or Muslim or disabled or Jewish authors, or authors translated into English, and so on) because those authors and their works will become a natural part of their literary diet that no single author is a sole representative of any group or perspective and can be appreciated solely on the basis of their craft.
but maybe the first baby step, as you said, has to be googling "Black woman authors." and maybe that's a little tokenizing! but when we're beginning from the rock bottom position of people struggling to name a single Black woman author at all, you have to start somewhere. I'm really glad to see people actually getting excited to do the work, and I hope they don't stop at reading one (1) book by Yaa Gyasi or Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie because a tumblr post made them feel uncomfortable.
I hope that makes sense and is a satisfying answer!
199 notes
·
View notes
Note
Since you've already talked about ships, what are your thoughts on the whole top/bottom debates here? Tbh I’m over this bottom tom/top harry trend these weeks. It doesn’t make sense for their dynamic and feels like pp are doing it just to be edgy or different. Flipping roles doesn’t make it unique, it just feels like flat ooc discourse. I don't think Tom’s pride and emotional repression fit a submissive role.
Holy shit, this is like a blast from the past since I haven't engaged with top/bottom discourse since 2014 (I had a different blog then) and I hoped I was past these days.
See, fictional characters, when it comes to this sort of stuff, are very flexible. You can write yourself into almost anything and make it realistic. Even if a character is a certain way, circumstances and conditions in a specific story will force the character to change to accommodate. It's how fictional characters work. Yes, they have their set traits, but they can still be pushed to do quite a bit. Especially when it comes to smut.
So personally, I don't have a fixed top/bottom designation for any of my ships. All of them switch depending on the situation, preferences, and the specific story being told with them. Becouse, contrary to what you think, the bottom position isn't always submissive and the top one isn't always dominant, and whatever sex position you prefer doesn't necessarily indicate anything regarding how submissive/dominant you are. These are not the same thing.
But if we talk about Tomarry/Harrymort specifically (I haven't really interacted with this pairing in some time, and I wrote my thoughts about them in general here), I only like them when they switch. "Mark him as his equal" and all that. My preferred Tomarry dynamic (back when I read it) was a constant push and pull, neither of them was ever the person in power/dominance in the relationship because they're equals — that's the point.
Harry isn't a submissive character either. Harry would never submit to Tom. Saying he is more likely to be submissive than Tom is OOC and a misunderstanding of his character. Harry doesn't bow down to others, so even when he is written as a bottom, he wouldn't be submissive about it.
Similarly, Tom can be written as a bottom without submitting control over to Harry. It can be done, and can be done interestingly (which is the most important thing when it comes to fanfiction and storytelling as a whole).
Tom is also weird and contradictory as a character. He's a control freak, so whatever position he's in, he'd have demands on how exactly things should go (he can do so both as a top or a bottom). But he's also so thirsty for validation and praise. I'm an advocate of Voldemrot having a praise kink, like, when I was writing my giant Voldemort psychoanalysis essays series from about a year ago the way I summarized it to my irl friends was "Voldemort has a praise kink" since his desire for praise is at the core of a lot of his important decisions.
Tom isn't some super dom who could never be vulnerable and doesn't have insecurities about anything — the guy literally tore his soul apart, what can be more self-hating than that!
Writing him as incapable of vulnerability and trust (eventually) feels like a boring and hollow character that is more cardboard than a person. Like, I have no interest in this sort of Voldemort because there is no spice to a character like that. No meat to chew on. And Voldemort in the books doesn't appear that way at all. He likes silly puns, and he forces others into his proximity when it seems he is vulnerable to make them uncomfortable; he doesn't like being vulnerable, but he's aware he has these vulnerabilities (imperfections he despises about himself). He talks at length about his muggle father because he's a sentimental loser who likes to monolog. He, somehow, still loves his mom. He wants to have a real human connection so badly that he completely missed what friendship means. He is a lonely nerd. He is impulsive and emotional. He likes to gossip about other people's relationships (yes, he does this in the books). He is a complex character you can have fun with, why limit yourself?
I used to like Tomarrymort becouse of the changes Tom's character would have to go through to be in a relationship with Harry. I read it because I love the idea of a character who got so used to hate and distrust, learning to be vulnerable. That was a huge part of what I found fun in these stories.
And Harry learned just as much from Tom in turn. He learned to like himself more, be confident in his abilities and cabalities. Learned that he has strengths beyond just Quidditch.
The fun is in this arc for both of them. Where they both become better (or, sometimes worse, depending on the story, but I usually preferred the ones where they got better) through their very explosive dynamic. They are foils and narrative mirrors, and pushing them together forces growth. And sex scenes in Tommarymort stories are an opportunity to explore that vulnerability, for both Tom and Harry. That's part of the appeal (at least for me).
