#net asset value (nav) calculation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Marketing 101 | For Emerging Managers
Inviting all emerging managers to join this amazing webinar. Secure your spot now: https:https:https://webinar.fundtec.in/meeting/register?sessionId=1336937368

#accounting#financial reporting#finance#investor services#fund administration#crypto business#net asset value (nav) calculation
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Is The Meaning Of NAV In Mutual Funds?
Navigating the world of mutual funds can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. Among the many terms and acronyms, "NAV" stands out as one of the most commonly used yet misunderstood terms. In this blog post, we'll demystify NAV in mutual funds and explain its significance in your investment journey.

Understanding NAV:
NAV, or Net Asset Value, is a fundamental concept in the world of mutual funds. It represents the per-unit market value of a mutual fund scheme's assets on a specific date. Essentially, it tells you what one unit of the fund is worth at a particular moment. But what does that really mean?
Calculation of NAV:
The calculation of NAV is straightforward. It involves two primary components: assets and liabilities.
Assets: These are the investments held by the mutual fund. This can include stocks, bonds, cash, and other securities. The total value of these assets is calculated daily.
Liabilities: These are the expenses and debts associated with managing the mutual fund. This can include management fees, administrative expenses, and other costs.
The formula for calculating NAV is as follows:
\[NAV = \frac{Total Value of Assets - Total Value of Liabilities}{Number of Outstanding Units}\]
Importance of NAV:
1. Price Determination: NAV is used to determine the price at which investors can buy or sell units of a mutual fund. When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially buying units at the current NAV.
2. Performance Evaluation: NAV also serves as a measure of a mutual fund's performance. Investors can track the changes in NAV over time to assess how well the fund is doing.
3. Comparing Funds: NAV allows investors to compare the prices of different mutual funds. However, it's essential to note that a higher NAV does not necessarily mean a better fund. What matters is the fund's performance relative to its NAV.
NAV and Mutual Fund Types:
It's important to understand that the significance of NAV can vary depending on the type of mutual fund:
1. Open-End Funds: These funds continuously issue and redeem units at their NAV. Investors buy and sell units at the NAV price, which is calculated at the end of each trading day.
2. Closed-End Funds: These funds have a fixed number of shares that are traded on stock exchanges. The market price of closed-end fund shares may be at a premium or discount to their NAV.
NAV and Market Fluctuations:
The NAV of a mutual fund can fluctuate daily due to changes in the value of its underlying investments. Factors such as market conditions, interest rates, and the performance of the fund's assets can impact NAV. During a market downturn, the NAV may decrease, and during a bull market, it may increase.
Conclusion:
In summary, NAV, or Net Asset Value, is a crucial concept in the world of mutual funds. It represents the per-unit market value of a mutual fund and is used for pricing and performance evaluation. Understanding NAV is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions about their mutual fund investments. It's a valuable tool that provides insight into the financial health and performance of a mutual fund, helping investors navigate the world of investing with confidence.
As you explore mutual fund investments, keep a close eye on the NAV, but remember that it's just one piece of the puzzle. A well-rounded investment strategy should consider factors like the fund's objectives, past performance, and fees in addition to the NAV. Happy investing!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
40+ CITCO Repeated Interview Questions & Answers

CITCO Technical Questions
Q1. About CITCO company?
A: Citco is a large privately owned global hedge fund administrator. It is the world’s largest hedge funds administrator Citco was founded in 1948. Fund managing over 1$ trillion in assets under administration. The CEO of CITCO is Christopher Smeets. (Verify once)
Q2. NAV and What are the types of NAV?
A: The value of the net asset (NAV) is defined as the value of the assets of the fund minus the value of its liability. In regard to mutual funds, the term ‘net asset value’ is widely used. It is a measure to calculate the value of the assets in funds. NAV is commonly used as a per-share value calculated for a mutual fund.
Types of NAV:
Daily net asset valuation
Basic calculation of Net Asset Value Total Assets – Total Liabilities The formula for the NAV = -------------------------------- Total no of outstanding units
Q3. Difference between Mutual funds and Hedge funds
A: Mutual funds are regulated investment products offered to the public and available for daily trading. Where Hedge funds are private investments that are only available to accredited investors. Hedge funds are known for using higher-risk investing strategies with the goal of achieving higher returns for their investors.
Q4. Present Sensex value
A: Do Google for the current Sensex value
Q5. About Hedge funds in detail
A: Hedge funds are another name for investment partnerships. The meaning of the word ‘Hedge’ is protecting oneself from financial losses; thus, Hedge funds are designed to do so. Although a risk factor is always involved, it depends on the return. The more the risk, the higher the return.
Hedge funds are alternative investments done by pooling funds involving several strategies to earn high returns for the investors. Hedge funds can be used for a range of securities compared to mutual funds. Hedge funds work for long & Short positions strategies which means investing in long positions i.e., buying stocks as well as short positions which means selling stocks with the help of borrowed money and then buying again when the price is low.
Q6. Corporate actions
A: A company initiates several actions, apart from those related to its business, that have a direct implication for its shareholders. These include sharing of surplus or profits with the shareholders in the form of dividends, changes in the capital structure through the further issue of shares, buyback, mergers and acquisitions, delisting, raising debt, and others. In a company that has made a public issue of shares, the interest of the minority investors has to be protected.
Mainly there are 2 types of corporate actions.
(i) Mandatory corporate actions include
a. Dividends
b. Bonds
c. Stock Split
d. Reverse Split
e. Mergers & De-Mergers
(ii) Non-Mandatory corporate actions include
a. Right issue
b. Buyback offers
Q7. KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti Money Laundering)
A: The Know Your Customer or Know Your Client guidelines in financial services require customer identification and screening, and ensuring you understand their risk to your business. To ensure that bank services are not misused.
AML – Anti Money Laundering. AML refers to all efforts involved in preventing money laundering. Such as stopping criminals from becoming customers and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
Q8. Full name of CITCO
A: Citco, also known as the Citco Group of Companies and the Curacao International Trust Company (CITCO).
Q9: Working Capital
A: Working Capital also known as Net Working Capital (NWC) is the difference between a company’s current assets – Such as cash, Accounts receivable, customers unpaid bills, and inventories of raw materials and finished goods and current liabilities such as accounts payable and debts. Net Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities.
Q10. Types of Trade in Mutual Funds
A: When you buy or redeem a mutual fund, you are directly purchasing and selling with the funds. Whereas with ETFs and stocks, you are trading on the secondary market. When you initiate a trade to buy or sell mutual funds shares it will be executed at the next available net asset value. Most mutual funds fall into 4 main categories
Money market funds
Bond funds
Stock funds
Target date funds
People Also Read: The Definitive Guide To Mastering The Top 20 Most Important Questions In Freshers Job Interviews
Q11. About IR Data processor with Example
A: The investors (IR) department is a division of a business, usually a public company, whose job it is to provide investors with an accurate account of company affairs. This helps private and institutional investors make informed decisions on whether to invest in the company. (IR) Department and work to communicate with investors, shareholders, government organizations, and the overall financial community.
