#maize production increase
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Decline of Wheat Farming in Kenya as Farmers Shift to Maize Farming
The area under cultivation of wheat in Kenya has been falling since 2019 as farmers shift to maize farming, according to data from the KNBS. In 2023, the area under wheat cultivation was 104,440 hectares compared to 2022 when it was 119,554 hectares, with production decreasing as a result. On the flip side, maize cemented its position as a staple food crop with the area dedicated to maize…
#agricultural productivity Kenya#bean imports Kenya#crop production in Kenya#Drought-resistant crops#fertilizer subsidies Kenya#food security Kenya#Irish potato farming#Kenya agricultural trends#Kenya crop cultivation#maize farming subsidies#maize farming trends#maize production increase#maize vs wheat farming#Mwea irrigation scheme#Narok wheat production#Quelea birds pest Kenya#rice production in Kenya#sorghum farming Kenya#wheat farming in Kenya#wheat production decline
0 notes
Photo

Agriculture in the Fertile Crescent & Mesopotamia
The ancient Near East, and the historical region of the Fertile Crescent in particular, is generally seen as the birthplace of agriculture. The first agricultural evidence comes from the Levant, from where it spread to Mesopotamia, enabling the rise of large-scale cities and empires in the region.
In the 4th millennium BCE, this area was more temperate than it is today, and it had fertile soil, two great rivers (the Euphrates and the Tigris), as well as hills and mountains to the north.
The Origins of Agriculture
The birth of agriculture was a pivotal moment in human history that allowed the earliest civilizations to arise in the Fertile Crescent. Despite it being called the "Cradle of Civilization", we now know that agriculture (and human civilization) also arose independently in other regions of the world. In central America, people domesticated maize and beans, and rice and millet and pigs were first domesticated in China, both without knowledge of earlier advances in the Near East.
The advent of agriculture occurred gradually in the hill country of south-eastern Turkey, western Iran, and the Levant, most likely because the region happened to be home to a wide range of plants and animals that lend themselves to domestication and human consumption. Fig trees were cultivated in modern-day Jordan by around 11,300 BCE. Wheat and goats were domesticated in the Levant by 9000 BCE, followed by peas and lentils in the Fertile Crescent and northern Egypt around 8000 BCE and olive trees in the Eastern Mediterranean by 5000 BCE.
Cattle was first domesticated around 8500 BCE, most likely from wild ox (aurochs) in the Near East. Based on recent genetic analyses of ancient cattle bones, it is estimated that all modern cattle in the world is descended from as few as 80 animals that were originally domesticated.
Horses were domesticated in the western Eurasian steppe by 4000 BCE and spread to the Near East at some point in the late 3rd millennium BCE. Grapevines were domesticated in modern-day Iran around 3500 BCE and spread to the Levant and Egypt by 3000 BCE, marking the end of the transition to agriculture. Even today, 90% of our calories come from foods that were domesticated in this first wave of the agricultural revolution.
Agriculture started most likely because hunter-gatherers who collected grains would have had to take them back to their camp in order to separate the grain from the chaff. During this process, some seeds inevitably fall to the ground. When humans returned to the same campsite the next year, cereals would be growing around the campsite, which they harvested again, causing more seeds to fall. As the amount of cereals around the site increased, the people stayed longer to harvest, eventually turning into semi-nomads with seasonal villages, such as the Natufian culture that flourished circa 12500-9500 BCE.
Over time, some of these semi-nomads decided to stay in their agricultural villages year-round to cultivate cereals, while others would continue as nomads. By 8500 BCE, the Middle East was home to many permanent villages whose inhabitants were primarily farmers. The agricultural revolution had begun. With the increase in food production from agriculture, more human life could be sustained, populations increased, and villages turned into cities that gave rise to the Mesopotamian civilizations. The historian Gwendolyn Leick writes:
By the seventh millennium BCE, the alluvial plains began to be cultivated, and by the fourth millennium, the first cities appeared in response to the need for an efficient agricultural administration. The first documents, pictographs written on clay, concerned the allocation of labor for fields and the distribution of the products. (Leick, 6)
It is important to note that the Fertile Crescent is not the only origin point of agriculture, but that there are other places all over the world where agriculture and the domestication of animals arose without any contact with the Fertile Crescent. Scholar Yuval Noah Harari writes:
Scholars once believed that agriculture spread from a single Middle Eastern point of origin to the four corners of the world. Today, scholars agree that agriculture sprang up in other parts of the world not by the action of Middle Eastern farmers exporting their revolution but entirely independently. People in Central America domesticated maize and beans without knowing anything about wheat and pea cultivation in the Middle East. South Americans learned how to raise potatoes and llamas, unaware of what was going on in either Mexico or the Levant. China's first revolutionaries domesticated rice, millet and pigs. America's first gardeners were those who got tired of combing the undergrowth for edible gourds decided to cultivate pumpkins. New Guineans tamed sugar cane and bananas, while the first West African farmers made African millet, African rice, sorghum and wheat conform to their needs. (Chapter 5)
Continue reading...
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
The UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization coined CSA in 2009 to describe practices aimed at increasing farm resilience and reducing the carbon footprint of a global food system responsible for up to 37 percent of annual greenhouse gas emissions. Since then, however, observers say that CSA has been usurped by the Gates-led corporate alliance, with programs like Water Efficient Maize for Africa serving as green-painted Trojan horses for industry. “CSA is an agribusiness-led vision of surveillance [and] data-driven farmerless farming, [which explains why] its biggest promoters include Bayer, McDonnell, and Walmart,” said Mariam Mayet of the African Centre for Biodiversity. “From a climate perspective, it entrenches the global inequalities of a corporate food regime. There’s no system shift at all.” Octavaio Sánchez, the grizzled director of Honduras’s National Association for the Promotion of Organic Agriculture, contends that policies that promote true resilience must focus on regenerating soils through the use of organic fertilizers, crop rotation, and the preservation of native seeds able to adapt to changing conditions. These are the cornerstones of a global agro-ecology movement that has emerged from the seed and food sovereignty coalitions of the past three decades. The peasant-led agro-ecology movement—with La Via Campesina and AFSA in front—rejects the familiar refrain from agribusiness promoters that it is condemning farmers to permanent poverty and stagnation. The movement’s position is supported by both a growing literature of case studies and the development of scientific agro-ecological practices. When Gates Foundation officers were preparing to launch AGRA in 2006, researchers at the University of Essex published a study showing that agro-ecological practices increased yields by an average of nearly 80 percent across 12.6 million farms in 57 poor countries. The authors concluded that “all crops showed water use efficiency gains,” which led to “improvements in food productivity.” The UN’s High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition recommended in 2019 that governments support agro-ecological projects and redirect “subsidies and incentives that at present benefit unsustainable practices,” a judgment based on similar studies undertaken around the world.
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deforestation is costing Brazilian farmers millions
Without trees to circulate moisture, the land is getting hotter and drier

DECADES OF INCREASING maize and soyabean production have turned Brazil into an agricultural powerhouse. They have also led to the destruction of vast swathes of the Amazon rainforest. That has long put farmers and environmentalists at loggerheads. But a study released in October by the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG) and Rainforest Foundation Norway (RFN) shows the extent to which deforestation is hurting farmers too.
