#plpro
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Also preserved on our archive
By Mary Van Beusekom, MS
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is more infectious than severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) viruses because it contains an enzyme that can efficiently circumvent a host cell's innate defense mechanism, Kobe University–led researchers in Japan suggest in the Journal of Virology.
The innate immune system attaches the molecular tag ISG15 to SARS-CoV-2's nucleocapsid protein, which contains the virus's genetic material, inhibiting viral replication. The team's laboratory experiments suggest that the virus's papain-like protease (PLpro) can remove the tag, recovering its ability to assemble new viruses and escape the innate immune response.
Discovery may lead to more effective drugs While the SARS and MERS viruses belong to the same virus family and also have an enzyme that can remove the ISG15 tag, their versions are less efficient and have a different primary target than that of SARS-CoV-2.
In a Kobe University news release today, senior author Ikuo Shoji, MD, PhD, said this finding may help guide the development of more effective and selective COVID-19 inhibitors that target SARS-CoV-2's nucleocapsid protein.
"We may be able to develop new antiviral drugs if we can inhibit the function of the viral enzyme that removes the ISG15 tag," he said. "Future therapeutic strategies may also include antiviral agents that directly target the nucleocapsid protein, or a combination of these two approaches."
Study Link: journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jvi.00855-24
Press Release: www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1061645
#mask up#covid#pandemic#wear a mask#public health#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease
SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease Catalog number: B2017053 Lot number: Batch Dependent Expiration Date: Batch dependent Amount: 50 µg Molecular Weight or Concentration: 36.8 kDa Supplied as: Powder Applications: a molecular tool for various biochemical applications Storage: -80°C Keywords: 2019-nCoV Plpro, COVID-19-Plpro, SARS-CoV-2 Plpro, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Papain-like…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Too big for concealment? Not a chance! #t5customkydex #t5militia #2arightsarecivilrights #staccatop #sti2011 #olight #plpro #concealedcarry https://www.instagram.com/p/CpOpjZDLNUT/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Human Species Protection Of The Environment Is Self-Serving~
BAFMnotes: Monetary Gain That Destroys Nature Destroys Future Cures...
"A study published in the scientific journal Molecules this month found that the molecule produced by the jararacussu pit viper inhibited the virus's ability to multiply in monkey cells by 75%.
"We were able to show this component of snake venom was able to inhibit a very important protein from the virus," said Rafael Guido, a University of Sao Paulo professor and an author of the study.
The molecule is a peptide, or chain of amino acids, that can connect to an enzyme of the coronavirus called PLPro, which is vital to reproduction of the virus, without hurting other cells.
Already known for its antibacterial qualities, the peptide can be synthesized in the laboratory, Guido said in an interview, making the capture or raising of the snakes unnecessary.
"We're wary about people going out to hunt the jararacussu around Brazil, thinking they're going to save the world ... That's not it!" said Giuseppe Puorto, a herpetologist running the Butantan Institute's biological collection in Sao Paulo. "It's not the venom itself that will cure the coronavirus."
0 notes
Text
Brazilian viper venom may become tool in fight against COVID, study shows

[Image description: a jararacussu snake, whose venom is used in a study against the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), is seen at Butantan Institute in Sao Paulo, Brazil August 27, 2021.]
Brazilian researchers have found that a molecule in the venom of a type of snake inhibited coronavirus reproduction in monkey cells, a possible first step toward a drug to combat the virus causing COVID-19.
A study published in the scientific journal Molecules this month found that the molecule produced by the jararacussu pit viper inhibited the virus's ability to multiply in monkey cells by 75%.
"We were able to show this component of snake venom was able to inhibit a very important protein from the virus," said Rafael Guido, a University of Sao Paulo professor and an author of the study.
The molecule is a peptide, or chain of amino acids, that can connect to an enzyme of the coronavirus called PLPro, which is vital to reproduction of the virus, without hurting other cells.
Continue reading.
#brazil#politics#science#coronavirus#covid 19#biology#medicine#brazilian politics#mod nise da silveira
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Veneno de Cobra contra o Coronavírus não é cloroquina não!
