#impetigo treatment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
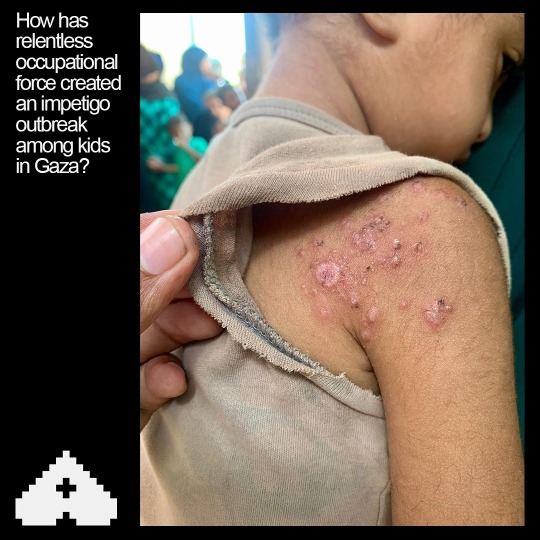
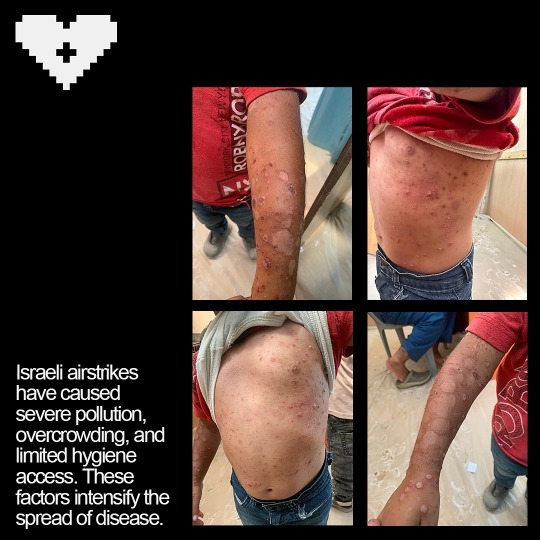
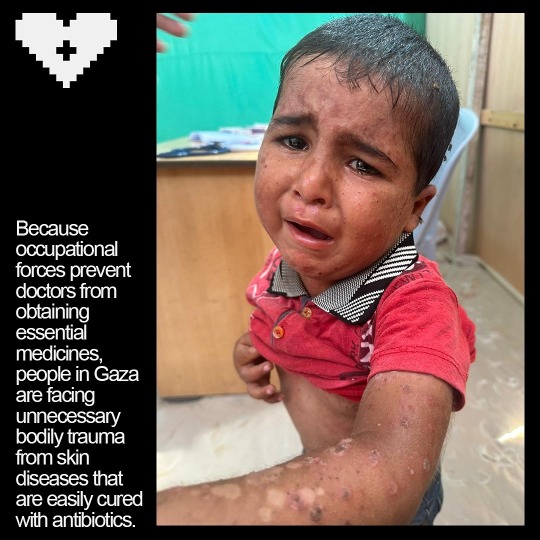
I Just need 5 minutes to read this maybe you can save our children👇😥💔
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that primarily affects young children but can occur in people of all ages. It is characterized by red sores or blisters that can ooze, crust over, and become itchy or painful. In environments such as displaced camps, where living conditions may be crowded and hygiene facilities limited, impetigo can spread rapidly among individuals.💔😥👇
In a displaced camp, where people are often living in close quarters within tents, the transmission of impetigo can be facilitated by several factors.
1. Close Contact: People in such settings frequently come into close contact with each other, which can easily transmit the bacteria that cause impetigo, namely Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes.
2: Shared Facilities: Shared resources like washing facilities, bedding, and clothing can become contaminated with bacteria and contribute to the spread of the infection.
3. Hygiene Challenges: Limited access to clean water and soap makes it difficult to maintain good personal hygiene, increasing the risk of infection and its spread.
4. Crowded Conditions: Overcrowding in tents can exacerbate the spread of impetigo, as the bacteria can be passed from person to person through skin-to-skin contact or through contaminated surfaces.
Preventing the spread of impetigo in such environments involves improving sanitation, educating residents about hygiene practices, and ensuring access to medical care for early diagnosis and treatment. Implementing effective infection control measures, such as regular cleaning of shared spaces and prompt treatment of affected individuals, is crucial in managing outbreaks and protecting the health of displaced populations.
