#object oriented design paradigm
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Jest: A Concept for a New Programming Language
Summary: "Jest" could be envisioned as a novel computer programming language with a focus on humor, playfulness, or efficiency in a specific domain. Its design might embrace creativity in syntax, a unique philosophy, or a purpose-driven ecosystem for developers. It could potentially bridge accessibility with functionality, making coding intuitive and enjoyable.
Definition: Jest: A hypothetical computer language designed with a balance of simplicity, expressiveness, and potentially humor. The name suggests it might include unconventional features, playful interactions, or focus on lightweight scripting with a minimalist approach to problem-solving.
Expansion: If Jest were to exist, it might embody these features:
Playful Syntax: Commands and expressions that use conversational, quirky, or approachable language. Example:
joke "Why did the loop break? It couldn't handle the pressure!"; if (laughs > 0) { clap(); }
Efficiency-Focused: Ideal for scripting, rapid prototyping, or teaching, with shortcuts that reduce boilerplate code.
Modular Philosophy: Encourages user-created modules or libraries, reflecting its playful tone with practical use cases.
Integrated Humor or Personality: Built-in error messages or prompts might be witty or personalized.
Flexibility: Multi-paradigm support, including functional, procedural, and object-oriented programming.
Transcription: An example code snippet for a Jest-like language:
// Hello World in Jest greet = "Hello, World!"; print(greet); laugh();
A Jest program that calculates Fibonacci numbers might look like this:
// Fibonacci in Jest fib = (n) => n < 2 ? n : fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
joke "What's the Fibonacci sequence? You'll love it, it grows on you!"; n = 10; print("The Fibonacci number at", n, "is:", fib(n));
Potential Domains:
Gamified education
Creative industries
AI-driven storytelling
Interactive debugging
Would you like me to refine or explore additional aspects?
Certainly! If we were to imagine Jest as the brainchild of a creative coder or team, their portfolio would likely include other innovative or experimental programming languages. Let’s expand on this concept and invent some plausible complementary languages the same inventor might have designed.
Related Languages by the Inventor of Jest
Pantomime
Description: A visual programming language inspired by gesture and movement, where users "drag and drop" symbols or create flowcharts to express logic. Designed for non-coders or children to learn programming through interaction.
Key Features:
Icon-based syntax: Conditional loops, variables, and functions represented visually.
Works seamlessly with Jest for creating visual representations of Jest scripts.
Sample Code (Visual Representation): Flowchart blocks: Input → Decision → Output.
Facet
Description: A declarative programming language focusing on creativity and modularity, aimed at artists, designers, and 3D modelers. Facet could integrate well with game engines and creative suites like Blender or Unity.
Key Features:
Embedded visual tools for shaders, animations, and simulations.
Simplified expressions for creative coding (e.g., animations and generative art).
Sample Code:
shape = circle(radius: 10, color: "blue"); animation = wave(shape, amplitude: 5, frequency: 2); render(animation, duration: 10s);
Quip
Description: A lightweight scripting language built for humor, similar to Jest, but more focused on natural language processing, chatbots, and interactive storytelling.
Key Features:
Syntax mirrors conversational English.
Designed for AI integration, especially in storytelling apps.
Sample Code:
character "Alice" says "Hello! What's your name?"; user_input -> name; character "Alice" says "Nice to meet you, {name}!";
Cryptic
Description: A language for designing cryptography algorithms and secure communications. Aimed at developers interested in blockchain, encryption, or cybersecurity.
Key Features:
High-level abstractions for cryptographic primitives.
Secure-by-design philosophy.
Sample Code:
key = generate_key(algorithm: "AES", length: 256); encrypted_message = encrypt("Hello, World!", key); print(encrypted_message);
Harmony
Description: A reactive programming language for building interactive user interfaces, designed to be highly interoperable with Jest and other tools in the suite. Perfect for web developers and app creators.
Key Features:
Two-way data binding with minimal boilerplate.
Component-based architecture.
Sample Code:
component Button { state: clicked = false; onClick() { clicked = !clicked; alert("Button clicked!"); } } render(Button);
Inventor’s Vision
The coder or team behind Jest and these complementary languages would likely be passionate about:
Accessibility: Making programming intuitive and fun for people of all skill levels.
Playfulness: Infusing coding with creativity, humor, and expressiveness.
Interoperability: Ensuring all their languages work well together for larger projects.
Would you like me to dive deeper into one of these languages, conceptualize others, or expand Jest further?
Expanded Concepts and Bridge Languages
Pantomime
Expansion: Adds support for AR/VR interfaces where users use gestures to program logic in 3D space. For example, drawing a loop physically creates a repetitive cycle.
Bridge Language: GestureScript: Converts AR/VR gestures from Pantomime into traditional code for broader applications.
Facet
Expansion: Enhanced for generative AI tools, allowing users to define complex artistic styles and AI-driven procedural designs.
Bridge Language: PixelForge: Focused on exporting Facet code into game engines, enabling real-time rendering pipelines for interactive environments.
Quip
Expansion: Includes pre-trained AI models for dynamic storytelling, allowing Quip scripts to evolve based on user interaction.
Bridge Language: Narrate: Combines Quip scripts with voice-to-text technologies for live storytelling in games or educational tools.
Cryptic
Expansion: Introduces quantum-safe cryptography primitives and allows simulation of blockchain-like ecosystems for testing purposes.
Bridge Language: CipherBridge: Translates Cryptic code into various blockchain frameworks like Ethereum or Solana.
Harmony
Expansion: Gains support for cross-platform development, allowing users to write code for web, mobile, and IoT devices simultaneously.
Bridge Language: Symphony: Converts Harmony components into platform-native scripts for seamless integration.
Additional Bridge Languages
Echo: Bridges Quip and Jest, enabling storytelling code to trigger functional scripts for immersive experiences.
Morph: A universal language that compiles any Jest family code into executable binaries for specific operating systems.
Thread: Integrates Cryptic and Harmony to build secure, reactive user interfaces for fintech applications.
Canvas: Bridges Facet and Pantomime to create interactive art in AR/VR, blending visual coding with gesture inputs.
Let me know if you'd like a deeper dive into any specific language or bridge concept!
Here's a detailed exploration of Echo, Morph, Thread, Canvas, and all previously mentioned languages, emphasizing their unique applications and advanced functionalities.
Expanded Bridge Languages
Echo
Purpose: Links storytelling elements in Quip with functional programming in Jest, enabling dynamic, immersive interactions between narrative and logic.
Key Features:
Story-driven logic triggers: e.g., a character’s dialogue prompts a database query or API call.
Integration with AI tools for real-time responses.
Use Case: AI-driven chatbots that incorporate both storytelling and complex backend workflows.
Sample Code:
story_event "hero_arrives" triggers fetch_data("weather"); response = "The hero enters amidst a storm: {weather}.";
Morph
Purpose: Acts as a meta-compiler, translating any language in the Jest ecosystem into optimized, platform-specific binaries.
Key Features:
Universal compatibility across operating systems and architectures.
Performance tuning during compilation.
Use Case: Porting a Jest-based application to embedded systems or gaming consoles.
Sample Code:
input: Facet script; target_platform: "PS7"; compile_to_binary();
Thread
Purpose: Combines Cryptic's security features with Harmony's reactive architecture to create secure, interactive user interfaces.
Key Features:
Secure data binding for fintech or healthcare applications.
Integration with blockchain for smart contracts.
Use Case: Decentralized finance (DeFi) apps with intuitive, safe user interfaces.
Sample Code:
bind secure_input("account_number") to blockchain_check("balance"); render UI_component(balance_display);
Canvas
Purpose: Fuses Facet's generative design tools with Pantomime's gesture-based coding for AR/VR art creation.
Key Features:
Real-time 3D design with hand gestures.
Multi-modal export to AR/VR platforms or 3D printers.
Use Case: Collaborative VR environments for designers and architects.
Sample Code:
gesture: "draw_circle" → create_3D_shape("sphere"); gesture: "scale_up" → modify_shape("sphere", scale: 2x); render(scene);
Deep Dive into Main Languages
Jest
Philosophy: A playful, expressive scripting language with versatile syntax tailored for humor, experimentation, and creativity.
