#its time for another Revolution
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Me, metaphorically whacking non Habsburg historians with a rolled up newspaper: it's not the Austro-Hungarian empire or Austria-Hungary until 1867. Before that it's Austria, the Austrian Empire, or the Habsburg Empire.
#grad school stuff#my personal pet peeve#every time someone calls it Austria-Hungary before the Ausgleich i gain another grey hair#brought to you by me seeing a historian of England discuss the 1848 revolutions in Hungary as happening in 'the Austro-Hungarian empire'#if it was Austro-Hungarian at that time the Hungarians wouldnt be trying to negotiate for autonomy#its contradictory
70 notes
·
View notes
Text

Incredible sequence of posts on the dash just now
#to be clear bc i know im swinging a bat at a hornets nest i think both of these posts make decent points#i am a socialist but i do not believe that revolutionary and reformist politics are necessarily mutually exclusive#multiple things can be true at once#capitalism is a fundamentally exploitative and violent system which must be swiftly dismantled for the sake of all life on the planet#and those who enter parliamentary politics in hopes of enacting reform often end up serving the interests of capital and western imperialis#but at the same time#we must not abrogate responsibility by refusing to exercise our hard-won democratic right to participate in elections#its an insult to the millions of people around the world living under authoritarian regimes for one thing and its fucking stupid for anothe#we must be realistic about the state of class consciousness in most western societies and work pragmatically with the tools available to us#we must also try to minimise harm and suffering as best we can and produce the best outcome for the greatest number of people#while also not leaving behind those who are marginalised#at times both reform and revolution seem impossible tasks and yet we must continue to work towards them both as best we can#on the topic of voting - i live in australia where its compulsory and where we also have preferential voting#which means that its impossible to “waste your vote” by voting for a minor party#i typically vote for our greens party - who are the largest minor party in the country and the most progressive on most issues#for example they're basically the only ones consistently condemning our (labour) government's support of israel#so to be clear for the americans reading these tags#if i lived in the USA i would vote in every election#i might sometimes vote for democratic candidates if they had genuinely progressive policies#but no i would not “vote blue no matter who”#okay i'm finished tilting at windmills now im just paranoid about being misinterpreted asdgfhjklk#voting#elections#the trolley problem#reform#revolution#leftist#socialism#marxist
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
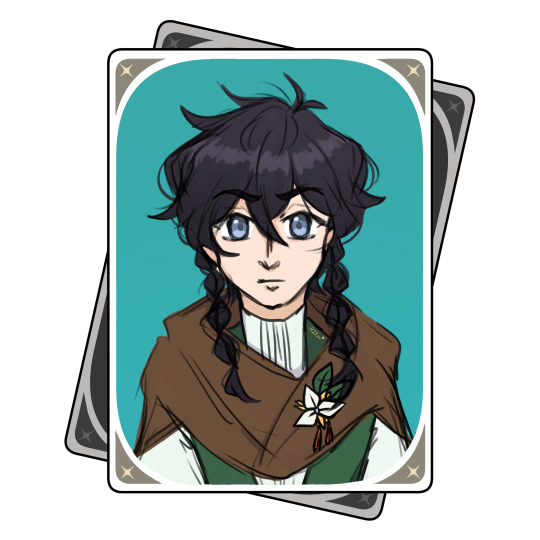

guys omg bard is leaked to be a new playable 5* for v5.0 😳😳??!?!?!???
bonus doodle sheet of bards i drew instead of sleeping

#tulip draws#nameless bard#himmel#he just wont get out of my brain#one bard leaves for a second to make way for yet another one#why wont they leave me aloooooone#anyway. what does the council think of nb meeting venti when he was Baby and Squishy#everything is the same except they meet when he was young and therefore they have more time tgt#ofc except the dying part#they live happily ever after#now what if archon bard since he didnt die.....#maybe I'LL die instead#anyway.#mond kids are raised on three things: music wine and REVOLUTION#we ignore that shitty kitty bard at the corner hes my first doodle to get things going#aka me realizing it is Not the time for pose studying so we do sillies#ok i gtg sleep fr its 638 am
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
You know, very rarely do I run into accounts of historical cannibalism that are completely new to me. But I did today and I'm frankly completely taken aback by this
Fro the article: "The Guangxi Massacre comprised a series of lynchings and massacres in the Chinese province of Guangxi between 1967 and 1968, during the Cultural Revolution. The official record shows an estimated death toll between 100,000 and 150,000. Methods of murder included beheading, beating, live burial, stoning, drowning, boiling, and disemboweling. In specific areas, including Wuxuan County and Wuming, Nanning, hundreds of incidents of human cannibalism occurred—even though no famine conditions existed. According to records that have been made public, at least 137 people were eaten, with thousands of people having participated in the cannibalism... In 1993, The New York Times stated that the incidents reported from Guangxi were apparently the most extensive episodes of cannibalism in the world in the last century or more. They were also different from any others in that those who took part were not motivated by hunger or psychopathic illness. Instead, the actions appeared to be ideological: the cannibalism, which the documents say took place in public, was often organized by local Communist Party officials, and people apparently took part together to prove their revolutionary ardor."
#I knew about the desperately bad famine conditions in this period so when I saw 'cannibalism during the cultural revolution'#that's what I assumed this was and from a historical viewpoint that's pretty normal and not particularly newsworthy#but this was something Totally Different#I had Never heard of this and frankly its so extreme that I don't even have another case to even really compare it to#and you know me I am not at all flustered by cannibalism but this bowled me over#the normalcy of the circumstances and within a homogeneous ethnic and cultural environment?#the scale?#the recentness? like my parents were alive when this happened#its on the level of other inexplicably extreme violence (rwanda or the french revolution) but generally those situations don't end#with fun family patriotic-solidarity-barbecues of the victims afterwards#I was so in disbelief I went looking for scholarly stuff on this because it just felt so extreme like it had to be be exaggerated#but legit research came up (mostly from the 90s when this story apparently broke globally)#I'm still not over this#at least this is something you can throw at the 'eat the rich' people next time they want to glorify guillotining throw pillow owners#guangxi massacre#history
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
It do feel like the last year/s has been building up new We Didn’t Start The Fire lyrics
#China is being kinda sus in the south sea#Ukraine is losing less than Russia to a point where they’re now trying to take more cities#uks farage riots#Bangladesh having its second revolution due to nepotism shit#USA going source dude trust me every time they say there’ll be a ceasefire after Israel massacres another 100 people#the megaquake set to happen to Japan soon#ships having to go round the cape of good hope like it’s fucking 1814#it do really be going on and on and on and oooon
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Viva La Revolution