Q12. About Bond Market
A: The bond market refers broadly to the buying and selling of various debt instruments issued by a variety of entities. Corporations and government issue bonds to raise debt capital to fund operations. In return, they promise to pay the original investment amount plus interest.
Q13. Types of Bonds
A: Some of the common types of bonds are
Zero – Coupon bond
Floating–rate bond
Convertible bonds
Amortization bonds
Callable bonds
Puttable bonds
Payments in kind (PIK) Bonds
Principal – Protected Note (PPN)
Inflation-Protected Securities
Q14. Types of Trade
Day Trading
Position Trading
Swing Trading
Short Term & Long-Term Trading
Q15. What is Private Equity
A: Private equity is an alternative form of private financing, away from public markets, in which funds and investors directly invest in companies. Private equity firms make money by charging management and performance fees from investors in a fund.
Q16. Trade Cycle
A: A trade cycle refers to the fluctuation in economic activities especially in employment, output and income, prices, profits, etc. It has been defined by different economists. According to Mitchell, the “Business cycle is of fluctuations in the economic activities of organized communities”
Q17. What is investment and capital market
A: An investment involves putting capital in bonds, stocks, real estate property, or a business and hopes of a greater payoff in the future than what was originally put in.
Journal entry: Cash a/c --------Dr To investor a/c
Q18. Derivatives
A: A capital market is a place where buyers and sellers indulge in trade (buying/selling) of financial securities like bonds, stocks, etc. The trading is undertaken by participations such as individuals and institutions. Read full page here...
People Also Read: MNC Companies Interview Questions For B.Com, MBA, CA, IPCC, PGDM Students
General/HR Questions
Note: Some of the answers to the questions, you will find here: Click to read
Self-introduction Click to read the answer
Family Background
How many emails can you respond to and reply to in a day?
Previous job role
Why I should hire you A: Although I have no experience, I am serious and willing to learn anything. That is to be learned for the enhancement of the growth of the organization as well as the self. I am also a hardworking, dedicated, trustworthy & Self-motivated person. Finally, I am confident I’ll be the best candidate for this position.
Read full page here...
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top 5 flexi cap mutual funds with highest sip returns in 7 years xirr calculator inr rs 20000 monthly investment has grown to 4235000 nifty bse 500 tri
Quant Flexi Cap Fund In 7 years, Quant Flexi Cap has given a 25.99 per cent annualised return. Its assets under management (AUM) are Rs 7,153 crore, while its net asset value (NAV) is Rs 110.26. Benchmarked against NIFTY 500 TRI, the fund has given annualised returns of 19.51 per cent since its launch in January 2013. With an expense ratio of 0.61 per cent, the fund has Rs 1,000 as the minimum…
0 notes
Text
How to Build a Strong Borrowing Base for Asset-Based Lending Success
If you're running a business and need working capital, Asset-Based Lending (ABL) can be a flexible and dependable solution. Unlike traditional loans that rely mainly on your credit score or profitability, ABL allows you to borrow money using your company’s assets—like receivables, inventory, or equipment—as collateral.
But how do lenders decide how much to lend? That’s where your borrowing base comes into play. In this blog, we’ll break down what a borrowing base is, how it’s calculated, and what steps you can take to build a strong one that helps you unlock more liquidity.

What Is a Borrowing Base?
Your borrowing base is essentially the value of your eligible assets that lenders are willing to lend against. It’s like a safety net for the lender—ensuring there’s enough collateral to recover funds in case of default.
A simple example:
Let’s say you have $1,000,000 in receivables and $500,000 in inventory.
If your lender offers an advance rate of 85% on receivables and 50% on inventory: Your borrowing base = (85% of $1,000,000) + (50% of $500,000) = $850,000 + $250,000 = $1.1 million
That means you could potentially borrow up to $1.1 million, depending on your agreement.
What Assets Typically Count?
Accounts Receivable (A/R)The most common asset used in ABL. Lenders prefer receivables that are:
Less than 90 days old
From creditworthy customers
Free from disputes or prior liens
InventoryCan include raw materials, finished goods, or work-in-progress. Lenders usually discount inventory more heavily due to its risk of obsolescence or market fluctuation.
Equipment or MachineryThis can be included in some ABL structures but usually has a lower advance rate and may require appraisal.
What Makes a Borrowing Base “Strong”?
A strong borrowing base isn’t just about quantity—it’s about quality. Here's what strengthens your position:
Accurate and updated records: Outdated data on receivables or inventory can reduce your borrowing power.
Stable customer base: Reliable customers who pay on time increase your receivables' value.
Diversification: Avoid concentration risk—don’t let one customer represent a huge share of your A/R.
Inventory turnover: Faster-moving inventory is better collateral than items that sit idle for months.
Clear title and no encumbrances: Assets should not be pledged elsewhere or under legal dispute.
How Do Lenders Evaluate the Borrowing Base?
Lenders usually perform regular field exams, review financial statements, and request borrowing base certificates. These documents must match your actual data. The more transparent and organized you are, the more trust you build.
Here’s where Private Credit Monitoring Software becomes very useful. These platforms help businesses track the value and eligibility of their collateral in real time. They automatically calculate borrowing base availability, reducing manual errors and improving lender confidence.
Role of Compliance and Oversight in ABL
When lenders approve large ABL facilities, they need to stay on top of risks—not just at the start of the loan, but throughout the life of the facility. This is where Lender Compliance Technology helps. It ensures borrowers follow covenants, maintain required financial ratios, and submit documentation on time.
A robust compliance framework protects both parties. Borrowers avoid unnecessary fees or breaches, while lenders minimize exposure to default.
Can Asset-Based Lending Support Risk Transfer?
Yes. In structured credit markets, asset-backed portfolios are often bundled and used in Significant Risk Transfer (SRT) transactions. Here, lenders can reduce their exposure by transferring portions of the credit risk to other investors. But a clean, reliable borrowing base is essential in these transactions—it builds trust, reduces complexity, and supports accurate modeling.
How Portfolio Technology Connects the Dots
Borrowing base evaluations are not one-off events—they evolve. As your business grows or assets fluctuate, your borrowing power changes.
If you're managing multiple facilities or operating in private credit, you’ll benefit from tools like Direct Lending Portfolio Management Technology. These platforms offer:
Real-time facility monitoring
Drawdown tracking
Covenant compliance alerts
Consolidated borrower and asset performance data
This kind of visibility helps your finance team stay proactive rather than reactive, especially when asset values change quickly.