Core Application: Writing scripts that blend functional programming with a whimsical, human-readable style.
Pantomime
Expanded Features: Includes AI-driven gesture recognition for predictive modeling and natural motion capture.
Advanced Use: Developing AR apps for rehabilitation therapy where exercises are coded as gestures.
Facet
Advanced Use: Procedural generation in games, defining terrains, weather systems, and NPC behaviors with artistic flair.
Quip
Advanced Features: Integrates pre-trained language models for nuanced, character-driven dialogue trees.
Advanced Use: Creating adaptive narratives in games where user decisions alter the story arc.
Cryptic
Advanced Features: Quantum-safe algorithms and AI-enhanced key generation for unbreakable security.
Advanced Use: Designing multi-layered blockchain ecosystems with Cryptic’s high-level abstractions.
Harmony
Advanced Features: Adaptive UIs that respond to user emotion, tracked via AI-enhanced cameras.
Advanced Use: Apps for mental health, where interfaces adjust to user stress levels.
Proposed New Bridge Languages
Chord
Bridges Harmony and Facet for designing interactive music-based visual art.
Use Case: Music videos where the visuals respond to real-time sound input.
Path
Links Cryptic and Canvas for secure AR/VR environments.
Use Case: Virtual meetings in secure, customized 3D spaces.
Fable
Connects Quip and Pantomime for storytelling via interactive gestures.
Use Case: VR education apps where lessons are taught through immersive narratives.
Would you like a specific implementation plan for any of these languages or applications?
#playstation7#deardearestbrands#ps7#digitalconsole#framework#python#celestiallink#Code#Script#Language#pantomime#Echo#Canvas#Fable#Morph#Bridge#Path#Chord#Harmony#Cryptic#Quip#Facet
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
Read a blog post that offhandedly mentioned how we're not seeing any radical advances in coding languages--calls it a 'decellerando'. D'ya think they can get any better?
It's complicated, but yeah, I broadly agree.
I don't know how much background knowledge you have, so to put it very simply: all programming languages are lists of things a computer should do, designing a programming language is a process of picking what the programmer is allowed to ask for and what the programmer is not allowed to ask for, and we are running out of ideas for what we might want to put in those two categories. (If you want to come up with creative ideas for a programming language, you have to come up with bad ideas for a programming language.)
The current debate is (again very simply) over whether a language should make it hard to write a program which is not well-formed ('dynamic', 'weak'), or whether it should make it hard to write a program which is not what you meant ('static', 'strong'). To use a math analogy: if I type 'twenty eight+14' into Desmos, should it return '42' or 'syntax error'?
I'm in camp 'what I mean', but I don't think other side is always in the wrong, either. There's a tension in both, I think, between the ways they require you think about your programs and the ways humans beings actually think. I suspect that may be intractable.
There are other debates, too. These all tend to rise in and out of public discussion at semi-regular intervals. One of the bigger ones is about 'objects'. To again oversimplify: if you were trying to represent Chess, would you say that a piece and the rules describing it are the same thing ('object oriented') or that the rules and the pieces are different things ('imperative', or maybe instead one of several other paradigms)? I tend to side against objects, but again there's an intractable tension in all approaches. Sometimes you wish you could have it both ways.
All of these debates have arisen because the compromises programming languages need to make are (mostly) no longer about what computer can and cannot do, but what human brains can and cannot do. There's still some cultural lag from when this wasn't the case -- not every idea has had its day in the sun -- but we're catching up fast. (Some people think that large language models will help them overcome what their brain cannot do. I am extremely skeptical.)
There is one space where I still think there's room for experimentation, and that's machine code. The real bare metal stuff. Unlike programming languages, good and fast computers are very expensive to design, build, and buy. This means that there are way more ways to build computers than have gotten a fair shake yet. Maybe one day VLIW will see the light...
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Python Programming Language: A Comprehensive Guide
Python is one of the maximum widely used and hastily growing programming languages within the world. Known for its simplicity, versatility, and great ecosystem, Python has become the cross-to desire for beginners, professionals, and organizations across industries.
What is Python used for

🐍 What is Python?
Python is a excessive-stage, interpreted, fashionable-purpose programming language. The language emphasizes clarity, concise syntax, and code simplicity, making it an excellent device for the whole lot from web development to synthetic intelligence.
Its syntax is designed to be readable and easy, regularly described as being near the English language. This ease of information has led Python to be adopted no longer simplest through programmers but also by way of scientists, mathematicians, and analysts who may not have a formal heritage in software engineering.
📜 Brief History of Python
Late Nineteen Eighties: Guido van Rossum starts work on Python as a hobby task.
1991: Python zero.9.0 is released, presenting classes, functions, and exception managing.
2000: Python 2.Zero is launched, introducing capabilities like list comprehensions and rubbish collection.
2008: Python 3.Zero is launched with considerable upgrades but breaks backward compatibility.
2024: Python three.12 is the modern day strong model, enhancing performance and typing support.
⭐ Key Features of Python
Easy to Learn and Use:
Python's syntax is simple and similar to English, making it a high-quality first programming language.
Interpreted Language:
Python isn't always compiled into device code; it's far done line by using line the usage of an interpreter, which makes debugging less complicated.
Cross-Platform:
Python code runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and even cell devices and embedded structures.
Dynamic Typing:
Variables don’t require explicit type declarations; types are decided at runtime.
Object-Oriented and Functional:
Python helps each item-orientated programming (OOP) and practical programming paradigms.
Extensive Standard Library:
Python includes a rich set of built-in modules for string operations, report I/O, databases, networking, and more.
Huge Ecosystem of Libraries:
From data technological know-how to net development, Python's atmosphere consists of thousands of programs like NumPy, pandas, TensorFlow, Flask, Django, and many greater.
📌 Basic Python Syntax
Here's an instance of a easy Python program:
python
Copy
Edit
def greet(call):
print(f"Hello, call!")
greet("Alice")
Output:
Copy
Edit
Hello, Alice!
Key Syntax Elements:
Indentation is used to define blocks (no curly braces like in different languages).
Variables are declared via task: x = 5
Comments use #:
# This is a remark
Print Function:
print("Hello")
📊 Python Data Types
Python has several built-in data kinds:
Numeric: int, go with the flow, complicated
Text: str
Boolean: bool (True, False)
Sequence: listing, tuple, range
Mapping: dict
Set Types: set, frozenset
Example:
python
Copy
Edit
age = 25 # int
name = "John" # str
top = 5.Nine # drift
is_student = True # bool
colors = ["red", "green", "blue"] # listing
🔁 Control Structures
Conditional Statements:
python
Copy
Edit
if age > 18:
print("Adult")
elif age == 18:
print("Just became an person")
else:
print("Minor")
Loops:
python
Copy
Edit
for color in hues:
print(coloration)
while age < 30:
age += 1
🔧 Functions and Modules
Defining a Function:
python
Copy
Edit
def upload(a, b):
return a + b
Importing a Module:
python
Copy
Edit
import math
print(math.Sqrt(sixteen)) # Output: four.0
🗂️ Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Python supports OOP functions such as lessons, inheritance, and encapsulation.
Python
Copy
Edit
elegance Animal:
def __init__(self, call):
self.Call = name
def communicate(self):
print(f"self.Call makes a valid")
dog = Animal("Dog")
dog.Speak() # Output: Dog makes a legitimate
🧠 Applications of Python
Python is used in nearly each area of era:
1. Web Development
Frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI make Python fantastic for building scalable web programs.
2. Data Science & Analytics
Libraries like pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib permit for data manipulation, evaluation, and visualization.
Three. Machine Learning & AI
Python is the dominant language for AI, way to TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-research, and Keras.
4. Automation & Scripting
Python is extensively used for automating tasks like file managing, device tracking, and data scraping.
Five. Game Development
Frameworks like Pygame allow builders to build simple 2D games.
6. Desktop Applications
With libraries like Tkinter and PyQt, Python may be used to create cross-platform computing device apps.
7. Cybersecurity
Python is often used to write security equipment, penetration trying out scripts, and make the most development.