Elon received no votes. Elon will take no oath.
The level of suffering inflicted by someone with wealth to last 10,000 years is perverse.
#its time my friends#time for another revolution#the upper class has forgotten how fragile the pedastals they build for themselves are#we must remind them that we have power in numbers and can revolt.
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
If I had shapeshifting powers like Odo I'd turn into an orangutan and teach other great apes sign language (but for real) and ignite Intelligent Super Ape Socialism
#i may have planet of the apes on my current sci-fi roster alongside ds9#the new ones that i never watched bc i grew up on the old ones and also didn't care for james franco & his involvement lol#thank caesar he was only in the first (which ho boy has some of the worst dialogue writing ive experienced in a long time)#if they make the CGI any further realistic it will be too much. the newest one was ever so slightly too uncanny imo#they are apes stop trying to give them more humanlike gestures/expressions. ape express self & communicate emotions in ape way not human#also the story was the worst. Rise had bad 2011 dialogue but a good story while Kingdom was v bad story which is way less forgivable#its trying to do too much & thus too many threads go unwoven by the end#like clearly its laying the groundwork for Noa igniting an ape educational revolution that leads to Ape City & its scientists but it should#have been more focused on that/the ape factions. but noo they hired a pretty young actress to get in the way for 2 hours so thats where the#story spent most of its time 🙄🙄🙄#best part of the human storyline was the 5 seconds of dichen lachman at the very end#Dawn and War were sick as hell though. really good movies & the ape mocap CGI goldilocks-ed in a way we'll probably never see again bc ever#every studio is convinced hyper-realism is the ultimate universal goal with sci-fi/fantasy visual effects 🙄#ANYWAY PLANET OF THE APES RANT FOR ANOTHER DAY IF I DONT STOP MYSELF NOW ILL YAP ABOUT IT ALL NIGHT I FUCKIN' LOVE PLANET OF THE APES#if intelligent aliens exist & are aware of earth they dont fuck w humans bc they see how we treat our ape cousins in this essay i will.....
1 note
·
View note
Text
"The man who has called climate change a “hoax” also can be expected to wreak havoc on federal agencies central to understanding, and combating, climate change. But plenty of climate action would be very difficult for a second Trump administration to unravel, and the 47th president won’t be able to stop the inevitable economy-wide shift from fossil fuels to renewables.
“This is bad for the climate, full stop,” said Gernot Wagner, a climate economist at the Columbia Business School. “That said, this will be yet another wall that never gets built. Fundamental market forces are at play.”
A core irony of climate change is that markets incentivized the wide-scale burning of fossil fuels beginning in the Industrial Revolution, creating the mess humanity is mired in, and now those markets are driving a renewables revolution that will help fix it. Coal, oil, and gas are commodities whose prices fluctuate. As natural resources that humans pull from the ground, there’s really no improving on them — engineers can’t engineer new versions of coal.
By contrast, solar panels, wind turbines, and appliances like induction stoves only get better — more efficient and cheaper — with time. Energy experts believe solar power, the price of which fell 90 percent between 2010 and 2020, will continue to proliferate across the landscape. (Last year, the United States added three times as much solar capacity as natural gas.) Heat pumps now outsell gas furnaces in the U.S., due in part to government incentives. Last year, Maine announced it had reached its goal of installing 100,000 heat pumps two years ahead of schedule, in part thanks to state rebates. So if the Trump administration cut off the funding for heat pumps that the IRA provides, states could pick up the slack.

Local utilities are also finding novel ways to use heat pumps. Over in Massachusetts, for example, the utility Eversource Energy is experimenting with “networked geothermal,” in which the homes within a given neighborhood tap into water pumped from underground. Heat pumps use that water to heat or cool a space, which is vastly more efficient than burning natural gas. Eversource and two dozen other utilities, representing about half of the country’s natural gas customers, have formed a coalition to deploy more networked geothermal systems.
Beyond being more efficient, green tech is simply cheaper to adopt. Consider Texas, which long ago divorced its electrical grid from the national grid so it could skirt federal regulation. The Lone Star State is the nation’s biggest oil and gas producer, but it gets 40 percent of its total energy from carbon-free sources. “Texas has the most solar and wind of any state, not because Republicans in Texas love renewables, but because it’s the cheapest form of electricity there,” said Zeke Hausfather, a research scientist at Berkeley Earth, a climate research nonprofit. The next top three states for producing wind power — Iowa, Oklahoma, and Kansas — are red, too.
State regulators are also pressuring utilities to slash emissions, further driving the adoption of wind and solar power. As part of California’s goal of decarbonizing its power by 2045, the state increased battery storage by 757 percent between 2019 and 2023. Even electric cars and electric school buses can provide backup power for the grid. That allows utilities to load up on bountiful solar energy during the day, then drain those batteries at night — essential for weaning off fossil fuel power plants. Trump could slap tariffs on imported solar panels and thereby increase their price, but that would likely boost domestic manufacturing of those panels, helping the fledgling photovoltaic manufacturing industry in red states like Georgia and Texas.
The irony of Biden’s signature climate bill is states that overwhelmingly support Trump are some of the largest recipients of its funding. That means tampering with the IRA could land a Trump administration in political peril even with Republican control of the Senate, if not Congress. In addition to providing incentives to households (last year alone, 3.4 million American families claimed more than $8 billion in tax credits for home energy improvements), the legislation has so far resulted in $150 billion of new investment in the green economy since it was passed in 2022, boosting the manufacturing of technologies like batteries and solar panels. According to Atlas Public Policy, a research group, that could eventually create 160,000 jobs. “Something like 66 percent of all of the spending in the IRA has gone to red states,” Hausfather said. “There certainly is a contingency in the Republican party now that’s going to support keeping some of those subsidies around.”
Before Biden’s climate legislation passed, much more progress was happening at a state and local level. New York, for instance, set a goal to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions from 1990 levels by 40 percent by 2030, and 85 percent by 2050. Colorado, too, is aiming to slash emissions by at least 90 percent by 2050. The automaker Stellantis has signed an agreement with the state of California promising to meet the state’s zero-emissions vehicle mandate even if a judicial or federal action overturns it. It then sells those same cars in other states.
“State governments are going to be the clearest counterbalance to the direction that Donald Trump will take the country on environmental policy,” said Thad Kousser, co-director of the Yankelovich Center for Social Science Research at the University of California, San Diego. “California and the states that ally with it are going to try to adhere to tighter standards if the Trump administration lowers national standards.”
[Note: One of the obscure but great things about how emissions regulations/markets work in the US is that automakers generally all follow California's emissions standards, and those standards are substantially higher than federal standards. Source]
Last week, 62 percent of Washington state voters soundly rejected a ballot initiative seeking to repeal a landmark law that raised funds to fight climate change. “Donald Trump’s going to learn something that our opponents in our initiative battle learned: Once people have a benefit, you can’t take it away,” Washington Governor Jay Inslee said in a press call Friday. “He is going to lose in his efforts to repeal the Inflation Reduction Act, because governors, mayors of both parties, are going to say, ‘This belongs to me, and you’re not going to get your grubby hands on it.’”
Even without federal funding, states regularly embark on their own large-scale projects to adapt to climate change. California voters, for instance, just overwhelmingly approved a $10 billion bond to fund water, climate, and wildfire prevention projects. “That will be an example,” said Saharnaz Mirzazad, executive director of the U.S. branch of ICLEI-Local Governments for Sustainability. “You can use that on a state level or local level to have [more of] these types of bonds. You can help build some infrastructure that is more resilient.”
Urban areas, too, have been major drivers of climate action: In 2021, 130 U.S. cities signed a U.N.-backed pledge to accelerate their decarbonization. “Having an unsupportive federal government, to say the least, will be not helpful,” said David Miller, managing director at the Centre for Urban Climate Policy and Economy at C40, a global network of mayors fighting climate change. “It doesn’t mean at all that climate action will stop. It won’t, and we’ve already seen that twice in recent U.S. history, when Republican administrations pulled out of international agreements. Cities step to the fore.”
And not in isolation, because mayors talk: Cities share information about how to write legislation, such as laws that reduce carbon emissions in buildings and ensure that new developments are connected to public transportation. They transform their food systems to grow more crops locally, providing jobs and reducing emissions associated with shipping produce from afar. “If anything,” Miller said, “having to push against an administration, like that we imagine is coming, will redouble the efforts to push at the local level.”
Federal funding — like how the U.S. Forest Service has been handing out $1.5 billion for planting trees in urban areas, made possible by the IRA — might dry up for many local projects, but city governments, community groups, and philanthropies will still be there. “You picture a web, and we’re taking scissors or a machete or something, and chopping one part of that web out,” said Elizabeth Sawin, the director of the Multisolving Institute, a Washington, D.C.-based nonprofit that promotes climate solutions. “There’s this resilience of having all these layers of partners.”
All told, climate progress has been unfolding on so many fronts for so many years — often without enough support from the federal government — that it will persist regardless of who occupies the White House. “This too shall pass, and hopefully we will be in a more favorable policy environment in four years,” Hausfather said. “In the meantime, we’ll have to keep trying to make clean energy cheap and hope that it wins on its merits.”"
-via Grist, November 11, 2024. A timely reminder.
#climate change#climate action#climate anxiety#climate hope#united states#us politics#donald trump#fuck trump#inflation reduction act#clean energy#solar power#wind power#renewables#good news#hope
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

