#microbial growth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

“Petri Dish” - Animated painting
#flora#microflora#i miss being a microbiologist but only sometimes#computer graphics#animated#animated painting#gif#artgif#moving art#experimental#experimental art#painting#i'll have new painting posted next week#and then this blog becomes the Halloweenzone!#microbial growth
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
What has replaced parabens and is this replacement harmful or not as well-studied as parabens? Are they as effective at preventing microbial growth and extending the shelf life of products?
In recent years, many companies have moved away from using parabens in their products and have turned to alternative preservatives. Some common alternatives to parabens include phenoxyethanol, benzyl alcohol, potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, and ethylhexylglycerin, among others.
Like parabens, these alternative preservatives are intended to prevent microbial growth and extend the shelf life of cosmetics and personal care products. However, like all chemicals, they have the potential to cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals, and there may be some concern about their safety over the long term.
Phenoxyethanol, for example, has been the subject of some controversy due to concerns about its potential toxicity and its potential to cause skin irritation. Similarly, benzyl alcohol has been associated with allergic reactions in some people.
At present, there is not enough research to determine the long-term safety of these alternative preservatives. However, regulatory agencies such as the US FDA and the European Union's SCCS have evaluated these ingredients and deemed them safe for use at the concentrations typically used in cosmetics and personal care products.
Ultimately, the choice of preservative is up to individual companies and consumers, who may choose to avoid certain ingredients for personal or environmental reasons. However, it is important to note that preservatives are a necessary component of many cosmetic and personal care products, as they help to prevent microbial growth and ensure product safety and efficacy.
#parabens#preservatives#phenoxyethanol#benzyl alcohol#potassium sorbate#sodium benzoate#ethylhexylglycerin#microbial growth#shelf life#science#chemistry#toxicity#skin irritation#allergy#US FDA#European Union SCCS
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Check the Best Quality of Nutrient Agar Media (TM 341) at TM Media
If you are looking for Nutrient Agar manufactured by TM Media is a versatile and widely used solid growth medium in microbiology. It serves as a nutrient-rich substrate supporting the cultivation of a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds. The composition of nutrient agar media includes peptones, beef extract, and agar, creating a well-balanced environment for microbial growth. This medium lacks selective or inhibitory components, making it suitable for the general cultivation and isolation of microorganisms from various sources. Nutrient Agar's simplicity and broad applicability make it a fundamental tool in laboratory settings for routine microbial culture, identification, and enumeration.
Visit the Website - https://www.tmmedia.in/

0 notes
Text


a couple of besties can be the current and previous incarnation of the same soul
#dan heng#imbibitor lunae#yin yue jun#dan feng#hsr leaks#hsr#honkai star rail#guess whose reviewing for exams again#you bet im reviewing very hard and understanding the factors that affect microbial growth#mhm like pH#temperature osmotic pressure and antimicrobial agents#hc that dan feng has squinty eyes like a reptile
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Will we ever find an artificial sweeter that is problem free? First it was saccharin but hat was possibly carcinogenic. Then aspartame, but I've read journal articles citing bad health effects (I often wonder if the sugar and corn syrup industries fund those studies), now it's Splenda/sucralose.
This is why I just use sugar.
The human body's inability to break down sucralose, an artificial sweetener found in many zero-calorie food and drink products, is well established by scientific research. The compound is so stable that it escapes wastewater treatment processing and is in drinking water and aquatic environments. "We can't break down sucralose, and a lot of microorganisms can't break it down, either, because it's a really tough molecule that doesn't degrade easily. So there are a lot of questions about how it is affecting the environment and whether it's something that could impact our microbial communities," said Tracey Schafer, an assistant research scientist for the University of Florida's Whitney Laboratory for Marine Bioscience and the soil, water and ecosystem sciences department, part of UF's Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Environment#Chemistry#Marine Bioscience#Artificial Sweeteners#Sucralose#harmful effects of stable sucralose molecules on microbial growth
239 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Opportunities in the Global Agricultural Microbials Market

Increase in investment in agricultural R&D and expansion of agricultural sectors in emerging economies is expected to drive the Global Agricultural Microbials Market growth in the forecast period, 2024-2028.
