#Net Asset Value (NAV) Calculation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Marketing 101 | For Emerging Managers
Inviting all emerging managers to join this amazing webinar. Secure your spot now: https:https:https://webinar.fundtec.in/meeting/register?sessionId=1336937368

#accounting#financial reporting#finance#investor services#fund administration#crypto business#net asset value (nav) calculation
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Is The Meaning Of NAV In Mutual Funds?
Navigating the world of mutual funds can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. Among the many terms and acronyms, "NAV" stands out as one of the most commonly used yet misunderstood terms. In this blog post, we'll demystify NAV in mutual funds and explain its significance in your investment journey.

Understanding NAV:
NAV, or Net Asset Value, is a fundamental concept in the world of mutual funds. It represents the per-unit market value of a mutual fund scheme's assets on a specific date. Essentially, it tells you what one unit of the fund is worth at a particular moment. But what does that really mean?
Calculation of NAV:
The calculation of NAV is straightforward. It involves two primary components: assets and liabilities.
Assets: These are the investments held by the mutual fund. This can include stocks, bonds, cash, and other securities. The total value of these assets is calculated daily.
Liabilities: These are the expenses and debts associated with managing the mutual fund. This can include management fees, administrative expenses, and other costs.
The formula for calculating NAV is as follows:
\[NAV = \frac{Total Value of Assets - Total Value of Liabilities}{Number of Outstanding Units}\]
Importance of NAV:
1. Price Determination: NAV is used to determine the price at which investors can buy or sell units of a mutual fund. When you invest in a mutual fund, you are essentially buying units at the current NAV.
2. Performance Evaluation: NAV also serves as a measure of a mutual fund's performance. Investors can track the changes in NAV over time to assess how well the fund is doing.
3. Comparing Funds: NAV allows investors to compare the prices of different mutual funds. However, it's essential to note that a higher NAV does not necessarily mean a better fund. What matters is the fund's performance relative to its NAV.
NAV and Mutual Fund Types:
It's important to understand that the significance of NAV can vary depending on the type of mutual fund:
1. Open-End Funds: These funds continuously issue and redeem units at their NAV. Investors buy and sell units at the NAV price, which is calculated at the end of each trading day.
2. Closed-End Funds: These funds have a fixed number of shares that are traded on stock exchanges. The market price of closed-end fund shares may be at a premium or discount to their NAV.
NAV and Market Fluctuations:
The NAV of a mutual fund can fluctuate daily due to changes in the value of its underlying investments. Factors such as market conditions, interest rates, and the performance of the fund's assets can impact NAV. During a market downturn, the NAV may decrease, and during a bull market, it may increase.
Conclusion:
In summary, NAV, or Net Asset Value, is a crucial concept in the world of mutual funds. It represents the per-unit market value of a mutual fund and is used for pricing and performance evaluation. Understanding NAV is essential for investors looking to make informed decisions about their mutual fund investments. It's a valuable tool that provides insight into the financial health and performance of a mutual fund, helping investors navigate the world of investing with confidence.
As you explore mutual fund investments, keep a close eye on the NAV, but remember that it's just one piece of the puzzle. A well-rounded investment strategy should consider factors like the fund's objectives, past performance, and fees in addition to the NAV. Happy investing!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Loan Against Mutual Funds Charges: Processing Fees, Interest & More Explained

Have you ever needed urgent funds but didn’t want to break your mutual fund investments?
You’re not alone. In 2025, with inflation, unexpected medical emergencies, education costs, and business needs rising, many investors are turning towards Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF) — a smart way to unlock liquidity without redeeming your assets.
If you’ve ever searched “what is LAS or LAMF,” or wondered about “loan against mutual funds interest rate,” or “who can apply for loan against mutual funds” — then this article is your one-stop guide.
What Is Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF)?
A Loan Against Mutual Funds is a type of Loan Against Securities (LAS) where you pledge your mutual fund units to a bank or NBFC in exchange for a loan. You don’t sell your investment—you simply borrow against it.
This helps retain your long-term financial goals while giving you immediate liquidity.
Why Consider a Loan Against Mutual Funds?
Here’s what makes LAMF an attractive option:
No need to redeem mutual funds
Lower interest rate than personal loans or credit cards
Instant digital processing in many cases
Flexible repayment options
Continue earning capital gains/dividends on mutual funds
Loan Against Mutual Funds vs. Loan Against Shares: A Quick Comparison
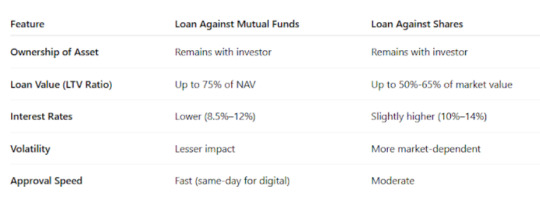
Minimum Balance Requirements – What You Should Know
Many banks have their own policies regarding minimum balance or value of mutual fund portfolio before approving the loan.
Here’s what you typically need:
A minimum of ₹25,000 to ₹50,000 in mutual funds (varies by lender)
Approved mutual fund types (Equity, Hybrid, or Debt)
Portfolio with consistent returns or stable value
For example:
HDFC Bank may require ₹50,000+ in approved mutual funds.