Final Thoughts
Building a strong borrowing base is both a science and an art. You need to maintain solid internal records, understand what lenders look for, and be proactive in monitoring asset quality. With the right practices and tools in place, Asset-Based Lending becomes more than just a loan—it becomes a strategic cash flow solution.
Whether you're a growing manufacturing firm, a distributor, or a business looking to stabilize cash flow, focusing on the health of your borrowing base can make all the difference.
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical advance rate in Asset-Based Lending?Advance rates vary but are often around 80–85% for receivables and 40–60% for inventory, depending on the asset’s risk.
Q2: Can I include all my receivables in the borrowing base?Not necessarily. Lenders may exclude receivables that are overaged, from foreign customers, or otherwise considered uncollectible.
Q3: How often is the borrowing base recalculated?Typically monthly or weekly, depending on the facility size and lender requirements.
Q4: Is software necessary for managing a borrowing base?While not mandatory, tools like Private Credit Monitoring Software can significantly reduce errors and streamline reporting, especially in larger facilities.
Q5: Can Asset-Based Lending help me grow my business?Absolutely. With a solid borrowing base, you can access liquidity faster and invest in operations without waiting for customer payments.
0 notes
Text
Loan Against Mutual Funds Online in 2025 – Fast Approval Without Selling Investments

In 2025, if you need urgent cash and own investments like mutual funds or shares, there's good news—you no longer need to sell your assets. Thanks to the rise of LAMF (Loan Against Mutual Funds) and LAS (Loan Against Shares), you can instantly apply for a digital loan without disturbing your portfolio. Whether it's for a wedding, education, travel, or medical emergency, you can unlock funds in minutes — no income proof, no selling, just swipe and go.
Let’s explore how a digital loan against mutual funds or shares works, who can apply, what the features, limits, eligibility, and more. This guide will clearly and naturally answer every user's question, utilizing all the important search keywords to help both readers and search engines trust and rank this content.
What is a Loan Against Mutual Fund (LAMF)?
A Loan Against Mutual Fund (LAMF) allows you to borrow money using your mutual fund units as collateral. Instead of redeeming your mutual funds, lenders provide you with a credit line or term loan based on the NAV (Net Asset Value) of your holdings.
Similarly, a Loan Against Shares (LAS) lets you pledge your equity shares and get funds instantly. The biggest advantage? You retain ownership and continue to earn returns, dividends, and capital gains while enjoying liquidity.
Top Features of Loan Against Mutual Funds & Shares (LAMF LAS)

How Does a Digital Loan Against Mutual Fund Work in 2025?
Log in to your Demat or Mutual Fund platform. Most AMCs and fintech apps now offer LAMF APIs directly integrated.
Select the funds to pledge. ELSS, debt, hybrid, and large-cap funds are typically eligible.
Get an instant offer based on NAV. The higher the NAV and fund stability, the better your loan terms.
E-sign documents and complete KYC online.
Loan is disbursed digitally – often within 30 minutes!
This is how a digital loan against mutual funds online saves you time, paperwork, and the stress of liquidating long-term wealth.
LAMF Eligibility & Documents – Who Can Apply in 2025?
Eligibility for Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF):
Age: 21 to 65 years
Must own eligible mutual fund units (ELSS, debt, hybrid, or equity)
Resident Indian with valid PAN & Aadhaar
Salary slip or ITR is not mandatory (many lenders skip this)
LAMF Documents Required:
PAN Card
Aadhaar or Passport/Voter ID
Mutual Fund Statement (CAS)
Cancelled Cheque (for loan disbursal)
Optional: Income proof for higher limits
You can also use a loan against mutual funds eligibility calculator available on most lending platforms to get your eligible amount instantly.
Top Use Cases – Why People Apply for a Loan Against Mutual Funds in 2025
Loan Against Mutual Funds for Wedding Expenses Don’t touch your SIPs or ELSS—get a short-term loan without penalty.
Loan Against Mutual Funds for Higher Education Quick and smart funding option without breaking your portfolio.
Loan Against Mutual Funds for Financial Planning Use for emergencies or opportunities while your investments grow.
Loan Against Mutual Funds for Financial Needs Medical emergencies, travel, family events, or even down payments.
Interest Rates, Processing Fees & Limits – All You Need to Know
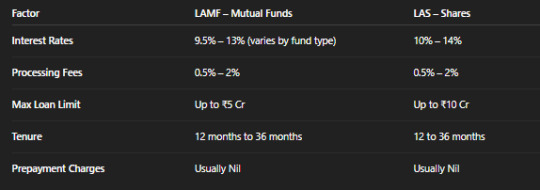
Digital loan platforms use LAMF APIs to instantly evaluate, process, and disburse loans, making the loan against mutual funds processing fees and interest rates transparent and user-friendly.
How to Apply for a Loan Against Mutual Funds Online – Step-by-Step (2025)
Visit a digital lending platform (like Groww, Zerodha, Paytm Money, or a Bank site)
Click on “Apply for Loan Against Mutual Fund.”
Enter PAN & link your MF folio or Demat
Select eligible funds (ELSS, debt, equity)
View the loan offer via the LAMF eligibility calculator
E-sign documents and submit KYC
Get instant disbursal to your linked bank account
Some fintech apps offer a loan against shares interest rates comparison to help you choose LAS vs LAMF smartly.
FAQs – Loan Against Mutual Funds or Shares in 2025
1. What is a loan against a mutual fund?
A Loan Against Mutual Fund (LAMF) allows you to borrow money without selling your investments by pledging them digitally.
2. Who can apply for a loan against mutual funds in India?
Any Indian citizen above 21 who holds mutual funds in their name can apply. Many platforms don’t require income proof or a high CIBIL.
3. Can I apply for a loan against ELSS mutual funds?
Yes, loan against ELSS is allowed, but with certain lock-in caveats. Many lenders accept ELSS if held for over 3 years.
4. How much can I borrow through LAMF?
Using a loan against mutual funds eligibility calculator, most users can obtain a loan of up to 70%-80% of their mutual fund's NAV.
5. Is LAS or LAMF better in 2025?
If you hold mutual funds, go for LAMF. If you own equity shares, LAS offers better liquidity options. Compare both using the Loan Against Securities Interest Rates before choosing.
Final Thoughts: Borrow Smart, Invest Smarter
In 2025, you no longer need to choose between growth and liquidity. With smart fintech platforms offering digital loans against mutual funds or shares, you get the best of both worlds — access to instant funds without selling your long-term assets.
Whether you’re planning a big event or tackling a financial emergency, LAMF or LAS ensures you get cash on tap with low documentation, transparent interest rates, and minimal stress. Just a few clicks, and you’re good to go — No Sell, Just Swipe.
