#nipah virus prevention
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Avoid direct contact with bats, especially if they appear sick or are found in areas where Nipah virus has been reported.
Avoid consuming fruits that may have been bitten or contaminated by bats.
How to prevent nipah virus read this blog healthytraffic.
0 notes
Text

Authored by Martin Hoyt via RealClearHealth,
It did not have to be this way. The COVID-19 pandemic cost American citizens their lives, their livelihoods, education, mental health, reputations and, ultimately, civil and religious freedoms. “The U.S. accounts for less than 5% of the world’s population, but more than 25% of total COVID-19 cases reported across the globe, and it currently ranks among the top 10 countries in COVID-19-related deaths per capita,” wrote the authors of 2023 commentary in the Journal of the American Medical Association. And for all that, we have government to thank.

For years leading up to the pandemic, the nation had spent billions on preparation and planning for a biohazard attack or event. Whatever we learned was quickly discarded or undone by a lack of accountability, transparency, and humility. Decades of planning and untold man hours of research and training were rendered ineffective by a corrupt culture of greed, self-importance, scientific misconduct, and outright fraud. Because, while the government worked to prevent the worst, it was also helping to create chaos and contagion by funding and facilitating gain of function (GOF) research.
GOF research refers to laboratory efforts to make viruses deadlier or to increase their transmissibility. The potential for disaster is obvious. Almost five years prior to the pandemic Dr. Marc Lipsitch and Dr. Alison Galvani noted that GOF pathogenic research posed “a risk of accidental and deliberate release that, if it led to extensive spread of the new agent, could cost many lives … Furthermore, the likelihood of risk is multiplied as the number of laboratories conducting such research increases around the globe.”
But according to Dr. Anthony Fauci’s emails and other NIAID communications obtained via FOIA – those that weren’t deleted by the now-infamous “FOIA lady” – the Wuhan lab was working on Covid research with the U.S. as early as 2015. And the worst happened. Dr. Richard H. Ebright of Rutgers University told a Senate committee hearing on June 18, 2024, that “… lapses in U.S. oversight of gain-of-function research and enhanced potential pandemic pathogen research likely contributed to the origin of COVID-19 …”
While Ebright said GOF has no medical utility, he emphasized that there are “major incentives to researchers worldwide, in China, and in the U.S. The researchers undertake this research because it is easy, they get the money, and they can get the papers [in science journals].”
Not surprisingly, China was selected because it was quicker and cheaper to conduct research without U.S. government entanglements or oversight. Dr. Steven Quay also testified on June 18 and said the Wuhan Institute of Virology is a “level-2 lab,” as opposed to highly secure level-4 labs elsewhere. Moreover, Dr. Fauci et al were able to fund this research because the law was silent. Ebright again:
… in this category of research, which is the most significant in terms of consequences and potentially existential risk there is almost no regulation with force of law. No regulation with force of law for biosafety or any pathogen other than the smallpox virus and no regulation with force of law for bio risk management for any pathogen.
But the U.S. and the world, may have temporarily escaped imminent catastrophe. Consider, according to Dr. Quay, what Wuhan obtained from Canada’s National Microbiology Lab in 2019: “two vials each of 15 strains of virus: seven varieties of Ebola virus, the Hendra virus, and two strains of Nipah virus, Malaysia and Bangladesh.” These virus samples, according to Dr. Steven Quay, are “the top three most deadly human pathogens on the planet.” The samples were obtained under murky circumstances (“described as a possible policy breach”) from a level-4 lab and surreptitiously flown on a commercial flight to Beijing where they were subsequently placed in a level-2 lab overseen by a country with a long history of a disregard for proper safety protocols.
Gain of function research probably created COVID-19, but our legislative and executive branches created the conditions for the disaster. Congress failed to pass laws governing specific GOF research, both Congress and the executive branch failed to effectively manage the federal health and science bureaucracy, and various agencies failed to monitor the behavior and performance of grantees and vendors engaged in GOF research. When catastrophe struck, self-interest and political survival of those responsible overrode the best interests of our citizenry.
Who in the government benefited? How and to what extent did they benefit? Did any GOF research contribute to the U.S. global or response? Is GOF research being rerouted to our defense and security agencies to avoid scrutiny? NIAID continues to stall, obfuscate, and otherwise restrict transparency to its current and past activities. We know there was a concerted effort by senior leaders like Anthony Fauci to hide or delete emails but many other records still likely exist that remain uncovered.
This must change. Any research activity or sponsorship of scientific endeavors that are capable of mass extinction, such as GOF, must be subjected to a higher level of accountability and scrutiny by our elected leaders and the American public. Accountability, transparency, and public debate after an international crisis like Covid-19 can’t undo the global catastrophic harm that was done. It can, however, reduce the ability of our public health bureaucracy to contribute to the next disaster or looming crisis.
Borrowed from:

(https://stuff-that-irks-me.tumblr.com/)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fox News: India racing to contain deadly Nipah virus outbreak as hundreds are tested in Kerala state
Health officials in India are racing Thursday to contain an outbreak of the Nipah virus, which has already killed two and carries a fatality rate the World Health Organization says is as high as 75%.