📚 Popular Python Libraries
NumPy: Numerical computing
pandas: Data analysis
Matplotlib / Seaborn: Visualization
scikit-study: Machine mastering
BeautifulSoup / Scrapy: Web scraping
Flask / Django: Web frameworks
OpenCV: Image processing
PyTorch / TensorFlow: Deep mastering
SQLAlchemy: Database ORM
💻 Python Tools and IDEs
Popular environments and tools for writing Python code encompass:
PyCharm: Full-featured Python IDE.
VS Code: Lightweight and extensible editor.
Jupyter Notebook: Interactive environment for statistics technological know-how and studies.
IDLE: Python’s default editor.
🔐 Strengths of Python
Easy to study and write
Large community and wealthy documentation
Extensive 0.33-birthday celebration libraries
Strong support for clinical computing and AI
Cross-platform compatibility
⚠️ Limitations of Python
Slower than compiled languages like C/C++
Not perfect for mobile app improvement
High memory usage in massive-scale packages
GIL (Global Interpreter Lock) restricts genuine multithreading in CPython
🧭 Learning Path for Python Beginners
Learn variables, facts types, and control glide.
Practice features and loops.
Understand modules and report coping with.
Explore OOP concepts.
Work on small initiatives (e.G., calculator, to-do app).
Dive into unique areas like statistics technological know-how, automation, or web development.
#What is Python used for#college students learn python#online course python#offline python course institute#python jobs in information technology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I made an app for PROTO. Written in Kotlin and runs on Android.
Next, I want to upgrade it with a controller mode. It should work so so I simply plug a wired xbox controller into my phone with a USB OTG adaptor… and bam, the phone does all the complex wireless communication and is a battery. Meaning that besides the controller, you only need the app and… any phone. Which anyone is rather likely to have Done.
Now THAT is convenient!
( Warning, the rest of the post turned into... a few rants. ) Why Android? Well I dislike Android less than IOS
So it is it better to be crawling in front of the alter of "We are making the apocalypse happen" Google than "5 Chinese child workers died while you read this" Apple?
Not much…
I really should which over to a better open source Linux distribution… But I do not have the willpower to research which one... So on Android I stay.
Kotlin is meant to be "Java, but better/more modern/More functional programming style" (Everyone realized a few years back that the 100% Object oriented programming paradigme is stupid as hell. And we already knew that about the functional programming paradigme. The best is a mix of everything, each used when it is the best option.) And for the most part, it succeeds. Java/Kotlin compiles its code down to "bytecode", which is essentially assembler but for the Java virtual machine. The virtual machine then runs the program. Like how javascript have the browser run it instead of compiling it to the specific machine your want it to run on… It makes them easy to port…
Except in the case of Kotlin on Android... there is not a snowflakes chance in hell that you can take your entire codebase and just run it on another linux distribution, Windows or IOS…
So... you do it for the performance right? The upside of compiling directly to the machine is that it does not waste power on middle management layers… This is why C and C++ are so fast!
Except… Android is… Clunky… It relies on design ideas that require EVERY SINGLE PROGRAM AND APP ON YOUR PHONE to behave nicely (Lots of "This system only works if every single app uses it sparingly and do not screw each-other over" paradigms .). And many distributions from Motorola like mine for example comes with software YOUR ARE NOT ALLOWED TO UNINSTALL... meaning that software on your phone is ALWAYS behaving badly. Because not a single person actually owns an Android phone. You own a brick of electronics that is worthless without its OS, and google does not sell that to you or even gift it to you. You are renting it for free, forever. Same with Motorola which added a few extra modifications onto Googles Android and then gave it to me.
That way, google does not have to give any rights to its costumers. So I cannot completely control what my phone does. Because it is not my phone. It is Googles phone.
That I am allowed to use. By the good graces of our corporate god emperors
"Moose stares blankly into space trying to stop being permanently angry at hoe everyone is choosing to run the world"
… Ok that turned dark… Anywho. TLDR There is a better option for 95% of apps (Which is "A GUI that interfaces with a database") "Just write a single HTML document with internal CSS and Javascript" Usually simpler, MUCH easier and smaller… And now your app works on any computer with a browser. Meaning all of them…
I made a GUI for my parents recently that works exactly like that. Soo this post:
It was frankly a mistake of me to learn Kotlin… Even more so since It is a… awful language… Clearly good ideas then ruined by marketing department people yelling "SUPPORT EVERYTHING! AND USE ALL THE BUZZWORD TECHNOLOGY! Like… If your language FORCES you to use exceptions for normal runtime behavior "Stares at CancellationException"... dear god that is horrible...
Made EVEN WORSE by being a really complicated way to re-invent the GOTO expression… You know... The thing every programmer is taught will eat your feet if you ever think about using it because it is SO dangerous, and SO bad form to use it? Yeah. It is that, hidden is a COMPLEATLY WRONG WAY to use exceptions…
goodie… I swear to Christ, every page or two of my Kotlin notes have me ranting how I learned how something works, and that it is terrible... Blaaa. But anyway now that I know it, I try to keep it fresh in my mind and use it from time to time. Might as well. It IS possible to run certain things more effective than a web page, and you can work much more directly with the file system. It is... hard-ish to get a webpage to "load" a file automatically... But believe me, it is good that this is the case.
Anywho. How does the app work and what is the next version going to do?
PROTO is meant to be a platform I test OTHER systems on, so he is optimized for simplicity. So how you control him is sending a HTTP 1.1 message of type Text/Plain… (This is a VERY fancy sounding way of saying "A string" in network speak). The string is 6 comma separated numbers. Linear movement XYZ and angular movement XYZ.
The app is simply 5 buttons that each sends a HTTP PUT request with fixed values. Specifically 0.5/-0.5 meter/second linear (Drive back or forward) 0.2/-0.2 radians/second angular (Turn right or turn left) Or all 0 for stop
(Yes, I just formatted normal text as code to make it more readable... I think I might be more infected by programming so much than I thought...)
Aaaaaanywho. That must be enough ranting. Time to make the app
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Explaine
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of "objects," which represent real-world entities. Objects combine data (attributes) and functions (methods) into a single unit. OOP promotes code reusability, modularity, and scalability, making it a popular approach in modern software development.
Core Concepts of Object-Oriented Programming
Classes and Objects
Class: A blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods).
Object: An instance of a class. Each object has unique data but follows the structure defined by its
Encapsulations
Encapsulation means bundling data (attributes) and methods that operate on that data within a class. It protects object properties by restricting direct access.
Access to attributes is controlled through getter and setter methods.Example: pythonCopyEditclass Person: def __init__(self, name): self.__name = name # Private attribute def get_name(self): return self.__name person = Person("Alice") print(person.get_name()) # Output: Alice
Inheritance
Inheritance allows a class (child) to inherit properties and methods from another class (parent). It promotes code reuse and hierarchical relationships.Example: pythonCopyEditclass Animal: def speak(self): print("Animal speaks") class Dog(Animal): def speak(self): print("Dog barks") dog = Dog() dog.speak() # Output: Dog barks
Polymorphism
Polymorphism allows methods to have multiple forms. It enables the same function to work with different object types.
Two common types:
Method Overriding (child class redefines parent method).
Method Overloading (same method name, different parameters – not natively supported in Python).Example: pythonCopyEditclass Bird: def sound(self): print("Bird chirps") class Cat: def sound(self): print("Cat meows") def make_sound(animal): animal.sound() make_sound(Bird()) # Output: Bird chirps make_sound(Cat()) # Output: Cat meows
Abstraction
Abstraction hides complex implementation details and shows only the essential features.
In Python, this is achieved using abstract classes and methods (via the abc module).Example: pythonCopyEditfrom abc import ABC, abstractmethod class Shape(ABC): @abstractmethod def area(self): pass class Circle(Shape): def __init__(self, radius): self.radius = radius def area(self): return 3.14 * self.radius * self.radius circle = Circle(5) print(circle.area()) # Output: 78.5
Advantages of Object-Oriented Programming
Code Reusability: Use inheritance to reduce code duplication.
Modularity: Organize code into separate classes, improving readability and maintenance.
Scalability: Easily extend and modify programs as they grow.
Data Security: Protect sensitive data using encapsulation.
Flexibility: Use polymorphism for adaptable and reusable methods.
Real-World Applications of OOP
Software Development: Used in large-scale applications like operating systems, web frameworks, and databases.