According to TechSci Research report, “Agricultural Microbials Market – Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Competition Forecast & Opportunities, 2028”, the Global Agricultural Microbials Market stood at USD 6.12 Billion in 2022 and is anticipated to grow with a CAGR of 8.64% in the forecast period, 2024-2028. The global agricultural microbials market is primarily driven by the increasing global food demand in response to the rapidly growing population. Farmers are turning towards sustainable farming practices for which microbials serve as an eco-friendly, cost-effective solution. Moreover, the rise in soil and water pollution due to excessive use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers has led to a surge in the adoption of agricultural microbials. These bio-based products enhance soil fertility and crop productivity without causing harm to the environment. Government policies and initiatives promoting organic farming and the use of bio-based agricultural inputs also significantly contribute to the market growth. Advancements in microbial technology and an increased understanding of the benefits of microorganisms in agriculture have further fueled the expansion of this market.
The global agricultural microbial market is experiencing significant growth due to multiple factors. Firstly, there is a growing demand for sustainable farming practices as the urgency for environmentally friendly solutions becomes increasingly apparent. Farmers and agricultural industries are seeking alternative methods that minimize the impact on ecosystems and reduce the use of harmful chemicals. Moreover, the expanding global population is placing immense pressure on the agricultural sector to produce more food.
To meet this demand, farmers are adopting innovative techniques that maximize crop yields and optimize resource utilization. The integration of beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa, has emerged as a crucial aspect of modern agriculture. These microorganisms play a vital role in enhancing soil fertility, promoting plant growth, and controlling pests and diseases.
By harnessing the power of these microorganisms, farmers can create a balanced ecosystem that supports long-term sustainability and productivity. These beneficial microorganisms contribute to nutrient cycling, improve soil structure, and enhance the overall health of agricultural systems. As a result, farmers can achieve higher crop yields, reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and minimize the negative environmental impact.
Browse over XX market data Figures spread through XX Pages and an in-depth TOC on "Global Agricultural Microbials Market.” https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/agricultural-microbials-market/4924.html
Furthermore, advancements in microbial technology are driving the growth of the agricultural microbial market. Continuous research and development efforts are leading to the discovery of new microbial strains and formulations with enhanced efficacy and specificity. Scientists and researchers are constantly exploring the potential of these microorganisms to develop customized solutions that address specific agricultural challenges.
Supportive government regulations and policies are also playing a crucial role in creating a favorable environment for the adoption of microbial products in agriculture. Governments around the world are recognizing the importance of sustainable farming practices and are implementing measures to promote the use of microbial solutions. This support not only encourages farmers to embrace these innovative technologies but also ensures the safety and efficacy of microbial-based products. Considering these factors, the agricultural microbial market is poised for further expansion in the coming years.
As farmers increasingly recognize the numerous benefits of using microbial solutions, the demand for these products is expected to grow significantly. This, in turn, will drive investment in research and development, leading to the development of more advanced and effective microbial-based solutions for sustainable agriculture. The future of agriculture lies in harnessing the power of beneficial microorganisms to create a more resilient and sustainable food production system.
The Global Agricultural Microbials Market is segmented into type, function, formulation, mode of application, crop type, regional distribution, and company.
Based on mode of application, the foliar segment accounted for a significant market share in 2022. The foliar spray technique enables faster nutrient uptake as the foliage rapidly absorbs essential nutrients, providing crops with the necessary elements. This technique offers ease of application and serves as a prompt correction treatment for deficiencies and diseases in plants. Soil application of microbials enhances plant growth, improves nutrient availability, and promotes overall soil health. Microbes possess the capability to solubilize minerals and convert organic matter into plant-accessible forms, thereby increasing the availability of nutrients such as potassium, iron, and calcium. Moreover, certain microorganisms are capable of remediating pollutants and contaminants in the soil through bioremediation processes.
The use of agricultural microbials contributes to sustainable agriculture by reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This, in turn, yields positive effects on the environment and human health. Incorporating agricultural microbials into soil management practices fosters environmentally friendly agricultural systems by promoting soil health, enhancing crop yields, and reducing dependence on chemical inputs. Based on region, North America accounted for the largest revenue share in 2022, driven by the increasing awareness of the benefits of microbial use in agriculture over synthetic chemicals.
