#machicolation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
10 (More) Random Entries from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture
The following entries were pulled from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture (1995).

Iznik tilework (architectural facet)
Fatimids (people)
Gujarat (region)
Susa (city)
Yasavi (shrine of Ahmed Yasavi) (building)
Ukhaidhir (building complex)
Machicolation (architectural facet)
Kharana (building)
Bedestan (structure type)
Anjar ('Ayn Jar) (city)
(Previously: 10 Random Entries from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture)

----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Iznik tilework (architectural facet)

Ottoman tiles produced from the mid-sixteenth century will have a distinctive under-glaze blue color and design.
Iznik is a town in north-west Anatolia famed for its pottery production. during the Ottoman period. Under the Byzantines the town was known as Nicea and enclosed within a large circuit wall which still survives. The city was one of the first towns to be conquered by the Ottoman Turks and contains the earliest dated Ottoman mosque known as the Haci Ozbek Cami.
Before 1550 the kilns of Iznik seem to have been mostly concerned with making pottery rather than tiles. Sometime around 1550 there was a change to tile production which was induced by the tiling of three great monuments, the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, the Suleymaniye Mosque in Damascus and the Suleymaniye complex in Istanbul. Before 1550 Ottoman tiles were hexagonal with bold cuerda sec designs, the new Iznik tiles were square and carried underglaze designs. The new shape and use of underglaze painting enabled large multi-tile compositions to be made. Another innovation of this period was the use of thick red slip as an underglaze color which gave Iznik pottery its distinctive appearance.
See also: Istanbul; Ottomans; Suleymaniye.
❯ Further reading ❯ (1) J. Raby, 'A seventeenth-century description of IznikNicea', Istanbuler Mitteilungen, 149-188, 1976; (2) J. Raby and N. Atasoy, lznik: The Pottery of Ottoman Turkey, London 1989. ❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 130. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) SOPA Images/Contributor; (2) Ayhan Altun; (3) Ayhan Altun.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Fatimids (people)

Caliphs who ruled North Africa, Egypt and Palestine from the tenth to the twelfth century.
The Fatimids were a religious dynasty who claimed descent from the prophet's daughter Fatima. In historical terms the Fatimids belonged to an extreme sect of Shi'a known as Ismailis who emerged as rivals to both the Umayyads of Spain and the Abbasid caliphate in Baghdad. The Fatimids' first successes were amongst the Berber tribes of North Africa who adopted the Fatimids as leaders. Their first conquest destroyed the Aghlabid rulers of Ifriqiyya (Tunisia) in 909 and replaced them with the Fatimid caliph the Mahdi Ubaid Allah. In the following years the Fatimids pursued an aggressive expansionist policy, conquering Tripoli and making raids on the French and Italian coasts. During the reign of the Caliph al-Mu'iz the empire was expanded westwards to include the whole of North Africa to the Atlantic Ocean and eastwards to Egypt and Palestine in 969. The conquest of Egypt began a new phase in Fatimid history with the foundation of Cairo as the imperial capital.
The architecture of the Fatimids can be divided into two periods, the North African period from 909 to 969 and the Egyptian period from 969 to 1171. The North African period was a time of expansion and religious extremism which can be seen in the architecture of the mosques. Examples of early Fatimid mosques are at Ajdabiya in Libiya and Mahdiya in Tunisia. The first of these was the mosque of Mahdiya, which was built like a fortress with two square comer towers flanking a single projecting monumental entrance. The mosque at Ajdabiya had a similar plan but lacks the monumental entrance facade. For ideological reasons, neither of these mosques had a minaret, a feature which remained absent until the last years of Fatimid rule in Egypt.
See also: Ajdabiya; Cairo (The Fatimid Period); Libiya; Mahdiya; Tunisia.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 86-87. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) J.M. Bloom; (2) Wikimedia Commons.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Gujarat (region)

Predominantly Hindu coastal region of western India with distinctive Islamic architecture. Gujarat is a fertile low-lying region located between Pakistan, Rajasthan and the Indian Ocean. The position of the region on the Indian Ocean has meant that it has always had extensive trading contacts particularly with the Arabian peninsula. It is likely that the first Muslims in Gujarat arrived sometime in the eighth century although there is little published archaeological evidence of this. The oldest standing mosques in the area are located at the old seaport of Bhadresvar in western Gujarat and have been dated to the mid-twelfth century although they may stand on older foundations.
The first Muslim conquest of the area took place at the end of the thirteenth century under the Ala al-Din the Khaliji sultan of Delhi. The earliest monument from this period is the Jami Masjid at Cambay which includes columns taken from ruined Hindu and Jain temples. The form of the mosque resembles that of the Quwwat al-Islam Mosque in Delhi with a rectangular courtyard with gateways on three sides and an arched screen in front of the sanctuary on the west side. Other early mosques built in a similar style include those of Dholka Patan and Broach all of which are located close to the coast. During the fifteenth century many mosques, tombs and other monuments were built in the regional capital Ahmadabad, the most significant of which are the Jami Masjid and the tomb of Ahmad Shah. These buildings incorporate many features from Hindu temple architecture including projecting balconies, perforated jali screens and square decorated columns. Monuments of the sixteenth century contain the same Hindu and Islamic elements combined in a more developed fashion as can be seen in the Jami Masjid of Champaner built in 1550. The Mughal conquest in the mid-sixteenth century brought Gujarat into the mainstream of architectural development. However, the architecture of the region exerted a considerable influence on the Mughal emperor Akbar, who built the city of Fatehpur Sikri in Gujarati style.
The secular architecture of Gujarat is mostly built of wood and characterized by elaborately carved screens and overhanging balconies. Another characteristic feature of the region is the use of step wells, or vavs, which consist of deep vertical shafts, approached via recessed chambers and steps. Sometimes these were very elaborate structures with multiple tiers of steps.
See also: Ahmadabad; India; Mughals; Qutb Minar.
❯ Further Reading ❯ (1) Z. A. Desai, 'Some Mughal inscriptions from Gujarat', Epigraphica Indica: Arabic and Persian Supplement, 1970, 63-92; (2) J. Jain-Neubauer, The Stepwells of Gujarat in Art Historical Perspective, New Delhi 1981; (3) E. Koch, '[The] Influence [of Gujarat] on Mughal architecture', in Ahmadabad, ed. G. Michell and S. Shah, Bombay 1988, 168-185; (4) M. Shokooy, M. Bayani-Wolpert and N. H. Shokooy, Bhadresvar: The Oldest Islamic Monuments in India, part of Studies in Islamic Art and Architecture, Supplements to Muqamas, vol. 2, Leiden 1988. ❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, pages 102-103. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Gujarat Tourism; (2) C. Krishna Gairola/University of Washington Libraries, Special Collections; (3) Booksfact.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Susa / Soussa / Sousse (city)