For that kind of explosive dynamic that is inherently vulnerable for both of them, in my preferred Tomarrymort dynamic, they switch. (But so do all my ships. I'm against fixed top/bottom dynamics since the answer is it would be what serves the story/scene/themes/character arcs best)
#harry potter#hp#hp meta#asks#anonymous#harry potter meta#harry james potter#ship talk#tommarymort#tommary#harrymort#Voldemort#tom riddle#tom marvolo riddle
93 notes
·
View notes
Note
AUGHHHAKAAKDHH
*Choking on water*
NOEL AND KUUYA DICK HCS???
AUAUAGHH AHAAHUAUA
i think we've already had some noel/kuuya penis discourse at some point (had noel battling small pp allegations for a hot minute) , and while its still ultimately up to everyones interpretation, i think the semi-conclusion that we came to is that noel is thicker and kuuya is longer ^^_b
#ask#anon#yandere oc#kuuya posting#noel posting#coke can noel confirmed semi-canon#i think ive said noels pp is like 5-6 inches#then i guess its like...... 1.7 inches in diameter#kuuya is around 6-7 x 1.4 then#and this is tmi but personally...................................................a bit of stretch is superior i fear
270 notes
·
View notes
Note
Sorry if you've already answered this. But what's wrong with the dbf fics? I understand and agree with what you're saying about the way people are writing ppcu characters and needing cultural context and how important it is. But I'm lost about the dbf fics. And I was curious how you feel about the large age gap fics too and if you feel that plays a part at all. Those are my favorite tropes, so I'm just trying to understand. TY!
hi, ty for asking, i tried to write a concise answer and add some links, but my unedited extended edition answer is under the 'keep reading'
in one sentence: I think the trope has become shorthand for the popular fics that often romanticize fetishized roles (white-coded young reader x hypersexualized but otherwise flattened joel) without awareness or intention
-> tl;dr (the bullet points--i really tried to be brief):
the tropes aren’t inherently harmful, there are often patterns in those fics that reinforce patriarchal, settler colonial white supremacist values (e.g. ‘taboo’ nature of the dbf trope is rooted in patriarchal father/daughter purity/women as property/purity as value)
the dbf tag often goes hand in hand with white-coded reader inserts (not a crime, but not inclusive) and hypersexualized ppcu characters (fetishization of pp as a latino disguised as a trope)
popular narratives reinforce systems of power—even when unintentional
personally, i enjoy tropes that also can often reinforce/romanticize stereotypes, and i have written them too. i want to be an anti-racist ally and do better
critiquing issues in tropes isn’t a call for censorship or an interpersonal conflict—it is part of being anti-racist and decolonizing internalized beliefs and being aware of the impact of storytelling
-> some links to consider for building your own critical media literacy:
i encourage folks to read from/look up videos of bell hooks, Kimberlé Crenshaw, Angela Davis, Oyèrónkẹ́ Oyěwùmí, and other BIPOC activists, thinkers, civil rights activists, philosophers, etc. to develop a critical, intersectional feminist lens for yourself
Race didn’t exist until European colonization introduced racism
for more fanfic specific related info (not about dbf but relevant to recurring discourse):
On Fanfiction, Fandom, and Why Criticism Is Healthy
What Fandom Racism Looks Like: Fandom Wank
fandom racism 101: feeling fragile
fandom racism 101: clocking and closing the empathy gap
the long answer:
(i hope this answers the question. i’ve never been concise in my life. and i wrote this half on my phone and half on my laptop. gonna just send tweet now before i hyperfixate on this for days and write 50 pages of thoughts you didn’t ask for <3)
I wanna preface by clarifying that for most of my rants i am not saying ‘in my opinion these tropes are bad and nobody should write or read them’ but that from a macro/zoomed out view of the fandom there are patterns that that reinforce racialized stereotypes or fetishize characters or idolize colonial/patriarchal values that have systemically been used to prop up structural racism from the bottom up. A dbf fic isn’t inherently racist or a microaggression; neither is an age gap or noncon or whatever trope. There is, however, a pervasive pattern where the dbf trope often goes hand in hand with factors that do reinforce white-coded reader inserts as young/pure/valuable and pp characters as flattened/fetishized, or rough/stoic without depth, or pervy/sleazy. These narratives can reinforce the white supremacist ideology/propaganda of' latino man = dangerous and rough' and 'white (coded) girl = pure/good' …and often the catalyst for his character development centers her reactions bc that ideology doesn’t accept a brown man having growth/redemption/softness without centering the white girl. Over time those fics become the most popular/praised and set the cultural tone in the fandom. A culture that puts white-coded reader x dbf joel fics on a pedestal—which doesn’t just appeal to more white readers but also tells BIPOC readers they aren’t being pictured, considered, or embraced. Repetition and emphasis of cultural narratives can reproduce and keep dominant ideologies in power–-even unintentionally. And the fics aren’t being read in a vacuum, we all exist within the context of a society built on power, privilege, and oppression.