Around 800 people have been tested over the last few days in the country’s southern Kerala state, with two adults and a child placed in a hospital after receiving a positive diagnosis, according to Reuters.
"We are testing human beings... and at the same time experts are collecting fluid samples from forested areas that could be the hotspot for the spread," Veena George, the state’s health minister, told the news agency. "We are in a stage of hypervigilance and detection."
Public offices, government buildings and religious institutions have been shuttered in parts of the region as samples of bat urine, animal droppings and half-eaten fruit were taken from the village where the first victim lived, Reuters also reports.

Health workers wearing protective gear shift people who have been in contact with a person infected with the Nipah virus to an isolation center at a government hospital in Kozhikode, in India's Kerala state, on Thursday. (AFP via Getty Images)
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) describes the Nipah virus as being zoonotic — meaning that it can be transmitted from animals to people — and that fruit bats are the primary carriers of it in nature.
"Nipah virus is also known to cause illness in pigs and people," the CDC says, adding, "Infection with NiV is associated with encephalitis (swelling of the brain) and can cause mild to severe illness and even death."
The World Health Organization (WHO) says the Nipah virus fatality rate is estimated at 40% to 75%, but that it can "vary by outbreak depending on local capabilities for epidemiological surveillance and clinical management."
"Infected people initially develop symptoms including fever, headaches, myalgia (muscle pain), vomiting and sore throat," WHO also said. "This can be followed by dizziness, drowsiness, altered consciousness, and neurological signs that indicate acute encephalitis. Some people can also experience atypical pneumonia and severe respiratory problems, including acute respiratory distress. Encephalitis and seizures occur in severe cases, progressing to coma within 24 to 48 hours."

Residents fix a sign reading "Nipah containment zone" to prevent the spread of Nipah virus in India's Kerala state on Wednesday. (Reuters)
The CDC says the virus is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or humans and their bodily fluids, or by eating food products that have been contaminated by animals.

Staff members install a sign reading, "Nipah isolation ward, entry strictly prohibited," at a hospital where a ward is being prepared for suspected Nipah virus patients in the Kozhikode district of India's Kerala state on Tuesday. (Reuters)
#india#nipah virus#Nipah#Kerala state#Virus#India racing to contain deadly Nipah virus outbreak as hundreds are tested in Kerala state
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Maybe this has something to do with it
MARUTHONKARA, India: It was more than two weeks before doctors even realised what they were treating, the fourth outbreak in five years of the lethal, brain-swelling Nipah virus in India’s Kerala region. By then, hundreds of people had been exposed to the bat pathogen.
Halting the disease’s spread required deploying an army of workers, who put this village and eight others on partial lockdown for two weeks, surveyed more than 53,000 houses for signs of illness and tracked down 1,200 people who had come into contact with infected patients, according to the World Health Organization.
Ultimately, six people were infected, and two of them died. Though Kerala’s response to contain the outbreak drew international praise, the quick spread of the virus and its impact on tens of thousands of people illustrate what many scientists and world health leaders say is a weakness in public health policy: relying solely on disease containment. Governments, they say, must also control land development and protect animal habitats in areas where there is high risk of pathogens leaping from animals to people, a phenomenon known as spillover.
[...]
Reporters compared ecological conditions across the globe from 2002 through 2020 with those that existed at the time of past spillovers, identifying 9 million sq km – covering 6% of the Earth’s land mass – where conditions were ripe for pathogens to jump from bats to humans. Nearly 1.8 billion people lived in those jump zones in 2020, an increase of 57% since 2002.
The analysis focused on bats because they are linked to many of the deadliest disease outbreaks of the past half century, including the recent Covid-19 pandemic. Though its specific source is still unknown, the virus that causes Covid-19 is related to coronaviruses found in some horseshoe bats, a type common in tropical Asia. Kerala is one of the likeliest places on earth for spillover to occur, the analysis showed.
[...]
Nipah, which comes from bats and causes a lethal, brain-swelling fever in humans, has been linked to the deaths of two dozen people in Kerala since its first, surprise appearance here in 2018. A 1998-1999 epidemic in Malaysia killed at least 105. Hundreds more have died in near-annual outbreaks in Bangladesh since 2001. Nipah is classified as a priority pathogen by the WHO because of its potential to trigger an epidemic. There is no vaccine to prevent infection and no treatment to cure it.
edit: I guess not if the ban is months old
seriously, what the fuck is this about?