Tunisian coastal city noted for its ninth-century Aghlabid buildings. Under the Byzantines the city was known as Justinianopolis in honor of Justinian who rebuilt it after the Vandal destruction. In 689 CE, it was captured by the Arabs and became one of the principal ports for the Aghlabid conquest of Sicily. In 827, the city was refortified with ramparts and walls built in the Byzantine style. Important Aghlabid buildings within the city include the ribat built or restored by Ziyadat Allah in 821, the Bu Fatata Mosque built in 840 and the Great Mosque established in 859.
See also: Aghlabids; Tunisia.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 271. ❯ Photos ❯ TravelFeed.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Yasavi (shrine of Ahmed Yasavi) / mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi) (building)

Shrine built by Timur for his son Jahangir between 1397 and 1399.
The shrine is located in the city of Turkestan (modern Yasi) in the Republic of Kazakhstan. The building is oriented north-south on a rectangular ground plan (65.5m by 46.5m) with portals at the south and north ends. The main doorway is the magnificent south portal which is flanked by huge cylindrical corner towers or minarets over 20m high. Behind the portal is the dome of the prayer hall rising to a height of over 37m. At the other end of the structure is the north facade in the center of which is the entrance to the mausoleum. The mausoleum is capped by a tall 'melon-shaped' ribbed dome set on a high cylindrical drum. Externally the building is well articulated with its two entrance facades, domes and an extensive covering of tilework. Internally, however, there is less feeling of unity beyond the principal rooms: leading off from the prayer hall and mausoleum are many smaller rooms with different vaulting systems which do not seem integrated in an overall design.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 310. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Yevgeniy Volkov/Shutterstock; (2) leszczem/Shutterstock; (3) AlexelA/Shutterstock.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Ukhaidhir / al-Ukhaidir Fortress (building complex)

Early Abbasid palace in the desert of south-western Iraq.
The palace stands in the desert west of the city of Kerbala and east of the oasis of Shithatha. The building is made out of rough-hewn limestone blocks and mud plaster with baked brick used for roofing vaults, resembling earlier Sassanian structures (cf. Kharana in Jordan). The palace may be divided into two structural phases, a central palace core and an outer enclosure wall added slightly later. The exterior curtain wall is composed of tall blind niches alternating with solid semi-circular buttress towers. On top of the wall there was a parapet which was cantilevered over the niches allowing a continuous series of slits (machicolation) which could protect the lower parts of the wall from attack. The main gateway is set between two quarter-round towers and contains a slot for a portcullis. To the right of the entrance on the outside there is a large stable block. The central core of the palace contains a mosque, a bath house and a main reception hall. The upper floor is reached by ramps running up at right angles to the axis of the main gateway. There are small tunnels running over the main vaults which provided cooling and ventilation.
Recent survey work in the vicinity of Ukhaidhir has demonstrated the development of the area during the early Islamic period, starting with the small palace at Tulul Ukhaidhir several kilometers to the north of the main palace. In addition there is an outer mud-brick enclosure containing a variety of mud-brick buildings which are now only visible as humps.
See also: Abbasids: Atshan, Khan; Iraq; Sassanians.
❯ Further reading ❯ (1) G. Bell, Palace and Mosque at Ukhaidhir: A Study in Early Muhammadan Architecture, Oxford 1914; (2) B. Finnster and J. Schmidt, Sasaidische und fruhislamische Ruinem im Iraq, Baghdader Miffeilungen 8, Berlin 1976. ❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 294. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Taisir Mahdi; (2) Mustafa Hamzah Almosawy.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Machicolation (architectural facet)

Downward openings or slits used defending a castle or fortification.
There are three types of machicolation, a box machicolation, concealed machicolation and continuous machicolation. A box machicolation resembles a projecting window or gallery and may also be used for this purpose. There are usually one or more slits in the floor and the box is normally located over a gate or doorway. Box machicolations were used in Roman times and their first use in Islamic structures is at Qasr al-Hayr (East and West).
Concealed machicolations are usually set into the roof above a vaulted passage leading from a gateway and are often used in conjunction with a portcullis. The first example in Islamic architecture comes from the eighth-century palace of Ukhaidhir in Iraq. These were frequently used in medieval Islamic fortifications.
Continuous machicolation consists of a parapet which is cantilevered over the front face of a wall with a series of downward openings. The earliest example of this is also at Ukhaidhir although it is not used later on in Islamic architecture.
See also: Fortification.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 167. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Bernard Gagnon; (2) Vyacheslav Argenberg/Getty.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Kharana / Qasr al-Kharana (building)

Early Islamic or Sassanian building in the Jordanian desert 60km east of Amman.
Kharana is a remarkably preserved square two-story structure with solid semi-circular and circular buttress towers. The building is made out of roughly-hewn stone blocks laid in courses covered with successive layers of plaster. There are three rows of vertical slits in the walls which have been interpreted as arrow slits, although. their height above the inside floor level makes this unlikely. The gateway is set between two quarter-round towers which lead into an entrance passage flanked with two long vaulted rooms that functioned as stables. Inside the building is a square courtyard with a series of undecorated rooms (for storage?) whilst on the upper floor the rooms are decorated with plaster/stucco designs similar to those at Ukhaidhir in Iraq. These include engaged pilasters, blind niches and decorative bosses. Two of the upper rooms have semi-domes resting on wide squinches at the end.
Although it was built before 710 (according to an inscription) and is Sassanian in style, the building is now generally believed to be early Islamic.
See also: Tunisia.
❯ Further reading ❯ S. Urice, Qasr Kharana in the Transjordan, Durham, NC: AASDR, 1987. ❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 147. ❯ Photos ❯ Haupt & Binder.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Bedestan (structure type)

