#pay self assessment tax bill
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Guide to Paying Self Assessment Tax Bill
New Post has been published on https://www.fastaccountant.co.uk/guide-to-paying-self-assessment-tax-bill/
Guide to Paying Self Assessment Tax Bill
For many individuals, the arrival of the self-assessment tax season can be a mix of anticipation and apprehension. The annual ritual of calculating income, tallying expenses, and filling out forms can seem daunting, but it’s an essential responsibility for those who are self-employed, receive income from multiple sources, or have complex financial affairs. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of paying self assessment tax, breaking down the process into manageable steps and shedding light on key considerations.
From understanding payment deadlines and available methods, to exploring potential penalties and seeking out expert guidance, our guide aims to demystify the journey toward fulfilling your tax obligations. Whether you’re a seasoned self-assessor or facing this task for the first time, our insights will help you navigate the maze of Paying self assessment tax with confidence and clarity.
Who needs to pay Self Assessment Tax?
If you fall into any of the categories mentioned earlier, you are likely required to pay Self Assessment Tax. It is important to determine your tax obligations and register for Self Assessment with HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) if necessary.
youtube
How is Self Assessment Tax calculated?
Self Assessment Tax is calculated based on the income you have earned and the expenses you have claimed in a tax year. You need to report your income from all sources, including self-employment, rental properties, dividends, and savings. Self Assessment Tax also takes into account any tax allowances and reliefs you may be eligible for.
Common Self Assessment Tax deductions
When calculating your Self Assessment Tax, there are several deductions you can claim to reduce your tax liability. These deductions include business expenses, capital allowances, pension contributions, charitable donations, and certain reliefs. It is important to keep accurate records and receipts for your deductions.
Tax allowances and reliefs
Tax allowances and reliefs can help reduce your tax liability. Commonly used allowances and reliefs include the Personal Allowance, Marriage Allowance, Trading Allowance, Marriage Allowance, and Capital Gains Tax allowances. You should familiarize yourself with these allowances and reliefs to ensure you are claiming all the tax benefits you are entitled to.
Deadlines for Payment
Important dates for Self Assessment Tax payment
It is crucial to be aware of the deadlines for paying self assessment tax bill to avoid any late payment penalties. The tax year in the UK runs from April 6th to April 5th the following year. The deadline for filing your Self Assessment Tax return is January 31st after the end of the relevant tax year.
Payment deadlines for Self Assessment Tax bills
Once you have filed your Self Assessment Tax return, the payment deadline for any tax owed is also January 31st. It is essential to make payment by this date to avoid late payment penalties and interest charges.
Methods of Payment
Various options for paying your Self Assessment Tax bill
HMRC offers several methods for paying your Self Assessment Tax bill. These include online payment, bank transfer, direct debit, payment by cheque, and payment by debit or credit card. Each method has its own benefits and considerations.
Benefits of different payment methods
The various payment methods offer different benefits depending on your circumstances. Online payment provides convenience and instant confirmation of payment. Bank transfers are suitable for individuals who prefer electronic banking. Direct debit offers ease and peace of mind, as payments are automated. Payment by cheque is an option for those who prefer traditional methods. Finally, payment by debit or credit card provides flexibility and ease of use.
Paying self assessment tax Online
Process of making an online payment
To make an online payment for your Self Assessment Tax bill, you will need to log in to your HMRC online account. Once logged in, select the option to make a payment and enter the relevant payment details, including the amount owed and the payment method.
Setting up an online account
If you do not already have an online account with HMRC, you will need to set one up before you can paying self assessment tax bill online. Setting up an account is straightforward and involves providing personal information, such as your name, address, and National Insurance number. You will also need to create a username and password to access your account.
Security measures for online payments
HMRC takes security seriously and utilizes various measures to protect your personal and financial information when making online payments. These measures include encryption, secure servers, and confidentiality protocols. It is important to keep your login details secure and regularly update your password to further enhance security.
Bank Transfer
Procedure for making a bank transfer
To make a bank transfer for your Self Assessment Tax bill, you will need the relevant bank details for HMRC. Log in to your online banking account or visit your local bank branch to initiate the transfer. Provide the necessary information, including the recipient’s account number and sort code, and the payment reference.
Required information for bank transfers
When making a bank transfer for your Self Assessment Tax bill, you must ensure you have the correct information. This includes HMRC’s bank account details, such as the account number and sort code, as well as your unique payment reference. Double-check the information before initiating the transfer to avoid any payment errors or delays.
Processing time for bank transfers
Bank transfers for Self Assessment Tax payments can take up to 3 working days to reach HMRC’s account. It is important to take this into consideration when making your payment to ensure it is received by the deadline. To avoid any potential late payment penalties, it is recommended to initiate the bank transfer well in advance of the deadline.
Direct Debit
Setting up a direct debit for Self Assessment Tax
Setting up a direct debit for your Self Assessment Tax bill allows HMRC to automatically collect the payment from your nominated bank account. To set up a direct debit, you will need to provide the necessary details, including your bank account number and sort code, as well as the payment frequency and date.
Advantages of using direct debit
Using direct debit to pay your Self Assessment Tax bill offers several advantages. Firstly, it eliminates the risk of forgetting to make the payment manually, as it is automated. Direct debit also provides peace of mind, as you can be confident that payments will be made on time. Additionally, direct debit offers flexibility in terms of payment frequency, allowing you to choose between monthly, quarterly, or annual payments.
Cancelling or changing a direct debit
If you need to cancel or change your direct debit arrangement for your Self Assessment Tax bill, you can do so by contacting your bank or updating the details online. It is important to notify HMRC of any changes to your direct debit to ensure that your payments are processed correctly.
Payment by Cheque
How to pay Self Assessment Tax bill by cheque
To pay Self Assessment Tax bill by cheque, ensure the cheque is made payable to HM Revenue and Customs. Write your unique payment reference on the back of the cheque and include your payment slip if provided. Finally, mail the cheque to the address provided by HMRC.
Mailing address for paying HMRC self assessment tax
The address for mailing cheque payments to HMRC for your Self Assessment Tax bill can be found on your payment slip or on HMRC website. It is important to use the correct address to ensure your payment is processed efficiently. If you are unsure of the correct address, contact HMRC for guidance.
Payment by Debit or Credit Card
Instructions for paying with a debit or credit card
To pay HMRC Self Assessment Tax bill by debit or credit card, you can do so online or over the phone. Follow the instructions provided by HMRC’s website or helpline to make the payment. You will need to enter the relevant payment details, including the card number, expiry date, and security code.
Acceptable card types
HMRC accepts various debit and credit card types for payment of your Self Assessment Tax bill. These cards may include Visa, Mastercard, Maestro, and American Express. It is important to check HMRC’s website or helpline for the most up-to-date information on acceptable card types.
Transaction fees and limits
When paying your Self Assessment Tax bill by debit or credit card, it is important to be aware of any transaction fees that may apply. These fees vary depending on the card type and the payment amount. Additionally, there may be limits on the maximum payment amount that can be made using a debit or credit card. Ensure you check the applicable fees and limits before making your payment.
Late Payment Penalties
Late payment of your Self Assessment Tax bill can result in penalties and interest charges. The penalties are calculated based on the amount owed and the number of days the payment is overdue. To avoid these penalties, it is crucial to make payment by the deadline specified by HMRC.
Appealing a Penalty
Grounds for appealing a penalty
If you believe a penalty for late payment of your Self Assessment Tax bill has been issued incorrectly, you have the right to appeal. Grounds for appealing a penalty may include exceptional circumstances, such as illness or bereavement, reasonable excuse, or if you believe the penalty has been calculated incorrectly.
Procedure for appealing a penalty
To appeal a penalty for late payment of your Self Assessment Tax bill, you will need to contact HMRC within 30 Days and explain your grounds for appeal. Provide any supporting documentation or evidence to strengthen your case. HMRC will review your appeal and make a decision based on the information provided.
Appeals process and timeline
The appeals process for late payment penalties follows a specific timeline. Once you have submitted your appeal, HMRC will review the case and provide a response within a reasonable timeframe. If you are not satisfied with the outcome of your appeal, you may have the option to escalate the case to an independent appeals tribunal for further review.
Paying Self Assessment Tax bill requires understanding the tax system, meeting payment deadlines, and choosing the most suitable payment method. By familiarizing yourself with the process and utilizing the available resources, you can ensure a smooth and hassle-free experience. Remember to keep accurate records, claim any relevant deductions, and seek professional advice if needed.
#pay self assessment tax#pay self assessment tax bill#pay self assessment tax online#paying hmrc self assessment tax#Paying self assessment tax#paying self assessment tax bill
0 notes
Text
Guide to Paying Self Assessment Tax Bill
For many individuals, the arrival of the self-assessment tax season can be a mix of anticipation and apprehension. The annual ritual of calculating income, tallying expenses, and filling out forms can seem daunting, but it’s an essential responsibility for those who are self-employed, receive income from multiple sources, or have complex financial affairs. In this article, we delve into the…