Sabe qual é a maior cobra peçonhenta do Brasil? É a surucucu, com seus pomposos 4,5 metros de comprimento. Mas não é da surucucu que queremos falar.
Mas qual é a segunda maior cobra peçonhenta do Brasil? É a jararacuçu, a grande estrela da ciência do momento e é dela que queremos falar.
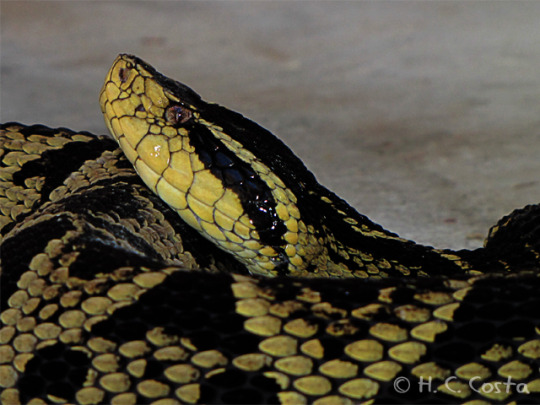

Bothrops jararacussu
A jararacuçu (Bothrops jararacussu) é um tipo de "jararaca" tamanho família, podendo atingir 2,2 metros na fase adulta. Aliás, seu nome já diz tudo; vem do tupi onde “jarara” significa “bote da cobra” e “uçu” significa “grande”.
Ela é encontrada principalmente na Mata Atlântica, em trechos que vão da Bahia ao Rio Grande do Sul. Mas também podem ser encontradas em outros biomas, em matas do Mato Grosso do Sul, Bolívia, Argentina e Paraguai.
Quando adultas, as jararacuçus têm hábitos noturnos, se alimentam de pequenos roedores, aves e anfíbios. Por meio da fosseta lacrimal (loreal), essas cobras detectam o calor (raios infravermelhos) emitidos por suas presas endotérmicas, como pequenos roedores. Além disso, seus dentes inoculadores de veneno são grandes, atingem 2,5 centímetros e podem injetar um bom volume de veneno em suas presas.

Fosseta Lacrimal (ou Loreal) da jararacussu, um termorreceptor
Aliás, o veneno da jararacuçu pode causar um "bom estrago", pois tem propriedades proteolíticas, coagulantes e necrosantes. As pessoas picadas por essa cobra podem sofrer edema e necrose na ferida, além de hemorragias e insuficiência renal. As vítimas devem receber soro antiofídico, de preferência o antibotrópico.
youtube
As jararacuçus não botam ovos; elas são vivíparas na verdade, isto é, os filhotes se desenvolvem no interior da fêmea, em uma espécie de útero. Cerca de 20 cobrinhas nascem prontas pela cloaca materna.
youtube
Pois é! E desse incrível réptil comum das matas brasileiras pode surgir um medicamento eficaz contra a COVID-19.
Epa, não estamos falando de cloroquina ou ivermectina não! Aqui é ciência meu amigo!
Pesquisadores do Instituto de Química (IQ) da Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP), campus Araraquara, descobriram um peptídeo no veneno da jararacuçu capaz de inibir a replicação do Sars-Cov2 (coronavírus).
Na verdade, há muitos trabalhos na literatura científica que demonstram que o veneno das jararacas e das surucucus têm propriedades antimicrobianas, especialmente contra protozoários e bactérias. Os pesquisadores da UNESP, com colaboração de cientistas da USP e da UFSCar, vislumbraram a possibilidade do veneno da jararacuçu também ter efeitos contra o coronavírus.
E têm! Pelo menos em macacos.
Ensaios laboratoriais demonstraram que certos peptídeos do veneno da jararacuçu reduzem em 75% a capacidade do coronavírus se multiplicar em células de macaco. Segundo os pesquisadores, os peptídeos presentes no veneno da jararacuçu inibiram a enzima viral PLPro, essencial para a replicação do coronavírus.
