#metamaterials
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Crafting the perfect bite of meat: Engineers develop metamaterials that mimic muscle and fat architecture
In a new publication in Nature Communications, Israeli and Palestinian engineers from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem pioneered the use of metamaterials to create whole cuts of meat. The work leverages cutting-edge materials science to overcome the long-standing challenges of replicating the texture and structure of traditional meat while offering a scalable and cost-effective production method that surpasses 3D printing technology. Metamaterials are composite materials whose properties arise from their structure rather than their composition. By adopting principles typically used in the aerospace industry, the team, led by Dr. Mohammad Ghosheh and Prof. Yaakov Nahmias from Hebrew University, developed meat analogs that mimic the intricate architecture of muscle and fat. These analogs are produced using injection molding, a high-capacity manufacturing process borrowed from the polymer industry, marking the first time this technology has been applied to alternative meat production.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Metamaterials#Food#Meat#Composites#Biomaterials#Injection molding#Hebrew University of Jerusalem
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
For the first time, scientists have demonstrated that negative refraction can be achieved using atomic arrays - without the need for artificially manufactured metamaterials. Negative refraction - a phenomenon where light bends in the opposite direction to its usual behaviour - has captivated researchers for its potential to revolutionise optics, enabling transformative technologies such as superlenses and cloaking devices.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text


Did you know there are currently smart materials and technologies, as well as active comouflage methods, in use and under research that can render objects, vehicles or persons invisible: not only to the naked eye, but also to security cameras?
This is especially concerning when dealing with corruption, fascism, other developments in military technologies this could be cross applied with, or covert operations involving human victims or sex traffick and other criminal government operations.
Here's a few examples:
"Next-gen Military Uniforms: Various military research programs are exploring smart uniforms that incorporate these technologies. For example, DARPA has been involved in developing "invisibility cloaks" that use smart fabrics to reduce the visibility of soldiers on the battlefield."
"MIT's Electromagnetic Metamaterials: Research at MIT has explored using metamaterials to create a "cloaking" effect in the electromagnetic spectrum. Although these are primarily experimental, they could eventually lead to applications where objects or people are rendered invisible to certain detection methods."
"BAE Systems' Adaptiv: This is a military camouflage technology developed for vehicles. Adaptiv uses hexagonal tiles that can change temperature to blend into the infrared spectrum of the background. While primarily developed for vehicles, the concept could theoretically be miniaturized for use on smaller objects or individuals."
"Duke University and University of California, Berkeley: Researchers at these institutions have been working on invisibility cloaks using metamaterials that can bend electromagnetic waves around an object, effectively making it invisible. Although this technology is currently limited and works mainly at specific wavelengths or in laboratory conditions, it demonstrates the potential for future applications."
"Invisibility Cloaks Based on Transformation Optics: This research area involves designing materials that guide light around an object, making it invisible. Companies and military research labs are exploring this, but practical, deployable versions are still speculative."
"Quantum Stealth by Hyperstealth Biotechnology Corp: This Canadian company has developed a material they claim can bend light around an object, rendering it invisible. The technology is said to work without cameras, batteries, or mirrors, and it could be used to conceal objects or people from view by manipulating light waves. However, the actual effectiveness and deployment status of this technology remain largely unverified in the public domain."
Ultimately, how these technologies, or other advanced weapons, can impact civilian populations left in the dark is a huge concern. There are multiple methods of intercepting or undermining the purpose of security cameras, this is one of many potentials.