Additionally, the region's market growth is propelled by the adoption of environment-friendly and organic farming practices. Central & South America is expected to emerge as one of the fastest-growing regions as farmers shift towards microbials as a replacement for chemical fertilizers. The profitability of organic farming and support from government and non-government organizations are projected to fuel market growth in the coming years.
The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to witness significant growth in the agricultural microbial sector, owing to its status as the largest producer of organic products. China and India, in particular, serve as key organic crop-producing countries in the region. In Europe, the expansion of organic crop areas and the increasing demand for organic products and biological fertilizers contribute to reduced chemical fertilizer usage and lower crop production costs. Government initiatives to promote organic farming are expected to drive the global agricultural biologicals market throughout the forecast period.
Major companies operating in Global Agricultural Microbials Market are:
BASF SE
Bayer Crop Science
Syngenta AG
Certis USA LLC
Marrone Bio Innovations, Isagro S.p.A
Verdesian Life Sciences LLC
Valent Biosciences LLC
Lallemand Plant Care
Agrilife Biosolutions Ltd.
Novozymes A/S
Download Free Sample Report https://www.techsciresearch.com/sample-report.aspx?cid=4924
Customers can also request for 10% free customization on this report.
“The future outlook for the global agricultural microbials market appears highly promising, fueled by an increasing awareness and adoption of sustainable farming practices. With the ever-growing global population, there is a pressing need to meet the rising demands for food production. As a result, the agricultural microbials sector is poised to experience substantial growth in the coming years. Furthermore, the market growth of agricultural microbials is expected to be boosted by the emergence of advanced biotechnological techniques. These advancements enable the development of innovative microbial solutions that cater to a wide range of agricultural applications. From crop protection to soil health management, these microbial solutions offer a broad spectrum of benefits to farmers, helping them achieve higher productivity and greater sustainability.
The global agricultural microbials market is poised for significant expansion in the coming years. The increasing awareness of sustainable farming practices, coupled with the need to meet the growing food demands of the global population, will continue to drive the adoption of microbials in agriculture. With the advancements in biotechnology, innovative microbial solutions will continue to revolutionize the way we approach agricultural production, paving the way for a more sustainable and productive future.,” said Mr. Karan Chechi, Research Director with TechSci Research, a research-based management consulting firm.
“Agricultural Microbials Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Trends, Opportunity, and Forecast, 2018-2028 Segmented By Type (Bacterial, Fungi, Virus, Protozoa), By Function (Soil Amendments and Crop Protection), By Formulation (Dry and Liquid), By Mode of Application (Foliar Spray, Soil Treatment, Seed Treatment, Others), By Crop Type (Cereals & Grains, Oilseeds & Pulses, Fruits & Vegetables, Others), By Region and Competition”, has evaluated the future growth potential of Global Agricultural Microbials Market and provides statistics & information on market size, structure and future market growth. The report intends to provide cutting-edge market intelligence and help decision makers take sound investment decisions. Besides, the report also identifies and analyzes the emerging trends along with essential drivers, challenges, and opportunities in Global Agricultural Microbials Market.
Browse Related Reports
Agricultural Disinfectants Market https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/agricultural-disinfectants-market/20635.html Probiotics in Animal Feed Market https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/probiotics-in-animal-feed-market/20673.html Mechanized Irrigation Systems Market https://www.techsciresearch.com/report/mechanized-irrigation-systems-market/20668.html
Contact
Techsci Research LLC
420 Lexington Avenue, Suite 300,
New York, United States- 10170
Tel: +13322586602
Email: [email protected]
Website: www.techsciresearch.com
#Agricultural Microbials Market#Agricultural Microbials Market Size#Agricultural Microbials Market Share#Agricultural Microbials Market Trends#Agricultural Microbials Market Growth
0 notes
Text
ORGANIC ALOE VERA OIL
It includes mucopolysaccharides, which hold moisture in the skin. It promotes the development of collagen and elastin fibers, making skin more elastic, supple, plump, softer, and younger appearing. It may also help to minimize the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and stretch marks. It is an effective hair care product. Aside from curing dandruff and dry scalp, it promotes hair development and strengthens strands. It may also be used as a conditioner to alleviate dry scalp. Pure Aloe Vera Oil has antibacterial properties. It contains antiseptics such as lupeol, salicylic acid, urea, nitrogen, cinnamonic acid, phenols, and sulfur. Thus, it promotes quicker wound healing and can help reduce scarring.