In my completely personal opinion I’m not drawn to dbf tropes bc the ‘risk’ associated with getting caught by reader’s dad or betraying dad isn’t something that resonates with me as relatable—but that is only my opinion and I wouldn’t tell other people not to read or write dbf fics just because they aren’t my favorite. I do encourage the writers and readers in the fandom that if they want to shift the cultural norm in this fandom to a more diverse and inclusive environment, they need to be critical of the fics they read/write/share, bc liking or disliking the tropes is an opinion---but the presence of patriarchal values and racial fetishization that serves white supremacy is just a fact. it's there in the power dynamics of the stories. and it's a fact that patriarchal values are historically interlinked with white supremacy. these values and stereotypes exist in other forms of popular media, not just fics--but it's in fanfic that we have more control over what is written and shared.
if you don't have internalized shame around sex and don't subscribe to patriarchal gender power roles, purity culture, property-based father-daughter relationships... there is nothing specifically taboo about fucking your dad's best friend. but in the context of our socially constructed norms it's a risque pairing that sets up a forbidden relationship that moves the story along and raises the suspense. and the characters themselves are usually written with those cultural values that portray the daughter's sexuality as reflecting on her father's honor even if you don't have those beliefs yourself. – like let's reaaaally consider why it’s taboo to fuck or date dad’s best friend…
or why it’s a cultural norm that dad’s get bent out of shape about who their daughters fuck…
or why virginity is treated like it reflects on a woman’s value….
why purity ceremonies exist….
we know that historically women have been treated as the patriarch’s property (dad or husband)... now dad has been betrayed by his best friend bc (following the patriarchy/property logic) he lowered his daughters value …his daughter betrayed his loyalty/disobeyed etc etc.
and sure, maybe it’s not that deep to folks reading and writing and it’s just another drop in the bucket along with movies and tv shows and jokes about dad’s with shotguns on their porch and girls being shamed for being sexual while boys are praised…but it also continues to normalize those ideas by repeating them over and over
...so now we can see that the dbf trope in itself is rooted in patriarchal values which are intertwined with puritanical christian values that were spread (enforced) by settler colonization (to societies that had different beliefs and kinship models and gender roles etc.).
and it’s not that christian values are racist, but that the historical context we live in—where puritanical patriarchal values are politicized and weaponized against marginalized folks like BIPOC, queer, disabled, etc.—means some of those values still prop up structural racism today
the dbf story model is starting from a foundation based on those values---and again, it’s not illegal to write that and it requires education and deconstruction work to see these patterns.
and it requires dedication to interrogate the beliefs they instill in us as individuals and our values—but if people want to change the narrative in a creative space where WE have creative control over the stories, then it’s worth:
1) considering for yourself what you’re reading and how it characterizes the characters and their dynamics
2) having empathy for BIPOC creators that continue to engage and write and share stories in this space even while systems that reinforce white supremacy are being idolized—intentionally or not.
PERSONALLY i don’t care for big age gap fics bc I feel like the trope can easily reinforce the capitalist and colonial fetishization of youth = beauty and virginity = value/something for men to conquer
i don't find that trope personally relatable whether it's traditionally aligned with the values or somehow subverting or satirizing them but you can still learn from reading things you don't relate to and by reading those fics and being confused by the appeal i was inspired to think more critically about the underlying message and why they're so popular
i imagine there is appeal in controlling those dynamics by writing them for yourself or reading them in a way that highlights or frames the benefits for the reader
i'm sure some are written with intention and read with awareness and i also believe some are consumed without critical consideration for the messages being internalized -- and like.. i really don't care if you're into the kink of age gap or dbf -- i'm into masochism and degradation which obviously can perpetuate stereotypes and fetishization and colonial gender framework too
it's not about what women 'should' be able to write and read... it's just calling awareness to the fact that it goes beyond the power dynamics on the surface. i don't believe women should be shamed for whatever kink they have and at the same time when the pervasive kink being praised stems from patriarchal or colonial values that historically oppressed folks with different beliefs, features, gender roles, etc. then it's also valid for folks to critique the harm that might come from continuing to support those stories without uplifting any other viewpoints or narratives.. like if dbf joel x white coded reader was popular and at the same time soft joel x latine reader or black reader or desi reader or east asian reader or any other framework that intentionally doesn't center a white reader were also popular and all over the dash, then it wouldn't be as concerning. if the fandom was full of diverse stories and different value systems and gender roles then it wouldn't be as important to critique.
