#macska
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Portugal - Coimbra
370 notes
·
View notes
Text
All right, animorphs book club, i've read the first book yesterday and i have a Very Important Question.
So if they are morphing into specific, individual animals (this exact cat called Dude, not just generally a cat), does that mean if they'd acquired a tortoiseshell cat, every time they morphed into it, the exact pattern would be different?

Since the tortie pattern is generated with random X chromosome inactivation that's not predicted by the DNA.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

🍂 Oleksandr K
#természet#nature#macska#cat#ősz#autumn#fall#háztető#rooftop#alvás#sleep#álom#dream#boszorkány familiárisa#witch's familiar#boszorkány#witch#pogány#pagan#boszorkányság#witchcraft
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cat color genes masterpost
I copied all my descriptions from the cat color gene tournament here, with pictures and all. I often type out the genotypes, so this is a guide to what each letter means. Under the cut because it's very long.
Disclaimer: Sometimes I don't use the most common designations of a gene or an allele, and I'd like to apologize to everyone who's bothered by this. I have a very good reason for it: I like it better my way.
Genetics guide
Agouti (agouti signaling protein gene, ASIP): this gene determines whether the individual hairs will be banded or not.
dominant allele: A - banded hairs, tabby cat (wild type)
recessive allele: a - no bands, solid cat (variant)

A_ means if there's already an A allele, the other one can be either A or a.
A homozygous recessive cat with wild type alleles on every other gene will be solid black. Combined with other allele variants the a allele can produce other solid colors, different types of smokes and several more.
Actually there are more "secret" alleles for this gene: the agouti alleles of the asian leopard cat and other wild feline species. In certain hybrid breeds, most notably bengals, there's even a special coloration called charcoal born from the combination of the domestic cat's solid and the asian leopard cat's agouti allele.
Ticked (dickkopf wnt signaling pathway inhibitor 4, DKK4): this gene determines if there is any full-colored hairs, or only banded.
dominant allele(s - researchers found at least two): Ti - only banded hairs, ticked tabby cat (variant)
recessive allele: ti - some hairs don't have bands, "patterned" tabby cat (wild type)

If this is the only gene with variant allele, we'll have a black ticked tabby [black tabbies are also called brown, and other, mostly breed-specific names]. Ticked tabbies are possible in every color.
Nonagouti covers up the tickedness (this is called recessive epistasis): we won't see what a solid cat's genotype is on this gene. (Except when other genes make it possible. But that's biology for you.)
Spotted (?): this hypothetic gene can break up the tabby pattern's stripes into spots.
dominant allele: Sp - spotted tabby cat (variant)
recessive allele: sp - striped tabby cat (wild type)
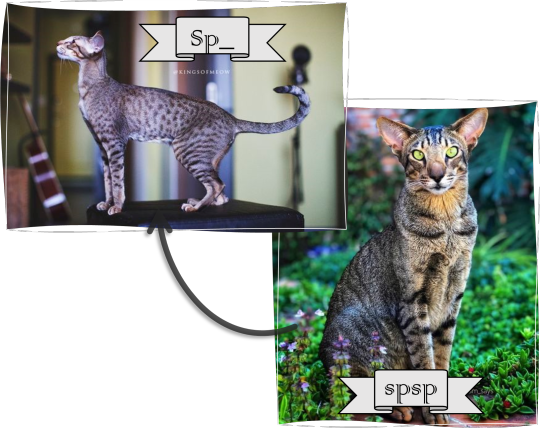

Alone the Sp allele makes a black (brown ect) spotted tabby cat; of course, in combinations with other variant alleles, it can produce a wide variety of different colored spotted tabbies.
Both a and Ti covers up the spotted gene: its effect normally only visible on a cat with the A_ titi genotype.
Mackerel [i use the name mackerel since every other gene here is named after the dominant allele] (transmembrane aminopeptidase Q, Taqpep): this gene determines the type of the tabby pattern.
Blotched and classic are synonym terms.
dominant allele: TMc - narrow vertical lines, mackerel tabby cat (wild type)
recessive allele: tbl - wide, swirling lines, blotched or classic tabby cat (variant)