#lamf#loan against mutual funds online#lamf eligibilty & documents#loan against elss#digital loan against mutual fund#how to apply loan against mutual funds#loan against mutual funds explained#features of loan against mutual funds#how does a loan against mutual fund work#loan against mutual funds faqs#lamf api#loan against mutual funds processing fees and interest rates#what is a loan against mutual fund#loan against mutual funds max limit#lamf eligibility#lamf loan#loan against mutual funds for wedding#loan against mutual funds eligibility calculator#loan against mutual funds for financial planning#apply for loan against mutual fund#loan against mutual funds for financial needs#loan against mutual funds features#loan against mutual funds for higher education#loan against mutual funds limit#loan against mutual funds eligibility and documents#digital loan against mutual funds interest rate#who can apply for loan against mutual funds#lamf documents#LAS#Loan Against Securities Interest Rates
0 notes
Text
Rule 11UA Compliance: Who is Authorized to Determine FMV for Tax Purposes?
Comprehensive Guide to Rule 11UA Valuation: Fair Market Value Determination for Tax Compliance
Table of Contents
Introduction to Rule 11UA Valuation
What is 11UA Valuation?
Who is Authorized to Conduct Valuation Under Rule 11UA?
Valuation Methods Under Rule 11UA
Net Asset Value (NAV) Method
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
Step-by-Step Rule 11UA Calculation (With Excel Examples)
Key Compliance Requirements & Documentation
Common Mistakes to Avoid in 11UA Valuation
FAQs on Rule 11UA Valuation
Conclusion: Best Practices for FMV Determination

1. Introduction to Rule 11UA Valuation
Rule 11UA of the Income Tax Rules, 1962, provides the framework for determining the Fair Market Value (FMV) of unquoted shares and securities for tax purposes. This rule is particularly relevant for:
Startups issuing shares under Section 56(2)(viib) (Angel Tax)
Companies transferring shares below FMV (Section 50CA)
ESOPs & Sweat Equity valuations
Foreign investments in Indian companies
The Income Tax Department mandates strict compliance with Rule 11UA to prevent tax evasion through undervaluation or overvaluation of shares.
Why is Rule 11UA Valuation Important?
✅ Avoids tax penalties and disputes with the IT Department ✅ Ensures transparency in share pricing ✅ Helps startups claim Angel Tax exemptions ✅ Complies with FEMA regulations for foreign investments
2. What is 11UA Valuation?
11UA Valuation refers to the process of calculating the Fair Market Value (FMV) of unquoted shares using the methods prescribed under Rule 11UA of Income Tax Rules, 1962.
When is 11UA Valuation Required?
Scenario
Relevant Section
Issue of shares above FMV
Section 56(2)(viib)
Transfer of shares below FMV
Section 50CA
Sweat equity shares & ESOPs
Section 17(2)(vi)
Startups raising angel funding
Section 56(2)(viib)
3. Who is Authorized to Conduct Valuation Under Rule 11UA?
The Income Tax Department recognizes only specific professionals for Rule 11UA valuation:
A. Registered Valuers (IBBI Approved)
Regulator: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)
Qualifications:
Must hold a Certificate of Registration (CoR)
Should have 5+ years of experience in valuation
Scope: Can perform NAV & DCF-based valuations
B. SEBI-Registered Merchant Bankers (Category-I)
Eligibility: Must be registered with SEBI as an Investment Banker
Preferred for: DCF valuations of high-growth companies
C. Chartered Accountants (CAs) & Cost Accountants (CMAs)
Conditions: Must have additional certification in business valuation (e.g., ICAI’s Registered Valuer course)
Limitations: Some valuations may require IBBI/SEBI approval
D. Independent Valuation Experts (CFA, ASA, etc.)
Must demonstrate recognized valuation credentials
Often used for complex valuations (brands, intangibles)
Key Point: The valuer must issue a detailed valuation report with methodology, assumptions, and supporting financials.
4. Valuation Methods Under Rule 11UA
Rule 11UA prescribes two primary valuation methods:
A. Net Asset Value (NAV) Method
Best for: Asset-heavy companies (real estate, manufacturing)
Formula:
FMV=(TotalAssets−TotalLiabilities)NumberofShares
FMV=
NumberofShares
(TotalAssets−TotalLiabilities)
Pros: Simple, based on audited financials
Cons: Ignores future earnings potential
B. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
Best for: High-growth startups, tech companies
Key Components:
Projected cash flows (5–10 years)
Discount rate (WACC)
Terminal value
Pros: Reflects future growth
Cons: Subjective assumptions

5. Rule 11UA Calculation in Excel (With Example)
Example 1: NAV Method
Particulars
Amount (₹)
Total Assets
50,00,000
Total Liabilities
20,00,000
Net Worth
30,00,000
Number of Shares
1,00,000
FMV per Share
₹30
Example 2: DCF Method (Simplified)
Year
Cash Flow (₹)
Discount Factor
Present Value (₹)
2024
10,00,000
0.909
9,09,000
2025
12,00,000
0.826
9,91,200
Terminal Value
1,50,00,000
0.683
1,02,45,000
Total Enterprise Value
₹1,21,45,200
(Download our free Rule 11UA Excel template [insert link])
6. Compliance Requirements & Documentation
To avoid tax disputes, maintain: ✔ Valuation Report (signed by authorized valuer) ✔ Audited Financial Statements (for NAV method) ✔ Projections & Assumptions (for DCF method) ✔ SEBI/IBBI Registration Certificate of valuer
7. Common Mistakes in 11UA Valuation
❌ Using unregistered valuers ❌ Ignoring latest IT Department guidelines ❌ Overlooking discounts for lack of marketability (DLOM) ❌ Inconsistent valuation dates & financial data
8. FAQs on Rule 11UA Valuation
Q1. Can a startup use Rule 11UA for angel tax exemption?
Yes, startups must comply with Rule 11UA for Section 56(2)(viib) exemptions.
Q2. Is DCF mandatory for all companies?
No, companies can choose NAV or DCF based on their business model.
Q3. How often should valuation be updated?
Only when issuing/transferring shares, unless specified otherwise.
Q4. What if valuation is not done as per Rule 11UA?
Risk of tax notices, penalties, or FMV adjustments by the IT Department.
9. Conclusion: Best Practices for Rule 11UA Compliance
Engage only IBBI/SEBI-registered valuers
Choose the right valuation method (NAV/DCF)
Maintain proper documentation
Stay updated with latest IT Department circulars
For Brand Valuation, Valuation Advisory, or complex assessments, consult a SEBI-registered merchant banker or IBBI-approved valuer.
#11ua valuation#11 ua valuation#what is 11ua valuation#rule 11ua valuation#rule 11ua of income tax rules 1962#rule 11ua calculation in excel#rule 11ua of income tax act#section 11ua valuation#who can do valuation under rule 11ua#brand valuation#Valuation Advisory
0 notes
Text
Mutual Fund vs ETF: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better for You?