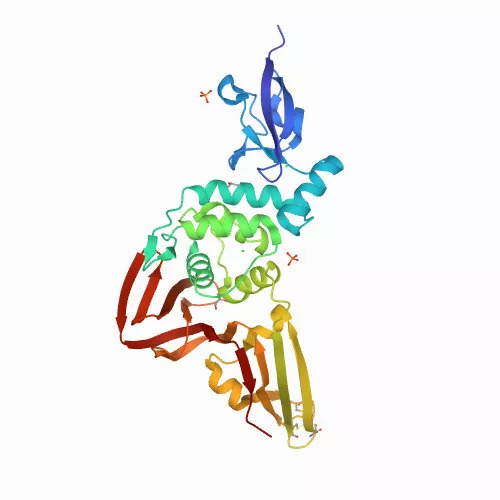
Estrutura Tridimensional da PLPro do coronavírus
A PLPro viral também age contra as proteínas humanas importantes para o funcionamento do sistema imunológico e do controle da pressão arterial. Quanto menos PLPro estiver presente nas células infectadas, ou quanto mais ela for suprimida, maior a possibilidade de não ocorrer a replicação viral. Segundo estudos científicos, todas as variantes de coronavírus apresentam o mesmo tipo de enzima PLPro, fato que favoreceria mais ainda a utilização terapêutica de peptídeos sintéticos parecidos com aqueles presentes no veneno da jararacuçu.

Recipientes com peptídeos anti-coronavírusFoto: Paulo Chiari/EPTV
Mas muita calma nessa hora! A boa ciência é cautelosa. Esses estudos científicos, financiados pela FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Ciência do Estado de São Paulo), deverão prosseguir ainda em uma fase pré-clínica, com a utilização de animais de laboratório. Se os ensaios laboratoriais atestarem eficiência e segurança nos animais, possivelmente os estudos prosseguirão por meio de testes em humanos. De qualquer forma, é mais uma arma da ciência contra o coronavírus.
E se ele de fato veio da natureza, talvez a própria natureza nos ensine como combater o coronavírus. A preservação de nossa biodiversidade é a preservação da saúde humana e estabelece sólidos alicerces para desenvolvimento sustentável.
Não há conquista humana que dure muito tempo se não houver a compreensão dos diversos aspectos biológicos por trás da diversidade dos seres vivos.
Veja também:
1-https://g1.globo.com/sp/sao-carlos-regiao/noticia/2021/08/25/pesquisa-da-unesp-de-araraquara-identifica-molecula-em-veneno-de-cobra-que-inibe-o-coronavirus.ghtml (acesso em agosto de 2021).
2- https://bv.fapesp.br/pt/auxilios/106364/estudo-da-acao-de-peptideos-sinteticos-como-antivirais-contra-o-sars-cov-2-covid-19-e-avaliacao-comb/ (acesso em agosto de 2021).
3-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nE3g6LB-xxA (acesso em agosto de 2021).
4-https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kdckgg7iWkg (acesso em agosto de 2021)
5-https://www.iq.unesp.br/#!/noticia/762/veneno-de-cobra-brasileira-tem-molecula-que-inibe-o-coronavirus (acesso em agosto de 2021).
6-https://revistagalileu.globo.com/Ciencia/Saude/noticia/2021/06/enzima-do-sars-cov-2-pode-quebrar-e-inativar-proteinas-humanas-importantes.html (acesso em agosto de 2021).
7-https://animalbusiness.com.br/colunas/animais-silvestres/jararacucu-a-segunda-maior-serpente-do-brasil/ (acesso em agosto de 2021).
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
SUNSHINE BIOPHARMA SIGNS EXCLUSIVE WORLDWIDE LICENSE WITH UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA FOR PLpro-BASED COVID-19 TREATMENT
http://dlvr.it/Sk7L3M
0 notes
Text
COVID-19 Treatments: Antiviral and Anti-inflammation
COVID-19
Treatments: Antiviral and Anti-inflammation

Antiviral
•Remdesivir and Nucleoside Analogues
•Chloroquine and its Family Members
Anti-inflammation
Antiviral Natural Products
COVID-19 Related Compound Libraries
The pandemic outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has spread all over the world and has been a great threat to humans for absence of specific effective anti-viral treatments. It is urgent to identify effective, safe, and available treatment strategy for COVID-19.
