#plant biodiversity
Text
"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
#colombia#brazil#urban#urban landscape#urban planning#cities#civil engineering#green architecture#green spaces#urban heat#urban heat island effect#weather#meteorology#global warming#climate change#climate hope#climate optimism#climate emergency#climate action#environment#environmental news#city architecture#bicycling#native plants#biodiversity#good news#hope#solarpunk#ecopunk#hopepunk
16K notes
·
View notes
Text









#free palestine#palestine#plants#biodiversity#environment#intersectional environmentalism#gaza#west bank#indigenous#resistance
13K notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
#videos#fave#habitat loss#habitat destruction#endangered species#brazil#species rehabilitation#plant rehabilitation#native plants#native plant rehabilitation#native species rehabilitation#brazil native plants#brazil plants#biodiversity#plant biodiversity
0 notes
Text
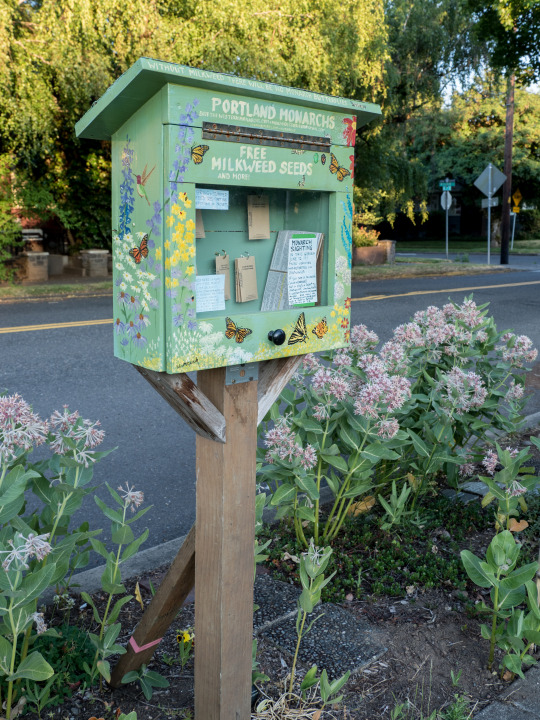


Butterfly Repopulation Station in Portland
Free seeds, information and also a patch of milkweed for Monarch Butterflies
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
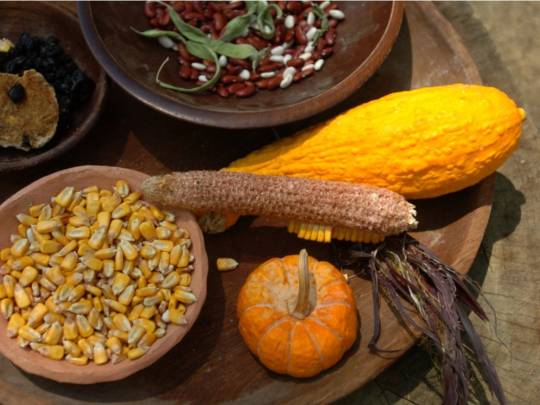
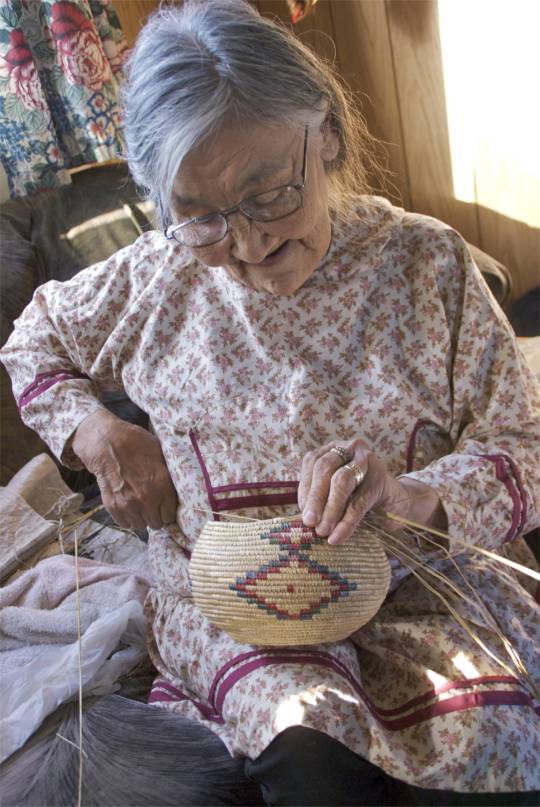