If you’re planning to grow your wealth smartly, you've likely come across the terms mutual fund and ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund). While both are popular choices for retail and institutional investors alike, the mutual fund vs etf debate is crucial for making informed investment decisions especially in 2025 when financial markets are more dynamic than ever. Partnering with a trusted SIP distributor in Gurgaon can also help you navigate these options with greater clarity and confidence.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down the mutual fund vs ETF puzzle with real-world context, easy comparisons, and actionable tips to help you decide what works best for your goals.
What Are Mutual Funds and ETFs?
Both mutual funds and ETFs are types of pooled investment vehicles. This means your money is combined with that of other investors and managed by professionals who buy and sell assets like stocks, bonds, or other securities.
But here’s where the differences begin:
Mutual Funds are priced once daily after market close. You purchase or redeem units at the Net Asset Value (NAV).
ETFs, on the other hand, trade like stocks on the exchange and can be bought or sold throughout the trading day.
ETF vs Mutual Fund Comparison: Key Differences at a Glance
Still wondering how to differentiate between mutual funds and ETFs? Here’s a quick breakdown:
Trading Flexibility
Mutual Funds: Bought or sold only once a day after market close, at the day’s NAV (Net Asset Value).
ETFs: Can be traded anytime during market hours like regular stocks, offering more flexibility.
Expense Ratio
Mutual Funds: Typically have higher expense ratios due to active fund management.
ETFs: Generally lower cost, especially in passively managed ETFs.
Minimum Investment
Mutual Funds: You can start with as little as ₹500–₹1000 through SIPs.
ETFs: You need to buy at least one unit, and the price depends on the ETF's market value.
Tax Efficiency
Mutual Funds: Can trigger capital gains taxes due to frequent internal trading by the fund manager.
ETFs: Usually more tax-efficient because of the “in-kind” redemption mechanism.
Liquidity
Mutual Funds: Less liquid; transactions settle after NAV is calculated.
ETFs: Highly liquid; you can enter or exit your position anytime during market hours.
These key points offer a solid etf vs mutual fund comparison that can guide your next investment move.
Which One Should You Choose?
The answer depends on your investing style and financial goals:
Choose Mutual Funds if:
You prefer automated SIPs and long-term wealth building
You value professional fund management
You want exposure to tax-saving schemes like ELSS
Choose ETFs if:
You are a cost-conscious investor
You prefer real-time control over trades
You want diversification with flexibility
As a leading SIP distributor in Gurgaon, we’ve seen that hybrid investors—those who allocate funds to both options—often enjoy a more balanced, resilient portfolio.
What’s the difference between mutual funds and ETFs? Mutual funds are bought at day-end NAV and are ideal for SIP-based investing, while ETFs trade like stocks and offer real-time flexibility with lower fees.
Real-Life Use Case
Take Ritika, a 30-year-old marketing manager from Gurugram. She uses a mutual fund for her tax-saving ELSS and long-term SIP, while investing in ETFs for short-term market exposure. Her approach balances automation with control—exactly what most modern investors aim for.
2025 Market Trends to Note
India’s ETF market is growing at 35% YoY, led by investor demand for low-cost options.
AMFI data shows that SIP inflows hit a record ₹19,000 crore/month as of March 2025.
SEBI’s push for investor awareness is increasing accessibility to both options.
So, it’s not just about mutual fund vs etf, but about aligning the product with your life stage, risk tolerance, and tax considerations.
Final Thoughts
The mutual fund vs ETF decision shouldn’t stress you out. Instead, think of it as selecting the best tools for different financial goals. Diversification doesn't mean choosing one over the other—it means using both wisely.
Ready to Make Smarter Investment Decisions
Still unsure about the right investment route for your goals? At BellWether, we don't just sell financial products—we help you build wealth strategies that work in real life. Whether you're keen on SIPs or intrigued by ETFs, our experts will help you create a custom plan suited to your needs.
5 Unique FAQs
1. Can I invest in both mutual funds and ETFs at the same time? Absolutely. Many investors use a blended approach—mutual funds for long-term SIPs and ETFs for tactical plays. This helps diversify risk and improve liquidity access.
2. Are ETFs suitable for beginners? Yes, especially passive ETFs that track indices like Nifty 50 or Sensex. Just ensure you have a Demat account, as ETFs trade like stocks.
3. Do mutual funds have lock-in periods? Some do. For example, ELSS mutual funds have a 3-year lock-in. But many open-ended funds are flexible and can be redeemed anytime post minimum holding.
4. Which is better during market volatility: ETF or mutual fund? Mutual funds with professional fund managers might perform better in volatile markets due to active decision-making. ETFs, however, offer real-time exit opportunities.
5. Do SIPs work with ETFs? Not directly. Most platforms don’t allow SIPs into ETFs yet. But you can manually invest a fixed amount monthly in ETFs to mimic SIP-style discipline.
#mutual fund vs etf#etf vs mutual fund comparison#SIP distributor in Gurgaon#invest smartly#passive investing India#financial planning India
0 notes
Text
How to Check Mutual Fund Performance: A Beginner’s Guide
How to Check Mutual Fund Performance
Introduction to Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are one of the simplest and most popular ways to grow wealth. They pool money from investors and invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, or other securities. But just like you check your phone’s battery or car’s mileage, you need to regularly track how your mutual fund is doing.

Why Checking Fund Performance is Important
Would you drive a car without a fuel gauge? Probably not. The same logic applies to your investments. Regularly checking a fund’s performance ensures your money is growing in the right direction and helps you decide whether to hold, switch, or exit.
Key Metrics to Track Mutual Fund Performance
Net Asset Value (NAV)
The NAV represents the per-unit price of a mutual fund. It changes daily based on market movements and reflects the fund’s current market value. But NAV alone doesn’t indicate performance — it should be compared with past NAVs or benchmarks.
Historical Returns (1-Year, 3-Year, 5-Year)
Look at how the fund performed over different time frames:
1-year return shows short-term trends.
3-year and 5-year returns reflect long-term consistency.
Expense Ratio
This is the fee charged by fund managers, expressed as a percentage. Lower expense ratios mean you keep more of your returns.
Risk Ratios
Sharpe Ratio: Higher is better, showing better risk-adjusted returns.
Standard Deviation: Indicates volatility. Lower is more stable.
Beta: Measures fund movement compared to the market. A beta of 1 means it moves in line with the market.
Alpha and Benchmark Comparison
Alpha shows a fund’s performance compared to its benchmark. A positive alpha means the fund outperformed its benchmark.
Tools and Platforms to Check Mutual Fund Performance
AMFI (Association of Mutual Funds in India)
Visit amfiindia.com for official mutual fund data, NAV updates, and performance charts.