The report shows that the practice of clear-cutting (removing all trees from a given area) in the Brazilian Amazon led to reduced crop yields, resulting in total economic losses of around $1bn between 2006 and 2019. After accounting for production costs, the net revenues for soyabeans dropped by 10% over that time, while maize revenues dropped by 20%. Beyond the balance-sheet, Anders Krogh, a specialist forest adviser at RFN, says these findings demonstrate the danger deforestation poses to global food security.
When ancient forests become rolling plains, a delicate balance of water cycles is disrupted. As trees respire, they convert water into vapour, which goes on to form large, dense rain clouds, and has a cooling effect on the region. This moisture-recycling process also influences atmospheric circulation, which plays a key role in temperature regulation in the Amazon basin.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#economy#farming#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/mochinomnoms/750399534369275905/your-talk-about-museums-and-ancient-artifacts
No no, please, do tell about the agriculture of Mexico! They made islands for agriculture?? What type of products grew on them? How did they work??
Do you have any recommendations of sites or works to see more of it?
Also you should see the type of economy Incas had, like, they didn’t have a writing system; which is why keeping languages like Quechua really complicated, and their economy was more family based? It’s kinda complicated to explain for me but it’s more akin to trading than anything modern in my opinion.
Chinampas! They're very cool and a super ingenious method of agriculture that doesn't affect the rainforest around them but utilizes the lakes! I'll be using this and this as my main source to reference.
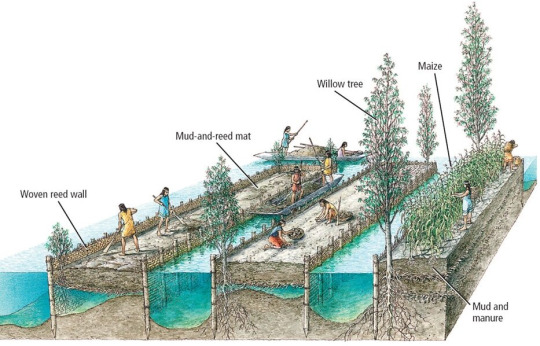
"Chinampa system is an historical system adapted to face hydrologic and climatic constraints and the pressure by the high city’s food demand. The chinampa farmers have been able to handle certain balance between the sustained yield and the environmental and technological management factors. This ecosystem performance has been based on the biological stability improvement, including sophisticated farming methods such as multiple cropping and shift of crops."
As you can see, they're man-made and developed by the Mexica (Aztecs) in the 14th century in the lakes of Xochimilco and Chalco, which surround Lake Texcoco, the lake that Mexico City takes residence in.

They're best described as “floating gardens” and due to the nutrient rich materials used to built them, are very fertile and can grow a great variety of crops. This of course includes Mexico's staple crop of maiz, but also beans, squash, tomatoes, chili peppers, and even flowers. The chinampas system provides a built-in natural irrigation system, and were home to aquatic wildlife and birds. This benefits the system further, as these animals increase the fertility and nutrients in the water and soil. There was also a drainage system, which facilitated the movement of water and sediments!
There were some cultural practices in association with chinampas, but they're best associated with the sort of 'urbanization' that Tenochtitlan was going under as the Mexica grew.
There have been much more recent studies done on the chinampas system, as modern agriculture as we know it is highly unsustainable due to lack of land and the general environmental concerns around agriculture. Utilizing chinampas in modern agricultural system has several benefits which include space efficiency, biodiversity, sustainable water management, carbon sesquention (migating climate change), and community engagement.
The last is particularly important, as it involves local communities in food production and builds on the concept of 'third-spaces' for people. Third spaces are typically places that individuals can spend time with their communities without the need to spend money for services or products. Libraries are the best example of this, but there have been others that have been lost over time.
This is not to say that chinampas don't exist anymore! They very much due primarily in San Gregorio, Xochimilco, Mexico City. THere are also some in San Luis, Tiahuac, and Mixiquic.


Other countries around the world have been inspired by chinampas, such as the Floating Gardens of Bangladesh, the Green Float project in Osaka Bay, Japan, and the Urban Rivers project in Chicago, USA.
There are some difficulties in maintaining current chinampas and bringing them back, as many of the original lakes were drained by the Spanish which reduced their ability to support agriculture. Earthquakes have also damaged them and the canals, as well as the scarcity of fresh water, pesticides, climate change, urban development, and water pollution.
I've gone on a bit long now, but I am familiar with the Inca and Quechua communication system you are referring to! It's a system based on knots if I'm not mistaken! I might be inclined to go into that in a future date!
#mochi asks#professor mochi#chinampas my beloved#nowadays theyre a popular tourist attraction#i think ryan and shane even went to a haunted one during buzzfeed unsolved
13 notes
·
View notes
Text


People
Hunger Has Natural Causes, Right?
Despite the fact that the world produces 1.5 times as much food as is needed to feed the human population, starvation and famine are endemic to modern capitalism. 900 million people die from starvation each year, but there is no global shortage of land to grow food. The UN estimates that there is enough land to feed a world population of 14 billion people. But what is it being used for? As in the ‘developed’ North, large landowners control the vast majority of land. In 83 countries, 3% of farmers control 79% of farmland, much of it left unused in order to maintain profits. Big Food made over $7bn profit from the South in 1990, and probably far more through transfer payments. It uses its economic power to force down the prices of rice, coffee, sugar, cocoa and cotton. Average prices in 1989 were 20% down on those of 1980. This led to an increase in foreign debt for Southern countries, with consequent increased economic hardship for the poor majority (higher taxes, inflation, etc.). Brazil has an area of farmland the size of India left uncultivated while 20 million rural poor are landless; the richest 1% owns 15 times as much land as the poorest 56% of Brazilian farmers. In Guatemala, 2% of landowners own 66% of the land. In the Philippines agribusiness producing sugar, cotton and pineapples for export has pushed 12 million peasants into the lowland forests.
Drought in Africa is part of a millennia-long cycle that human societies adapted to. It is cash crop exploitation, the market economy and taxation that produce starvation, not drought. During the 1970s, when famines first began to be reported regularly, ships that brought relief supplies to the port of Dakar left carrying peanuts, cotton, vegetables, and meat. In Bangladesh, often cited as the model for the Malthusian argument, 90% of the land is worked by sharecroppers and labourers. Many starved after the 1974 floods, while hoarders held on to four million tons of rice. In the mid-80’s severe famines occurred in the Sahel countries of Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger, Senegal and Chad yet during the same period record harvests of cotton were exported to the industrial centres of the world.