If every other gene is wild type except this, we'll have a black blotched tabby cat, but of course the tbl allele can produce lots of different colored classic tabbies.
All of the previously mentioned genes are able to nullify the effect of this one, so a mackerel or a blotched tabby must have A_ titi spsp genotype.
Additional annoyed remark: Despite the name, the so-called classic pattern is actually both the newer and the less common worldwide. My only guess for why it's named like that: it's the more common one in England. Well, thanks. (That's why I actually prefer the name blotched over classic.)
Brown (tyrosinase-related protein-1, TYRP1): this gene determines the quantity of the functional eumelanin.
dominant allele: B - full pigment production, black cat (wild type)
"middle" allele: b - less pigment, chocolate cat (variant)
recessive allele: bl- even less pigment, cinnamon cat (variant)
Order of dominance: B > b > bl
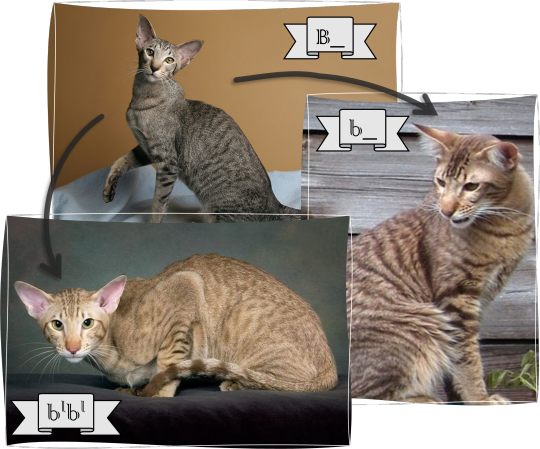

If every other allele is wild type except this, we'll have a chocolate or cinnamon mackerel tabby cat. (On the picture the cinnamon cat is spotted rather than striped, because i couldn't find a decent mackerel. So sad.) Chocolate and cinnamon cats are possible in every pattern.
Dilute (melanophilin, MLPH): this gene determines the distribution of the pigments.
dominant allele: D - even pigment distribution, dark cat (wild type)
recessive allele: d - clumped, uneven pigment distribution, diluted cat (variant)
black -> blue
chocolate -> lilac
cinnamon -> fawn

In these pictures the difference isn't that striking between the black and the blue mackerel tabby, but if you look up at the header, in solid cats it's much more pronounced.
For further comparison of undiluted and diluted color pairs on one picture (to eliminate differences in lightening):


black vs blue and red vs cream
Every possible color and pattern can be diluted (with the only exception of white).
Orange (?): this yet unidentified gene determines the type of the most prominent pigment: eumelanin on pheomelanin.
allele: O - mainly pheomelanin, red-based cat (variant)
allele: o - mainly eumelanin, black-based cat (wild type)
This gene is special in two related ways: first, it's located on the X chromosome, which means tomcats only have one allele; second, the alleles are codominant - if a cat carries both of them, it'll show both phenotypes: this is how we get tortoiseshell cats. This explains why almost all tortoiseshell cats are females - every tortie needs two different X chromosomes.