View On WordPress
#pay self assessment tax#pay self assessment tax bill#pay self assessment tax online#paying hmrc self assessment tax#Paying self assessment tax#paying self assessment tax bill
0 notes
Text









from @/wtp.resist on Instagram:
Tax Day is Monday, April 15th... just 4 days away ‼️ 💸 ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ Follow this outline for an easy-to-understand guide on how to participate in war tax resistance this year. If you are unable to participate in war tax resistance but still wish to legally protest, please see slide #7. We want to encourage people to think big and act with courage, but we also understand not everyone can resist in the same way, so we wanted to provide several measures of resistance and resistance support in our Act I — War Tax Resistance — Tax Blackout 2024 Campaign. ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ Our #TaxBlackout goal is 50 million people... with 16% of the U.S. population participating with at least 5% being redirected to vetted emergency relief in Gaza, Washington D.C. will receive a message loud and clear: ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ We will not fund Genocide and Imperialism!
transcript of all slides under the cut
slide 1: Act I Tax Resistance
by @ WTP.resist / We the People
The Tax Blackout 2024 Guide
Tax Resistance
slide 2: Is It Illegal?
Taking any type of direct resistance or civil disobedience action for peace often means taking risks. War tax resistance is no exception.
Since World War I, only two war tax resisters (James Otsuka (1949) and J. Tony Serra (2005)) have been brought into Federal court, convicted, or jailed because of war tax resistance. Most resisters have been taken to court for failure to file, "falsifying" 1040 forms, contempt of court (by refusing to produce records), or (in the early 1970s) "fraudulently" claiming too many dependents on their W-4 form.
slide 3: Filing And Refusing - Step-By-Step
How to File as a War Tax Resister (typical process):
1. File your Form 1040 on or before April 15
Fill out the form per IRS filing instructions. To avoid being considered a "frivolous filer" (an IRS category) and being subject to frivolous filing penalties, do not make claims or write your thoughts on the form.
2. You can enclose a letter that explains your refusal to pay part (or all) of your taxes
Many war tax resisters send letters to explain their refusal to pay is an act of conscience, of civil disobedience. War tax resistance is about refusal to pay for war, not promoting tax evasion or challenging the constitutionality of taxation or war taxes.
slide 4: Filing And Refusing - Step-By-Step
3. Refusal Options:
Refuse a symbolic amount, a percentage (at least 5%), or refuse all of the federal income tax (see next slides).
4. Withholding Adjustments:
Salaried employees can increase the # of deductions on their W-4 form at any time to owe federal income taxes on April 15, and then can choose how much you want to refuse. Take the form home fill it out and return only the first page of the form, not the worksheet (page 3), to your employer. If you are self-employed and don't use a W-4 form, you must adjust the amount of estimated taxes you pay quarterly to resist when you file.
slide 5: Methods Of Resistance
1. File and Refuse to Pay
This involves filling out a 1040 form and refusing to pay either a token amount of your taxes (we are asking at least 5%) a percentage representing a "military" portion, or the total amount (since a portion of whatever is paid still goes to the military).
2. Refuse to File a Tax Return
NWTRCC recommends filing your taxes or the IRS will file on your behalf. They cannot garnish wages until the tax debt has been assessed, which can take some time. The statute of limitations begins at the point the tax is assessed.
slide 6: Methods Of Resistance Continued
3. Earn Less Than The Taxable Income
This can involve having such a low income that you are not required to file federal income tax returns (approximately $12,550 for a single person in 2021), or it can mean filing and taking deductions so that no income tax is owed.
4. Tariffs and Excise Taxes
Today, thousands of people continue to "Hang Up On War" by refusing to pay the small amount on their local telephone bill listed as "Federal Excise Tax" or "Federal Tax." This federal excise tax, like many others, pays into the general fund of the U.S. government - the same place your federal income taxes go. The monies in the general fund help to pay for the Pentagon, the militarization of our culture, and war.
slide 7: Ways To Legally Resist
Send a letter of protest with your 1040 tax form. Enclose it along with (but do not staple it to) your form. Send copies to your elected officials.
Write letters to editors protesting taxes for war, especially when people are thinking about taxes during tax filing season between January and April.
Write a message of protest on the check you send with your tax forms.
Pay the tax with hundreds of small-denomination checks or coins.
Lobby for Peace Tax Fund legislation that would allow conscientious objectors to pay taxes to a fund that would not be used for military spending.
slide 8: Remember!
If at any time you have questions about risks and how to prepare:
War Tax Resistance Counselor: NWTRCC.org/resist/contacts-counselors
War Tax Resistance Hotline: TEL: +1-800-269-7464
slide 9: Sources
Is It Illegal?
nwtrcc.org/resist/consequences
Methods of Resisting:
nwtrcc.org/resist/how-to-resist/
Legal Protest
nwtrcc.org/resist/how-to-resist/
Step-By-Step
nwtrcc.org/resist/war-tax-resistance/filing-and-refusing-step-by-step/
Tax Withholding Calculator
irs.gov/individuals/tax-withholding-estimator
#tax resistance#war tax resistance#we the people#free palestine#palestine#EndIsraelsGenocide#tax blackout 2024#anti imperialism
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
The post thread goes deeply into "this is literal, it is not a metaphor" and at some point mentions that no one had offered advice on how to buy a condo.
This blog is "not financial advice" and this is not financial advice it is... more of... a general list... of suggestions... on how to buy a condo. In the United States.
At no point am I considering this easy, simple, fair, possible widespread.
It sucks. It is expensive. It is hard. It is confusing.
I'm hoping to take at least a tiny bit of sting out of it.

Look around your area. Go to real estate offices, they often have postings in the window. Go to their websites. Go on to Zillow or whatever but understand those prices are, hm, spicy and high, frequently. You want to get a gauge of "this is how much a condo of that size is in my area." Or the area you want to move into.
Mortgages are typically 3 - 5% downpayment, up to 20%.
If you put down less than 20%, you will very likely have to pay something called "private mortgage insurance" (PMI)
Names aside -- it's an extra payment with your mortgage payment.
It covers the lender in case you can't make the payments.
It goes away once you've made enough payments to have gained 20% equity.

Downpayment
This is the the hardest part. It sucks. I'm not going to sugar coat it.
3% of a $100,000 condo is $3,000.
Your mortgage is $97,000.
Your payment is going to be just under $600 + property taxes + PMI (probably 1.5 - 2% of the mortgage) + insurance + association costs.
Here is a basic calculator to play with numbers.
One of the things you should do when looking for a condo is look for first time home buyer's programs.
Google "first time home buyer's program {city}."
Go to City Hall. Go to your bank.
Hell, if you work for a giant company, check your benefits.
I've seen that before with folks -- it's rare, yeah, but check everywhere.
15 Year versus 30 Year Mortgage
This question is academic while you're starting out. Go with a 30 year. It keeps your cost of entry cheaper.
In time, you can refinance. You can (almost always) pay more monthly too.
Unless your mortgage lender is offering you a crazy-good-deal on a 15 year mortgage, plan on 30. Shorter mortgages exist because when you have money, you can get a better deal. If you're following this ramble, it is unlikely to apply. Plan on 30. Figure out a better plan later.

Property Tax
You'll hear a term called "escrow" bandied about. You'll pay an amount on top of your mortgage payment, this amount varies based on your mortgage, property taxes, insurance too probably, and it sits in a savings account.
You cannot touch this savings account.
Your bank will say "For easy math of this ramble, your mortgage is $500/month. Your insurance is $100/month, your property taxes are $600/twice a year... which is $100/month.
"So your total bill is $500 + 100 + 100. Of this amount, $500 goes to your mortgage. $200 goes to this escrow savings account.
"Twice a year, as your bank, we'll withdraw the cash for your insurance and pay them directly. We'll withdraw the cash and pay the property taxes."
Your bank is in touch with the insurance company and the property tax folks regularly to ensure they have enough in your escrow. Your mortgage will fluctuate slightly accordingly.

Association Fees
These vary wildly from area-to-area and even building-to-building so keep this in mind while you're hunting.
This pays for maintenance, the building's improvements, the building's property taxes... etc.
Some condo buildings are self-managed by the owners. Some have hired an agency to do the managing. Some blend.
While you are condo hunting, ask about the association fee. Try to get details "How much was it last year? 3 years ago? 5 years ago?" You want to see how often they are raised and by how much.
Also ask about "special assessments." This is an out-of-the-blue and/or long-term-planned "The condo association needs everyone to pay up $X."
They should be rare. Once every handful of years... like, once or twice every 10 years. That is a very rough guide, not a tight guideline. The more common they are? The worse shape the building and/or association is in.
Check what the association fees cover. Will someone come to your condo and handle emergency plumbing? Do they handle landscaping?
What rules do they have?

"This feels impossible."
It sucks. It's expensive.
There are closing costs on top of all this crap (money you pay during the initial purchase to handle a billion things.) It's more complicated than it feels like it should be.
As you start planning "I want to live here, I can pay $X, that fits within the basic numbers" go talk to a bank. Multiple banks. Community banks, big banks, credit unions, shop around.
"Is this a hard pull on my credit?"
That's the one that hurts it by looking at it. You shouldn't have this until you get fairly deep in the process, but it's just a good question to ask.
If someone makes you uncomfortable for not knowing? Fucking leave immediately. You're the boss. This is your house. These people are working for you. I'm not advocating rudeness, I am advocating if someone is making you feel like shit, leave.
This covers literally everyone in the transaction.
This is a high-value (it costs a lot of money) low-volume transaction (people do not typically buy many properties in life).
You, the customer, are the rarest commodity.
Never let anyone talk down to you.
If you're not ready now, but will be someday, and want info? Go get it. Make the connections. Realty agent, banker, everyone whom has info about your situation you want.
This doesn't cover everything, I'm hoping it's enough to get you started figuring out what questions to ask and whom to ask.

"Okay but this still feels impossible."
It sucks.
I don't have an answer if you are underpaid at your job. I'm a huge advocate of "people should get paid what they are worth." I hope your situation improves.
Anyone saying "stop buying coffee and shove it in a jar" is not being helpful.
Don't spend energy on them.
Do spend energy on, "I need $X for a downpayment and closing costs. How do I get it?" Work backwards from there on a plan. Keep your cheddar in a high yield interest bank account.
I'm cheering you on.
It isn't much, I hope it helps, a little.
There are going to be local plans and laws and rules that will help and hurt you. Ask questions of local folk. Get them to help you make a plan, of city hall's housing department and various (multiple) banks. It's their job. It is literally their job.