Cash crops go to feed the global supermarket, yielding higher profits for international capital and accelerating global industrialisation. Mexican soil and labour supplies almost 70% of the US market for much winter and early spring vegetables. The result is that agriculture for local consumption is squeezed out and the prices of staple foods rise. Up to 50% of total meat production in Central America is exported, mainly to North America. The “Green Revolution” of the 1970s and 1980s, that the ruling class said would feed the hungry, has in fact only supplied the global supermarket. The same will certainly be true of the ‘wonder crops’ of the GM revolution. The corporate claims that GM and industrial food production in general will ‘feed the world’ are straightforward lies. The maize/soya/ animal product system they are pushing so heavily is not a rational way to produce food — an acre of cereal is estimated to produce 5 times as much protein as one devoted to meat production, an acre of legumes (beans, peas, lentils) 10 times as much and an acre of leafy vegetables 15 times as much.
#hunger#humans#world hunger#classism#ecology#climate crisis#anarchism#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Emerging infectious agents: an unusual case of Metapneumovirus pneumonia in an adult patient by Graziana Francesca Greco in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
Abstract
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV), a relatively new virus, is a common cause of acute respiratory infection, especially common in the pediatric population. Despite hMPV infection in adults is possible, this rarely results in serious clinical manifestation. Here, we describe a hypoxemic respiratory failure related to pneumonia in an adult patient in whom hMPV was detected in respiratory samples.
Keywords
Human Metapneumovirus; SARS-CoV-2; Covid-19.
CASE HISTORY
A 61-yr-old caucasian man presented to the Emergency Department (ASST Mantua Hospital, Mantua, Italy) with fever up to 39°C, poorly responsive to antipyretics, nocturnal dyspnea and productive cough with mucus-purulent sputum for three days. On physical examination he appeared in good general condition, collaborating and oriented. The following parameters were recorded: blood pressure 140/90mmHg, heart rate of 100 beats min-1; respiratory rate of 23 breaths min-1; and body temperature of 38.4°C. His arterial oxygen saturation on room air was 87%. Chest examination revealed abnormal breath sounds with rhonchi and fine crackles in the middle lobe and inferior lobes bilaterally, no wheezes were heard. Laboratory findings revealed lymphocytosis (81000 x 103/µl), low platelet count (113000 x 106/µl) and an increase in alanine transaminase value (59 U/L), total bilirubin value (1.13 mg/dL) and CPR value (112 mg/L). Room air arterial blood gas analysis showed a normocapnic hypoxemia: pH 7.43, carbon dioxide tension 40.5 mmHg, oxygen tension 60.4 mmHg, and HCO3 24 mmol L-1. The SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test on nasopharyngeal swab was negative. A chest radiograph showed multiple, small, patchy opacities in the right upper and middle lobe and no pleural effusion was observed. Based on these findings he was admitted to the Respiratory Department.
His medical history included chronic lymphocytic leukemia in follow-up which did not require any specific treatment. He denied taking any medications or to be a smoker, he drinks a glass of wine once a day and has no known allergies. The patient was a farmer who cultivates wheat and maize but he had no animal exposure and no travel history in the last few years. There is no family history or childhood history of respiratory complaints. He was vaccinated with three dosesagainst the SARS-CoV-2 infection (Pfizer) but not against the influenza virus.
Based on the patient’s presentation and testing results, on suspicion of bacterial pneumonia he was empirically treated with IV Piperacillin/Tazobactam, the patient required oxygen support at 3L min-1 and an inhalation therapy with Beclomethasone/Formoterol was set up ex adiuvantibus. In the following days, several microbiological investigations were carried out to determine the etiology of pneumonia: blood culture, urinoculture, sputum culture, Legionella, Haemofilus and Pneumococcus serologic tests, Legionella pneumophila and Pneumococcal urinary antigen test, all of which were negative.
A nasopharyngeal swab FilmArray Respiratory Panel Assay (NP FARP) was then requested: it was positive for human Metapneumovirus and the result was confirmed by repeating the test. For non responder fever and further increase of CPR (230 mg/l) and PCT (0.27 ng/ml), Levofloxacin and later Meropenem were added in the perspective of a resistant bacterial etiology. On the 6th hospitalization day a chest computed tomography (CT) scan was obtained (Figures 1 and 2) which demonstrated large opacities with gradient borders, distributed in the peribronchial area at the right upper lobe, middle lobe and both the lower lobes; they tended to the confluence configuring parenchymal consolidations with aerial bronchogram at the level of the cost-phrenic angle. Imaging also showed bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy (max diameter 3.4 x 2 cm), splenomegaly and absence of pleural effusion. Blood chemistry tests for HIV, Aspergillus antigen and galactomannan were also investigated but turned out negative. To rule out other infectious agents the patient underwent bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) into the middle lobe. BAL provides material for various microbiological and cytological tests: Gram stain, culture, Koch’s bacillus DNA, Galactomannan, Cytomegalovirus and P. Jirovecii and immunological analysis were negative. From respiratory virus panel on BAL only human Metapneumovirus was isolated, this unique microbiological data was according to the NP FARP’s result, thus supporting and confirming the new hypothesis of a viral pneumonia in an adult patient with probable secondary mild immunosuppression due to his hematological disease. About ten days after entering the ward, there was a gradual decrease of CPR and a progressive improvement in clinical conditions and respiratory function to allow the suspension of oxygen therapy. At the end of hospitalization, pulmonary function tests were performed and showed a restrictive syndrome (FEV1/FVC 76.2, TLC 68% and VC 79% of predicted) and mild reduction of diffusion capacity (DLCO 62% and KCO 99%), probably representing the residual functional impairment due to viral pneumonia. The patient finally suspended all therapies and at discharge was referred for a one-month follow-up visit.
DISCUSSION
Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV), a relatively new virus first discovered in 2001, has been detected in 4-16% of patients with acute respiratory infections [1] [2] [3]. In particular, a recent review of 48 previous articles, including 100,151 patients under the age of five hospitalized for CAP, identified this virus as a cause of pneumonia in 3.9% of patients [4]. A recent study of 1386 hospitalized adult patients identified hMPV pneumonia in only 1.64%, indicating that it was much less common than in the infant population [5]. Metapneumovirus causes disease primarily in infants, but rarely can infect immunosuppressed individuals and elderly as well. Seroprevalence studies have shown that 90-100% of 5-10 years old children have previous infection [6]. Reinfection can occur during adulthood because of defected immunity acquired during the first contact with hMPV and/or because of different viral genotypes. The incubation period varies widely but is typically 3-5 days. The disease severity depends on the patient's condition and it ranges from mild upper airway infection to life-threatening pneumonia or bronchiolitis [7]. Clinically, Metapneumovirus infection is often indistinguishable from RSV infection, particularly in the pediatric population, and common symptoms include hypoxemia, cough, fever, upper and lower airway infections and wheezing [8]. hMPV infant patients are often hospitalized for bronchiolitis and pneumonia [9]. In young adults, a flu-like syndrome with fever may occur in a small number of instances, but infection in geriatric subjects may cause severe clinical manifestations such as pneumonia and, in rare cases, death [10].