Special closed form of Turkish market where goods of high value were traded. The usual form of bedestan is a long domed or vaulted hall two storeys high with external shop units.
Originally, bedestan referred to the area of a market where cloth was sold or traded from the bezzaz han (cloth market). The earliest bedestans were probably specific areas of a general bazar or market. The earliest known bedestan is the Beysehir Bedestan built in 1297 according to an inscription above the gateway. The building consists of a closed rectangular courtyard covered by six domes supported on two central piers. There are doorways on three sides and on the outside there are small open shop units, six on the east and west sides and nine on the north and south sides.
During the Ottoman period bedestans developed as a specific building type and became the center of economic life in a city. Because they could be locked, they were often used for jewelry or money transactions and came to be regarded as signs of prosperity in a city. Ottoman bedestans were built in a variety of forms and may include features such as external shops, internal cell units and arastas (arcades). The simplest plan consists of a square domed hall with one or two entrances like those at Amasya or Trabzon. More complicated structures like the Rustem Pasha Bedestan in Erzerum consist of a central enclosed courtyard surrounded by a closed vaulted corridor containing shop units.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 33. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Mustafa Cambaz; (2) GarySandyWales; (3) selimaksan.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
❯ ❯ Anjar ('Ayn Jar) (city)

Umayyad city in Lebanon.
Anjar was built by the Umayyad caliph al-Walid in 714-715 CE. The city is contained within a rectangular enclosure (370m north-south and 310m east-west) supported by a series of solid semi-circular buttress towers and four hollow corner towers. There are four principal gateways and the walls were originally crowned with stepped merlons (crenellation). Internally the city is built to a regular plan recalling earlier Byzantine and Roman cities. There are four principal colonnaded streets which meet at the center in a tetrapylon. Many of the buildings are built of alternating courses of ashlar blocks and layers of baked brick. There is a series of shop units (3.5m wide and 5m deep) lining the main streets behind the colonnades. In the south-east quadrant of the city is a palace within a rectangular enclosure (about 70 by 60 m). The interior of the palace is divided into four units arranged symmetrically; at the south end there is a building with a triple aisles and an apse resembling a basilical hall, this is duplicated at the north end. To the north of the palace is the mosque which is entered from the west street. The mosque is a rectangular structure (47m by 30m) with a small central courtyard surrounded by two aisles on the west, east and qibla (south) sides whilst there is one aisle on the north side. On either side of the mihrab are two entrances which lead into a narrow lane that connects with the palace. There is a small bath house next to the north gate which comprises a square vaulted hall, leading via two intermediate rooms into a hot room.
❯ Text ❯ Peterson (1995) Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, page 20. ❯ Photos ❯ (1) Malcolm P. Chapman; (2) Henryk Sadura; (3) Eric Lafforgue/Art in All of Us/Contributor.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Current article: 10 (More) Random Entries from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture
Previous article: 10 Random Entries from the Dictionary of Islamic Architecture
#islamic architecture#writeblr#writing research#masterpost#writing#writing tips#writing advice#culture#novel writing#fiction writing#worldbuilding#writing stuff#architecture research#construction material#fatimids#gujarat#susa#sousse#yasavi#ahmed yasavi#ukhaidhir#machicolation#kharana#iznik tiles#izkik#bedestan#anjar#architecture#spelling and pronunciation may differ#exact dates may differ
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The 48th edition of the 2023 Richard Murray Newsletter.
topics
27th Cento poetry round Literary opposition to gaza Black Woman Photographers grant recipient
Dates with Astrology plus Astronomy
IF YOU MADE IT THIS FAR: do you know what a machicolation is, standardization of grammar, lesson in the plight of the palestinean, Dark Academia
U.R.L. https://rmnewsletter.over-blog.com/2023/08/11/26/2023-rmnewsletter.html
#rmnewsletter #rmaalbc
#rmnewsletter#poetry#cento#poem#opposition#gaza#israel#blackwomanphotographers#flickr#grant#photographers#woman#dates#astrology#astronomy#machicolation#shadversity#standardization#grammar#lesson#history#plight#palestinean#darkacademia#dark#academia#black#artist#writer#calligraphy
0 notes
Text
etho consistently misidentifying crenellations in bdubs' tower builds is the funniest thing because it's all on account of 3rd life episode 2 but both he and bdubs have forgotten the original joke and etho's just dragging its carcass around.
#peter posts#crenellations go on TOP like a CRown. machicolations is a word neither of them have successfully articulated with their real human mouths
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last season's anime: Frieren episode 7-10
Shit I guess I'm full on liveblogging this one now.
This time we have episode 7 dir. Naoto Uchida (known for work on Mob Psycho 100), episode 8 dir. Tomoya Kitagawa (who also directed ep. 2), episode 9 dir. Kōki Fujimoto (key animator on a whole buncha stuff, this is his debut as an episode director), and episode 10 dir. Nobihide Kariya (who debuted not so long before as an episode director on Bocchi).
So at the end of the last post about Frieren, I commented that I found the demons underwhelming as antagonists, and hoped they would have their motivations fleshed out some more beyond 'ontologically evil baddies'. Well.
lmao.

So Frieren and the gang are travelling. We get a lot more on the Great Mage Flamme, who is Frieren's mentor figure. At this rate... she's probably gonna turn out to still be alive or some shit.
They roll up in another ridiculously picturesque town. The backgrounds in this show are apparently based heavily on the concept art paintings of Seiko Yoshioka, who gets credited under various roles including 'layout designer' and even 'worldview illustrator'. She did a crazy amount of work to design all the different settings, giving them distinctive cultural motifs and architectures and colour palettes and so on.

Since this town covers a whole four-episode arc, we get a number of different views of it. There's definitely a reasonable amount of historical care put into the design of those city walls - even sketchy and in the distance you can spot the hoardings and appropriately narrow crenellations, as well as the machicolations on the tops of the towers. (Though unfortunatelly some of those details seem to get forgotten in the later episodes.)
The streets in the town seem kinda wide and clean but it fits the austere vibe. The main thing I'm wondering is what exactly they eat in this town - it's triple-walled in hostile territory without much in the way of farmland in sight, or indeed roads that aren't tiny.

I'm pretty sure they built a model of at least parts of this town in 3D, because as well as certain 3D tracking shots (unfortunately hampered by the lack of any parallax mapping on the floor)...