ICICI Bank offers loans starting from ₹10,000 if it’s processed digitally.
Tip: Always check with your bank or NBFC for the latest minimum NAV requirement.
Charges Involved in LAMF
Understanding the charges is crucial before you proceed:

Looking for the lowest interest rate of loan against mutual fund in India? Always compare loan against securities interest rates online before choosing.
Digital Loan Against Mutual Funds: Fast & Paperless
Gone are the days of branch visits and heavy paperwork. With digital loan against mutual fund services by ICICI, HDFC, Axis, and fintechs like Paytm and Groww:
Instant eligibility check via PAN + mobile
e-KYC + e-Sign
Loan disbursed in a few hours
Manage everything via app
Many even show you the digital loan against mutual funds interest rate transparently before applying.
Documents Needed
You usually don’t need many documents. If applying digitally:
PAN Card
Aadhaar (linked to mobile)
Mutual fund folio details
Bank account proof
If applying offline or for higher amounts, income proof and address proof may be needed.
Who Can Apply for Loan Against Mutual Funds?
If you've been wondering who can apply for loan against mutual funds, here's the answer:
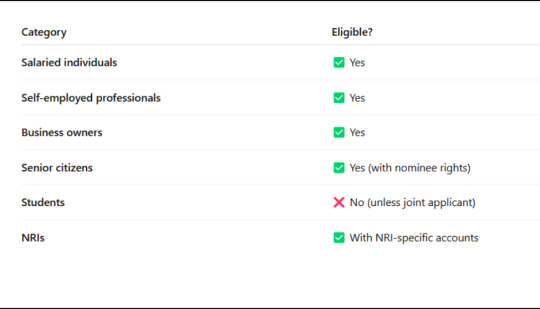
Things to Keep in Mind Before Applying
Loan tenure: Usually up to 36 months. Choose based on your repayment capacity.
Prepayment options: Check if there are charges.
Mutual Fund Type: Some lenders only accept debt or equity-oriented funds.
Ownership: Joint holding mutual funds may need consent of all holders.
Interest Calculation: It’s usually daily reducing balance.
5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I apply for a loan against SIP mutual funds?
Yes, if your SIP investments have accumulated to a minimum NAV (₹25K to ₹50K). The loan is based on NAV, not just SIP frequency.
2. How much loan can I get against my mutual fund?
Typically, up to 75% of your NAV (Net Asset Value). Some equity funds allow up to 50–60%.
3. Will my mutual funds get sold during the loan?
No. They are pledged, not sold. You still own them unless you default.
4. Is loan against mutual funds better than a personal loan?
Yes, it’s cheaper and quicker if you have an MF portfolio. You save on interest and still retain your investment benefits.
5. Are there any tax benefits on LAMF?
No direct tax benefits, but since it’s not an income, it doesn’t increase your taxable income like some withdrawals might.
Final Thoughts: Should You Go for LAMF?
If you’re looking for an instant loan with lower interest rates, don’t want to disturb your long-term financial goals, and want flexibility—Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF) is a smart choice.
Especially with digital loan against mutual fund options and competitive loan against mutual funds interest rates offered by top banks and NBFCs, it’s now easier than ever to get the funds you need without hassle.
Pro Tip: Always compare loan against shares interest rates, loan against securities interest rates, and LAMF offers to pick the one that suits you best.
#Loan Against Securities (LAS)#Loan Against Mutual Funds#Loan Against Mutual Funds Interest Rate#Loan Against Securities Interest Rates#Loan Against Shares#loan against shares interest rates#LAMF#digital loan against mutual funds interest rate#digital loan against mutual fund#who can apply for loan against mutual funds
0 notes
Text
What is XIRR? The Right Way to Track Your SIP Returns

When you invest in mutual funds through SIP (Systematic Investment Plan), you're investing a fixed amount regularly—usually monthly. Over time, as market values fluctuate, your investments grow. But how do you measure the true return from this scattered and systematic investment? The answer lies in XIRR.
Let’s understand what XIRR is, and why it is the most accurate way to track your mutual fund SIP returns.
What is XIRR?
XIRR (Extended Internal Rate of Return) is a financial metric used to calculate the annualized return on investments where there are multiple cash flows at different intervals. It takes into account each investment date, amount, and the final redemption amount to give you a true picture of your investment performance.
In simple terms: XIRR shows the average yearly return you earned across all your SIPs—even if they were made on different dates and amounts.
Why XIRR is Ideal for SIPs?
In SIPs, you're investing the same amount every month, but at different NAVs (Net Asset Values). This means:
Each investment is made on a different date
Each amount is compounded differently
Market fluctuations affect every SIP installment uniquely
Using a simple average return won’t capture this complexity. That’s where XIRR shines.
How Does XIRR Work?
XIRR calculates the return based on:
Each investment amount and date
The final redemption amount and date
The time period each investment was held
It uses a formula that estimates the rate at which your total inflows and outflows break even over time.
Example:
Let’s say you invested ₹5,000 monthly from Jan 2022 to Dec 2024 (total ₹1.8 lakh). On 1st Jan 2025, the value of your mutual fund is ₹2.1 lakh.