times, places, and practices that I want to learn from to imagine a hopeful future for humanity 🍃
the three sisters (squash, beans, maize) stock photo - alamy // anecdote by Ira Byock about Margaret Mead // art by Amanda Key // always coming home by Ursula K. Le Guin // Yup'ik basket weaver Lucille Westlock photographed by John Rowley // the left hand of darkness by Ursula K. Le Guin // photo by Jacob Klassen // the carrier bag theory of fiction by Ursula K. Le Guin // article in national geographic // the dawn of everything by David Graeber and David Wengrow // braiding sweetgrass by Robin Wall Kimmerer // the birchbark house by Louise Erdrich // photo by John Noltner
I'm looking for more content and book recs in this vein, so please send them my way!
#solarpunk#hopepunk#braiding sweetgrass#just a collection of books and pictures that make me hopeful for the future#margaret mead#robin wall kimmerer#nature#ursula k le guin#ursula k. le guin#the left hand of darkness#the carrier bag theory of fiction#the dawn of everything#anthropology#future#hopecore#native plants#biodiversity#sustainability#eco#eco friendly#louise erdrich#civilization
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Native Plant Info Masterlist...2!
This will be a USA centric post sadly, mostly focused on the East, since I am unfamiliar with resources outside of my area.
iNaturalist lets you upload pictures of any organisms and get them identified by the community, but if you don't want to upload, you can still lurk and look through all the photos being posted in your area to develop familiarity with the plants
Wildflower Search lets you toggle between photos of leaves, flowers, fruits etc. of each plant, gives loads of links to other sites that provide info, lets you search by flower color, plant type, time of year, and about a dozen other search criteria- very cool site
Wildflower.org is another very good site- has a search function where you can search plants by various traits and qualities
Find native plants by the number of butterflies that use them
Butterfly host plant list
Keystone species for every USA ecoregion for butterflies and bees
UNC Chapel Hill's 2022 Flora of the Southeastern United States. The ultimate EXHAUSTIVE compendium of plants. You can download it but beware it is over 2,000 pages long
Illinois Wildflowers is an excellent resource for plants found throughout the southeast and Midwest
Virginia Wildflowers
Northern Forest Atlas Awesome high quality photos of trees and leaves, buds, etc.
Name That Plant is a great resource focused on the Carolinas and Georgia
Maryland Biodiversity has much information on plants and many other creatures
Sarracenia.com is all about carnivorous plants
Native Beeology is focused on native bees of New York State
Also try looking up "[your state] native plant society" as many states have one! It could be a great way to find opportunities to get involved.
#usa centric#native plants#native plant gardening#gardening#plants#nature#flowers#bees#save the bees#no lawns#kill your lawn#fuck lawns#biodiversity#conservation#us centric#trees
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - June 8-14
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $Kaybarr1735! And if you tip me and give me a way to contact you, at the end of the month I'll send you a link to all of the articles I found but didn't use each week!
1. Rare foal born on estate for first time in 100 years

“The Food Museum at Abbot's Hall in Stowmarket, Suffolk, is home to a small number of Suffolk Punch horses - a breed considered critically endangered by the Rare Breeds Survival Trust. A female foal was born on Saturday and has been named Abbots Juno to honour the last horse born at the museum in 1924. [...] Juno is just one of 12 fillies born so far this year in the country and she could potentially help produce more of the breed in the future.”
2. The cement that could turn your house into a giant battery

“[Scientists] at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have found a way of creating an energy storage device known as a supercapacitor from three basic, cheap materials – water, cement and a soot-like substance called carbon black. [... Supercapacitators] can charge much more quickly than a lithium ion battery and don't suffer from the same levels of degradation in performance. [... Future applications of this concrete might include] roads that store solar energy and then release it to recharge electric cars wirelessly as they drive along a road [... and] energy-storing foundations of houses.”
3. New road lights, fewer dead insects—insect-friendly lighting successfully tested