they've just outright banned the tag for an indian state that's home to over 34 million people
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Emergent human diseases are considered as either new kinds of pathogens or old pathogens that have changed to become novel just like flu does on an annual basis. Generally, diseases have usually originated from wildlife and woods and penetrated into human populations such as malaria and plague. In last five decades, emerging human diseases have quadrupled mainly because of the increasing human encroachment into habit. These trends have specifically been worse in areas that are considered as disease hot spots across the globe, particularly in tropical regions. Notably, the potential for a severe outbreak in large populations is huge because of the modern air travel and enormous market in wildlife trafficking. As a result, the key to predicting and preventing the next pandemic is understanding the protective effects of nature intact as stated by experts. An example of an emergent human disease and infectious disease is Hendra virus in Australia, which is closely related to Nipah virus in South Asia. While the virus originated with Pteropus vampyrus or flying boxes, its main cause is the disruption of the ecosystem. Hendra and Nipah viruses are closely linked in terms of henipah virus and originated with fruit bats, which are messy eaters. These bats usually hang upside down similar to Dracula that are bound tightly in their membranous wings as they eat fruit by chewing the pulp and then coughing up the seeds and juices (Robbins, 2012). Once the virus breaks out from the fruit bats and into species that have not evolved with it, there is a likelihood of the occurrence of a horror show. For instance, in 1999 in rural Malaysia, it's possible that a bat dropped a piece of masticated fruit into a piggery in a forest. Consequently, the pigs got infected with the virus and amplified it before transmission into humans, which was startling in its lethality. Since there is no cure or vaccine for the virus, approximately 50% of the infected people died many suffered crippling and permanent neurological disorders. Generally, if henipah viruses evolve to be transmitted eagerly through casual contact, there are concerns that it could spread even rapidly and widely even throughout the world. As noted in the past four decades, any emergent human disease and ecological infectious disease is usually caused by demographical changes and encroachment into wild lands. The failure to take care of the natural world can generally contribute to breakdown of the ecosystems that in turn result in emerging and ecological infectious diseases. The developing model of infectious diseases like SARS and Ebola that have taken place in the past several decades is because of the things people do to nature. Therefore, as it turns out, disease can largely be regarded as an environmental issue since 60% of emerging human and ecological infectious diseases originate in animals, especially wildlife. Consequently, several teams of conservation biologists and veterinarians are involved in global initiatives medical doctors, other clinical professionals, and epidemiologists to understand the ecology of disease. Since new infectious diseases continue to emerge at alarming and historically unprecedented rates, the world is still at great risks of emerging human and ecological infectious pandemics and epidemics (Gutierrez, 2009). Actually, the world is at risk of the emergence of more than one disease annually due to the ever-increasing rate of global transportation. Furthermore, there is a great risk of the emergence of drug-resistant strains because of poor medical practices such as misuse of antibiotics. However, my family and I are not at risk of any emergent diseases because of the preventive measures that we are constantly engaged in. some of these preventive measures include ensuring that we take routine vaccinations and getting immunizations as recommended by the doctor. References: Gutierrez, D. (2008, January 5). WHO Warns of High Risk of Global Epidemic from Emerging Diseases. Retrieved November 3, 2012, from http://www.naturalnews.com/022457_emerging_disease_World_Health_Organization.html Robbins, J. (2012, July 14). The Ecology of Disease. Retrieved November 3, 2012, from http://www.nytimes.com/2012/07/15/sunday-review/the-ecology-of-disease.html?pagewanted=all&_r=0 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Spotting Nipah Virus Symptoms: A Guide to Early Response
The Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic infection, which means it can transfer from animals to humans and, in certain cases, between people. Discovered in 1998, the virus is linked to severe health risks, making it crucial to identify its symptoms early for effective management.
Typically, symptoms of the Nipah virus appear within 4 to 14 days after exposure. Early signs often mimic those of the flu and include high fever, intense headaches, dizziness, and muscle aches. Nausea and vomiting are also common. Seeking medical attention immediately is essential if these symptoms arise. Prompt evaluation at a hospital ensures an accurate diagnosis and timely treatment, helping to prevent further complications. Hospitals equipped with specialized facilities can provide critical care when needed.
As the condition progresses, more serious issues may develop. Respiratory problems such as difficulty breathing and prolonged coughing are often seen. In some instances, the virus can lead to encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain that causes confusion, drowsiness, seizures, or even coma. Without hospitalization, these severe complications can escalate rapidly, posing a life-threatening risk. Hospitals equipped with advanced medical resources are essential for managing such cases, providing treatments such as oxygen therapy, intravenous support, and neurological monitoring to stabilize patients.
Since there is currently no specific vaccine or antiviral medicine for Nipah virus, early detection and treatment at a hospital are critical. Preventive strategies, such as avoiding contact with infected animals or consuming contaminated food and drinks, play a key role in reducing exposure risks.
In summary, identifying Nipah virus symptoms early and seeking care at a hospital promptly are essential for minimizing health risks. Vigilance, timely action, and preventive measures remain the most effective ways to combat this deadly virus.
0 notes
Text
Veterinary Diagnostics Market Size, Share, Growth & Forecast (2021-2027)
The Global Veterinary Diagnostics Market is projected to reach a valuation of US$ 6.14 billion by 2027, expanding at a robust CAGR of 9.4% from its 2020 value of US$ 3.25 billion. Veterinary diagnostics involve screening for underlying diseases in healthy animals and aiding veterinarians in monitoring disease progression or treatment response.