The XIRR formula will calculate how much return (in %) per year you earned on your SIPs from start to end.
Benefits of Using XIRR
Gives accurate annualized return on irregular cash flows
Helps compare different investment options
Reflects actual performance of SIP-based investments
Can be used to track partial withdrawals or top-ups
How to Calculate XIRR?
You don’t need to do complex math. Just use:
In Excel or Google Sheets:
List all SIP amounts as negative values (outflows)
Add the current value or redemption as positive value (inflow)
Add corresponding dates
Use the formula: =XIRR(values, dates)
It will instantly show the annualized return percentage.
Tools That Automatically Show XIRR:
Most mutual fund platforms (NJ Wealth, CAMS, Zerodha Coin, Groww, etc.)
Mutual fund account statements
Portfolio tracking apps like Kuvera, Paytm Money, and ET Money
Final Thoughts
XIRR is the most reliable way to track your SIP returns. Unlike simple returns or CAGR, XIRR adjusts for the timing and flow of your investments—giving you a real-world view of how your mutual fund is performing.
So, next time you check your portfolio, don’t just look at the current value—check the XIRR to know how well your money is truly working for you.
0 notes
Text
What is NAV in mutual funds?
NAV, or Net Asset Value, is the price per share or unit of a mutual fund. It represents the total value of the fund's assets minus its liabilities, divided by the number of outstanding shares. NAV is calculated at the end of each trading day and is a crucial metric for investors, as it determines the price at which they can buy or sell shares of the fund. it is calculated as:
NAV= Total Assets - Total Liabilities / Total Unit Outstanding
Key Points about Net Asset Value (NAV):
Represents Per-Unit Price – NAV determines the price at which investors buy (purchase price) and sell (redemption price) mutual fund units.
Calculated Daily – NAV changes daily based on the market value of the underlying assets (stocks, bonds, etc.).
Not an Indicator of Performance – A higher or lower NAV does not mean a better or worse fund; returns depend on percentage growth.
Impacts SIP and Lump Sum Investments – Investors get units based on NAV at the time of purchase.
Excludes Market Trading Impact – Unlike stocks, mutual funds are traded at NAV, not market fluctuations during the day.
0 notes
Text
Mutual Fund Investment Advisor in India: Grow Your Wealth with Battu Investments.

Mutual Fund Investment Advisor in India: Grow Your Wealth with Battu Investments.
Entrusting your financial journey to a knowledgeable mutual fund investment advisor might be the turning point. BATTU INVESTMENTS, we are proud to be your exclusive mutual fund advisor, providing unrivaled knowledge in navigating the complexities of the financial markets. Our experienced team of advisers recognizes that each investor is unique, so we personalize our strategies to your specific objectives and risk tolerance. With a dedication to in-depth market analysis, we assist you through the ever-changing universe of investment options, ensuring your portfolio is not just well-managed but also poised for development. Beyond the figures, our open communication and client-centric approach develop trust, allowing you to make educated decisions.
Why Choose Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds offer a range of benefits that make them an ideal choice for investors:
Diversification: Spread your investments across various assets to minimize risk.
Professional Management: Access to expert fund managers who optimize your investments.
Flexibility: Choose from a variety of fund types to suit your financial goals and risk appetite.
Affordability: Start investing with as little as ₵500 per month through SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans).
Liquidity: Easily redeem your investments when needed.
BENEFITS OF MUTUAL FUNDS INVESTMENT
Diversification
Mutual funds allow investors to diversify their portfolios across various securities, reducing the impact of individual asset performance on the overall investment. This diversification helps mitigate risk and increase the potential for consistent returns.
Professional Management
With mutual funds, investors benefit from the expertise of professional fund managers who conduct in-depth research and analysis to make investment decisions. These experienced professionals have the knowledge and resources to identify investment opportunities and manage risks effectively.
Accessibility and Affordability
Mutual funds provide access to a wide range of investment opportunities that may not be readily available to individual investors. Moreover, the minimum investment requirements for mutual funds are often relatively low, making them affordable and accessible to a broad investor base.
Liquidity
Investors can easily buy or sell mutual fund shares based on the fund's net asset value (NAV), which is calculated at the end of each trading day. This liquidity allows investors to convert their investments into cash quickly if needed.
Transparency
Mutual funds are required to provide regular updates and reports on their holdings, performance, and expenses. This transparency enables investors to stay informed about their investments and make well-informed decisions.
TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
Equity Funds
Equity funds invest primarily in stocks, aiming for long-term capital appreciation. They can focus on specific sectors, regions, or market capitalizations, offering investors the opportunity to participate in the potential growth of different segments of the stock market.
Bond Funds
Bond funds invest in fixed-income securities such as government bonds, corporate bonds, or municipal bonds. These funds provide regular income through interest payments and are generally considered less risky than equity funds.
Balanced Funds
Balanced funds, also known as hybrid funds, invest in a combination of stocks and bonds. They seek to balance the potential for capital appreciation with income generation, making them suitable for investors seeking a balanced approach to growth and income.
Index Funds
Index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These funds offer broad market exposure and generally have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds.