As COVID-19 is a viral infectious disease with major symptoms of fever and pneumonia, antiviral and anti-inflammation related supportive therapies are important treatments for severe cases.

Schematic of SARS-CoV-2 infection[1-3]
COVID-19 in caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2). SARS-CoV-2 belongs to coronavirus (CoV) who have four main structural proteins: spike (S), membrane (M), envelope (E), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins.
After primed by a protease called TMPRSS2 (transmembrane protease, serine 2), the S protein mediates the CoV entry into host cells by attaching to a cellular receptor named ACE2, followed by fusion between virus and host cell membranes. Genome replication and subgenomic RNA transcription after entry carry on with the participation of many nonstructural proteins such as Mpro (main protease or 3CLpro), PLpro (papain-like protease) and RdRp (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase). Then the structural proteins are translated, assembled into mature virions, and released via vesicles by exocytosis.
What’s worth mentioning, the vast release of cytokines (such as IL-1β, GM-CSF, IL-6, IL-10) by the immune system in response to severe infection of SARS-CoV-2 called cytokine storm contributes largely to the mortality of COVID-19.
Antiviral
All the proteins and subcellular structures participated in the life cycle of CoVs are promising targets for treatment of disease caused by CoVs. It is inspiring that numbers of promising agents with potential of antiviral have been reported to deal with COVID-19.
GroupCompoundMechanism of action
Inhibitors of viral protein synthesis
Lopinavir
[4]
Ritonavir
[4]
Protease inhibitor.
Inhibitors of viral RNA
polymerase/RNA synthesis
Remdesivir
[5]
GS-443902
[6]
GS-443902 trisodium
[6]
Favipiravir
[7]
Ribavirin
[8]
Nucleoside analogue, prodrug, RdRp inhibitor.
Inhibitors of viral entry
Chloroquine
[5]
Chloroquine phosphate
[5]
Hydroxychloroquine sulfate
[5]
Increasing endosomal pH required for virus/cell fusion, as well as interfering with the glycosylation of ACE2.
Camostat mesylate
[9]
Nafamostat mesylate
[10]
Inhibiting Sprotein priming and S protein-driven cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 mediating by TMPRSS2.
Umifenovir hydrochloride
[11]
Might inhibit the fusion process.
Inhibitors of Mpro
Ebselen
[12]
Carmofur
[12]
PX-12
[12]
SARS-CoV-2-IN-1
[13]
Binding with Mpro of SARS-CoV-2.
Inhibitor of viral proteins trafficking
Ivermectin
[14]
Inhibit importin α/β-mediated nuclear transport, which in turn blocks the nuclear trafficking of viral proteins.
Enhance antiviral immune response
Nitazoxanide
[15]
Interferon-beta 1
[16]
Regulates inflammation pathways.
Remdesivir and Nucleoside Analogues
Remdesivir is an adenosine analogue, which incorporates into nascent viral RNA chains and function as inhibitor of RdRp. Remdesivir has been reported to inhibit numbers of RNA viruses (including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2) infection in cultured cells and showed effects for treating COVID-19 in clinical. Except for remdesivir, its metabolites and several nucleoside analogues are also reported to have the antiviral ability.
ConditionCompoundMechanismStatus
Anticancer
Nucleoside & Nucleotide
Analogues
Gemcitabine
Targets DNA polymeraseApproved
5-Azacytidine
Traps DNA methyltransferaseApproved
Cytarabine
Targets DNA polymeraseApproved
Antiviral
Nucleoside & Nucleotide
Analogues
Remdesivir
[5]
GS-443902
[6]
GS-443902 trisodium
[5]
Remdesivir nucleoside monophosphate
Remdesivir and its metabolites, inhibitors of RdRp.Phase III
Favipiravir
Targets RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)Approved
Tenofovir
Targets nucleotide reverse transcriptaseApproved
Asunaprevir
Targets NS3 proteaseApproved
Antibacterial
Nucleoside & Nucleotide
Analogues
Linezolid
Inhibits bacterial protein synthesisApproved
Nitrofurantoin
Inhibits bacterial DNA, RNA and protein synthesisApproved
Isoniazid
Acts on the mycobacterial cell wallApproved
Chloroquine and Its Family Members
Chloroquine is a widely-used anti-malarial and autoimmune disease drug, has recently been reported as a potential broad spectrum antiviral drug. Chloroquine is known to block virus infection by inhibiting the fusion of virus and host cell by increasing endosomal pH and interfering the function of ACE2. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are proposed to be used to treat COVID-19 in clinical trials.
