#indonesia export statistics
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Seair Exim Solutions provides reliable Indonesia export data, featuring detailed shipment records and trade statistics. Unlock key market insights to drive your business growth and enhance export strategies effectively.
0 notes
Text
When you do not know a thing about the issue at stake...
...perhaps it's better to remain silent.
Some of you know, others don't - and that's fine - but my main field of expertise is labor law.
I just read this in anger and disbelief:

Look, lady. I don't care who the hell you are, what you do for a living or why you felt entitled to answer those insistent questions on your side of the fandom. I suppose you are North American and have no idea of how things work on this side of the pond. It is fine: I might know what a Congress filibuster is, for example, but I'd be severely unable to judge the finer points of competence sharing between Fed and state level.
The difference between you and me?
I keep my mouth shut and/or do my own research before opening it in public.
Have you no shame to write things like: 'It was discovered clothing factories in Bulgaria and Portugal made it and how workers were exploited, mostly women, because these factories were in special economic zones in these countries exempt from EU employee rights and regulations.'
HOW DARE YOU? What strange form of illiterate entitlement possessed you to utter such things with confidence, comfortably hidden behind a passive voice ('it was discovered')?
Portugal joined the EU in 1986. Bulgaria (and my country) joined the EU in 2007. I have given 5 relentless years of my life to make this collective political project a reality, along with hundreds of other people my age who chose to come back home from the West and put their skills to good use for their country. In doing so, I rejected more than 10 excellent corporate job offers in France and China. To see you come along and write such enormities is like having you spit in my face.
Article 4 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union (aka The Treaty of Rome) is formal and clear, as far as competence sharing between the EU and its Member States goes (the UK was still, back then, a full member of the EU - it quit on February 1st 2020):

That means that ALL the EU regulations are being integrated into the national legislation of the Member States. This is not a copy/paste process, however. And because it is a shared competence area, the Member States have a larger margin of appreciation into making the EU rules a part of their own. While exceptions or delays in this process can be and are negotiated, the core principles are NEVER touched.
Read it one hundred times, madam, maybe you'll learn something today:
THERE ARE NO SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONES IN THE EUROPEAN UNION. THE WHOLE FUCKING EUROPEAN UNION IS A SPECIAL ECONOMIC ZONE, THIS IS WHY IT IS CALLED THE SINGLE MARKET.
What the fuck do you think we are, Guangzhou? We'd wish, seeing the growth statistics!
Now, for the textile industry sector and particularly with regard to the Bulgarian market, a case very similar to my own country. Starting around 1965, many big European textile players realized the competitive advantage of using the lower paid, readily available Eastern European workforce. In order to be able to do business with all those dour Communist regimes, the solution was simple and easy to find: toll manufacturing.
It worked (and still does!) like this:
The foreign partner brings its own designs, textiles and know-how into the mix - or more simply put, it outsources all these activities. The locals transform it into the finished product, using their own workforce. The result is then re-exported to the foreign partner, who labels it and sells it. In doing so, he has the legal obligation to include provenance on the label ('made in Romania', 'made in Indonesia', 'made in Bulgaria' - you name it).
The reason you might find less and less of those 'made in ' labels nowadays at Primark and more and more at Barbour, Moncler and the such is the constant raise of the workers' wages in Eastern Europe since 1990 (things happened there, in 1989, maybe you remember?). We are not competitive anymore for midrange prêt-à-porter - China (Shein, anyone?), Cambodia and Mexico do come to mind as better suppliers. To speak about 'exploited female labourers in rickety old factories' is an insult and a lie. They weren't exploited back in the Eighties, as they are not now (workers in those factories were and still are easily paid about 50% more than all the rest) and the factories being modernized and constantly updated was always a mandatory clause in any contract of the sort. Normal people in our countries rarely or ever saw those clothes. You had to either be lucky enough for a semi-confidential store release or bribe someone working there and willing to take the risk, in order to be able to buy the rejected models on the local market.
If I understood correctly, you place this critical episode at the launch of the limited SRH & Barbour collection, for the fall of 2018. How convenient for you, who (I am told by trusted people) were one of the most vocal critics of S during Hawaii 2.0!
And as far as Barbour goes, it never pretended to manufacture everything in the UK only:
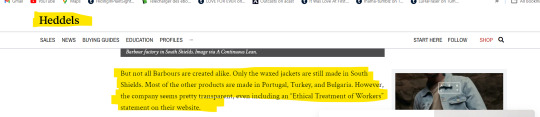
This information is absolutely true. You can read the whole statement, signed in October 2017 by one of their Directors, Ian Sime, here: https://www.barbour.com/us/media/wysiwyg/PDF/Ethical_Statement_October_2017.pdf
And a snapshot for you:

Oh, and: SEDEX is a behemoth in its world, with more than 75.000 companies joining as a member (https://www.sedex.com/become-a-member/meet-our-customers/). Big corporations like TESCO, Dupont, Nestle, Sainsbury's or Unilever included.
I am not Bulgarian, but I know all of this way better than you'll probably ever do. The same type of contracts were common all over Eastern Europe: Romania, Poland, the GDR (that's East Berlin and co, for you) and even the Soviet Union. I am also sure your Portuguese readers will be thrilled to see themselves qualified by a patronizing North American as labor exploiters living in a third-world country with rickety factories.
You people have no shame and never did. But you just proved with trooping colors you also have no culture and no integrity. More reasons to not regret my unapologetic fandom choice.
I expect an angry and very, very vulgar answer to this, even if I chose to not include your name/handle. The stench of your irrelevance crossed an ocean.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Correct and also I don't think people realise how much capitalism relies on the west exporting their problems to 'third world countries'. It's not just labour. Waste, plastics, co2, are all exported. The west brags about reducing co2 emissions, but we're not actually producing less co2. It's because we buy more from China, thus changing where the co2 is produced. We export our 'recycling' to Indonesia, and then get angry when a country handling way more than it's fair share of waste dumps much of it into the ocean. It all makes the west look better in statistics, but it's a lie.
Western governments have every incentive to stop labour, emissions, waste regulations in these countries while simultaneously denouncing them as 'underdeveloped'. If you want your jobs back, you want the earth clean, you need to support development and regulations in non-western countries.
I feel like this bears repeating: the reason that manufacturing has moved out of the US and into other, poorer countries is that labor is less expensive in those countries, because labor laws are worse. It's cheaper for companies to produce things in Bangladesh because in Bangladesh you can pay your workers less and extract longer hours from them and generally treat them worse. This means that if you're an American who has been hurt by manufacturing moving out of the US, your most important allies are labor activists in the countries to which manufacturing has moved.
The US achieved the labor protections it did (like basic safety regulations, the 8-hour workday, and the weekend) through the work of unions and of the broad left-wing coalition that was the labor movement of the early twentieth century. These rights are among the principle reasons that labor is expensive here. If you don't want labor to be moved abroad, it is literally in your own self interest to support labor movements in poor countries where labor is cheep. If people in in places like Bangladesh had these same rights, there wouldn't be nearly the same incentive for companies to move labor out of the country.
If you're an American suffering from industrial decline in the Rust Belt, for instance, then supporting these movements isn't bleeding heart altruism, it is a policy in your rational self-interest.
22K notes
·
View notes
Text
Which Country is No. 1 in Coffee?

Coffee is one of the most popular beverages worldwide, consumed by millions of people daily. While many countries produce coffee, only a few dominate the global market. The quest for the “No. 1” country in coffee production leads to a fascinating exploration of the history, cultivation practices, flavor profiles, and the current state of coffee in various regions. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of coffee to determine which country holds the title of the top coffee producer and explore the factors contributing to its success.
The History of Coffee Production
The Origins of Coffee
Coffee’s history can be traced back to ancient Ethiopia, where the Coffea arabica plant was first discovered. According to legend, a goat herder named Kaldi observed his goats becoming energetic after eating coffee cherries. This discovery eventually led to the cultivation of coffee plants and the establishment of coffee trade routes.
The Spread of Coffee Cultivation
From Ethiopia, coffee made its way to the Arabian Peninsula, particularly Yemen, where it gained immense popularity in the 15th century. By the 17th century, coffee had reached Europe, and its popularity spread rapidly. Today, coffee is grown in over 70 countries, primarily located in the “Coffee Belt,” which lies between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
Current Coffee Production Landscape
Global Coffee Production Statistics
As of recent statistics, Brazil consistently ranks as the world’s largest coffee producer, followed by countries such as Vietnam, Colombia, and Indonesia. According to the International Coffee Organization (ICO), these countries dominate the market, contributing significantly to global coffee production.