Save our children from this war. Link for donation 👇🔗🍉
Verified by OOB master list line 395 👍
Sending you lots of love and hugs for standing with us🇵🇸🍉🙏
@fairuzfan @sayruq @longlivepalestina @nabulsi @self-hating-zionist @thenewgothictwice @el-shab-hussein @risoria @palipunk @palestine @intersectionalpraxis @fallahifag @sealuai @malcriada @mangocheesecakes @youdontknowwhotfiamm @farcillesbian @stil-lindigo @apsswan @star-and-space-ace @rainbowywitch @marscodes @oursapphirestar @annoyingloudmicrowavecultist @boyvandal-blog @the-bastard-king @13ag21k @agentfascinateur
#palestine#free gaza#gaza#gaza genocide#gaza strip#fuck israel#rafah#education#north gaza#film#art#advertising#architecture#animals#black and white#nail art#artists on tumblr#my art#digital art#artwork#he#self help#human rights#humanization#humanity#history#children
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
¶ … HIV and AIDS Content Knowledge for Dental Professionals: HIV Defined and the History of HIV Research Methodology, Statistical Data Analysis and Study Limitations Expected Results THE DIFFERENCES IN THE LEVEL OF HIV AND AIDS CONTENT KNOWLEDGE FOR DENTAL PROFESSIONALS: Infectious diseases, whether hepatitis, flu, herpes, HIV, AIDS, impetigo, encephalitis, measles, Rocky Mountain Fever, or a host of others have plagued mankind for centuries. Without doubt new infectious diseases will appear in the world's population for centuries to come. However, no disease has been more detrimental to populations all over the world that than of HIV and AIDS. Although this paper is not intended to moralize, theorize, pontificate, or set moral standards on the HIV and AIDS issue it is extremely important to know that the epidemic affects citizenry all over the globe. As such all individuals alike, wherein no known cure is available, must take precautionary measures to limit exposure and infection. To these ends professions that are directly involved in treating HIV infected or AIDS patients must be ever vigilant when treating those afflicted. At the same time the helping professions must not refuse treatment because of fear, lack of epidemiological knowledge, or stigmatic impressions. The remainder of this paper will concentrate on one helping profession, i.e., dentistry, with respect to dental service and HIV infection and control. The intended purpose of the paper is to set into motion, by way of a research proposal, a study to determine whether or not the dental profession is effectively delivering dental services to vaccinated people infected with the HIV virus. Literature Review History of HIV in the U.S. And HIV Defined. Before any attempt is made to present a historical accounting of HIV and AIDS there must first exist a clear understanding as to what is HIV and what is AIDS. Broadly defined HIV is the virus and AIDS is the resulting disease (Stebbing, Gazzard & Douek, 2004). As such HIV destroys the human body's immune system and develops into AIDS, thus making the body susceptible to other diseases. What must be kept at the forefront discussion is that all people who are HIV positive do not necessarily have the AIDS disease. This is important to remember as the general public consensus is that HIV and AIDS are one in the same thing. The first AIDS cases were reported in 1981 through 1996 more than 510,000 AIDS cases and more than 315,000 deaths have been reported in the United States alone (Holmberg, 1996). This is only the beginning of the HIV infection as it is estimated that nearly 1 million Americans have been infected with the virus through the mid-1990s but had not yet developed clinical symptoms (UN, 1998). No cure or vaccine has been invented to cure AIDS and many of those infected with HIV may not even be aware that they carry and can spread the virus. Scientists and doctors are constantly being challenged, as the HIV virus and AIDS disease are one of the most intense public-health problems in the world today. The reported total number of aids cases in the United States is increasing explosively. What is more, public health experts believe that the actual cases of aids are only a small fraction of the total problem, and that is the part that is visible. Not so obvious but just as real are the much larger numbers of people who are infected with aids but have not yet developed any symptoms. Some of these individuals may never realize they have been infected. Many, however, will be the new aids cases in the years to come and all of those infected, even if they do not have any symptoms, can spread the disease to others. In fact we might well be on the verge of a new plague rivaling the influenza epidemic that swept throughout the world at the end of World War 1, or the dreaded Black Plague of the Middle Ages. A third frightening factor about aids is its deadliness. Over 60% of those in whom aids was diagnosed have died; the majority die within two years of diagnosis. Though it can kill quickly, this new disease can also produce great suffering. Disfiguring sores, pneumonia that leave the patient gasping for breath, an endless series of infections that can strike almost any organ or system of the body, and, even progressive blindness. Any or all of these may accompany the development of aids (Lerman-Golomb, 1995). When aids first appeared on the United States, it seemed to be confined to only a few small groups of the population, contracting in a few large cities. Since then, it has spread to every state of the union penetrating in cities, towns, and rural areas. Aids and HIV have been reported in virtually every country in the world; the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates between five and ten million are already infected. Aids strikes men, women, and children and has no race barrier. No longer confined to the original narrow "risks groups," among these homosexual men, people having multiple sex partners and intravenous drug users, it has gradually found a way of spreading into every level of society and striking people from groups that were once believed to be "safe." The medical epidemic of aids has given rise to another epidemic, the epidemic of fear. In some cities, parents are fearful that their children may catch aids form classmates and some have boycotted the school, keeping the children at home. People have abandoned dear friends and loved ones suffering from the disease for fear of getting it themselves (Myer & Sussser, 2003). In addition, many of the helping professions silently refuse treatment of HIV infected or AIDS' patients for fear of contacting the virus or disease. The work of medical researchers has been an encouraging chapter in the ongoing stories of aids and HIV. Considering the disease was recognized only a few years ago and that its agent, HIV, is one of the most complex and baffling organisms on