“Tailored and shielded road lights make the light source almost invisible outside the illuminated area and significantly reduces the lethal attraction for flying insects in different environments. [...] The new LED luminaires deliver more focused light, reduce spill light, and are shielded above and to the side to minimize light pollution. [... In contrast,] dimming the conventional lights by a factor of 5 had no significant effect on insect attraction.”
4. When LGBTQ health is at stake, patient navigators are ready to help

“[S]ome health care systems have begun to offer guides, or navigators, to get people the help they need. [... W]hether they're just looking for a new doctor or taking the first step toward getting gender-affirming care, "a lot of our patients really benefit from having someone like me who is there to make sure that they are getting connected with a person who is immediately going to provide a safe environment for them." [... A navigator] also connects people with LGBTQ community organizations, social groups and peer support groups.”
5. Tech company to help tackle invasive plant species

“Himalayan balsam has very sugary nectar which tempts bees and other pollinators away from native plants, thereby preventing them from producing seed. It outcompetes native plant species for resources such as sunlight, space and nutrients. [...] The volunteer scheme is open to all GWT WilderGlos users who have a smartphone and can download the Crowdorsa app, where they can then earn up to 25p per square meter of Balsam removed.”
6. [Fish & Wildlife] Service Provides Over $14 Million to Benefit Local Communities, Clean Waterways and Recreational Boaters

“The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is distributing more than $14 million in Clean Vessel Act grants to improve water quality and increase opportunities for fishing, shellfish harvests and safe swimming in the nation’s waterways. By helping recreational boaters properly dispose of sewage, this year’s grants will improve conditions for local communities, wildlife and recreational boaters in 18 states and Guam.”
7. Bornean clouded leopard family filmed in wild for first time ever

“Camera traps in Tanjung Puting National Park in Indonesian Borneo have captured a Bornean clouded leopard mother and her two cubs wandering through a forest. It's the first time a family of these endangered leopards has been caught on camera in the wild, according [to] staff from the Orangutan Foundation who placed camera traps throughout the forest to learn more about the elusive species.”
8. Toy library helps parents save money 'and the planet'

“Started in 2015 by Annie Berry, South Bristol's toy library aims to reduce waste and allow more children access to more - and sometimes expensive - toys. [...] Ms Berry partnered with the St Philips recycling centre on a pilot project to rescue items back from landfill, bringing more toys into the library. [...] [P]eople use it to support the environment, take out toys that they might not have the space for at home or be able to afford, and allow children to pick non-gender specific toys.”
9. Chicago Receives $3M Grant to Inventory Its Trees and Create Plan to Manage City’s Urban Forest

“The Chicago Park District received a $1.48 million grant [“made available through the federal Inflation Reduction Act”] to complete a 100% inventory of its estimated 250,000 trees, develop an urban forestry management plan and plant 200 trees in disadvantaged areas with the highest need. As with the city, development of the management plan is expected to involve significant community input.”
10. Strong Public Support for Indigenous Co-Stewardship Plan for Bears Ears National Monument