but one narrative reigns supreme in so many of the tropes bc the patriarchal/colonial values are ubiquitous bc colonizers did their job and the system reinforces itself as it was intended to
it's popular bc it's familiar and relatable to white people and keeps white people centered and comfortable
and if you're comfortable you're less likely to advocate for change
and if you're centered you're more susceptible to seeing non-white people or non-western values as 'other' and 'other' is the first step to dehumanizing people that don't look like you or believe in the same things as you, and it's easier to stay complacent when bad things only happen to 'other's or people you could consider 'less than human' dehumanizing others was historically the foundation for oppressing BIPOC and is being used as rhetoric TODAY (e.g. with conservative ideology in the US branding immigrants as 'others' to placate white folks into being unfazed when immigrants or brown citizens even have their rights violated or worse). aka there are real world consequences to accepting one narrative and upholding it. you don't have to come to tumblr and be an advocate and an ally-- but if you care about BIPOC and marginalized people and it's a part of your value system to be an ally or to be anti-racist then it's worth being critical of what you consume, create, and promote
as another thought experiment, walk with me:
imagine if instead of the most popular fics being reader x joel (hbo joel) imagine if the most popular fics were AUs with joel x sarah’s mom (hbo sarah)... imagine what the fandom would feel like if the most popular pairing was joel and a Black woman?… how might white folks feel? how might BIPOC readers feel? imagine if instead of reader x javier peña being popular… imagine if there were AUs with javi x helena everywhere; or Dave York x carol or Clint Flood x Grace, OR imagine even if they weren’t even canon pairings but javi was most commonly written with a latine coded reader that could speak spanish with him? how would your dash be different?
…i’m not saying those ideas should be the goal.. just maybe imagine what a space would feel like if it weren’t centered on white-coded women as the lovable and fuckable mc and sit with that hypothetical for a while… (and no it still wouldn’t be just flipping the system bc Black and brown folks still don’t have the systemic power and privilege in or out of the fandom) again… it’s not that people are writing these stereotypes or reinforcing hegemony intentionally and that’s because the system is working! it’s keeping the people in power in power by continuing to oppress non-white people (and queer folks and disabled folks and non-christian folks etc) from so many ‘drops in a bucket’ that the oppressed are drowning in an ocean and the white folks are floating on pool floaties and can’t even see how deep the water is.. like white people don’t have to think about a world where the ‘blank slate’ isn’t relatable to them bc it doesn’t exist in western culture and folks write what they know and learn from society and popular media and other fics.. so of course folks are rewriting and enjoying these tropes and they aren’t doing it with malicious intent and there are likely BIPOC folks who are used to the same narratives and find ways to relate or enjoy what they can… but there are also folks who have been faced with these systems of oppression so overtly, for so long they can’t unsee it… anyway, changing what tropes are popular won’t solve structural racism
At the same time, giving folks a safe space to be in community, to share knowledge and learn together, and to be a space that doesn’t uphold white supremacy would make a difference for some folks and would be a drop into a new bucket so to speak.
and, what we consume DOES impact our beliefs and values; and our values shape the relationships we build irl, and the way we vote, and the causes we fight for, and the passions we dedicate our lives to. so maybe on the surface it doesn’t seem that deep to praise a dbf one shot but it also doesn’t take a herculean effort to make a dbf one shot where the reader isn’t white coded, there isn’t a white girl in the moodboard, and where the ppcu character is more than a fetishized projection. even just start with one of those three. i know it’s exhausting to have to do the work (reflecting and making critical choices) to consider the ethics of fanfic, but it’s exhausting for BIPOC folks to live in a world where they still are oppressed and microaggressed and targeted daily… and I, PERSONALLY, want to be someone that contributes to positive change i don’t mean you can’t have your favorite tropes, i just encourage you that if you’d like to be an anti-racist ally consider promoting/writing/reading any trope with intention and even interrogating your own beliefs as an exercise for your own personal growth (and maybe you still love those tropes and personally relate or enjoy them in a way that matters to you and that’s okay, we can all like different things) for example, i like infidelity fics—i get why a lot of people hate them and i think they can reinforce racialized narratives and colonial/patriarchal hegemony, too. i still enjoy the taboo of the dynamic and i’ve tried to write that trope with intention so that my characters are whole people not just a ‘dangerous latino’ that doesn’t stay faithful and writing a reader that is equally culpable in instigating and doesn’t just melt into his arms but talks back and has empowered sexuality and confidence etc. etc. those are things i think help to combat the basic racialized narrative and add something more complex even if it’s just small references to their inner emotions or lives or whatever else makes them more than a cardboard cutout.
and, i also fuck up.
i love a toxic/fuckboy/emotionally constipated man trope (is there a better name for that? probably) which could easily fall into the same issues of the brown man being overly sexualized/fetishized, ‘dangerous’, ‘stoic’, etc. and i think i am guilty of reproducing these stereotypes in my fuckboy joel fic bc he’s flattened and sexualized and the dynamic is entrenched in the same narrative romanticizing coercion and helpless submission. I didn’t give him much depth or the reader a lot of overt internal conflict or awareness or obvious consent/willingness.. so i have just as much work to do in dismantling my own writing and desires tbh.
and like, i want to list a million excuses to defend it—’it was my first fic’, or ‘well, at least fuckboy joel isn’t the popular trope in the fandom’ but i know i would actually love it if that were the popular trope!
i love that dynamic of the toxic/we shouldn’t but we can’t help it/but we’re not gonna communicate about this effectively/but maybe we’ll process our emotions through sex type of story, yep. i love emotionally avoidant disasters (bc they are relatable to me!).