I'm cheering you on.
When I grow up I wanna be upper middle class.
206K notes
·
View notes
Text
Don’t Panic: Your Step-by-Step Plan to Tax Debt Relief
When tax bills pile up, most people feel a knot in their stomachs. The fear can stop you from taking the steps needed to fix the issue. Tax debt won't go away on its own, but help exists for those who seek it.
The key lies in making a clear plan rather than hiding from the problem. HMRC actually works with folks who show they want to sort things out. They offer payment plans for those who can't pay all at once.
Gather all your tax papers and check the exact amount you owe. This simple step helps cut through the fog of worry that clouds your mind.

Taking Action
Call HMRC directly to talk about your case before they chase you. Most agents will work with you if you reach out before they send notices. Their job focuses on getting paid, not making your life harder.
Ask about "Time to Pay" plans that spread costs over months or years. These plans fit your budget and make large tax bills more doable. The monthly amounts often surprise people by how small they seem.
If you owe from past years, look into the Debt Management unit at HMRC. They handle older cases with more tools to help you settle up properly.
Finding Extra Help
Debt loans for bad credit offer a way to clear tax bills quickly. These debt consolidation loans for bad credit pay off HMRC in full while giving you better terms in the UK. The peace of mind from settling tax debt often makes this worth it.
Bad credit won't stop most tax debt loan firms from helping you. They care more about your plan to stay on track going forward. Many look past credit scores to see the full story.
Debt loan firms can clear your tax slate much faster than payment plans. Your tax stress ends right away instead of hanging over you for years.
Stop the Bleeding—File All Missing Returns
Your tax troubles will only grow worse when returns remain unfilled with HMRC. The tax office shows little interest in helping folks who haven't sent in their proper forms. Many people wrongly think they should wait until they can pay before filing their tax returns.
The penalties for late filing stack up much faster than those for late payment in the UK system. HMRC adds £100 fines right away and then piles on more charges every few months that pass. These extra costs can double or triple your original tax bill when left too long without action.
Ask About Penalty Relief
HMRC does offer ways to cancel or lower penalties for people with good reasons for their tax troubles. The tax office calls this "reasonable excuse" relief, and it helps many people slash their bills. Your job loss, serious illness, or family crisis might qualify as valid grounds for missing deadlines.
The process starts with a simple letter explaining your situation to HMRC in clear, honest terms. Your appeal needs to show why normal tax duties became impossible during your difficult time. The tax office reviews these cases with more human understanding than most people expect.
Pick the Right Payment Option
The Time to Pay scheme stands as HMRC's main tool for helping those who owe taxes who cannot pay at once. This plan spreads your tax debt across monthly payments that match what you can truly afford. The payments run for up to 12 months in most cases, giving you room to breathe.
Self-assessment taxpayers can set up these plans online without even speaking to an agent on the phone. The online system works for debts under £30,000 and takes just minutes to arrange through your tax account. Larger debts need phone calls but still get sorted with minimal stress.
Those facing extreme money troubles can request a "hardship" review from HMRC in special cases. The tax office sometimes agrees to settle for less when it sees no way you could ever pay the full amount.
Avoid Future Tax Trouble
Your PAYE code needs checking each year to make sure enough tax comes out of your wages. The wrong code can leave you short at year-end with a surprise bill you never planned for. Many people live through tax stress once, then fix their codes to prevent it from happening again.
Self-employed people should put money aside each month rather than waiting for the yearly bill. The smart approach saves 25-30% of all income in a separate account just for tax payments. This simple habit turns tax time from a yearly dread into a smooth, planned event.
A basic tax review with an adviser costs less than most people think and saves pounds in the long run. The adviser spots claim you might miss and steers you clear of common filing errors. Their help proves especially useful for anyone with mixed-income sources or rental property.
Direct lender loans in the UK
Moving past tax debt opens doors to cleaner credit and less stress in your daily life. Many people look back and wish they had faced their tax issues months or years earlier. The weight that lifts from your shoulders makes the whole process worth every step you take.
Direct lender loans in the UK offer a fresh start when tax debts have grown too large for normal payment plans. These loans clear your HMRC slate in one move and put you back in control. The terms often beat what HMRC offers for those with larger tax bills to settle.
The loan structure gives you one set monthly cost instead of changing tax bills and fees. Your budget becomes easier to plan, and you gain certainty about when the debt will end. This mental relief alone makes many borrowers glad they chose this path to fix their tax troubles.
Conclusion
Staying clear of new tax problems begins with adjusting your tax code or increasing your withholding amount. Many people fall into debt simply because they don't take enough tax from their paychecks throughout the year. A quick form sent to HMRC can fix this issue and prevent nasty surprises when the filing season arrives.
Getting help from a tax professional or reliable software saves more money than it costs in most cases. These tools catch deductions you might miss and help avoid errors that trigger HMRC reviews. Keeping simple records throughout the year makes filing accurate returns much easier.
0 notes
Text
How Can Landlords Simplify Filing Landlord Tax and Stay HMRC Compliant?
For landlords in the UK, managing taxes can be a complicated process—especially with changes in buy-to-let tax regulations, evolving mortgage interest relief rules, and the growing use of buy-to-let Ltd companies (SPVs) for property investments. Whether you own properties personally or through a buy-to-let SPV account, ensuring you file landlord tax correctly is essential to avoid penalties and maximize tax efficiency.