#usda certified#antioxidants#infused oils#moisturized skin#skin lightening#scalp eczema#hair growth#cure dandruff#anti bacterial#anti microbial
0 notes
Text
Articolo: Inoculanti microbici per la tolleranza allo stress da siccità
Microbial inoculants for drought stress tolerance Authors: Domenico Prisa 1, * and Roberto Fresco 2 1 Council for Agricultural Research and Economics, Research Centre for Vegetables and Ornamental Crops, Via dei Fiori, 8, 51012 Pescia (PT), Italy. 2 CREA Research Centre for Engineering and Agri-food Transformation, Council for Agricultural Research and Economics, Via della Pascolare, 16, 00016…

View On WordPress
#agricoltura sostenibile#biofertilizers#biofertilizzanti#inoculants#microbial inoculants#PGPB#plant growth promoting rhizobacteria#sustainable agriculture
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text

Antimicrobial coatings have emerged as a ground breaking solution. These advanced coatings offer an additional layer of protection by inhibiting the growth and spread of harmful microorganisms on various surfaces. Read More: https://cmibloggers.blogspot.com/2023/06/exploring-benefits-of-antimicrobial.html
#coherent market insights#Chemical and Materials Industry#Advanced Materials#Global Antimicrobial Coatings Market#Pathogen inhibition#Microbial growth prevention#Infection control#Surface protection#Hygiene enhancement
0 notes
Text
The global agricultural microbial market size grew from $5.1 billion in 2022 to $6.02 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.9%.
#agricultural microbial market research#agricultural microbial market report#agricultural microbial market trends#agricultural microbial market size#agricultural microbial market forecast#agricultural microbial market growth#global agricultural microbial market#agricultural microbial market share#agricultural microbial market analysis#agricultural microbial market segments
0 notes
Text
Scientists are very serious.
This is a post about science. And soup.
Dr. Elinne Becket, a microbiologist from Cal State University, is in the middle of one of those Fridge Experiments that happens to us all - except in this case, she is uniquely placed to unravel the science down to the microbial level.
While cleaning out her fridge, Dr. Becket found that a tub of family-recipe beef vegetable soup had turned bright blue. “Ok I'm outing myself here,” she tweeted, “but there was forgotten beef soup in our fridge we just cleaned it out and it was BLUE?!?!? Wtf contam would make it blue??? Like BRIGHT blue!! Even w/ all my years in micro I'm not handling this well.“
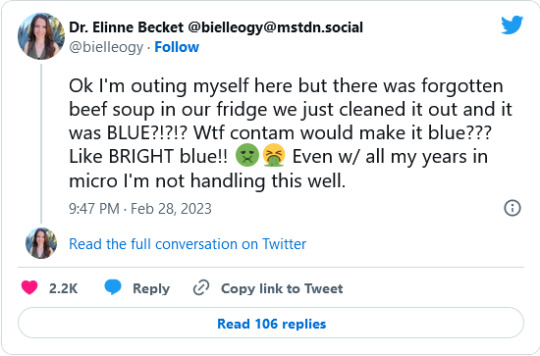
Read on for a breathless and ongoing saga of Soup and Science, and the wonderful international community that is Academic Twitter.
Academic Twitter quickly reminded her of her Responsibilities to Scientific Inquiry. (Cue the chanting from around the world of “CLONE THE SOUP! CLONE THE SOUP!”)
“I can’t believe y’all talked me into going back into the trash.” she tweeted in response, over a photo of a puddle of beautiful Mediterranean-sea blue soup in the trash bin, with bits of veg and noodles arising from the depths.