...we also get shots like this one, which feature a crazy 3-point perspective:

I wouldn't say it's impossible to draw this, but it would be a hell of a lot easier to block it out roughly in 3D and then paint in the details.
Mind you, that's not even the wildest perspective we get in this episode. Check this out:

Absolutely bananas. I love it.
But tbh the praise I have for this arc is pretty limited to this kind of technical stuff. Let's get into the story. (Though you can be sure I'll have more to say about the animation!)
At this point the story shifts gears from this fairly low-key exploration of grief and the passing of time, into more standard action anime territory.
Shortly after arriving in this town, our heroes discover that it has been infiltrated by demons in the guise of peace emissaries. Frieren attempts to attack immediately, but she allows herself to be subdued rather than harm the guards, so off she goes to jail.

Luckily, wizard jail still has pretty generous visiting hours, so she's able to explain the deal with demons to the gang. Frieren declares that demons always lie to gain an advantage over humans, illustrated through a flashback in which a young girl demon begged for mercy, only to betray the townspeople a bit later. Having been proven right, Frieren summarily executes the girl.
I think it's worth comparing this storyline to a couple of other similar storylines in other works of fiction.
First of all, in NieR Replicant/Gestalt, there is the story 'The Little Mermaid', which was adapted into a segment in the game in the remake. A postman takes pity on a girl on a shipwreck, not realising that she is a terribly powerful monster who is struggling to maintain her human appearance. The girl starts killing people to try to maintain her connection with the postman. Eventually, the player shows up and discovers what's been going on. Their intervention provokes the girl to revert to monster state and there's a big boss fight. However, at stake in the fight is the girl's identity. Depending on how you play the boss fight, there are two possible endings, and both of them make overt parallels between the monster girl and your party member Kainé, and one portrays the grief of the postman who cannot let go of his affection for the monster.

Secondly, the second episode of last year's Tengoku Daimakyou features a woman who is trying to protect a monster which she believed to have taken on the consciousness of her son after it ate him. The monster has been curiously non-hostile to the woman - she persuades our protagonists to back off, and they agree. Then it abruptly kills her! Oh shit. Fight scene, they kill the monster, etc.
But as they depart, the protagonists are left discussing whether the monster could really have had the son affecting its actions, whether it was just drawn to prey etc. The monster's motivations are left distinctly unclear, and the protagonists conclude there's no way to know the truth. Throughout the rest of the season, the exact nature of the monsters remains an open question.
In both cases, we either know or it is strongly implied that the monsters are fundamentally human, or derived from humans somehow. A certain amount of effort is spared to try and at least raise the question of the monster's subjectivity, and even if a monster has to die, they play it for tragedy.
So, let's return to Frieren. We're introduced to the demon girl. She ate a kid, but she staves off execution by pleading for her mother.

The villagers decide to give her a chance to atone. Before long, she kills the village chief who took pity on her. Frieren's party show up and she does small Shaft head tilt...

She's no longer pretending and talks in a much more level voice. She explains that she wanted to give a replacement daughter to the family of the girl she ate, by removing the village chief, for the sake of living in peace. This goes down about how you'd expect. Frieren goes ahead and kills her. As she's dying, Frieren asks why she called for her mother when demons don't raise kids. The answer she gets:


She is surprisingly forthcoming on this front, and honestly, self-preservation is something like an understandable motivation. The impression you get from this flashback sequence is a being that is amoral, and encountering humans as something alien and, honestly, kinda threatening. Why she killed the girl in the first place is an open question - they explicitly say that the demons don't have to eat humans. Even if she kinda felt like it, you'd think she'd be able to figure out it would be an unwise move.
But as far as the show is concerned, the point of this flashback is to establish one thing: demons are lying liars who lie. Frieren is the only one who knows the truth, which is that you must shoot them on sight.
You might think the show would leave some doubt about whether Frieren is justified in having such a severe attitude towards the demons - is she just prejudiced? But nah we go pretty much straight into the demons saying 'Frieren is right about everything, now let'ss discuss our evil plan'.

Props to this guy (he has some longish German name I can't remember) for making this random bench feel like a throne though. Like on some level he's just soft-voiced evil anime aristocrat guy but he does pull it off.
Anyway, one thing definitely doesn't seem to add up. Frieren says that demons are solitary creatures who speak in a human voice only to deceive, but the demons seem to be pretty happy to natter away to each other when no humans are around and express all sorts of thoughts and even express (fairly reserved) emotions. The boy is arrogant, the girl is protective of her boss, etc. The guy is a smooth liar and manages to wriggle out of being killed by the earl by playing the 'we're the same, let's put an end to this' card. But we're constantly reminded it's fake, he's a lying liar who's ontologically evil.
I think the super-deceptive adversary with no qualms about telling any lie is something that can be done well to create an incredibly paranoid scenario. I can't believe I'm mentioning ratfic again in the space of two posts, but this is something Worth The Candle performed very effectively. Though honestly the fantasy of the perfect manipulator who plays everyone like a fiddle is a recurring device in fantasy.
Here... the acting is strong on our main sussy demon dude. But as a worthy adversary, he's not super convincing. He lets his underling run off and get killed, and his response when the jig is up is to reveal that he's super OP and kill everyone nearby, except the governor, who he tortures. So the manipulation angle seems questionably motivated, like he wants the earl to lower the barrier so the demon army can come in... but you're kind of left wondering why he didn't already just go and kill everyone in the city since nobody who isn't Fern or Frieren can touch him. I guess he's trying to get that low chaos route.
I won't continue the beat-by-beat summary. There is a cool fight scene in Frieren's jail cell though, which has some well-integrated 3D. Frieren totally no-sells the boy's attack and cuts his arms off. Lotta dismemberment in these episodes! The main demon guy has some tasty blood-based powers, lots of monofilament whip slicing imagery (also a thing in Tengoku Daimakyou oddly enough). In general the action scenes in this show continue to be super tight. There is a pretty cute bit where Stark is trying to free the earl and can't cut through the rope holding him to a chair, the earl is going 'leave me', and I was sitting there going like 'why not destroy the chair', and then Stark does. So props for that.
Towards the end of ep 8, we learn that Frieren is actually a suuuuper scary battle mage. She was the one who researched the demon killing spell. OOooooohhh.

Seems our demon guy hasn't changed his style in 80 years lol.