Money Market Funds
Money market funds invest in short-term, low-risk securities such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. They are characterized by high liquidity and stability, making them suitable for investors looking for capital preservation and easy access to cash.
How do I choose a Financial Advisor?
Determine your needs
Research Advisor Types
Check Qualifications and Credentials
Understand the Fee Structure
Availability and Convenience
SEBI Regulations for MF Financial Advisors
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates mutual funds in India. SEBI has introduced a variety of restrictions for mutual fund financial advisers (MFAs) to protect investors' interests.
The key Regulations For a mutual Fund Advisor Include
Registration
Suitability
Conflicts of Interest
Code of Conduct
Battu Investments: Your Trusted Mutual Fund Advisor
At Battu Investments, we simplify the mutual fund investment process and provide tailored advice to help you achieve your financial aspirations. Here’s how we make a difference:
1. Personalized Investment Strategies
We understand that every investor is unique. Our experts take the time to understand your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before recommending the most suitable mutual funds.
2. Comprehensive Fund Selection
With access to top-performing mutual funds in India, we help you build a diversified portfolio that aligns with your objectives. Whether you’re looking for equity, debt, or hybrid funds, we’ve got you covered.
3. Expert Guidance
Our experienced advisors stay updated on market trends and fund performance to provide you with informed recommendations. We’re here to guide you at every step, from fund selection to portfolio management.
4. Systematic Investment Planning
SIPs are a disciplined way to invest in mutual funds. Battu Investments helps you set up SIPs tailored to your budget and goals, ensuring consistent wealth creation over time.
5. Transparent Processes
We prioritize transparency in all our dealings. You can trust us to provide clear insights into fund performance, charges, and potential risks.
We Help To Mutual Fund Investment
Customized Investment Strategies
We understand that every investor has unique financial goals and risk tolerance. Our team of experienced professionals works closely with you to develop customized investment strategies that align with your specific needs and objectives.
Diversification and Risk Management
We help you build a well-diversified mutual fund portfolio by considering your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial goals. Our aim is to optimize your returns while managing risk effectively through diversification across different asset classes and investment styles
Professional Expertise
With our expertise in the financial industry, we stay updated with market trends and conduct thorough research to identify top-performing mutual funds. We carefully analyze fund performance, historical data, and fund manager track records to select funds that align with your investment objectives.
Continuous Monitoring and Performance Evaluation
We continuously monitor the performance of the mutual funds in your portfolio to ensure they remain in line with your expectations and goals. If necessary, we recommend adjustments or rebalancing to optimize your investment returns.
Secure Your Financial Future Today
Investing in mutual funds doesn’t have to be complicated. With Battu Investments, you get the expertise and tools you need to make informed decisions and achieve your financial dreams. Start your journey to financial freedom today.
Visit Battu Investments for expert mutual fund advice and solutions tailored to your needs!

Amit Ashok Battu, Certified Personal Financial Advisor (CPFA-1), MBA (Marketing) and B.E (Mech) is Mutual Fund Distributor and founder of BATTU Investments , a Mutual Fund, Life Insurance and FDs Distribution Firm. We do not take any fees from Clients.
Address:
303, shreenath enclave, near ketkar brothers, shreehari kute marg, nashik-422002
Phone: 9422758038 9422703746
Email: [email protected]
Productshttps://battuinvestments.in/best-mutual-funds-investment-service-india.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/sbi-life-insurance-co-ltd.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/lic-life-insurance-corporation-company-in-india.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/hdfc-deposits-secure-your-saving.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/shreeram-deposits-secure-and-rewarding-fixed-deposits.html
Our Serviceshttps://battuinvestments.in/financial-investment-planning-service-analysis.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/wealth-management-financial-services.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/insurance-planning-service-company.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/tax-planning-and-service-management.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/best-retirement-investment-services-planning-india.html
Goal Based Planninghttps://battuinvestments.in/best-child-education-planning.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/best-wedding-plan-for-child-marriage.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/dream-house-planner-with-battu-investments.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/your-dream-car-planning-financial-possibilities.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/dream-vacation-planning-investments-with-mutual-funds-sip.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/family-protection-life-insurance-plan.htmlhttps://battuinvestments.in/custom-goal-planning-financial-success.html
1 note
·
View note
Text
Caldwell Unifies Funds to Boost Dividend Investment Opportunities
Caldwell Investment Management Ltd. has successfully merged the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund with the Caldwell U.S. Dividend Advantage Fund, reinforcing its position in dividend-focused investing. This merger, effective October 30, 2019, consolidates the two portfolios into one unified entity, the Caldwell U.S. Fund.
This strategic move reflects Caldwell’s broader goal of streamlining its fund offerings and optimizing growth potential for investors. The merger was executed on a tax-deferred basis, ensuring no immediate tax implications for unitholders. Caldwell Investment Management also absorbed all associated costs and administrative expenses, safeguarding investor returns from any additional financial burdens.
Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund unitholders automatically transitioned into the Caldwell U.S. Fund under favorable exchange terms. For every unit held, Series A investors received 0.6527 units in the Caldwell U.S. Fund, while Series F unitholders gained 0.7781 units. These exchange ratios were determined by assessing the net asset values (NAV) of each fund as of October 29, 2019. The calculated ratios facilitated a fair and transparent process, ensuring investors were neither advantaged nor disadvantaged by the integration. Check here to learn more.