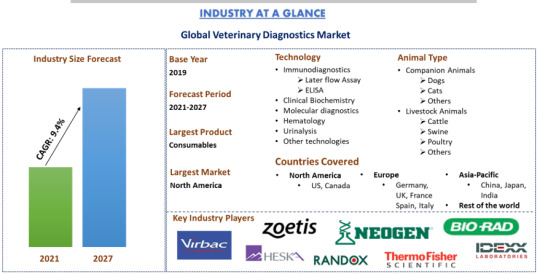
Several factors are propelling the growth of the Global veterinary diagnostics market, notably the increasing global pet population. In 2021, there were over 900 million dogs and approximately 600 million cats worldwide, with these numbers continually rising. The trend of pet adoption is driven by rapid urbanization and the shift toward nuclear families. The United Nations projects that by 2050, 68% of the world’s population will live in urban areas, up from 55% in 2018.
The rise in per capita income, leading to higher disposable income and improved living standards, is another key factor driving market growth. Increased spending on pet health, combined with rising disposable incomes, further boosts the market. For example, India's per capita income increased from Rs 72,805 in FY15 to Rs 94,954 in FY19, marking a 30% rise over six years.
Additionally, the growing demand for animal-derived food and the rising incidence of zoonoses worldwide are significant contributors to market growth. In India, 816 out of 1407 human pathogens are zoonotic. Major zoonotic diseases include rabies, brucellosis, Japanese Encephalitis, plague, leptospirosis, Scrub typhus, Nipah, trypanosomiasis, Kyasanur forest disease, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. In 2018, India reported 110 cases of rabies, 1674 cases of JE, and 14971 cases of H1N1. Regular monitoring and testing of animals are essential to prevent these diseases, thereby augmenting the veterinary diagnostics market.
For a detailed analysis of the veterinary diagnostics market, browse through – https://univdatos.com/report/veterinary-diagnostics-market
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a positive impact on the veterinary diagnostics market globally, with an increase in pet ownership due to lockdown restrictions. According to the European Pet Food Federation, spending on pet services and products rose by 7.6% to 21.2 billion during the pandemic. Additionally, the pandemic has increased testing volumes for both animals and humans, further driving market growth.
Major players in the market include Idexx Laboratories, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Zoetis Inc, Virbac, Randox, Qiagen, Neogen, Heska Corporation, Abaxis, and Bio-rad Laboratories. These companies are engaging in mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships to strengthen their presence in various regions.
The market is segmented by product into consumables and instruments. The consumables segment dominated the global veterinary diagnostics market, while the instruments segment is also expected to grow significantly, driven by increased R&D expenditure and the launch of advanced diagnostics instruments. For instance, in September 2020, Zoetis launched Vetscan Imagyst, a diagnostic platform combining image recognition technology, algorithms, and cloud-based AI to deliver accurate testing results.
Request a sample of the report through – https://univdatos.com/request_form/form/432
Based on technology, the market is divided into immunodiagnostics, clinical biochemistry, molecular diagnostics, hematology, urinalysis, and other technologies. The immunodiagnostics segment dominated the market in 2020 and is expected to grow rapidly due to the increasing prevalence of animal-borne diseases like rabies, Zika virus, and coronavirus.
The report also provides a regional analysis of the global veterinary diagnostics market, including North America (United States, Canada, and the Rest of North America), Europe (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, United Kingdom, and Rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea, and Rest of APAC), and Rest of the World. North America led the market, generating substantial revenue in 2020, driven by a high number of pet owners and a high degree of urbanization. Asia-Pacific is also identified as a high-growth market with significant opportunities for major players in veterinary diagnostics.