Combined with other variant alleles every possible color and pattern can occure as tortoiseshell, but the O allele is epistatic over a lot of genes: for example agouti (the phenotype of every orange cat is tabby, even the genetically solid ones) and brown (since eumelanin is mostly absent thus can't change - the genotypes OO B_, OO b_and OO blbl all mean red cat).
The dilute version of red is called cream.
The dilution level is always the same in the colors of a tortoiseshell: the undiluted black, chocolate and cinnamon is paired with red, the diluted blue, lilac and fawn are paired with cream.
White (receptor tyrosine kinase, KIT): this gene determines the size of the area the pigment producing cells (the melanocytes) reach.
dominant allele: W - basically no melanocytes, white cat (variant)
allele(s): ws - limited area is covered, white-spotted cat (variant)
allele: w - all of the body is covered by the melanocytes, full-colored cat (wild type)
recessive allele: wg - only the paws remain white, gloved cat (variant)
Order of dominance: W > ws = w > wg
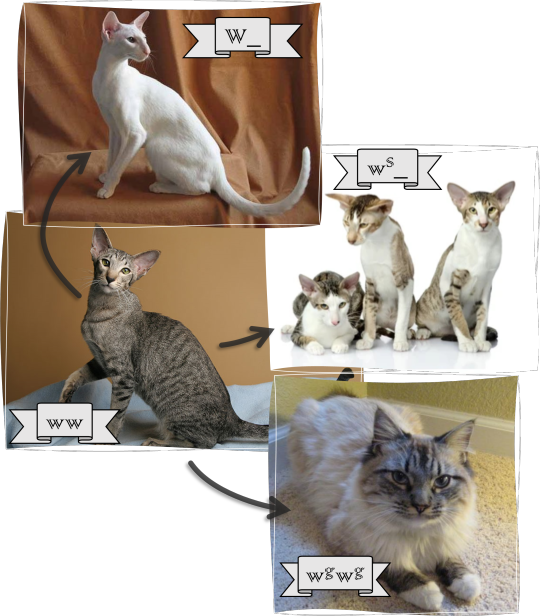

Since the gloving allele is kind of specific to the breed, I used a birman cat to illustrate it.
Lots of alleles here! Actually I'm not sure what's the most accepted opinion about them, but since these variant are all mapped to KIT, I considered them alleles.
If every other gene shows the wild type except for this, we'll have a white, or a white-spotted black mackerel tabby cat, but thanks to the ws allele(s) every color and pattern can be combined with white patches. However, the W allele is epistatic over every other gene: if a cat has one or two copies of W, it will be white regardless everything else.
ws is interesting: it has an additive effect, a cat with the wsws genotype will have more white than a cat with only one copy of it.
wg is fully recessive: the gloved phenotype only present if the cat's genotype is wgwg.
Color restriction (tyrosinase, TYR): mutations on this gene will result in temperature-sensitivity in the pigment production, the cats will be lighter on the warm and darker on the cooler areas of their bodies.
dominant allele: C - regular pigment production, full colored cat (wild type)
allele: cb - moderately reduced pigment production: burmese color restriction, sepia cat (variant)
allele: cm - reduced pigment production, bangkok color restriction, mocha cat (variant)
allele: cs - highly reduced pigment production: siamese color restriction, pointed cat (variant)
recessive allele: c - no pigment production, albino cat (variant)
Dominance order: C > cb = cm = cs > c
Now this group is a lot. Not only five different alleles (mocha was found relatively recently in Thailand), but the middle three are all intermediate with each other meaning that actually we have eight different phenotypes (illustration from messybeast; full color and albino are absent):
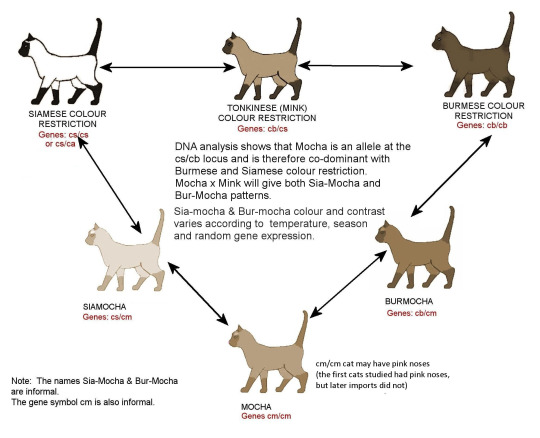
I used solid cats for illustration, because in the thai breed (the cats i used belong to this) they are often preferred over tabbies, so it's easier to find pictures; also, it's much more simple to compare them.
(Photos from The Thai Cat Center and Bangkok Mocha Cat, and Pangur from @pangur-and-grim as an albino cat)
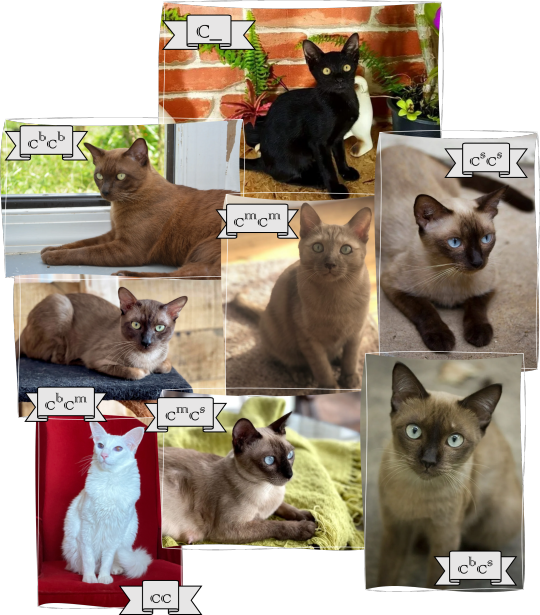