As described in this case, it was not surprising that antibiotics and corticosteroids were administered in most patients infected with Metapneumovirus mainly for two reasons: in most cases the specific diagnostic tests for hMPV are not carried out at admission and/or physicians prefer to continue steroid and antibiotic treatment to control potential unidentified bacterial infections in patients in which no etiological agent had been identified associated with hMPV infection. The overuse of these drugs could therefore be reduced through the adoption at admission of specific diagnostic tests for such etiological agent, especially if specific risk factors are present (age, immunodepression, etc.). In addition, the adoption of such tests could reduce the nosocomial spread of this virus, allowing an early isolation of the infected patient [11].
Conflicts of interest: The authors certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript. Funding: The authors report no involvement in the research by the sponsor that could have influenced the outcome of this work.
Authors’ contributions : All authors contributed equally to the manuscript and read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
#Human Metapneumovirus#sars cov 2#covid 19#jcrmhs#Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences quartile
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
WHY CHOOSING THIS STORE
The Natural Health Store is built entirely for people. You can also buy items at retail. Here products are manufactured and sold in a healthy and clean manner. Made naturally without any artificial fertilizers. You tell customers how to prepare products in a healthy way. The products produced in this route are low in cost and high in quality.It plays an important role in health. This is what people want in today's world. Using this method not only increases the immunity of a person but also plays an important role in their health. Many friends visit this Anganwadi. Its capable employees clear the doubts of the customers about its product.
STORE FACILITY
Cooling facility is also provided to prevent spoilage. Coconuts are produced in large quantities and sold to small scale enterprises at low prices. The company has its own coconut trees. Coconut water is produced without any additives. The price is low and the quality is high. The rice we use on a daily basis is grown in our own company. Rice is produced by organic farming without any admixture. Rice is also delivered to small shops. A customer service has been introduced for which you can report any defect in the goods.
Nutrition Value Of Milk:
Milk is the most essential food for man and child. It is rich in many nutrients. The most important of them are calcium, protein, vitamin D, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and zinc.
Natural Milk Preparation:
Natural milk productioncontains they own 10 acres of land and a green cow farm. It has 50 cows. Pure milk is obtained from these cows. These cows eat natural foods such as paddy, fodder crops, cotton paddy, groundnut paddy, maize straw and unfertilized fodder. The cow is very healthy by eating this. The milk produced by it is very clean and of good quality. The cow milk obtained from here is taken to the natural Anganwadi. It is also maintained in a clean manner. Cooling facility is also provided to prevent spoilage
Cow Milk Uses:
Normally used for drinking. Mostly used in small tea shops. Widely used in hotels and bakery shops. Widely used in bank and new offices. Festivals and wedding events play an important role Various food items, snacks and many other products are produced in it like curd, buttermilk, paneer, curd, ice cream, Butter, almond milk.
Milk Health Benefits:
⦁ Strengthens bones and plays an important role in maintenance. ⦁ Milk contains high quality protein which is essential for muscle growth and maintenance. ⦁ It plays an important role in controlling minor heart disorders and blood pressure diseases. ⦁ Promotes tooth growth and reduces tooth decay. ⦁ It also helps in weight gain. Reduces effects on gut health and digestive problems.
Nutrient Value Of Coconut:
Coconut is very important. highly versatile and nutritious, with different a range of culinary and health benefits. Coconut is combination of water, carbohydrates, protein, vitamins and minerals. Coconut is produced coconut milk, coconut oil etc.
Natural coconut oil preparation:
It has its own 30 acre coconut grove where coconut oil is produced organically. The trees are grown naturally without any admixture. Take the coconut from the coconut tree and break it into small pieces and dry it in the sun. It should be dried in the sun for two or three days.Pure coconut oil is made from the dry coconut without adding any artificial additives. The oil should be kept in the sun for two or three days. Then the oil is brought to our facility and packaged.
Advantages Of Coconut:
Coconut plays an important role in all households. Used to make more snacks. Cooking plays an important role. Coconuts are mostly used in festivals and temples. Coconut milk and coconut oil are used in large bakeries
Coconut Health Benefits:
⦁ Coconuts are rich in calcium and magnesium which gives good strength to the bones. ⦁ High consumption of coconut oil helps control blood sugar levels. ⦁ Helps to reduce body weight. ⦁ Being rich in fiber plays an important role in heart health. ⦁ Consuming coconut milk helps in skin growth. ⦁ Protects hair from stress, stimulates hair growth, eliminates dandruff problem. ⦁ Increases immunity, Drinking fresh water increases energy. ⦁ Being rich in fiber, it helps in digestion.
Advantages of health store:
⦁ Only fresh products available. ⦁ Materials are always clean. ⦁ You can also buy the item online. If there is any doubt about the goods then the customer can be contacted. ⦁ Products prepared without any adulteration. ⦁ The price will be low and the quality of the products will be high. ⦁ No shipping coast.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Designing A Traditionalist Commune
Inspired by chatting with @tradgirllife and @unprofessionalcat about this kind of thing and wanting to share my plans; this is going to be one long post.
Village Layout
Throughout, I will be presupposing a commune of c.100 families adding up to c.500 people. Also, because UK and US English sometimes use the same name for different plants and vice versa, all plants will also come with scientific names. Additionally, this is calibrated to the climate and ecology of Britain; adjust for where you live.
At the centre of the village is the church, which will also double as the meeting place for the village (this will be important later). It sits at the centre of 1000 acres of communally-held sheep pasture planted with clover, (trifolium pratense) dandelions (taraxacum officinale), yarrow (achillea millefolium) and maize (zea mays; this one is useful if the potato crop fails), with this same space including various other facilities - a printing shop, a blacksmith's, a stream for water and a glassworks. The dead are also buried here, with small, subtle gravestones.
Ringing that are houses (design will be discussed soon), each with an acre of land containing potatoes (peel helps feed chickens and a very dense, low-effort-to-prepare carbohydrate source), sweetcorn, beans and squash (the sweetcorn forms a trellis for the beans, the beans fix nitrogen for the sweetcorn and the squash helps both retain moisture) and carrots and onions (carrots ward off onion flies and onions ward off carrot flies), and a fruit grove with chickens (the trees provide the chickens with interesting insects to eat and that in turn keeps the trees pest-free). As for area, 4000 square feet (doubled to 8000 for paths and storage) will feed a single person on a vegetarian diet for a year. There are 43,650 square feet in an acre. 8000X5 = 40,000 for vegetables, with the remaining 3650 square feet being used for chickens and fruit.
Ringing that, in turn, is a forest of Himalayan birch (betula utilis) for firewood and writing material, Sitka spruce (picea sitchensis) for timber and resin/glue and white willow (salix alba) for baskets, painkiller and tannin (for leather-making) production with ponds containing tench (tinca tinca) and mallards (anas platyrhynchos) for meat and eggs (in addition, ground fish bones can be added to chicken feed). Ground shrubs will be similar to those in the sheep field.
House Design
Houses will be built out of straw bales, with a foundation of stones (to prevent damp seeping in), a coating of limewash (to add resistance to fire and water) and wooden cladding (to stop rain; Britain is very wet. Feel free to leave this out in a dry area). Straw bale building is cheap and (if you tie the bales tightly) very warm and surprisingly fire-resistant. However, I envision repairs and new houses leading to a gradual replacement with timber buildings. Rooves consist of a timber frame upon which is placed soil in which to grow herbs for consumption (for the UK I'm thinking oregano, yarrow, parsley, sage, rosemary and thyme). This will necessitate strong rooves with gentle slopes, but will be doable, and will increase cultivation space and take advantage of the UK's fairly high rainfall.