The merger represents more than just operational consolidation—it strengthens the Caldwell U.S. Fund by increasing its asset base, which can lead to enhanced diversification and greater economies of scale. Unitholders benefit from broader exposure to dividend-paying equities, a hallmark of Caldwell’s investment philosophy. The transition also positions the fund to pursue higher returns while mitigating risks through expanded market participation.
By streamlining its product lineup, Caldwell eliminates redundancy and sharpens its focus on high-performing funds. This decision aligns with an industry-wide trend of fund managers consolidating similar offerings to reduce overhead and enhance competitive edge. As Caldwell continues to adapt to changing market dynamics, the merger underscores its proactive approach to fund management and long-term value creation.
For investors, the merger unlocks opportunities by combining resources and expanding the pool of dividend-focused assets. A larger fund often translates into improved liquidity and cost efficiencies, which can enhance performance over time. Additionally, with Caldwell Investment Management covering all costs, investors reap the benefits without bearing the financial strain typically associated with such transactions.
Founded in 1990, Caldwell Investment Management has built a solid reputation for managing dividend-driven equity portfolios. The Toronto-based firm caters to both Canadian and U.S. markets, emphasizing consistent income generation and capital growth. Through disciplined investment strategies and a client-first approach, Caldwell has earned the trust of individual and institutional investors alike.
The merger reflects Caldwell’s ongoing mission to refine its fund offerings in response to market conditions. In an era of financial uncertainty, the strengthened Caldwell U.S. Fund offers a resilient investment vehicle focused on dividend yields and stability. As economic landscapes shift, Caldwell’s ability to adapt positions its investors for sustainable long-term success.
For those seeking reliable dividend income and growth, the newly enhanced Caldwell U.S. Fund represents a compelling investment opportunity. Caldwell’s unwavering dedication to operational excellence ensures that investors remain well-positioned for future prosperity.
(Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not reflect the views of Caldwell Investment Management)
0 notes
Text
Indicative Net Asset Value (iNAV) in Mutual Funds
NAV is an intraday, real-time estimate of the Net Asset Value (NAV) of an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF). iNAV is calculated at the end of the day and is based on the assets and liabilities of the fund.
iNAV - What is it and why is it important?

0 notes
Text
In the age of digital transformation, the role of a Real Estate Fund Administrator has become indispensable for ensuring the smooth operation and growth of real estate funds. Fundtec’s commitment to innovation, industry expertise, and client-centric approach positions it as a key partner in navigating the complexities of fund administration. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, Fundtec remains dedicated to delivering cutting-edge solutions that drive the success of real estate funds and other investment vehicles.
#Real Estate Fund Administration#Property Accounting#Investor Services#Net Asset Value (NAV) Calculation#Property Valuation#Lease Management#Compliance Management#Regulatory Reporting#Asset Appraisal#Portfolio Analysis#Investor Relations#Reconciliation#Property Acquisition#Asset Disposition#Fund Performance Reporting#Property Due Diligence#Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) Administration#Asset Management#Financial Reporting#Real Estate Fund Technology
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive NAV and Portfolio Accounting Services.
The Ascent Group provides highly accurate Net Asset Value (NAV) calculations and detailed portfolio accounting services. These offerings ensure that clients have a clear, real-time view of their financial standing, helping them make informed, timely decisions based on precise and reliable data.
0 notes
Text
Benefits of SIP Investments: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) have become one of the most popular and reliable ways to invest in mutual funds. With their disciplined approach and flexibility, SIPs help investors build wealth over time without the stress of market timing. If you’re looking to start investing but aren’t sure why SIPs are a great option, this blog will guide you through the key benefits of SIP investments.

What is an SIP?
A Systematic Investment Plan, or SIP, is an investment method that allows you to invest a fixed amount regularly in mutual funds. SIPs help you develop a disciplined saving habit and make investing easier, especially for beginners.
Key Benefits of SIP Investments
1. Disciplined Savings
SIPs instill a habit of regular investing. By setting aside a fixed amount every month, you create a disciplined approach toward financial planning, ensuring that you stay on track with your goals.
2. Rupee Cost Averaging
SIP investments automatically take advantage of market volatility through rupee cost averaging. When markets are down, you buy more units; when markets are up, you buy fewer units. This approach helps lower the overall cost per unit over time, reducing the impact of market fluctuations.
Example: If you invest ₹5,000 monthly in an SIP, you buy more units when the NAV (Net Asset Value) is low and fewer units when the NAV is high. Over time, this averages out your investment cost.
3. Power of Compounding
One of the most powerful benefits of SIPs is the compounding effect. By reinvesting your returns, you can grow your wealth significantly over the long term. Starting early amplifies the effect of compounding, enabling you to achieve your financial goals faster.
4. Flexibility
SIPs are highly flexible, allowing you to:
Start with a small amount (as low as ₹500 per month).
Modify your investment amount.
Pause or stop your SIP without any penalty.This flexibility makes SIPs ideal for investors at all income levels.