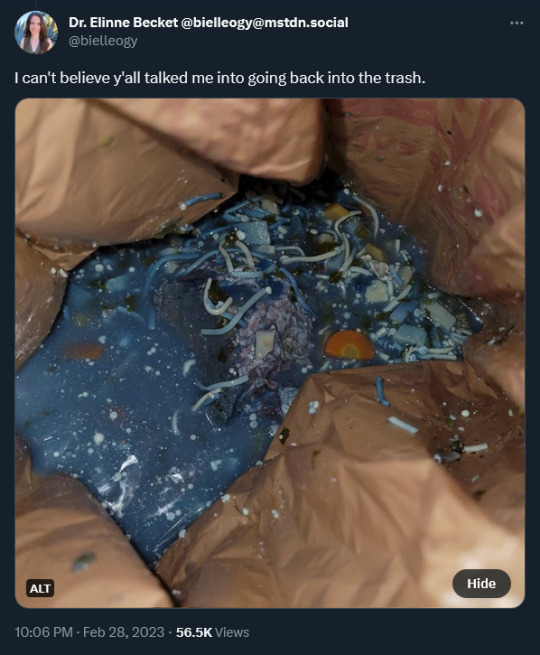
Scientists being scientists, Dr. Becket agreed to take a sample and send it to colleagues for cloning and microbial analysis.This involved getting arms-deep into the trash bin of Old Soup. “I’m never forviging @ATinyGreenCell (genomic biologist Sebastian Cocioba) for this.” Dr. Becket tweeted, with a photo of a properly dipped and snipped and VERY blue q-tip in a small clear plastic tub.
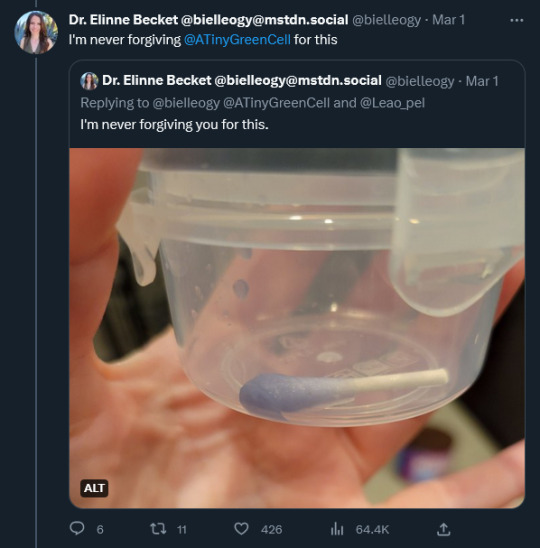
Diving into decomposing soup was not the only hazard. She writes: “My mom (who made the soup for my birthday) came across this thread and now 1) I have to answer for letting her soup spoil and 2) she's worried @ATinyGreenCell will figure out her secret recipe.“
Dr. Becket and Sebastian were able to culture the Blue Goo!
Becket posted a photo of three petri plates of streaked beef bouillon agar at 72 hours incubation, at 37C, room temp and 4C. She writes: “Left the plates where they were for another 2 days, except the 37°C one was brought to RT, which then grew white stuff over the yellow stuff and stinks to high heaven. RT looked the same. 4°C had impressive growth. Restreaked them all onto TECH agar, awaiting results!”

Sebastian, from his lab, tweeted a photo of three more covered petri dishes, with early results: “Great progress on isolating the glowy microbe from our #BlueSoup! It's so fluorescent the streak is GREEN. Still needs another restreak as it seems there is a straggler but should clear up in the next plate. Exciting!”
Then yesterday, Sebastian tweeted out an updated photo of his plates under daylight and blacklight. “Whatever grew on the #BlueSoup colony plates overnight glows under UV, but only on King's Agar B! That particular media is used to tease out fluorescein expression in pseudomonads. What are the chances that the same cell line expresses fluorescent AND blue pigments?“

“Looking closer, there definitely is a handful of different microbes showing distinct phenotypes. Could be that the blue producer and the fluorescent microbes are totally different microbes!”
At which point, Professor Cynthia Whitchurch of Norwich, England, responded: “Consistent with P. fluorescens being at least part of the #BlueSoup community. The fluorescence is due to production of the siderophore pyoverdine which is up-regulated when iron availability is limited. P. aeruginosa produced this too but my guess is you have blue Pf.”
And Australian agricultural researcher @WAJWebster helpfully tweeted a petri dish of ALL KINDS of colourful bacterial colonies from white to yellow to orange to stark black, with a cheerful: “You need bact-o--colours? I got you, fam.”