“[The NFW has a] plan to collaboratively steward Bears Ears National Monument to safeguard wildlife, protect cultural resources, and better manage outdoor recreation. The plan was the result of a two-year collaboration among the five Tribes of the Bears Ears Inter-Tribal Coalition and upholds Tribal sovereignty, incorporates Traditional Ecological Knowledge, and responsibly manages the monument for hunting, fishing, and other outdoor recreation while ensuring the continued health of the ecosystem.”
June 1-7 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#horse#rare breed#energy storage#clean energy#biodiversity#street lights#lgbtq#health#native plants#invasive species#incentive#fws#water#fishing#swimming#clouded leopard#indonesia#library#kids toys#interdependence#bristol#uk#funding#native#outdoor recreation#animals#wildlife
735 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Non-Native Plants Are Contributing to a Global Insect Decline
The impact of introduced plants on native biodiversity has emerged as a hot-button issue in ecology. But recent research provides new evidence that the displacement of native plant communities is a key cause of a collapse in insect populations and is affecting birds as well...
#non-native plants#invasive species#environment#conservation#insect decline#insect#insects#entomology#biodiversity#animals#nature#botany#plants#non-native invasive species
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Living Species, by the Numbers
Species of Mammals: ~5,500
Species of Birds: Between 10,000 and 20,000 (lots of disagreement)
Species of nonavian Reptiles: Between 10,000 and 20,000 (see above)
Species of Amphibians: more than 7,000
Species of "Fish": more than 33,000
Species of Echinoderms (star fish, sea urchins, etc.): ~7,500
Species of Arthropods: over 2,000,000 and growing (only 1,257,000 described but all researchers know that is a gross underestimate)
Species of Molluscs: > 100,000
Other Bilaterans (wormy things): ~85,000
Corals & Jellyfish: ~16,000
Sponges: ~11,000
Fungi: > 6,000,000
Plants: > 400,000 (plants species are weird)
"Protists": unknown, but more than 100,000 and is severely underestimated
"Bacteria": who the fuck knows. there are too many. Our bodies are half bacteria. possibly in the trillions.
This is what we mean by mammal bias: mammals are the smallest group on here, and yet, because we are mammals, they get the most research money, the most screen time, the most conservation funding, the most love, the most interest. That's ridiculous. That's patently nonsense. Mammals are not "more evolved" than anything on this list - we're all modern life and thus, equally evolved. The other groups of life deserve at least more attention, more care, more interest, even if we can never get it to be proportional. In fact, you can even see mammal bias in this list - because mammals are so well studied, that's the only species count that is NOT vague.
We rely on ALL of these creatures because we are part of a complex biosphere where all of these organisms work together to allow the flow of nutrients and energy through the system. We are all descendants of each biosphere that came before. Mammal bias - focusing only on things that we share the closest genetic ties to - is not only ignorant, its self defeating.
Kill the mammal bias in your head. Kill it now. Because its gross, its inaccurate, and mammals do not in fact rule the world. Bacteria do, and if we *must* give it to an animal, that animal would be Arthropods.
This has been a PSA. Please reblog to spread, because I'm tired of dealing with mammal bias in my own house.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Plant native plants
What's up, northern hemisphere homies? Spring is coming and soon, many of you may be looking toward gardening. When you're deciding what to plant, I have two words for you to consider:
Native. Wildflowers.
There are huge benefits to planting native plants over store-bought plants.
Native plants are already adapted to the local soil. Lots of ornamental plants (especially lawn grass) pull nutrients out of the soil without giving anything back. Native plants are much better at supporting the nutrient cycle.
They are low-maintenance. Because native plants are already adapted to your local conditions, they need much less care and maintenance. You can save time and money on fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, and water.
Native plants support the local ecosystem. The plants have evolved alongside with animals, meaning they feed local insects, birds, and other animals. They also provide shelter for wildlife, attract pollinators, and boost the local animal populations.
They increase biodiversity. In my country, huge swaths of native land have been bulldozed and replaced with ecologically damaging farmland, lawns, and non-native ornamental plants. By planting natives you help restore the ecological balance and can get an idea of what the land used to look like. Planting natives on your property can spread the seeds to other locations through wind or animal dispersal.
They are sustainable. You can harvest seeds off of your natives and grow your garden, give them to other people, or scatter them in the wild.
They are diverse and unique. How many gardens are full of the same old standards like peonies, daffodils, and tulips? Native plants often look much more unique and interesting than the same old ornamentals. Here are some local species from my area that I think are much better looking than a lot of ornamental cultivars. (top to bottom: prairie blazing star, showy tick trefoil, Virginia bluebell, dutchman's britches, bottle gentian).
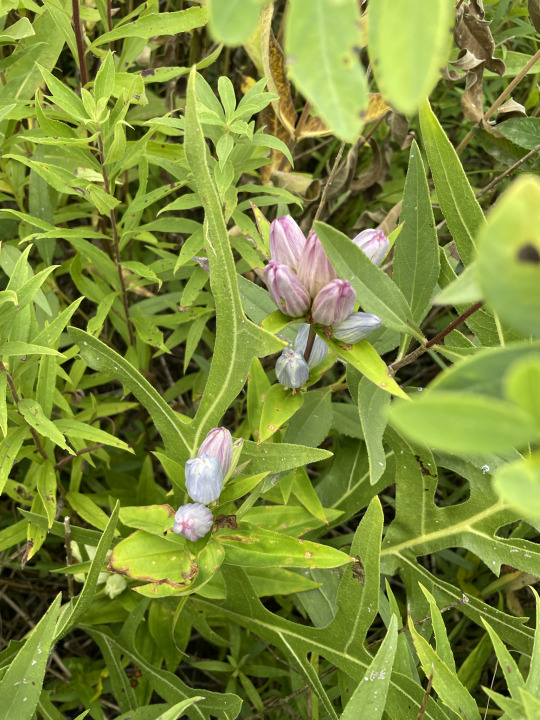