And she did not think it too many.
So we already knew that Frieren was part of the party that killed the demon king, the last living person who knew Flamme, etc. etc., so it's not exactly surprising to see once again that she's kind of a big deal. What we seem to be setting up here - or at least maybe I'm just hoping for something more than 'only our hero is wise enough to know coexistence is impossible and a war of annihilation is the only option' - is to suggest a parallel between Frieren and the demons. They're incredibly long-lived, they love to obsessively study magic, they both have a very cold affect, they're calm under fire. If it turned out that Frieren is a demon that would be a fun angle, but I don't think it really tracks. Rather, the framing is suggesting that, when confronted with demons, Frieren is not so different...
We get a title drop in any case - turns out the anime title is an in-story title for its main character. In Japanese: 葬送のフリーレン Sousou no Frieren. 葬送 is translated by jisho.org as
attending a funeral procession; seeing off the deceased; burial of someone's remains; observing a burial
The fansub I'm watching translate it (when used for the character) as 'Frieren the Elegy', which has about the right vibe! In the context for the show title, they translate the same phrase as Frieren: An Ageless Elegy which involves a little more interpolation, but I think it works. The official English title is Frieren: Beyond Journey's End, which is very direct but not a bad subtitle at all. Then again, maybe the bar is in the floor since 'Delicious in Dungeon'.
Anyway, after all that setup, we finally get the big fight episode. Because you see, in contrast to the earlier story which skipped over decades in a montage, this arc spans a whole four episodes. It's not badly done, but it's definitely feeling much more like a standard fight-driven show at this point.
We also meet Aura, one of the demon generals. She looks like a youngish girl and has a habit of doing the sanpaku eye smirk.



Her schtick is that she has magic scales that let her dominate people. Then she cuts their heads off and walks their corpses around. This is represented by a big army of suits of armour, mostly rendered in CG. They've done some kind of filter to make the linework less even, but the difference in shading style is quite noticeable.
From there it's a lot of 'my gambit vs your gambit' and 'who has more mana'. The fights are, without doubt very nicely animated, although the CG castle set used for the big camera moves feels a bit... lacking in detail compared to the gorgeous painted backgrounds. Anyway, Stark wins his fight by the power of GUTS and DETERMINATION, and Fern wins her fight by being a fast analytical type who can stay cool under fire and also knows Frieren's special demonbuster spell. Though a lot of Fern's fight is just kind of both participants standing still with impassive expressions shooting either blood or big laser beams at each other or zipping all around the castle.
Of course, the major turning points in the fight hinge on flashbacks to moments with mentor figures. This is an anime, and more specifically, it's Frieren.
One thing that is interesting is that the 'point of view' indicated by internal monologue often moves from Fern to the demon guy. We get to see him try to think through how to beat her, unsuccessfully. By contrast Stark's fight takes Stark's POV. I don't think we're expected to sympathise with the demon exactly, it's a way of underlining just how badass Fern has now become thanks to Frieren's levelling up regime.
I admit Frieren has lost me a bit by this point. It's not that it's bad at being a fight anime, it hits us with a whole series of stylishly composed and strongly animated cuts. Not novel necessarily, but absolutely well-executed. But it's not a very interesting direction to take the story! I don't care about this town, we'll be leaving it in an episode or two anyway, and the only named character in it is the earl. I wanna know more about the demons but what we get is kinda just a succession of Guys With Powers. He can make his blood fly around and stab people. She can copy anyone's moveset. He has a monofilament wire. She has a magic scale that mind controls you if she has more mana.

So how does Frieren beat the magic scales? ez. It's kind of spelled out as soon as they introduce the scales, but they spend a whole episode explaining how she's been using a relentless mana retention regimen for the last thousand years to hide her power level so that demons underestimate her. It kinda belabours the point lol. Like it kinda has to because if it doesn't try to make a big deal out of the mana hiding thing, you're just left with 'Frieren wins because her number is bigger'. But... Frieren wins because her number is bigger.
I don't hate fight-driven anime. They can be a ton of fun. But honestly, after the emotional impact of the first few episodes, taking it this way seems like it's wasting the early show's strengths. But, I hear episode 11 sees the return of Keiichirō Saitō as enshutsu, and it's said to be one of the best episodes in the show, so I'm not gonna drop it! It's certainly more than pretty enough to be worth watching through to the end.
There is a good amount of nice stuff in this last episode. The pseudo-Roman town is a cool depiction of a different material culture a thousand years prior to the main story. The 'field of flowers' magic is called back as a specific invention of Flamme - Frieren's whole deal is to kind of go around doing things to commemorate dead people and it turns out the flowers thing lets her do it twice over! We get to set up some parallels - Frieren could intuit that Flamme was a super OP mage, and Himmel could do the same for her.