But how can landlords make tax filing easier? What are the best practices for managing rental income taxes, and how does one file buy-to-let Ltd accounts without errors? In this guide, we’ll break down everything landlords need to know about filing landlord tax, including how to structure a buy-to-let SPV and streamline the tax reporting process.
1. What Is Landlord Tax, and Who Needs to File It?
If you earn income from renting out property in the UK, you are required to report and pay tax on your rental profits. This applies whether you: ✔️ Own a single rental property or multiple investment properties. ✔️ Rent out property as an individual or through a buy-to-let Ltd company. ✔️ Operate as a resident or non-resident landlord.
Types of Taxes Landlords Need to Pay
1️⃣ Income Tax on Rental Income – If you own property personally, you must report rental profits via Self-Assessment and pay income tax at rates of 20%, 40%, or 45%, depending on your earnings.
2️⃣ Corporation Tax for Buy-to-Let Ltd Companies – If you operate through a buy-to-let SPV, you pay corporation tax (currently 25%) instead of income tax on rental profits.
3️⃣ Capital Gains Tax (CGT) on Property Sales – If you sell a rental property, you may owe capital gains tax at 18% or 28%, depending on your tax bracket.
4️⃣ Stamp Duty Land Tax (SDLT) for Landlords – Buying a rental property typically incurs a 3% SDLT surcharge on top of standard stamp duty rates.
Keeping track of these tax obligations is essential for staying compliant with HMRC and ensuring landlords do not face unexpected tax bills.
2. How Can Landlords File Their Rental Tax Efficiently?
The Self-Assessment tax return (SA100) is the most common way landlords file landlord tax in the UK. The deadline for online submission is 31 January each year.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Landlord Tax
Step 1: Calculate Rental Profits
To determine taxable income, landlords must subtract allowable expenses from total rental income.
Step 2: Deduct Allowable Expenses
Landlords can reduce taxable income by deducting: ✔️ Property management fees ✔️ Repairs and maintenance (not improvements) ✔️ Mortgage interest relief (limited for individuals) ✔️ Insurance and utility bills (if paid by the landlord) ✔️ Advertising and letting agent fees
Step 3: Report Rental Income on a Self-Assessment Tax Return
Log into HMRC Self-Assessment.
Use the property income section to enter rental earnings and expenses.
Review calculations before submitting your return.
Step 4: Pay Any Tax Due
Landlords must pay any tax owed by 31 January. Those with high rental profits may also need to make Payments on Account towards the following year’s tax bill.
For landlords using a buy-to-let Ltd company, the tax filing process is different—let’s explore how to file buy to let Ltd accounts next.
3. How to File Buy-to-Let Ltd Accounts?
Many landlords now hold property investments through a Limited Company (SPV) to benefit from corporation tax rates and full mortgage interest deductions.
What Is a Buy-to-Let SPV?
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is a Limited Company set up solely for property investment. Instead of paying income tax on rental income, landlords pay corporation tax, which can be more tax-efficient.
Steps to File Buy-to-Let Ltd Accounts
✅ Step 1: Maintain Proper Accounting Records
Keep track of rental income and expenses using accounting software or spreadsheets.
Ensure all property-related transactions are recorded under the company’s name.
✅ Step 2: Prepare Financial Statements At the end of the financial year, landlords must prepare:
Profit & Loss Statement (showing rental income and expenses).
Balance Sheet (listing company assets and liabilities).
✅ Step 3: File Corporation Tax Return (CT600)
Submit Company Tax Return (CT600) to HMRC annually.
Pay corporation tax (25%) on rental profits.
✅ Step 4: Submit Annual Accounts to Companies House
File company accounts with Companies House within 9 months of the end of the financial year.
Using an accountant who specializes in buy-to-let SPV accounts can help ensure accurate filings and tax efficiency.
4. What Are the Tax Advantages of Using a Buy-to-Let Ltd Company?
Many landlords switch to a buy-to-let Ltd company due to tax benefits, including:
✔️ Lower Corporation Tax – Currently 25%, lower than higher-rate income tax (40%-45%). ✔️ Full Mortgage Interest Relief – Unlike individual landlords, Ltd companies can deduct 100% of mortgage interest as an expense. ✔️ Easier Tax Planning – You can retain profits within the company or reinvest in more properties without paying personal tax immediately.
However, there are also downsides: ❌ Higher administrative costs (accounting, company filings). ❌ Limited access to mortgage products (not all lenders offer SPV mortgages). ❌ Higher stamp duty when transferring existing properties.
5. Common Mistakes Landlords Should Avoid When Filing Tax Returns
📌 Failing to Declare All Rental Income – HMRC has strict rules on undeclared rental earnings and can issue penalties.
📌 Incorrectly Claiming Expenses – Capital improvements (e.g., extensions) are not deductible, but repairs are.
📌 Missing Filing Deadlines – Late filing results in £100+ penalties, with extra fines for unpaid tax.
📌 Not Using a Buy-to-Let Ltd Company Correctly – If your SPV accounts are not filed properly, you may face HMRC audits and legal issues.
Final Thoughts: Why Filing Landlord Tax Correctly Matters
Whether you own rental property as an individual or through a buy-to-let Ltd company, staying compliant with HMRC tax rules is essential to avoid penalties and optimize tax savings.
✔️ If you’re filing landlord tax personally, ensure you track rental income and allowable deductions before submitting your Self-Assessment tax return. ✔️ If you hold properties in an SPV, ensure you file buy-to-let Ltd accounts correctly, pay corporation tax, and submit returns to Companies House. ✔️ Consulting an expert on buy to let SPV accounts can help landlords navigate tax laws, structure investments efficiently, and reduce tax burdens legally.
By keeping accurate records and using tax-efficient strategies, landlords can maximize rental profits while staying fully compliant with UK tax laws. 🚀
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Filing Landlord Tax and Buy-to-Let Ltd Accounts
1. Do I need to file a tax return if I rent out a property in the UK?
Yes. If you earn more than £1,000 per year in rental income, you must declare it to HMRC by filing a Self-Assessment tax return. If you operate through a Buy-to-Let Ltd company (SPV), you must file buy-to-let Ltd accounts and pay corporation tax on rental profits.
2. What expenses can landlords deduct when filing rental income tax?
Landlords can deduct allowable expenses to reduce their taxable rental profits. These include: ✔️ Mortgage interest (limited relief for individual landlords, but fully deductible for Ltd companies). ✔️ Property repairs and maintenance (excluding improvements). ✔️ Letting agent and management fees. ✔️ Council tax and utility bills (if paid by the landlord). ✔️ Insurance, legal fees, and accountant fees.
3. How do I file buy-to-let Ltd accounts for my rental company?
If you operate under a Buy-to-Let Ltd company (SPV), you must: 📌 Keep detailed financial records of rental income and expenses. 📌 Submit annual accounts to Companies House within 9 months of your financial year-end. 📌 File a Corporation Tax Return (CT600) to HMRC and pay 25% corporation tax on profits. 📌 Report any dividends or salary withdrawals if taking income from the company.
4. Should I set up a Buy-to-Let Ltd company (SPV) for rental properties?
A Buy-to-Let Ltd company (SPV) can be more tax-efficient, especially for landlords in the higher tax bracket (40% or 45%), as corporation tax is only 25%. Additionally, Ltd companies can fully deduct mortgage interest, unlike individual landlords. However, Ltd companies face higher administrative costs, stricter mortgage rules, and limited flexibility in withdrawing profits.
5. What happens if I don’t file my landlord tax or buy-to-let Ltd accounts on time?
Failure to file landlord tax or buy-to-let Ltd accounts can result in: ❌ A £100 fine for missing the Self-Assessment deadline (31 January). ❌ Increased penalties for continued late filing. ❌ HMRC investigations and potential backdated tax payments. ❌ Companies House penalties for late Ltd account filings.
To avoid fines and legal issues, landlords should file tax returns on time and ensure buy-to-let SPV accounts are correctly maintained. 🚀
#buytolet#investmenttax#60 tax trap calculator#landlordtax#united kingdom#tax refund#taxplanning#rentalincome#taxfiling#taxseason
0 notes
Text
Can you really pay HMRC with an Amex or credit card?
Earning Avios on your Self-Assessment, PAYE or Corporation Tax bills Savvy points earners look for any opportunity to put spend through a credit card and earn points, but HMRC aren’t big fans of American Express. In fact, they don’t allow it at all. There are some sneaky ways to get around this, but the bigger question is – is it worth it? What type of taxes does this article cover? I’m using…
0 notes
Text
Need Urgent Cash? Unlock Your Property’s Value with a Low-Interest LAP!
Struggling with high-interest loans? Switch to a Loan Against Property!
If you're burdened with high-interest loans or need a substantial amount for an emergency, a Loan Against Property (LAP) is a smarter alternative. It offers lower interest rates and higher loan amounts because it is secured against your property. Let’s explore how you can unlock your property's true value!
Facing a Cash Crunch? Here’s How Loan Against Property Works
A mortgage loan against property allows you to borrow money by pledging your home, office, or commercial space. Banks assess your property’s value and offer a loan of 50-75% of its market price. This lump sum can be used for business expansion, medical expenses, education, or even a wedding.
Finding the Best LAP Deals: Where to Get the Lowest Interest Rates
Banks and NBFCs offer different property mortgage loan interest rates based on credit score, property type, and income. Here’s a comparison of the best banks for loans against property in India:
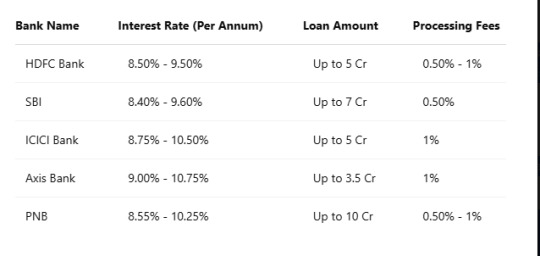
Not Sure If You’re Eligible? Check the Loan Against Property Criteria
Many people miss out on LAP because they think they won’t qualify. Here’s what you need:
Age: Minimum 21 years old
Employment: Salaried or self-employed
Income Stability: A steady source of income to repay the loan
Property Ownership: Must be in your name with clear legal titles
Confused About Paperwork? These Are the Documents You Need
Applying for a loan against property is easy if you have the right documents:
Identity Proof: Aadhar, PAN, Passport, Voter ID
Address Proof: Utility bills, Rent agreement, Passport
Income Proof: Salary slips, IT returns, Bank statements
Property Papers: Title deed, Sale deed, Property tax receipt
Business Owner? Consider a Loan Against Commercial Property
If you own a commercial property, you can get a higher loan amount with more flexible repayment terms. A loan against commercial property is ideal for:
Expanding your business
Buying machinery or equipment
Managing working capital needs
Hidden Charges? Here’s What You Should Know About LAP Fees
Many borrowers forget to check the loan against property processing fees and end up paying more. Here’s what to expect:
Processing Fees: 0.5% - 1% of the loan amount
Legal Charges: For property verification and valuation
Prepayment Penalty: Some banks charge if you repay early
Want to know your EMI? Use a Loan Against Property EMI Calculator
Before taking a LAP, check how much you’ll pay monthly with an EMI calculator. Enter:
Loan Amount
Interest Rate
Repayment Tenure: The tool will show your exact EMI so you can plan your finances better.
Insider Tips to Secure the Best Loan Against Property Deal
Banks won’t tell you these tricks, but we will!
Compare Multiple Lenders—Never settle for the first offer you get.
Improve Your Credit Score—A score above 750 gets you better rates.
Negotiate Processing Fees—Some banks may reduce or waive charges.
Choose the Right Tenure—Longer tenure means lower EMI, but higher interest.
Understand Fixed vs. Floating Rates—Fixed rates provide stability; floating rates can be cheaper in the long run.
FAQs: What People Ask Before Taking a Loan Against Property
1. What is the maximum loan amount I can get?
Banks usually offer 50-75% of your property’s market value as a loan.
2. Is LAP cheaper than a personal loan?
Yes! Loan against property interest rates are much lower than personal loans, making it a cost-effective option.
3. How long does it take for LAP approval?
The process takes 5-15 days, depending on documentation and verification.
4. Can I get a LAP on agricultural land?
No, banks do not provide secured property loans on agricultural land. Only residential and commercial properties qualify.
5. Can I transfer my LAP to another bank for a lower interest rate?
Yes! You can do a balance transfer to a bank offering lower rates and save on interest costs.
Conclusion: Is a Loan Against Property Right for You?
If you own a property and need a big loan at low interest rates, then a loan against property is an excellent choice. Just make sure to compare lenders, check for hidden processing fees, and use an EMI calculator before applying. Need expert help? Get started today and make the most of your property’s value!
Check out the best loan against property option in quick approval in just 2 minutes!
#LAP#Loan Against Property#Loan Against Property Interest Rate#Mortgage loan against property#Property mortgage loan interest rates#Secured property loans#Home equity loan in India#Loan against commercial property#LAP eligibility criteria#Loan against property processing fees#Best banks for loan against property#Loan against property documents required#Loan against property EMI calculator
0 notes
Text
Why Do Mortgage Applications Get Declined? Common Mistakes and How To Fix Them
Whether you’re a first-time-buyer or home mover, navigating mortgages can feel tricky. Before starting your journey to property-ownership, it’s important to understand how mortgage applications work, the possible pitfalls, and how to demonstrate your financial circumstances to lenders effectively, to receive the best outcome.
In this guide, the team at Diamond Property Finance will explore common reasons why mortgage applications get declined in the UK. It will also give you practical tips to improve your eligibility and affordability.
Understanding Mortgage Declines in the UK
In the active UK housing market, getting a mortgage is crucial for many people who want to buy homes. The process can be complex, as lenders carefully review applications to check if a borrower’s finances are sound, often requiring the assistance of solicitors.
Whilst different lenders may have different rewers can handle their repayments for the entire mortgage term.
This complete review looks at many parts of your financial history. It includes your credit score, how steady your income is, any debts you already have, and even how you spend your money.
The Impact of Your Credit Score & Income Verification
Your credit score is of paramount importance to lenders when you apply for a mortgage as it shows them how likely you are to pay back money. This score comes from your history of borrowing and paying back loans, credit cards, and even bills for services on time, ensuring no payments are missed or in arrears. A higher score means you manage your money well, which makes you a safer bet for lenders.
On the other hand, a lower score can come from missing payments, not paying back loans, or having issues with the court, which makes lenders feel less confident in lending you money.
Similarly, lenders also want to be sure that you have income coming in to pay back the loan on a monthly basis. The’ll look closely at your job status and income, assessing whether you have a stable job in order to make monthly mortgage payments.
When applying for a mortgage, you usually need to show proof of income. This documentation can include payslips, bank statements, or tax returns to prove how much you earn. People who are self-employed or have a variable income may need to show extra documents, like business accounts or contracts
Top Reasons for Mortgage Application Rejections
Facing a mortgage decline can be disheartening but it’s not necessarily the end of the road. It’s important to know the common reasons for rejection as this knowledge can arm you better for future applications.
Every application is different, but some reasons for declining are more common than others. Let’s take a closer look at these reasons to help you understand where issues might arise.
Inadequate Income or Debt-to-Income Ratio
One common reason clients receive a mortgage decline is when they don’t have enough income to cover the loan amount they request. Lenders look closely at your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) as this ratio shows the part of your total income that goes to paying off debts.
If your DTI is high, it means a lot of your income already goes to debts. This can make it hard to take on new mortgage repayments. Lenders typically like applicants who have a lower DTI, as it shows they have more financial flexibility.
Before applying for a mortgage, it is important to check your affordability. Look at your income, your expenses, and the loan amount you want.
Issues with Property Valuation and Type
The property you want to mortgage is checked during the application process. A professional will evaluate it to find its market value, then this value will affect how much the lender is willing to lend you. If the value is less than what you agreed to pay, it can impact your application.
The type of mortgage you want matters too, especially when considering private bank lenders. Different mortgages have different eligibility criteria. For example, loans for first-time buyers or new homes have different eligibility criteria than standard residential mortgages. Similarly, private Bank mortgages are often bespoke and may require different financial documentation to prove high-net-worth status.
aIt is important that the property meets the lending guidelines, and that your finances also match the specific needs of the mortgage.
Navigating Financial History Challenges
Past money problems do not have to keep you from getting a mortgage as previous adverse credit or bankruptcy may no longer be relevant at the time of application, but can still affect the decision of lenders. To assess affordability, they’ll look at late payments, missed payments, County Court Judgments (CCJs), and Individual Voluntary Arrangements (IVAs) when they check your application.
The good news is that you can take steps to fix these issues and improve your application. Let’s look at ways to make your financial profile better.
Overcoming Past Financial Missteps
A blotted credit history can worry lenders however, it doesn’t always mean they will decline your application. If you deal with past money mistakes, it shows you are committed to managing your finances well.
First, get a copy of your credit report from online credit score platforms including Experian or Equifax. Look it over carefully for any errors like wrong addresses or accounts that are not yours. Fixing these mistakes can help improve your credit score and demonstrate your creditworthiness.
Addressing Frequent Job Changes or Gaps in Employment
Employment history is important for lenders because it shows them how stable your income is. If you change jobs often or have gaps in work, it might raise concerns. Be ready to explain clearly why you changed jobs as mortgage lenders will want to know the reasons for your moves to see if you will be able to repay stable loan payments in the long run.
You can provide extra documents, like references or contracts, to back up your work history. Clearly explaining your career path and any gaps can help build trust in you as an applicant.
Strategies to Enhance Your Mortgage Application
A strong mortgage application includes important details that provides an overall picture of how good your financial profile is. By knowing what factors lenders look at, you can improve your chances of getting the mortgage you want.
Improving Your Credit Score
As your credit score is very important when securing a mortgage, there are steps you can take to improve your credit score over time.
Register on the Electoral Roll: Make sure you are registered at your current address. This ensures lenders can check who you are and builds your credit history.
Manage Existing Debts: Show that you can handle debts well by always paying your credit cards, loans, and bills on time.
Reduce Credit Utilisation: Try to use less than 50% of your credit limit. Using too much credit can harm your score.
Check for Errors: Regularly look at your credit report and if you find any mistakes, report them right away.
Preparing Your Documentation Thoroughly
Correct and meticulous documentation is critical for a smooth mortgage application. Lenders will require that you provide a comprehensive collection of documentation proving your financial situation.DocumentDescriptionProof of IdentityPassport, driver’s license, or national identity cardProof of AddressRecent utility bills, bank statements, or council tax billsProof of IncomeLast three months’ payslips (if employed), tax returns (if self-employed), or benefit statements (if applicable)Bank StatementsLast three to six months’ statements, clearly showing income and expenditureExisting Credit CommitmentsStatements for credit cards, loans, overdrafts, or other financial obligations to demonstrate your current debt levels
By organising these documents meticulously, you facilitate a more efficient application process.
How to avoid a mortgage decline
As a mortgage applicant, knowing why mortgage applications get rejected can help you overcome pitfalls ahead of going through the process. Key takeaways to consider ahead of applying:
Remember that lenders will look at factors such as your credit score, income, debt, and financial history before deciding if you qualify for a mortgage.
Some key reasons for declining applications include not enough income, high debt compared to income, bad credit history, and problems with the property’s value.
You can boost your chances of getting approved by ensuring your paperwork is correct, fixing issues on your credit report, and keeping your finances healthy.
If your application is turned down, you can fix the issues and try again after improving your financial situation.
Before applying stay informed and take action if something isn’t quite right. If you’re unsure of where to start, need some advice of applying for a mortgage or if you need help with overcoming rejection challenges, our expert team at Diamond Property Finance have been assisting clients with declined applications for many years.
We can help. Get in touch today to get started on your application journey.
0 notes
Text
Common tax mistakes online sellers make & how to avoid them
The rise of e-commerce, freelancing, and online side hustles has made it easier than ever to earn money online. However, many online sellers unknowingly make tax mistakes that can lead to penalties from HMRC. Whether you're selling through eBay, Etsy, Amazon, or your own website, staying tax-compliant is crucial. Below are some of the most common tax mistakes online sellers make—and how to avoid them.
Failing to register for self-assessment
Many online sellers assume they don’t need to register with HMRC if their earnings are small. However, if your income exceeds £1,000 per tax year, you must register for self-assessment and declare your earnings.'
How to avoid it:
Register for self-assessment via HMRC’s website before the deadline.
Keep track of all your earnings, even from small side gigs.
Not keeping proper financial records
HMRC requires accurate records of all income and expenses. Many online sellers fail to keep receipts, invoices, and transaction details, leading to miscalculations or tax underpayments.
How to avoid it:
Use accounting software like Xero or QuickBooks to track sales and expenses.
Store digital copies of invoices and receipts.
Regularly update your records to avoid last-minute errors.
Misunderstanding tax-deductible expenses
Many sellers either overclaim or underclaim expenses. Claiming personal expenses as business-related can trigger an HMRC investigation, while failing to claim legitimate deductions means paying more tax than necessary.
How to avoid it:
Claim only genuine business expenses, such as website hosting fees, packaging, and shipping costs.
Keep a clear separation between personal and business finances.
Ignoring VAT thresholds
If your online business’s turnover exceeds £90,000 (as of 2024), you must register for VAT. Many sellers fail to do this, leading to unexpected tax bills and penalties.
How to avoid it:
Monitor your turnover regularly to stay below or prepare for VAT registration.
Understand VAT rules for international sales if selling outside the UK.
Not declaring income from multiple platforms
Many sellers earn money across multiple platforms (e.g., eBay, Etsy, Shopify, Amazon) but only report income from one source, thinking HMRC won’t notice. However, HMRC has digital tools to track undeclared earnings.
How to avoid it:
Report all sources of income, including dropshipping, affiliate marketing, and freelancing.
Stay updated on HMRC’s digital tax investigations.
Failing to respond to HMRC nudge letters
Recently, HMRC has been sending nudge letters to online sellers suspected of undeclared income. If ignored, these letters can lead to deeper investigations or even penalties.
To understand how HMRC tracks online income and what to do if you receive a nudge letter, check out this detailed guide on HMRC’s crackdown on undeclared online income.
Final thoughts
Staying compliant with HMRC is essential for online sellers to avoid penalties and keep their business running smoothly. By understanding tax obligations, keeping proper records, and declaring all income sources, you can ensure compliance and peace of mind.
Need expert advice on handling your online business taxes? Consult an accountant to stay ahead of HMRC regulations.
0 notes
Text
From Confused to Confident: Mastering Self Assessment Tax Returns in 2025