earth, the achievement is an astonishing" (Silverstein, 1999). In a brief span of time, researcher have found the cause of the disease and learned much about it and the ways it is passed from one person to another. They have found many effective treatments for many of the infections that accompany aids and drugs that can also slow the process of the disease and enable people with it to live longer and feel better. Medical researchers are how searching for more effective means of treating aids and working on vaccines, to prevent it (Lerman-Golomb, 1995). Because there is no effective vaccine or therapy, education and risk reduction are the best ways by which to combat the epidemic. Avoiding behaviors that place people at risk could practically stop the further spread of AIDS. This can be achieved through education and the involvement of local community groups, statewide organizations, and national governments. The focus of the intended research, therefore, will be on the educational variable with respect to the dentistry profession. Research Question and Hypothesis Of the nearly 168,000 dentists and 112,000 dental hygienists practicing in America today all are subject to the HIV virus by the very nature of their work. On a day-to-day basis both dentists and hygienists are confronted with an array of potential HIV transmitting vehicles, whether needle pricks, bites, aerosol and splatters, and other patient materials (Kohn, et al., 2003). As such dentists and their staff must be ever vigilant with respect to the manner in which they service their patients. Attempting to control the possibility of spreading the HIV virus all dental practices must formulate a safety procedure that is preemptive of disease infiltration. To this end Pascoe, McDowell & Springer, (2002) advocate that the first step in dealing with AIDS in a dental office is to recognize the symptoms and/or manifestations through a patient's history and their observable physical conditions followed by various precautionary examination and treatment steps. However, no matter the seriousness of any infectious disease the issue of whether or not dental professionals followed needed protocol is of importance as well. According McCarthy, Koval, John, & MacDonald (1999) the majority of dentists and hygienist do but the need still exist for mandatory continuing education to apprise dental professionals of new developments. With respect to preventative measures in a dental practice the ADA makes the following practice components for dealing with HIV situations: 1. Use of personal protection gear. 2. Instrument sterilization. 3. Disinfecting of all surfaces and equipment. 4. X-ray asepsis. 5. Dental laboratory asepsis. 6. Liability. Not only should dental offices be vigilant and cautious when treating HIV patients but the patient has a responsibility as well. Although dentists are the first to notice the clinical changes that signal the onset of the HIV virus makes them pivotal to helping HIV individuals maintain maximum health in the arena of diversity. Unfortunately all too frequently the relationship between patient and dentist is adversarial. Patients, usually out of fear hide their medical status because of immediate discrimination and rejection form the dentist. Conversely, the mistrust and lack of openness makes caring dentists, as well as other medical professionals, feel frustrated, betrayed and somewhat abused. The primary focus in all situations is base on each person's personal condition. Dentists and all other dental professionals cannot plead ignorance as a reason for refusing to treat an HIV infected individual. Codes of conduct for dentists and standard of practice issued by the government and professional licensing boards make clear that which the dentist must know about HIV just as in any other medical condition. Dentists may not refuse HIV infected patients because they are infectious. In addition studies have shown that HIV poses nothing vaguely approaching a significant risk in the transmission of the HIV virus in a dental office. What this means is that with proper safety mechanisms put into place HIV transmission is not likely a health risk. In fact the Supreme Court of the United States, in 1987, established a two-part test for determining when an infectious disease justifies discrimination: risk to others must be reasonable accommodated and the remain risk must still be significant. The first step in the attainment of a desired research goal is to develop a scientific approach toward the situation, event, occurrence, or phenomenon being investigated. As such no research question can be answered if first it is not stated in testable terms or form. For the proposed research investigative endeavor the following research question is presented: To what extent will there exist statistically significant overall differences and relationships in the level of HIV content knowledge garnered by dentists and dental hygienists? Main Effects Null Hypotheses: 1. Medical content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 2. Use of personal protection gear content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 3. Instrument sterilization content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 4. Disinfecting of all surfaces and equipment content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 5. X-ray asepsis content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 6. Dental laboratory asepsis content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. 7. Liability content knowledge level between dentists and dental hygienists will not be statistically significantly different at the ( < .05 p level. Interaction Null Hypothesis: There will be no statistically significant interaction at the ( < .05 p level between and amongst seven primary dependent variables of medical information, use of personal protection gear, instrument sterilization, disinfecting of all surfaces and equipment, X-ray asepsis, dental laboratory asepsis, and liability. Research Methodology, Statistical Data Analysis and Data Collection Procedures A stratified random sampling technique is recommended for the selection of participants within the study. A truly random selection cannot be utilized due to geographical and time logistics. The stratified sample will be chosen from representative dentists and dental hygienists within the metropolitan area of insert city here. In total 90 (45 dentists and 45 dental hygienists) participants will be administered a content knowledge questionnaire designed to produce information as to the participants' level of knowledge with respect to the seven areas of content knowledge. The resulting numerical information will be tabulated and analyzed by the Analysis of Variance statistical technique (ANOVA). As the ANOVA only has the ability