We also get some worldbuilding stuff about the demons: they have to constantly display their power level to determine their place in the demon pecking order bc they're soooo individualistic. This seems a little dubious to me - like are the demons really so dumb? Is 'hide your power level' such an incomprehensible concept? It seems like it would lead to some kind of Diplomacy-like situation where other demons would team up to take you down.
Honestly, I think what bothers me about all this is like... I don't like the concept of an ontologically evil monster at the best of times, but the demons are obviously not mindlessly malevolent with no inner lives. They talk and scheme and feel things (such as 'proud of their magic'). They have an honour system. But the narrative doesn't quite seem to be able to acknowledge that this is what it's doing. Besides levelling up their magic, we have no idea what the demons want, still, except that it seems to involve killing humans sometimes.
Anyway! kvin has an article about this section, so if you'd like to read about who did which bit and how they worked together resourcefully and where the storyboard creates imagery of separation and so on, there ya go! It sounds from this article like the manga gets a better handle on what it's trying to do with the demons later on, so I'll hold out hope.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
I loved this contrast between the Romantic notion of the Crusades and the down-to-earth practicality of a soldier:
His heart was like a war-horse, and said, Ha, ha! as the boat bounded over the waves that were to land him under the ancient machicolated walls where the Crusaders made their last stand in the Holy Land. Not that Kinraid knew or cared one jot about those gallant knights of old: all he knew was, that the French, under Boney, were trying to take the town from the Turks, and that his admiral said they must not, and so they should not. - Sylvia's Lovers, Elizabeth Gaskell
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
welsknight: so the crenellations in the castletown fortifications…
comments section: wowww he even has machicolations!
me, who knows nothing about medieval architecture: yes very structurally sound :) yayyyy
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
absolutely machicolating over here (being dropped through a hole onto a group of invaders)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's build a wizard tower!
#wizard#wizardcore#wizard blogging#wizard shit#wizard tumblr#wizardblr#wizardblogging#wizard posting#poll#let's build a wizard tower
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
There in the ancient Gothic doorway stood a human figure. It was that of a man clad in a skullcap and long mediaeval tunic of dark color. His long hair and flowing beard were of a terrible and intense black hue, and of incredible profusion. His forehead, high beyond the usual dimensions; his cheeks, deep-sunken and heavily lined with wrinkles; and his hands, long, claw-like, and gnarled, were of such a deathly, marble-like whiteness as I have never elsewhere seen in man. His figure, lean to the proportions of a skeleton, was strangely bent and almost lost within the voluminous folds of his peculiar garment. But strangest of all were his eyes, twin caves of abysmal blackness, profound in expression of understanding, yet inhuman in degree of wickedness. These were now fixed upon me, piercing my soul with their hatred, and rooting me to the spot whereon I stood. Title and author: The Alchemist, a Gothic horror tale by H. P. Lovecraft (1908) Plot: The narrator, Antoine, is the last descendant of a noble family cursed by a sorcerer named Charles Le Sorcier, who swore revenge for the death of his father Michel Mauvais2. Antoine discovers that Charles still lives thanks to an elixir of eternal life, and that he is responsible for the premature deaths of his ancestors. Antoine confronts Charles in a subterranean chamber of the castle, where he reveals his secret and tries to kill him with a poison3. Antoine manages to escape but is horrified to hear Charles say that he is the very sorcerer who cursed his family six centuries ago. Theme: The tale explores themes such as the hereditary curse, the supernatural revenge, alchemy, and cosmic horror. Style: The tale is written in an archaic and elaborate style, typical of Lovecraft’s works, and makes references to elements of medieval history and culture. The tale also presents a dark and oppressive atmosphere, and a surprising and terrifying climax. The main characters of the tale “The Alchemist” by H. P. Lovecraft are: Antoine: The narrator and last descendant of a cursed noble family. Charles Le Sorcier: The sorcerer who cursed Antoine’s family and lives thanks to an elixir of eternal life. Michel Mauvais: Charles’s father, whose death by an ancestor of Antoine triggered the curse. First Paragraph: High up, crowning the grassy summit of a swelling mound whose sides are wooded near the base with the gnarled trees of the primeval forest, stands the old chateau of my ancestors. For centuries its lofty battlements have frowned down upon the wild and rugged countryside about, serving as a home and stronghold for the proud house whose honored line is older even than the moss-grown castle walls. These ancient turrets, stained by the storms of generations and crumbling under the slow yet mighty pressure of time, formed in the ages of feudalism one of the most dreaded and formidable fortresses in all France. From its machicolated parapets and mounted battlements Barons, Counts, and even Kings had been defied, yet never had its spacious halls resounded to the footsteps of the invader. Last Paragraph: Suddenly the wretch, animated with his last burst of strength, raised his hideous head from the damp and sunken pavement. Then, as I remained, paralyzed with fear, he found his voice and in his dying breath screamed forth those words which have ever afterward haunted my days and my nights. “Fool,” he shrieked, “can you not guess my secret? Have you no brain whereby you may recognize the will which has through six long centuries fulfilled the dreadful curse upon your house? Have I not told you of the great elixir of eternal life? Know you not how the secret of Alchemy was solved? I tell you; it is I! I! I! that have lived for six hundred years to maintain my revenge, FOR I AM CHARLES LE SORCIER!”




Antoine at 90 years old
Antoine at 30 years old
Antoine searching the castle
Charles Le Sorcier in flames
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Porte Cailhau
Historical landmark in Bordeaux, France
Built in 1495, this monument with a castle-like exterior was once the main gate to the city.
The Port Cailhau, thirty-five metres tall, was integrated into the city walls. In 1864, it was rented by a public letter writer and a person whose job was to weigh salt. They were both evicted in order to renovate the monument. There is a magnificent view of the oldest bridge in Bordeaux, the Pont de Pierre, from here.
Address: Pl. du Palais, 33000 Bordeaux, France
Architectural style: Gothic architecture
Phone: +33 5 56 00 66 00
The city gate in a defensive tower


Sitting at an outdoor table of the café 'Frères Cailloux' on pedestrian Place du Palais you can have plenty of time to study the architecture of this defensive tower-gate, at least its side facing the city. When the tower was built at the end of the 15th century the quay on its other side, by the Garonne, was not as we see it today, since it was sloping and paved with 'cailloux' (pebbles) from the river. Hence the name, based on a Gascon version of the word.


It is possible at certain opening hours to enter the building. The architecture is a mixture of the Gothic and the Renaissance and the tower was not detached from the ramparts as we can see on some remains at its rounded walls. There are machicolations all around it and on the roof are conical towers with in the middle a taller and thinner tower, that has a steep pyramid hip roof.



The tower was built in the times of King Charles VIII the Affable, after his 'victory' at the battle of Fornovo (near Parma) against a League under the command of the Venetians, who also saw themselves as victors. Historians talk of a tactic victory of the Venetians and a strategic victory of the French. The effigy of King Charles VIII can be seen on the river side of the tower, flanked on his left side by a Bishop of Bordeaux, who had joined him in battle, while on the right is a sculpture of Saint John the Evangelist.


On the city side, by the Place du Palais, the decoration on the tower is a crest with fleur-de-lys, held by two angels. The name of the place refers to the former residence of the Duke of Aquitaine, the 'Palais de l'Ombrière', which was torn down in the year 1800 after a big fire had destroyed much of it. From the Porte Cailhau it is not far to the Porte de Bourgogne, another city gate, but almost 300 years younger and of a very different character.