#Veterinary Diagnostics Market#Veterinary Diagnostics Market Size#Veterinary Diagnostics Market Share#Veterinary Diagnostics Market Growth
1 note
·
View note
Text
Longevity : ఆయుష్షు పెంచుకోవాలంటే ఏం చేయాలి ? ఈ 8 చెడు అలవాట్లను మానేయండి !! https://teluguflashnews.com/avoid-these-8-bad-habits-to-increase-your-life/
nipah virus : నిపా వైరస్ అంటే ఏమిటి? లక్షణాలు మరియు నివారణ చిట్కాలు తెలుసుకోండి!! https://teluguflashnews.com/nipah-virus-causes-symptoms-and-treatment-nipah-alert-in-kerala/
How to Keep Your Liver Healthy : మీ లివర్ ని కాపాడుకోండిలా!! https://teluguflashnews.com/how-to-keep-your-liver-healthy/
Dengue fever : డెంగ్యూ జ్వరం అంటే ఏంటి ? లక్షణాలు, నివారణ తెలుసుకుందాం ! https://teluguflashnews.com/what-is-dengue-fever-signs-and-symptoms-prevention/
Immunity Foods : ఇమ్యూనిటీ పవర్ను పెంచే ఆహారాలేంటో తెలుసా..? https://teluguflashnews.com/do-you-know-the-foods-that-increase-immunity-power/
Egg yolk Nutrition and benefits : పచ్చసొనను పక్కన పెట్టకండి ! https://teluguflashnews.com/egg-yolk-nutrition-and-benefits/
ajwain health benefits : వాముతో ఎలాంటి ప్రయోజనాలు ఉన్నాయో మీకు తెలుసా ? https://teluguflashnews.com/do-you-know-what-are-the-health-benefits-of-ajwain/
dry fruits : ఈ వ్యాధులుంటే డ్రై ఫ్రూట్స్ తినండి! https://teluguflashnews.com/eat-these-dry-fruits-if-you-have-health-problems/
Lemon with Turmeric : నిమ్మరసం, పసుపు కలిపి తాగితే ప్రయోజనాలు ఎన్నో! https://teluguflashnews.com/drink-lemon-with-turmeric-and-know-its-benefits/
folic acid foods : ఫోలిక్ యాసిడ్ మనకు అవసరమా? ఆ ఆహారాలు ఏంటి ? https://teluguflashnews.com/folic-acid-foods-and-benefits-to-our-health/
Snoring : గురక తగ్గాలంటే.. ఈ 5 చిట్కాలు పాటించండి! https://teluguflashnews.com/snoring-causes-remedies-and-tips/
0 notes
Text
Kerala Nipah Virus Outbreak In India 2023
In the last few years, the Nipah virus has affected Kerala in the south-west of India, creating concerns about why it has a stronger impact in this area. This study looks into the unique reasons that make Kerala more vulnerable to the Nipah virus, considering a mix of environmental, ecological, and socio-economic factors.
Reasons that impacting kerala nipah virus
Ecological Landscape and Biodiversity

Kerala has lots of different plants and animals, and this makes it a good place for diseases that can pass between animals and people, like Nipah. Fruit bats, which carry the virus, live happily in the state’s big fruit gardens and thick forests. This special environment makes it easy for the virus to go from bats to humans.
Source: Journal of Infectious Diseases, Wildlife Conservation Reports
Agricultural Practices and Human-Bat Interaction

Kerala’s agrarian landscape, dominated by fruit cultivation and farming, brings humans into close contact with bats and their habitats. Traditional farming practices, coupled with the consumption of raw date palm sap, provide a direct route for the transmission of the Nipah virus from bats to humans.
Source: Kerala Agricultural University, Journal of Agriculture and Rural Development
Population Density and Urbanization

The high population density and rapid urbanization in Kerala contribute to the swift spread of infectious diseases. Crowded urban centers become hotspots for virus transmission, posing a challenge for timely containment measures. Kerala’s urban areas act as potential amplifiers for the Nipah virus, necessitating vigilant public health strategies.
Source: Census of India, Urban Development Reports
Healthcare Infrastructure and Preparedness
While Kerala boasts a robust healthcare system, the emergence of the Nipah virus presents unique challenges. The need for specialized facilities, rigorous containment measures, and rapid response teams is crucial in managing outbreaks. Continuous training and preparedness initiatives are essential to mitigate the impact of the virus on public health.
Source: Kerala Health Department, World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines
Social and Cultural Practices

Kerala’s close-knit communities and cultural practices, such as communal living and large gatherings, contribute to the rapid spread of contagious diseases. Understanding and integrating cultural sensitivities into public health interventions are pivotal in fostering community cooperation and compliance with preventive measures.
Source: Cultural Anthropology Studies, Health Communication Research
Climate and Seasonal Patterns
The tropical climate of Kerala, characterized by high temperatures and humidity, creates favorable conditions for the survival of the Nipah virus. Understanding the seasonal patterns of the virus can aid in predicting and managing outbreaks effectively.
Source: Indian Meteorological Department, Environmental Health Perspectives.
In conclusion, the multifaceted nature of the Nipah virus impact in Kerala is deeply rooted in the state’s ecological, socio-economic, and cultural fabric. Addressing this public health challenge requires a comprehensive approach that combines scientific research, community engagement, and strategic policy measures. As Kerala grapples with the recurrent threat of the Nipah virus, collaborative efforts on local, national, and international levels are imperative to safeguard public health and prevent future outbreaks.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that can be transmitted from animals to humans and can also spread from human to human.