Subfamily Members
Relationship
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Status and Indication
Chloroquine Subfamily
Chloroquine
Representative DrugAutophagy, RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase, TLR
Approved:
Malaria, Tumor, Rheumatoid Arthritis,
COVID-19, etc
Preclinical Research:
Chikungunya Virus
Didesethyl Chloroquine
Major Metabolite of
ChloroquineAutophagy, RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase
Preclinical Research:
Malaria, Chikungunya Virus
Hydroxychloroquine
Less Toxic Metabolite of
ChloroquineAutophagy, RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase, TLR
Approved:
Malaria, Tumor, Rheumatoid Arthritis,
COVID-19, etc
Preclinical Research:
Chikungunya Virus
Cletoquine
Major Active Metabolite of
HydroxychloroquineAutophagy, RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase
Preclinical Research:
Chikungunya Virus,
Antirheumatic
Ferroquine Subfamily
Ferroquine
Chloroquine AnalogAutophagy, Ferroptosis
Phase II:
Malaria
Preclinical Research:
Tumor, Virus
Desmethyl Ferroquine
Major Metabolite of
FerroquineAutophagy, RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase
Preclinical Research:
Malaria, Virus
SARS-CoV-IN 1
SARS-CoV-IN 2
SARS-CoV-IN 3
Derivative of Ferroquine
Preclinical Research:
Malaria, SARS-CoV
Other Subfamily
Primaquine
Chloroquine AnalogROS
Approved:
Malaria, HIV
Mefloquine
Chloroquine AnalogHeme polymerase
Approved:
Malaria
Preclinical Research:
Osteoporosis
Amodiaquine
Chloroquine AnalogHeme polymerase
Approved:
Malaria
Preclinical Research:
Ebola Virus
N-Desethyl amodiaquine
Major Active Metabolite of
Amodiaquine
Preclinical Research:
Malaria
Anti-inflammation
Current management for COVID-19 is supportive therapy as there is still no effective cure.
Respiratory failure from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is reported to be the leading cause of mortality of COVID-19. The primary cause of ARDS is cytokine storm characterized by excessive and uncontrolled release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-6, IL-1, IL-17, IL-2, GM-CSF) after infection. So anti-inflammation are the most important supportive therapy for patients with severe COVID-19.
Therapeutic options for anti-inflammation in patients with COVID-19 include steroids, selective cytokine blockade, JAK inhibition, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
CompoundMechanism of action
Methylprednisolone
[17]
Glucocorticoids suppress cytokine storm manifestations in patients with COVID-19.
Dexamethasone
[18]
A glucocorticoid receptor agonist and the first drug save lives by one-third among patients critically ill with COVID-19.
Anakinra
[19]
An interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonist may be beneficial for treating severe COVID-19 patients.
Tocilizumab
[20]
Sarilumab
[21]
Recombinant human IL-6 monoclonal antibody thus blocking IL-6 signaling and its mediated inflammatory response, as a therapeutic option against COVID-19.
Baricitinib
[22]
A dual inhibitor of JAK and AAK1 (AP2-associated protein kinase 1, a regulator ofendocytosis) as the possible candidate for treatment of COVID-19 because of its relative safety and high affinity.
Chloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine
[5]
CQ and HCQ can regulate immune system by affecting cell signaling and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Melatonin
[23]
Plays a role of adjuvant medication in the regulation of immune system, inflammation and oxidation stress.
Antiviral Natural Products
Many natural products have broad-spectrum antiviral effects by inhibiting various steps in viral infection and replication. Natural products can also function as immunomodulators, suppressing inflammatory reaction. Some of them are reported to have the potential of inhibiting coronavirus and may be promising candidate agents for COVID-19. Take emodin as an example, it has been shown to inhibit the interaction of SARS-CoV S protein with its receptor ACE2[24].