Bordeaux, France 🇫🇷
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
i lvoe the people telling me french names for castle parts in the notes of that post because i do know. i do know and they're way cooler and often provided alongside english ones but you have to admit it is kind of funny that english retained mostly the words of anglo-saxon origin given that features like machicolations/machicolis were increasingly decorative rather than functional after the norman conquest despite the proliferation of castles under william's rule
#peter posts#it's too bad i've given up on old french. i was working thru some hagiography translations a long time ago#also theres no sarcasm in this post i love. crastle and medieval languages
2 notes
·
View notes
Text










Caernarfon Castle is located in the county of Gwynedd in Caernarfon, Wales. The medieval castle was first built in 1283 by Edward I of England to help control the newly conquered land from Normans’ attacks and capture Wales. The castle is located upon a 394 AD Roman fort along the Menai Strait at the mouth of the Seiont River. It is the most ambitious of King Edward’s iron ring of castles as it included town walls. The medieval castle has a long history of attacks, so modifications, including the King’s Gate, were added to help with defenses throughout the years. In 1294, Welsh leader Madog Ap Llywelyn attacked and burned the castle. King Edward I, retook the castle and built the King’s Gate, a massive structure with a drawbridge over a pit with several portcullis, gates, guardhouses, and machicolations. By 1330, the castle had undergone the last of its extensions. The castle has two upper and lower inner courtyards and twelve octagonal towers built into the curtain wall that offer accommodations. The Queens Tower was once called the Banner Tower. It is the highest tower and the one that displays the flag. The Cistern Tower collected rainwater into a stone-lined tank, while the Well Tower had a fifty-foot-deep well. The Eagle Tower has three turrets with three floors, a spiral staircase, and a basement with access to the river through a portcullis. The Eagle Towers has ten sides with 18 feet thick walls to allow passages to be carved from them on the upper floors. The castle was besieged twice, once in the 15th century by Owain Glyn Dwr, who became the Prince of Wales from 1404-15. By the mid-16th century, a military was no longer needed, and the castle fell to ruin, while some of its wings were used as a county prison. Restoration of the castle began in the 19th century. In 1908, Caernarfon Castle was handed over to the Office of Works, who continued repairs. In the 20th century, the castle was used for a couple of royal ceremonies. Prince Charles received his formal title at Caernarfon Castle. The interior boasts circular stone fireplaces, a shop, and the Royal Welsh Fusiliers Museum, which houses uniforms, guns, medals, and exhibitions.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What we should have in our castle
In order to design the castle furnishings in Gothic style, we need to study the basic units that exist
youtube
The main tower and side towers with huge windows. Due to indoor factors, the window layout needs to be changed.
The fence itself, as a defensive measure, is not only used in a simple way. Machicolations can also be modified according to the structure of the city wall.
Some attack equipment can be placed inside the city, and various defenses can be added at the entrance, such as a murder hole attacking from the second floor.
Based on the principle of protecting the main city, finances, and food, consider the protection measures of the city from the perspective of attack, such as the granary being close to the main city.
youtube
There should be training and entertainment venues within the city.
We should consider adding stables, which are indeed things that should be protected.
We should consider items that adapt to the environment, such as fireplaces.
At the same time, we should consider lighting design, such as large windows.
And we need to pay attention to the building structure, such as the switch between stone and wood.
These are the functions that appear in the video:
Firewood granary pasture Toilet stable well bedroom Kitchen and dining room lounge outer city barracks Wengcheng Arsenal balcony Internal defense measures Built in church ballroom The living room Guard Room Hall, Court Secondary stage, lobby, living room, lounge The servant's room Warehouse Dungeon Trap room, fake floor, floor spikes, etc
1 note
·
View note
Text

Farming Sugar Cane with Allays - Tinker World 5 (018)
I want to add a sugar cane farm to my farming tower. Like the rest of the farms in this tower, I'm using an allay to collect the harvested sugar cane. It turns out, allays and scaffolding don't mix but that's okay. I have a fix.

Once that's done, it's time pretty up the tower. The texture and gradient gets a little clean-up and I've added windows to which help break up the face. The tower is topped with a combination of the battlements and machicolations.

Watch the episode on YouTube!
0 notes
Text

Deogiri/Daulatabad
Aurangabad, MH.
Panorama put together with Luminar, a photobombing exhortatory sign in the foreground removed using Pixelmator.
DAULATABAD FORT Daulatabad Fort (19°57' N: 75° 15'E) built on a 200 meter high conical hill, was one of the most powerful forts of the medieval Deccan. The entire ort compex consists of an area measuring approximately 94. 83 hectares, and represents a unique combination of military engineering, amazing town planning with unique water management system and architectural marvels with strong political and religious hold. It was founded by The Yadavas of Deogiri ("The hill of Gods") in 11th Century A.D. After Various attacks, the Khilji Dynasty annexed Daulatabad in 12th Century A.D. Sultan Muhammad-bin Tughluq, renamed Deogiri as Daulatabad ("Abode of Wealth") and got the capital shifted from Delhi to Daulatabad in 1328 A.D. But for various reasons he re-transferred his capital back to Delhi. In a quick succession of political events the area was wrested from the imperial authority and the Bahamani rulers under Hasan Gangu extended their control over Daulatabad as well. By 1499 the Nizam Shahis of Ahmednagar not only captured but also made Daulatabad as their capital in 1607 A.D. Daulatabad was finally captured by Mughals under Akbar and Shah Jahan, after a prolonged siege in 1633 A.D. For a short period Daulatabad was under the control of the Marathas before the Nizams of Hydrabad took control of it in 1724 A.D. The fort is one of the most complex and intricate forts of Deccan, having the honor of the capital of Yadavas for over a Century (1187-1294), capital of India during Tughlaq period (1328), and Capital of Njzamshahis of Ahmednagar (1607 A.D.) Daulatabad is also important in religious point of view, that from here the Sufism spread in Deccan. It is here that the famous medieval saint Janardhana Swami, the Guru of Ekanath attained Samadhi on the top of the hill. The defense system consists of two moats (Dry and Wet Moat) and a glacis, three encircling fortification walls with wall walks, Machicolations Bastions at regular intervals, Zigzag and lofty gates with iron Spinks, Strategic position of gun-turrets and Andheri. The combination of Hill and Land Fort, is divided into small sectors encircled by fortification walls. The fortified Ambarkot is planned for common people. Mahakot area having four distant lines of enclosure walls served the residential area for higher class of the society. The kalakot is the royal residential area with double line of fortifications. The balakot is the pinnacle portion where the pride of honor, the flag flutters. The fort consists of structures like Stepped wells, Reservoirs, Minar, Hammam, Baradari, Various Palaces, Andheri, Temples, Mosques, beside 10 unfinished rock cut caves. The water management system is unique with a network of terracotta pipe lines, drains etc. Because of its strategic location and its strong protective defenses it is aptly called as an impregnable fort and its possession was craved by most powerful dynasties ruling between 12th - 17th Century A.D. Its ownership became a matter of pride and prestige and haughty arrogance.
#Sony#WalkCam#RX100M2#history#Deogiri#Daulatabad#Aurangabad#Maharashtra#India#panorama#Luminar#Pixelmator
0 notes
Text
Oh, my, how the mighty have fallen. And by "mighty" I mean "dude who said 'machicolations' a lot".
Do you remember that Aussie sword guy who used to talk about medieval weapons?