My concepts for the development progress of an Iterators Puppet
-my ideas below
-Feasibility Study
[1]: First autonomous control module, any instruction to be given must be done manually through physical means (the keys), outputs were shown through the screen. A very primitive system, however, did its job proving the greater machine concept was achievable. While it does look like a lens above the monitor, this was a simple status gauge for benchmarking.
-Prototyping and Development
[2]: Now with the capability to wirelessly and audibly communicate to receive instructions and inputs. The system was no longer directly integrated into the facility, and resided on the first instance of an iterator's arm. This was considered a feat due to the complications with isolating the control module from the rest of the iterators components, while keeping processing power. A permanent connection/umbilical was needed to sustain life and function though.
To “talk” back, they were crafted with multidimensional projectors, the mobile arm allowing the angles and variance for this projection. Only later into development were advanced speakers installed for optimized understanding, however the extra computing power required to synthesize proper speech was found to strain the contained module, so this function had rare use in the end.
[3]: At this point there was a change in perspective in the project. What once were machines to simply compute and simulate, were now planned to be the home, caregiver, and providers. The further the project came to fruition the more religious importance was placed upon these “random gods”. From this stance not only did the puppets have to manage and control their facilities, they had to communicate with the people and priests. To represent benevolent beings who will bring their end and salvation. In this process iterators began to take a more humanoid shape, to better reflect their parents. Development was focused on compacting the puppet closer to the size of an ancient for this purpose. This stage was the first to incorporate a cloak/clothing into their design considerations, to further akin themselves in looks. The cloak would hide the iterators' engineered bodies and give a body to their silhouette.
[4]: As bioengineering and mechanics were rapidly progressing due to the void fluid revolution, this allowed plenty of margin for developing the outer design of the iterator puppets. This prototype was the first to incorporate limbs for the purpose of body language. This was another step in the drive to give a body to their random gods.
-Final Iterations
[5]: First generation iterators had the final redesign of puppet bodies. Far different from their first designs, they are fully humanoid. Their bodies are shaped to be organic and as full of life as they could at the time. Their center of sapience has fully settled within their body, as can be seen as their unconscious use of limbs without the direct intention for communication. This can also see how they manage their work, where many of the functions (which can be done with just an internal request) are operated through physical gestures of their limbs. Their puppet chambers also allow for full comprehensive projection, where many of their working monitors are displayed. It is seen how iterators prefer to utilize their traversal arm to transfer between the current working projection window.
These designs were hardy and nearly self-sufficient, only requiring minimal power from their umbilical to charge. (However was still limited in the terms of internal power production, for this first generation extensive batteries sufficed)
[6]: Later generation not only incorporated advanced bioengineering internally, but externally. While still a hardened shell, their body plates have been incorporated into the organics of the puppet, maintaining the protective requirements while barely leaving a trace of hinges or plates. This “soft” skin had drawbacks, such as reduced durability to the first generations, this was offset by the greatly enhanced repair speeds and capability this type of skin allowed.
Internal power generation was implemented into these late generation models. If the case arose, the Puppet could be disconnected from their umbilical and still be conscious from an undefined period of time. (However this would limit the operating capacity of the puppet when running self sufficiently) This greatly eased maintenance works, as the Puppet could still run the greater facility wirelessly while work was done on the chamber, arm or whatever as needed.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I've said it before and I'll say it again: my absolutely favorite thing about Nona the Ninth, and the reason it's one of my favorite books of all time, is the love.
Nona is six months old. She's been 'born' into a cruel world; a city crammed with refugees, under seige from a hostile empire. She lives in the body of another girl, a girl her caretakers knew and cared about. She is a weapon, a symbol of destruction, the promise of the revolutions salvation or its obliteration.
And yet. At no point in the book is Nona ever hated. Her friends love her; they make space for her, they are patient when she doesn't understand something and make an effort to include her at every opportunity. The teacher and the Angel love her, as much as they love all their students; they treat Nona as an equal, and even when they're worried about her they show her courtesy and dignity. Camilla, Palamedies, and Pyrra love her; they braid her hair, make sure she eats, buy her stupid fish'n'chip shop shirts and share ass jokes with her. Even Corona and We Suffer are kind and patient when they don't have to be. The only time Nona ever experiences cruelty is when Hot Sauce shoots her for being a zombie, and even then Hot Sauce forgives her only a few chapters later.
Nona the Ninth is ultimately about love- loving and being loved. It's in every second, every word of Nona's being. It says: "Even when we are terrible, even when we are scared and hateful, we cannot help but love."
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
107 years ago today an organized group of workers in the Russian Empire decided they had had enough of war, misery, the oppression of women, and of a corrupt democracy that had promised much and changed nothing, the Tsar still in his palaces, the workers still giving their life for a cause foreign to the working class of Europe and the world. Most bolsheviks were industrial workers, with an insufficient formal education, precarious salaries and conditions. The working class in the Russian Empire had tried liberal democracy, had seen its hipocrisy in the months following the election of the provisional government, and understood their historic goal of progressing further beyond the democracy of the landowner, businessman and aristocrat. It wasn't the first time the proletariat had attempted to take power, both worldwide and in the Russian Empire, but this time they were ready, educated, an organized enough.
The armies of 14 imperialist powers combined could not stop the will of a mass of workers that had realized their worth, their potential, and most importantly, their dignity. They no longer had to bow down to paternalism, electoralism, and the capitalists to whom they sold their labor, no armed intervention, no amount of propaganda, no adventurist distraction, could take away from that fact. This isn't a fantasy, it isn't idealistic, it's a historical fact, that revolutions are possible, have happened, succeeded, and that the opportunity presents itself sooner than most expect. The only task at hand is to organize towards it. Agitation, education, an actual dual power structure predicated on a unified will, not on voluntarism and horizontalism.
I understand the topic at hand for the last 2 days and many more to come will be the results of the US election. But the US is not the only liberal democracy that increasingly creates disappointment among the social majority. After all the posting about the various liberals that make up the US electoral environment, it is imperious that nobody falls into despair. Not in a self-care way, not in the way most left-liberals have been talking about, referring to an abstract sense of "preparing", but because of the simple necessity for this election to further erode any popular faith in reformism, whether it's Trump's reforms, Harris' reforms, Bernie's reforms, or Stein's reforms. Wallowing in despair is as useful as placing yet more stake into whoever is wheeled out next to promise even less, in what will most certainly be also called the most important elections of our lifetimes.
Return to the working class of the Russian Empire, of a fractured and hungry China, to the colony of Indochina, to the plantation island that was Cuba. And I urge you to exercise some perspective. These masses of people had suffered more than you for longer than you. Nobody's asking you to feel guilty about your economic position in the world, we're asking you to realize that, for as long as there have been modes of production predicated on the exploitation, division and discrimination of a producing class, there have always been options, better options than sinking into despondent depression. They have managed to cast off their yoke and build towards a society not based on exploitation. They're not utopias, and mistakes have been and will be committed, but they all realized and understood that it's better to commit our own mistakes, than to toil under the rational oppression by another class for any longer.
#seriousposting#I have comrades in my party who began their activity as communists before the USSR fell. they're still going and are as convinced as ever
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
─── ❝𝓝ot in this 𝓛ife❞