Game Development: Objects represent game entities like characters and environments.
Banking Systems: Manage customer accounts, transactions, and security.
E-commerce Platforms: Handle products, users, and payment processing.
Machine Learning: Implement models as objects for efficient training and prediction.
Conclusion
Object-Oriented Programming is a powerful paradigm that enhances software design by using objects, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It is widely used in various industries to build scalable, maintainable, and efficient applications. Understanding and applying OOP principles is essential for modern software development.
: pythonCopyEdit
class Car: def __init__(self, brand, model): self.brand = brand self.model = model def display_info(self): print(f"Car: {self.brand} {self.model}") my_car = Car("Toyota", "Camry") my_car.display_info() # Output: Car: Toyota Camry
Encapsulation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Normally I just post about movies but I'm a software engineer by trade so I've got opinions on programming too.
Apparently it's a month of code or something because my dash is filled with people trying to learn Python. And that's great, because Python is a good language with a lot of support and job opportunities. I've just got some scattered thoughts that I thought I'd write down.
Python abstracts a number of useful concepts. It makes it easier to use, but it also means that if you don't understand the concepts then things might go wrong in ways you didn't expect. Memory management and pointer logic is so damn annoying, but you need to understand them. I learned these concepts by learning C++, hopefully there's an easier way these days.
Data structures and algorithms are the bread and butter of any real work (and they're pretty much all that come up in interviews) and they're language agnostic. If you don't know how to traverse a linked list, how to use recursion, what a hash map is for, etc. then you don't really know how to program. You'll pretty much never need to implement any of them from scratch, but you should know when to use them; think of them like building blocks in a Lego set.
Learning a new language is a hell of a lot easier after your first one. Going from Python to Java is mostly just syntax differences. Even "harder" languages like C++ mostly just mean more boilerplate while doing the same things. Learning a new spoken language in is hard, but learning a new programming language is generally closer to learning some new slang or a new accent. Lists in Python are called Vectors in C++, just like how french fries are called chips in London. If you know all the underlying concepts that are common to most programming languages then it's not a huge jump to a new one, at least if you're only doing all the most common stuff. (You will get tripped up by some of the minor differences though. Popping an item off of a stack in Python returns the element, but in Java it returns nothing. You have to read it with Top first. Definitely had a program fail due to that issue).
The above is not true for new paradigms. Python, C++ and Java are all iterative languages. You move to something functional like Haskell and you need a completely different way of thinking. Javascript (not in any way related to Java) has callbacks and I still don't quite have a good handle on them. Hardware languages like VHDL are all synchronous; every line of code in a program runs at the same time! That's a new way of thinking.
Python is stereotyped as a scripting language good only for glue programming or prototypes. It's excellent at those, but I've worked at a number of (successful) startups that all were Python on the backend. Python is robust enough and fast enough to be used for basically anything at this point, except maybe for embedded programming. If you do need the fastest speed possible then you can still drop in some raw C++ for the places you need it (one place I worked at had one very important piece of code in C++ because even milliseconds mattered there, but everything else was Python). The speed differences between Python and C++ are so much smaller these days that you only need them at the scale of the really big companies. It makes sense for Google to use C++ (and they use their own version of it to boot), but any company with less than 100 engineers is probably better off with Python in almost all cases. Honestly thought the best programming language is the one you like, and the one that you're good at.
Design patterns mostly don't matter. They really were only created to make up for language failures of C++; in the original design patterns book 17 of the 23 patterns were just core features of other contemporary languages like LISP. C++ was just really popular while also being kinda bad, so they were necessary. I don't think I've ever once thought about consciously using a design pattern since even before I graduated. Object oriented design is mostly in the same place. You'll use classes because it's a useful way to structure things but multiple inheritance and polymorphism and all the other terms you've learned really don't come into play too often and when they do you use the simplest possible form of them. Code should be simple and easy to understand so make it as simple as possible. As far as inheritance the most I'm willing to do is to have a class with abstract functions (i.e. classes where some functions are empty but are expected to be filled out by the child class) but even then there are usually good alternatives to this.
Related to the above: simple is best. Simple is elegant. If you solve a problem with 4000 lines of code using a bunch of esoteric data structures and language quirks, but someone else did it in 10 then I'll pick the 10. On the other hand a one liner function that requires a lot of unpacking, like a Python function with a bunch of nested lambdas, might be easier to read if you split it up a bit more. Time to read and understand the code is the most important metric, more important than runtime or memory use. You can optimize for the other two later if you have to, but simple has to prevail for the first pass otherwise it's going to be hard for other people to understand. In fact, it'll be hard for you to understand too when you come back to it 3 months later without any context.
Note that I've cut a few things for simplicity. For example: VHDL doesn't quite require every line to run at the same time, but it's still a major paradigm of the language that isn't present in most other languages.
Ok that was a lot to read. I guess I have more to say about programming than I thought. But the core ideas are: Python is pretty good, other languages don't need to be scary, learn your data structures and algorithms and above all keep your code simple and clean.
#programming#python#software engineering#java#java programming#c++#javascript#haskell#VHDL#hardware programming#embedded programming#month of code#design patterns#common lisp#google#data structures#algorithms#hash table#recursion#array#lists#vectors#vector#list#arrays#object oriented programming#functional programming#iterative programming#callbacks
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
The unit testing conversation: is there an equivalent for object oriented languages? I'm the closest thing my company has ever had to a developer and I have zero formal training. I made them a reasonably complicated power app that is now a load bearing component of our booking system (matching nurse skill sets to patient needs across multiple clinics). My boss will never hold me to any standards because he knows less than I do and I'd really like to have good practice. When I test my code I mostly just ... Pretend to be a user and make sure when I try and get a specific clinician I know can do something, she shows up. Repeat 1000 times until I think I've tried everything. Is unit testing relevant to me? Should I be doing something different but equivalent? My company is a charity, even though I'm working somewhat outside my job description I'm really helping people with my work and I'd like to do a good job.
The sticking point here is not so much OO languages per se— OO does just fine with unit testing if you use objects as your interface boundaries, which is harder not to do with most contemporary OO languages— but GUIs. Unit testing is particularly unpleasant in GUIs, and OO happens to be a good paradigm for doing GUIs, which is why it was the dominant one for so long. To be honest, I do very little GUI programming of any kind (both at work at at play I'm kind of a backend person who only makes UIs if I absolutely have to) so I don't have a ton of advice here, and all I can offer are general guidelines:
Gary Bernhardt's "functional core, imperative shell" mindset is a good guideline to keep in mind when you're working in situations that must, by necessity, have a lot of state which makes unit testing tough, including GUIs. Try to design your applications around with that mindset as much as you can, and then do the unit tests on the functional core.
OO was the dominant paradigm for GUIs for decades, but recently it is starting to get superseded by things like functional reactive programming. Because I'm not a UX/webdev person I'm not fully in the know here, but webdev seems to be moving strongly in the functional reactive direction, and the latest desktop GUI frameworks like React Native and SwiftUI are as well. Obviously it's not always possible in your job to throw out the whole codebase and start over in a whole new language/paradigm, but it's precisely because unit testing with GUIs is kind of a hassle that the industry is trending in this direction. Start brushing up on that if it's relevant.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unlock the Power of Python Programming: A Complete Guide
Python programming has become one of the most sought-after skills in the world of technology. Its simplicity, flexibility, and vast ecosystem of libraries make it a top choice for both beginners and experienced developers. In this guide, we will explore various aspects of Python programming, from basic concepts to advanced applications like machine learning and web development.
Python Programming: A Beginner-Friendly Language
Python programming is renowned for its readability and straightforward syntax, making it ideal for beginners. Whether you are just starting to code or transitioning from another language, Python offers a smooth learning curve. Key Python programming concepts include variables, data types, and control structures, which are essential for writing functional code.
youtube
Python Data Structures: Organizing Data Efficiently
One of the core strengths of Python programming is its rich set of data structures. Lists, dictionaries, tuples, and sets help you store and manage data effectively. Understanding Python data structures allows you to create more efficient programs by organizing and manipulating data effortlessly.