5. Achieving Financial Goals
SIPs can be tailored to meet your specific financial goals, such as:
Short-term goals (vacations, gadgets, or weddings).
Medium-term goals (down payment for a home or car).
Long-term goals (retirement, child’s education, or wealth creation).
6. Low Entry Barrier
You don’t need a large sum to start investing with an SIP. This feature makes it easier for beginners and individuals with limited funds to begin their investment journey.
7. No Need to Time the Market
Timing the market can be stressful and unpredictable. SIPs eliminate this challenge by spreading your investments over time. With consistent contributions, you reduce the risk of investing a lump sum at the wrong time.
8. Diversification
By investing in SIPs, you gain access to a diversified portfolio of mutual funds, which reduces your investment risk. Depending on your risk appetite, you can choose equity, debt, or hybrid mutual funds through SIPs.
9. Emotional Control
SIPs help you stay disciplined, even during volatile markets. They remove the emotional aspect of investing by automating the process, ensuring that you don’t make impulsive decisions based on fear or greed.
10. Tax Efficiency
Although SIPs themselves don’t offer direct tax benefits, investing in tax-saving mutual funds (ELSS) through SIPs can provide tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, making them a tax-efficient investment option.
How to Start an SIP Investment
Set Your Financial Goals: Define your short-term and long-term goals.Choose the Right Mutual Fund: Select a mutual fund based on your goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon.Decide Your SIP Amount: Calculate how much you can afford to invest monthly.Start Early: The earlier you start, the better your returns due to compounding.Track Your Investments: Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure you’re on track to meet your goals.
Why Choose SIP Investments with AssetPlus?
At AssetPlus, we make SIP investments seamless and hassle-free. With our platform, you can:
Compare and choose from a variety of mutual funds.
Use tools like Best SIP Calculators to estimate your returns.
Get expert guidance to align your investments with your financial goals.
Conclusion
SIPs are an excellent way to build wealth over time, offering benefits such as rupee cost averaging, compounding, and disciplined savings. They are perfect for both beginners and experienced investors who want to achieve their financial goals without the stress of market timing.
Ready to start your SIP Journey? Explore SIP options with AssetPlus and take the first step toward financial freedom using Best Online SIP Calculators in India.
#sip calculator#sip calculator online#online sip calculator#sip return calculator#sip investment plan calculator
0 notes
Text
5 Key Terms Every Investor Should Know About Financial Services in Haridwar

Most investors venture into financial services without fully understanding some of the most important terms. This often leads to confusion and poor decision-making. That’s where Haridwar MF comes in. Offering financial services in Haridwar, they simplify even the most complex concepts to help you make smarter financial choices.
Key Terms You Should Know
Understanding key terms is essential to start your financial journey on the right foot. Whether you’re new to investing or have some experience, these five terms will provide clarity and confidence in managing your investments.
1. SIP (Systematic Investment Plan)
A Systematic Investment Plan is a way to invest in mutual funds with discipline. Instead of investing a large amount at once, you contribute a fixed sum at regular intervals—weekly, monthly, or quarterly. If you wish to get started, reach out to a mutual fund investment advisor in Haridwar.
Why It’s Important
Encourages consistent investing
Helps build wealth over time
Reduces the risk of market volatility
If you invest ₹5K monthly through an SIP, you not only develop a habit of saving but also benefit from rupee cost averaging, which averages out your investments even with market fluctuations.
2. NAV (Net Asset Value)
The Net Asset Value is known as the price of one unit of a mutual fund. It’s calculated at the end of each trading day based on the fund's total assets minus its liabilities.
Why It’s Important
Determines the cost of buying or selling fund units
Reflects the performance of the mutual fund
If you’re investing in a mutual fund with a NAV of ₹20 and you invest ₹10,000, you’ll own 500 units of that fund. NAV changes daily, so tracking it helps assess the growth of your investment.
3. Diversification
Diversification means spreading your investments across various asset classes to maximize returns and reduce risk.
Why It’s Important
Minimizes the impact of a poor-performing asset
Balances risk and reward
For example, instead of putting all your money into stocks, you can also invest in bonds or mutual funds to safeguard against market downturns. Experts can help you create a diversified portfolio tailored to your financial goals.
4. Expense Ratio
The Expense Ratio is the annual fee mutual funds charge for managing your investment. It can be expressed as a percentage (%) of your total investment.
Why It’s Important
Affects your overall returns
Helps you compare funds
For example, if a mutual fund has an expense ratio of 1.5%, it means ₹1.50 out of every ₹100 you invest goes toward management costs. While a lower expense ratio is generally better, the quality of fund management also matters.
5. Risk Appetite
Risk appetite is your ability and willingness to take financial risks. It depends on factors like age, income, financial goals, and market experience.
Why It’s Important
Helps select suitable investment products
Balances expectations and reality
For instance, if you’re in your 20s with a stable income, you may have a high-risk appetite and can invest in equity funds for higher returns. Conversely, retirees may prefer low-risk debt funds for stability.
Conclusion
Understanding these five key terms is the first step to becoming a confident investor. With the right knowledge, you can make informed decisions, optimize your investments, and work towards achieving your financial goals.