Please note that all of these varieties are very changeable; the pictures (especially those of the heterozygotes) are far from representing all cats carrying the respective genotypes.
Alone these variants makes some type of a black (seal) mackerel tabby point cat, but every type of color restriction can occure together with all possible colors and patterns.
***The color restriction gene won the Cat Color Gene Tournament!***
Inhibitor (?): this unidentified gene reduces the pheomelanin production, thus removes the warm tones of the fur (the hairs have white-black banding instead of yellow-black).
dominant allele: I - reduced pheomelanin, cooler toned cat (variant)
recessive allele: i - normal pheomelanin, warmer toned cat (wild type)

If every other allele is wild type except for this, we'll have a black silver mackerel tabby cat. Combined with other alleles it can produce lots of different silver (tabby) and smoke (solid) varieties.
Wide band (?): This hypothetic gene makes the yellow bands on the agouti hairs wider, resulting in a lighter, yellowish pelt. Based on the width of the pale bands we can differentiate between golden (middle band width) and shaded (maximal band width, color is pushed up into the tip).
dominant allele: Wb - reduced area of eumelanin, warmer toned cat (variant)
recessive allele: wb - normal area of eumelanin, cooler toned cat (wild type)
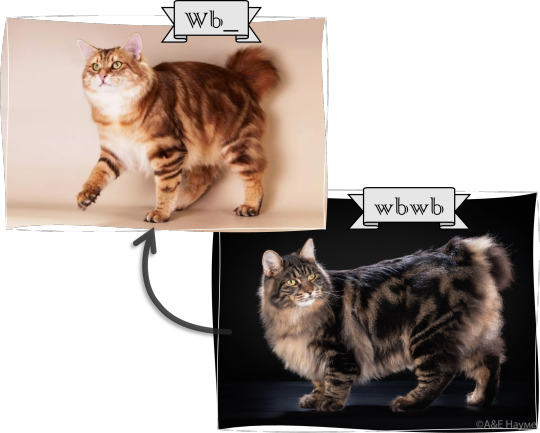

Golden is quite a mess; right now there is one identified gene (found first in siberians), but persians and many more breeds must have different gene(s), based on the interaction with the inhibitor gene (siberian golden + silver = bimetallic, persian golden + silver = silver shaded or chinchilla), and the inheritance patterns (the siberian alleles are recessive, while persian golden appears to be dominant). Since lots of breeds allow golden, and sometimes it can be found even in stray cats, I say who knows what genes and alleles are out there! This is all a hardly understood, very exciting and currently researched area.
If every other gene stays wild type except for this, we'll have a black golden mackerel tabby or a black golden shaded cat. Combined with other alleles it can produce lots of different golden and silver varieties.
Low-grade white (?): Again, hypothetic gene(s). Even with the extreme variability of the white spotting allele(s), the existence of some independently inherited genes is strongly suspected. Their effects most commonly manifest as a white locket: a small white patch on the chest or the belly, and/or a white tail tip. I'm not sure if there is any consensus whether these are more likely to be recessive or dominant alleles.
Dilute modifier (?): This unidentified gene changes the color of a diluted cat, the coloration becomes more brownish.
dominant allele: Dm - (variant)
recessive allele: dm - (wild type)
blue, lilac, fawn -> caramel
cream -> apricot