to determine if a statistical significance will occur within the comparison, a modified orthogonal ANOVA will be necessary to determine whether or not any differences might possibly exist (Ferguson, 1966). Should main effects be non-significant and one of their interaction counterparts statistically significant, then a test for simple effects will be employed to determine the whereabouts of the interaction. The ANOVA is best suited for multiple interactions over the single independent "t" Test as it allows for independent and dependent variable interaction accountability (Kerlinger, 1964). Study Limitations Due to the number of possible measurement variables that can be associated with the concept of HIV content knowledge those chosen for the proposed study have been limited to the seven listed above. Other intervening variables that might possibly affect the results of the study (religion, socio-economic class, length of practice, and gender) will be left to further research activities. In addition, the study will be limited to general practice dentistry. Expected Results No single study has the ability to answer all question impacting upon an event, occurrence, situation, product, or phenomenon. As such many questions are left unanswered and without discourse. The primary principle of any investigation is not only to present formidable information relative to a research question but also to present the reader research questions that need additional investigation. To this end the present proposed research study, while providing current data with respect to the level of HIV content knowledge of dentists and dental hygienists must be followed by continued research investigations into areas such as professional collaboration, HIV / AIDS management, information technology, and training. References AIDS epidemic update: December 1998. UN AIDS Joint United Nations Program on HIV / AIDS Ferguson, George A. (1966). Statistical Analysis in Psychology and Education. New York: McGraw-Hill. Holmberg, SD. (1996). The Estimated Prevalence and Incidence of HIV in 96 large U.S. Metropolitan areas, Am J. Public Health Kerlinger, Fred N. (1964). Foundations of Behavioral Research. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Lerman-Golomb, Barbara (1995). AIDS, Austin, TX: Raintree Steck-Vaughn. McCarthy, G.M., J.J. Koval, M.A. John, and J.K. MacDonald. 1999. Infection Control Practices Across Canada: Do Dentists Follow the Recommendations? Journal of the Canadian Dental Association 65 (9): 506-511. McCray E, (1986). Occupational Risk of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Among Healthcare Workers. New Eng J. Med, 314:1127-32, 1986. https://www.paperdue.com/customer/paper/disease-prevention-strategies-for-as-long-109270#:~:text=Logout-,DiseasePreventionStrategiesForaslongas,-Length2pages Myer L, Morroni C, Susser ES. (2003) The social pathology of the HIV / AIDS pandemic International Journal of Epidemiology; 32(2): 189-192. Pascoe, Gary P., McDowell, John, and Bradley-Springer, Lucy (2002). A Case-Based Self- Study Module for Dental HealthCare Personnel. Mountain Plains AIDS Education and Training Center University of Colorado Health Sciences Center. Silverstein, Alvin (1999). AIDS: An All-About Guide for Young Adults. Springfield: Enslow Publishers. Stebbing, Justin, Gazzard, Brian, and Daniel C. Douek. The New England Journal of Medicine Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chapter 4: Medical Esthetic Procedure Contraindications

So you’re considering getting some medical esthetic procedures done. That’s hot! But before you schedule an appointment or consultation here’s a quick guide of contraindications to be aware of!!

What is a Contraindication?
A contraindication is a condition we look for in the medical field that serves as a reason to not continue forward with a medical treatment due to potential harm the treatment may cause to a patient!
Laser Hair Removal:


Herpes and Cold Sores: Can you get laser hair removal with herpes or cold sores? Yes! But only if there is not an active breakout. We do warn the clients that the lasers we use are powerful enough to cause a herpes or cold sore breakout to occur so please proceed with caution!
Retinol: Use of Retinol’s are a huge no no! It can cause severe damage, burning or scaring if a laser is used! If you are on Retinol please stay off of it for 1 week before your laser hair removal procedure.
Seizures + Epilepsy: If you have a history of epilepsy please refrain from getting any laser or light treatment as it can induce seizures.
Bacterial Skin Infections: Infections can spread to other parts of the body if a laser is used.
Impetigo: This highly contagious superficial skin infection is something we as your medical esthetician should be aware of before continuing with treatment.
Cellulitis: This infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue should be cleared before you continue with any laser or light therapy.
Folliculitis: Laser treatments are not performed in areas of folliculitis but several hair removal lasers have been approved by the FDA for pseudofolliculitis barbae treatment.
Fungal Infections: Ringworm and Yeast Infections can not be treated with laser or light therapy until cleared.
Viral Infections: Active viruses are considered major contraindications for laser and light therapy.
Shingles: If there is an active outbreak laser treatment will not be used.
Common Skin Warts (HPV): Although some lasers are used to remove persistent warts, they are still considered contraindications.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): You will not be disqualified as a candidate for laser treatment, unless the outbreak is in an area of proposed treatment.
Open Lesions, Rashes and Sunburns: This includes open lesions from picking at the skin. Any unknown lesions or rashes will be considered contraindications. Sunburns are known to disrupt the skin barrier and are considered contraindications. Any suspicious lesions should always be evaluated by a physician prior to treatment.
Accutane: You must be off of Accutane for at least six months to a year, depending on a physician’s  preference prior to treatment with laser or light therapy.
Immediate Post-Operative Face Lift, Blepharoplasty or Neck Lift: Treatment is avoided for clients who are in post op from these treatments until a physician has given approval for laser or light treatment. 
Pregnancy and Lactation: Pregnancy and lactation are considered contraindications women who are pregnant or lactating, should wait after pregnancy + breastfeeding so a child will not be exposed before beginning or continuing laser or light treatment. 
Laser Tattoo Removal:
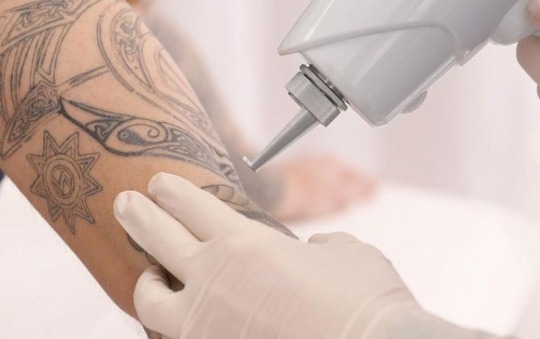
Laser tattoo removal shares the same contraindications as laser hair removal.