BUT those tropes without depth and/or with white-coded sexually submissive reader inserts.. it’s just as harmful as dbf fics with fetishized joel’s and fragile young reader inserts that are written without intention or examination. in fact, the longer i think about it, i should add an edit to my fuckboy joel fics and point out my own critique and maybe edit them (maybe then i’ll even figure out the end of the story bc it would probably help if i DID give joel more depth the whole time). I’m sure there’s more i can reflect on too. so anyway, i’ll repeat myself again: i don’t think structural racism and power, privilege, and oppression are systems that people are individually responsible for… but i do think that in this specific niche hobby where we are in control of what we create… we have an opportunity to uplift different narratives than traditional media and we have the power to be more diverse and inclusive than any network or editor would allow.. so, consume and produce whatever you want; reading a fic doesn’t make you a bad person.
and at the same time, if you want to be an anti-racist ally then be critical of what you consume and promote and listen when BIPOC folk speak out about their concerns.
I’m not great at simplifying concepts the way some folks are. I think dbf and age gaps often go hand in hand with white-coded readers and fetishized Joel’s which from a zoomed out perspective shows that people most enjoy reading those dynamics so more people keep writing them. But white-coded readers aren’t inclusive and perpetuate the ideas that women should be soft, fragile, aka the angel of the house (an ideology that says women are ‘naturally’ submissive and domestic) and fetishize Joel (a Latino character—when referring to the version played by pedro) by flattening him into a deviant or dangerous man controlled by lust. Maybe there are many dbf fics that have more nuance and interrogation of these stereotypes, but that isn’t clear from the copious moodboards of small white woman ankles and hands ya know?
Hope some of this helps, feel free to make your own decisions and form your own opinions about what you want to read and write someone accused me of hiding behind academic jargon and i'm aware that i'm not great at breaking down complex topics so if you have questions i can try again
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Queer/LGBTQ History in the Soviet Union
Since I started working on my novel, I’ve done a lot of research on LGBTQ history in the Soviet Union, which became a special interest for me. Since I always love to spread my special interests, here’s a bibliography of useful sources about queer history in the USSR. I believe this to be reasonably complete (I scoured JSTOR for articles and books) but I’d love to hear if I forgot anything. I’m also down to answer questions or help people access these resources if you DM me.
Books
Homosexual Desire in Revolutionary Russia - Dan Healey (2001)
Focuses on 1917-1940s. If you only read one book off this list, make it this one. Despite some outdated terminology, this remains the most central and accessible text on this topic, and it’s a good choice to read first to get a basic grasp. It combines a good sense of the broader context with a lot of fascinating details.
Russian Homophobia: From Stalin to Sochi - Dan Healey (2017)
Effectively a sequel to the above book, a series of historical anecdotes which cover 1945-2017.
Regulating Homosexuality in Soviet Russia, 1956-91: A Different History - Rustam Alexander (2021)
This book examines Soviet queer history through the lens of official discourse, i.e., the police, Gulag officials, the secret police, and doctors. This is useful both for understanding people in these professions, and for understanding people who were subjected to official control.
Gay Lives and ‘Aversion Therapy’ In Brezhnev’s Russia, 1964-1982 - Rustam Alexander (2023)
Red Closet: The Hidden History of Gay Oppression in the USSR - Rustam Alexander (2023)
This book attempts to bridge popular history and academic history, and doesn’t quite succeed - it has a lot of interesting information in it, but if you can, read Alexander’s other work (including the articles below) first.
Lesbian Lives in Soviet and Post-Soviet Russia - Francesca Stella (2014)
Chapter Two, “Lesbian Relationships in Late Soviet Russia,” contains a lot of valuable information. I admit I found the writing style rather dry.
Out of the Blue: Russia's Hidden Gay Literature: An Anthology - Kevin Moss (1996)
This anthology of literature in translation mostly features pre-Revolutionary and post-Soviet fiction, but it’s the only source for English translations of several valuable Soviet artistic works and primary sources, including Mikhail Kuzmin’s diaries and works by Gennady Trifonov.
Soviet and Post-Soviet Sexualities - Edited by Richard C.M. Mole (2019)
Queer History of Belarus in the second half of the 20th century: a preliminary study - Uladzimir Valodzin (2016)
Forced underground: homosexuals in Soviet Latvia - Rita Ruduša (2014)
Moscow - Yevgeny Fiks
Not an academic research book, but photographs of "gay cruising sites in Soviet Moscow, from the early 1920s to the USSR's dissolution in the early 1990s."