adrian tepes x gn!reader
─ summary; Adrian meets the reincarnation of his past love in Paris but, feeling guilty for their past death, decides to leave to keep them safe.
word count; 2.1k
cw; angst, reincarnation, castlevania nocturne adrian/alucard
request; Hello! Been adoring the Nocturne Alucard fics(*´ω`*) If requests are still open, could I request Nocturne-era Alucard with a s/o that’s reincarnated from his first partner(from the original series or otherwise), maybe running into them in Paris? I’m always a sucker for immortal/one of their partners that keeps reincarnating.
a/n; hiii im rlly glad you're enjoying my nocturne alucard fics! i hope this is to your liking!! <3
─ navigation
─ masterlist

The city of Paris was a paradox—a place of beauty and chaos, revolution and romance. To Alucard, it was yet another passing fragment in the long tapestry of his existence. He walked through the streets with an almost spectral presence, unnoticed by those who bustled around him. The air was thick with the scent of damp stone, the occasional waft of bread from a nearby bakery, and the distant clang of bells. Yet none of it pierced the veil of his thoughts.
His immortality, once a shield, had become a heavy burden. Time had dulled his passion, and though he fought for the greater good, he often wondered if his presence truly mattered. In his long life, he had loved and lost, and the memory of those losses had become his constant shadow.
Tonight was no different. He wandered through the dimly lit streets, drawn to the life around him yet untouched by it. The people were ghosts of their own kind—passing figures who would fade with the dawn of another century. He had resigned himself to this rhythm, the endless march of time without end.
Until he felt it.
A tug, faint and almost imperceptible, pulled at something deep within him. It wasn’t physical—no sound or sight had alerted him—but an ache in his chest that stilled his steps. Alucard froze, his golden eyes narrowing as he scanned the crowded square ahead. It was as though the very air had shifted, humming with energy that only he could feel.
And then he saw you.
You stood by a vendor’s cart, a soft lantern glow illuminating your face. You were studying a trinket with quiet curiosity, the way your head tilted and your fingers grazed the item achingly familiar. For a moment, Alucard thought he was seeing a ghost—a cruel trick of his memory. But no, this was different. You were no phantom. You were real, your breath forming faint clouds in the cold air.
His heart, long quiet in its rhythm, seemed to stutter.
You didn’t look exactly the same—your features were new, your clothing suited to this era—but there was no mistaking the essence of you. He had memorized that essence, once cherished it with all the passion of his immortal soul. He had mourned its absence for lifetimes.
And now, impossibly, you were here.
Alucard didn’t realize he had moved until he was closer, his steps silent on the cobblestones. The crowd seemed to part around him, the world narrowing until only you remained. As if sensing his gaze, you looked up, your eyes meeting his.
The moment stretched endlessly.
Your expression flickered with surprise, then confusion, and finally, something deeper—something that mirrored the ache in his chest. “Do I know you?” you asked, your voice soft yet laced with curiosity.
Alucard’s throat tightened. How could he explain centuries of longing in a single moment? “I… don’t believe we’ve met,” he said, though the words tasted like a lie. His voice was steady, but his golden eyes betrayed him, shining with emotions too vast to contain.
You studied him, your brows furrowing slightly. “Are you sure? You seem so familiar, like someone I’ve… known before.”
The quiet recognition in your voice nearly unraveled him. He fought to maintain his composure, his mind a whirlwind of thoughts. Could it truly be you? Or was this some cruel twist of fate—a reincarnation without memory, a soul that had moved on while his remained anchored to the past?
He took a step closer, his movements careful, reverent. “Some souls,” he said softly, “are destined to meet again.”
Your lips parted slightly, and for a moment, you seemed at a loss for words. Then you smiled—a small, tentative thing, but it lit up the space between you. “I don’t know why, but that feels… right. Like I’ve been waiting for this.”
Alucard felt his breath catch. The way you looked at him now, with trust and curiosity, was so achingly familiar. His heart—long silent and cold—felt alive again, beating in time with a hope he dared not name.
“May I ask your name?” he asked, his voice gentle.
You told him, and the sound sent a shiver through him. It was different, yet it carried an echo of the name he had whispered in lifetimes past. He repeated it, savoring the way it felt on his tongue.
“What about you?” you asked, tilting your head. “Who are you?”
For a moment, he hesitated. The name “Alucard” was the shield he wore, the identity he had forged to bear the weight of his lineage. But here, with you, it felt wrong. He wanted you to know him—not the son of Dracula, not the immortal warrior, but the man beneath.
“Adrian,” he said finally, the name quiet yet full of meaning. “You can call me Adrian.”
Your smile widened, and the sight of it made his chest ache. “It’s nice to meet you, Adrian.”
As the two of you wandered through the cobbled streets, a quiet understanding passed between you. You spoke of small things—the city, the people, the revolution brewing in every shadow. Yet, underneath it all, there was an unspoken bond, a connection that transcended words.
But with every step, the weight of the past began to press heavier on Alucard’s heart. He couldn’t ignore it—the memory of your previous life, the way he had failed to protect you, the moment you had been torn from him because of his presence in your world.
You had died because of him.
He stopped walking, his golden eyes clouded with sorrow. You noticed his sudden silence, turning to face him with concern. “Adrian? What’s wrong?”
He opened his mouth to speak but faltered, the words catching in his throat. How could he explain the truth without condemning himself? How could he tell you that loving him, being near him, was a danger you didn’t deserve?
“I… can’t stay,” he said finally, his voice low and heavy.
Your eyes widened, confusion and hurt flashing across your face. “What? Why?”
“I shouldn’t have approached you,” he said, his gaze falling to the ground. “It was selfish of me. I thought… I thought I could handle seeing you again, but I can’t. I’ve already caused you so much pain. I won’t do it again.”
“Adrian,” you whispered, stepping closer. “I don’t understand. What are you talking about?”
He closed his eyes, his fists clenching at his sides. “You don’t remember, but I do. You died because of me. In another life, you loved me, and it led to your end. I can’t let that happen again. I can’t risk losing you a second time.”
Your heart ached at the raw pain in his voice, but before you could respond, he turned away.
“Wait!” you called, your voice trembling. “Will I ever see you again?”
He stopped, his back to you, his golden hair catching the faint light of the lanterns. For a moment, he said nothing, the silence stretching endlessly. Then, he spoke, his voice barely above a whisper.
“𝓝𝓸𝓽 𝓲𝓷 𝓽𝓱𝓲𝓼 𝓵𝓲𝓯𝓮.”
And with that, he vanished into the night, leaving you alone with a heart full of questions and the faint echo of a love you couldn’t remember but couldn’t forget.