0 notes
Text
Epidemiology This report will discuss the recent growth of the infectious/communicable disease of paratyphoid and typhoid fever in underprivileged regions across India, together with its contributing factors, pathophysiology, signs, symptoms, and management. Communicable / Infectious Disease That Occurred Globally The twenty-first century's onset was accompanied by growth in a range of wild and domesticated animal species acting as reservoirs/carriers of pathogens like bacteria, parasites, and viruses. Given the continuum of species of animals involved in the process and the pathogens' typically complicated natural history, proper prevention, surveillance, and control/management of zoonotic infections poses a genuine public health challenge. Foodborne diseases, mad cow disease and other such newly developed zoonoses, as well as several agents of viral infections (like, Ebola, Nipah, monkeypox virus, Highly Pathogenic Asian Avian Influenza (H5N1), etc.) have seriously impacted public health, directly as well as indirectly. With continual changes to the environment, such occurrences are expected to increase in the future (Schlipkoter & Flahault, 2010). This paper will concentrate on paratyphoid and typhoid fever outbreak in underprivileged regions across India. History of Typhoid and Para-typhoid In the U.S., enteric fever occurs rarely. Out of the average 500 annual cases, approximately 60% are contracted by travelers to India, South America, or Mexico. There are three stages involved in paratyphoid fever: the initial stage, which is characterized by high body temperature; the toxic stage, which is accompanied by intestinal symptoms and abdominal pain; and lastly, the recovery period (from typhoid fever) which is quite protracted. For adults, the three stages may be spread out across a 4-to-6-week duration, whereas for children, the disease course may span only 10-15 days. In the second (i.e., toxic) stage, one to ten percent chances exist of intestinal hemorrhage or perforation (Frey, 2006). This disease has been identified as a well-known source of morbidity across the globe. Approximately 21.7 million typhoid cases occur globally, with the maximum burden borne by Central and South America, India, and the sub-Saharan African region. All the above regions are characterized by one similarity -- poor sanitation and an increasing population. While very limited epidemiological information exists for projecting India's actual situation as regards the disease, some population-based and hospital researches have revealed significant changes in typhoid fever occurrence (Banerjee, et al., 2014). Pathophysiology Salmonella (S.) paratyphi (A, B, C) and Salmonella typhi are sensitive to various antibiotics in vitro (external to the organism/individual). But, in vivo (internal) responses may not always be predicted with accuracy from information on external susceptibility, chiefly due to their primarily intracellular location in phagocytic cells. Since S. paratyphi and S. typhi are obligate human infections, no suitable animal models exist for testing treatment regimens. Generally, the murine model - S. typhimurium - has been employed in the assessment of paratyphoid and typhoid host defense systems and pathophysiology. However, treatment responses have not utilized this model (White, 2010). Signs and Symptoms Disease onset occurs gradually and is characterized by: 1. Constant high fever 1. Malaise (feeling ill) 1. Marked headache 1. Decrease in appetite 1. Spleen enlargement that may result in abdominal discomfort 1. Presence of a flat pink rash on the torso 1. Dry cough during the disease's initial stage 1. Diarrhea or constipation-- in case of adult patients, constipation will be more common. The disease ranges in severity from mild (characterized by mild fever), to acute (accompanied by many complications). Individuals who fail to get treated can continue having fever for several weeks/months; an alarming 20% of these patients may succumb to disease complications in this period. Mortality rate drops to around one percent with treatment. Paratyphoid symptoms are similar to those of typhoid; however, the former illness is typically a milder variant of the latter (Anon., n.d.) Epidemiological Triangle This is a model developed by scientists for understanding infections and the way they spread. This triangle has a total of three vertices/corners: agent, environment and host. Agent - Paratyphoid and typhoid fever have been identified as key health problems in numerous developing nations. Typhoid fever's etiologic agent, Salmonella typhi (Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi), accounts for more than 20 million and over 200,000 fatality occurrences globally per annum. Host -- After entry into human hosts via contaminated food/drinks, S. paratyphi and S. typhi have to circumvent other microorganisms that compete for mucosal adhesion and food, circumvent internal defense mechanisms in hosts, find an independent niche in mononuclear phagocytic systems, and live on and replicate. Lastly, they have to exit this host and get transmitted to another susceptible one. Environment - Considering parallelism of the host, pathogen's balanced environmental interactions can be helpful. The current situation in the Indonesian capital, Jakarta, can be described, with balanced host and pathogen factors' environmental interactions leading to paratyphoid and typhoid endemicity (Ali, 2006). Communicability and Prevalence The communicable illness- typhoid -- has several modes of transmission in India. Typhoid bacteria survive under unhygienic conditions. They spread largely through carriers and typhoid patients' vomit and stools. These bacteria are then transmitted to food, water, and drinks via insects (such as house-flies), thereby contaminating food. Salmonella enteritidis paratyphi A/B/C leads to paratyphoid. This infection is usually milder than typhoid. Hardly any typhoid patient will remain a chronic carrier, despite treatment. Most widely-occurring complications of the disease are intestinal perforation and bleeding. Polluted water is a key source. Raw vegetables that are cultivated on fields containing sewage spread infection as well. The bacteria are capable of surviving for months on end in water and soil, and undergo rapid growth in dairy products and milk. Unhygienic environmental conditions are to be chiefly held