Fox Badge The Steel Yard
#ledhulahoop#actve camouflage#smart materials#nanotech#transformation optics#pixel#camouflage technology#futurism#meta materials#metamaterials#quantum stealth#transformationoptics#nanofibres#hula hoop#light performance#led show
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pretty awesome
"The sensor works purely mechanically and doesn't require an external energy source. It simply utilises the vibrational energy contained in sound waves," Robertsson says. Whenever a certain word is spoken or a particular tone or noise is generated, the sound waves emitted -- and only these -- cause the sensor to vibrate. This energy is then sufficient to generate a tiny electrical pulse that switches on an electronic device that has been switched off. The prototype that the researchers developed in Robertsson's lab at the Switzerland Innovation Park Zurich in Dübendorf has already been patented. It can distinguish between the spoken words "three" and "four." Because the word "four" has more sound energy that resonates with the sensor compared to the word "three," it causes the sensor to vibrate, whereas "three" does not. That means the word "four" could switch on a device or trigger further processes. Nothing would happen with "three." Newer variants of the sensor should be able to distinguish between up to twelve different words, such as standard machine commands like "on," "off," "up" and "down." Compared to the palm-sized prototype, the new versions are also much smaller -- about the size of a thumbnail -- and the researchers are aiming to miniaturise them further.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bulk–spatiotemporal vortex correspondence in gyromagnetic zero-index media
Huang, X., Lai, Y., Hang, Z. H., Zheng, H. & Chan, C. T. Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials. Nat. Mater. 10, 582–586 (2011). Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar Nguyen, V. C., Chen, L. & Halterman, K. Total transmission and total reflection by zero index metamaterials with defects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 233908…
#Humanities and Social Sciences#Magneto-optics#Metamaterials#multidisciplinary#Science#Topological insulators
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hidden Tech Wonders: Mind-Blowing Innovations You’ve Probably Never Heard Of
While mainstream technology like smartphones, AI chatbots, and electric vehicles dominate headlines, there’s an entire world of cutting-edge innovations quietly shaping the future. These mind-blowing technologies may not yet be household names, but they are already transforming industries and redefining possibilities. From advancements in health and science to revolutionary materials and…
#Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI)#CRISPR Gene Editing#Metamaterials#Nanomedicine#Solid-State Batteries
0 notes
Text
Shapeshifting Space Stations? New Metamaterial Could Revolutionize Space Habitats
Scientists have developed a flexible metamaterial inspired by nature that could enable the construction of adaptable space habitats and telescopes capable of changing shape in orbit.
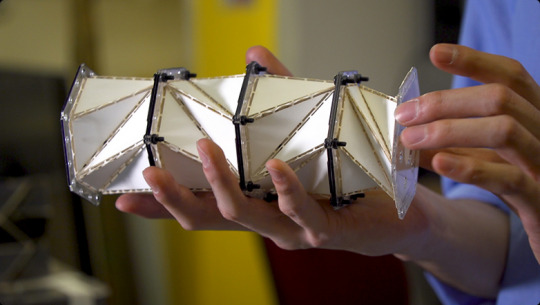
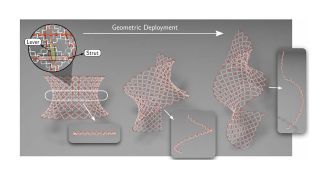
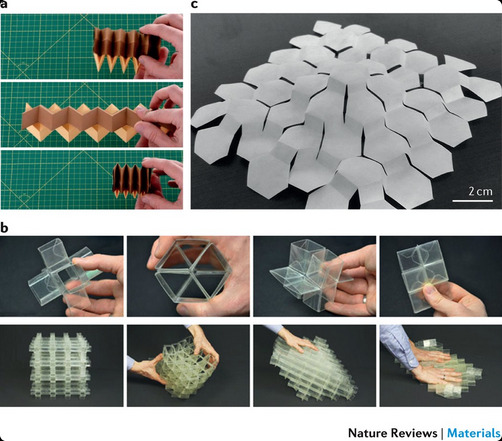
0 notes
Text
China Unveils Cutting-Edge Stealth Coating That Redefines Anti-Stealth Radar Evasion

China Unveils Cutting-Edge Stealth Coating That Redefines Anti-Stealth Radar Evasion In a significant advancement in military technology, the Chinese military has announced the development of a groundbreaking radar-defeating coating designed to conceal targets from anti-stealth radars. This innovative coating, which is paper-thin yet highly effective, can absorb low-frequency electromagnetic waves (EM), marking a remarkable leap in stealth technology. Transforming Stealth Aircraft Detection This breakthrough has the potential to revolutionize how stealth aircraft evade radar detection, particularly against EM waves emitted from various angles. Historically, radar-absorbing materials have had limited success in countering radar systems, a costly lesson highlighted by the detection and subsequent downing of an F-117A "Nighthawk" during the late 1990s in Yugoslavia. Developed by researchers at China's National University of Defence Technology (NUDT), this new material can absorb wavelengths ranging from 70 to 20 cm, which are primarily used by anti-stealth P-band and L-band radars. These frequency bands are critical in detecting stealth aircraft, making this coating a vital development for military applications. Unique Properties of the Coating What distinguishes this stealth coating is its lightweight and flexible nature, allowing for large-scale production that is economically viable for military use. Composed of metamaterials, the coating exhibits extraordinary properties not found in natural materials. When low-frequency EM waves strike the surface, these metamaterials convert the incoming energy into heat, dissipating it quickly and thereby significantly reducing the radar signature. Strategic Implications Chinese researchers have indicated that this development is crucial for enhancing future warfare strategies, potentially providing the country with a competitive edge on the global stage. As advancements continue in stealth technology through innovative