Forsythia suspensa
Lonicera japonica Thunb
Ephedra
Semen Armeniacae amarum
Isatis indigotica L
Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai
Houttuynia cordata
Pogostemon cablin
Rheum
Rhodiola rosea
Glycyrrhiza uralensis
Menthol
COVID-19 Related Compound Libraries
It is urgent to develop drugs to treat COVID-19 quickly. The drug repurposing using visual screening technology in clinical and approved compounds can greatly shorten timeline and improve the efficiency of the development of anti-COVID-19 drugs.
As mentioned above, the reported candidate drugs for COVID-19 include agents targeting viruses (such as HIV and SARS-CoV) and inflammation. It indicates that all the antiviral, anti-infection and anti-inflammation related chemicals may have the potential to be effective in treatment of COVID-19.
Compound libraryDescription
Anti-COVID-19 Compound Library
Chemicals with potential anti-COVID-19 activity targeted 3CL protease, Spike protein, NSP15, RdRp, PLpro and
ACE2 collected by visual screening in
Drug Repurposing Compound Library (HY-L035)
.
Anti-Virus Compound Library
Compound library containing all kinds of molecules with anti-virus activity.
Anti-Infection Compound Library
Antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic compound library.
Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
Antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and antiparasitic compound library.
Anti-infection:
Antibiotic
Arenavirus
Bacterial
CMV
EBV
Enterovirus
Filovirus
Fungal
HBV
HCV
HCV Protease
HIV
HIV Protease
HPV
HSV
Influenza Virus
Orthopoxvirus
Parasite
Reverse Transcriptase
RSV
SARS-CoV
TMV
Virus Protease
VSV
References:
[1]. Azkur, A.K., et al., Immune response to SARS‐CoV‐2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID‐19. Allergy, 2020.
[2]. Strope, J.D., C.H.C. PharmD and W.D. Figg, TMPRSS2: Potential Biomarker for COVID‐19 Outcomes. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2020. 60(7): p. 801-807.
[3]. Tay, M.Z., et al., The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nature reviews. Immunology, 2020. 20(6): p. 363-374.
[4]. Lim, J., et al., Case of the Index Patient Who Caused Tertiary Transmission of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea: the Application of Lopinavir/Ritonavir for the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia Monitored by Quantitative RT-PCR. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 2020. 35(6).
[5]. Wang, M., et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Research, 2020. 30(3): p. 269-271.
[6]. Yang, K., What do we know about remdesivir drug interactions? Clinical and Translational Science, 2020.
[7]. Cai, Q., et al., Experimental Treatment with Favipiravir for COVID-19: An Open-Label Control Study. Engineering, 2020.
[8]. Elfiky, A.A., Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19. Life Sciences, 2020. 248: p. 117477-117477.
[9]. Hoffmann, M., et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell, 2020. 181(2): p. 271-280.e8.
[10]. Hoffmann, M., et al., Nafamostat Mesylate Blocks Activation of SARS-CoV-2: New Treatment Option for COVID-19. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 2020. 64(6).
[11]. Deng, L., et al., Arbidol combined with LPV/r versus LPV/r alone against Corona Virus Disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study. Journal of Infection, 2020. 81(1): p. e1-e5.
[12]. Jin, Z., et al., Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature, 2020.
[13]. Zhang, L., et al., Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors. Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science), 2020. 368(6489): p. 409.
[14]. Sharun, K., et al., Ivermectin, a new candidate therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, 2020. 19(1).
[15]. Toby Pepperrell, V.P.A.O., Review of safety and minimum pricing of nitazoxanide for potential treatment of COVID-19. Journal of Virus Eradication, 2020. 6: p. 52-60.
[16]. Hung, I.F., et al., Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. The Lancet (British edition), 2020. 395(10238): p. 1695-1704.
[17]. Wang, Y., et al., A retrospective cohort study of methylprednisolone therapy in severe patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2020. 5(1).
[18]. Ledford, H., Coronavirus Breakthrough: Dexamethasone Is First Drug Shown to Save Lives. NATURE, 2020.