Filing your self assessment tax returns can feel overwhelming — especially with changing rules, complex forms, and the risk of errors. Whether you're a UK resident, a non-resident earning UK income, or someone navigating HMRC’s system for the first time, understanding the process is crucial.
With the right guidance, you can move from feeling confused to confident when filing your self assessment tax returns in 2025. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process, highlight key tips, and explain how tools like the UK tax resident calculator can simplify your filing — especially if you’re submitting a tax return for non resident status.
1. What Are Self Assessment Tax Returns?
A self assessment tax return is HMRC's system for collecting income tax that hasn’t been automatically deducted from your salary, pension, or savings.
Who Needs to File a Self Assessment Tax Return?
✅ Self-Employed Individuals ✅ Freelancers and Contractors ✅ Landlords Earning Rental Income ✅ Company Directors (not paid through PAYE) ✅ High Earners (earning over £100,000 annually) ✅ Non-Residents with UK Income
If you’re unsure whether you need to file, HMRC offers a UK tax resident calculator that helps determine your residency status — a crucial factor in whether your income is taxable in the UK.
2. Key Changes to Self Assessment Tax Returns in 2025
Tax regulations evolve, and 2025 introduces several updates that may affect how you file:
1. Digital by Default
HMRC continues its “Making Tax Digital” initiative, encouraging individuals to file their self assessment tax returns online.
Paper submissions are still accepted but are slower and risk higher error rates.
2. Stricter Penalties for Late Filings
Penalties for late filing now start at £100 immediately after the deadline, with increasing fines for prolonged delays.
3. Enhanced Guidance for Non-Residents
HMRC now provides clearer instructions for those filing a tax return for non resident status, reducing the risk of overpayment.
3. How to Determine Your Residency Status with the UK Tax Resident Calculator
Residency status plays a major role in your tax obligations. If you live abroad but earn UK income, your residency status will determine how much tax you pay.
Using the UK Tax Resident Calculator
The UK tax resident calculator helps assess your status based on key factors:
✅ Number of days spent in the UK during the tax year ✅ Your primary home’s location ✅ Ties to the UK (e.g., family, employment, or property)
Why Is This Important?
If you qualify as a non-resident, you may only be taxed on your UK-sourced income — potentially reducing your overall tax liability. This is crucial when filing a tax return for non resident status.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Self Assessment Tax Returns
Follow these steps to confidently file your self assessment tax returns in 2025:
Step 1: Register for Self Assessment
First-time filers must register with HMRC.
After registration, you’ll receive a Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) — required for filing.
Step 2: Gather Your Financial Information
Ensure you have: ✅ P60/P45 (employment income) ✅ Bank statements (for interest earned) ✅ Rental income records (if you’re a landlord) ✅ Foreign income details (for a tax return for non resident) ✅ Expense receipts (to claim deductions)
Step 3: Use the UK Tax Resident Calculator
Before filing, use the UK tax resident calculator to confirm your residency status and determine which income sources must be reported.
Step 4: Complete Your Self Assessment Online
Log into your HMRC account.
Follow the guided steps, ensuring you declare all income streams, allowable expenses, and deductions.
Step 5: Claim Allowances and Deductions
Key deductions that reduce your tax bill include: ✅ Mortgage interest (for landlords) ✅ Business expenses (for self-employed individuals) ✅ Charitable donations ✅ Pension contributions
Step 6: Submit Your Tax Return and Payment
The filing deadline is 31 January 2026 for online submissions.
Payments must also be made by this deadline to avoid penalties.
5. Special Considerations for Non-Residents
If you’re filing a tax return for non resident status, be aware of these key points:
✅ Declare UK-Sourced Income Only: Non-residents are typically taxed only on UK earnings, not global income. ✅ Claim Double Taxation Relief: If you’re taxed abroad, you may qualify for relief to avoid paying tax twice. ✅ NRLS Registration: Non-resident landlords should register for the Non-Resident Landlord Scheme (NRLS) to prevent tax deductions at source.
Using the UK tax resident calculator ensures you accurately determine your status and avoid paying unnecessary tax.
6. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Self Assessment Tax Returns
Even seasoned filers can make costly mistakes. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for:
❌ Missing the Deadline: The deadline for online filing is 31 January 2026. Late submissions can lead to fines starting at £100. ❌ Forgetting to Declare Side Income: Income from side jobs, freelance work, or investments must be reported. ❌ Failing to Claim Deductions: Missing out on eligible expenses could mean overpaying tax. ❌ Incorrect Residency Status: Misjudging your status using the UK tax resident calculator can result in overpayment or fines. ❌ Incomplete Records: Always keep proof of income, expenses, and deductions for at least 5 years in case of HMRC inquiries.
7. Why Using Tax Software Can Make Filing Easier
Tax software can simplify filing your self assessment tax returns and ensure you meet deadlines while maximizing deductions.
Benefits of Tax Software:
✅ Step-by-Step Guidance: Ensures you don’t miss key entries. ✅ Automatic Calculations: Reduces errors and ensures accurate totals. ✅ Integrated UK Tax Resident Calculator: Helps determine if you should file a tax return for non resident status. ✅ Faster Refunds: Submitting online speeds up refund processing.
Popular platforms like TaxCalc, GoSimpleTax, and Taxfiler provide comprehensive support for UK residents and non-residents alike.
Conclusion
Filing your self assessment tax returns in 2025 doesn’t have to be stressful. By understanding key changes, using tools like the UK tax resident calculator, and staying informed about non-resident tax rules, you can file with confidence.
Whether you’re a freelancer, landlord, or expat handling a tax return for non resident status, following the right steps will ensure accuracy and potentially boost your refund.
Embrace the power of preparation — start your self assessment journey today and secure your financial future!
FAQs
1. When is the deadline for filing my self assessment tax return in 2025?
The deadline for online submissions is 31 January 2026. If you’re filing by paper, the deadline is 31 October 2025.
2. How do I use the UK tax resident calculator?
Visit the official HMRC website and follow the calculator’s prompts. It evaluates your residency status based on the number of days you’ve spent in the UK and your personal ties.
3. Do non-residents need to report foreign income?
Non-residents are generally taxed only on UK-sourced income. However, if you have global earnings that fall under UK tax rules, you may still need to declare them.
4. Can I amend my self assessment tax return after submission?
Yes. You can make changes to your self assessment tax returns online up to 12 months after the filing deadline.
5. What happens if I file my tax return late?
HMRC issues an immediate £100 fine for late submissions, with additional penalties accumulating over time.
#SA109#TaxSavings#TaxAccountant#Finance#Taxd#TaxFiling#TaxReturns#TaxdUK#FinancialPlanning#TaxSeason#Tax#UKTaxSelfAssessment#TaxationServices#TaxReturnOnline#FinancialServices
1 note
·
View note
Text
Self-Employed? Here’s How You Can Get a Home Loan Without Income Proof