© STVRBOYY — do not copy, translate, modify, or plagiarize my work. reblogs are appreciated!

#adrian tepes x reader#alucard x reader#netflix castlevania#castlevania x reader#castlevania#adrian fahrenheit tepes#adrian tepes#adrian tepes x you#castlevania nocturne season 2#castlevania alucard#alucard tepes#castlevania x you
531 notes
·
View notes
Text

I feel that one of the most overlooked aspects of studying the French Revolution is that, in 18th-century France, most people did not speak French. Yes, you read that correctly.
On 26 Prairial, Year II (14 June 1794), Abbé Henri Grégoire (1) stood before the Convention and delivered a report called The Report on the Necessity and Means of Annihilating Dialects and Universalising the Use of the French Language(2). This report, the culmination of a survey initiated four years earlier, sought to assess the state of languages in France. In 1790, Grégoire sent a 43-question survey to 49 informants across the departments, asking questions like: "Is the use of the French language universal in your area?" "Are one or more dialects spoken here?" and "What would be the religious and political impact of completely eradicating this dialect?"
The results were staggering. According to Grégoire's report:
“One can state without exaggeration that at least six million French people, especially in rural areas, do not know the national language; an equal number are more or less incapable of holding a sustained conversation; and, in the final analysis, those who speak it purely do not exceed three million; likely, even fewer write it correctly.” (3)
Considering that France’s population at the time was around 27 million, Grégoire’s assertion that 12 million people could barely hold a conversation in French is astonishing. This effectively meant that about 40% of the population couldn't communicate with the remaining 60%.
Now, it’s worth noting that Grégoire’s survey was heavily biased. His 49 informants (4) were educated men—clergy, lawyers, and doctors—likely sympathetic to his political views. Plus, the survey barely covered regions where dialects were close to standard French (the langue d’oïl areas) and focused heavily on the south and peripheral areas like Brittany, Flanders, and Alsace, where linguistic diversity was high.
Still, even if the numbers were inflated, the takeaway stands: a massive portion of France did not speak Standard French. “But surely,” you might ask, “they could understand each other somewhat, right? How different could those dialects really be?” Well, let’s put it this way: if Barère and Robespierre went to lunch and spoke in their regional dialects—Gascon and Picard, respectively—it wouldn’t be much of a conversation.
The linguistic make-up of France in 1790
The notion that barely anyone spoke French wasn’t new in the 1790s. The Ancien Régime had wrestled with it for centuries. The Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts, issued in 1539, mandated the use of French in legal proceedings, banning Latin and various dialects. In the 17th and 18th centuries, numerous royal edicts enforced French in newly conquered provinces. The founding of the Académie Française in 1634 furthered this control, as the Académie aimed to standardise French, cementing its status as the kingdom's official language.
Despite these efforts, Grégoire tells us that 40% of the population could barely speak a word of French. So, if they didn’t speak French, what did they speak? Let’s take a look.
In 1790, the old provinces of the Ancien Régime were disbanded, and 83 departments named after mountains and rivers took their place. These 83 departments provide a good illustration of the incredibly diverse linguistic make-up of France.