Articles
The Queer Life of Lieutenant Petrenko: The KGB and Male Homosexuality in the Ukrainian SSR of the 1960s - Rustam Alexander (2023)
"With a Shade of Disgust": Affective Politics of Sexuality and Class in Memoirs of the Stalinist Gulag - Adi Kuntsman, Slavic Review, Vol. 68, No. 2 (Summer, 2009), pp. 308-328
“Not a Personal Matter”: Soviet Conservative Discourse on Homosexuality in the 1960s and 1970s - Irina Roldugina (2024)
An inconspicuous sexual dissident in the Georgian Soviet republic: Subjectification, social classes and the culture of suspicion in the late Soviet period - Arthur Clech (2021)
Gay in the Gulag - Yaroslav Mogutin (1995)
Using the Past to Save the Present: Soviet Transgender History and Its Implications for Present-Day Trans Rights in Russia - Yana Kirey-Sitnikova (2025)
Transsexual and intersex individuals in Soviet medicine and jurisprudence - Yana Kirey-Sitnikova (Date of release unclear - recent)
The Trans Man Whose Pioneering Surgery Was A State Secret For Decades - Daniil Turovsky, Buzzfeed News (2018)
Documenting the queer self: Kaspars Aleksandrs Irbe (1906-1996) in between unofficial sexual knowledge and medical-legal regulation in Soviet Latvia - Ineta Lipša (2021)
Taming the desire: Pavel Krotov’s “bisexual” closet - Rustam Alexander (2021)
The inner lives of queer comrades in early Soviet Russia - Artem Langenburg interviewing Irina Roldugina, openDemocracy.net (15 December 2017)
‘Why are we the people we are?’ Early Soviet homosexuals from the first-person perspective: New sources on the history of homosexual identities in Russia - Ira Roldugina in Soviet and Post-Soviet Sexualities (2019)
Criminal Prosecution of Homosexuals in the Soviet Union (1946-1991): Numbers and Discourses - Uladzimir Valodzin (2020)
"With a Shade of Disgust": Affective Politics of Sexuality and Class in Memoirs of the Stalinist Gulag - Adi Kuntsman (2009)
“Not a Personal Matter”: Soviet Conservative Discourse on Homosexuality in the 1960s and 1970s - Irina Roldugina (2023)
Political Homophobia in Soviet Lithuania Revisited: The Case of the Dissident Viktoras Petkus - Rasa Navickaitė (2024)
Translating queer texts in Soviet Russia: A case study in productive censorship - Brian James Baer (2010)
Usto Mumin: The Life and Work of a Great Artist as Seen in Recent Books - Eleonora Shafranskaya and Boris Chukhovich
An interview with two authors about their books, which cover the history of Usto Mumin, a queer artist in the early Soviet period. Their books do not appear to exist in English, so I present this interview in their stead.
Dissertations
The Queer Legacy of Ivan the Terrible - Maya Garcia (2023)
A book analyzing multiple depictions of Ivan the Terrible that depict queer characters; the first depiction analyzed is a pre-Revolutionary opera by Tchaikovsky, but the dissertation then moves on to discuss several Soviet works.
Fifty Shades of Vice: Decolonizing the Soviet Homophobic Legacy - Feruza Aripova (2023)
Contains some very useful research on queer history in Uzbekistan specifically
52 notes
·
View notes
Note
Fulford, Tim. “Sighing for a Soldier: Jane Austen and Military Pride and Prejudice.” Nineteenth-Century Literature, vol. 57, no. 2, 1 Sept. 2002, pp. 153–178. https://doi.org/10.1525/ncl.2002.57.2.153.
So I'm reading this and I kind of think he's full of it on many accounts, but I also feel like he and I haven't read the same Pride and Prejudice?
For instance, he says, "Obscure to everyone, Wickham is all appearance; only when Elizabeth starts to get some information from Mrs. Gardiner's dim memories of his Derbyshire youth is she forced to question what lies beneath the polished manners and the sleek uniform." But as far as I can tell, Mrs. Gardiner's dim memories don't do a thing about Wickham, but make up a bad thing about Darcy? Elizabeth's enlightenment comes from Darcy's letter, then is backed up by Mrs. Reynolds, isn't it?
Further, he says Colonel Fitzwilliam is in the militia, when I thought he was in the regulars. He also seems to ignore that Fitzwilliam is the son of an Earl.
Can you confirm that this guy sounds like he's not read the book at times?
Elizabeth defends Wickham to Mrs. Gardiner at Christmas and doesn't change her opinion of him at all. The "dim memories" are a scene prior and are about Darcy, and they also don't change opinion:
Mrs. Gardiner had seen Pemberley, and known the late Mr. Darcy by character perfectly well. Here, consequently, was an inexhaustible subject of discourse. In comparing her recollection of Pemberley with the minute description which Wickham could give, and in bestowing her tribute of praise on the character of its late possessor, she was delighting both him and herself. On being made acquainted with the present Mr. Darcy’s treatment of him, she tried to remember something of that gentleman’s reputed disposition, when quite a lad, which might agree with it; and was confident, at last, that she recollected having heard Mr. Fitzwilliam Darcy formerly spoken of as a very proud, ill-natured boy.