Brazil: Approximately 37% of the world’s coffee production.
Vietnam: Roughly 17% of global coffee output.
Colombia: Accounts for about 8% of world coffee production.
Indonesia: Approximately 7% of global coffee output.
Brazil: The Undisputed Leader
Overview of Brazilian Coffee
Brazil has held the title of the largest coffee producer for over 150 years. The country’s vast land area, favorable climate, and diverse microclimates contribute to its dominance in the coffee industry. Brazil primarily grows Arabica and Robusta beans, with Arabica accounting for about 75% of its total production.
Coffee Growing Regions in Brazil
Minas Gerais: Known for its high-quality Arabica coffee, Minas Gerais is Brazil’s leading coffee-producing state. The region’s mountainous terrain and rich soil create ideal conditions for coffee cultivation.
Espírito Santo: This state is renowned for its robust Robusta beans. The climate and soil in Espírito Santo provide excellent growing conditions, resulting in a unique flavor profile.
São Paulo: Another major coffee-growing region, São Paulo produces a variety of coffee types, known for their smooth, chocolatey flavor and medium acidity.
Factors Contributing to Brazil’s Success
1. Ideal Climate and Geography
Brazil’s vast land area and diverse geography contribute to its successful coffee cultivation. The country experiences a variety of climates, from tropical to temperate, allowing for the production of different coffee varieties.
2. Large-Scale Production
Brazil is known for its large-scale coffee farms, which benefit from economies of scale. This mass production allows Brazil to supply coffee at competitive prices, further solidifying its position as the top producer.
3. Research and Development
The Brazilian government and various organizations invest in research and development to improve coffee farming practices. Innovations in pest control, irrigation, and crop management have helped Brazilian coffee farmers increase yields and enhance the quality of their beans.
4. Strong Export Market
Brazil’s well-established export market plays a significant role in its coffee production success. The country exports coffee to over 100 countries, making it a key player in the global coffee trade.
Other Notable Coffee-Producing Countries
While Brazil holds the title of the largest coffee producer, several other countries significantly contribute to global coffee production. Here are some of the top contenders:
Vietnam: The Rising Star
Overview of Vietnamese Coffee
Vietnam is the second-largest coffee producer in the world, primarily known for its Robusta beans. Vietnamese coffee has gained popularity in recent years, particularly in specialty coffee markets.
Coffee Growing Regions in Vietnam
Central Highlands: This region is the heart of Vietnamese coffee production, with provinces such as Dak Lak, Lam Dong, and Gia Lai leading the way. The altitude and favorable climate conditions in the Central Highlands contribute to the quality of the beans.
Unique Characteristics of Vietnamese Coffee
Vietnamese coffee is often characterized by its bold, strong flavor and lower acidity. The country’s traditional brewing method, which includes using a drip filter called a “phin,” creates a unique coffee experience.
Colombia: The Home of High-Quality Arabica
Overview of Colombian Coffee
Colombia is famous for its high-quality Arabica coffee, often regarded as some of the best in the world. Colombian coffee is known for its smooth, well-balanced flavor and bright acidity.
Coffee Growing Regions in Colombia
Antioquia: This region produces mild coffee with a smooth finish. It is one of Colombia’s largest coffee-producing areas.
Huila: Known for its vibrant acidity and fruity notes, Huila coffee is highly sought after in specialty markets.
Quindío: This region is celebrated for its rich, full-bodied coffee with nutty undertones.
Indonesia: The Land of Unique Flavors
Overview of Indonesian Coffee
Indonesia is known for its diverse coffee varieties, particularly from regions such as Sumatra, Java, and Sulawesi. The country produces both Arabica and Robusta beans, with a focus on specialty coffee.
Coffee Growing Regions in Indonesia
Sumatra: Sumatra coffee is known for its earthy, full-bodied flavors with low acidity. The wet-hulling process used in Sumatra contributes to its unique taste.
Java: Java coffee is characterized by its smooth, sweet profile with hints of chocolate and nuts.
Unique Characteristics of Indonesian Coffee
Indonesian coffee often features bold, rich flavors and low acidity, making it a favorite among coffee enthusiasts. The country’s unique processing methods also contribute to the distinctive taste of its beans.
Factors Influencing Coffee Quality
1. Altitude
The altitude at which coffee is grown significantly affects its flavor profile. Higher altitudes often produce beans with greater acidity and more complex flavors due to slower maturation processes.
2. Climate
Climate plays a crucial role in coffee cultivation. Ideal growing conditions include consistent rainfall, moderate temperatures, and ample sunlight. Regions with microclimates can produce unique flavor profiles due to variations in weather patterns.
3. Soil Composition
The soil in which coffee is grown affects its flavor. Volcanic soils, rich in nutrients, are particularly favorable for coffee cultivation. Different minerals in the soil can impart distinct flavors to the coffee beans.
4. Processing Methods
The way coffee beans are processed after harvesting can impact their flavor. Common methods include dry processing, wet processing, and honey processing. Each method imparts different flavor characteristics to the final product.
5. Farming Practices
Sustainable and ethical farming practices contribute to the quality of coffee. Shade-grown coffee, for example, often has a better flavor due to the natural ecosystem supporting the coffee plants.
The Future of Coffee Production
Challenges Facing Coffee Farmers
Despite Brazil’s dominance and the success of other coffee-producing countries, the coffee industry faces numerous challenges:
1. Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to coffee production, affecting rainfall patterns, temperatures, and the prevalence of pests and diseases. As global temperatures rise, many traditional coffee-growing regions may become unsuitable for cultivation.
2. Economic Instability
Coffee farmers often face economic instability due to fluctuating market prices, trade tariffs, and changing consumer preferences. Many smallholder farmers struggle to make a sustainable living, leading to concerns about the future of coffee cultivation.
3. Sustainability Concerns
The coffee industry is increasingly scrutinized for its environmental impact. Deforestation, pesticide use, and water consumption are significant concerns that must be addressed to ensure the sustainability of coffee production.
Innovations in Coffee Farming
To combat these challenges, the coffee industry is exploring various innovations:
1. Sustainable Farming Practices
Farmers are adopting sustainable practices, such as agroforestry and organic farming, to reduce environmental impact and improve coffee quality. These practices can help maintain biodiversity and improve soil health.
2. Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology, such as precision agriculture and data analytics, are helping farmers optimize their coffee cultivation practices. These tools enable farmers to monitor crop health, manage irrigation, and improve yield.
3. Climate-Resilient Varieties
Researchers are developing climate-resilient coffee varieties that can withstand changing environmental conditions. These new varieties may help mitigate the impact of climate change on coffee production.
Conclusion
While Brazil reigns supreme as the world’s largest coffee producer, countries like Vietnam, Colombia, and Indonesia significantly contribute to the global coffee landscape. Each region offers unique flavors, cultivation practices, and challenges, shaping the future of coffee production.
As consumers, our appreciation for coffee goes beyond the cup. Understanding the origins of our favorite brew and supporting sustainable practices can help ensure that coffee remains a cherished beverage for generations to come. Whether you’re sipping a rich Brazilian brew or a vibrant Colombian cup, remember the journey it took to reach your hands and the hard work behind each bean.
0 notes
Text
The Rising Export Market of Jaggery from India: Insights and Opportunities (2023-24)
Jaggery, a traditional unrefined sugar derived from sugarcane or palm sap, has long held a significant place in Indian culture, praised for its nutritional and medicinal benefits. This article explores India's jaggery export landscape for 2023-24, including key statistics, top exporters, market size, and HS codes, shedding light on why this sweetener has become a highly valued export product.

Introduction to Jaggery: An Indian Heritage Product
Jaggery, also known as gur in Hindi, has been a staple in Indian cuisine and Ayurveda for centuries. Unlike refined sugar, jaggery is rich in vitamins and minerals, making it a healthier alternative that has found increasing popularity worldwide. Approximately 55% of the world's jaggery is produced in India, highlighting the country's dominance in this industry. Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh are the largest jaggery-producing states, contributing significantly to India’s agricultural economy. Colombia, the second-largest producer, accounts for only 11% of global production, underscoring India’s unparalleled position.