And, like, he seemed pretty good at talking about swords and shit. He seemed to have a good grasp of the history and tactics. He'd analyze movie weapons for their realism and that was fun. He did demonstrations with real weapons. For a time I really looked forward to his videos popping up in my feed.
He seemed like a harmless sword-fighting aficionado.
But then I guess he wanted to spread his wings. So he started down an anti-woke path. Giving questionable critiques about media and feminism. He started defending boob armor by showing historical examples even though most of those were decorative and not battle ready like in the games.
Then he admitted he was a fan of The Daily Wire.
And that was disappointing.
I missed him nerding out about swords, ya know?
Well, Shad decided to spread his wings again.
He has become...
*bad French accent* An artiste.
You see, he types words into a little box. Then a little robot does a google image search and steals a bunch of art. Then that robot reconfigures that art to be nearly indistinguishable from the source material. Well... aside from the occasional artist watermark.

Whoops!
A.I. art is very difficult. Sometimes when you type words into the box you get a woman with 5 lopsided anime tiddies. Or 20 fingers on one hand. It takes time and effort and experience to type in the perfect magic words so that you get something close to your imagination that doesn't belong in some sort of Lovecraftian horror ripoff.
For example, check out this cool "pirate hat" I asked A.I. to place on my head.
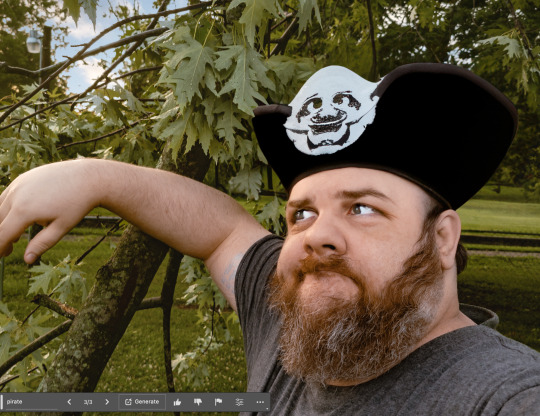
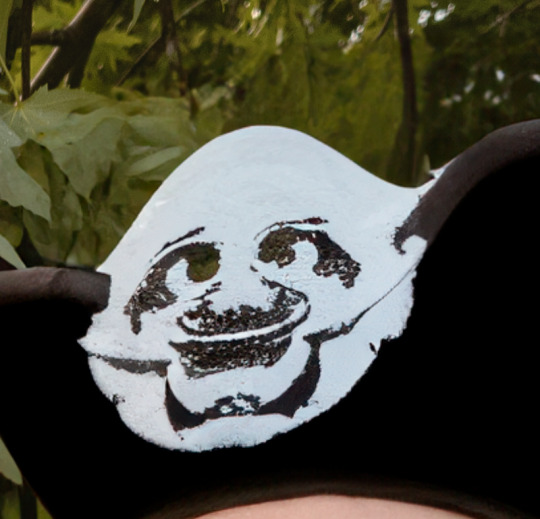


Clearly, I am not skilled enough at typing words into a box to get a proper pirate hat.
It. Is. Not. Easy.
I heard someone say you have to type things in a box for 10,000 hours before you start getting truly masterful generations.
I mean, you can't type "marathon runners" and expect that to actually work.
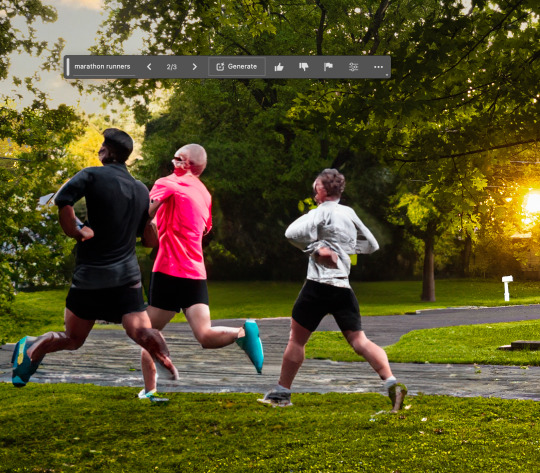

THIS REQUIRES SKILL, PEOPLE.
And I am a lowly amateur. I can only dream of becoming the box-typist Shad has honed himself into.
The thing is... Shad is very upset.
He is upset that you don't like his "art" and he is ready to die on this hill.
So... before he croaks on a mound of bullshit, he has something to show you. He has created something truly brilliant and when you see it, he is convinced you will validate his considerable efforts.
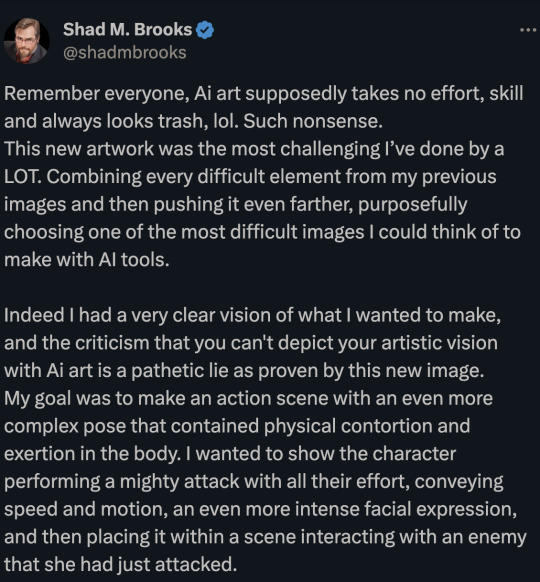

Before I show you his "Not. Easy." artistic masterpiece I'd like you to sit with what he has said for a second.
Ruminate in the verbiage.
Process the ideas and points of view presented.
Digest his plea for you to accept and love his hard won battle after typing words into a box to manifest his imaginings.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Have you sat?
Ruminated?
Processed?
Digested?
Okay, here it is...

8K notes
·
View notes