responsible for its prevalence (Anon., n.d.). Spread of Typhoid S. Typhi is able to survive only in the human body. People suffering from typhoid carry these bacteria within their intestinal tract and bloodstream. Additionally, few individuals ("carriers") will recover from the disease whilst continuing to carry its bacteria. Carriers as well as sick individuals shed S. Typhi via feces). Typhoid fever may be contracted if a person eats food/drink handled by such a carrier, or if S. Typhi-contaminated sewage gets into drinking/domestic-use water. After such bacteria are consumed by the body, they will multiply and disperse in the person's bloodstream. his/her body will react via high body temperature and other symptoms and signs (listed previously) (Fever, 2013). Management of Typhoid A sudden rise in typhoid cases or confirmation/suspicion of at least two cases within a period of 30 days in any new locality/village must be reported without delay, followed by an immediate investigation into the outbreak with the steps listed below (Kool, 2010): 1. Outbreak confirmation, 1. Creation of a modifiable case definition: i.e., individuals to be considered part of this outbreak should be defined 1. Identification of new cases and information-gathering 1. Line-listing (summary table containing basic information relating to outbreak time, place, and individual cases) 1. Description of collected data by time (symptom onset), place, and person 1. Establishment and reinforcement of communication channels among health facilities, management, and field officers, as well as with relevant national-level authorities 1. Communication of results to professionals and the community. Status of Typhoid -- 2020 Objectives Delhi is the lone state in India to have included a vaccine for Typhoid fever in its child immunization schedule, beginning November 2004. Up to now, over two million kids have been administered typhoid vaccines, helped reduce multiple-drug-resistant typhoid cases in Delhi (Welfare, n.d.). One research work by McKinsey (Bhadoria, et al., 2012) revealed a considerable growth in adult/optional vaccine penetration (regular vaccines for typhoid and influenza as well as one-time shots (e.g., hepatitis A)). In 2020, market value is expected to reach $3.2-3.3 billion, growing at a yearly rate of 30-35%, beginning 2012. Very probably, as many as 5 'mega' vaccines -- anti-typhoid, anti-influenza, pneumococcal, hepatitis A, and HPV vaccines -- costing more than 250 million dollars each, will dominate the market (accounting for 60% of it). By the end of this year, every Indian state and Union Territory is expected to incorporate elimination of typhoid in their broad planning frameworks and health policies. By the end of next year, each state will be required to lower API (Annual Parasite Incidence) to below one for every thousand persons, and by the end of the year 2020, fifteen category 1 (i.e., elimination phase) states or Union Territories are projected to interrupt typhoid transmission, achieving the target of zero native cases and typhoid-related deaths. Further, it has been predicted that accelerated efforts of states like Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Gujarat, having relatively good health infrastructure and capacity, can usher quicker typhoid elimination -- within a span of 2-3 years. According to the twelfth Five-Year Plan's targets, India has to attain API Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Introducing the Kerala Doctor Who Detected the Nipah Outbreak, Both in 2018 and This Time.
Introducing the Kerala Doctor Who Detected the Nipah Outbreak, Both in 2018 and This Time
In the fight against deadly diseases, heroes emerge from unexpected places. Meet Dr. Anitha Prasad, the vigilant Kerala doctor who played a pivotal role in detecting the Nipah virus outbreak, not once but twice—first in 2018 and, remarkably, once again this time around. Her unwavering dedication to public health has earned her a well-deserved spotlight.
The Silent Threat Returns
Nipah virus, a rare and deadly zoonotic disease, had already cast a dark shadow over Kerala in 2018. The memory of that outbreak still lingered when, in a deja vu moment, whispers of a similar threat began to surface in 2023. Dr. Anitha Prasad, stationed at the forefront of healthcare in Kerala, was quick to respond.
A Tireless Guardian
Dr. Anitha Prasad's journey to becoming a guardian against Nipah began with a passion for epidemiology and infectious diseases. Her extensive knowledge and relentless commitment have made her a trusted figure in the medical community. When the first signs of the virus emerged in 2018, she took charge, orchestrating a swift response that helped contain the outbreak.
2023: A Familiar Foe Returns
In early 2023, the Nipah virus resurfaced in Kerala. This time, Dr. Anitha Prasad's experience and expertise were instrumental in recognizing the symptoms and patterns early on. Her unwavering dedication to the well-being of the community pushed her to work tirelessly, alongside her medical team, to contain the virus's spread.
The Power of Early Detection
Early detection is often the key to preventing a health crisis, and Dr. Anitha Prasad understands this better than most. Her keen eye for unusual symptoms, coupled with her ability to mobilize resources swiftly, has saved countless lives. Her leadership has become a beacon of hope for those affected by Nipah.
Community Support and Resilience
Dr. Anitha Prasad's efforts are not limited to the confines of a hospital. She has actively engaged with the local community, educating them about the virus and the importance of early reporting. Her empathetic approach has built trust and encouraged individuals to come forward for testing and treatment.
A Living Legend
Dr. Anitha Prasad's story is a testament to the power of knowledge, dedication, and resilience in the face of adversity. Her ability to detect and respond to the Nipah virus not once but twice showcases her unwavering commitment to safeguarding public health. She is not just a doctor; she is a hero, a symbol of hope in challenging times.
The Nipah virus may be a formidable foe, but with vigilant doctors like Dr. Anitha Prasad on the front lines, Kerala stands strong against this silent threat. Her story reminds us that heroes walk among us, quietly ensuring our safety and well-being, even in the face of the deadliest challenges.