So that is just 100% false.
As for Colonel Fitzwilliam, I'm looking and I can't see an exact text reference that says he's in the normal army, but that has always been my assumption and I've never heard anyone say ever that he's in the militia. Maybe it's something that wouldn't be done by someone of his status? There I am not sure.
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi, first thanks a lot for all the thoughts and resources and readings you have shared! do you know of any psych critical or maybe even just psych historical or general sociology/history books or articles on the concept of narcissism and narcissistic personality disorder?
i actually hate pretty much everything i've read that's specifically about narcissism because i think it suffers from a miserable tendency to either close-read freud or to overstate the importance of like three specific theoretical currents in the usa in the 1960s–70s culminating in the ostensibly blazing social commentary of christopher lasch. i get more mileage out of developing a general critique of psychiatric taxonomy and then applying that to local examples of narcissistic and npd diagnostics. but these are texts that according to my notes did contain at least a modicum of useful primary/archival research that a person could potentially repurpose or that provided some historical context i valued:
Albou, Philippe (2006) Mythologie et étymologies médicales. Histoire des Sciences Médicales (p. 273).
Rudnytsky, Peter L.; Bókay, Antal; Giampieri-Deutsch, Patrizia (1996) Ferenczi's turn in psychoanalysis. New York University Press
Lunbeck, Elizabeth (2014) The Americanization of Narcissism. Harvard University Press
Olsen, Ole Andkjaer; Køppe, Simo (1987) Some developments in the history of the concept of narcissism. Psychoanalysis and Contemporary Thought (pp. 489-531).
Ansbacher, Heinz L. (1985) The significance of Alfred Adler for the concept of narcissism. American Journal of Psychiatry (pp. 203-206).
there's also like a shitload written on concepts of amour-propre versus amour de soi, but that maps into early alienist discourses in kind of unpredictable and polysemic ways. idr reading anything specifically on narcissistic personality disorder that was like, a history book and not a self-help carceral screed :/ sorry
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
Not to reawaken the vaginoplasty scars discourse. People who don't think vaginoplasties leave any scars other than the ones on the sides of the labias, might wanna read some vaginoplasty procedures, for example the:
Peritoneal Pull-Through Vaginoplasty TL;DR: incision made at the abdomen to help build the vaginal canal from that side. handy dandy link where it's described, no graphic pictures: https://www.mtfsurgery.net/peritoneal-pull-through-vaginoplasty.htm Penile inversion Vaginoplasty TL;DR: If not enough tissue from pp to make vagoo of the depth that you want, skin grafts can be taken from the abdomen or scrotum. handy dandy link where it's described, no graphic pictures: https://www.mtfsurgery.net/mtf-vaginoplasty.htm Looking at just pictures which will only show the actual genitalias, which are indeed the focus of most post-op picture taking, and not what else needs to be done during a surgery and could result in scarring is not enough- Educate yourself owo
.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
If, as Isaac West observes, use of the public bathroom is “one of the most, if not the most, quotidian practices of citizenship,” then this chapter argues that surveillance criminalizing public bathroom use is one element of a larger effort to secure citizenship and spatial belonging through the apprehension of physical difference. [...]
Writing about the concept of civilization in the late nineteenth-century United States, Gail Bederman describes it as an “explicitly racial concept” that “denoted a precise stage in human racial evolution”: one that had evolved past primitive or barbaric characteristics. Drawing on Darwinism, this logic rationalized white supremacy through claims that people of color simply had not developed in the same ways or at the same rate as white people, situating civilization itself as a racial characteristic and producing and solidifying distinct racial categories. Bederman notes that gender was crucial in distinguishing civilized societies from the less advanced, with the former identified in part by clear binary gender divisions. [...] Moreover, in the era of formal Jim Crow, while bathrooms marked for white people were typically separated into men’s and women’s spaces, those labeled “colored” were often unmarked by gender at all, a practice that aligns with civilizational discourse. [...]
Yet citizenship status and gender status cannot be pulled apart [...]: just as the previous two chapters of this book traced specific aspects of the Department of Homeland Security that produce and rely on a gendered citizenship, we might consider how campaigns for neighborhood safety and family values regularly invoke a kind of good citizenship that is determined in part through gender attributes. [...]
We need only consider the emphasis on birth certificates to understand the extent to which anxieties about citizenship undergird these bathroom scenes, since those documents mark not only state-approved sex designation, but also legal citizen status. In the most formal sense, birth certificates purportedly confirm citizenship and thus one’s legal belonging to the nation-state. At the same time, they can serve as evidence of citizenship in a more informal or cultural sense: if producing appropriate paperwork is one way of complying with state regulations and requests, then doing so performs good citizenship. [...]