materials like this, the balance of military capabilities worldwide may begin to shift. The Ongoing Technological Arms Race With China's persistent advancements in anti-stealth technology, this new coating represents more than just a military upgrade; it signifies a strategic shift in defense capabilities. It underscores the growing importance of metamaterials in modern military applications and reflects the ongoing technological arms race among global powers. Conclusion This latest innovation in stealth technology could have profound implications for global military dynamics, setting a new standard for what stealth technology can achieve in contemporary warfare. As nations race to enhance their defense systems, China's development of this advanced stealth coating may redefine the future of aerial combat and radar evasion. Read the full article
#anti-stealthradar#Chinastealthtechnology#Chinesemilitaryinnovation#electromagneticwaves#metamaterials#militarytechnologyrevolution#radarabsorbingmaterials#stealthcoating
0 notes
Text
How Emerging Applications in Aerospace and Defense Propel Metamaterial Market Growth
Emerging applications in aerospace and defense are key drivers for growth in the metamaterial market, as these sectors demand advanced materials capable of unique electromagnetic, acoustic, and thermal manipulation. Metamaterials, with their engineered properties, are transforming capabilities in these fields by enhancing radar and communication systems, improving stealth technology, and enabling advanced imaging.
Aerospace Applications: Enhancing Performance and Efficiency
In aerospace, metamaterials are increasingly used to improve the performance and efficiency of aircraft systems. By using lightweight and flexible metamaterials, aerospace engineers can create components that reduce the overall weight of aircraft, enhancing fuel efficiency and lowering operational costs. Additionally, metamaterials are employed in advanced antenna systems, where they improve signal reception and minimize interference. This is crucial for aircraft that rely on sophisticated navigation and communication systems.
Metamaterials are also utilized in satellite technology, where they enable improved signal transmission and reduced interference, which is essential for maintaining secure and uninterrupted communication. The materials’ unique wave-manipulation capabilities allow for miniaturization of components, which is valuable in the compact environments of satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). With the growing demand for space exploration and satellite-based communication, metamaterials are set to play a vital role in advancing aerospace technologies.
Defense Applications: Revolutionizing Stealth and Communication
In the defense sector, metamaterials are indispensable for developing stealth technology. By manipulating electromagnetic waves, metamaterials can reduce an object's visibility to radar, making aircraft and vehicles "invisible" or "cloaked" from detection. This capability is highly desirable for military operations, as it enhances the stealth capabilities of fighter jets, ships, and ground vehicles. Metamaterials allow for the bending and redirection of radar waves, making it challenging for radar systems to detect and track these assets.
Another significant defense application is in improving radar systems themselves. Metamaterials can be used to create advanced radar systems with better range, resolution, and accuracy. The materials’ ability to control electromagnetic waves allows for better targeting and communication, which is crucial for defense operations. Additionally, metamaterials in radar technology enable more compact and lightweight devices, which are easier to deploy and maneuver.
In communications, metamaterials help create high-performance antennas that maintain clear, secure connections even in challenging environments. This is vital for defense, where reliable communication channels are essential for coordination and intelligence. For instance, metamaterial-based antennas can enhance satellite and radio communication by reducing signal interference and improving bandwidth, which ensures consistent, high-quality communication between ground units and aerial or satellite systems.
Key Innovations Driving Metamaterial Demand in Aerospace and Defense
Several innovations in metamaterials are directly impacting aerospace and defense applications. One example is the development of tunable metamaterials, which can adjust their properties in real-time. This adaptability is valuable in defense scenarios where conditions change rapidly. Tunable metamaterials allow systems like antennas and radar to dynamically adjust to new frequencies or signal conditions, improving responsiveness and effectiveness.
Another advancement is the development of metamaterial absorbers, which are crucial for stealth applications. These absorbers can dissipate electromagnetic energy, reducing the radar cross-section of military assets. As defense agencies worldwide focus on enhancing stealth capabilities, the demand for these metamaterials is expected to grow. Additionally, innovations in thermal metamaterials that control heat flow and temperature distribution are being used in aerospace to manage the extreme conditions that aircraft and spacecraft endure during flight.