Jaggery Export Data for 2023-24: Key Figures
In the fiscal year 2023-24, India exported a staggering 516,746.10 metric tons (MT) of jaggery and confectionery products, valued at Rs. 3,570.77 crores (430.88 million USD). These exports reached a wide range of markets, including the United States, Indonesia, Kenya, the UAE, and Nepal. Notably, February 2024 saw a significant spike in exports, with 1,886 shipments representing a 22% year-over-year increase from February 2023 and a 26% growth from the previous month.
Export Performance and Market Growth
According to updated data, India recorded a total of 15,924 jaggery shipments between March 2023 and February 2024. These shipments were executed by 1,241 exporters and received by 2,969 importers worldwide. This marked a 12% increase in shipments compared to the previous year, indicating the growing global demand for Indian jaggery.
Australia, the UAE, and the United States are among the top import markets for Indian jaggery, reflecting the product's widespread appeal. Additionally, India remains the world’s largest jaggery exporter, with 106,108 global shipments, far surpassing competitors like Sri Lanka (3,005 shipments) and Vietnam (621 shipments).
Top Jaggery Exporters in India
Several companies have established themselves as leading exporters of jaggery from India. Here is a list of top exporters making a mark in the global market:
Royaldivine Produce Products LLP
Krishived Organic Farm
Subbamart Impex
Shiva Ruthra Exports
Clora Export Pvt. Ltd.
Mahalaxmi Overseas
Nani Agro Foods
Yuvaraju Agro Impex
Aum Exports
Balaji Jaggery Farm
These companies have set high standards for quality and consistency, making Indian jaggery highly sought after in international markets.
Global Jaggery Export Landscape: Top Exporting Countries
Beyond India, several countries also play a crucial role in the global jaggery export market. Here is a list of the top jaggery-exporting nations:
Thailand: $864.7 million
China: $480.9 million
France: $439.9 million
Netherlands: $214.4 million
United States: $191.9 million
Belgium: $129.0 million
Germany: $105.7 million
Malaysia: $88.9 million
Austria: $73.1 million
Italy: $66.5 million
Thailand leads the way, with an impressive export value of $864.7 million, followed by China and France. However, India’s position as the largest jaggery exporter highlights its superior capacity and strong global demand.
The Growing Indian Jaggery Market
The packaged jaggery market in India was valued at INR 63.5 billion in 2023. This market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.68% from 2023 to 2032, reaching an estimated INR 186.0 billion. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising awareness of jaggery’s health benefits and an increasing preference for natural sweeteners.
Why Exporting Jaggery from India is Profitable
India’s jaggery export market is a highly profitable venture for several reasons:
High Production Capacity: India produces 60-70% of the world’s jaggery. Around 15% of the sugarcane crop in India is dedicated to jaggery and Khansari (unrefined sugar) production.
Growing Global Demand: As consumers worldwide become more health-conscious, the demand for natural sweeteners like jaggery has surged.
Versatility and Cultural Significance: Jaggery, also known as Bellam in Telugu, Vellam in Tamil, and Charkara in Malayalam, plays a crucial role in many Indian and global cuisines. It is also valued for its medicinal properties.
Given these factors, India has a robust infrastructure of jaggery manufacturers ready to meet the increasing global demand.
Key HS Codes for Jaggery Export
To efficiently navigate the export business, understanding HS codes is crucial. Here are some important HS codes for jaggery:
1701: Cane or beet sugar and chemically pure sucrose in solid form
17011310: Cane Jaggery
17011410: Other cane sugar
These HS codes help streamline international trade and ensure compliance with global export standards.
Tools and Platforms for Jaggery Export Insights
For businesses looking to tap into the jaggery export market, having access to reliable trade data is essential. Platforms like ExportImportData.in provide comprehensive trade data, including updated lists of importers and exporters, HS codes, and shipment details across 100+ countries. This information helps businesses make informed decisions and capitalize on opportunities in the international market.
Conclusion: The Future of Jaggery Export from India
India’s jaggery export market is a testament to the country’s strong agricultural heritage and trading capabilities. As the global demand for natural sugar substitutes continues to rise, jaggery has become a valuable export product. By understanding key HS codes, keeping track of export statistics, and partnering with established exporters, businesses can successfully navigate this profitable industry.
For those interested in exploring jaggery export opportunities or needing assistance with trade data, platforms like ExportImportData.in offer valuable resources. Stay informed, leverage the right data, and be a part of India’s growing jaggery export story.
#JaggeryExport#IndianTrade#GlobalMarket#SugarCane#ExportImportData#AgricultureBusiness#TradeInsights#SweetOpportunities
0 notes
Text
Why Exporting Dry Ginger from India is Profitable and Find Reliable Buyers

For thousands of years, ginger has been treasured for its aromatic flavor and medicinal properties. This spice, originating in Asia, has been widely used in Arabic, Indian, and Asian herbal traditions. Today, it stands as one of the healthiest spices, packed with essential minerals and bioactive compounds that benefit the body and mind. The global demand for ginger has made India a major player in the market, especially for dry ginger exports.
In 2023, China, the Netherlands, Thailand, India, and Brazil were among the top ginger exporters, while the European Union, United States, Netherlands, Japan, and Pakistan were the biggest importers. Exporting dry ginger from India is a lucrative business opportunity, but the main challenge lies in finding reliable buyers. This guide will cover the reasons for the profitability of dry ginger export from India, important data insights, and strategies for locating dependable buyers.
Why Exporting Dry Ginger from India is Lucrative
India’s role as a prominent ginger producer and exporter, combined with rising global demand, makes dry ginger exports from the country highly profitable. The success of this business, however, depends on a few critical factors:
Growing Global Demand
In 2023, the dried ginger market was valued at $1.5 billion, with projections showing growth to $2.39 billion by 2030. This increasing demand presents a huge opportunity for exporters, especially from India.
India’s Dominance in the Spice Market
India is the world’s leading spice exporter, making it a prime source for high-quality ginger. The profitability of ginger exports aligns well with India’s established reputation and infrastructure in the spice industry.
Production Costs and Export Regulations
The cost of cultivating premium ginger, processing it, and meeting export regulations can impact profitability. However, the dry ginger export business offers substantial potential for those with a well-researched strategy that considers production expenses, regulatory compliance, and market trends.
Thorough analysis of these factors is essential to boost profitability in this sector. Conducting comprehensive research and gathering accurate, current data on dry ginger exports can enhance the likelihood of success.
Leading Ginger-Producing Countries Worldwide
The global ginger market is competitive, with several countries contributing to the production of this sought-after spice. India leads as the top producer, with Nigeria, China, Nepal, Indonesia, and Thailand following closely behind. Among these, India stands out as the largest producer, with an annual production of around 178,000 metric tons. This significant output positions India as a major force in the dry ginger export industry.
Key Ginger-Producing States in India
India’s ginger production is concentrated in a few major states. Madhya Pradesh leads with approximately 692,000 metric tons, accounting for over 31% of national production. Karnataka follows with about 306,000 metric tons, and Assam produces around 170,000 metric tons. These states play a crucial role in meeting both domestic and international demand for ginger, solidifying India’s position in the global market.
Dry Ginger Export Statistics from India
India’s impact on the dry ginger market is significant. As per dry ginger export data, India exported around 10,000 shipments of dry ginger, driven by over 1,065 exporters catering to 2,353 buyers worldwide. India holds the top position in global dry ginger exports, with its primary export destinations including Morocco, the United States, and the UAE. This dominance highlights India’s importance in meeting the rising demand for ginger across various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and herbal remedies.
Top Dry Ginger Exporting Countries and Market Shares
When it comes to dry ginger exports, Nigeria and China are India’s closest competitors. Nigeria holds a market share of approximately 22%, followed by China at 21.9%. India ranks third, with about 16.5% of global exports. Other countries like Germany, the Netherlands, Vietnam, and the United States also contribute to the global supply but in smaller quantities. India's strong market position makes it an ideal source for dry ginger, especially for buyers looking for quality and quantity.
Major Export Destinations for Indian Dry Ginger
India’s dry ginger exports reach various countries worldwide, with the top markets being Morocco, the United States, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Spain, Egypt, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands. These countries rely on India’s ginger exports due to the spice's quality, consistency, and medicinal value. Although India’s dry ginger exports reached over $129 million in 2021, recent years have seen fluctuations in export volumes, emphasizing the importance of a reliable buyer network.