Do some research about which species are local to your area and see if your local garden stores have any native species. A lot of places will have naturalist groups who will sell native plants or their seeds or can point you to places you can get them. You may be able to harvest seeds directly off the plant if there are natural areas near you. However if you are harvesting natural plants, check local laws and see who owns the property. The general rule of thumb is that for abundant native species, you can safely harvest about half of the seeds without impacting the regrowth next year. For rarer species, you shouldn't take more than a quarter. If a lot of people are harvesting in the same area, they may be taking too much.
165 notes
·
View notes
Text

goldenrod at dekorte park, nj - yashica mg-1 & 400 speed color film - developed at eliz digital & scanned with minolta dimage dual iii
#35mm#plants#flowers#fog#new jersey#35mm photography#film photography#35mm color photography#35mm film#green#nature#meadow#flower#goldenrod#wildflowers#botany#biology#ecology#biodiversity#environment
267 notes
·
View notes
Text
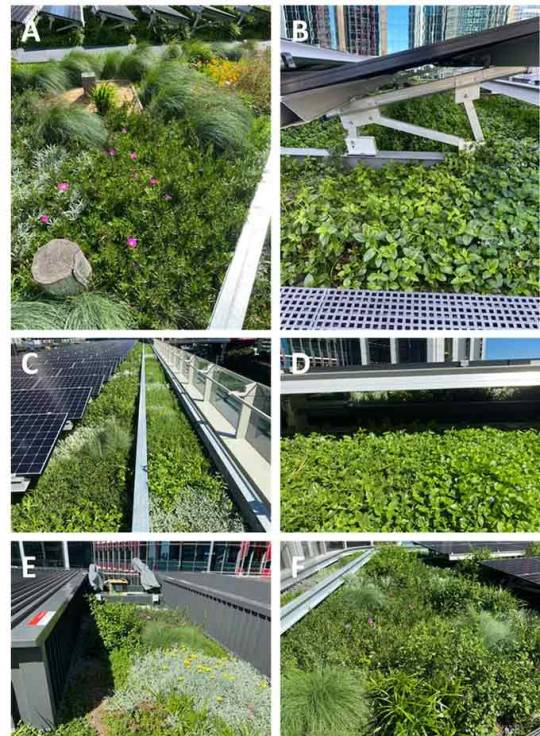
"As solar panels heat up beyond 25°C, their efficiency decreases markedly. Green roofs moderate rooftop temperatures. So we wanted to find out: could green roofs help with the problem of heat reducing the output of solar panels?
Our research compared a “biosolar” green roof — one that combines a solar system with a green roof — and a comparable conventional roof with an equivalent solar system. We measured the impacts on biodiversity and solar output, as well as how the plants coped with having panels installed above them.
The green roof supported much more biodiversity, as one might expect. By reducing average maximum temperatures by about 8°C, it increased solar generation by as much as 107% during peak periods. And while some plant species outperformed others, the vegetation flourished.
These results show we don’t have to choose between a green roof or a solar roof: we can combine the two and reap double the rewards...
How did the panels affect the plants?
In the open areas, we observed minimal changes in the vegetation cover over the study period compared to the initial planted community.
Plant growth was fastest and healthiest in the areas immediately around the solar panels. Several species doubled in coverage. We selected fast-growing vegetation for this section to achieve full coverage of the green roof beds as soon as possible.
The vegetation changed the most in the areas directly below and surrounding the solar panels. The Baby Sun Rose, Aptenia cordifolia, emerged as the dominant plant. It occupied most of the space beneath and surrounding the solar panels, despite having been planted in relatively low densities.
This was surprising: it was not expected the plants would prefer the shaded areas under the panels to the open areas. This shows that shading by solar panels will not prevent the growth of full and healthy roof gardens.