Market Growth and Future Prospects
The growing adoption of metamaterials in aerospace and defense is contributing to rapid market growth. With rising global defense budgets, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, the demand for advanced materials that can provide a strategic advantage is increasing. As the market continues to expand, partnerships between government agencies and private sector companies are expected to drive further innovations, bringing new metamaterial applications into mainstream use.
As aerospace firms look to make aircraft more efficient and governments seek to enhance military capabilities, metamaterials offer transformative solutions that cater to these needs. The ongoing research and development in this field are likely to yield new types of metamaterials with even more specific functionalities tailored to meet the unique challenges of aerospace and defense. The industry’s future holds promising opportunities as metamaterials become integral to achieving advanced capabilities in these high-tech sectors.
Metamaterials are revolutionizing aerospace and defense by enabling capabilities that were once science fiction. Through enhanced stealth, improved communication, and lighter, more efficient materials, metamaterials are proving essential for modern aerospace and defense applications. As these industries evolve, the demand for metamaterials will only increase, driving the market’s growth and making them a cornerstone of future technological advancements.
0 notes
Text
Biochemistry and materials science 🐌👴🏽

100 notes
·
View notes
Text
In metamaterials design, the name of the game has long been "stronger is better." Metamaterials are synthetic materials with microscopic structures that give the overall material exceptional properties. A huge focus has been in designing metamaterials that are stronger and stiffer than their conventional counterparts. But there's a trade-off: The stiffer a material, the less flexible it is. MIT engineers have now found a way to fabricate a metamaterial that is both strong and stretchy. The base material is typically highly rigid and brittle, but it is printed in precise, intricate patterns that form a structure that is both strong and flexible.
Read more.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Metamaterials are artificial materials that do not occur in nature. Their components function like atoms in conventional materials but have special optical, electrical and magnetic properties. Interaction between the components is crucial to a metamaterial’s functionality. Previously a component could usually interact only with its immediate neighbors. Researchers at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have developed a mechanical metamaterial with which these interactions can also be triggered at greater distances within the material. Potential uses of the material include measuring forces and structural monitoring. The findings have been published in Nature Communications.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#Microwave hyperthermia#metasurfaces#near-field focusing#cancer therapy#tumor treatment#microwave technology#hyperthermia treatment#electromagnetic waves#focused energy#oncology innovation#metamaterials#precise therapy#non-invasive cancer treatment#thermal ablation#medical metasurfaces#advanced cancer treatment#microwave energy#targeted therapy#cancer research#medical technology.#Youtube
0 notes
Video
youtube
Afterlife/Otherside Ghostface projection experiment # 282
#youtube#shorts#afterlife#otherside#projection#experiment#infrared#ir#photonics#metasurface#light#metamaterials#ghostface#demonstration#luma#colour grading#miniature#spirits#ghosts#interdimentional#light beings#review#evidencebased
0 notes
Text
Status Update: Generalized Lorentz-Drude model of Dielectrics.
This week I continued to venture into the realm of nonlinearities by learning about the Lorentz model followed by the Drude model for metals.
It was fun employing the whole "statistical ensemble" trick to relate the microscopic dipole moments of individual atoms being subjected to an applied Electric Field to the macroscopic property of Material Polarization and further towards the Electric Flux Response of a material.
Once again, complex numbers rear their heads and there's growing pains in understanding the physical significance behind "complex dielectric" with the "real permittivity" all while trying to connect it with notions of conductivity in terms of both free space responses and material responses contributing to the total Electric Flux.
It is kinda neat how the complex refractive indexes extinction coefficient can be used to ??? Let us see where a materials absorption is highest near points of resonance?
And furthermore, a interesting connection to metamaterials was established when I realized that if the resonances of our doped elements are in frequencies way below our materials resonances, we do some cool stuff with the maths.
Something something we can use the dielectric permittivity at DC and at very high (infinity) to calculate the plasma frequency of a metal.
Now my plan is to deep dive into crystal anisotropy, do some numerical examples of tensor rotation, and hopefully that will help me better understand optical components like quarter wave plates and all that stuff.
And before anyone asks, no, Optical Rectification, the second order chi nonlinearity is NOT the mechanism of solar panels, that's the photoelectric effect 😉
#Lorentz#Drude#Dielectrics#loss#extinction coefficient#resonances#material polarization#material science#Optics#physics#electric flux#metamaterials#nonlinearities#math#Optical Rectification#refractive index#permittivity#plasma frequency#SoundCloud
1 note
·
View note