Functions in Python Programming: Building Reusable Code
Functions are a fundamental part of Python programming. They allow you to break down complex problems into smaller, reusable chunks of code. Python functions not only promote code reusability but also make your programs more organized and easier to maintain.
Loops in Python Programming: Automating Repeated Tasks
Loops are an essential feature in Python programming, allowing you to perform repeated operations efficiently. With Python loops such as for and while, you can iterate over sequences or perform tasks until a specific condition is met. Mastering loops is a key part of becoming proficient in Python.
Object-Oriented Programming in Python: Structured Development
Python programming supports object-oriented programming (OOP), a paradigm that helps you build structured and scalable software. OOP in Python allows you to work with classes and objects, making it easier to model real-world scenarios and design complex systems in a manageable way.
Python Automation Scripts: Simplify Everyday Tasks
Python programming can be used to automate repetitive tasks, saving you time and effort. Python automation scripts can help with file management, web scraping, and even interacting with APIs. With Python libraries like os and shutil, automation becomes a breeze.
Python Web Development: Creating Dynamic Websites
Python programming is also a popular choice for web development. Frameworks like Django and Flask make it easy to build robust, scalable web applications. Whether you're developing a personal blog or an enterprise-level platform, Python web development empowers you to create dynamic and responsive websites.
APIs and Python Programming: Connecting Services
Python programming allows seamless integration with external services through APIs. Using libraries like requests, you can easily interact with third-party services, retrieve data, or send requests. This makes Python an excellent choice for building applications that rely on external data or services.

Error Handling in Python Programming: Writing Resilient Code
Python programming ensures that your code can handle unexpected issues using error handling mechanisms. With try-except blocks, you can manage errors gracefully and prevent your programs from crashing. Error handling is a critical aspect of writing robust and reliable Python code.
Python for Machine Learning: Leading the AI Revolution
Python programming plays a pivotal role in machine learning, thanks to powerful libraries like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch. With Python, you can build predictive models, analyze data, and develop intelligent systems. Machine learning with Python opens doors to exciting opportunities in artificial intelligence and data-driven decision-making.
Python Data Science: Turning Data Into Insights
Python programming is widely used in data science for tasks such as data analysis, visualization, and statistical modeling. Libraries like pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib provide Python programmers with powerful tools to manipulate data and extract meaningful insights. Python data science skills are highly in demand across industries.
Python Libraries Overview: Tools for Every Task
One of the greatest advantages of Python programming is its extensive library support. Whether you're working on web development, automation, data science, or machine learning, Python has a library for almost every need. Exploring Python libraries like BeautifulSoup, NumPy, and Flask can significantly boost your productivity.
Python GUI Development: Building User Interfaces
Python programming isn't just limited to back-end or web development. With tools like Tkinter and PyQt, Python programmers can develop graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for desktop applications. Python GUI development allows you to create user-friendly software with visual elements like buttons, text fields, and images.
Conclusion: Python Programming for Every Developer
Python programming is a versatile and powerful language that can be applied in various domains, from web development and automation to machine learning and data science. Its simplicity, combined with its extensive libraries, makes it a must-learn language for developers at all levels. Whether you're new to programming or looking to advance your skills, Python offers endless possibilities.
At KR Network Cloud, we provide expert-led training to help you master Python programming and unlock your potential. Start your Python programming journey today and take the first step toward a successful career in tech!
#krnetworkcloud#python#language#programming#linux#exams#coding#software engineering#coding for beginners#careers#course#training#learning#education#technology#computing#tech news#business#security#futurism#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Evolution of Programming Paradigms: Recursion’s Impact on Language Design
“Recursion, n. See Recursion.” -- Ambrose Bierce, The Devil’s Dictionary (1906-1911)
The roots of programming languages can be traced back to Alan Turing's groundbreaking work in the 1930s. Turing's vision of a universal computing machine, known as the Turing machine, laid the theoretical foundation for modern computing. His concept of a stack, although not explicitly named, was an integral part of his model for computation.
Turing's machine utilized an infinite tape divided into squares, with a read-write head that could move along the tape. This tape-based system exhibited stack-like behavior, where the squares represented elements of a stack, and the read-write head performed operations like pushing and popping data. Turing's work provided a theoretical framework that would later influence the design of programming languages and computer architectures.
In the 1950s, the development of high-level programming languages began to revolutionize the field of computer science. The introduction of FORTRAN (Formula Translation) in 1957 by John Backus and his team at IBM marked a significant milestone. FORTRAN was designed to simplify the programming process, allowing scientists and engineers to express mathematical formulas and algorithms more naturally.
Around the same time, Grace Hopper, a pioneering computer scientist, led the development of COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language). COBOL aimed to address the needs of business applications, focusing on readability and English-like syntax. These early high-level languages introduced the concept of structured programming, where code was organized into blocks and subroutines, laying the groundwork for stack-based function calls.
As high-level languages gained popularity, the underlying computer architectures also evolved. James Hamblin's work on stack machines in the 1950s played a crucial role in the practical implementation of stacks in computer systems. Hamblin's stack machine, also known as a zero-address machine, utilized a central stack memory for storing intermediate results during computation.
Assembly language, a low-level programming language, was closely tied to the architecture of the underlying computer. It provided direct control over the machine's hardware, including the stack. Assembly language programs used stack-based instructions to manipulate data and manage subroutine calls, making it an essential tool for early computer programmers.
The development of ALGOL (Algorithmic Language) in the late 1950s and early 1960s was a significant step forward in programming language design. ALGOL was a collaborative effort by an international team, including Friedrich L. Bauer and Klaus Samelson, to create a language suitable for expressing algorithms and mathematical concepts.
Bauer and Samelson's work on ALGOL introduced the concept of recursive subroutines and the activation record stack. Recursive subroutines allowed functions to call themselves with different parameters, enabling the creation of elegant and powerful algorithms. The activation record stack, also known as the call stack, managed the execution of these recursive functions by storing information about each function call, such as local variables and return addresses.
ALGOL's structured approach to programming, combined with the activation record stack, set a new standard for language design. It influenced the development of subsequent languages like Pascal, C, and Java, which adopted stack-based function calls and structured programming paradigms.
The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the emergence of structured and object-oriented programming languages, further solidifying the role of stacks in computer science. Pascal, developed by Niklaus Wirth, built upon ALGOL's structured programming concepts and introduced more robust stack-based function calls.
The 1980s saw the rise of object-oriented programming with languages like C++ and Smalltalk. These languages introduced the concept of objects and classes, encapsulating data and behavior. The stack played a crucial role in managing object instances and method calls, ensuring proper memory allocation and deallocation.
Today, stacks continue to be an integral part of modern programming languages and paradigms. Languages like Java, Python, and C# utilize stacks implicitly for function calls and local variable management. The stack-based approach allows for efficient memory management and modular code organization.
Functional programming languages, such as Lisp and Haskell, also leverage stacks for managing function calls and recursion. These languages emphasize immutability and higher-order functions, making stacks an essential tool for implementing functional programming concepts.
Moreover, stacks are fundamental in the implementation of virtual machines and interpreters. Technologies like the Java Virtual Machine and the Python interpreter use stacks to manage the execution of bytecode or intermediate code, providing platform independence and efficient code execution.
The evolution of programming languages is deeply intertwined with the development and refinement of the stack. From Turing's theoretical foundations to the practical implementations of stack machines and the activation record stack, the stack has been a driving force in shaping the way we program computers.
How the stack got stacked (Kay Lack, September 2024)
youtube
Thursday, October 10, 2024
#turing#stack#programming languages#history#hamblin#bauer#samelson#recursion#evolution#fortran#cobol#algol#structured programming#object-oriented programming#presentation#ai assisted writing#Youtube#machine art
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Coding to Creation: Java's Versatile Influence
Java, often described as the "king of programming languages," stands as a monumental force that has significantly influenced the trajectory of modern software development. For over two decades, Java has proven its versatile, powerful, and dependable programming language, underpinning a vast array of applications, platforms, and systems that permeate our digital landscape. In this comprehensive exploration, we will embark on a journey to unravel the essence of Java, delving deep into what makes it indispensable and why it continues to be the preferred choice for programmers across diverse domains.

What is Java?