I put here a cat in all three diluted colors to compare them with the caramel tabby. It's hard to spot the differences, isn't it?
Since this is a dilute modifier, the D allele covers it, and we can only see its effect on cats with dd genotype.
It can be found only in a few breeds: orientals (including related breeds), burmese, different rexes. To our current knowledge, of course.
Extension (melanocortin 1 receptor, MC1R): This gene replaces eumelanin with pheomelanin resulting in a yellowish or reddish furred cat. The change often happens gradually during the first years of the cat's life.
dominant allele: E - eumelanin remains, black adjacent cat (wild type)
recessive alleles: e, er, ec - pheomelanin takes over, yellow/red adjacent cat: amber, russet or serdolik (variant)
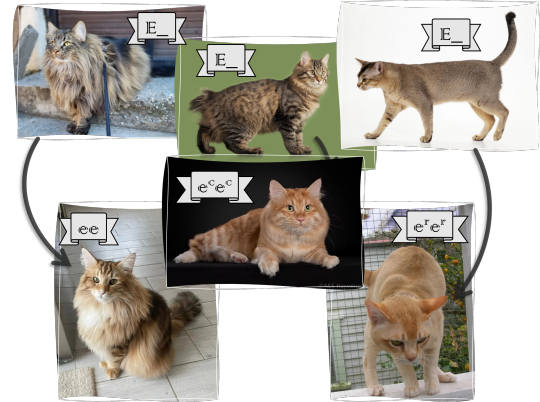

All three recessive variants are new mutations found recently in different breeds: the color amber in the 1990s in norwegian forest cats, the color russet in 2007 in burmese, and the color carnelian or serdolik in 2018 in kurilian bobtails (at least that's the first mention). We don't know anything about their interactions, or their effects on cats outside of their respective breeds.
The gene only effects eumelanin, so the O allele is epistatic over the it. However, because of the properties of the overpowering pheomelanin, every e allele is epistatic over agouti, so the tabby patterns will show up on aa cats as well.
Wide band (serine peptidase, CORIN): This hypothetic gene makes the yellow bands on the agouti hairs wider, resulting in a lighter, yellowish pelt.
dominant allele: Wb - eumelanin on normal sized area, darker cat (wild type)
recessive alleles: wbSIB, wbeSIB, wbBRI - eumelanin on reduced area, lighter cat (variant)

Ohhh, citizens of tumblr, we're really in it now. So. In the moment, we have, I believe, three mutations found on this gene: the sunshine (wbSIB) and extreme sunshine (wbeSIB) in the siberian breed, and the copper (wbBRI) in british cats. (I only show the sunshine and the copper here.) The novelty of these mutations means that the breeders still often call them simply golden instead of the new names, so it's difficult to find reliable data. Further complicating the situation, most likely both breeds have more wide band gene(s) beyond CORIN, and especially the copper cat above is the result of the combination of several wb genes.
Karpati (?): This unidentified gene makes the extremeties (face, ears, legs, tail) white kinda like a reverse colorpoint cat, and causes a roaning effect: scatters white hairs everywhere on the body.
dominant allele: K - whited extremities, karpati cat (variant)
recessive alleles: k - normal pigmant production, full colored cat (wild type)

Karpati seems to show intermediate inheritance with significantly more white on a homozygous then a heterozygote cat. This gene is studied for a very short time, and mostly on heterozygotes since they are much more common. The cats appearence changes during their life and also with the seasons: they born very similar to a fever coated kitten but with white ears, then to the end of their first year they almost completely lose the white (at least the heterozygous cats - the homozygotes become darker but still keep strange white patterns), then slowly gain it back as they age.
The karpati mutation is present in the stray cat population in middle-east Europe (including Hungary where I live, wahoo! and indeed, I can regularly see one or two karpaties in facebook adoptions groups and such). It's also introduced to some established breeds (LaPerm, Sphynx ect) and the creation of its own breed also began under the Transylvanian name.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Excuse me, Tumblr, I feel I must raise awareness of how beautiful my cat Kifli* is.
*He is named for a delicious Hungarian crescent roll.
@mostlycatsmostly 💖