Fund House Websites
Every mutual fund company publishes detailed performance reports and factsheets on their official sites.
Mobile Apps
Apps like Groww, Kuvera, and Paytm Money provide instant fund performance tracking, SIP returns, and portfolio analysis.
Financial News Websites
Sites like Moneycontrol, Value Research, and ET Money offer fund ratings, comparison tools, and insights.
How to Analyze SIP Performance
Tracking SIP returns is slightly different:
Check CAGR (Compounded Annual Growth Rate) for overall performance.
Use SIP calculators available on most apps and websites.
Compare SIP returns with lump sum returns for better insights.
Understand Portfolio Holdings and Sector Allocation
See where your money is invested — sectors, stocks, or bonds. Funds heavily concentrated in one sector can be riskier.
Interpreting Risk-Return Trade-Off
High returns often come with high risk. A balanced risk-return ratio is ideal for steady wealth creation.
How to Compare Similar Category Funds
Never compare a small-cap fund with a large-cap fund. Always compare funds within the same category (e.g., large-cap funds) using:
Returns over the same period
Risk ratios
Expense ratios
Red Flags to Watch in a Mutual Fund’s Performance
Consistent underperformance against benchmarks and category peers
High expense ratio
Sudden changes in fund management
Low asset size (AUM) for equity funds
Should You Exit if a Fund is Underperforming?
Not always. Analyze if it’s a short-term market phase or a genuine fund issue. Stay invested if the fundamentals are strong.
Common Mistakes in Tracking Fund Performance
Looking only at recent returns
Ignoring expense ratio
Not comparing against the right benchmark
Panic selling during market corrections
Tips for Long-Term Mutual Fund Tracking
Check performance quarterly or bi-annually
Focus on consistency, not just returns
Review SIPs annually
Monitor changes in fund objectives or management
Real-Life Example: How Tracking Saved an Investor from Losses
Amit invested ₹2 lakhs in an equity fund that performed well initially but started lagging behind its category and benchmark for 18 months. Regularly tracking his fund’s return and risk metrics, he switched to a better-performing fund, saving himself from an eventual 15% dip.
Final Thoughts
Regularly tracking your mutual fund performance ensures your financial goals stay on course. Use a mix of official sites, apps, and financial news platforms to stay updated. Always remember — patience is key, but blind patience can be costly. Stay informed, stay invested.
FAQs
Q1: How often should I check my mutual fund performance? Once every 3-6 months is ideal, unless market conditions or personal financial goals demand sooner.
Q2: Is NAV enough to judge a mutual fund? No, NAV alone isn’t enough. Compare historical returns, risk ratios, and benchmarks.
Q3: Which tools are best for tracking mutual fund performance? AMFI, Moneycontrol, Groww, and Value Research are among the best.
Q4: What does a high Sharpe Ratio mean? It means better risk-adjusted returns — a good sign for a mutual fund.
Q5: Can I switch mutual funds if it underperforms? Yes, but only after reviewing the reasons for underperformance and assessing alternative options.
0 notes
Text
How Businesses Should Handle Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Proper Valuation Under the Income Tax Act is not just a legal requirement—it's a strategic tool for businesses to ensure compliance, avoid litigation, and drive accurate financial planning. Whether you’re a startup raising funds, a company undergoing restructuring, or a business facing scrutiny from tax authorities, getting your valuation right is essential.
In this article, we’ll explore how businesses should approach valuation in the context of the Income Tax Act, the key methodologies involved, and common challenges to avoid.
Understanding the Need for Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Valuation under the Income Tax Act becomes relevant during several key business transactions, such as:
Issue of shares (Section 56(2)(viib)): Especially in startups and private companies issuing shares at a premium.
Transfer of assets or shares: Involving capital gains (Section 50CA and 50D).
Mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring: To determine fair market value (FMV) for taxation purposes.
Wealth declaration and scrutiny assessments: Where the assessing officer may question the declared value.
The objective of these valuations is to determine a fair and accurate representation of an entity's worth, ensuring that income, gains, or losses are taxed appropriately.
Key Provisions Governing Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Valuation Under the Income Tax Act for Share Issuance – Section 56(2)(viib)
When a closely held company issues shares to a resident at a price exceeding the fair market value, the excess may be treated as income from other sources and taxed accordingly. This anti-abuse provision aims to curb the practice of laundering black money through inflated valuations.
To determine FMV, businesses can choose either:
Net Asset Value (NAV) Method
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
The choice of method must be justified with proper documentation and ideally backed by a Category I Merchant Banker valuation report.
Transfer of Shares – Section 50CA
When shares of an unlisted company are transferred for consideration lower than the FMV, the FMV is deemed to be the sale consideration for capital gains computation. This clause ensures capital gains aren’t avoided by under-reporting sale value.
The Valuation Under the Income Tax Act here must be based on recognized methods—typically involving a certified merchant banker or a chartered accountant following prescribed guidelines.
Valuation for Capital Gains – Section 50D
In scenarios where consideration is not determinable, like in barter transactions or asset exchanges, Section 50D applies. It mandates that the FMV of the asset transferred will be considered the sale value.
Acceptable Valuation Methods Under the Income Tax Act
Understanding acceptable valuation methodologies is crucial for businesses to comply with tax norms and avoid disputes. These include:
1. Net Asset Value (NAV) Method
This method calculates the value of a business based on the net assets recorded in its books. While straightforward, NAV is more suited for asset-heavy companies and may not reflect true value for tech or service-based firms.
2. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
DCF is a forward-looking method that estimates value based on projected future cash flows discounted to present value. It’s widely used in startup valuations and is accepted by tax authorities if backed by reasoned assumptions and certified reports.
3. Comparable Company Multiple (CCM) Method
Although not specifically mentioned under the Act, this method is useful during litigation or in determining arm’s length pricing for transfer pricing cases.
Compliance Tips for Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Preparing Documentation
Ensure that all assumptions, methodologies, and calculations used in the valuation are documented thoroughly. A proper valuation report from a Category I Merchant Banker or qualified CA can be vital.
Consistency Across Reporting
The valuation used for tax purposes should align with that used for other statutory or financial reporting, like under Companies Act or FEMA, unless justifiable differences exist.
Maintain Forecast Integrity
Especially when using the DCF method, ensure your cash flow projections are realistic and based on verifiable data. Overly aggressive forecasts can lead to tax disputes and potential penalties.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make in Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
1. Ignoring Regulatory Changes
Tax provisions related to valuation are dynamic. Failing to stay updated on the latest notifications and CBDT circulars can result in non-compliance.
2. Overstating or Understating Valuation
Artificial inflation or deflation of valuation—either to attract investors or reduce tax liability—can attract heavy scrutiny under Sections 56, 50CA, and 50D.