Discourses of bathroom contagion merge fears of “real germs” with “the fear of the other”; hence, public toilets provoke more anxiety than other germ-riddled public objects like computer terminals and doorknobs. Concerns about bathroom cleanliness are as much about bodily interactions and the difficulty of regulating public space as they are about actual dirt or waste. The racial integration of some U.S. workplaces during World War II, for example, prompted tremendous white anxiety about shared bathrooms, even as Black people had long cleaned toilets and beds, prepared food, and cared for children as part of their domestic work in white households. But this “private service work reinforced racialized gender hierarchies in ways that public intimacy undermined them.”
— Toby Beauchamp (2019), Going Stealth: Transgender Politics and US Surveillance Practices, pp. 81 - 101
In his book, Beauchamp argues that anti-trans bathroom bills should be understood as a form of state surveillance that is inextricable from anti-immigration and border security practices: these bills deputize members of the public to conduct bodily assessments of other people to determine whether they meet the criteria of a 'good citizen,' giving them the power to report 'fraudsters' to the authorities if a transgender person is found inhabiting a public bathroom. The criteria by which these assessments are conducted are explicitly white supremacist ones; not only because the imagined body of the 'good citizen' is one that reflects the ideals of white, bourgeois, cissexual bodies* (as clearly demarcated, binary gender roles is a sign of advanced white civilization, and perversion of these demarcations is a perversion of white civil life), but also because one of the primary forms of evidence that you belong in a gender-segregated public space (such as a bathroom) is a birth certificate, one issued by the state - as he says: "if producing appropriate paperwork is one way of complying with state regulations and requests, then doing so performs good citizenship." (p 93). Beauchamp criticizes the framing that trans people are treated like "second class citizens," as it accepts the white racial imaginary of (white) trans people being unfairly denied the benefits of full white citizenship; we should therefore understand gender segregated spaces not as a "remix" of "old" "historic" forms of racial segregation, but as a contemporary enforcement mechanism of it. Binaohan emphasizes this in their 2014 book Decolonizing Trans/Gender 101, arguing that non-white trans people are always "in public," denied any sort of private realm; they are always visible and marked as potential threats to white citizenship. (p. 39)
This is likewise reflected in Jenny Evang's 2022 work Is Gender Ideology Western Colonialism?, where she argues that anti-trans discourse situates the presumed natural state of 'sex' as being corrupted by an overly decadent form of Western cultural advancement, which is both degenerating the Western world and 'duping' the Global South into forsaking their relationship with nature, an argument that "[frames] “non-Western societies” as “more traditional” when it comes to gender, sexuality, and the family, since “gender ideology” has not yet gone as far there as in the West. Thus their argument relies on essentializing the very same conceptualization of “cultural difference” that structures femonationalist arguments in the first place, namely, that racialized, imagined elsewheres are stuck in a more traditional gender pattern, unable to keep up with the rampant development of the West." (p. 370). Locating the origin of transgenderism in the West reproduces notions of civilizational development, where the West is secure in its supreme cultural position but has merely gone "too far," "in the wrong direction," creating the circumstances of its own downfall - a downfall which is attributed both to mass immigration (particularly immigration of Muslims) and Marxism. (p. 372)
Fears of 'gender ideology' engulfing the Western world are inextricable from concerns about the maintenance of white social hygiene, as 'gender ideology' has been called "Ebola from Brussels" (p. 371), linking the corruption of binary, hierarchical, cissexual gender to a disease afflicting the body-politic of the white nation-state. The last paragraph of the quoted passage above from Beauchamp further demonstrates the fundamental interconnectedness between race, gender, and hygiene: The racial integration of some U.S. workplaces during World War II, for example, prompted tremendous white anxiety about shared bathrooms, even as Black people had long cleaned toilets and beds, prepared food, and cared for children as part of their domestic work in white households. But this private service work reinforced racialized gender hierarchies in ways that public intimacy undermined them." (p. 101) Discourses regarding public hygiene are civilizational discourses, as a clean world is a civilized world, and a civilized world can only be a white world.
*Beauchamp explicitly brings up that one of the 'problems' of using biometric data to scan the public for potential terrorists or 'fraudulent citizens' is the white inability to tell the difference between people belonging to different racial groups, i.e., the idea that all non-white people look too much alike and therefore must undergo even more intense scrutiny (p. 95).
97 notes
·
View notes
Text

Wut r yew talking about?? New drama? Discourse? ARE YOU CRAZY?!?!?! xD Dream and Tommy r still friends lawl xD they just announced they’re gonna be streaming together soon ;PP (Yes, this is my way to cope)
#dream smp#furry art#dsmp fanart#mcytblr#dreamwastaken#dream fanart#tommyinnit#tommyinnt fanart#digital art#furry artist#somewhat 2010s nostalgia#discduo#discduo fanart#primeboys#primeboys fanart#wolfy's art
26 notes
·
View notes