List of Top Dry Ginger Exporters in India
India has numerous dry ginger exporters, each contributing to the industry's growth. Some of the leading exporters include Jai Commercial Centre, 2win Enterprises, Shree Shyam Impex, Aaha Impex Pvt. Ltd, Priya Exports, Anantagriexports, Savaliya Agri Commodity Export Pvt Ltd, Apex International, Surendraray & Co, and Basil Food Export. These companies are among the most reliable in India’s dry ginger export industry, consistently meeting international demand with quality products.
How to Find Reliable Buyers for Dry Ginger Exports
Securing trustworthy buyers is essential for sustained success in the dry ginger export business. Exporters can benefit from data-driven platforms such as Eximpedia.app, which provides extensive insights on global dry ginger export trends, buyer information, and real-time data. Eximpedia offers an extensive database covering over 130 countries, including key markets like Bangladesh, Vietnam, the US, and Turkey.
Using such platforms, dry ginger exporters in India can gain valuable insights into demand patterns, market trends, and competitive pricing, enabling them to make informed business decisions. Eximpedia’s database also provides access to up-to-date export-import data, enabling exporters to identify reliable buyers and understand regulatory requirements for different countries. By conducting thorough research and using tools like Eximpedia, exporters can streamline their buyer acquisition process, enhancing their success in the dry ginger export market.
Final Thoughts
The global demand for dry ginger presents a lucrative opportunity for Indian exporters, given the country's dominance in ginger production. However, entering the export market requires careful planning, reliable data, and a strong buyer network. By leveraging platforms like Eximpedia, conducting market research, and staying informed on industry trends, Indian exporters can thrive in the international ginger market. With a comprehensive strategy, the potential for profit in the dry ginger export business from India is immense, catering to the growing demand worldwide.
#Dry ginger export from India#ginger export from India#dry ginger export data#dry ginger exporters in India#top 10 ginger importing countries#dry ginger hsn code
0 notes
Text
How to Start a Profitable Seeds Export Business from India: A Complete Guide

India, with its rich agricultural diversity and vast range of crop varieties, offers tremendous potential for starting a seeds export business. The seeds industry is one of the most economical means to boost agricultural production and is central to food production worldwide. By supplying quality seeds, a significant portion of productivity can be achieved at minimal costs, with 20–25% of productivity directly attributed to seed quality. In this guide, we’ll explore how you can launch and grow a successful seeds export business in India.
Why Start a Seeds Export Business?
Starting a seeds export from India can be a highly profitable venture. India’s seed industry requires relatively lower investment than traditional commercial crops while providing greater profitability. Furthermore, there is a high demand for Indian seeds, including oilseeds, pulses, and various other crops, in global markets. Some of the primary states for seed production include Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and Haryana.
Key Steps to Start Seeds Export Business in India
1. Conduct Market Research and Identify Scope
The first step in any export business is to conduct thorough market research. Identify which seeds are in high demand in international markets, understand the policies surrounding seed export, and gain insights into India’s export potential. Some of the most commonly exported seeds from India include sunflower, safflower, mustard, groundnut, sesame, tamarind, cotton, castor, cumin, and chia seeds. India exports $70 million worth of seeds annually, with a significant share going to countries like the United States, the Netherlands, the United Arab Emirates, and China.
2. Obtain Necessary Licenses and Documentation
To export seeds from India, you’ll need to obtain licenses and complete documentation as per the Indian government's regulations. This includes submitting an application to the EXIM Committee of the Department of Agriculture and Cooperation, which will then recommend it to the DGFT (Directorate General of Foreign Trade). Here are some essential documents you’ll need:
Form A
Identity proof (e.g., PAN card, Aadhaar)
Authorization from the company
Treasury Challan for Rs. 1,000
Location map of the business premises
Company registration certificate with Memorandum of Association (MOA)
Importer-Exporter Code (IEC)
3. Gather Key Statistics on Seeds Export from India
Staying informed about the latest data on India’s seed exports is crucial for competitive advantage. For instance, India exported $223.52 million worth of groundnuts in 2023, primarily to Southeast Asian countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines. Understanding these statistics allows you to identify which seeds have high export value and which countries are the main importers.
4. Major Export Destinations for Indian Seeds
India exports seeds to numerous countries across continents. Each type of seed has its leading destination markets. For example:
Oilseeds: United States, UAE, Netherlands, and Singapore.
Groundnuts: Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Iran.
Sesame Seeds: Vietnam, South Korea, the United States, and Russia.
Sowing Seeds: United States, Mexico, UAE, and Bangladesh.
Knowing these primary destinations allows you to focus your efforts on high-demand countries and better strategize your export plans.
5. Identify Potential Seed Buyers
Finding reliable buyers is essential for success in the seeds export business. Participating in trade shows, buyer-seller gatherings, exhibitions, and B2B portals are excellent ways to connect with potential buyers. Some popular platforms like Seair Exim Solutions provide data-driven insights on potential buyers, helping you obtain key information like port names, country of origin, and shipment values.
6. Meet Market Entry and Export Requirements
Each country has its own regulatory requirements for imported seeds, so ensure your seeds comply with your target countries' pest risk analysis and other regulations. This might involve sampling, field trials, or other procedures to confirm seed quality and compliance. When setting prices, consider factors like freight and insurance costs to make your products competitively priced in international markets.
Major Indian Seed Exporters
Many companies in India are already thriving in the seeds export business, setting a benchmark for quality and reliability. Some of the leading seed exporters in India include SeedEXIM, HL Agro, Bombay Super Hybrid Seeds Limited, and Yuvaraju Agro Impex. These companies are known for their seed export expertise and can inspire new entrants.
Conclusion: Establishing Your Seed Export Business in India
Starting a seeds export business in India requires careful planning, in-depth market knowledge, and compliance with various regulations. However, by following this comprehensive guide, you can successfully navigate the complexities of the industry and build a profitable business. Take the time to conduct market research, identify key buyers, and ensure your products meet international standards.
India’s potential for seeds export is vast, with opportunities for new businesses to expand and thrive. By understanding the market and securing the necessary licenses, you can position yourself for success in this lucrative industry.
#seeds export from India#export seeds from India#export of seeds from India#seed exporters in India#chia seeds export from India#cumin seeds export from India
0 notes
Text
Edible Oil Exports from India: A Comprehensive Overview of the Growing Industry
India's edible oil market is robust, playing a crucial role in the global edible oil industry. With an expanding export landscape, India has made significant strides, positioning itself as one of the prominent players in the edible oil sector. This article delves into the statistics, top exporters, importing countries, and the overall impact of Edible Oil Exports from India on the global market.

The Importance of Edible Oil in India
Edible oil is a staple in Indian households and culinary traditions, with regional preferences dictating the type of oil used. Northern India favors mustard oil, while coconut oil is commonly used in the south. India stands as the second-largest consumer of edible oil worldwide and is also one of the leading producers. As Indian edible oils gain popularity globally, India has risen as a key exporter of edible oils.
Edible Oil Production in India: An Overview
India's agricultural economy benefits significantly from oilseed production. For the fiscal year 2023-2024, India produced an estimated 39.59 million tons of oilseeds, contributing between 5-6% of the world’s oilseed production. Key oilseed-producing states in India include:
Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu: Groundnut production
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan: Soybean production
Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal: Mustard production
These regions collectively contribute over 95% of the country’s edible oil production.
Growth Projections for India’s Edible Oil Market
The edible oil market in India is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2022 to 2027, reaching USD 268.9 million. With increasing urbanization, changing food habits, and rising disposable income, demand for high-quality edible oils is set to grow. The Indian edible oil market is expected to expand from 24.7 million metric tons in 2023 to 27.9 million metric tons by 2032.
Key drivers include:
Urbanization: Changing eating habits and food choices
Increased disposable income: Rising preference for premium oils
Processed food demand: Usage of edible oil as a preservative and flavor enhancer
Edible Oil Export Data: India (2023-24)
India exported 7,070 shipments of edible oil from March 2023 to February 2024, with 300 exporters supplying products to 1,798 buyers globally. This marked a 115% increase in shipments compared to the previous year. Notably, India’s exports of oil meals, oilseeds, and minor oils reached 3.46 million tons, valued at Rs 14,609 crores in the fiscal year 2022-2023.