3. Inadequate Professional Advice
Valuation is not just a number; it’s a strategic and legal exercise. Engaging qualified valuation professionals ensures accuracy and defensibility.
Consequences of Incorrect Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Failing to adhere to proper valuation protocols can lead to:
Tax demand notices and penalties
Disallowance of share premium as income
Litigation with income tax authorities
Loss of investor confidence
In severe cases, incorrect valuation may be interpreted as a willful attempt to evade tax, inviting prosecution under relevant sections.
Best Practices for Handling Valuation Under the Income Tax Act
Engage a Registered Valuer or Category I Merchant Banker
Particularly when mandated under Section 56(2)(viib).
Conduct Periodic Valuations
Especially useful for fast-growing startups where FMV can change rapidly.
Keep Stakeholders Informed
Ensure that internal finance teams, auditors, and legal advisors are aligned.
Reconcile Valuation for Multiple Authorities
Valuation under FEMA, Companies Act, and Income Tax Act can differ; proper reconciliations should be maintained.
Conclusion
Handling Valuation Under the Income Tax Act is not merely a compliance checkbox—it’s a vital component of responsible business management. Accurate valuations protect businesses from tax pitfalls, ensure smooth investor relations, and uphold corporate credibility.
By staying updated on regulatory expectations, adopting best practices, and consulting qualified professionals, businesses can navigate the valuation landscape with confidence and clarity.
0 notes
Text
In the age of digital transformation, the role of a Real Estate Fund Administrator has become indispensable for ensuring the smooth operation and growth of real estate funds. Fundtec’s commitment to innovation, industry expertise, and client-centric approach positions it as a key partner in navigating the complexities of fund administration. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, Fundtec remains dedicated to delivering cutting-edge solutions that drive the success of real estate funds and other investment vehicles.
#Real Estate Fund Administration#Property Accounting#Investor Services#Net Asset Value (NAV) Calculation#Property Valuation#Lease Management#Compliance Management#Regulatory Reporting#Asset Appraisal#Portfolio Analysis#Investor Relations#Reconciliation#Property Acquisition#Asset Disposition#Fund Performance Reporting#Property Due Diligence#Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) Administration#Asset Management#Financial Reporting#Real Estate Fund Technology
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Mutual Fund NAV and Returns
Introduction If you're stepping into the world of mutual fund investing, one term you'll come across frequently is Net Asset Value (NAV). For many investors, especially beginners, NAV can seem like a confusing number—some even believe that a low NAV means a fund is cheaper or better. This is a common myth.
In reality, NAV is simply the per-unit value of a mutual fund and has little to do with the fund's performance or quality. Understanding how NAV works is key to making smarter, well-informed investment decisions.
In this guide from Zebu, we’ll break down everything you need to know about NAV, how it’s calculated, what affects it, and how it relates to your investment returns.
1. What is NAV (Net Asset Value)? Definition of NAV NAV is the per-unit price of a mutual fund, calculated as:
NAV=Total Assets – Total Liabilities Total Outstanding Units NAV= Total Outstanding Units Total Assets – Total Liabilities It reflects the current market value of each unit of the mutual fund.
How NAV Works in Mutual Funds When you invest in a mutual fund, you buy units at the current NAV.
Example: If NAV is ₹10 and you invest ₹10,000, you receive 1,000 units.
If the NAV rises to ₹15 in a year, your investment becomes ₹15,000.
Important: NAV is just the entry or exit price. It does not determine how much the fund will grow.
2. How is NAV Calculated? NAV is calculated at the end of each trading day based on the value of the underlying assets.
NAV=Market Value of All Securities + Cash Holdings – Liabilities Total Outstanding Units NAV= Total Outstanding Units Market Value of All Securities + Cash Holdings – Liabilities Example: Market value of holdings: ₹500 crore
Cash: ₹10 crore
Liabilities: ₹5 crore
Units: 50 crore
NAV=(500+10–5)50 =₹10.10 NAV= 50(500+10–5) =₹10.10 With Zebu’s real-time tracking tools, you can monitor NAV updates with precision.
3. The Relationship Between NAV and Mutual Fund Performance Myth: Lower NAV = Cheaper Fund This is incorrect. NAV only tells you the per-unit price, not whether a fund is a good investment.
Example:
Fund A (NAV ₹10) grows 20% → NAV becomes ₹12
Fund B (NAV ₹100) grows 20% → NAV becomes ₹120
Both deliver the same 20% return.
Zebu’s fund comparison features help debunk such myths and guide you towards better decisions.
4. What Factors Affect Mutual Fund NAV? a) Market Performance of Assets Equity Funds: Move with stock prices.
Debt Funds: Impacted by interest rates and bond yields.
b) Expense Ratio Higher expenses reduce NAV over time.
Zebu displays the Expense Ratio of all funds clearly, so you know your costs upfront.
c) Dividend Payouts NAV drops when dividends are paid.
Growth funds reinvest profits, leading to higher NAV over time.
d) Investor Activity Heavy buying increases cash inflow.
Large redemptions during market dips may reduce NAV temporarily.
5. NAV and Returns: How to Measure Performance a) Absolute Returns Simple difference between buying and current NAV.
Absolute Return =(Ending NAV – Starting NAV) Starting NAV×100 Absolute Return= Starting NAV(Ending NAV – Starting NAV) ×100 b) CAGR (Compounded Annual Growth Rate) CAGR=(Ending NAV Starting NAV)1𝑛–1 CAGR=( Starting NAV Ending NAV ) n1 –1 c) Rolling Returns Shows consistency over different periods. Zebu's tools allow you to track rolling returns with ease.
d) XIRR (for SIP Investors) Crucial for calculating returns from monthly investments.
Zebu’s SIP calculator with XIRR support is a powerful ally for long-term investors.
6. How to Use NAV When Selecting a Mutual Fund ✅ Don’t Judge by NAV Alone A higher or lower NAV does not reflect performance quality.
✅ Evaluate Fund Performance Over Time Use 3, 5, and 10-year CAGR for better insights.
✅ Assess the Fund Manager's Track Record Strong leadership = better decisions = consistent returns.
✅ Mind the Expense Ratio Lower cost = better long-term NAV growth. Zebu highlights this in every fund listing.
✅ Compare with Benchmarks A good fund consistently beats its benchmark index.
7. Common Misconceptions About NAV ❌ NAV is not the same as a stock price.
❌ A lower NAV does not make a fund “cheaper.”
❌ NAV is not a performance metric.
❌ Dividend payouts reduce NAV—they are not “extra” returns.
Zebu helps clarify these misconceptions through curated investor education content.
8. Why Understanding NAV Matters for Investors Empowers informed decision-making.
Helps compare mutual funds more effectively.
Prevents reliance on misleading assumptions.