#financial planning advisors in Haridwar#Financial Services Company in Haridwar#financial planning experts in Haridwar#financial consultant company in Haridwar#personal financial planning in Haridwar#best financial planning advisor in Haridwar#financial goal planner in Haridwar#goal based financial planning in Haridwar#personal financial advisor in Haridwar#financial investment advisor in Haridwar
0 notes
Text
Caldwell Completes Merger of Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund and U.S. Dividend Advantage Fund
Caldwell Investment Management Ltd. has successfully completed the merger of two of its key investment funds, the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund and the Caldwell U.S. Dividend Advantage Fund, effective October 30, 2019. The combined entity will now operate under the name Caldwell U.S. Fund, consolidating the strengths and objectives of both funds into a unified investment vehicle.
A Tax-Deferred Merger
The merger was carried out on a tax-deferred basis, ensuring that investors did not incur any tax liabilities from the transaction. Furthermore, Caldwell Investment Management Ltd. took responsibility for all costs and expenses associated with the merger, ensuring a seamless transition for investors. This approach was designed to minimize disruptions and provide a smooth process for both new and existing unitholders.
Conversion Details
As part of the merger, Series A and Series F units of the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund were converted into Series A and Series F units of the Caldwell U.S. Fund, respectively. The conversion ratios were as follows:
Series A units of the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund were converted at a ratio of 0.6527 units of the Caldwell U.S. Fund for each unit of the Clearpoint Global Fund.
Series F units of the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund were converted at a ratio of 0.7781 units of the Caldwell U.S. Fund for each Clearpoint Global Fund unit.
These exchange ratios were calculated based on the net asset value (NAV) per unit of each series as of October 29, 2019. By carefully calculating these ratios, Caldwell ensured a fair and transparent transition, reflecting the value of each investment.
Seamless Transition for Investors
The merger was structured to be as seamless as possible for investors. Former unitholders of the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund automatically became unitholders of the Caldwell U.S. Fund without the need for any further action. Similarly, investors who were already unitholders of the Caldwell U.S. Dividend Advantage Fund will continue their investments without interruption. The transition was designed to provide continuity and maintain the integrity of investment strategies across the newly merged fund.
About Caldwell Investment Management Ltd.
Founded in 1990 and headquartered in Toronto, Caldwell Investment has built a reputation as a trusted firm specializing in dividend-paying equity mandates. With a focus on funds invested in both Canadian and U.S. markets, Caldwell employs disciplined investment strategies aimed at providing stable, long-term returns for its clients. The firm’s innovative and client-focused approach has earned it a strong standing in the investment management industry.
The merger of the Clearpoint Global Dividend Fund and the Caldwell U.S. Dividend Advantage Fund reflects Caldwell’s commitment to optimizing its fund offerings and providing streamlined investment solutions. The newly formed Caldwell U.S. Fund continues the legacy of its predecessor funds, with a focus on maintaining the strategic investment approaches that have made them successful.
Looking Forward
As Caldwell Investment Management Ltd. moves forward with the newly merged Caldwell U.S. Fund, investors can expect the same level of expertise, transparency, and commitment that has defined Caldwell’s approach for decades. By consolidating the strengths of its funds, Caldwell is positioned to continue delivering value to both individual and institutional investors across North America.
Follow them on Facebook to read more.
(Disclaimer: This article is not affiliated with Caldwell Investment Management.)
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mutual Fund Investing Detailed Information
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments, or other assets. Professional fund managers oversee the mutual fund, aiming to achieve the fund’s investment objectives while managing risks.

1. Key Features of Mutual Funds
A. Professional Management: Fund managers analyze and select investments based on the fund’s stated objectives. B. Diversification: Mutual funds invest in a range of assets, reducing the risk of significant losses from a single investment. C. Liquidity: Investors can usually buy or sell mutual fund shares at the fund’s net asset value (NAV), calculated daily. D. Affordability: Mutual funds allow investors to access a diversified portfolio with relatively small initial investments. E. Variety: They come in different types tailored to various investment goals (e.g., growth, income, preservation of capital).
2. Types of Mutual Fund
A. Equity Mutual Fund: An Equity Mutual Fund is a type of mutual fund that primarily invests in stocks (equities) of companies. The objective of equity mutual funds is to generate capital appreciation (growth in the value of investments) over the long term. These funds are best suited for investors looking for potentially higher returns and who are willing to accept a higher level of risk compared to other types of mutual funds, such as debt or money market funds.
B. Debt Mutual Fund: A Debt Mutual Fund is a type of mutual fund that primarily invests in fixed-income securities, such as government bonds, corporate bonds, treasury bills, commercial paper, and other money market instruments. These funds are designed for investors seeking regular income and capital preservation with lower risk compared to equity mutual funds.
C. Hybrid Mutual Fund: A Hybrid Mutual Fund is a type of mutual fund that invests in a mix of equity (stocks) and debt (fixed-income securities) to balance the risk and reward. These funds aim to provide growth potential through equity investments and stability through debt investments. Hybrid funds are ideal for investors seeking a moderate risk-reward profile.