Top export destinations for Indian edible oil include the United States, China, and the Netherlands. In February 2024 alone, India shipped 503 edible oil cargoes, representing a 14% decrease from January 2024 and a 5% drop from February 2023 on a year-over-year basis.
Leading Indian Edible Oil Exporters
India's top edible oil exporters include major companies contributing to the country’s substantial exports:
Adani Wilmar Limited
Agro Tech Foods Ltd. (ConAgra Brands Inc.)
BCL Industries Ltd.
Bunge India Private Limited
Cargill India Private Limited
Emami Agrotech Limited
Gulab Oil And Foods Pvt. Ltd.
Sri Basant Oils Ltd.
AJ-overseas Trade
Shiv Nandi Oil
These companies play a vital role in meeting global edible oil demands, consistently delivering high-quality products.
Top Global Exporters and Importers of Edible Oil
Global demand for edible oil is substantial, with Malaysia leading the way as the largest exporter, followed by Indonesia and the Netherlands.
Top Exporting Countries
Malaysia - USD 1.66 billion
Indonesia - USD 1.52 billion
Netherlands - USD 424 million
Germany - USD 354 million
China - USD 342 million
Top Importing Countries
China - USD 786 million
Netherlands - USD 515 million
United States - USD 325 million
Malaysia - USD 271 million
Germany - USD 225 million
China, the Netherlands, and the United States represent significant markets for Indian edible oil exports, providing Indian exporters with opportunities for trade growth.
How Exportimportdata.in Supports Edible Oil Exporters
For those interested in entering the edible oil export market, platforms like Exportimportdata.in offer comprehensive, real-time data on edible oil exports and imports by country, connecting exporters with genuine buyers worldwide. The platform’s insights allow businesses to optimize trade strategies and make informed decisions.
Final Thoughts
India’s edible oil export market is growing, with significant global opportunities for Indian exporters. By adhering to international standards, maintaining quality, and implementing effective marketing strategies, Indian exporters can capitalize on this expanding sector. Exportimportdata.in offers the resources needed to support this journey, ensuring access to reliable and actionable data.
FAQ
Who are the top edible oil exporters from India?
Key exporters include Adani Wilmar, Agro Tech Foods Ltd., BCL Industries, Bunge India, and Cargill India.
Which countries import the most edible oil?
China, the Netherlands, the U.S., Malaysia, and Germany are among the largest importers.
What is the market growth expectation for edible oils in India?
The market is expected to grow from 24.7 million metric tons in 2023 to 27.9 million metric tons by 2032.
How much edible oil did India export between March 2023 and February 2024?
India exported 7,070 shipments, with a 115% increase compared to the previous year.
For more details on India’s edible oil export statistics and to connect with potential buyers, visit Exportimportdata.in.
#EdibleOilExports#IndianEdibleOil#EdibleOilMarket#IndiaExports#OilseedProduction#GlobalTrade#IndianAgriculture#ExportBusiness#IndianExporters#EdibleOilIndustry#TradeData#ExportImportData#GlobalMarkets#EdibleOilExporters#IndiaToWorld#SustainableExports#EdibleOilDemand#MustardOil#CoconutOil#ExportStatistics#EdibleOilConsumers#FoodIndustry#ExportTrends#ImportExportBusiness#TradeOpportunities
1 note
·
View note
Text
TOP NEWS Agricultural Commodities > France cuts wheat and barley crop estimates, raises maize forecast > Ukraine winter grain sowing 72% complete, ministry says > Turkey relaxes wheat import rules as ban due to expire, millers say > Russia’s Grain Exporters Union starts publishing indicative prices for wheat > Strong foreign demand pushes Ukraine sunseed prices to record high, analyst says > NOPA September US soybean crush up sharply to 177.320 mln bushels > GRAINS-Corn and soybeans regain a little ground after sell-off > Brazil's target to double cocoa output by 2030 is realistic, says WCF > Brazil's soybean crop seen up 12.7% in 2024/25, Conab says > Export Summary-US sells soybeans to China; Egypt buys sunflower oil > VEGOILS-Palm oil extends declines on weaker rivals; export data caps losses > POLL-US corn harvest 47% complete, soy 67% done, USDA data shows > Indonesia rice output seen down 2.43% in 2024, statistics bureau says > SOFTS-London cocoa hits one-month high on supply jitters, coffee falls > LIVESTOCK-CME cattle futures fall on technical trading, retail price caution
0 notes
Text
How to Import Furniture from Indonesia: Key Insights, Steps, and Statistics
Importing furniture from Indonesia presents a lucrative business opportunity due to the country's reputation for high-quality craftsmanship and reasonable prices. Whether you are a seasoned importer or new to the trade, understanding Indonesia's furniture import data, key steps, required documents, and the applicable HS codes is crucial for a smooth and successful importing experience. In this article, we will cover everything you need to know, from market research to finding reputable suppliers, so you can confidently import furniture from Indonesia.

Overview of Indonesia’s Furniture Import Market
Indonesia is a significant player in the global furniture trade, known for its high-quality craftsmanship, especially in outdoor and teak furniture. Based on data from March 2023 to February 2024, 10,757 shipments of furniture were imported globally from Indonesia, marking a 2% year-over-year increase. This growth highlights Indonesia’s strong presence in the furniture market. The United States, India, and Russia lead in global furniture imports, with the US importing over 4.5 million shipments, making it the largest furniture importer from Indonesia.
However, February 2024 saw a decline in furniture imports from Indonesia, with 403 shipments—a sequential drop of 26% from January 2024 and a 60% year-over-year decrease compared to February 2023. Despite this short-term dip, the global demand for Indonesian furniture remains strong, particularly in the US, India, and Russia.
Why Does Indonesia Import Furniture?
Despite being a major exporter of furniture, Indonesia imports furniture to meet the demand for diverse styles and choices in its local market. While the country’s furniture industry focuses heavily on exports, this has led to criticism for neglecting the domestic market. The local demand is especially strong in the middle-to-upper market segments, where international brands like IKEA have seen significant growth.
In 2022, Indonesia recorded a total import value of $331 million USD for furniture, with $290 million USD coming from China. This reflects the country’s reliance on imports to cater to the local market’s evolving preferences.
Key Steps to Import Furniture from Indonesia
Step 1: Market Research and Requirements
Before importing furniture, it's essential to research the market and understand the types of furniture in demand. Whether it’s office furniture, home decor, or high-end custom pieces, knowing local design preferences and materials will help you choose the right products.
Step 2: Registering a Legal Entity
To import furniture, you must first establish a legal business entity in Indonesia. Foreign investors can set up either a PT PMA (Foreign-Owned Limited Liability Company) or a Local PT (Limited Liability Company), depending on their specific business needs.
Step 3: Obtaining Necessary Documents and Licenses
To legally import furniture into Indonesia, several key documents are required:
Import License
Letter of Credit
Bill of Entry
Country of Origin Certificate
Commercial Invoice
Customs Clearance
Export License
Step 4: Understanding HS Codes and Import Duties
Furniture imports fall under Chapter 94 of the HS Code. The applicable codes include:
Wooden furniture: HS Code 9403.60
Metal furniture: HS Code 9403.20
Plastic furniture: HS Code 9403.70
Import duty rates in Indonesia typically range from 5% to 20%, depending on the material, type of furniture, and country of origin.
Step 5: Marketing and Selling Imported Furniture
Once you've imported the furniture, it’s essential to market your products effectively. Whether you’re selling through physical stores or online platforms, a robust marketing strategy will help you succeed. Additionally, using platforms like IndonesiaTradeData.com to access shipment data and analyze market trends will provide valuable insights for scaling your business.
Indonesian Teak Furniture Imports
Teak furniture, especially popular in outdoor settings, is a major export product for Indonesia. Between November 2022 and October 2023, Indonesia imported three shipments of teak wood, marking a 200% year-over-year increase. Despite the small number of shipments, this growth highlights the rising demand for teak wood imports.
India, the United States, and the United Kingdom are the top importers of Indonesian teak wood, with India leading the way, importing 73,835 shipments, followed by the US and the UK.
Finding Outdoor Furniture Suppliers in Indonesia
Finding reliable furniture suppliers is crucial for a successful import business. IndonesiaTradeData.com is a useful platform for accessing updated data on Indonesian outdoor furniture suppliers, including shipment values, port details, HS Codes, and more. This data-driven approach will help you make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Conclusion
Importing furniture from Indonesia can be a profitable venture if approached with the right strategy. By conducting thorough market research, registering your business, obtaining the necessary documents, and using accurate data insights, you can successfully navigate the Indonesian furniture import process. Platforms like IndonesiaTradeData.com offer valuable resources for analyzing market trends and connecting with reliable suppliers, helping you grow your business in the competitive global furniture market.