Inside, the centre of the house is a wood-burning stove over which the cooking is done. Surrounding that are chairs which people sit on to consume meals, with wooden bookcases (books are printed on birch bark, with charcoal-based ink, wool string and spruce resin for binding and a leather cover) and assorted ornaments. I'm a man, ornamenting houses isn't my thing - women and girls reading this, provide your ideas. Windows are fairly small due to local production limitations, and so there are quite a few of them. In winter, the house is lit with candles made from beeswax or tallow (so we'll want a few beekeepers) and reeds (from around the ponds), made by one of these processes.
To the side are bedrooms. These are fairly unadorned, consisting of a wooden bed, a mattress made from wool and/or feathers, a blanket and pillow of the same and some personal possessions. Also there should be a spinning wheel for the woman of the house to use.
To the back and just outside is the compost toilet. It consists of a wooden shack over a chamber for excreta and another chamber for composting. A bit of guttering funnels urine outside into a barrel of straw (also for composting). Washing is done in a metal tub, with soap made of animal fat or vegetable oil and wood ash.
Clothing
Clothes are made of wool, dyed with nettles (urtica dioica) for grey-green, dandelions for pale yellow, and whatever else is locally available. In addition, natural sheep colours give a range of white, grey, brown and black. Shoes will be made of sheepskin, and some people taking up shoemaking will thus be much appreciated.
In terms of clothing, I'm not particular about styles. I imagine that men will dress something like this and women something like this, but I am very much not particular. I'm a man.
Diet
As composed from the ingredients above, mostly potatoes accompanying vegetable stews of a considerable range. Some treats, such as pancakes, cider and meat, but mostly fairly plain.
Political System
The village is governed by two bodies - the magistrates and the assembly.
The magistrates consist of three randomly-selected adult citizens, with the proviso that they cannot have committed a crime in the last three years and they cannot serve consecutive terms. They meet weekly to judge crimes and set the agenda for the assembly.
The assembly consists of all adults of the community, meeting monthly to vote on proposed laws and actions and vote on applicants for citizenship. The citizenship can vote to modify proposed laws.
Due to the lack of state apparatus, crimes are punished by fines (for minor crimes, especially property crimes), exile (for major crimes - those who are exiled have their crimes, date of exile and sentence length tattooed on their non-dominant hands) or execution (for serious crimes, although this needs to be put up to the assembly and only violent or sexual crimes can be capital).
Note to say if you like this and/or would like to live here, reblog with any comments, questions or criticisms you have.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's switch to "Organic" Cigarettes

Inhaling smoke produced by burning cured tobacco leaves or any other herb is commonly referred to as smoking. While smoking cigarettes is bad for your health, smoking herbs is regarded to be good for your general well-being. Smoking natural herbs helps lessen smokers' cravings because many of them don't contain nicotine.
It is regarded as a helpful strategy for reducing the propensity to smoke and ultimately quitting. These days, herbal cigarettes come in well-liked flavours including menthol, cherry, and vanilla. According to Ayurveda, Ayurvedic Cigarette smoking is a daily habit.
It is applied both therapeutically and preventively. Many types of herbs have distinct health benefits when smoked.
Some advantages of several often used herbs are recommended for smoking.

1. Lobelia
It is frequently referred to as Indian tobacco, and it is highly helpful for quitting smoking because it is very similar to actual nicotine but without addictive qualities. Because they are completely herbal and have no negative side effects, organic cigarettes created from lobelia in betel leaves can be advantageous for smokers.
2. Peppermint
The nerves are calmed and blood circulation is improved by peppermint. It is a potent purifying substance that may revive and heal both the body and mind. Peppermint, which is renowned for its curative qualities, helps facilitate easy breathing with smoking herbal cigarettes by cleaning the lungs and respiratory passages.
3. Extract from gotu kola
This extract is intended to strengthen the liver, increase blood flow, boost memory, reduce inflammation, and relieve stress. Throughout the beginning of time, smoking herbal cigarettes was very useful to people who used the herb gotu kola to stay healthy.
4. Hops
Hops are one of the main components in Western folk medicine since they are a mild sedative that guarantees a relaxing effect. Physical urges can be suppressed with the aid of muscle relaxants and tonics containing hops.
5. Skullcap
Insomnia, hysteria, delirium tremens, anxiety, and withdrawal symptoms from tranquillizers are just a few of the illnesses that this powerful medicinal herb has reported to be helpful in treating.
It is high in vitamins and used as a sedative to support the central nervous system. It balances the neurological system and lessens neurotic apprehension. Moreover, it has been proven to be very successful in treating anxious headaches and restlessness. It is the best herb for organic cigarettes.
6. Wild Oat
Wild oat is a well-known herbal remedy that is frequently used to treat liver and kidney ailments. ailments and joint discomfort. It eases depression and is a natural tonic that both men and women use to increase vigour and vitality. Wild oat, which is well known for their antidepressant properties, is used to lessen stress and anxiety in organic cigarettes. Moreover, it has strong antioxidant properties that slow down the ageing process.
The Perks Of Herbal Cigarettes
Herb smoking has been practised for ceremonial, religious, and even medical purposes for thousands of years. By choosing herbal cigarettes instead, which are both environmentally and healthfully friendly, one can avoid all of these. Organic cigarettes have a variety of health advantages, some of which are covered below.
1. Tobacco Free
It's simple to find free herbal cigarettes, often known as tobacco free cigarettes. An assortment of consumable goods is used instead of tobacco. The mixture is made up of herbs including maize silk, rose petals, banana skins, and more. These cigarettes are typically used as an alternative to traditional tobacco products and as a quit-smoking aid.
2. Nicotine free
Because they are 100% tobacco and nicotine free and contain a special blend of all-natural herbs, nicotine free herbal cigarettes offer a healthier alternative to typical tobacco cigarettes without the addictive qualities of nicotine. The combination of relaxing herbal mixes is a trustworthy tobacco alternative and a fantastic place to start for anyone trying to give up smoking. When it comes to enhancing your health, herbal cigarettes can be an alternative to cigarettes.
3. Protective of passive smokers
More than 4,000 chemical compounds are inhaled when you smoke tobacco. Consider the defence and cleaning effort your respiratory system, as well as your entire body, are required to perform each time you smoke a cigarette. Not only are you impacted, but they are exposed to passive smoking, as well as your loved ones. On the other hand, herbal cigarettes pose no risk to the smoker or those around him.
Some claim that all forms of smoking are bad, however smoking organic cigarettes in moderation can improve your health. By smoking these herbal cigarettes, one can benefit from the medicinal properties of the herbs. Every herb, herbal smoke, herbal bud, and herbal smoking blend has unique properties and therapeutic benefits, therefore using herbs sparingly can improve health and solve issues.