What were the biodiversity impacts?
We used environmental DNA (eDNA) surveys to compare biodiversity on the green roof and conventional roof. Water run-off samples were collected from both roofs and processed on site using portable citizen scientist eDNA sampling equipment to detect traces of DNA shed by the species on the roof.
The eDNA surveys detected a diverse range of species. These included some species (such as algae and fungi) that are not easily detected using other survey methods. The results confirmed the presence of bird species recorded by the cameras but also showed other visiting bird species went undetected by the cameras.
Overall, the green roof supported four times as many species of birds, over seven times as many arthropods such as insects, spiders and millipedes, and twice as many snail and slug species as the conventional roof. There was many times the diversity of microorganisms such as algae and fungi.
Encouragingly, the green roof attracted species unexpected in the city. They included blue-banded bees (Amegilla cingulata) and metallic shield bugs (Scutiphora pedicellata).
How did the green roof alter temperatures?
The green roof reduced surface temperatures by up to 9.63°C for the solar panels and 6.93°C for the roof surfaces. An 8°C reduction in average peak temperature on the green roof would result in substantial heating and cooling energy savings inside the building.
This lowering of temperatures increased the maximum output of the solar panels by 21-107%, depending on the month. Performance modelling indicates an extensive green roof in central Sydney can, on average, produce 4.5% more electricity at any given light level.
These results show we don’t have to choose between a green roof or a solar roof. We can combine them to take advantage of the many benefits of biosolar green roofs.
Biosolar roofs can help get cities to net zero
The next step is to design green roofs and their plantings specifically to enhance biodiversity. Green roofs and other green infrastructure may alter urban wildlife’s activities and could eventually attract non-urban species.
Our green roof also decreased stormwater runoff, removed a range of run-off pollutants and insulated the building from extremes of temperature. A relatively inexpensive system provides all of these services with moderate maintenance and, best of all, zero energy inputs.
Clearly, biosolar green roofs could make major contributions to net-zero cities. And all that’s needed is space that currently has no other use."
-via GoodGoodGood, May 12, 2024
#green#green roof#biosolar#solar power#solar panels#rooftop solar#solarpunk#native plants#australia#sydney australia#biodiversity#conservation#climate change#climate action#climate hope#global warming#temperature#climate adaptation#cooling#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Folks, if you are talking about or sharing anything about “native plants”, please mention *your* location and *where* the plants are native to, not only country-wise but environment-wise.
So many people are learning about rewilding, gathering, foraging and gardening for food in harmony with the environment entirely online. Making your information clear for those people takes you little effort and limits confusion and misinformation getting out there.
The internet isn’t only “not just America”; many nations contain different environments with materially different conditions.
I live in Scotland. Most of the gardening and foraging information I get in the UK is calibrated for the south of England, which is a really different environment from mine - spring can come up to a month later and the south is semi-arid, which Scotland is *not*.
These days I actually look at a lot of Danish and Swedish gardening advice because their environment is a lot closer to mine. And that’s within one small nation. The world is wide and full of incredible diversity.
I am seeing UK-based pages sharing information about “native lawns” which contain plants from arid areas of the US because there’s no specificity in the original post. A small amount of information in the post, even a few lines, about locations, environments, context and goals would prevent this sort of confusion and incorrect information from spreading.
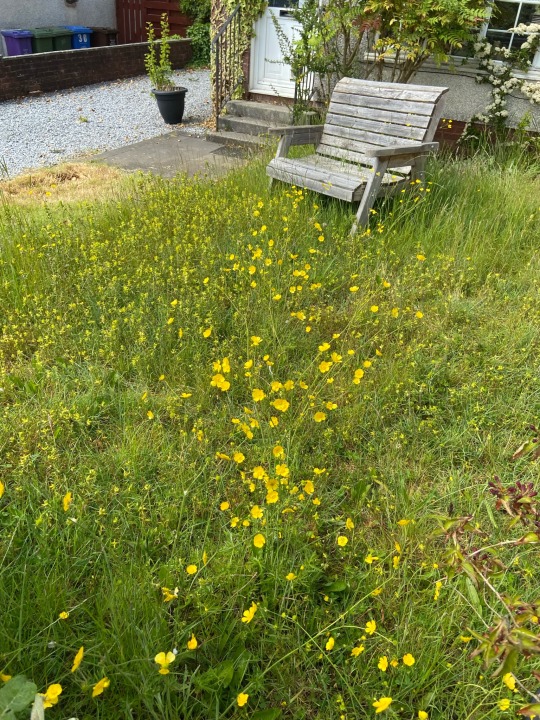