FAQ
What are the key steps to importing furniture from Indonesia?
Find a reputable supplier, obtain necessary permits and licenses, prepare export documentation, and access reliable import-export data.
Which documents and licenses are required to import furniture into Indonesia?
You will need an Import License, General Import License (API-U), Certificate of Origin, and a Commercial Invoice, among other documents.
Why does Indonesia import furniture despite being a major exporter?
Indonesia imports furniture to meet local demand, particularly for international brands, due to the focus on exports leaving gaps in the domestic market.
#FurnitureImports#IndonesiaFurniture#TeakFurniture#OutdoorFurniture#ImportBusiness#IndonesiaTrade#FurnitureSuppliers#IndonesiaTeak#HSCode#FurnitureImportData#ExportImport#ImportLicenses#FurnitureIndustry#GlobalTrade#TeakWood#MarketResearch#FurnitureExport#IndonesiaBusiness
0 notes
Text
Top Countries That Import Wheat

One of the most significant crops, wheat is essential to the world's food supply chain. On account of its widespread usage in producing essential food products like bread, pasta, and other basic food items, it is no surprise that its demand remains high worldwide. Many countries, especially those that have limited domestic production, rely heavily on imports to meet their food security needs. In this article, we will explore the top countries that import wheat and also highlight the key import statistics, and analyse market trends. If you're an exporter looking to export bulk wheat, then understanding these countries' market demands can play a significant role in your success.
Global Wheat Trade Overview
Frankly speaking, the international wheat market is vast and dynamic, and it is driven by a variety of factors such as population growth, economic development, changing dietary preferences, and climatic conditions.
In 2023, the market for wheat imports worldwide was estimated to be worth $55 billion. Not to add, a sizable portion of it came from the top importing nations. The Middle East, Asia, and Africa are the main importers of wheat. These nations either have inadequate local production or have unfavourable climates that make cultivation impractical.
1. Indonesia
Indonesia has emerged as one of the largest wheat importers in the world. It is no surprise that in 2022 the country imported approximately 11.5 million metric tons of wheat. This reflects its growing population and increasing dependence on wheat-based food products. Although Indonesia does not produce wheat domestically due to unsuitable climatic conditions. However, it remains a significant consumer, with a thriving noodle and bakery industry driving demand. The country's major suppliers include Australia, Ukraine, and Canada.
2. Egypt
Egypt consistently ranks among the world’s top wheat importers. In 2022, Egypt imported nearly 9.8 million metric tons of wheat, according to the USDA. Wheat is a crucial component of the Egyptian diet, particularly for bread, which is a staple food for much of the population. The Egyptian government also heavily subsidised bread, ensuring a steady demand for imported wheat. Historically, Egypt has sourced a significant portion of its wheat from Russia and Ukraine, but supply chain disruptions have led the country to diversify its suppliers, including turning to Romania, France, and the United States.
3. Turkey
Turkey is another key wheat importer, with imports reaching over 10.8 million metric tons in 2022. Despite being a major producer of wheat, Turkey imports substantial quantities for processing and re-exporting. The country boasts one of the largest wheat flour milling industries in the world, processing imported wheat to manufacture flour, which is then exported to neighbouring regions. Russia and Ukraine are primary wheat suppliers to Turkey, followed by Germany and Lithuania.
4. Nigeria
Nigeria is Africa’s largest wheat importer, with imports standing at approximately 6.6 million metric tons in 2022. The country’s growing population, coupled with increasing urbanisation and the rising popularity of bread and noodles, has led to greater demand for wheat. Local wheat production in Nigeria is minimal due to climatic limitations, which forces the country to rely heavily on imports, mainly from the United States, Canada, and Argentina.
5. Bangladesh
Bangladesh is among the top wheat importers in South Asia. In 2022, the country imported nearly 6.5 million metric tons of wheat. As a growing economy with a population exceeding 165 million, Bangladesh has experienced a sharp rise in wheat consumption, particularly in urban areas. Most of the imported wheat is used for producing bread, noodles, and biscuits. Russia and Ukraine have been primary suppliers, but due to geopolitical tensions, Bangladesh has been increasingly sourcing wheat from India, Canada, and Australia.
6. Pakistan
Although Pakistan is a wheat-producing country, it is also a significant importer due to supply-demand imbalances caused by domestic shortfalls. In 2022, Pakistan imported approximately 3 million metric tons of wheat, mainly to stabilise local markets and curb rising food inflation. Wheat imports are typically sourced from Russia, Ukraine, and Central Asian countries. The government also imports wheat to build reserves and ensure price stability during times of crisis or drought.
7. Philippines
In 2022, the Philippines brought in about 6.8 million metric tons of wheat from overseas. Like Indonesia, the nation does not cultivate wheat on its own, but consumption is nonetheless high, especially when it comes to making noodles and bakery goods. Canada, Australia, and the United States are the Philippines' main suppliers of wheat.
Market Trends and Insights
Several factors continue to shape the global wheat import landscape. Supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical issues, such as the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, have had a profound impact on wheat prices and availability. Both countries are major wheat exporters, and any disruption in their production or export routes reverberates across the global market. Many countries are now seeking to diversify their wheat import sources to reduce dependence on specific regions.
Furthermore, climate change is playing an increasing role in determining the reliability of wheat production worldwide. Exporters targeting countries with significant wheat import demands must stay informed about climate patterns, international trade policies, and consumer preferences.
Conclusion
Growing populations, shifting dietary preferences, and insufficient domestic production are the main causes of the dominance of countries such as Indonesia, Egypt, Turkey, and Nigeria in the world's wheat imports. In order to effectively penetrate these markets and export bulk wheat, exporters must have a thorough understanding of these countries' import requirements. It will be essential to monitor market developments and diversify supply chains in order to maintain stability and growth in this industry as the demand for wheat rises globally.
0 notes
Text

Seair Exim Solutions provides reliable Indonesia import data to help you analyze trade trends and opportunities. Access detailed shipment records, import statistics, and market insights to enhance your business decisions. Empower your trade strategy with accurate and up-to-date data.
#Import Data Indonesia#indonesia import data#indonesia trade data#indonesia import and export data#Indonesia Shipment data#indonesia import export data#indonesia export and import statistics
0 notes
Text
Vision Sensing Algorithms Market Promising Growth and by Platform Type, Technology and End User Industry Statistics, Scope, Demand by 2033
Vision Sensing Algorithms Market size was valued at USD 29.77 Billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 261.56 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 24.6% during the forecast period 2024-2033.
The competitive analysis of the Vision Sensing Algorithms Market offers a comprehensive examination of key market players. It encompasses detailed company profiles, insights into revenue distribution, innovations within their product portfolios, regional market presence, strategic development plans, pricing strategies, identified target markets, and immediate future initiatives of industry leaders. This section serves as a valuable resource for readers to understand the driving forces behind competition and what strategies can set them apart in capturing new target markets.
Market projections and forecasts are underpinned by extensive primary research, further validated through precise secondary research specific to the Vision Sensing Algorithms Market. Our research analysts have dedicated substantial time and effort to curate essential industry insights from key industry participants, including Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), top-tier suppliers, distributors, and relevant government entities.
Receive the FREE Sample Report of Vision Sensing Algorithms Market Research Insights @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/sample-request/vision-sensing-algorithms-market/10279/
Market Segmentations:
Global Vision Sensing Algorithms Market: By Company • Arcturus • Elementary • Instrumental • Mech-Minded Robotics • Landing AI • Intel • NVIDIA • Qualcomm • eWEEK • Kitov Global Vision Sensing Algorithms Market: By Type • Image Classification • Object Detection • Object Tracking • Semantic Segmentation • Instance Segmentation Global Vision Sensing Algorithms Market: By Application • Agriculture • Computer • Others
Regional Analysis of Global Vision Sensing Algorithms Market
All the regional segmentation has been studied based on recent and future trends, and the market is forecasted throughout the prediction period. The countries covered in the regional analysis of the Global Vision Sensing Algorithms market report are U.S., Canada, and Mexico in North America, Germany, France, U.K., Russia, Italy, Spain, Turkey, Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, and Rest of Europe in Europe, Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific (APAC) in the Asia-Pacific (APAC), Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa (MEA) as a part of Middle East and Africa (MEA), and Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of South America as part of South America.
