#marburg virus vaccine
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Oxford University scientists have recently commenced human testing of a highly anticipated Marburg virus vaccine. This significant development offers hope in the fight against one of the world’s deadliest pathogens. The Marburg virus, closely related to Ebola, has been responsible for numerous outbreaks, primarily affecting health workers in the affected regions.
#human testing#human trials#human trials of marburg vaccine#marburg virus vaccine#oxford university#vaccine development#vaccine for marburg virus#viral hemorrhagic fever
1 note
·
View note
Text
I’m currently in a Marburg Virus Vaccine Trial (I was in a successful Ebola Vaccine Trial in 2015, collecting those hemorrhagic fevers!)
What amused me was that my vaccination visit coincidenced with the Murderathin Equinox event, so I was wearing my heart very much on my sleeve for the first 5 visits…
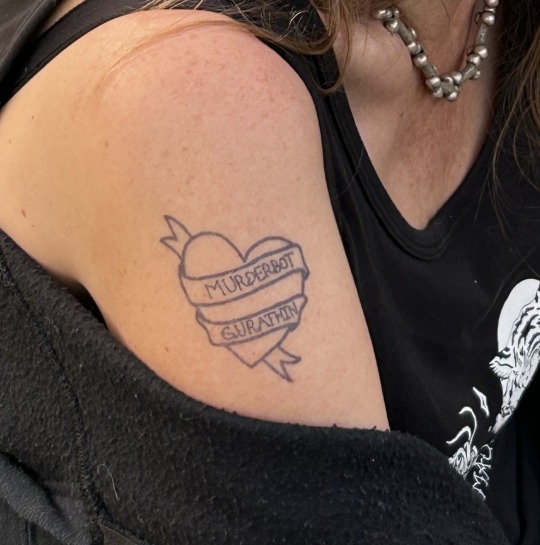
They injected right in Murderbot’s name…not that you could see the injection site (no side effects whatsoever— same as the Ebola Vaccine)
The temporary tattoo lasted ~2 weeks—much longer than any inflammation at the injection site
I did recommend the books to all the staff at the vaccine centre…

#murderbot#the murderbot diaries#murderbot diaries#gurathin#secunit#gurathin my beloved#murderathin#marburg virus#vaccines#vaccines work#ebola#vaccine trials#tattoos#temporary tattoos#Murderbot Gurathin equinox
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mereka telah meletakkan suar magnet, jadi bukan sahaja orang akan diubah secara biologi, tetapi mereka akan ditandakan.
Dan ini dimiliki dan dikendalikan oleh Rockefeller.
Ini adalah sebahagian daripada inisiatif Barcode for Life untuk menandakan dan mengenal pasti semua bentuk kehidupan.
Tiada lagi bentuk kehidupan yang suci.
Jadi, itulah yang mereka lakukan, mereka mengubah kita sedikit supaya kita boleh dipatenkan.
Situasi COVID ini adalah pengenalan pertama bagi sebuah konstruksi, satu bentuk kehidupan baru.
Mereka telah belajar cara menggabungkan kehidupan biologi dan robotik.
Dan tujuannya adalah untuk pemusnahan, kerana mereka tidak mahu apa-apa dari dunia lama.
Mereka mahukan dunia baru dan mereka mahu menjelang 2025 semua manusia lama dihapuskan.
Dan mana-mana manusia mulai sekarang pada asasnya perlu direkayasa di makmal dan dipertingkatkan dan ditambah serta sebahagian daripada matriks.
Mereka sedang mengubah suai dan menyambung semula badan kita.
Setiap daripada kita sekarang mempunyai 20 hingga 30,000 nanozarah.
Mereka mahu meletakkan cip dalam otak manusia, tetapi mereka tidak mahu melakukan pembedahan.
Oleh itu, selepas bertahun-tahun, akhirnya mereka menghasilkan gel.
Gel ini dipanggil hidrogel atau titik kuantum, titik kuantum Bill Gates.
Jadi apa yang akan berlaku dengan vaksin adalah anda akan disuntik dengan vaksin itu dan kemudian ia akan membentuk dirinya sendiri.
Dan kemudian ia menyerbu ke seluruh tubuh anda dan melintasi penghalang darah-otak anda dan mengambil alih otak anda.
Ia menuai cecair dalam badan anda, kelembapan anda ketika ia tumbuh dan ia berkembang sehingga kita bukan lagi manusia.
Kita termakan.
Kami adalah nod dalam komputer kuantum dan diri biologi mati kerana tiada apa yang tinggal.
Satu-satunya cara untuk mengelakkannya adalah dengan mengatakan tidak kepada ujian COVID kepada vaksinasi.