FAQ
1. Do organic cigarettes pose any risks? Even though they are advertised as a healthier choice, organic cigarettes do not pose risks. 2. Does tobacco appear in organic cigarettes?
Nope, tobacco is not present in most organic cigarettes. Yet, no artificial fertilisers or pesticides were utilised in the growth of the herbal tobacco used in organic cigarettes. 3. Do organic cigarettes have fewer negative effects than regular cigarettes?
Regarding the herbs used in their manufacturing, organic cigarettes are not more dangerous than conventional ones. They don't contain tobacco. 4. Does the flavour of organic cigarettes differ?
Because they contain herbal tobacco, organic cigarettes may have a different flavour than conventional cigarettes.
Also read: Here is How Organic Cigarette Franchisors are Building a Nicotine Free Market
#herbal cigarettes#smoking organic cigarettes#organic cigarettes#clove cigarettes#nicotine free tobacco#best herbal cigarettes#herbal tobacco#herbal tobacco pipe
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Where Can You Find the Best Quality Cereals Exporters From Rajasthan?
Introduction
Rajasthan, the land of kings, is not only renowned for its rich cultural heritage and majestic forts but also for its agricultural prowess. The state is a significant contributor to India's agricultural output, particularly in the production of cereals. With its vast arid and semi-arid regions, Rajasthan has become a hub for cultivating high-quality cereals that are in demand both domestically and internationally. Among the many exporters in the region, Neelam International stands out as a leading name in the export of the best quality cereals from Rajasthan.

This article delves into the reasons why Rajasthan is a prime location for cereal production, the factors that contribute to the high quality of its cereals, and why Neelam International is considered one of the best quality cereals exporters from Rajasthan. We will also explore the global demand for Indian cereals, the export process, and the prospect of the cereal export industry in Rajasthan.
Rajasthan: The Cereal Bowl of India
Geographical Advantage
Rajasthan's unique geographical location and climatic conditions make it an ideal region for cereal cultivation. The state is characterized by its vast stretches of arid and semi-arid land, which are well-suited for crops like wheat, barley, maize, millet, and sorghum. The Thar Desert, which covers a significant portion of the state, has a distinct ecosystem that supports the growth of hardy cereal crops that can thrive in low-water conditions.
Soil Quality
The soil in Rajasthan is predominantly sandy and loamy, which is well-drained and ideal for cereal cultivation. The state's soil is rich in essential minerals and nutrients, which contribute to the high quality of the cereals produced. Additionally, the use of traditional farming methods combined with modern agricultural practices ensures that the cereals are of the highest quality.
Climate
Rajasthan experiences extreme climactic conditions, with hot summers and cold winters. These conditions are favourable for the cultivation of certain types of cereals, particularly those that are drought-resistant. The state receives limited rainfall, which necessitates the use of innovative irrigation techniques to ensure a consistent supply of water for the crops.
The Cereal Export Industry in Rajasthan
Global Demand for Indian Cereals
India is one of the largest producers of cereals in the world, and Rajasthan plays a significant role in this production. The global demand for Indian cereals has been steadily increasing due to their high quality, nutritional value, and competitive pricing. Indian cereals are exported to various countries across the globe, including the Middle East, Africa, Europe, and North America.
Export Process
The export of cereals from Rajasthan involves several steps, including cultivation, harvesting, processing, packaging, and transportation. The cereals are carefully selected and processed to ensure that they meet international quality standards. The packaging is done in a way that preserves the freshness and quality of the cereals during transit. The transportation process is also meticulously planned to ensure that the cereals reach their destination in optimal condition.
Government Support
The Indian government has been actively promoting the export of agricultural products, including cereals. Various schemes and initiatives have been introduced to support farmers and exporters in Rajasthan. These include subsidies, financial assistance, and technical support to improve the quality of cereals and enhance their export potential.
Neelam International: A Name Synonymous with Quality
Company Overview
Neelam International is a leading exporter of cereals from Rajasthan, with a reputation for delivering the best quality cereals to clients across the globe. The company has been in the business for several decades and has established itself as a trusted name in the cereal export industry. With a strong focus on quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, Neelam International has become a preferred choice for buyers looking for high-quality cereals from Rajasthan.
Product Range
Neelam International offers a wide range of cereals, including wheat, barley, maize, millet, and sorghum. The company sources its cereals directly from farmers in Rajasthan, ensuring that only the best quality produce is selected for export. The cereals are processed and packaged using state-of-the-art technology to maintain their freshness and nutritional value.
Quality Assurance
Quality is at the core of Neelam International's operations. The company follows stringent quality control measures at every stage of the production process, from cultivation to packaging. The cereals are tested for various parameters, including moisture content, protein content, and purity, to ensure that they meet international standards. Neelam International is also certified by various international bodies, which is a testament to its commitment to quality.
Global Reach
Neelam International has a strong global presence, with clients in over 50 countries. The company has established long-term relationships with its clients, thanks to its consistent delivery of high-quality cereals and excellent customer service. Neelam International also participates in various international trade fairs and exhibitions to showcase its products and expand its reach.
Sustainability Practices
In addition to its focus on quality, Neelam International is also committed to sustainable practices. The company works closely with farmers to promote sustainable farming methods that minimize the environmental impact of cereal cultivation. Neelam International also invests in renewable energy and waste management initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint.
The Future of Cereal Exports from Rajasthan
Increasing Demand
The global demand for cereals is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by factors such as population growth, urbanisation, and changing dietary habits. Rajasthan, with its abundant cereal production, is well-positioned to capitalise on this demand. The state's focus on quality and sustainability will further enhance its reputation as a reliable source of high-quality cereals.
Technological Advancements
The adoption of advanced agricultural technologies is expected to play a key role in the future of cereal exports from Rajasthan. Technologies such as precision farming, drone surveillance, and AI-based crop monitoring can help improve crop yields and quality. Neelam International is at the forefront of adopting these technologies to enhance its production processes and maintain its competitive edge.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government's continued support for the agricultural sector will also contribute to the growth of cereal exports from Rajasthan. Initiatives such as the Agricultural Export Policy, which aims to double agricultural exports by 2025, will provide a boost to the cereal export industry. Additionally, the government's focus on improving infrastructure, such as roads and ports, will facilitate the smooth transportation of cereals to international markets.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future looks promising, there are also challenges that need to be addressed. These include the impact of climate change on cereal production, the need for better storage facilities, and the competition from other cereal-exporting countries. However, with the right strategies and investments, these challenges can be turned into opportunities for growth.
Conclusion
Rajasthan's unique geographical and climatic conditions, combined with its rich agricultural heritage, make it a prime location for cereal production. The state's focus on quality and sustainability has earned it a reputation as a reliable source of high-quality cereals. Among the many exporters in the region, Neelam International stands out as a leading name in the export of the best quality cereals from Rajasthan.
With its commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, Neelam International has established itself as a trusted partner for clients across the globe. The company's focus on sustainable practices and adoption of advanced technologies further enhance its competitive edge.