Click to Purchase Vision Sensing Algorithms Market Research Report @ https://stringentdatalytics.com/purchase/vision-sensing-algorithms-market/10279/
Key Report Highlights:
Key Market Participants: The report delves into the major stakeholders in the market, encompassing market players, suppliers of raw materials and equipment, end-users, traders, distributors, and more.
Comprehensive Company Profiles: Detailed company profiles are provided, offering insights into various aspects including production capacity, pricing, revenue, costs, gross margin, sales volume, sales revenue, consumption patterns, growth rates, import-export dynamics, supply chains, future strategic plans, and technological advancements. This comprehensive analysis draws from a dataset spanning 12 years and includes forecasts.
Market Growth Drivers: The report extensively examines the factors contributing to market growth, with a specific focus on elucidating the diverse categories of end-users within the market.
Data Segmentation: The data and information are presented in a structured manner, allowing for easy access by market player, geographical region, product type, application, and more. Furthermore, the report can be tailored to accommodate specific research requirements.
SWOT Analysis: A SWOT analysis of the market is included, offering an insightful evaluation of its Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Expert Insights: Concluding the report, it features insights and opinions from industry experts, providing valuable perspectives on the market landscape.
Report includes Competitor's Landscape:
➊ Major trends and growth projections by region and country ➋ Key winning strategies followed by the competitors ➌ Who are the key competitors in this industry? ➍ What shall be the potential of this industry over the forecast tenure? ➎ What are the factors propelling the demand for the Vision Sensing Algorithms? ➏ What are the opportunities that shall aid in significant proliferation of the market growth? ➐ What are the regional and country wise regulations that shall either hamper or boost the demand for Vision Sensing Algorithms? ➑ How has the covid-19 impacted the growth of the market? ➒ Has the supply chain disruption caused changes in the entire value chain? Customization of the Report:
This report can be customized to meet the client’s requirements. Please connect with our sales team ([email protected]), who will ensure that you get a report that suits your needs. You can also get in touch with our executives on +1 346 666 6655 to share your research requirements.
About Stringent Datalytics
Stringent Datalytics offers both custom and syndicated market research reports. Custom market research reports are tailored to a specific client's needs and requirements. These reports provide unique insights into a particular industry or market segment and can help businesses make informed decisions about their strategies and operations.
Syndicated market research reports, on the other hand, are pre-existing reports that are available for purchase by multiple clients. These reports are often produced on a regular basis, such as annually or quarterly, and cover a broad range of industries and market segments. Syndicated reports provide clients with insights into industry trends, market sizes, and competitive landscapes. By offering both custom and syndicated reports, Stringent Datalytics can provide clients with a range of market research solutions that can be customized to their specific needs.
Reach US
Stringent Datalytics
+1 346 666 6655
Social Channels:
Linkedin | Facebook | Twitter | YouTube
0 notes
Text
Ginger Market Growth, Trends, Forecast 2023-2030
BlueWeave Consulting, a leading strategic consulting and market research firm, in its recent study, estimated the Global Ginger Market size at USD 4.91 billion in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, BlueWeave expects the Global Ginger Market size to expand at a CAGR of 7.12% reaching a value of USD 6.67 billion by 2030. An increasing demand for ginger across a range of industries, including personal care, pharmaceutical, and nutraceutical, is expected to propel the Global Ginger Market.
By volume, BlueWeave estimated the Global Ginger Market size at 15.46 million metric tons in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, BlueWeave expects the Global Ginger Market size to expand at a CAGR of 3.81% reaching the volume of 20.08 million metric tons by 2030. Major growth factors for the Global Ginger Market also include the wide application of ginger in the food and beverages sector and the high use of ginger as herbal medicine.
Opportunity: Increasing demand for dried ginger
Dried ginger is gaining significant traction in the market, particularly in European countries. According to the EU CBI, The Netherlands, Germany, and the United Kingdom, are the top major ginger importing countries in Europe for dried ginger. The rising demand for dried ginger as a health ingredient and a wide application of ginger in various dishes and beverages, such as tea/herbal infusions and high Asia population living in the United Kingdom is directly influencing the demand for dried ginger, driving the overall Global Ginger Market.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/ginger-market/report-sample
Impact of Escalating Geopolitical Tensions on Global Ginger Market
The escalating geopolitical tensions are disrupting the growth of the Global Ginger Market. For instance, both Palestine and Israel are major imports of gingers, particularly dry ginger. According to statistics from the Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC), Israel imported USD 6.11 million worth of ginger in 2021, mostly from China (USD 3.31 million), India (USD 1.11 million), Brazil (USD 768,000), Thailand (USD 446,000), and South Korea (USD 288,000). Israel also exported USD 149,000 worth of ginger to Palestine in the same year. However, with Israel’s military occupation of Palestine, trade activities of ginger with and between these two countries were halted, which negatively impacted the Global Ginger Market.
Global Ginger Market
Segmental Coverage
Global Ginger Market – By Application
Based on application, the Global Ginger Market is segmented into food industry, pharmaceuticals industry, and others (cosmetics industry). The food industry segment holds the largest share of the Global Ginger Market. The growth of the market is mainly attributed to the use of ginger in various foods and beverages to provide both sweet and savory flavors. Ginger is a significant part of many Asian cuisines, owing to its flavor and medicinal properties, such as providing better digestion and improving immunity. However, the pharmaceuticals industry segment is anticipated to register a high growth rate over the forecast period owing to making medicines for the treatment of numerous ailments, such as nausea, colds, and migraines.
Global Ginger Market – By Region
The in-depth research report on the Global Ginger Market covers a number of country-specific markets across five major regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, and Middle East and Africa. Asia Pacific dominates the Global Ginger Market owing to high ginger production in the region. India led the ginger production in 2020 with 43% of the world total, followed by other Asian countries, including China, Nepal, Indonesia, and Thailand, according to the data by the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations. Additionally, ginger was strongly consumed as an herbal medicine in ancient cultures, such as in China and India, which drives demand for ginger in the Asia Pacific region.
Competitive Landscape
Major players operating in the Global Ginger Market include Indian Organic Farmers Producer Company Limited, Buderim Ginger, Litehouse, Inc., The Watkins Co, Morton & Bassett, McCormick, Guangxi Yongjiang Food Industry Co., Ltd, Floracopeia, SA Rawther Spices (P) Ltd, The Herbs N Spices, The Ginger People, and Sun Impex.
To further enhance their market share, these companies employ various strategies, including mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, joint ventures, license agreements, and new product launches.
Contact Us:
BlueWeave Consulting & Research Pvt. Ltd
+1 866 658 6826 | +1 425 320 4776 | +44 1865 60 0662
0 notes
Text
The Growing Impact of Nashik Onions on Global Trade
Nashik, located in Maharashtra, India, is renowned for its high-quality onions, which are characterized by their distinct bitter taste and remarkable shelf life. This city significantly contributes to Maharashtra's status as the largest onion-producing state in India, accounting for nearly 40% of the nation’s onion crop. The thriving onion trade in Nashik, particularly in Lasalgaon, positions the city as a crucial player in the global onion market.

Why Nashik is Famous for Onions
Nashik's unique geographical features, including its fertile black and red soil and favorable climate, create ideal conditions for onion cultivation. Unlike many other states, which typically harvest onions twice a year, Maharashtra boasts a three-harvest cycle. This ability to produce onions more frequently helps meet the high domestic and international demand. As a result, Nashik onions are highly sought after, known for their pungent flavor and long-distance travel viability, making them excellent for export.
Key Facts and Statistics About Onion Production in Nashik
The onion market in Nashik is a vibrant hub of economic activity, significantly influencing India’s position as a top onion exporter. In the fiscal year ending March 31, 2023, India exported a record 2.5 million metric tonnes of onions, underscoring its importance in Asian markets. Key statistics about onion production in Nashik include:
Maharashtra’s dominance in onion production, contributing to 40% of the total crop.
A significant reduction in summer onion plantation area by 40% this year, totaling 2.21 lakh hectares in Nashik.
Fluctuating onion prices in wholesale markets, with prices dropping dramatically from 4,500 rupees to 1,200 rupees per 100 kg over recent months.