Akan ada topeng hidrogel di mana setiap nafas yang anda ambil, anda akan bernafas dalam zarah hidrogel ini.
Mereka telah menyebarkan semua sin bios, nano, sin bios ini ke dalam badan kita.
Mereka boleh membawa racun dan dikatakan mereka menerima arahan bergerak dari frekuensi yang disasarkan kepada mereka.
Seperti yang saya katakan dengan topeng, ujian COVID dan vaksin, adalah penting untuk tidak mengambilnya.
Ia bioakumulatif, yang bermaksud semakin banyak yang anda perolehi, ia kekal di dalam badan anda dan ia tidak akan keluar.
#senjata boiologi#science#rockefeller#barcode#covid 19#covid#covid vaccine#nanoparticles#nanotechnology#project 2025#suntikan vaksin#vaksin#vaksinasi#vaksin bahaya#vaksin mrna#anti vaksin#vaccineinjury#vaccine damage#vaccine genocide#vaccine#vaccines#covid19#marburg virus#virus x#viruses#corona virus#virus#x virus#mrna#mrna vaccine
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is This the End?
Thank you for reading and following. I wanted to express my appreciation before this happens today in just a few hours and I become a zombie. No action is needed? Pffft! Plenty of action is needed. The reason? Continue reading Untitled

View On WordPress
#5g#alert#comedy#covid#eas#end of the world#funny#gaba#gabba#humor#marburg virus#pfizer#ramones#vaccine#zombie
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rwanda initiates vaccine study to stem the Marburg virus spread
#Ebola-like disease#experimental vaccine#healthcare workers#Marburg virus#Rwanda outbreak#Sabin Vaccine Institute#vaccine trial
0 notes
Text
Selon le Dr Rashid A. Buttar, les vaccins contre le Covid contiennent tous des cellules dormantes du virus Marburg (poison) encapsulées dans des nanoparticules lipidiques qui peuvent être activées à l'aide de fréquences 5G spécifiques. Les personnes vaccinées se comporteront comme des zombies car la fonction de leur cortex frontal cérébral a été endommagée.
Cela tuera des millions de personnes dans le monde, ce qui donnera à l'OMS le pouvoir de dicter la politique à tous les gouvernements. Dr. Rashid A. Buttar says the Covid shots all contain a dormant Marburg virus(poison) sleeper cells encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles which can be activated using specific 5G frequencies. The vaxxed will behave like zombies because their frontal cortex brain function have been damaged.
This will kill millions worldwide, giving the WHO the power to dictate policy to all governments.
0 notes
Text
Real weird seeing largely practical posts about the emergency alert tomorrow on Tumblr, all "if you have a secret phone, make sure to turn it off", then checking Twitter & seeing thousands of people declaring that the emergency alert is a 5G signal that will activate the Marburg virus nanobots hidden in every COVID vaccine and cause a literal, not metaphorical, zombie apocalypse
478 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Today, December 20, marks the official end of the Marburg Virus Disease outbreak in Rwanda. It has been 42 days – two full incubation periods – since the last confirmed case left the national Marburg treatment centre after testing negative.
In previous outbreaks, Marburg, which is caused by a virus related to Ebola, has killed up to 88 per cent of people infected. And Rwanda had never seen this disease within its borders before the current outbreak began in September. Despite Rwandan physicians having never encountered it before, the mortality rate observed in this outbreak is under 23 per cent – the lowest-ever death rate for a Marburg outbreak in Africa.
While the virus initially spread fiercely in two major hospitals in the capital Kigali and among family members of one of the initial cases, Rwanda’s rapid response, with implementation of strict infection prevention and control, isolation and containment of cases, prompt initiation of aggressive supportive care, delivery of investigational therapeutics and vaccines, and tracing and monitoring of contacts quickly brought the outbreak under control. The rate of new cases halved between the outbreak’s second and third weeks and dropped by around 90 per cent thereafter.
One of the most remarkable aspects of this response was an international effort, initiated and led by the Rwandan government, to administer thousands of doses of a promising experimental vaccine to front-line health workers under a clinical trial protocol, with the first subjects vaccinated in a remarkably short timeframe.
...
Rwanda, for its part, has invested heavily in its healthcare system and has incorporated epidemic preparedness into its national health policies. Rwanda has well-trained medical staff working in well-run hospitals and community-based health services. It has been investing in technology-based disease surveillance systems and its laboratories can handle fast, accurate diagnostic testing at scale.