#cats#pets#my photos#my cats#cats of tumblr#catblr#macska#macskák#cica#cicák#kifli#tumbli#magyar#magyar macska#magyar tumblr#saját kép#mostlycatsmostly
519 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fő a biztonság
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

home office
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

Csináltam saját suskamacskát!
Osszátok!
Vagy szorozzátok!
Csak dőljön a pénz!
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ma azt álmodtam,
hogy felhő vagyok.
Nem áll távol tőlem, a színem hófehér, mint napos időben a felhőké - ha nem koszolom össze magam, ahogy ez néha megtörténik -, a bundám puha és könnyű. Szoktam felhőket nézni az erkélyről, így tudom, miről beszélek. Amikor felhő vagyok, minden felett lebegek, nálam közelebb senki nincs a Naphoz. Lenézek a Földre, sok-sok százmillió macska otthonára, és elégedettség tölti el a szívemet, mert tudom, hogy nekem van ott a legjobb, legszeretőbb családom. Így aztán soha nem vagyok sokáig felhő, mert szeretnék visszatérni hozzájuk. Lehet, hogy mindig mindenki valami másra vágyik?
Fura dolog az élet.
"Amikor verset ír az ember, mindíg más volna jó, a szárazföld helyett a tenger, kocsi helyett hajó.
Amikor verset ír az ember nem írni volna jó,"

26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hungary - Tuzsér
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
segitsetek kerlek a macskamnak keresek uj gazdat
the story goes the following:
oktober vegefele befogadtam lenyegeben az utcarol egy kiscicat. egy jo baratnom egy muzeumban dolgozik, ahova masodik eve egy macska megszult egy kinti szeferben. ket kolyke volt, baratnom keresett nekik gazdat, mert ott nem maradhattak, en meg befogadtam a mindjart 7 eves, vak nyulam melle a calicot, mert ugyis szerettem volna egyet. na, ez most jelenlegi eletem legrosszabb dontese volt, ugyanis
kulon kellett szeparalnom a nyulat es a macskat, mert castor (a nyulam) azota is full stresszben van, meg igy kulonvalasztva is
az anyagi helyzetem korulbelul honaprol honapra romlik, sokkal kevesebbet keresek, mint amirol szo volt, es nem birok eltartani igy ket allatot, hogy a rohejesen olcso lakberre is ugy kell osszekaparnom minden forintot mindig
illetve hat ebbol az anyagi helyzetbol adodoan szerencsetlen macskat meg orvoshoz se tudom elvinni, ennyire nincs penzem
es ezek mellett vendeglatoskent nem tudok annyit itthon lenni a macskaval, amennyi figyelmet igenyel

a cicat Lucanak hivjak, termeszetesen kislany. nagyon baratkozos, nagyon nagyon jatekos es eleven, szobatiszta, es egyaltalan nem agressziv. ja, es persze calico letere nagyon bujos.
segitsetek konyorgom, nagyon ketsegbe vagyok esve
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
round 4 - week 2 - 1 of 4

brought to you by: gobi
macska (hungarian) vs misse (swedish)
info and propawganda under the cut!
macska /ˈmɒt͡ʃkɒ/
-ka is a diminutive so its sound like it means "little macs" - except there's no "macs", that word doesn't exist, only macska: little macs, which is very true because all cats are babies.
Macska is just a little switcheroo away from makacs (cs is a single letter in hungarian) which means stubborn which is what cats are C:
misse /mɪs̪ːɛ/
S is sound that cats have the easiest time understanding i think and the M sound like Meow
104 notes
·
View notes