The Major Onion Market: Lasalgaon
Lasalgaon, near Nashik, stands as Asia's largest onion market and a critical hub for onion exports from India. The Agriculture Produce Market Committee (APMC) in Lasalgaon plays a pivotal role in regulating onion trade. However, it faced challenges when onion trading ceased in protest against the imposition of a 40% export levy by the government.
Major Export Destinations
India’s onion exports primarily target neighboring countries and beyond. In the 2022-23 period, the major destinations for Indian onions included:
Bangladesh
Malaysia
United Arab Emirates
Sri Lanka
Nepal
Indonesia
Top Onion Exporters in Nashik
The onion export landscape in Nashik features several prominent exporters, including:
Sunrise Exports
Ratan Trading Company
Zameer Traders
Omas Enterprises
Shri Radhe Krishna Trading Company
Sambha Agro FPC Ltd.
Ss-Mariner International Pvt Ltd.
B.K.P. Traders
Saptashrungi Traders
Shrikant Trading Company
These exporters are instrumental in connecting local producers with international markets, ensuring the global demand for Nashik onions is met.
Red Onion Suppliers in Nashik
In addition to general onion exports, Nashik is also home to a variety of red onion suppliers, such as:
Jayachandra Foods Private Limited
Az Overseas
JJ. Agrofarm Private Limited
Swastik Traders
Alka Impex
Eagle International Export & Import
Shree Ambe Traders
Sadguru Food Processing
Sree Ram Traders
Krishna International
These suppliers specialize in delivering high-quality red onions to domestic and international markets.
Government Regulations on Onion Exports
In response to domestic market fluctuations, the Indian government has extended the ban on onion exports until March 31, 2024. This decision aims to stabilize prices and ensure sufficient domestic availability of onions, especially leading up to the general elections. The government’s policy change, initially announced in December 2023, reflects ongoing concerns over domestic supply.
Conclusion
Nashik's onion exporters are vital in bridging local agriculture with global markets, showcasing the region's agricultural strength. With the assistance of platforms like ExportImportData.in, stakeholders can access valuable export import data and insights necessary for navigating the onion trade landscape. This data-driven approach empowers exporters to make informed decisions and seize opportunities in the ever-evolving global marketplace.
If you're looking to explore more about onion exporters in Nashik or require detailed export import data bank information, visit ExportImportData.in to gain insights and strategies tailored to your needs.
#NashikOnions#OnionExport#MaharashtraAgriculture#GlobalTrade#AgriculturalExports#LasalgaonMarket#ExportImportData#OnionSuppliers#IndianAgriculture#FoodExports#OnionMarket#NashikExporters#TradeInsights#IndiaExports#SustainableFarming#CulinaryEssentials#ExportImportDataBank#FarmToTable#FreshProduce#AgroBusiness
0 notes
Text
Rise of Tea Export from India: A Statistical Analysis

Tea is a globally cherished beverage, whether it's Turkish Oralet, Assamese, or Moringa ole from Egypt. In India, a day often begins with a cup of tea, a tradition echoed worldwide where tea serves as an immune booster, energizer, relaxant, and social drink. By 2022, India had dedicated 6.19 lakh hectares to tea cultivation, with 80% of its domestic production, marking it as one of the top tea-consuming nations globally.
However, the true origins of tea lie in India's regions like Nilgiris, Darjeeling, and Assam, renowned for their premium taste and distinctive quality. This article delves into the rising trend of tea exports from India, providing detailed market insights, export data, and highlighting top Indian tea exporters. Let's explore this fragrant journey together.
Why Are Tea Exports from India Profitable?
India stands as the world's second-largest tea producer. Several factors contribute to the profitability of Indian tea exports:
High Production Volume: Historically, over 80% of mid-20th century Indian tea production was destined for the global market.
Strong Industry Structure: The Indian tea industry is robust, with a well-organized system encompassing growing, processing, trading, and exporting.
Economic Contribution: Tea cultivation significantly impacts the Indian economy, contributing to GDP and providing extensive employment opportunities.
Diverse Tea Regions: Key tea-producing regions include Assam, Darjeeling, Nilgiri, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal, each offering unique flavors and varieties.
Top Tea Producing Countries
The leading tea-producing nations in 2022 were:
China leads the world in tea production with an impressive output of 2.2 million tonnes. India follows as the second-largest producer, contributing 1.2 million tonnes to the global market. In third place is Kenya, with a production of 432,000 tonnes, while Sri Lanka ranks fourth with 340,000 tonnes. Vietnam and Turkey are close contenders, producing 214,000 tonnes and 212,000 tonnes respectively. Iran comes next, with a production of 160,000 tonnes, followed by Indonesia at 148,000 tonnes. Argentina produces 105,000 tonnes, securing the ninth spot, and Japan rounds out the top ten with an output of 85,000 tonnes.
Major Types of Tea Exported from India
India exports various types of tea, each with unique characteristics:
Black Tea: Dominates Indian tea exports, especially varieties from Assam, Darjeeling, and Nilgiri, known for their robust flavors.
Green Tea: Though less exported than black tea, green tea is gaining popularity due to its health benefits and refreshing taste.
Oolong Tea: A semi-oxidized tea combining elements of green and black tea, growing in popularity in some international markets.
For accurate and updated data on tea exports from India, including suppliers and export data, Eximpedia.app is a reliable resource.
India Tea Export Data: 2023-24
Preliminary statistics for January 2024 highlight the following:
All India:
Quantity exported: 20.10 M.kgs
Value: Rs. 499.50 crores
Unit price: Rs. 24.85/Kg
Comparison with January 2023:
Quantity exported decreased by 2.19%.
Export value fell by 10.45%.
Unit price dropped by 8.45%.
Top Tea Exporting Countries
Here are the major tea exporting countries, highlighting India's position:
In terms of export value, China leads the list with an impressive $2.1 billion, making it the top exporter. Kenya follows as the second-largest exporter, with an export value of $1.2 billion. Sri Lanka ranks third, with exports amounting to $732.4 million. India comes in fourth place with exports valued at $687.9 million. Poland secures the fifth spot with an export value of $262.8 million, closely followed by Germany, which has exports worth $242.5 million, placing it in sixth position. Japan ranks seventh with an export value of $189.9 million. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) ranks eighth with exports totaling $152.2 million. The United Kingdom (UK) is ninth with exports valued at $135.7 million, while Vietnam completes the top ten list with an export value of $130.7 million.
Key Destinations for Indian Tea Exports
India exports tea to over 25 countries. The primary destinations include:
Russia
Iran
UAE
USA
UK
Germany
China
During 2021-2022, India exported significant quantities to Russia (32.5 million kg), Ukraine (1.68 million kg), and Kazakhstan (6.48 million kg). The CIS countries collectively received 42.5 million kg, constituting 21% of total exports. The US, UAE, and Iran also ranked among top importers, with exports valued at $277.3 million.
Leading Tea Importing Countries
In 2022, global tea imports amounted to $6.62 billion, with the top 10 importing countries accounting for 61.3% of this value:
China leads the world in tea production with an impressive output of 2.2 million tonnes. India follows as the second-largest producer, contributing 1.2 million tonnes to the global market. In third place is Kenya, with a production of 432,000 tonnes, while Sri Lanka ranks fourth with 340,000 tonnes. Vietnam and Turkey are close contenders, producing 214,000 tonnes and 212,000 tonnes respectively. Iran comes next, with a production of 160,000 tonnes, followed by Indonesia at 148,000 tonnes. Argentina produces 105,000 tonnes, securing the ninth spot, and Japan rounds out the top ten with an output of 85,000 tonnes.
Finding Top Tea Exporters in India
To discover leading Tea exporters in India, visit Eximpedia, a comprehensive data-driven platform. Eximpedia provides authentic, current international trade information for over 130 countries. It offers extensive data on tea exports, including HS codes and detailed export statistics.
Conclusion
Global tea production and consumption are poised to grow over the next decade, driven by rising demand in emerging markets like China, India, and Japan. While entering the global tea market may seem challenging, it offers rewarding opportunities. Leveraging platforms like Eximpedia can help transform local expertise into a successful international venture. For any queries regarding tea exports from India, visit Eximpedia.app and schedule a free live demo today!
#Tea exports from India#India tea export#tea exporting countries#Tea exporters in India#Tea exporters#top tea exporters in india
0 notes