Red Tattoo Ink: Red tattoo ink is known to be allergenic. If you have experienced an allergic reaction to red tattoo ink, be aware that another allergic reaction may occur if a red ink tattoo is being removed by laser. 
Retinol + Accutane
Pregnancy and Lactation
Bacterial Infections
Viral Infections
Fungal Infections
History of Epilepsy or Seizures
Open Skin Lesions, Sunburns and Rashes
Microneedling:

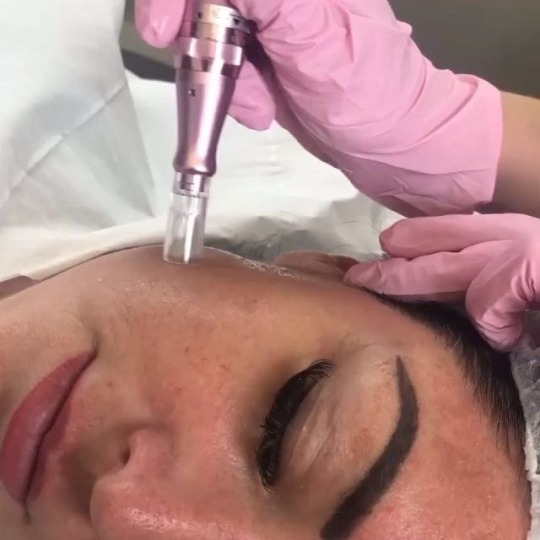
Herpes + Coldsores: Please wait until an outbreak is fully healed! Estheticians can avoid microneedling the mouth area if you do have an outbreak but it is best to wait until the outbreak is fully healed to avoid any spreading.
Active Acne: Areas of active acne can be skipped over but if there is an all over outbreak it is best to wait.
Rosacea: Clients with vascular rosacea can receive treatment, but not pustular or nodular rosacea wait until the information has settled.
Atopy, Asthma, Hay Fever and Allergies: Any patient with a history of allergies maybe prone to urticaria, after needling due to the release of histamines.
Anticoagulants: Any supplements, known to prolong, bleeding time, may not necessarily be discontinued from treatment, but the risk of bruising increases.
Drugs and Supplements Associated with Photosensitivity: Any drug and supplement that can cause photosensitivity including Accutane is considered a contraindication. 
Fitzpatrick III and Above: Those with darker skin tones are not disqualified from treatment but it should be known that skin will appear puffy, bruising, if present might be visible in thin skinned areas and erythema (skin redness)  when super-imposed on brown, appears much darker. Patience with melasma or post. Inflammatory hyperpigmentation must understand that lesions will appear darker for several months before improving.
PSA: There are certain ingredients to avoid using when it comes to dermal needling. Ingredients to avoid include preservatives, fragrances, emulsifiers, emollient acids, dyes, coloring agents, and UV filters 
Before receiving a dermal needling treatment, you may be asked by your provider about allergy or medication, history, blood pressure/medication, bleeding disorders, eczema, psoriasis, immune system disorders, keloid, scarring, major illnesses, heart conditions, anemia and a lot of other general medical questions.
Body Contouring
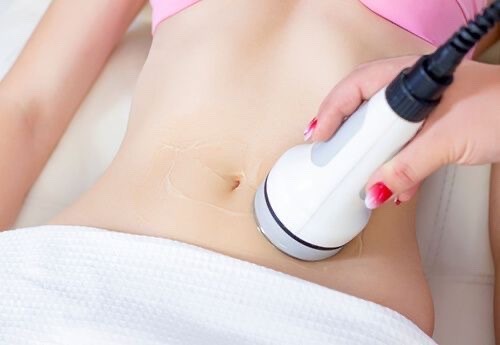
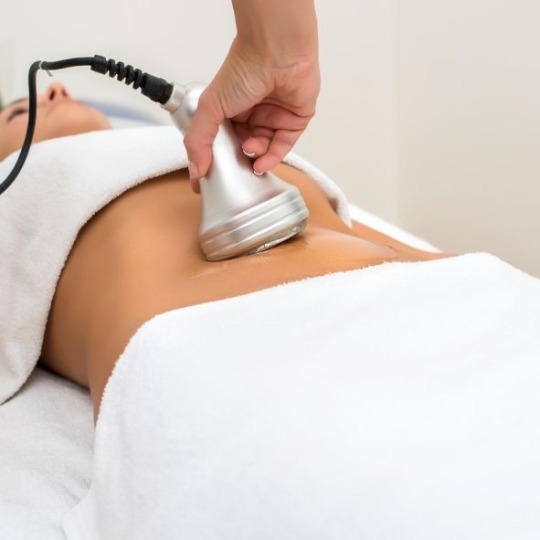
Pregnancy and Breast-Feeding
HIV/AIDS
All forms of Cancer
Undergoing Chemotherapy
Immunodeficiency
Lupus
High Blood Pressure
Uncontrolled Diabetes
Keloid Scarring
Excessive Pigmentation
Vein Inflammation
Steroid Medication
Chemical Peels + Laser Resurfacing
Sunburn
Recent Surgery or Scars: Wait 6 months
Open Lesions, Skin Diseases, Inflammation, Varicose Veins, Infection, Metal Implants, Metal Screws, Metal Contraceptive Coil + Prothesis/Silicone Implants: Area will be avoided
Antibiotics: Must wait until completed medication course
Depilatory Creams: Wait 2 weeks
IPL or Laser Treatment: Area that received laser or light therapy must wait 2 weeks before receiving body contouring.