As the global demand for cereals continues to grow, Rajasthan is well-positioned to capitalise on this opportunity. With the support of the government and the adoption of advanced technologies, the cereal export industry in Rajasthan is poised for a bright future. Neelam International, with its strong global presence and commitment to quality, will continue to play a key role in this growth story.
In conclusion, if you are looking for the best quality cereals exporters from Rajasthan, look no further than Neelam International. With its unwavering commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, the company is your trusted partner for all your cereal export needs.
Figures and Facts:
Rajasthan's Contribution to India's Cereal Production:
Rajasthan is one of the top cereal-producing states in India, contributing significantly to the country's total cereal output.
The state produces over 10% of India's total wheat production and is a major producer of barley, maize, millet, and sorghum.
Global Demand for Indian Cereals:
India is the second-largest producer of wheat and rice in the world.
Indian cereals are exported to over 100 countries, with the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia being the major markets.
Neelam International's Global Reach:
Neelam International exports cereals to over 50 countries across the globe.
The company has a strong presence in the Middle East, Africa, Europe, and North America.
Government Initiatives:
The Indian government's Agricultural Export Policy aims to double agricultural exports by 2025.
The government has introduced various schemes to support farmers and exporters, including subsidies and financial assistance.
Sustainability Practices:
Neelam International promotes sustainable farming practices among its partner farmers.
The company has invested in renewable energy and waste management initiatives to reduce its environmental impact.
Keywords:
Best Quality CEREALS Exporters from RAJASTHAN
Neelam International
Cereal Export Industry
Rajasthan Cereal Production
Global Demand for Indian Cereals
Sustainable Farming Practices
Agricultural Export Policy
High-Quality Cereals
Cereal Export Process
Advanced Agricultural Technologies
By choosing Neelam International, you are not only getting the best quality cereals from Rajasthan but also supporting sustainable and ethical farming practices. The company's commitment to quality and customer satisfaction makes it the ideal partner for all your cereal export needs.
0 notes
Text
Record 70Million Bags of Maize Harvest: How Government Policies on Fertiliser Subsidies Are Paying Off
“Discover how Kenya’s record maize harvest of 70 million bags is reshaping the nation’s food security, driven by government subsidies and favorable weather conditions.” “Kenya’s maize harvest hits an all-time high! Learn about the factors behind the bumper crop and its impact on the country’s agricultural future.” “Explore the success story of Kenya’s maize harvest reaching 70 million bags,…
#agricultural policy#agricultural success#bumper crop#Crop management#crop yield#farming techniques#fertiliser subsidies#Food security#food supply chain#government subsidies#harvest season#Kenya Agriculture#Kenyan economy#kenyan farmers#Kenyan weather#maize bags#maize cultivation#Maize farming#maize farming challenges#maize harvest#maize harvest 2024#maize market#maize prices#maize production#maize production increase#maize storage#maize surplus#maize yield#record maize harvest#sustainable farming
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Choose the Right Chelated Micronutrient Fertilizer for Your Farm

Choosing the right chelated micronutrient fertilizer is essential for ensuring optimal crop health and maximum yield. While macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are crucial, micronutrients such as iron, zinc, manganese, copper, and boron are equally vital for plant growth.
At Central Biotech, we offer high-quality chelated micronutrient fertilizers designed to enhance nutrient uptake and soil fertility. Here’s how to choose the right one for your farm.
1. Understand Your Soil and Crop Needs
The first step in selecting the right fertilizer is identifying soil deficiencies and crop-specific nutrient requirements. Conducting a soil test helps determine which micronutrients are lacking.
Iron (Fe): Needed for chlorophyll production, crucial for crops like wheat, rice, and citrus fruits.
Zinc (Zn): Helps in enzyme function and growth, essential for cereals, maize, and fruit trees.
Manganese (Mn): Improves photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism, vital for legumes and vegetables.
Copper (Cu): Aids in protein synthesis, beneficial for grains and vegetables.
Boron (B): Supports flowering and fruiting, important for oilseeds and root crops.
2. Choose the Right Chelating Agent
Chelation prevents nutrients from binding with soil particles, ensuring better absorption by plant roots. Different chelating agents work in various soil conditions:
EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid): Ideal for neutral and mildly acidic soils, best for foliar applications.
DTPA (Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid): Suitable for alkaline soils, commonly used for iron and zinc fertilizers.
EDDHA (Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid)): Best for highly alkaline and calcareous soils, providing maximum nutrient availability.
3. Select the Right Application Method
Soil Application: Provides long-term nutrient availability, best for prevention of deficiencies.
Foliar Spraying: Quick absorption through leaves, ideal for correcting nutrient deficiencies rapidly.
4. Trust Central Biotech for Quality Micronutrients
At Central Biotech, we offer ISO 9001:2015 certified chelated micronutrient fertilizers that enhance crop productivity, soil health, and sustainability. With scientifically formulated solutions, we ensure maximum nutrient efficiency for your farm.
Conclusion
Choosing the right chelated micronutrient fertilizer is essential for healthy crops, increased yield, and sustainable farming. By understanding soil conditions, crop requirements, and chelating agents, you can maximize nutrient uptake and prevent deficiencies. Central Biotech provides premium chelates for iron, zinc, manganese, boron, and copper, ensuring your farm thrives.
Enhance your crop health and yield with Central Biotech’s premium chelated micronutrient fertilizers! Explore our products today at Central Biotech!
0 notes
Text
South Africa government green-lights yellow maize imports from Brazil

In some coastal areas of South Africa, it is cheaper to import yellow maize from South America than sourcing it locally.
Fears of a possible shortage of yellow maize have been averted with a decision by the national department of agriculture to allow yellow maize imports from Brazil.
The National Agricultural Marketing Council estimated earlier this year that it might be necessary to import 383 000 tonnes of yellow maize – a crucial ingredient in animal feed – amid shrinking local production and rising prices brought about by lower rainfall in the country’s maize-producing regions.
While price increases have moderated since the 19% rise between January and May, it is still R275-R300 per tonne cheaper for animal feed manufacturers in the Western Cape, Eastern Cape and possibly also parts of KwaZulu-Natal to import yellow maize than transport it locally from the production areas.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#south africa#south african politics#economy#farming#international politics#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Boom Sprayer Innovations: What’s New in Agricultural Spraying Technology?

Agriculture is constantly evolving, and farmers today need advanced equipment’s to increase productivity and efficiency. One such essential equipment’s is the boom sprayer. Over the years, boom sprayers have undergone several improvements to ensure better coverage, reduced chemical wastage, and higher crop yields. Mitra Boom Sprayer is at the forefront of these advancements, offering reliable and efficient spraying solutions for farmers.
In this blog, we will explore the latest innovations in boom sprayers and how they are transforming modern farming.
1. High-Precision Nozzles for Better Coverage (Single twin or Double twin)
One of the biggest innovations in boom sprayers is the development of high-precision nozzles. These nozzles ensure even distribution of pesticides, fertilizers, and herbicides, reducing the chances of over-spraying or under-spraying.