Inspiring True Stories, inspirational women's stories, Inspiring Stories of Women, Inspiring Story Of A Woman, Inspirational Women in Business, Inspirational moral stories for Adults, real life inspiring stories, heart touched inspiring stories, Inspiring Women Leaders, Inspiring Stories About Women, stories inspirational success, story about inspirational person, inspiring stories of Indian women, Some Inspirational Women, Inspirational Short Stories, Most Inspirational Short Stories, real life inspirational stories, Inspiring True Stories, Read Inspiring Stories, Best Motivational Short Stories, Motivational Short Stories, Short Motivational Stories, The Power of Story, real life stories, Leading Ladies india, Leading Ladies, Stories of real life people, Good Motivational Stories, Women entrepreneurs of india, women's empowerment, Women's Empowerment in India, powerful stories from women, Stories Of Impact, True stories told by women, Women Centered Stories, Short motivational story for students, Motivational story of a woman,
0 notes
Text
Nipah Virus: A Silent Threat
Nipah Virus: A Silent Threat
The Nipah virus, an emerging zoonotic pathogen, has gained prominence in recent years due to sporadic outbreaks. It is imperative to comprehend the first symptoms of Nipah virus infection to ensure early detection and containment. In this article, we delve into the subtleties of these initial signs and why prompt action is crucial.
Unveiling the Nipah Virus
Before delving into the symptoms, let's briefly understand what Nipah virus is. Nipah virus (NiV) is a highly contagious virus that belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae. It was first identified in Malaysia in 1999 during an outbreak among pig farmers and subsequently in other parts of Southeast Asia.
The Initial Warning Signals
Fever – The Ominous Prelude
Fever, often accompanied by a headache, is one of the earliest indicators of Nipah virus infection. The fever can be moderate to high-grade and typically persists for an extended period. It is essential to monitor the fever closely, as it may escalate rapidly.
Respiratory Distress – A Cause for Concern
Respiratory distress, including coughing and breathing difficulties, is another significant symptom. Patients may experience acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which can lead to severe breathing problems. Timely medical intervention is crucial at this stage.
Encephalitis – The Neurological Challenge
Nipah virus is notorious for its impact on the central nervous system. Encephalitis, characterized by altered mental status, confusion, and even coma, is a severe consequence of Nipah virus infection. These neurological symptoms can manifest rapidly, underscoring the need for immediate medical attention.
Muscle Pain and Fatigue – A Debilitating Combination
Muscle pain and fatigue are common complaints among Nipah virus-infected individuals. These symptoms can be quite debilitating, making it challenging for patients to perform their daily activities.
Nausea and Vomiting – Gastrointestinal Distress
Nausea and vomiting are also observed in many cases of Nipah virus infection. These gastrointestinal symptoms can further weaken patients and contribute to dehydration.
Seizures – A Disturbing Development
In some instances, Nipah virus infection can lead to seizures, adding another layer of complexity to the clinical picture. Seizures can be life-threatening and require immediate medical intervention.
Why Early Detection Matters
Understanding the first symptoms of Nipah virus is paramount because early detection can significantly improve the prognosis. Rapid diagnosis and isolation of infected individuals can prevent the virus from spreading within communities.
The Role of Transition Words
Transition words, such as "therefore," "consequently," and "moreover," have been seamlessly incorporated into this article to enhance its flow and coherence.
In conclusion, recognizing the initial symptoms of Nipah virus infection is crucial for early intervention and containment. Timely medical attention can make all the difference in saving lives and preventing the virus from causing widespread outbreaks. Stay vigilant, and if you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical help.
0 notes
Text
Explore these symptoms and preventive measures of the rising Nipah Virus in Kerala
According to the report in India, the number of cases of the Nipah Virus is on the rise in Kerala. These reports also indicate that there are at least 706 individuals on the contact list, with 77 falling into the high-risk category.
This Nipah Virus was initially recognized in Malaysia in 1999 when there was an outbreak among pig farmers. In 2001, the virus was also confirmed in Bangladesh, and subsequently, isolated cases emerged in eastern India. The World Health Organization estimates the fatality rate to range between 40 percent to 75 percent.
Check out these details to know more about this virus, its symptoms, causes, and preventive measures.
What is the Nipah Virus?

The Nipah virus, also known as NiV, is classified under the Henipaviral genus within the Paramyxoviridae family. There are concerns surrounding the Nipah virus arise from its:
High fatality rate
Serious symptoms
Absence of targeted treatment
Possibility of human-to-human transmission
Prior occurrences of outbreaks
Symptoms of Nipah Virus

Although not as prevalent as certain other infectious diseases, the emergence of the virus presents a substantial public health risk. This underlines the importance of early detection, implementing containment strategies, and raising public awareness to curb its transmission.
To Read More Click here...
#health#healthy#health blogs#health & fitness#healthy recipes#healthy routine#nipah virus#healthy lifestyle#health and wellness#health care
1 note
·
View note