Areas with Botox: Wait 3 months before receiving body contouring.
Areas with Dermal Filler: Wait 2 weeks before receiving body contouring.
Sun Tan: Will be avoided
Chronic Inflammation: Speak with your healthcare provider before proceeding forward with a body contouring treatment.
PSA: Before receiving body contouring, your hydration levels will be checked your body must be 40% or higher for your hydration level. Hydration levels below 40% can cause cat like scratch sensations when receiving body contouring. Which is why low levels of hydration are considered a contraindication and you must wait until your hydration levels are at 40% before receiving treatment.

30 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ad from 1966 for pHisoHex skin cleanser, which was taken off the over-the-counter market in 1972 (but is still available by prescription) -- "Both Phisoderm and Phisohex were removed by drugstores and retail outlet stores when the Food and Drug Administration halted the production and distribution of products containing more than 1% of hexachlorophene" says Wikipedia -- and OTC products bearing the 'pHiso' name today are based in salicylic acid.
Personal experience: pHisoHex works better than pHisoDerm, which was advertised to teens in the 1980s as an anti-acne treatment. When I was a kid, pHisoHex was still an OTC product so my mother used it on me and my first two sibs after a bath when we were babies. Also, circa 1984 I somehow got impetigo on my fingers; the doctor-prescribed treatment was pHisoHex and the product was just as I remembered it. Quite effective and I do miss it, honestly.
0 notes
Text
5 Common Illnesses Treated at Hillsboro Urgent Care
Health concerns often arise without warning, and being prepared to respond quickly can make all the difference. At times like these, access to timely care becomes essential. That’s where Hillsboro Urgent Care plays a vital role. Their team is well-equipped to handle a wide range of conditions, offering expert common illnesses treatment to patients of all ages. Understanding which ailments are frequently seen at urgent care centers can help individuals recognize symptoms early and seek care when needed. Here are five of the most common illnesses and injuries treated at Hillsboro Urgent Care.

1. Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections are among the most common reasons patients visit urgent care facilities. These infections can affect the sinuses, throat, airways, or lungs, and they range from mild to severe.
Common Types of Respiratory Infections
Common Cold: A viral infection of the nose and throat, the common cold is usually harmless but can be quite uncomfortable. Symptoms include a runny nose, sore throat, cough, congestion, and sneezing.
Influenza: Often more severe than a cold, the flu can cause high fever, body aches, fatigue, and a dry cough. It’s crucial to get treatment early to prevent complications.
Bronchitis: This condition involves inflammation of the bronchial tubes and often follows a cold or respiratory infection. Symptoms include a persistent cough, production of mucus, and fatigue.
At Hillsboro Urgent Care, clinicians offer targeted common illnesses treatment for respiratory conditions, including medication management, breathing support, and preventive guidance.
2. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are another common ailment, especially among women. They occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, leading to symptoms like a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
Understanding UTIs
UTIs are among the most frequently treated conditions, especially in women. Symptoms include a constant urge to urinate, burning during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
Most UTIs stem from bacteria such as E. coli entering the urinary tract. Although anyone can get a UTI, anatomical differences make women more susceptible. Hillsboro Urgent Care provides rapid testing and effective antibiotics to address UTIs promptly. Alongside treatment, they offer practical advice on prevention, such as staying hydrated and practicing good hygiene.
3. Skin Infections
Skin infections are a common reason for urgent care visits, as they can be painful and unsightly. These infections can arise from bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Types of Skin Infections
Cellulitis: A bacterial infection that affects the skin and its underlying tissues, cellulitis can cause redness, swelling, and pain. It often requires antibiotic treatment.
Impetigo: This contagious bacterial skin infection is common in children and causes red sores that can rupture and ooze.
Fungal Infections: Conditions like athlete's foot and ringworm fall under this category, characterized by itchy, scaly patches on the skin.
Hillsboro Urgent Care offers evaluation and treatment for skin concerns, ensuring early intervention and preventing complications. Their common illnesses treatment for skin conditions includes both prescription and over-the-counter options.
4. Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal problems can range from mild discomfort to severe conditions that require immediate attention. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Common Gastrointestinal Conditions
Gastroenteritis: Often referred to as the stomach flu, this condition involves inflammation of the stomach and intestines, causing symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and cramps.
Food Poisoning: Caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages, food poisoning can lead to severe stomach pain, fever, and dehydration.
Acid Reflux: A condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus), causing heartburn.
The team at Hillsboro Urgent Care provides supportive care such as rehydration, anti-nausea medications, and guidance for symptom relief, making GI health a key focus of their common illnesses treatment offerings.
5. Minor Injuries
Minor injuries such as cuts, sprains, and fractures are common occurrences that can benefit from prompt attention at an urgent care facility. These injuries, while not life-threatening, can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities.
Types of Minor Injuries
Cuts and Lacerations: These require proper cleaning and sometimes stitches to prevent infection and promote healing.
Sprains and Strains: Injuries to ligaments or muscles that can cause pain, swelling, and limited movement. Treatment often involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E).