Langue d’oïl dialects dominated the north and centre, spoken in 44 out of the 83 departments (53%). These included Picard, Norman, Champenois, Burgundian, and others—dialects sharing roots in Old French. In the south, however, the Occitan language group took over, with dialects like Languedocien, Provençal, Gascon, Limousin, and Auvergnat, making up 28 departments (34%).
Beyond these main groups, three departments in Brittany spoke Breton, a Celtic language (4%), while Alsatian and German dialects were prevalent along the eastern border (another 4%). Basque was spoken in Basses-Pyrénées, Catalan in Pyrénées-Orientales, and Corsican in the Corse department.
From a government’s perspective, this was a bit of a nightmare.
Why is linguistic diversity a governmental nightmare?
In one word: communication—or the lack of it. Try running a country when half of it doesn’t know what you’re saying.
Now, in more academic terms...
Standardising a language usually serves two main purposes: functional efficiency and national identity. Functional efficiency is self-evident. Just as with the adoption of the metric system, suppressing linguistic variation was supposed to make communication easier, reducing costly misunderstandings.
That being said, the Revolution, at first, tried to embrace linguistic diversity. After all, Standard French was, frankly, “the King’s French” and thus intrinsically elitist—available only to those who had the money to learn it. In January 1790, the deputy François-Joseph Bouchette proposed that the National Assembly publish decrees in every language spoken across France. His reasoning? “Thus, everyone will be free to read and write in the language they prefer.”
A lovely idea, but it didn’t last long. While they made some headway in translating important decrees, they soon realised that translating everything into every dialect was expensive. On top of that, finding translators for obscure dialects was its own nightmare. And so, the Republic’s brief flirtation with multilingualism was shut down rather unceremoniously.
Now, on to the more fascinating reason for linguistic standardisation: national identity.
Language and Nation
One of the major shifts during the French Revolution was in the concept of nationhood. Today, there are many ideas about what a nation is (personally, I lean towards Benedict Anderson’s definition of a nation as an “imagined community”), but definitions aside, what’s clear is that the Revolution brought a seismic change in the notion of French identity. Under the Ancien Régime, the French nation was defined as a collective that owed allegiance to the king: “One faith, one law, one king.” But after 1789, a nation became something you were meant to want to belong to. That was problematic.
Now, imagine being a peasant in the newly-created department of Vendée. (Hello, Jacques!) Between tending crops and trying to avoid trouble, Jacques hasn’t spent much time pondering his national identity. Vendéen? Well, that’s just a random name some guy in Paris gave his region. French? Unlikely—he has as much in common with Gascons as he does with the English. A subject of the King? He probably couldn’t name which king.
So, what’s left? Jacques is probably thinking about what is around him: family ties and language. It's no coincidence that the ‘brigands’ in the Vendée organised around their parishes— that’s where their identity lay.
The Revolutionary Government knew this. The monarchy had understood it too and managed to use Catholicism to legitimise their rule. The Republic didn't have such a luxury. As such, the revolutionary government found itself with the impossible task of convincing Jacques he was, in fact, French.
How to do that? Step one: ensure Jacques can actually understand them. How to accomplish that? Naturally, by teaching him.
Language Education during the Revolution
Under the Ancien Régime, education varied wildly by class, and literacy rates were abysmal. Most commoners received basic literacy from parish and Jesuit schools, while the wealthy enjoyed private tutors. In 1791, Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand (5) presented a report on education to the Constituent Assembly (6), remarking:
“A striking peculiarity of the state from which we have freed ourselves is undoubtedly that the national language, which daily extends its conquests beyond France’s borders, remains inaccessible to so many of its inhabitants." (7)
He then proposed a solution:
“Primary schools will end this inequality: the language of the Constitution and laws will be taught to all; this multitude of corrupt dialects, the last vestige of feudalism, will be compelled to disappear: circumstances demand it." (8)
A sensible plan in theory, and it garnered support from various Assembly members, Condorcet chief among them (which is always a good sign).
But, France went to war with most of Europe in 1792, making linguistic diversity both inconvenient and dangerous. Paranoia grew daily, and ensuring the government’s communications were understood by every citizen became essential. The reverse, ensuring they could understand every citizen, was equally pressing. Since education required time and money—two things the First Republic didn’t have—repression quickly became Plan B.
The War on Patois
This repression of regional languages was driven by more than abstract notions of nation-building; it was a matter of survival. After all, if Jacques the peasant didn’t see himself as French and wasn’t loyal to those shadowy figures in Paris, who would he turn to? The local lord, who spoke his dialect and whose land his family had worked for generations.
Faced with internal and external threats, the revolutionary government viewed linguistic unity as essential to the Republic’s survival. From 1793 onwards, language policy became increasingly repressive, targeting regional dialects as symbols of counter-revolution and federalist resistance. Bertrand Barère spearheaded this campaign, famously saying:
“Federalism and superstition speak Breton; emigration and hatred of the Republic speak German; counter-revolution speaks Italian, and fanaticism speaks Basque. Let us break these instruments of harm and error... Among a free people, the language must be one and the same for all.”
This, combined with Grégoire’s report, led to the Décret du 8 Pluviôse 1794, which mandated French-speaking teachers in every rural commune of departments where Breton, Italian, Basque, and German were the main languages.
Did it work? Hardly. The idea of linguistic standardisation through education was sound in principle, but France was broke, and schools cost money. Spoiler alert: France wouldn’t have a free, secular, and compulsory education system until the 1880s.
What it did accomplish, however, was two centuries of stigmatising patois and their speakers...
Notes
(1) Abbe Henri Grégoire was a French Catholic priest, revolutionary, and politician who championed linguistic and social reforms, notably advocating for the eradication of regional dialects to establish French as the national language during the French Revolution.
(2) "Sur la nécessité et les moyens d’anéantir les patois et d’universaliser l’usage de la langue francaise”
(3)On peut assurer sans exagération qu’au moins six millions de Français, sur-tout dans les campagnes, ignorent la langue nationale ; qu’un nombre égal est à-peu-près incapable de soutenir une conversation suivie ; qu’en dernier résultat, le nombre de ceux qui la parlent purement n’excède pas trois millions ; & probablement le nombre de ceux qui l’écrivent correctement est encore moindre.
(4) And, as someone who has done A LOT of statistics in my lifetime, 49 is not an appropriate sample size for a population of 27 million. At a confidence level of 95% and with a margin of error of 5%, he would need a sample size of 384 people. If he wanted to lower the margin of error at 3%, he would need 1,067. In this case, his margin of error is 14%.
That being said, this is a moot point anyway because the sampled population was not reflective of France, so the confidence level of the sample is much lower than 95%, which means the margin of error is much lower because we implicitly accept that his sample does not reflect the actual population.
(5) Yes. That Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand. It’s always him. He’s everywhere. If he hadn’t died in 1838, he’d probably still be part of Macron’s cabinet. Honestly, he’s probably haunting the Élysée as we speak — clearly the man cannot stay away from politics.
(6) For those new to the French Revolution and the First Republic, we usually refer to two legislative bodies, each with unique roles. The National Assembly (1789): formed by the Third Estate to tackle immediate social and economic issues. It later became the Constituent Assembly, drafting the 1791 Constitution and establishing a constitutional monarchy.
(7) Une singularité frappante de l'état dont nous sommes affranchis est sans doute que la langue nationale, qui chaque jour étendait ses conquêtes au-delà des limites de la France, soit restée au milieu de nous inaccessible à un si grand nombre de ses habitants.
(8) Les écoles primaires mettront fin à cette étrange inégalité : la langue de la Constitution et des lois y sera enseignée à tous ; et cette foule de dialectes corrompus, dernier reste de la féodalité, sera contraint de disparaître : la force des choses le commande
(9) Le fédéralisme et la superstition parlent bas-breton; l’émigration et la haine de la République parlent allemand; la contre révolution parle italien et le fanatisme parle basque. Brisons ces instruments de dommage et d’erreur. .. . La monarchie avait des raisons de ressembler a la tour de Babel; dans la démocratie, laisser les citoyens ignorants de la langue nationale, incapables de contréler le pouvoir, cest trahir la patrie, c'est méconnaitre les bienfaits de l'imprimerie, chaque imprimeur étant un instituteur de langue et de législation. . . . Chez un peuple libre la langue doit étre une et la méme pour tous.
(10) Patois means regional dialect in French.
#frev#french revolution#cps#mapping the cps#robespierre#bertrand barere#language diversity#amateurvoltaire's essay ramblings
772 notes
·
View notes
Note
For the Reverse Unpopular Opinion meme, Lamarckism!
(This is an excellent ask.)
Lamarck got done a bit dirty by the textbooks, as one so often is. He's billed as the guy who articulated an evolutionary theory of inherited characteristics, inevitably set up as an opponent made of straw for Darwin to knock down. The example I recall my own teachers using in grade school was the idea that a giraffe would strain to reach the highest branches of a tree, and as a result, its offspring would be born with slightly longer necks. Ha-ha-ha, isn't-that-silly, isn't natural selection so much more sensible?
But the thing is, this wasn't his idea, not even close. People have been running with ideas like that since antiquity at least. What Lamarck did was to systematize that claim, in the context of a wider and much more interesting theory.
Lamarck was born in to an era where natural philosophy was slowly giving way to Baconian science in the modern sense- that strange, eighteenth century, the one caught in an uneasy tension between Newton the alchemist and Darwin the naturalist. This is the century of Ben Franklin and his key and his kite, and the awed discovery that this "electricity" business was somehow involved in living organisms- the discovery that paved the way for Shelley's Frankenstein. This was the era when alchemy was fighting its last desperate battles with chemistry, when the division between 'organic' and 'inorganic' chemistry was fundamental- the first synthesis of organic molecules in the laboratory wouldn't occur until 1828, the year before Lamarck's death. We do not have atoms, not yet. Mendel and genetics are still more than a century away; we won't even have cells for another half-century or more.
Lamarck stepped in to that strange moment. I don't think he was a bold revolutionary, really, or had much interest in being one. He was profoundly interested in the structure and relationships between species, and when we're not using him as a punching bag in grade schools, some people manage to remember that he was a banging good taxonomist, and made real progress in the classification of invertebrates. He started life believing in the total immutability of species, but later was convinced that evolution really was occurring- not because somebody taught him in the classroom, or because it was the accepted wisdom of the time, but through deep, continued exposure to nature itself. He was convinced by the evidence of his senses.
(Mostly snails.)
His problem was complexity. When he'd been working as a botanist, he had this neat little idea to order organisms by complexity, starting with the grubbiest, saddest little seaweed or fern, up through lovely flowering plants. This was not an evolutionary theory, just an organizing structure; essentially, just a sort of museum display. But when he was asked to do the same thing with invertebrates, he realized rather quickly that this task had problems. A linear sorting from simple to complex seemed embarrassingly artificial, because it elided too many different kinds of complexity, and ignored obvious similarities and shared characteristics.
When he went back to the drawing board, he found better organizing schema; you'd recognize them today. There were hierarchies, nested identities. Simple forms with only basic, shared anatomical patterns, each functioning as a sort of superset implying more complex groups within it, defined additively by the addition of new organs or structures in the body. He'd made a taxonomic tree.
Even more shockingly, he realized something deep and true in what he was looking at: this wasn't just an abstract mapping of invertebrates to a conceptual diagram of their structures. This was a map in time. Complexities in invertebrates- in all organisms!- must have been accumulating in simpler forms, such that the most complicated organisms were also the youngest.
This is the essential revolution of Lamarckian evolution, not the inherited characteristics thing. His theory, in its full accounting, is actually quite elaborate. Summarized slightly less badly than it is in your grade school classroom (though still pretty badly, I'm by no means an expert on this stuff), it looks something like this:
As we all know, animals and plants are sometimes generated ex nihilo in different places, like maggots spontaneously appearing in middens. However, the spontaneous generation of life is much weaker than we have supposed; it can only result in the most basic, simple organisms (e.g. polyps). All the dizzying complexity we see in the world around us must have happened iteratively, in a sequence over time that operated on inheritance between one organism and its descendants.
As we all know, living things are dynamic in relation to inorganic matter, and this vital power includes an occasional tendency to gain in complexity. However, this tendency is not a spiritual or supernatural effect; it's a function of natural, material processes working over time. Probably this has something to do with fluids such as 'heat' and 'electricity' which are known to concentrate in living tissues. When features appear spontaneously in an organism, that should be understood as an intrinsic propensity of the organism itself, rather than being caused by the environment or by a divine entity. There is a specific, definite, and historically contingent pattern in which new features can appear in existing organisms.
As we all know, using different tissue groups more causes them to be expressed more in your descendants, and disuse weakens them in the same way. However, this is not a major feature in the development of new organic complexity, since it could only move 'laterally' on the complexity ladder and will never create new organs or tissue groups. At most, you might see lineages move from ape-like to human-like or vice versa, or between different types of birds or something; it's an adaptive tendency that helps organisms thrive in different environments. In species will less sophisticated neural systems, this will be even less flexible, because they can't supplement it with willpower the way that complex vertebrates can.
Lamarck isn't messing around here; this is a real, genuinely interesting model of the world. And what I think I'm prepared to argue here is that Lamarck's biggest errors aren't his. He has his own blind spots and mistakes, certainly. The focus on complexity is... fraught, at a minimum. But again and again, what really bites him in the ass is just his failure to break with his inherited assumptions enough. The parts of this that are actually Lamarckian, that is, are the ideas of Lamarck, are very clearly groping towards a recognizable kind of proto-evolutionary theory.
What makes Lamarck a punching bag in grade-school classes today is the same thing that made it interesting; it's that it was the best and most scientific explanation of biological complexity available at the time. It was the theory to beat, the one that had edged out all the other competitors and emerged as the most useful framework of the era. And precisely none of that complexity makes it in to our textbooks; they use "Lamarckianism" to refer to arguments made by freaking Aristotle, and which Lamarck himself accepted but de-emphasized as subordinate processes. What's even worse, Darwin didn't reject this mechanism either. Darwin was totally on board with the idea as a possible adaptive tendency; he just didn't particularly need it for his theory.
Lamarck had nothing. Not genetics, not chromosomes, not cells, not atomic theory. Geology was a hot new thing! Heat was a liquid! What Lamarck had was snails. And on the basis of snails, Lamarck deduced a profound theory of complexity emerging over time, of the biosphere as a(n al)chemical process rather than a divine pageant, of gradual adaptation punctuated by rapid innovation. That's incredible.
There's a lot of falsehood in the Lamarckian theory of evolution, and it never managed to entirely throw off the sloppy magical thinking of what came before. But his achievement was to approach biology and taxonomy with a profound scientific curiosity, and to improve and clarify our thinking about those subjects so dramatically that a theory of biology could finally, triumphantly, be proven wrong. Lamarck is falsifiable. That is a victory of the highest order.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