At its core, Java is a high-level, object-oriented, and platform-independent programming language that defies the conventional limitations of traditional coding. Conceived in the mid-1990s through the visionary efforts of James Gosling and his adept team at Sun Microsystems (now seamlessly integrated into Oracle Corporation), Java introduced a revolutionary concept that continues to define its identity: "Write Once, Run Anywhere." This groundbreaking principle signifies that Java applications exhibit a remarkable adaptability, capable of executing seamlessly on various platforms, provided a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) stands ready to facilitate their execution. This single feature alone positions Java as an unparalleled workhorse, transcending the boundaries of operating systems and hardware, and ushering in an era of software portability and compatibility.
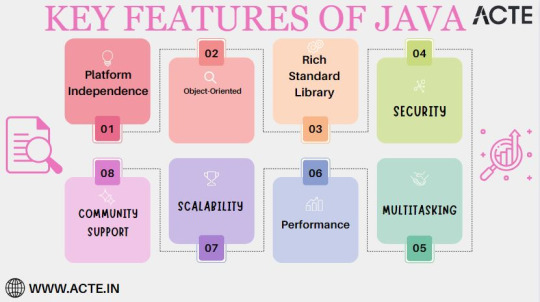
Key Features of Java:
Platform Independence: Java's unparalleled platform independence is the cornerstone of its success. Code authored in Java is liberated from the confines of a single operating system, enabling it to traverse across a plethora of platforms without requiring any cumbersome modifications. This inherent portability not only obliterates compatibility concerns but also streamlines software deployment, eliminating the need for platform-specific versions.
Object-Oriented Paradigm: Java's steadfast adherence to the object-oriented programming (OOP) paradigm cultivates a development environment characterized by modularity and maintainability. By encapsulating code into discrete objects, Java empowers developers to construct intricate systems with greater efficiency and ease of management, a quality particularly favored in large-scale projects.
Rich Standard Library: The Java Standard Library stands as a testament to the language's comprehensiveness. It comprises a vast repository of pre-built classes and methods that cater to a wide spectrum of programming tasks. This comprehensive library significantly reduces development overhead by offering readily available tools for commonplace operations, bestowing developers with the invaluable gift of time.
Security: In an era marred by cyber threats and vulnerabilities, Java emerges as a paragon of security-conscious design. It incorporates robust security features, including a sandbox environment for executing untrusted code. Consequently, Java has become the de facto choice for building secure applications, particularly in industries where data integrity and user privacy are paramount.
Community Support: The strength of Java's thriving developer community is an asset of immeasurable value. This vast and active network ensures that developers are never left wanting for resources, libraries, or frameworks. It provides a dynamic support system where knowledge sharing and collaborative problem-solving flourish, accelerating project development and troubleshooting.
Scalability: Java is not confined by the scale of a project. It gracefully adapts to the demands of both modest applications and sprawling enterprise-level systems. Its versatility ensures that as your project grows, Java will remain a steadfast companion, capable of meeting your evolving requirements.
Performance: Java's Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler serves as the vanguard of its performance capabilities. By dynamically optimizing code execution, Java ensures that applications not only run efficiently but also deliver exceptional user experiences. This, coupled with the ability to harness the power of modern hardware, makes Java a preferred choice for performance-critical applications.
Multithreading: Java's built-in support for multithreading equips applications to execute multiple tasks concurrently. This not only enhances responsiveness but also elevates the overall performance of applications, particularly those designed for tasks that demand parallel processing.
Java is not merely a programming language; it represents a dynamic ecosystem that empowers developers to fashion an extensive array of applications, ranging from mobile apps and web services to enterprise-grade software solutions. Its hallmark feature of platform independence, complemented by its rich libraries, security fortifications, and the formidable backing of a robust developer community, collectively underpin its enduring popularity.
In a world where digital innovation propels progress, Java stands as an essential cornerstone for building the technologies that sculpt our future. It's not merely a language; it's the key to unlocking a boundless realm of opportunities. For those seeking to embark on a journey into the realm of Java programming or aspiring to refine their existing skills, ACTE Technologies stands as a beacon of expert guidance and comprehensive training. Their programs are tailored to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to harness the full potential of Java in your software development career.
As we navigate an era defined by digital transformation, Java remains a trusted companion, continually evolving to meet the ever-changing demands of technology. It's not just a programming language; it's the linchpin of a world characterized by innovation and progress. Let ACTE Technologies be your trusted guide on this exhilarating journey into the boundless possibilities of Java programming.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Python Development Course: Empowering the Future with Softs Solution Service

Python, a high-level programming language, has emerged as a favorite among developers worldwide due to its emphasis on readability and efficiency. Originating in the late 1980s, Python was conceived by Guido van Rossum as a successor to the ABC language. Its design philosophy, encapsulated by the phrase "Beautiful is better than ugly", reflects a commitment to aesthetic code and functionality.
What sets Python apart is its versatile nature. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. This flexibility allows developers to use Python for a wide range of applications, from web development and software engineering to scientific computing and artificial intelligence.
Python’s standard library is another of its strengths, offering a rich set of modules and tools that enable developers to perform various tasks without the need for additional installations. This extensive library, combined with Python’s straightforward syntax, makes it an excellent language for rapid application development.
One of Python's most significant contributions to the tech world is its role in data science and machine learning. Its easy-to-learn syntax and powerful libraries, like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib, make it an ideal language for data analysis and visualization. Furthermore, frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch have solidified Python's position in the development of machine learning models.
Education in Python programming has become crucial due to its growing demand in the industry. Recognizing this, institutions like Softs Solution Service, IT training institute in Ahmedabad, have stepped up to provide comprehensive Python Development Training. Their Online Python Development Course is tailored to meet the needs of both beginners and seasoned programmers. This course offers an in-depth exploration of Python's capabilities, covering everything from basic syntax to advanced programming concepts.
The course structure usually begins with an introduction to Python's basic syntax and programming concepts. It then progressively moves into more complex topics, such as data structures, file operations, error and exception handling, and object-oriented programming principles. Participants also get to work on real-life projects, which is vital for understanding how Python can be applied in practical scenarios.
A significant advantage of online courses like the one offered by Softs Solution Service is their accessibility. Students can learn at their own pace, with access to a wealth of resources and support from experienced instructors. Additionally, these courses often provide community support, where learners can interact with peers, share knowledge, and collaborate on projects.
Python's future seems bright as it continues to evolve with new features and enhancements. Its growing popularity in various fields, including web development, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and scientific research, ensures that Python developers will remain in high demand.
In summary, Python is not just a programming language; it's a tool that opens a world of possibilities for developers, data scientists, and tech enthusiasts. With resources like the Online Python Development Course from Softs Solution Service, mastering Python has become more accessible than ever, promising exciting opportunities in the ever-evolving world of technology.
#IT Training and Internship#Softs Solution Service#IT Training Institute in Ahmedabad#Online Python Development Course#Python Development Training#Python Development Course
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Swift for iOS App Development

Introduction
Swift is multi-paradigm, a general-purpose programming language that was developed by Apple Inc. for its different operating systems like iOS, tvOS, macOS, watch OS. It supports Linux, Darwin, free BSD like multiple OS, It is a static and strongly typed discipline. Swift is designed to work along with Apple’s Cocoa framework and Objective C library to work in Apple products. Extension filename for the swift files is .swift to support core components from Objective C.
Through many core concepts, Apple supports Swift is associated with Objective-C, dynamic dispatch, late binding, extensible programming to catch software bugs. Swift has features addressing some common programming errors like null pointer dereferencing and provides easier syntax to avoid the pyramid of doom. Swift supports types, structures, and classes, where Apple promotes in programming paradigms as protocol-oriented programming.
Benefits of Swift Programming Language
1. Open-Source Community
Swift is an open-source as well as a developer-friendly programming language. The developers for iPhone applications can explore, enhance Swift language, contribute to bug fixes, add new features and platforms, and so much. In Swift, an open-source, made with a strong community of developers.
2. Readability for Easy Code
Swift programming language is easiest to read and write. It uses simple syntax for the iPhone App Development language. Swift is similar to Objective C. You have to write so few lines of code compared to Objective C using simple and clean syntax throughout the code. In Objective C, it is necessary to add semicolons at the end of the parenthesis for conditional statements due to getting errors while compiling. But in Swift, these are not required. This has made Swift more simple and clean and user friendly as compared to C/C++. Hence, almost all language programmers can easily grasp with Swift and develop iOS applications.