In early September, after months of planning, Rwandan scientists and health officials joined CEPI and other private sector partners to walk through a “tabletop exercise” about the 100 Days Mission. It was through this in-person training exercise that key relationships between disease outbreak experts, Rwandan health authorities and researchers, vaccine developers and clinical trial specialists were cemented.
...
We also have no doubt that with the right focus and funding, such nationally-led, globally-supported, life-saving responses to novel disease outbreaks could be accomplished by any government in any region. By taking a proactive approach and using the 100 Days Mission as a game plan, all countries can get ahead of epidemic and pandemic threats and neutralise their catastrophic potential."
Read the full piece here: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/global-health/science-and-disease/partnerships-preparedness-halted-rwanda-marburg-outbreak/
https://www.telegraph.co.uk/global-health/science-and-disease/partnerships-preparedness-halted-rwanda-marburg-outbreak/
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
By Tulio de Oliveira
Dr. Oliveira is the director of the Centre for Epidemic Response and Innovation in South Africa.
As a virus scientist in South Africa, I’ve been watching with dread as H5N1 bird flu spreads among animals in the United States. The pathogen poses a serious pandemic threat and has been detected in over 500 dairy herds in 15 states — which is probably an undercount. And yet, the U.S. response appears inadequate and slow, with too few genomic sequences of H5N1 cases in farm animals made publicly available for scientific review.
Failure to control H5N1 among American livestock could have global consequences, and this demands urgent attention. The United States has done little to reassure the world that it has the outbreak contained.
The recent infection of a pig at a farm in Oregon is especially concerning as pigs are known to be “mixing bowls” for influenza viruses. Pigs can be infected by both avian and human influenza viruses, creating a risk for the viruses to exchange genetic material and potentially speed up adaptation for human transmission. The H1N1 pandemic in 2009 was created and spread initially by pigs. Beyond the risks to its own citizens (there are over 45 cases of people in the United States getting the virus in 2024), the United States should remember that the country where a pandemic emerges can be accused of not doing enough to control it. We still hear how China did not do enough to stop the Covid-19 pandemic. None of us would want a new pandemic labeled the “American virus,” as this could be very damaging for the United States’ reputation and economy.
The United States should learn from how the global south responds to infectious diseases. Those of us working in the region have a good track record of responding to epidemics and emerging pandemics, and can help the United States identify new virus strains and offer insights into how to control H5N1. This knowledge has not come easily or without suffering; it has developed from decades of dealing with deadly diseases. We’ve learned one simple lesson: You need to learn your enemy as quickly as possible in order to fight it.
We did this during Covid. In November 2021, my colleagues and I, and others in Botswana, discovered the Omicron variant. We quickly and publicly warned the world that it could rapidly spread. This kind of transparency is not always easy because it can come at large economic cost. For example, after we shared our Omicron discovery, countries around the world imposed travel bans on South Africa ahead of December holidays, spurring backlash. Our team received death threats, and we needed security for our labs. One estimate suggests South Africa lost $63 million in canceled bookings from December to March.
But it was the right thing to do. That’s why it’s so frustrating that genomic sequences of H5N1 animal cases in the United States are not quickly made available. Sharing genomes of virus samples immediately is crucial for understanding the threat and giving the world time to prepare, including developing antivirals and vaccines. Rwanda, for example, was recently bold enough to go public with the detection of the deadly Marburg virus. Health responders there worked around the clock, and within about a month, they seem to have controlled the outbreak. Other countries in Africa have similarly and openly shared data about the spread of Mpox.
I’ve worked for decades with American scientists, and this summer I toured many of the country’s top scientific research institutions and was a speaker at one of its largest annual virology meetings. I know how flabbergasted many American scientists are about the country’s slow response to the H5N1. One highly respected American virologist, David O’Connor, told me that “it seems that the United States is addicted to gambling with H5N1. But if you gamble long enough, the virus may hit a jackpot.” A jackpot for the virus would fuel a global pandemic.
It is time to respond forcefully to this threat. The world’s scientists are here to help, in the same way as the United States has helped us so many times. Countries need to continue to support one another; we need an international scientific and medical force that can work together to respond to new epidemics and potential pandemics, including diagnosing and genetically analyzing every single sample of H5N1.
I understand that it’s not easy to persuade businesses, such as the meat and dairy industries, to allow the testing of all of their animals and staffs, and to make that data public quickly. But I also know that in the end, doing so protects lives, lessens economic damage and creates a safer world.