For self-employed individuals, getting a home loan without income proof can be challenging. Most banks and financial institutions require salary slips, income tax returns (ITR), and proof of steady income to process loan applications. However, freelancers, small business owners, and gig workers often lack formal income documentation despite having consistent earnings.
If you're self-employed and looking to buy a house, don’t worry! There are alternative ways to secure a home loan without traditional income proof. This article will explore the best strategies, alternative documents, and financial tips to help you qualify for a home loan without salary slips or ITR.
Why Do Lenders Require Income Proof for Home Loans?
Banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) assess a borrower’s ability to repay a home loan by verifying their monthly income, job stability, and financial discipline. For salaried individuals, this is straightforward because of fixed monthly earnings. However, self-employed individuals often have fluctuating incomes and irregular cash flow, making lenders cautious.
To compensate for the lack of formal income documents, lenders may require alternative financial proof or collateral to approve a home loan.
Alternative Ways to Get a Home Loan Without Income Proof
1. Use Bank Statements as Income Proof
Even if you don’t have salary slips or ITR, consistent bank transactions can prove your financial stability. Banks may consider the average monthly balance and inflows from business revenue, freelance payments, or client transactions.
✔ Solution: Maintain a healthy balance in your bank account for at least 6-12 months before applying for a loan.
2. Show Business Revenue and Cash Flow
If you run a small business, lenders may accept business revenue as proof of income. Even if you don't have ITR, providing invoices, purchase orders, and audited profit and loss statements can strengthen your application.
✔ Solution: Organize your business transactions and tax payments to demonstrate financial credibility.
3. Opt for a Low Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio
A lower Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio means a higher down payment, reducing the lender’s risk. If you can pay 30-50% of the property value upfront, banks may be more willing to approve your loan even without income proof.
✔ Solution: Save a larger down payment before applying to increase approval chances.
4. Apply with a Co-Applicant or Guarantor
Having a co-applicant (spouse, parent, or sibling) with a stable income can significantly improve your loan approval chances. Similarly, a loan guarantor with a strong credit profile provides security to lenders.
✔ Solution: If possible, apply with a co-borrower who has regular income proof to enhance your credibility.
5. Provide Alternative Asset Proof
Many lenders approve home loans if you can show alternative assets, such as:
Fixed deposits (FDs)
Mutual funds or stock investments
Rental income from other properties
Gold holdings or other financial assets
✔ Solution: Show strong asset value as financial backup to assure lenders of repayment ability.
6. Choose a Housing Finance Company (HFC) Over Traditional Banks
Housing Finance Companies (HFCs) such as HDFC, LIC Housing Finance, and Indiabulls Housing Finance offer more flexible loan eligibility criteria compared to traditional banks. They consider bank statements, property value, and alternative documents rather than just ITR.
✔ Solution: Apply with HFCs that specialize in home loans for self-employed individuals.
7. Improve Your CIBIL Score
A strong CIBIL score (750 or above) boosts your chances of getting a home loan, even without income proof. Lenders trust borrowers with good repayment history, credit card usage, and responsible financial behavior.
✔ Solution: Pay off existing debts, clear outstanding credit card bills, and avoid frequent loan applications before applying for a home loan.
Best Banks and NBFCs Offering Home Loans Without Income Proof
Several Indian banks and NBFCs offer home loans to self-employed individuals without salary slips or ITR, based on alternative documents. Some of these include:
🔹 HDFC Home Loans – Allows loans based on bank statements and property value. 🔹 LIC Housing Finance – Accepts alternative financial proof and business transactions. 🔹 Indiabulls Housing Finance – Offers flexible home loan options for freelancers and business owners. 🔹 Bajaj Finserv – Provides home loans with minimal documentation, focusing on CIBIL scores and assets. 🔹 SBI Home Loans (Non-Salaried Category) – Custom loan plans for self-employed professionals.
✔ Tip: Compare interest rates, processing fees, and tenure options before selecting a lender.
Key Tips to Increase Home Loan Approval Chances
✔ Maintain a consistent bank balance and avoid frequent withdrawals. ✔ Avoid multiple loan applications at the same time, as it may reduce your creditworthiness. ✔ Maintain a strong repayment history to increase your credit score. ✔ Choose longer loan tenure to reduce the monthly EMI burden. ✔ Be ready with alternative documents such as business revenue reports, rental income, and asset statements.
Final Thoughts
Getting a home loan without income proof is challenging but not impossible for self-employed individuals. By using alternative documentation, improving credit scores, and opting for the right lender, you can secure a home loan and achieve your dream of homeownership.
With proper financial planning and documentation, you can confidently apply for a home loan, even without salary slips or ITR. Start preparing today, and take a step closer to owning your dream home!
0 notes
Text
How to Get a Personal Loan If You Are a Freelancer?
Introduction
A personal loan is a versatile financial tool that can help individuals meet their financial needs, whether for medical emergencies, home renovations, education, weddings, or business investments. However, for freelancers and self-employed professionals, securing a personal loan can be more challenging than it is for salaried employees.
Since freelancers do not have a fixed salary or employer-backed income, lenders consider them as higher-risk borrowers. As a result, they often face higher interest rates, stricter eligibility criteria, and additional documentation requirements. But does that mean freelancers cannot get a personal loan? Not at all!
In this article, we will explore the steps to secure a personal loan as a freelancer, the eligibility criteria, required documents, and practical tips to improve your loan approval chances.
1. Challenges Freelancers Face While Applying for a Personal Loan
Freelancers and self-employed professionals earn income from multiple sources, which can fluctuate every month. This makes lenders cautious while offering them personal loans.
✔️ Irregular Income: Since freelancers do not receive a fixed monthly salary, lenders consider them financially unstable. ✔️ Lack of Employer Verification: Banks and NBFCs prefer salaried individuals because they have stable jobs and employer-backed income proofs. ✔️ Higher Risk for Lenders: Freelancers are considered high-risk borrowers because their income may vary based on market conditions, client payments, or industry demand. ✔️ Strict Loan Approval Process: Due to unstable earnings, many freelancers face higher rejection rates or receive loans at higher interest rates.
💡 Tip: If you are a freelancer, prepare to show stable income proof and strong credit history to increase approval chances.
2. Personal Loan Eligibility Criteria for Freelancers
Although freelancers face stricter lending criteria, most banks and NBFCs offer personal loans if the applicant meets the following eligibility requirements:
✔️ Age Requirement: 21 to 60 years. ✔️ Minimum Annual Income: ₹2-3 lakh (varies by lender). ✔️ Credit Score: 750+ (higher credit scores improve approval chances). ✔️ Business Stability: At least 2-3 years of steady freelance income. ✔️ Bank Statements & ITR: Proof of regular income through bank transactions and income tax returns (ITR).
💡 Tip: If you are a freelancer, maintain consistent income records and file your ITR to meet lender eligibility requirements.
3. Documents Required for Freelancers Applying for a Personal Loan
Since freelancers do not have a salary slip, lenders require alternative financial documents to verify their income stability.
✔️ Identity Proof (KYC Documents): Aadhaar Card, PAN Card, Voter ID, Passport, or Driving License. ✔️ Address Proof: Utility Bill, Rental Agreement, Passport, or Voter ID. ✔️ Income Proof:
Last 6 to 12 months' bank statements.
Income Tax Returns (ITR) for the last 2-3 years.
Invoices and payment receipts from clients. ✔️ Business Proof (if applicable): GST Registration, Business License, or Work Contracts.
💡 Tip: If you do not have an ITR history, start filing tax returns as proof of stable earnings.
4. How to Increase Your Chances of Getting a Personal Loan as a Freelancer?
If you are a freelancer and want to secure a personal loan with better interest rates and flexible terms, follow these essential steps:
4.1 Maintain a High Credit Score
A credit score of 750 or above improves your chances of getting a personal loan at lower interest rates.
✔️ Pay credit card bills and EMIs on time. ✔️ Avoid multiple loan applications at once. ✔️ Keep your credit utilization below 30%.
💡 Tip: If your credit score is low, improve it before applying for a personal loan.
4.2 Show Consistent Income Through Bank Statements
Since freelancers do not have salary slips, lenders rely on bank statements to assess their financial stability.
✔️ Deposit client payments in a single bank account to show steady inflow. ✔️ Avoid frequent cash withdrawals, as lenders prefer digital transactions. ✔️ Ensure stable earnings for at least 6-12 months before applying.
💡 Tip: If possible, generate monthly invoices to maintain a professional financial record.
4.3 File Your Income Tax Returns (ITR) Regularly
ITR is one of the most important documents for freelancers applying for a personal loan.
✔️ File ITR for at least the last 2-3 years. ✔️ Ensure your ITR shows a taxable income above ₹2-3 lakh. ✔️ Keep Form 16A (Tax Deducted at Source) from clients as proof.
💡 Tip: If you do not have ITR history, start filing tax returns immediately to improve your financial credibility.
4.4 Apply for a Loan with an NBFC or Digital Lender
Many banks have strict policies for freelancers, but NBFCs and fintech lenders offer personal loans with flexible terms.
✔️ NBFCs have lower eligibility criteria than banks. ✔️ Digital lenders provide instant approval based on alternative credit scoring. ✔️ Some fintech lenders consider freelance contracts and client payments for loan approval.
💡 Tip: Compare multiple lenders before choosing the best personal loan offer.
4.5 Consider Applying with a Co-Applicant or Guarantor
If your income stability is low, adding a co-applicant (spouse, sibling, or parent) with a steady salary can increase loan approval chances.
✔️ A co-applicant with a good credit score strengthens your application. ✔️ You can secure a higher loan amount with a lower interest rate.
💡 Tip: Choose a co-applicant who has a stable job and a credit score above 750.
4.6 Choose a Loan with Affordable EMIs
Since freelance income can fluctuate, it is essential to choose an EMI plan that fits your budget.
✔️ Use a personal loan EMI calculator before applying. ✔️ Select a loan tenure that offers a comfortable EMI amount. ✔️ Opt for flexible repayment options like step-up or bullet repayment plans.
💡 Tip: Do not take a loan with high EMIs that may become difficult to repay during slow business months.
5. Best Lenders Offering Personal Loans for Freelancers
Several banks, NBFCs, and digital lenders offer personal loans to freelancers. Here are some options:
✔️ HDFC Bank Personal Loan – Flexible eligibility for self-employed applicants. ✔️ Bajaj Finserv Personal Loan – Quick approval with minimal documentation. ✔️ IDFC First Bank Personal Loan – Suitable for freelancers with ITR history. ✔️ MoneyTap & KreditBee (Fintech Lenders) – Instant approval for freelancers with variable income.
💡 Tip: Compare interest rates, loan tenure, and prepayment charges before applying.
Final Thoughts
Getting a personal loan as a freelancer requires careful financial planning and proper documentation. While it may be more challenging than for salaried individuals, it is not impossible.
Key Takeaways:
✔️ Maintain a strong credit score (750+) to improve approval chances. ✔️ Show consistent income through bank statements and ITRs. ✔️ Compare lenders to get the best personal loan interest rates. ✔️ Consider applying with a co-applicant for better loan terms.
By following these strategies, freelancers can successfully secure a personal loan and meet their financial needs without hassle.
For expert financial advice and the best personal loan offers, visit www.fincrif.com today!
#personal loan#loan apps#fincrif#nbfc personal loan#bank#personal loans#personal loan online#finance#loan services#personal laon#Personal loan#Personal loan for freelancers#Personal loan for self-employed#Freelancer loan eligibility#How to get a loan as a freelancer#Best personal loan options for freelancers#Instant loan for self-employed individuals#Low-interest personal loan for freelancers#Documents required for a freelancer loan#Personal loan for gig workers#Self-employed personal loan approval#How can a freelancer get a personal loan in India?#Best banks offering personal loans for freelancers#Loan eligibility criteria for self-employed professionals#What documents do freelancers need for a personal loan?#How to improve personal loan approval as a freelancer?#Personal loan without income proof for self-employed individuals#How to apply for a personal loan as a freelancer online?#Which banks offer the best personal loan for freelancers?#How to get a low-interest personal loan as a freelancer?
0 notes
Text
Common Accounting Mistakes Small Businesses Make and How Online Services Can Help