Fractures: Although more serious than sprains, minor fractures can often be treated with splints or casts to ensure proper healing.
Hillsboro Urgent Care’s clinical staff is trained to evaluate and manage a wide array of minor injuries with prompt and compassionate care. Being aware of the most common conditions treated at urgent care helps individuals act quickly when symptoms arise. Whether it's a respiratory infection, UTI, skin infection, GI distress, or minor injury, Hillsboro Urgent Care is prepared to provide the support and medical intervention patients need. With a focus on efficient common illnesses, their team ensures every patient receives attentive, timely care. To learn more or to plan a visit, contact Hillsboro Urgent Care. With experienced providers and convenient access, they are committed to keeping the community healthy, one visit at a time.
0 notes
Text
Skin Infections: When Should You See a Doctor?
Skin infections are common conditions caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that affect the skin’s surface or deeper layers.
While many skin infections are mild and can be treated at home, some can become severe or even life-threatening if ignored. Knowing when to see a doctor is crucial to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
This guide will help you recognize the warning signs of serious skin infections and understand when immediate medical care is necessary.

If you’re in Roorkee and suspect a skin infection, consulting a trusted Dermatologist in Roorkee like Dr. Hera Tabassum at Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic can provide you with expert care and personalized treatment plans.
What Are Skin Infections?
Skin infections occur when harmful microorganisms invade your skin, leading to symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, itching, and sometimes pus or blisters.
These infections can range from minor irritations to severe conditions requiring urgent medical attention. C
ommon types include bacterial infections like cellulitis, fungal infections such as ringworm, viral infections like herpes, and parasitic infestations such as scabies.
Common Types of Skin Infections and Their Symptoms
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial skin infections include cellulitis and impetigo. Symptoms often involve redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and sometimes pus-filled blisters or sores.
Cellulitis, in particular, can spread rapidly and may be accompanied by fever and chills.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, such as ringworm and athlete’s foot, usually cause itchy, scaly, and red patches. These infections thrive in warm, moist areas and can be persistent if untreated.
Viral Infections
Viral skin infections include herpes simplex and warts. They often present as clusters of blisters, sores, or rough textured skin. These infections may recur periodically.
Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections like scabies and lice cause intense itching and rash, often with small bumps or tracks on the skin. They spread through close personal contact.
When to See a Doctor: Key Warning Signs
Many skin infections improve with basic care, but you should seek medical advice promptly if you notice any of the following:
Rapidly spreading rash: A rash that spreads quickly and causes you to feel unwell may indicate a serious infection such as necrotizing fasciitis, which requires urgent care.
Signs of cellulitis: Redness, swelling, warmth, and pain that worsen rapidly, especially if accompanied by fever or chills.
Pus-filled blisters or wounds: Presence of pus, fluid-filled blisters, or sores that ooze requires professional evaluation.
Rash with fever: Any rash covering a large area or accompanied by fever or chills should be assessed promptly.
Skin infection not improving: If the infection does not get better or worsens despite home treatment, see a doctor.
Infected wounds: Swelling, redness, pus, or red streaks near a wound may signal spreading infection.
Persistent itching or hives: Skin reactions that last long or worsen could indicate an underlying issue needing medical treatment.
Changes in moles or skin patches: Any change in size, shape, color, or symptoms like bleeding or pain should be examined by a dermatologist.
If you are looking for a qualified Skin Specialist in Roorkee, Dr. Hera Tabassum is a leading dermatologist, dermatosurgeon, and cosmetologist known for her expertise and compassionate care.
She holds an MBBS and MD in Dermatology from the prestigious JNMCH, AMU (Aligarh), has cleared the Specialty Certificate Examination (MRCP-SCE) from the Royal College of Physicians in London, and completed advanced training in dermatosurgery, aesthetics, and lasers.
What to Expect During a Medical Evaluation
When you visit a healthcare provider for a skin infection, they will perform a physical examination to assess the affected area.
In some cases, doctors may order tests such as skin swabs, cultures, or blood tests to identify the cause of infection.
Treatment may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungal or antiviral medications, and proper wound care.
Severe infections might require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics or surgical intervention.
At Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic, patients receive thorough evaluations using the latest diagnostic techniques to ensure accurate diagnosis and customized treatment plans.
At-Home Care Tips for Mild Skin Infections
For minor skin infections, proper at-home care can help speed healing and prevent complications:
Clean the affected area gently with mild soap and water.
Apply over-the-counter antiseptic or antifungal creams as directed.
Keep the area dry and avoid scratching or picking at lesions.
Use clean dressings if there is an open wound or blister.
Avoid sharing towels, clothing, or personal items to prevent spreading infection.
Monitor symptoms closely and seek medical help if the infection worsens.
Prevention Tips to Avoid Skin Infections
Preventing skin infections is possible with simple daily habits:
Maintain good personal hygiene by washing hands and bathing regularly.
Avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or clothing.
Treat cuts, scrapes, and wounds promptly with cleaning and appropriate dressings.
Manage chronic skin conditions like eczema carefully to reduce infection risk.
Wear breathable clothing and keep skin dry, especially in hot or humid environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: When should I seek emergency care for a skin infection? A: If you experience rapid swelling, spreading redness, severe pain, fever, or pus-filled blisters, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Q: How long do skin infections typically last? A: Mild infections may resolve within a week with proper care, but severe infections can take longer and require medical treatment.