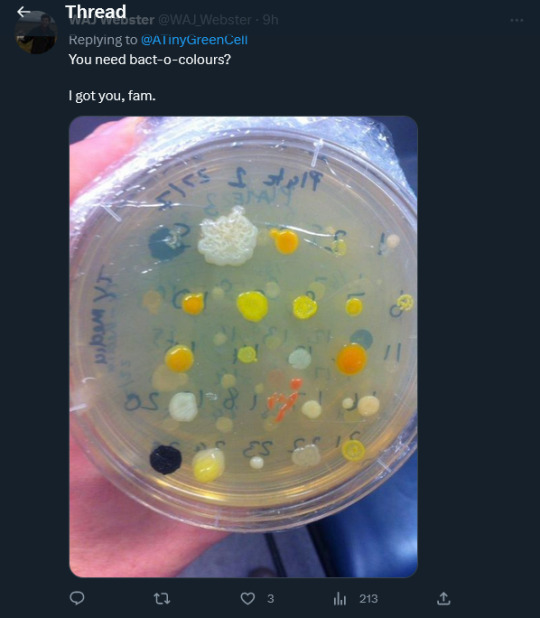
The best part is that as of today, March 9, 2023, THE BLUE SOUP MYSTERY CONTINUES. WE ARE WATCHING SCIENCE HAPPENING!
A paper is being written. And Dr. Becket’s mum is getting an author credit as the proprietary owner of the #BlueSoup recipe.

Dr. Becket’s Twitter is here: https://twitter.com/bielleogy
Sebastian Cocioba’s Twitter is here: https://twitter.com/ATinyGreenCell
Fun IFLS story is here: https://www.iflscience.com/microbiologist-investigates-after-her-beef-soup-turned-blue-in-the-freezer-67894?fbclid=IwAR0H27KqVZhzzrosnjzzKkxuKASZ-0L0Lt6hGwCRDJK8xvFbbSlyS4JvwlM
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
#Microbial Control Chemical Market#Microbial Control Chemical Market Trends#Microbial Control Chemical Market Growth#Microbial Control Chemical Market Industry#Microbial Control Chemical Market Research#Microbial Control Chemical Market Reports
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
declassified ex-patreon post: the empty city

Pictured (click tha link for full piece) - Rosy Wing and Patches on a romantic evening, before Rosy's death. Aerial displays are an important courtship activity, serving to reinforce the pair's bond year after year.
The endless city is exactly what it sounds like. It covers the top of the Houndstooth mountain range like a growth of moss on a boulder. It comprises of buildings made entirely of pure white limestone right down to the window latticework and roof shingles. The doorways and rooms are scaled strangely, not appearing to conform to human sizes, and the horizontal architecture alignment (i.e not built to accommodate flying creatures) seems to suggest that insects didn't build it either. There are no organic materials naturally occurring within the city, not even microbial life, although some has been introduced in recent years by expeditioneers. Some parts of the city have been claimed by the rich patrons of expedition teams, and are guarded 24/7 by armed patrols - usually these territories are held for easier ingress into the deeper parts of the city for teams owned by the patron in question.
There is a boundary wall, with no gates. Roads within the city that lead outwards terminate at these walls as though there should be a gate or portcullis, but there are none. Many patrons have chosen to sink funding into constructing their own proprietary doorways in secret, strategic locations. Spies who figure out where a rival team enters the city can choose to report back, to allow their own teams to stage an ambush, or they can demand payment in return for conveniently forgetting what they have learned. Money rules everyone in the city; it is so hostile to sustained life that purchasing basic supplies from the closest mountainside towns is the only way to get any food at all, so exploring is an expensive business. But it can also be lucrative, if you become one of the few lucky enough to find uncharted regions, or figure out a way to penetrate deeper without simply wandering in endless circles.
Theran insects are considered ideal employees for expeditions - cheap and easily exploited, those new to the game are often satisfied with being paid in food and trinkets. But as the years go on, more and more of them have begun to learn how to exploit the system for their own ends, and that amassing capital of their own can lead to many advantages. Human employees are always necessary on any serious expedition, because only humans can wield firearms.