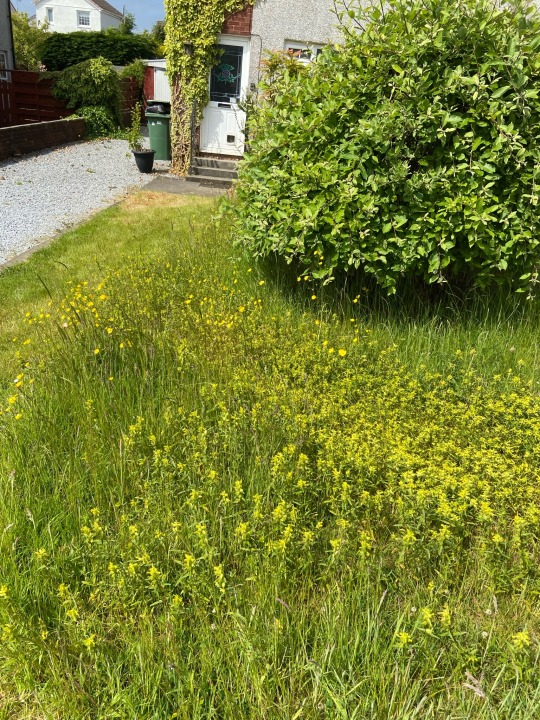
A lot of people are really enthusiastic and ready to be engaged in gardening for food, rewilding, gardening in harmony with the environment, soil preservation etc, but confusion and feeling they can’t trust information sources can really kill that. Make it easy for people new to the movement where you can, please.
ID: some photos of my native rewilded lawn from Scotland, UK, containing buttercups with butterfly eggs on them, yellow rattle, a willow tree, wild orchids, and many different grasses, and my small garden pond upcycled from a Belfast Sink surrounded by wild grasses, ladies’ mantle and wild geraniums and with woundwort and pondweed growing in it. There is a short path mowed in the lawn to allow safe passage of mobility devices and a wooden bench sitting in the long grass. A somewhat overgrown gravel drive and a front door with three steps up to it can be seen. The photos were taken in early June 2023.
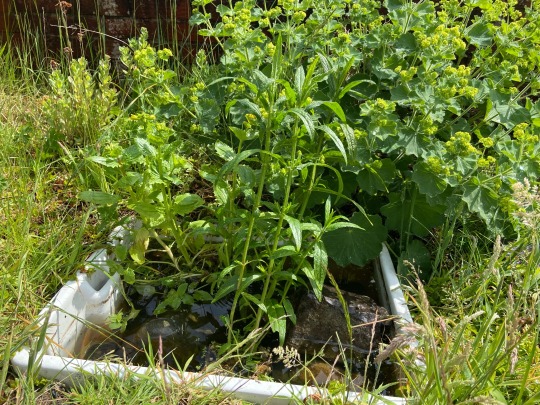


#rewilding#rewilding uk#rewilding scotland#soilhealth#food gardening#native plants#foraging#disabled gardener#clarity#teaching and learning online#prevent confusion and misinformation#biodiversity
513 notes
·
View notes
Text
*casually posts this at the same time to further my agenda of growing native plants instead of grass and shitty ornamentals*