Mitra Boom Sprayer uses advanced nozzle technology to provide precise spraying, ensuring that every part of the crop gets the required amount of chemicals. This helps in saving resources while improving crop health and yield.
2. Uniform Spray Distribution Across Large Fields(Manual controller)
In traditional spraying methods, uneven distribution of chemicals can lead to ineffective pest and disease control. Modern boom sprayers are designed with wide, well-balanced booms that distribute sprays evenly across large areas.
Mitra Boom Sprayer comes with well-engineered booms that maintain a uniform height above the crop, ensuring consistent spray coverage. This means better protection and nutrition for crops with minimal chemical wastage.
3. Larger Tank Capacity for Increased Efficiency (HDPE Material)
Farmers working on large farms need a sprayer that can cover more area without frequent refilling. Boom sprayers now come with larger tank capacities, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Mitra Boom Sprayer is designed with a spacious tank, allowing farmers to spray large fields without interruptions. This saves time, fuel, and labor, making farming more cost-effective.
4. Adjustable Boom Height for Different Crops (Height adjustment upto 6ft)
Different crops require different spraying heights to ensure optimal application. Modern boom sprayers come with adjustable boom heights, allowing farmers to spray crops of various heights efficiently.
Mitra Boom Sprayer offers an easy-to-adjust boom system, making it suitable for spraying in diverse crops such as wheat, cotton, maize, and vegetables. This adaptability ensures maximum spray effectiveness for different types of farming.
5. Anti-Drift Technology to Reduce Chemical Wastage
Drift occurs when wind carries sprayed chemicals away from the intended area, leading to wastage and environmental concerns. Advanced boom sprayers now feature anti-drift technology, which helps in minimizing chemical drift.
Mitra Boom Sprayer uses specially designed nozzles and optimal pressure control to reduce drift, ensuring that chemicals reach the crops without being wasted. This makes spraying more efficient and eco-friendly.
6. Strong and Durable Frame for Longevity (Made up with MS material and processed with the powder coating to prevent from rusting)
Durability is a key factor when investing in farm equipment. Modern boom sprayers are now built with strong, corrosion-resistant frames to withstand tough agricultural conditions.
Mitra Boom Sprayer is made using high-quality materials that ensure long-lasting performance, even in harsh weather and rough terrains. This makes it a valuable investment for farmers looking for reliable equipment.
7. User-Friendly Operation for All Farmers (Easy to use and installed by trained service engineer)
Earlier, operating a boom sprayer required significant technical knowledge. Now, modern boom sprayers are designed with user-friendly controls, making them easy to operate for all farmers.
Mitra Boom Sprayer features a simple control system that allows farmers to adjust spray settings quickly and easily. Whether a farmer is new to mechanized spraying or an experienced user, Mitra Boom Sprayer makes the process smooth and hassle-free.
8. Low Maintenance for Cost Savings (Due to the high quality Diaphrgm Pump)
Maintaining farm equipment can be costly and time-consuming. Innovations in boom sprayer design have led to models that require less maintenance, reducing repair costs and downtime.
Mitra Boom Sprayer is designed with durable components and an efficient cleaning system, minimizing the need for frequent repairs. This ensures farmers get maximum usage with minimal maintenance costs.
9. Efficient Use of Pesticides and Fertilizers
Modern boom sprayers help in applying the exact amount of pesticides and fertilizers needed, reducing unnecessary use of chemicals. This helps in lowering costs while promoting sustainable farming.
With Mitra Boom Sprayer, farmers can achieve optimal chemical application, leading to healthier crops and higher yields without excessive chemical use.
10. Compact Design for Easy Storage
Space is often a concern for farmers when storing large machinery. Newer boom sprayers are now designed to be compact and foldable, making storage more convenient.
Mitra Boom Sprayer comes with a foldable boom, allowing farmers to store the sprayer easily when not in use. This ensures better space management and protection of equipment.
Conclusion
The latest innovations in boom sprayer technology are making farming more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. From high-precision nozzles to anti-drift technology and user-friendly controls, modern boom sprayers are helping farmers achieve better crop protection and increased yields.
Mitra Boom Sprayer is designed with all these advanced features, ensuring that farmers get the best spraying experience. Whether you have a small farm or a large agricultural field, Mitra Boom Sprayer is the perfect solution for your spraying needs.
Invest in Mitra Boom Sprayer today and experience the latest in agricultural spraying technology!
0 notes
Text


Biotechnology and the future of humanity
Biocide or Genocide?
The high cost of chemical and mechanical inputs and expensive new seed varieties favours large farmers over small; they are bankrupted, lose their land and end up either in the huge and squalid shanty towns and slums that surround so many majority world cities or as agricultural labourers on big farms or plantations. Here they may be one of the over 40,000 ‘Third World’ farm workers killed each year as a result of contact with agro-chemicals. A 1994 UN report estimated 1,000,000 people a year are made ill as a result of over- exposure to agro-chemicals. The increasing use of animal products as well as leading to the misery, waste and pollution of factory farming is also responsible for the erosion of biodiversity and peoples livelihoods in the majority world. For example almost all of Central America’s lowland and lower montane rainforest has been cleared or severely degraded mainly in order to raise cattle for export. The crops most grown under ‘Green Revolution’ and GM regimes of industrial food production are maize and soya, not for human consumption but for animal feed. Small scale organic farming systems based around plants and supporting the producers directly are being destroyed in favour of chemical soaked monocultures to feed the farm animals necessary to feed the animal product heavy global food economy.
Because ‘pests’ and ‘weeds’ can rapidly become immune to herbicides and biocides chemicals don’t even do what they say they do; pesticide use in the US increased by 500% between 1950–1986 yet estimated crop loss due to pests was 20%, exactly the same as in 1950. The damage done by the production and use of biocides and artificial fertilisers is almost unimaginable. Pesticide pollution of the natural world (air, water & soil) is one of the major reasons for the staggering loss of biodiversity (estimated at a loss of 30,000 species a year) we are witnessing as the world is slowly turned into a huge agro-chemical-industrial facility. Pesticide and artificial fertiliser pollution, along with other petro-chemical forms of pollution and increased exposure to radiation, are responsible for massive rates of cancer and birth abnormalities. Then there are the ‘accidents’ which show the system’s inhumanity even more clearly: such as the 1984 explosion at Union Carbide’s insecticide factory in Bhopal, India which left 3,000 dead and 20,000 permanently disabled. Or the less well-publicised events in Iraq in 1971–1972 when large quantities of wheat seed that had been treated with anti-fungus compounds containing mercury were ‘accidentally’ baked into bread. 6,000 neurologically deranged people were admitted to hospital and at least 452 died. Corporate propagandists would have us believe that these are unfortunate side effects of a beneficial technology we desperately need to ‘feed the world. Yet, as anyone who takes the trouble to find out the facts must be aware, the world produces more food than is necessary to feed the human population and the reasons people go hungry are landlessness, poverty, and social dislocation caused by capitalist oppression and war.
#genocide#biocide#classism#ecology#climate crisis#anarchism#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate#anarchy works
5 notes
·
View notes