Good accounting is key to running a successful small business. However, many business owners make common mistakes that can lead to financial problems, tax issues, and HMRC penalties. Online accounting services can help prevent these mistakes by providing accurate, automated, and easy-to-use financial tools. Here are some common accounting mistakes and how online services can help:
1. Not Keeping Accurate Records
Many small businesses fail to track their income and expenses properly. Poor record-keeping can lead to incorrect tax filings and missed deductions. Online accounting software, such as QuickBooks, Xero, and FreeAgent, automatically records transactions, categorises expenses, and generates financial reports.
2. Mixing Personal and Business Finances
Using the same bank account for personal and business transactions makes it difficult to track business finances. Online accounting services help by linking directly to business bank accounts, making it easier to separate personal and business expenses.
3. Forgetting to Track VAT and Taxes
Many small businesses forget to account for VAT and other taxes, leading to unexpected tax bills. Online accounting software calculates VAT, Corporation Tax, and Self-Assessment tax automatically. It also sends reminders for tax deadlines, ensuring you stay compliant with HMRC rules.
4. Not Sending Invoices on Time
Late invoicing leads to cash flow problems. Many businesses forget to send invoices or fail to track payments. Online accounting services offer automated invoicing, payment reminders, and tracking tools to ensure customers pay on time.
5. Failing to Reconcile Bank Transactions
Failing to match business transactions with bank statements can lead to errors and missing funds. Online accounting software connects to your bank and reconciles transactions in real time, helping you spot any discrepancies quickly.
6. Ignoring Payroll Compliance
If you have employees, you must report payroll details to HMRC correctly and on time. Online accounting services integrate with payroll software, ensuring compliance with Real Time Information (RTI) reporting and automating tax deductions for employees.
7. Not Backing Up Financial Data
Losing financial data due to system failures can be a disaster for a small business. Cloud-based accounting services securely store financial data online, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring quick access when needed.
8. Mismanaging Cash Flow
Many small businesses struggle with cash flow management, leading to late payments and financial instability. Online accounting tools provide real-time cash flow tracking, helping business owners plan expenses and avoid cash shortages.
9. Missing Tax Deductible Expenses
Small businesses often fail to claim all allowable expenses, which can result in overpaying tax. Online accounting software tracks deductible expenses automatically, ensuring you maximise tax savings.
10. Not Seeking Professional Help
Trying to handle accounting without expert guidance can lead to costly mistakes. Many online accounting platforms offer expert support from accountants and tax advisors, helping businesses stay compliant and make better financial decisions.
Conclusion
Accounting mistakes can cost small businesses time and money. Online accounting services help by automating financial tasks, tracking expenses, and ensuring compliance with HMRC regulations. Using cloud-based solutions like QuickBooks, Xero, or FreeAgent can reduce errors, improve cash flow, and make tax filing easier. By switching to online accounting, small businesses can focus on growth without worrying about financial mistakes.
0 notes
Text
How to Qualify for a Solar Loan: Eligibility, Credit Score, and Documentation