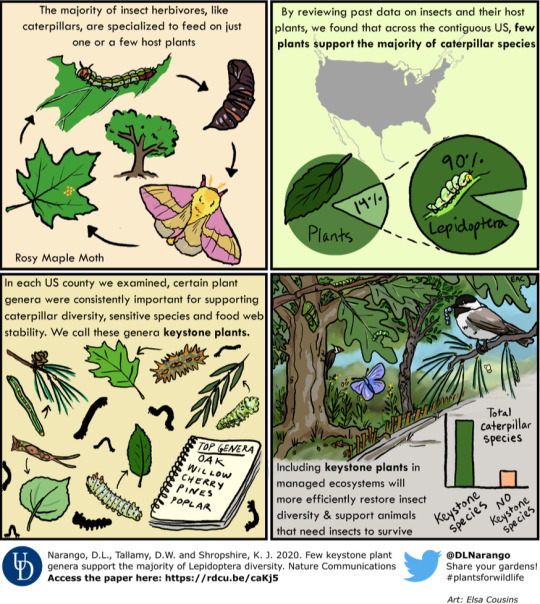

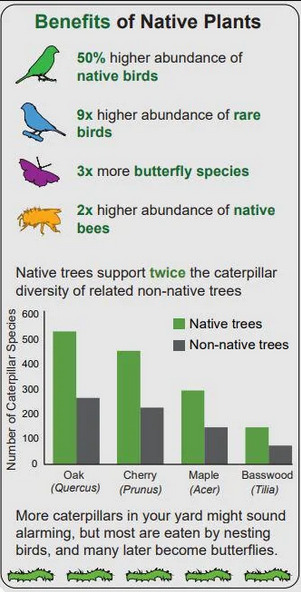

#gardening#water conservation#biodiversity#kill your lawn#native plants#native pollinators#pollinator garden#climate change#sustainability#environmental rehabilitation#habitat restoration#wildflowers#native flowers#animals#water crisis#didnt mean to post that grass one whoops. i think i skimmed it and wasnt thinking about it too much#but ig its true grass would be better than roads. lets just uh. make it native grass yaknow?
289 notes
·
View notes
Text

The surprising diversity of Pineapples (Ananas comosus).
The Active Pineapple Germplasm Bank (Pineapple AGB) of Embrapa Cassava & Fruits (Embrapa/ CNPMF) has more than 700 accessions under field conditions. As backups, there are copies kept in a greenhouse, with one or two plants per accession, cultivated in plastic pots with commercial substrate. An in vitro gene bank was established in 2003, and during the past few years, several studies have been carried out to improve the in vitro conservation protocol. Currently, about 60% of the AGB’s accessions are preserved by this protocol. Another conservation strategy used is cryopreservation of shoot tips and pollen grains, with well-defined methods. One of the most significant advances in the pineapple germplasm conservation has been the implementation of a quality control system, which enabled to define standard operation procedures (SOP) towards a more efficient and safer germplasm conservation.
Source:
Vidigal Souza, Fernanda & Souza, Everton & Aud, Fabiana & Costa, Eva & Silva, Paulo & Andrade, Eduardo & Rebouças, Danilo & Andrade, Danilo & Sousa, Andressa & Pugas, Carlos & Rebouças, Érica & França, Beatriz & França, Rivã. (2022). Advances in the conservation of pineapple genetic resources at Embrapa Cassava and Fruits. 28. 28-33.
#katia plant scientist#botany#plant biology#plant science#plants#fruit#pineapple#pineapples#biodiversity#agriculture#conservation#genetic diversity#sustainable agriculture#tropical plants#science#biology
324 notes
·
View notes
Text

the beautiful biodiversity of plant seeds, genera silene, poppies, oxalisa and solanaceae by J.D. Frei.
#biodiversity#plant photography#nature photography#photography#botanical art#botany#biology#naturecore#seeds#j. d. frei#cottagecore#aesthetic#beauty of nature
33 notes
·
View notes