The Season 2 Poster Details
From top to bottom :)

This is a Buddy Holly song Everyday which was originally supposed to be the Good Omens theme :)
Neil talks about it in the Introduction to the Script Book: “In the scripts, Buddy Holly’s song ‘Every Day’ runs through the whole like a thread. It was something that Terry had suggested in 1991, and it was there in the edit. Our composer, David Arnold, created several different versions of ‘Every Day’ to run over the end credits. And then he sent us his Good Omens theme, and it was the Good Omens theme. Then Peter Anderson made the most remarkable animated opening credits to the Good Omens theme, and we realised that ‘Every Day’ didn’t really make any sense any longer, and, reluctantly, let it go. It’s here, though. You can hum it.”

And there is also the Buddy Holly Everyday record! :)

Book The Crow Road by Iain Banks. The novel describes Prentice McHoan's preoccupation with death, sex, his relationship with his father, unrequited love, sibling rivalry, a missing uncle, cars, alcohol and other intoxicants, and God, against the background of the Scottish landscape

Book Lord Jim by Joseph Conrad. An early and primary event in the story is the abandonment of a passenger ship in distress by its crew, including a young British seaman named Jim. He is publicly censured for this action and the novel follows his later attempts at coming to terms with himself and his past and seeking redemption and acceptance.
Important themes in Lord Jim include the consequences of a single, poor decision, the indifference of the universe, and the inability to know oneself or others.

There is book The Body Snatcher by Robert Louis Stevenson. Its characters were based on criminals in the employ of real-life surgeon Robert Knox (1791–1862) around the time of the notorious Burke and Hare murders (1828). Neil said: Oddly enough, episode 3 will take us to a little stint of body snatching in the era.
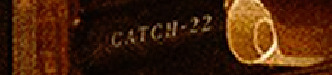
There is Catch-22 book by Joseph Heller that coined the term Catch-22: situation from which an individual cannot escape because of contradictory rules or limitations.

Is there only one hand or are there two? :) EIther 6 ;), or 6:30 :).

Through the window we can see the coffeeshop Give Me Coffe or Give Me Death where Nina works! :)

Azi is wearing his nifty glasses :).


Crowley is wearing his new glasses, they are RIGARDS X UMA WANG - THE STONE ECLIPSE (VINTAGE BLACK/BLACK STONES) - $435




There is the Holy Bible Aziraphale used in Season 1 :)

There seems to be a broken phone :).