[19]. Dimopoulos, G., et al., FAVORABLE ANAKINRA RESPONSES IN SEVERE COVID-19 PATIENTS WITH SECONDARY HEMOPHAGOCYTIC LYMPHOHISTIOCYTOSIS. Cell host & microbe, 2020.
[20]. Luo, P., et al., Tocilizumab treatment in COVID‐19: A single center experience. Journal of Medical Virology, 2020. 92(7): p. 814-818.
[21]. Benucci, M., et al., COVID‐19 pneumonia treated with Sarilumab: A clinical series of eight patients. Journal of Medical Virology, 2020.
[22]. Cantini, F., et al., Baricitinib therapy in COVID-19: A pilot study on safety and clinical impact. The Journal of infection, 2020.
[23]. Rui Zhang, X.W.L.N., COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment. Life Sciences, 2020. 250(117583).
[24]. Ho, T., et al., Emodin blocks the SARS coronavirus spike protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 interaction. Antiviral Research, 2007. 74(2): p. 92-101.
0 notes
Text
Crystal structure and activity profiling of deubiquitinating inhibitors-bound to SARS-CoV-2 papain like protease revealed new allosteric sites for antiviral therapies
Preliminary report; Emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2 still threaten the effectiveness of currently deployed vaccines, and antivirals can prove to be an effective therapeutic option for attenuating it. The papain-like protease (PLpro) is an attractive target due to its sequence conservation and critical role in the replication and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2. PLpro also plays very important role in modulation of host immune responses by deubiquitinating (DUBs) or deISGylating host proteins. Thus, targeting PLpro serves as a two-pronged approach to abate SARS-CoV-2. Due to its structural and functional similarities with the host DUB enzymes, an in-house library of DUB inhibitors was constituted in this study. Five promising compounds exhibiting high binding affinities with the substrate binding site of PLpro were identified from a library of 81 compounds with in silico screening, docking, and simulation studies. Interestingly, lithocholic acid, linagliptin, teneligliptin, and flupenthixol significantly inhibited the proteolytic activity of PLpro. Each of these compounds abrogated in vitro replication of SARS-CoV-2 with EC50 values in the range of 5-21 micro M. In addition, crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro and its complex with inhibitors have been determined that revealed their inhibitory mechanism. The findings of this study provide the proof-of-principle that the DUB inhibitors hold high potential as a new class of therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, this is the first study that has opened a new avenue towards not only targeting PLpro active site but also simultaneously directing towards restoration of antiviral immune response of the host for deterring SARS-CoV-2. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.11.516107v1?rss=1%22&utm_source=dlvr.it&utm_medium=tumblr Read more ↓
0 notes
Photo

Built Like A Tank 🦾 #t5customkydex #t5militia #t5duty #builtlikeatank #beretta #92fscompact #olight #plpro #edc #igmilitia #holster #holsterdaddy #personaldevelopment #warriormindset #warriormentality #getoutandtrain #goat #vikingbeard #valkyrie #norseman #blackflag #shoplife https://www.instagram.com/p/CYrWjGPrqEE/?utm_medium=tumblr
#t5customkydex#t5militia#t5duty#builtlikeatank#beretta#92fscompact#olight#plpro#edc#igmilitia#holster#holsterdaddy#personaldevelopment#warriormindset#warriormentality#getoutandtrain#goat#vikingbeard#valkyrie#norseman#blackflag#shoplife
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Siguiente objetivo farmacológico COVID-19: "Tijera molecular" viral
Siguiente objetivo farmacológico COVID-19: “Tijera molecular” viral

[ad_1]