With Zebu’s expert insights, smart analytics, and investor-first platform, understanding and tracking NAV is easier than ever especially in 2025’s fast-moving markets.
Conclusion NAV is an important number, but it’s just one part of the bigger picture. Investors should focus on performance trends, expense ratios, consistency, and portfolio quality—not just the NAV.
Zebu empowers investors to go beyond the surface by offering smart comparison tools, expert-backed research, and transparent data to guide every investment decision.
Disclaimer This blog is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Please consult a SEBI-registered advisor before investing. For accurate, official data, refer to sources like SEBI, NSE, BSE, RBI, AMFI, or respective AMC websites.
#zebu#finance#investment#financialfreedom#investwisely#investors#investing#makemoney#investmentgoals#mutual funds
0 notes
Text
How are mutual funds versus ETFs traded?
Mutual Funds:
Mutual funds cannot be traded throughout the day. Instead, they are bought and sold at the end of the trading day based on their Net Asset Value (NAV), which is calculated after the market closes. This means that if you place an order to buy or sell shares of a mutual fund during the day, your transaction will be executed at the NAV price, which is determined after the market has closed. As a result, mutual fund investors do not have the flexibility to react to intraday market movements.
Mutual Funds: Mutual funds are typically actively managed by portfolio managers who make decisions on behalf of the fund’s investors. These managers research, select, and monitor securities (stocks, bonds, or other assets) within the fund to meet specific investment goals. In actively managed funds, the goal is often to outperform a particular market index or sector. The managers use their expertise to decide which securities to buy or sell, and they adjust the fund’s portfolio based on market conditions and economic forecasts.
Some mutual funds, however, are passively managed, meaning they aim to replicate the performance of a particular index (like the S&P 500). These funds still have managers, but their role is limited to maintaining the fund’s portfolio in line with the index’s performance.
ETFs:
ETFs trade like individual stocks on the stock exchange and can be bought or sold anytime during market hours. The price of an ETF fluctuates throughout the day based on supply and demand, and investors can buy or sell shares at the market price at any given moment, just as they would with a stock. This flexibility allows ETF investors to react to market movements in real-time, which is a key difference between mutual fund versus ETF.
ETFs: Most ETFs are passively managed, meaning they track a specific market index (e.g., S&P 500, NASDAQ-100, etc.). The fund’s portfolio is designed to mirror the index it tracks by purchasing the same securities in the same proportions as the index. This approach generally aims to match the performance of the index, rather than outperform it. However, there are also actively managed ETFs, where fund managers make decisions about the securities in the ETF’s portfolio based on research, market trends, and strategies.
The management of ETFs tends to be more hands-off compared to mutual funds, particularly with passive ETFs, as the goal is simply to track the performance of an underlying index rather than exceed it.
For more check our website: Best Stock Market Course In India
#ISMT#MutualFunds#ETFs#Investing101#ETFvsMutualFund#StockMarketBasics#FinanceTips#TradingETFs#MutualFundTrading#InvestmentStrategies#FinancialEducation#PersonalFinance#MoneyMatters#SmartInvesting#InvestorTips#MarketInsights#LearnFromISMT#ISMTInstitute
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is XIRR? The Right Way to Track Your SIP Returns

When you invest in mutual funds through SIP (Systematic Investment Plan), you're investing a fixed amount regularly—usually monthly. Over time, as market values fluctuate, your investments grow. But how do you measure the true return from this scattered and systematic investment? The answer lies in XIRR.
Let’s understand what XIRR is, and why it is the most accurate way to track your mutual fund SIP returns.
What is XIRR?
XIRR (Extended Internal Rate of Return) is a financial metric used to calculate the annualized return on investments where there are multiple cash flows at different intervals. It takes into account each investment date, amount, and the final redemption amount to give you a true picture of your investment performance.
In simple terms: XIRR shows the average yearly return you earned across all your SIPs—even if they were made on different dates and amounts.
Why XIRR is Ideal for SIPs?
In SIPs, you're investing the same amount every month, but at different NAVs (Net Asset Values). This means:
Each investment is made on a different date
Each amount is compounded differently
Market fluctuations affect every SIP installment uniquely
Using a simple average return won’t capture this complexity. That’s where XIRR shines.
How Does XIRR Work?
XIRR calculates the return based on:
Each investment amount and date
The final redemption amount and date
The time period each investment was held
It uses a formula that estimates the rate at which your total inflows and outflows break even over time.
Example:
Let’s say you invested ₹5,000 monthly from Jan 2022 to Dec 2024 (total ₹1.8 lakh). On 1st Jan 2025, the value of your mutual fund is ₹2.1 lakh.
The XIRR formula will calculate how much return (in %) per year you earned on your SIPs from start to end.
Benefits of Using XIRR
Gives accurate annualized return on irregular cash flows
Helps compare different investment options
Reflects actual performance of SIP-based investments
Can be used to track partial withdrawals or top-ups
How to Calculate XIRR?
You don’t need to do complex math. Just use:
In Excel or Google Sheets:
List all SIP amounts as negative values (outflows)
Add the current value or redemption as positive value (inflow)
Add corresponding dates
Use the formula: =XIRR(values, dates)
It will instantly show the annualized return percentage.
Tools That Automatically Show XIRR:
Most mutual fund platforms (NJ Wealth, CAMS, Zerodha Coin, Groww, etc.)
Mutual fund account statements
Portfolio tracking apps like Kuvera, Paytm Money, and ET Money
Final Thoughts
XIRR is the most reliable way to track your SIP returns. Unlike simple returns or CAGR, XIRR adjusts for the timing and flow of your investments—giving you a real-world view of how your mutual fund is performing.
So, next time you check your portfolio, don’t just look at the current value—check the XIRR to know how well your money is truly working for you.
0 notes
Text
What is NAV in mutual funds?
NAV, or Net Asset Value, is the price per share or unit of a mutual fund. It represents the total value of the fund's assets minus its liabilities, divided by the number of outstanding shares. NAV is calculated at the end of each trading day and is a crucial metric for investors, as it determines the price at which they can buy or sell shares of the fund. it is calculated as:
NAV= Total Assets - Total Liabilities / Total Unit Outstanding
Key Points about Net Asset Value (NAV):
Represents Per-Unit Price – NAV determines the price at which investors buy (purchase price) and sell (redemption price) mutual fund units.
Calculated Daily – NAV changes daily based on the market value of the underlying assets (stocks, bonds, etc.).
Not an Indicator of Performance – A higher or lower NAV does not mean a better or worse fund; returns depend on percentage growth.
Impacts SIP and Lump Sum Investments – Investors get units based on NAV at the time of purchase.
Excludes Market Trading Impact – Unlike stocks, mutual funds are traded at NAV, not market fluctuations during the day.
0 notes