3. Slower compilation speed
Compilation speed is much slower in Swift projects. As Swift is a more complex language and more feature-rich, it is harder to ensure that everything is exact. Each time, this costs time and money. Swift programming language is approximately 2.6x faster than Objective C. Swift is super-fast for iPhone application development.
4. Less Error-Prone
Null value as nil pointers is handled in different ways in Objective-C. Whenever you call a method with a nil pointer variable, nothing returns. But, it becomes the source of a huge list of bugs that the developer is unaware of and brings his efficiencies to the zero level. But, this is not the case with the Swift programming language. While defining the method, the iPhone app developer can define whether the value exists or it is nil (null). So, if the developer has mistakenly taken nil optional value, Swift triggers the runtime crash. This crash forces the iPhone app developer to resolve the bug right away and remains on the line of code with the nil pointer’s optional value. Hence, Swift is strict for iPhone app developers to develop bug and exception-free apps.
5. Multiple Devices Support
Swift is a programming language that supports iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, Apple TV, and Mac devices that are developed by Apple. Swift is not just limited to, support Apple devices, but Linux and Windows devices as well. In fact, about its new upcoming operating system, So, Swift is not going to just limit it to Apple devices. Across the technology world, it will support multiple devices.
6. Dynamic Libraries Support
Dynamic libraries are executable for code that can be linked to an app. This feature allows links against the latest versions of the Swift language. Dynamic libraries are directly uploaded to the memory on the initial size of the app and ultimately increasing app performance.
7. “Playgrounds” Backed
Playgrounds enable programmers to test out a new algorithm without having to create a complete app. Apple has added code execution to Playgrounds to help programmers create a group of code or write an algorithm while receiving feedback. With the help of data visualizations, this feedback loop can improve the speed at which code can be written. To make app development easier and more approachable necessary to do Playgrounds and Swift together for Apple’s efforts.
8. High-Level Performance
Swift is 3.4X quicker than Objective C. Also, the code execution is quicker than Objective C. Swift supports dynamic libraries and multiple devices that improve the speed through which the apps are developed and updated. This ultimately improves the performance of the Swift apps to a great extent.
The Benefit of Swift over Objective C:
1. Swift is the latest programming language that is developed by Apple and can be run on various cross-platform operating systems such as Linux, Darwin, Free BSD, etc. whereas Objective C is a general-purpose object-oriented programming language used by Apple in its operating systems and APIs Cocoa, etc.
2. Swift has safe programming patterns, the syntax in Objective C, complete access to Cocoa frameworks whereas Objective C also supports the same features as C++ except for STL and includes foundational frameworks.
3.Swift has object-oriented and procedural features in its language and in-built functionalities in its library whereas Objective C has different data types, tokens to recognize the identifiers, declarations, and assignments and pre-processor to define constants.
4.Swift supports different operators such as Arithmetic Operators, Logical Operators, Bitwise Operators, Relational Operators, Assignment Operators, Range Operators, and Miscellaneous Operators whereas Objective C also supports the same operators except for range and pre-processors which are not the part of the compilation process.
5.Swift supports Dictionaries, Functions, Closures, Enumerations, Structures, etc. whereas Objective C supports Posing, Extensions, dynamic binding, Protocols, Composite Objects, Memory Management, and Enumerations.
6.Swift supports optional chaining, typecasting, generics, protocols, subscripts, etc., whereas Objective C allows dynamic dispatch, auto-generation of accessors to access member variables and properties, and allows a method and a name to share the same identifier.
7.In Swift, calling a method will be decided at compile time and is similar to object-oriented programming whereas in Objective C, calling a method will be decided at runtime.
8.In Swift, errors can be handled using protocols to avoid the unexpected flow of program control whereas Objective C has nil which can be safely handled in a powerful way by safely sending messages to nil objects.
9.In Swift, operator overloading is supported and is global in terms of scope and simplicity whereas Objective C does not support default parameters but can be implemented by multiple methods manipulation and also does not support private members.
10.In Swift, Arc (Automatic Reference Counting) is the feature that handles the garbage collection where emptied memory is allocated to the required processes whereas Objective C does not support stack-based memory objects and allocating memory in Objective C is very expensive and it plays a key role in writing successful programs for the delivery of efficient applications.
11.In Swift, class objects are declared as general object-oriented programming languages whereas Objective C has an embedded object inside an object, by means a private declare object will be embedded into the main object along with some primitive methods.
12.In Swift, advanced operators exist to handle the manipulation of the complex value whereas Objective C has a fast enumeration feature where collections are core components of this feature.
Advantages:
1. Swift is open-sourced and easy to learn. 2. Swift is fast, safe, and expressive. 3. Swift is approachable and familiar like C and C++ code can be added by Swift programmers into Swift applications. 4. Swift is the future of Apple’s development. 5. Swift is enterprise-ready.
Disadvantages:
1. The language is still quite young and the talent pool is limited. 2. Swift is considered a “moving target” as it is a new language and the numbers of swift programmers are few. 3. Poor interoperability with third-party tools and IDEs. 4. Lack of support for earlier iOS versions.
Conclusion
The Swift programming language seems to be the future of developing high-performing and it is also a secured app. And, this is the reason it is being adopted by Apple’s competitors as well. Looking at the benefits Swift offers, sooner it will reach the top of the app development charts.
There are several factors during every time organizations start a new mobile project to take into account, whether decided to use Swift or Objective-C for development. Selecting the most appropriate language depends on the project and team context preference for a particular programming language. Swift takes a lot of useful components from Objective-C for allowing developers to write safer, more reliable code. It is a leading programming language for creating engaging and also a user-friendly mobile app.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering C++ Without Meltdowns: A Realistic Guide for Students
C++ isn’t just another programming language — it’s the blueprint behind many of the world’s most powerful systems. But for students, mastering C++ can often feel like hitting one roadblock after another, especially when facing tight deadlines and complex homework.
Whether it’s confusing pointer logic, segmentation faults, or classes that just won’t compile, C++ homework can quickly turn into a frustrating experience.
So, what’s really going on — and how can you overcome it efficiently without burning out?
🚧 What Makes C++ Homework So Challenging?
C++ blends both low-level and high-level programming features. That gives it power but also introduces complexity:
You manually manage memory (unlike languages like Python or Java)
Syntax is strict, and one missing ; or wrong pointer can crash everything
You’re expected to understand both procedural and object-oriented paradigms
Concepts like recursion, inheritance, file handling, and templates are often layered into the same assignment
This means even a "simple" program can take hours if you're missing a single concept.
🔍 Common Student Struggles (and How to Tackle Them)
❌ Struggle: Managing dynamic memory allocation ✅ Tip: Always pair new with delete, and test in small code blocks.
❌ Struggle: Confusion with classes, objects, and inheritance ✅ Tip: Draw class diagrams and understand relationships before coding.
❌ Struggle: Debugging large, monolithic code ✅ Tip: Break code into smaller functions or classes, and compile/test often.
🎓 When It’s Time to Get Help
There’s a big difference between learning support and code copying. If you find yourself:
Spending hours without real progress
Not understanding the logic behind template classes or pointers
Repeating the same mistakes without knowing why
…then it's time to consider professional help. Guided assistance helps you learn smarter — with clean explanations, working code, and feedback tailored to your level.
That’s where C++ homework help becomes a valuable learning resource. Instead of guessing or Googling endlessly, you can get step-by-step support from professionals who’ve solved similar problems hundreds of times.
⚡ Tools, Topics, and Tasks We Commonly Help With
Pointers, references, and memory allocation
OOP concepts like inheritance and polymorphism
File I/O operations and exception handling
STL: vectors, maps, stacks, queues
Recursion and dynamic programming
Sorting, searching, and data structure implementation
Whether it's a simple class design or a complete data structure assignment, there’s support available for every challenge.
✅ Final Takeaway
C++ is tough — not because you’re not smart, but because it demands clear thinking and deep understanding. The good news? With the right approach, structure, and expert support, you can absolutely master it.