The cakes behind Aziraphale are Eccles cakes :).
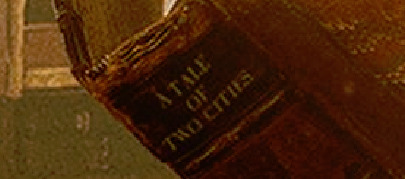
Azi is reading A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens published in 1859, set in London and Paris before and during the French Revolution. The novel tells the story of the French Doctor Manette, his 18-year-long imprisonment in the Bastille in Paris, and his release to live in London with his daughter Lucie whom he had never met. The story is set against the conditions that led up to the French Revolution and the Reign of Terror.


Another book there is Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen - Neil said said that we will learn a lot about Jane Austin we didn’t know before.

And finally the Treasure Island book by - again :) - Robert Louis Stevenson, an adventure novel with pirates.


There are three geckos cuties. Who are they? Pets? Is Ligur haunting the bookshop? Who knows :).

A mysterious pamphlet, 'The Resurrectionists’ leaflet. (unofficial spoiler :)).

Also there is an old camera... mmm 🤔 Did Azi made some photos (of what? Him and Crowley, ducks? :)) Will we see them? :)

Their positions is an homage to the book covers! :)(x)
Will update this as fandom discovers new things! :)❤
#good omens#gos2#season 2#posters#s2 poster details#fun fact#robert louis stevenson#jane austen#joseph heller#charles dickens#can't waiiiit#wahoo!
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

k-707 2025 BOLD UPDATE INSTRUCTIONS
Hello everyone :)
The new k-707 is going to be released in the coming days :D but as it is a kind of new experience, we have some kinda instructions in order to get everything working fine.
Step right up, folks, for the grand unveiling of our biggest project yet! The K-707 isn’t just a mod—it’s a green revolution. Taking on almost every flower, patch of grass, bush, and tree makes this even more massive than the K-505. And trust us, our brains are already feeling the strain! :D
But before instructions, let me tell you the k-707 story ;)
We really hope you'll enjoy it. We worked hard on it with 5 rules :
Replace EVERY tree of the game
NO overrides with crazy high polygons amount
Follow as much as possible the Maxis directions ( trees style )
Decrease amount of polygons where it is possible
No trees defying gravity and laws of physics
It took long for few reasons ...
At first, we always knew the first version was a vast experiment. When ea made its direct x11 update, it was time to make a bold update ... but we didn't want simply remove the non-strictly-dds-x2 images and replace them ... we wanted more. We always wanted more, even we are not kinda ea gurus :D ( hey EA ! don't you want hire some true creators with a long term vision of your game ? ) <- poll : would you like k-hippie as maxis creators or not ? :D
Joke apart, it was difficult. Almost 1 year long, we searched and searched solutions to get rid of all problems we met when replacing foliage on a debug tree, or modifying anything on a debug tree ( for info : we are not blender gurus nor sims 4 core users )
All we knew was few lines :
When cloning a tree, you cannot lose the any of the vert color data. I suspect whatever tool(s) you are using to do the cloning is losing this data, since this setup is somewhat unique to trees.
The vertex color layout for trees is as follows. Green and Blue are ignored for channels 1…4 : Color 0 RGB Surface color tint Color 1 R Rustle direction X Color 2 R Rustle direction Y Color 3 R Rustle direction Z Color 4 R Rustle phase ( game generates two wind scales that change over time, this term interpolates between the two )
The pipeline keeps the rustle information in a vertex color format for what the game engine will load, which means it’s in the range 0 and 1. The shader remaps this into a 0.5 to -0.5 range before scaling it and applying the offset to the leaves. Note that these directions are clamped but not normalized ( they’re allowed to be different lengths ) The WindMagnitude material parameter acts as a scaling factor.
So, we started with this information, begging in vain for some help, both inside the Sims community and outside ... but nobody helped us. And frankly, it interested no-one except us and our beloved followers :)
We found multitude of tutorials ( funny how many they are as soon as it is clothes related ) but nothing related to our specific target. We paused our research many times, made direct x11 updates for our other k-mods and so on. Until ... zaceitorius in July 13rd 2024
Who is zaceitorius ? We do not know. A simple member of sims4studio with 6 posts who gave us a simple bright clue which seems obvious after all, but yet very very precious indeed !
And here we are today. 300 trees and numerous plants later ... <- another reason why it took a long time :D
We made a lot of vertex experiments, we lost data colors, remade again and again some other experiments and well, we are still experiment, remake small details which seem important to us and so on ... And for now, it works :D And now you are warned : the k-707 is far from perfect.



And now, the instructions :)
The k-707 covers both trees & plants, both debug and lot trees & plants
What's new ? No more than usual. We tracked all the non-strictly-dds-x2 images, reshaped some trees ( such as the multitude of oaks ), added some flowers ( where we removed them in 2021 ) but kept many foliage we already did. We tried to simplify many details but added some others and replaced some plants.
How many stuff it represents ? We do not know. Many indeed. We stopped the count :D
Because of its size ( and our love for our sanity ), THE RELEASE WILL ROLL OUT IN PARTS ( not slowly but piece by piece ). If we waited until it was all perfect, you’d be seeing it around ( maybe ) September 2025 ... Let’s not tempt fate—or burnout! :D
The K-707 is neatly organized for your convenience :
Each DLC gets 2 folders : one for plants, one for trees.
The base game gets 4 folders ( a bit different since most of the greenery is drawn from there ) divided into lots and debug folders.
Expansions which have very few greenies ( City, Get to Work, University ) get the same folder named : k-hippie-k707-multi-greeny-2025
IMPORTANT :
Leave them in each of their folders ( or create your owns based on a similar methodology )
If you merge files : we can’t help troubleshoot if it doesn’t work anymore, so be smart ;)
You’re free to do as you like, but we strongly recommend keeping this tidy folder setup. If you need to troubleshoot down the line, it’ll save you a major headache.
And for the mavericks out there who love merging files—go for it, but know this : we won’t be able to help if things go haywire.


Now, we could wax poetic about how stunning the K-707 is, how every leaf, petal, and blade of grass is crisper, richer, and beautifully integrated into your worlds—but hey, we'll do it later, inside the release post :D
We could do more, more realistic trees and so on but we do not want integrate crazy high poly models. We do not want an unplayable game isn't it ? ;)
The k-707 is not yet finished. We got some more work to do on it, shape the last details, and some re-checks.
But here is what is new compare to the previous version : we kinda cracked ( a bit only ) the code. Trees swinging in the wind like it’s a dancing contest ? No more. Trees defying gravity and laws of physics by groveling into the ground ? No more. Just remember we do not have the hands upon the worlds construction, so, when trees are not into the ground, well, call your reseller aka EA itself ...

#sims 4 custom content#sims 4#sims 4 wysiwyg#sims 4 cc#k-hippie talk#ts4#the sims 4#k-hippie#k-mods#k-707#k hippie#k-505#sims 4 green#sims 4 expansions#sims 4 base game#sims 4 trees#sims 4 plants#ts4 overrides#sims 4 overrides
263 notes
·
View notes