The world cannot afford to gamble with this virus, letting it spread in animals and hoping it never sparks a serious outbreak — or crossing our fingers that its effects won’t be serious in people. Time will tell. I hope we are not watching the start of a new pandemic unfold, with both the American and the international communities burying our heads in the sand rather than confronting potential danger.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Goodbye forever to the Marburg virus outbreak in Rwanda. In real life: 27th September to 20th December 2024. And in my life: 12th April to 20th April 2025. It felt like an eternity, but now it's all over. Goodbye Dr Yvan Butera, Minister for State of Health. Goodbye the study authors with the same surname of Sibomana. Goodbye Minister of Health Dr Sabin Nsanzimana. For some reason the Sabin vaccine with emergency access shared your name. Goodbye my friends. Goodbye Goodbye Goodbye
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Epidemik" Marburg Akan Diaktifkan Dalam Vaxxed (Melalui Lipid Nanopartikel) dan 5G (Isyarat Berdenyutan 18 GHz)
Marburg akan diaktifkan dalam Vaxxed melalui 5G
Todd Callender di The Prather Point untuk membincangkan patogen Marburg yang dijangka menjadi sumber PLANdemic seterusnya, yang akan digunakan untuk memaksa mereka yang tidak disuntik masuk ke kem kuarantin FEMA di mana tembakan bunuh akan diberikan.
#vaksin#vaksinasi#vaksin bahaya#vaccines#vaccine#vaccineinjury#vaccine damage#vaccine genocide#vaccinations#marburg#marburg virus
1 note
·
View note
Text
by Michael Nevradakis, Ph.D.
The U.S. has committed $667 million to the World Bank’s Pandemic Fund, a “multilateral financing mechanism dedicated to strengthening pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response.”
Including the U.S. commitment, the fund raised nearly $1 billion in its latest pledge campaign — half of its $2 billion target — amid warnings of a greater-than-50% chance of a new pandemic in the next 25 years.
The Pandemic Fund was established in 2022 by the member states of the G20. Its largest private contributor — at $15 million — is the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, which also holds seats on the fund’s governing board.
Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, a global public-private partnership that promotes vaccines — and is heavily funded by the Gates Foundation — also holds a seat on the Pandemic Fund’s board.
In an op-ed published last week in Fortune, Drs. Chatib Basri and Sabin Nsanzimana, co-chairs of the Pandemic Fund Board, said the “rapid spread of mpox and bird flu, and the recent Marburg virus outbreak, underscore the immediate need for new and sustained investments in pandemic preparedness to bolster our collective defenses.”
Fear of mpox and bird flu helped the fund reach commitments totaling $982 million at last week’s G20 Finance and Health Ministers’ joint meeting in Brazil. The fund also secured “co-financing from international organizations” totaling $1.8 billion.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

I’ve managed to combine two of my passions! I’m currently participating in a vaccine trial (new vaccine against Marburg Virus) and I have a (temporary) Murderbot/Gurathin tattoo for the Equinox event
This (being vaccinated in a MB/G heart tattoo) was not intentional—they usually vaccinate my left arm—but you know, reasons*
I have recommend The Murderbot Diaries to several scientists working on the trial
Spot the vaccination site!
*I have a real tattoo on the left arm, they preferred to inject in tattoo-less skin
#murderbot#the murderbot diaries#murderbot diaries#gurathin#secunit#gurathin my beloved#murderathin#vaccines#vaccine#vaccine trial#MBGequinox#equinox event
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Scientist Working Towards A Vaccine For Filoviruses
Filoviruses are among the globe's most lethal—indeed, so dangerous they can be handled only in high-security laboratories. Yet, more than five decades after the discovery of the Marburg virus and nearly 50 years after the first outbreak involving its infamous cousin—the Ebola virus—questions still abound about the family Filoviridae.
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-04-scientists-vaccine-filoviruses-ebola-deadly.html#google_vignette
0 notes
Text
1. Introduction to Animal Virology & Immunology
Animal virology is the study of viruses that infect animals, their replication mechanisms, pathogenesis, and transmission. It plays a crucial role in veterinary medicine, zoonotic disease control, and vaccine development. Animal immunology focuses on the immune response of animals to infections, vaccines, and immunotherapies, providing insights into disease prevention and treatment.
Understanding animal virology and immunology is essential for combating viral outbreaks, protecting livestock health, preventing zoonotic spillovers, and ensuring food security.