La enzima SARS-CoV-2-PLpro se visualiza con una inserción de la interacción del inhibidor viral. El bloqueo de los efectos de la enzima puede resultar útil para detener las infecciones por coronavirus. Crédito: Imagen cortesía de Shaun K.Olsen, PhD, laboratorio del Centro de Ciencias de la Salud de la Universidad de Texas en San Antonio (Joe R. y Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine)
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Viral 'molecular scissor' is next COVID-19 drug target #covidー19 #coronarvirus “American and Polish scientists, reporting Oct. 16 in the journal Science Advances, laid out a novel rationale for COVID-19 drug design—blocking a molecular "scissor" that the virus uses for virus production and to disable human proteins crucial to the immune response. "This enzyme executes a double-whammy," Dr. Olsen said. "It stimulates the release of proteins that are essential for the virus to replicate, and it also inhibits molecules called cytokines and chemokines that signal the immune system to attack the infection," Dr. Olsen said. SARS-CoV-2-PLpro cuts human proteins ubiquitin and ISG15, which help maintain protein integrity. "The enzyme acts like a molecular scissor," Dr. Olsen said. "It cleaves ubiquitin and ISG15 away from other proteins, which reverses their normal effects." #fstp #msls #medicalscienceliaison https://www.instagram.com/p/CGeRMsMDUIf/?igshid=1m9zaog1pad84
0 notes
Photo

Sig Saturday 🤎 #t5customkydex #t5militia #t5eoor #2arightsarecivilrights #sigsaturday #steelchallenge #pistolshooting #sigsauer #p320 #m17 #olight #plpro #pewpew #pewpewlife #2a #gunsdaily #holsterdaddy #gunsofinstagram #vikingbeard #tacticalviking #norseman #valkyrie https://www.instagram.com/p/CPLddbEL1AW/?utm_medium=tumblr
#t5customkydex#t5militia#t5eoor#2arightsarecivilrights#sigsaturday#steelchallenge#pistolshooting#sigsauer#p320#m17#olight#plpro#pewpew#pewpewlife#2a#gunsdaily#holsterdaddy#gunsofinstagram#vikingbeard#tacticalviking#norseman#valkyrie
2 notes
·
View notes
Link

Viral papain-like cysteine protease (PLpro, NSP3) is essential for SARS-CoV-2 replication and represents a promising target for the development of antiviral drugs. Here, we used a combinatorial substrate library and performed comprehensive activity profiling of SARS-CoV-2 PLpro. On the scaffold of the best hits from positional scanning, we designed optimal fluorogenic substrates and irreversible inhibitors with a high degree of selectivity for SARS PLpro. We determined crystal structures of two of these inhibitors in complex with SARS-CoV-2 PLpro that reveals their inhibitory mechanisms and provides a molecular basis for the observed substrate specificity profiles. Last, we demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 PLpro harbors deISGylating activity similar to SARSCoV-1 PLpro but its ability to hydrolyze K48-linked Ub chains is diminished, which our sequence and structure analysis provides a basis for. Together, this work has revealed the molecular rules governing PLpro substrate specificity and provides a framework for development of inhibitors with potential therapeutic value or drug repurposing.
0 notes
Link
يمكن أن تساعد الأدوية التي تم وضعها لعلاج السارس في مكافحة "كوفيد-19". توصل إلى هذا الاستنتاج العلماء في معهد "وولتر وأليزا هول" للبحوث العلمية في أستراليا. وجاء ذلك في مقال نشرته مجلة The EMBO Journal العلمية.واكتشف الخبراء أشكالا جديدة من الأدوية التي يمكن ان تمنع مركب PLpro بصفته إنزيما محوريا لـ SARS-CoV-2 (السارس) من الانتشار.من المعلوم أن هذا المركب يتضمنه كل فيروس تاجي. ويلعب دورا محوريا في إصابة الخلايا وتكاثر العامل الممرض داخلها.وكانت البحوث المختبرية قد أكدت فعالية الأدوية ضد "كوفيد – 19" التي تستهدف السارس أيضا.واستخدم العلماء السنكروترون ANSTO بغية إدراك كيفية تعامل مركب Plpro مع بروتينات الإنسان كما اكتشفوا أعضاء يحتمل أن تستهدفها أدويتهم وأجروا بعد ذلك اختبارا للمركبات الطبية القادرة على قفل هذا التعامل.يذكر أن الأدوية القادرة على تعطيل عمل مركب Plpro قد لا تكون مفيدة ضد "كوفيد – 19" فحسب بل وضد فيروسات تاجية أخرى إذا قدر ظهورها في المستقبل.المصدر: لينتا. رو
0 notes