The 'why' of all this is the curious part - why sink huge sums of money into a dangerously competitive expedition when the city appears to be completely empty? It has become more of a vanity project than anything else, with many wealthy patrons convinced that they will one day profit off of the land they capture, selling homes to people on this new frontier. Others believe that the city is evidence for the existence of god, and that they are exploring purgatory, or indeed heaven. Either way it's believed that one day, all their expense will be paid off a thousandfold, and their speculative betting on the city will, essentially, make the line go up.
[today's words below]
One day, approximately 20ish years ago, the Houndstooth mountains appeared. They appeared in two parallel dimensions but at the exact same point, destroying anything that had been standing there before. On Earth, this was half of the city of Quern. On Thera, it was a gigantic forest of Tithe trees. There is evidence that the mountains will disappear within another 20 years, just as they did millions of years ago, during the first appearance. At that time, Earth insects were able to cross the mountain range to colonise a world that had nothing but plants (which had likely also travelled there a million years before by the same method). Before those mountains disappear for another million years, the people of Quern and Thera must figure out what lies at the heart of the city at the top of those mountains.
So the story was about a team of expeditioneers, funded/owned by a wealthy patron, who travel into the city to find its heart. The ending of the story was relatively simple - the city was an allegory for obsession and grief, and was shaped like a fractal - if you happen to take the correct turn, a thousand times in a row, you travel 'deeper' into it, into the limbs of the fractal, and the truth is that it is endless. there is no heart of the city, there is no core, there's nothing lying in wait in there but it captures the minds & imaginations of expeditioneers and patrons alike. that's why i drew an ouroboros in that pic, it's fully metaphorical. the city is EMPTY. The characters trapped in this expedition (and their grief-fuelled justifications for expeditioning at all) have to make the conscious choice to stop exploring, to turn their back on the sunk cost fallacy, to stop chasing what might lie around the next corner, and go home. But that's much harder than it sounds.
look at some of the insects in my setting tag and enjoy
#setting: thera#i know it's not a NEW setting but still it feels crazy for me to dump yet another Place into this blog#but i do have a good 40k words of this story written so hey i might post some excerpt if you can stand my 1st person only#slush draft writing style which i use to nail character voices
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
"An international research team has found almost a million potential sources of antibiotics in the natural world.
Research published in the journal Cell by a team including Queensland University of Technology (QUT) computational biologist Associate Professor Luis Pedro Coelho has used machine learning to identify 863,498 promising antimicrobial peptides -- small molecules that can kill or inhibit the growth of infectious microbes.
The findings of the study come with a renewed global focus on combatting antimicrobial resistance (AMR) as humanity contends with the growing number of superbugs resistant to current drugs.
"There is an urgent need for new methods for antibiotic discovery," Professor Coelho, a researcher at the QUT Centre for Microbiome Research, said. The centre studies the structure and function of microbial communities from around the globe.
"It is one of the top public health threats, killing 1.27 million people each year." ...
"Using artificial intelligence to understand and harness the power of the global microbiome will hopefully drive innovative research for better public health outcomes," he said.
The team verified the machine predictions by testing 100 laboratory-made peptides against clinically significant pathogens. They found 79 disrupted bacterial membranes and 63 specifically targeted antibiotic-resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.
"Moreover, some peptides helped to eliminate infections in mice; two in particular reduced bacteria by up to four orders of magnitude," Professor Coelho said.
In a preclinical model, tested on infected mice, treatment with these peptides produced results similar to the effects of polymyxin B -- a commercially available antibiotic which is used to treat meningitis, pneumonia, sepsis and urinary tract infections.
More than 60,000 metagenomes (a collection of genomes within a specific environment), which together contained the genetic makeup of over one million organisms, were analysed to get these results. They came from sources across the globe including marine and soil environments, and human and animal guts.
The resulting AMPSphere -- a comprehensive database comprising these novel peptides -- has been published as a publicly available, open-access resource for new antibiotic discovery.
[Note: !!! Love it. Open access research databases my beloved.]"
-via Science Daily, June 5, 2024
#superbugs#bacteria#viruses#microbiology#antibiotics#medicines#public health#peptides#medical news#antibiotic resistance#good news#hope#ai#artificial intelligence#pro ai#machine learning
184 notes
·
View notes