2. Major Animal Viruses & Their Impact
Animal viruses can be categorized based on their genome type (DNA or RNA viruses) and the species they infect. Some key viruses include:
🦠 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) – Affects cattle, pigs, and sheep, causing economic losses. 🦠 Avian Influenza Virus (AIV) – Highly contagious in poultry; some strains (e.g., H5N1, H7N9) can infect humans. 🦠 African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) – A deadly disease in pigs with no effective vaccine. 🦠 Rabies Virus – A fatal zoonotic virus affecting mammals, including dogs and wildlife. 🦠 Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) – Affects poultry, causing respiratory and neurological issues. 🦠 Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) – Affects pigs, leading to reproductive failure and respiratory illness. 🦠 Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV) – Causes immunosuppression and reproductive issues in cattle. 🦠 Canine Parvovirus (CPV) – A severe viral disease affecting dogs, especially puppies.
3. Immune Response in Animals
The animal immune system defends against viral infections through innate and adaptive immunity:
🔹 Innate Immunity – The first line of defense, including barriers (skin, mucosa), phagocytes, and interferons. 🔹 Adaptive Immunity – Involves B cells (antibody production) and T cells (cell-mediated immunity). 🔹 Cytokines & Interferons – Proteins that regulate immune responses and inhibit viral replication. 🔹 Mucosal Immunity – Crucial in protecting against respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses.
4. Diagnostic Techniques in Animal Virology
🔬 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) – Detects viral DNA/RNA with high accuracy. 🔬 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) – Identifies viral antigens and antibodies in serum. 🔬 Virus Isolation & Culture – Growing viruses in cell cultures for study. 🔬 Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) – Identifies novel and emerging viruses. 🔬 Serological Tests – Detects immune responses to viral infections.
5. Vaccines & Immunotherapy in Veterinary Medicine
💉 Live Attenuated Vaccines – Weakened viruses that provide strong immunity (e.g., Newcastle disease vaccine). 💉 Inactivated Vaccines – Killed viruses, safe but may require boosters (e.g., rabies vaccine). 💉 Recombinant Vaccines – Genetically engineered vaccines for precise immune response (e.g., FMDV vaccines). 💉 mRNA Vaccines – An emerging technology for rapid vaccine development. 💉 Monoclonal Antibodies – Used for targeted virus neutralization and treatment.
6. Zoonotic Viruses & One Health Approach
Many animal viruses can jump to humans (zoonoses), making virology crucial for public health. Examples include:
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2) – Originated in animals and caused global pandemics.
Influenza A Virus (H5N1, H1N1, H7N9) – Spreads from birds to humans.
Rabies Virus – 100% fatal in humans if untreated.
Ebola & Marburg Viruses – Spill over from bats to primates and humans.
The One Health approach integrates human, animal, and environmental health to prevent zoonotic spillovers.
7. Emerging Trends in Animal Virology & Immunology
🚀 AI & Machine Learning in Virology – Predicting viral outbreaks and vaccine efficacy. 🚀 CRISPR-Based Antiviral Strategies – Precision gene editing to fight viral infections. 🚀 Nanotechnology in Vaccine Delivery – Enhancing immune response through nano-vaccines. 🚀 Synthetic Biology for Virus Control – Engineering antiviral peptides and genetic resistance. 🚀 Microbiome & Immunity Research – Exploring gut microbiota's role in immune modulation.
Biotechnology Scientist Awards
Visit Our Website : http://biotechnologyscientist.com
Contact Us : [email protected]
Nomination Link : https://biotechnologyscientist.com/member-submission/?ecategory=Membership&rcategory=Member…
#sciencefather#researchawards#Scientist#Scholar#Researcher #AnimalVirology #VeterinaryImmunology #ZoonoticDiseases #VirusResearch #VeterinaryVaccines #LivestockHealth #OneHealth #VeterinaryScience #AnimalInfectiousDiseases #AvianFlu #ASFV #RabiesPrevention #FMDV #CanineVirology #MolecularVirology #CRISPRBiotech #AnimalHealth #VeterinaryMedicine #PCRDiagnostics #VeterinaryVaccination #EmergingViruses #BovineHealth #SwineFlu #VeterinaryEpidemiology #BiotechInnovation #Immunotherapy
👉 Don’t forget to like, share, and subscribe for more exciting content!
Get Connected Here: =============
Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61572562140976
Twitter : https://x.com/DiyaLyra34020
Tumblr : https://www.tumblr.com/blog/biotechscientist
Blogger: https://www.blogger.com/u/1/blog/posts/3420909576767698629
Linked in : https://www.linkedin.com/in/biotechnology-scientist-117866349/
Pinterest : https://in.pinterest.com/biotechnologyscientist/
0 notes
Text
An untreatable Ebola-like virus is on the rise in Tanzania, global health chiefs have warned.
Marburg, one of the deadliest pathogens ever discovered, has already infected nine people, killing eight of them.
There are currently no vaccines or treatments available meaning medics are forced to focus on helping patients survive the infection instead.
0 notes