Don’t wait until the last minute. Break problems down. Practice regularly. And when you're stuck, reach out for help that strengthens your understanding — not shortcuts your success.
C++ doesn’t have to feel like a battle. With the right strategy, it can become one of your strongest skills.
0 notes
Text
Master Python Programming with an Expert-Led Python Course Today
Python is one of the most popular programming languages in the world today. Whether you’re a beginner or aiming to upskill, enrolling in a Python course is your best gateway to mastering this versatile language. With its simple syntax and robust capabilities, Python is used in web development, data science, artificial intelligence, and automation.
In today’s competitive tech world, learning Python is more than a trend—it’s a necessity. Fortunately, an expertly designed Python course offers the right mix of foundational theory and hands-on training. In this article, we’ll explore why a Python course is essential, what you’ll learn, and how it opens doors to diverse career paths.
Why Should You Choose a Python Course Today?
Choosing a professional Python course is the smartest move for career growth. Python is beginner-friendly, highly readable, and widely used in both startups and Fortune 500 companies. Therefore, taking a structured Python course helps you learn faster, build projects, and gain real-world experience.
Moreover, Python supports multiple programming paradigms and has an extensive standard library. From data analysis to web applications, a Python course helps you unlock these potentials efficiently. If you're switching careers or starting your tech journey, now is the perfect time to invest in a reliable Python course.
What You Will Learn in a Professional Python Course
A comprehensive Python course covers everything from basic to advanced concepts. With structured modules and interactive lessons, you get to learn step-by-step with proper guidance. Additionally, most Python courses provide lifetime access to materials, assignments, and real-time projects.
Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll typically learn in a Python course:
Introduction to Python syntax and variables
Data types, operators, and conditional statements
Loops, functions, and error handling
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python
Working with libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib
File handling and data manipulation
Web development using Flask or Django
Basic to advanced data structures
Capstone projects and portfolio building
Each of these topics is critical for any developer. By the end of the Python course, you will not only write clean, efficient code but also build industry-ready projects.
Career Benefits of Enrolling in a Python Course
Pursuing a Python course comes with a wide range of career advantages. Python developers are in high demand across industries. Whether you’re looking to become a data analyst, web developer, or automation engineer, Python skills are essential.
Furthermore, a Python course adds credibility to your resume. Most Python courses offer certifications that are recognized by tech employers. These certificates showcase your commitment to continuous learning and your readiness to take on real-world tasks.
Not only this, but many Python courses also provide placement support, resume building, and interview preparation. Hence, completing a Python course significantly boosts your employability.
Key Features to Look for in a Quality Python Course
Instructor-led video tutorials and recorded sessions
Quizzes and assignments for every module
Real-time doubt resolution and mentorship
Access to coding exercises and live projects
Lifetime access and free updates
Globally recognized certification
In addition, some top Python courses also offer internship opportunities, community support, and weekly coding challenges. These features help solidify your learning and provide hands-on experience in problem-solving.
How Python Course Helps Beginners and Professionals Alike
Whether you're a student, a working professional, or a freelancer, a Python course adapts to your goals. Beginners benefit from the slow-paced, foundational approach, while professionals can directly jump into advanced modules.
Moreover, Python’s simplicity and power make it an ideal first programming language. Unlike traditional programming languages, Python allows you to focus on solving problems instead of worrying about complex syntax. That’s why a good Python course makes learning both effective and enjoyable.
Affordable Learning with High Returns
You don’t need to break the bank to enroll in a quality Python course. Many top-rated platforms offer affordable packages with EMI options, discounts, or free trial periods. Compared to university degrees, a Python course offers a faster and more practical route to tech careers.
Also, the return on investment is high. Python developers enjoy competitive salaries and flexible job options. Once you complete a Python course, your chances of landing freelance gigs or full-time roles increase drastically.
Final Thoughts: Enroll in a Python Course and Build Your Future
In conclusion, taking a Python course is a smart decision if you want to future-proof your career. It equips you with skills in high demand and opens doors to various job roles in tech.
From writing your first line of code to deploying full-scale applications, a well-structured Python course guides you at every step. With expert trainers, practical assignments, and real-time support, you can master Python in just a few months.
Don’t wait. Take the leap and enroll in a Python course today. Your coding journey begins now!
0 notes
Text
Python Interview Questions for Beginners

Python is one of the most popular and beginner-friendly programming languages in the world. Known for its simple syntax, vast library support, and versatility, Python is widely used in web development, data science, automation, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and more. For beginners stepping into the software development world, Python is often the first language learned—and one of the most asked in job interviews.
If you're preparing for an entry-level software developer, data analyst, or backend programming role, it's crucial to understand the common Python interview questions that hiring managers may ask. This blog is designed specifically for beginners, covering basic to slightly advanced Python concepts with clear explanations, examples, and tips to help you succeed in your technical interviews.
Why Python for Beginners?
Python is popular because of its:
Simple syntax that mimics natural language
Huge standard libraries and third-party packages
Active community support
Use in multiple domains like web development, automation, and data science
Because of its readability and ease of learning, many tech companies use Python for interviews—especially for candidates just starting out.
What You'll Learn in This Blog
This guide includes:
Basic Python syntax and structure
Frequently asked beginner-level questions
Coding examples and logic building
Common mistakes to avoid
Preparation tips for freshers
Whether you’re a recent graduate or transitioning to a tech career, these Python interview questions for beginners will help you build confidence and prepare thoroughly.
Sample Python Interview Questions for Beginners
Let’s look at a few important questions with simple answers:
Q1. What is Python?
A: Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. It supports object-oriented, procedural, and functional programming paradigms and is known for its simplicity and readability.
Q2. What are Python’s key features?
Easy to learn and use
Interpreted language
Dynamically typed
Extensive libraries and frameworks
Portable and open-source
Supports OOP (Object-Oriented Programming)
Q3. What are Python data types?
Common data types include:
int – Integer
float – Decimal numbers
str – Strings
bool – Boolean (True/False)
list, tuple, set, dict – Collection types
Q4. What is the difference between a list and a tuple?
A list is mutable (can be changed), declared with [].
A tuple is immutable (cannot be changed), declared with ().
my_list = [1, 2, 3] my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
Q5. What are conditional statements in Python?
Conditional statements allow decision-making in code using: if condition: # do something, elif another condition: # do something else, else: # fallback
Q6. What are loops in Python?
Python supports for and while loops:# For loop example for i in range(5): print(i)
Q7. What is a function in Python?
A function is a block of code that performs a specific task:def greet(name): return "Hello, " + name
Q8. What is the difference between is and ==?
== checks value equality
is checks identity (object memory location)
Q9. What is indentation in Python?
Python uses indentation (spaces or tabs) to define code blocks. It is mandatory and replaces {} used in other languages.
Q10. How is Python different from other languages like Java or C++?
Python is interpreted, not compiled.
It has simpler syntax and fewer lines of code.
Python uses dynamic typing.
No need for explicit memory management.
Tips to Prepare for Python Interviews (as a Beginner)
Understand the basics thoroughly – Practice syntax, data types, loops, and functions.
Write code daily – Use platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or Replit to code simple problems.
Build mini-projects – Even small projects like calculators, to-do apps, or form validators show practical knowledge.
Revise common errors – Like indentation errors, mutable vs immutable types, etc.
Use mock interviews – Practice with peers or online interview simulators.
Useful Resources to Learn Python
Python Official Docs
FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy, W3Schools
YouTube channels like Programming with Mosh, Tech With Tim
Books: “Automate the Boring Stuff with Python” by Al Sweigart
Conclusion
Mastering Python interview questions for beginners is the first step toward launching your career in tech. By focusing on core concepts, writing clean code, and understanding how Python works behind the scenes, you’ll be well-prepared for any entry-level developer interview.
Remember, interviews are not just about the right answer — they’re about showing your approach, logic, and eagerness to learn. Keep practicing, stay curious, and you’ll soon land your first role in the tech world with confidence!
#PythonInterviewQuestions#PythonForBeginners#LearnPython#FresherInterview#TechInterviewPrep#PythonCoding#PythonBasics#ProgrammingJobs#InterviewTips#CareerInTech
0 notes
Text
0 notes