Switching to solar energy is an excellent investment that helps reduce electricity bills while promoting sustainability. However, the high upfront cost of solar panel installation can be a challenge for many homeowners and businesses. This is where solar loans come in, offering flexible financing options that allow individuals to install solar systems without bearing the entire cost at once.
To secure a solar loan, lenders assess various factors such as eligibility criteria, credit score, and necessary documentation. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to qualify for a solar loan and maximize your chances of approval.
1. Understanding Solar Loans
A solar loan is a financing option designed to help homeowners and businesses install solar photovoltaic (PV) systems by offering structured repayment plans. These loans allow individuals to enjoy immediate energy savings while spreading the cost of the solar system over several years.
Solar loans can be secured or unsecured, with interest rates varying based on the borrower’s creditworthiness and lender policies. Many banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), and fintech platforms offer solar financing at competitive rates.
2. Eligibility Criteria for a Solar Loan
Lenders evaluate several factors to determine whether an applicant qualifies for a solar loan. The general eligibility criteria include:
A. Age Requirement
For salaried individuals, the applicant should typically be between 21 to 60 years.
For self-employed individuals and business owners, the maximum age limit is usually 65 years.
B. Employment Type
Salaried professionals working in government or private sector jobs are eligible.
Self-employed individuals and business owners can apply, but they may need to show proof of a stable income.
C. Income Stability
Lenders require a minimum monthly income to ensure the borrower can repay the loan.
Income requirements vary but typically start from ₹20,000 per month for salaried individuals and ₹3-5 lakh annual turnover for businesses.
D. Location and Property Ownership
The applicant must own the property where the solar system will be installed.
Some lenders may require the property to be located in an approved urban or semi-urban area.
Tip: Check with different lenders as eligibility criteria may vary across financial institutions.
3. Importance of Credit Score for Solar Loans
Your credit score is one of the most critical factors that determine loan approval and interest rates. In India, lenders typically check CIBIL scores before approving solar loans.
Credit Score Requirements:
750 and above → Excellent (Best interest rates and quick approval).
650 – 749 → Good (Eligible for loans, but with slightly higher interest rates).
550 – 649 → Average (Approval possible but with higher interest rates and stricter conditions).
Below 550 → Poor (Difficult to get approval; may require a guarantor or collateral).
How to Improve Your Credit Score for a Solar Loan?
Pay existing EMIs and credit card bills on time.
Reduce outstanding debt before applying for a new loan.
Avoid multiple loan applications within a short period.
Check your credit report for errors and rectify them before applying.
Tip: If your credit score is low, consider applying with a co-applicant or offering collateral for better approval chances.
4. Documents Required for a Solar Loan
Having the correct documents ready speeds up the loan approval process. The required documents generally include:
A. Identity and Address Proof
Aadhaar Card / PAN Card
Passport / Voter ID / Driving License
Utility bills or rental agreement (for address verification)
B. Income Proof
For salaried applicants:
Latest salary slips (last 3 months)
Form 16 or ITR (Income Tax Returns) for the last 2 years
Bank statements (last 6 months)
For self-employed/business owners:
Business registration certificate or GST details
Profit and loss statement / ITR for the last 2 years
Bank statements (last 6-12 months)
C. Property Documents
Proof of property ownership (Sale deed, property tax receipt, etc.)
NOC (No Objection Certificate) from relevant authorities (if required)
D. Solar System Details
Quotation or invoice from a registered solar panel vendor or EPC contractor
Technical specifications of the solar PV system
Estimated savings and return on investment (ROI) report
Tip: Some lenders may offer pre-approved solar loans to existing customers with a strong repayment history.
5. How to Apply for a Solar Loan?
Step 1: Research Lenders
Compare solar loan offerings from banks, NBFCs, fintech platforms, and government-backed schemes for the best interest rates and flexible repayment terms.
Step 2: Check Your Eligibility
Use online eligibility calculators provided by banks to see if you qualify before applying.
Step 3: Gather Required Documents
Ensure all necessary KYC, income proof, and property-related documents are in place.
Step 4: Apply Online or Offline
Many lenders offer online applications through their website or mobile app.
Alternatively, you can visit the nearest bank or NBFC branch for offline processing.
Step 5: Loan Approval and Disbursement
Once your application is submitted, the lender will conduct a credit assessment and document verification.
Upon approval, the loan amount will be disbursed directly to the solar vendor or your bank account.
Tip: Some states in India offer subsidies on solar loans under the PM-KUSUM scheme and state-specific solar programs.
Final Thoughts: Make the Switch to Solar with the Right Loan
A solar loan is a smart financing option that makes solar panel installation affordable while allowing homeowners and businesses to enjoy long-term energy savings.
✔️ Check your eligibility criteria before applying. ✔️ Maintain a good credit score for better loan terms. ✔️ Prepare the necessary documents to speed up approval. ✔️ Compare lenders to get the best interest rates and flexible repayment options.
By following these best practices, you can easily qualify for a solar loan, transition to clean energy, and reduce your electricity costs.
0 notes
Text
Why Every Self-Employed Person Needs the HMRC CGT Calculator
Imagine this: You’ve finally taken the plunge and decided to register as self-employed in the UK. You’re excited, ready to build your business, and looking forward to financial freedom. But then, tax season arrives, and suddenly, you’re faced with an unexpected question: What about capital gains tax (CGT)?

Many self-employed professionals assume CGT only applies to property investors or stock traders, but here’s the reality—if you sell business assets like equipment, vehicles, or even intellectual property, you could owe CGT. That’s where the HMRC CGT Calculator becomes your best friend.
Understanding CGT as a Self-Employed Professional
If you’re self-employed and decide to sell an asset related to your business, such as:
A van used for deliveries
Office equipment
Business shares
You might have to calculate and report capital gains. The HMRC CGT Calculator helps estimate how much tax you owe based on your sale price, purchase price, and any deductions available.
How to Use the HMRC CGT Calculator?
Enter the details of your sold asset – Original purchase price, selling price, and any improvements.
Account for business expenses – Legal fees, maintenance costs, and more.
Calculate your tax rate – Depending on your income bracket, CGT varies (10% for basic rate taxpayers, 20% for higher rate taxpayers).
Apply available reliefs – Business Asset Disposal Relief can significantly reduce your tax liability.
Why This Matters to You?
Many newly self-employed individuals overlook CGT, thinking it doesn’t apply to them. But ignoring it can lead to penalties. When you register as self-employed in the UK, you’re responsible for reporting all taxable income—including gains from asset sales.
The HMRC CGT Calculator isn’t just a tool; it’s a necessity to keep your tax bills in check and ensure you only pay what’s required. Before selling any business assets, run the numbers. You might save more than you think!
Conclusion
Capital Gains Tax can be a hidden liability for the self-employed, but with the right tools like the HMRC CGT Calculator, you can stay ahead of your tax obligations. Whether you're selling business equipment or shares, being proactive with tax calculations ensures you keep more of your hard-earned money. Stay informed, plan wisely, and always check before you sell!
FAQs
1. Do I need to pay CGT if I am self-employed? Yes, if you sell business assets such as vehicles, equipment, or shares at a profit, you may owe Capital Gains Tax. The HMRC CGT Calculator helps estimate your liability.
2. How can I reduce my CGT liability? You can apply for reliefs like Business Asset Disposal Relief, deduct business expenses, and ensure you use your annual CGT allowance to lower your tax bill.
3. When do I need to report CGT to HMRC? You must report and pay CGT within 60 days of selling a property or by the Self-Assessment deadline for other assets.
4. What happens if I don’t report CGT on time? Failure to report CGT on time can result in penalties and interest charges from HMRC. It’s crucial to use the HMRC CGT Calculator to estimate your tax and submit it before the deadline.
5. Does CGT apply if I transfer business assets to a family member? Yes, in most cases, CGT applies even when transferring assets to family members. However, certain reliefs, such as Gift Hold-Over Relief, may allow you to defer the tax liability.
#buytolet#investmenttax#taxplanning#tax refund#landlordtax#60 tax trap calculator#united kingdom#rentalincome#taxfiling
0 notes