D. Index Mutual Fund: An Index Mutual Fund is a type of mutual fund designed to replicate the performance of a specific market index such as the S&P 500, Nifty 50, or Sensex. Instead of actively managing the portfolio, the fund passively tracks the index by holding the same securities in the same proportions as the underlying index.
E. Sector Mutual Fund: A Sector Mutual Fund is a type of mutual fund that focuses its investments in a specific industry or sector of the economy, such as technology, healthcare, energy, financial services, real estate, or infrastructure. These funds aim to capitalize on the growth potential of a particular sector but come with a higher level of risk due to their lack of diversification.
3. Select Invest Mode
A. Systematic Investment Plan (SIP): A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a disciplined investment strategy where an investor invests a fixed amount of money at regular intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly) into a mutual fund. It is a convenient way to build wealth over time by taking advantage of rupee cost averaging and the power of compounding.
B. Systematic Withdrawal Plan: A Systematic Withdrawal Plan (SWP) is a facility offered by mutual funds that allows investors to withdraw a fixed amount of money at regular intervals (e.g., monthly, quarterly) from their investment. It is commonly used by retirees or individuals seeking a steady stream of income while keeping their principal invested. C. Systematic Transfer Plan (STP): A Systematic Transfer Plan (STP) is a mutual fund investment strategy that allows an investor to transfer a fixed amount of money at regular intervals from one mutual fund scheme to another within the same fund house. It is typically used to balance risk and returns by moving money from a lower-risk fund (like debt funds) to a higher-risk fund (like equity funds) or vice versa.
4. Benefits of Mutual Fund
Mutual funds offer several benefits that make them a popular investment choice for individuals seeking to grow their wealth, generate income, or achieve financial goals. Here are the key benefits of investing in mutual funds:
A. Professional Management Expertise: Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers with expertise in selecting and managing investments. Research-Based Decisions: Fund managers use extensive research, data analysis, and market insights to make informed investment decisions. B. Diversification Risk Reduction: Mutual funds invest in a wide range of securities (stocks, bonds, etc.), reducing the impact of poor performance in any single investment. Broad Exposure: Even a small investment provides exposure to multiple asset classes, sectors, and geographies. C. Liquidity Ease of Access: Most mutual funds can be bought or sold easily, offering high liquidity compared to other investment options like real estate or fixed deposits. Redemption Flexibility: Investors can redeem their units at the prevailing Net Asset Value (NAV) at any time, subject to exit load (if applicable). D. Affordability Low Initial Investment: You can start investing in mutual funds with a small amount (e.g., ₹500 or $10), making them accessible to all types of investors. Systematic Investment Plan (SIP): Allows regular investments in small amounts, fostering disciplined savings. E. Variety of Investment Options Asset Classes: Equity, debt, hybrid, index funds, and more. Themes and Sectors: Specialized funds focus on sectors (e.g., technology, healthcare) or themes (e.g., ESG, growth funds). Risk Profiles: Funds cater to various risk appetites, from conservative to aggressive. F. Tax Benefits Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS): Offers tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act in India. Tax Efficiency: Mutual funds, especially equity funds, are more tax-efficient than many traditional investments due to lower tax rates on capital gains. G. Transparency Regular Updates: Fund houses provide detailed reports on portfolio holdings, NAVs, and performance. Regulated: Mutual funds are regulated by authorities like SEBI (India), SEC (USA), ensuring investor protection and accountability.
0 notes
Text
ULIP Calculator - Calculate Returns on ULIP | Investment Calculator
ULIP stands for Unit Linked Insurance Plan. It is a type of investment product that combines life insurance coverage with investment opportunities. Unit Linked Insurance Plans are one of the popular investment options for individuals who want to invest in equity and debt markets while also securing life insurance.With alock-in periodof 5 years, it offers excellent returns. To measure the returns, you can use a ULIP calculator. The ULIP calculator enables comprehensive risk assessment, allowing individuals to gauge potential returns and benefits amidst market uncertainties.
What is the ULIP Calculator? A ULIP calculator is a tool provided by insurance companies or financial institutions to help potential customers estimate the returns and benefits they can expect from investing in a ULIP. A ULIP or Unit Linked Insurance Plan calculatoris a valuable tool that aids in estimating the returns and benefits individuals can expect from investing in a ULIP. It is essential to comprehend the functionalities and advantages of a ULIP calculator, particularly in risk assessment. It offers clarity on investment strategies, and tax planning insights, and aids in setting realistic expectations.
How to calculate your ULIP Investment Returns Online? Unit Linked Insurance Plans are one of the popular investment options for individuals who want to invest in equity and debt markets while also securing life insurance. However, understanding how to calculate ULIP investment returns can be a bit tricky, especially for those who are new to the investment world. Here are the steps to follow to calculate ULIP returns online.
Gather the Required Information Before you start calculating your ULIP investment returns, you need to gather some essential information. The following are the details you need to have:
The amount of premium paid The frequency of premium payment The total number of premiums paid The investment duration
Understand the Calculation Methodology The returns on ULIPs are calculated based on the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the fund. The NAV is the value of the assets held by the fund minus its liabilities divided by the total number of units held by the investors.
Use Online Calculators The calculator will then display the returns generated by the ULIP investment during the chosen period.
0 notes