Q: Are skin infections contagious? A: Some infections, like fungal and viral types, can spread through direct contact or sharing personal items. Always practice good hygiene.
Q: Can I treat skin infections without antibiotics? A: Mild infections might resolve with topical treatments and hygiene, but bacterial infections often require antibiotics prescribed by a doctor.
Q: What are the signs of cellulitis? A: Redness, warmth, swelling, pain, and fever are common signs. Cellulitis can spread quickly and needs prompt medical care.
Conclusion
Skin infections can range from minor irritations to serious medical emergencies. Recognizing the warning signs—such as rapidly spreading rash, fever, pus, or non-healing wounds—is essential to seek timely medical attention.
If you need a reliable Dermatologist in Roorkee or a Skin Specialist in Roorkee, Dr. Hera Tabassum at Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic offers expert diagnosis and advanced treatment options to help you heal safely and effectively.
Call to Action
Experiencing symptoms of a skin infection? Don’t wait. Schedule your consultation today at Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic, Roorkee, for expert care from one of the region’s leading dermatologists and get your skin back to healthy, glowing condition.
0 notes
Text
Common conditions treated at quick care clinics
When a medical issue arises and your primary care doctor isn't available, finding quick care near me or urgent care near me open now can be a lifesaver. These clinics bridge the gap between emergency rooms and traditional doctor’s offices by offering timely medical attention for non-life-threatening conditions. Understanding what they treat can help you decide when a quick care visit is the right choice.

What Is a Quick Care Clinic?
Quick care clinics, also known as urgent care centers, are walk-in medical facilities that treat a variety of common illnesses and injuries. They are designed to provide fast, affordable care, especially when your regular physician is unavailable or when you're traveling. Many clinics are open extended hours, including evenings and weekends, making it easy to search for an urgent care near me open now and get prompt treatment.
1. Cold, Flu, and Upper Respiratory Infections
One of the most common reasons people search for quick care near me is for relief from symptoms of colds, the flu, or upper respiratory infections. These include cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, fever, and fatigue. Quick care providers can assess your symptoms, prescribe medications if necessary, and advise on how to recover effectively.
2. Minor Injuries
Quick care clinics are ideal for treating minor injuries that don’t require an emergency room visit. These include sprains, minor fractures, bruises, small cuts, and burns. Clinicians often have access to basic diagnostic tools like X-rays and can provide splints, stitches, or wound care on the spot.
3. Ear Infections
Ear pain, especially in children, often leads families to search for urgent care near me open now. Quick care providers can diagnose and treat ear infections promptly, relieving discomfort and preventing complications. They may prescribe antibiotics if a bacterial infection is detected.
4. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are another common condition treated at urgent care clinics. Symptoms such as burning during urination, frequent urges to go, and lower abdominal pain can be addressed quickly with a visit to a walk-in clinic. Timely diagnosis and treatment help prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys.
5. Allergic Reactions
Mild to moderate allergic reactions, such as hives, rashes, or itching, are often managed at urgent care centers. While severe allergic reactions require emergency care, quick care clinics can treat common allergic flare-ups from food, environmental allergens, or insect bites.
6. Skin Rashes and Infections
Skin issues like rashes, athlete’s foot, poison ivy, and minor infections (like cellulitis or impetigo) can be irritating and uncomfortable. Quick care clinics provide evaluation and treatment, often including topical or oral medications to relieve symptoms and clear the infection.
7. Stomach Issues
Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and mild abdominal pain are also common reasons people look up quick care near me. While these symptoms can be caused by many different conditions, urgent care providers can help determine the cause and suggest effective treatments or refer patients for further testing if needed.
8. Pink Eye and Other Eye Issues
Conjunctivitis (pink eye), styes, and minor eye injuries can be assessed and treated at most urgent care clinics. Getting prompt care helps prevent the spread of infection and alleviates discomfort quickly.
9. Asthma and Breathing Difficulties
Quick care clinics can offer relief for non-severe asthma attacks or other minor breathing difficulties. They may provide nebulizer treatments, prescribe inhalers, and help manage flare-ups before they become more serious.
10. Vaccinations and Preventive Care
Many people don’t realize that urgent care clinics also offer vaccinations for flu, tetanus, COVID-19, and travel. If you're in a rush or your doctor isn’t available, searching urgent care near me open now can help you stay on track with immunizations and preventive services like blood pressure checks or cholesterol screenings.
Why Choose Quick Care?
Quick care clinics combine convenience, accessibility, and affordability. Whether you're dealing with a sudden illness or a minor injury, these facilities offer a smart alternative to the emergency room. By searching for quick care near me when you need medical attention fast, you can avoid long waits and high ER costs while still receiving expert care.
In summary, quick care clinics are equipped to handle a broad range of non-emergency health conditions. They provide a reliable and efficient option when you're feeling unwell or injured and need care—especially when time and accessibility matter most.
0 notes
Text
Bacterial Skin Infection Treatment in Katni – Dr. Nargis Anshari
Skin is the largest organ of the body and acts as a protective barrier against harmful microorganisms. However, when bacteria invade the skin through cuts, wounds, or even pores, it can lead to various types of skin infections. If you're suffering from a bacterial skin infection in Katni, Dr. Nargis Anshari offers advanced and effective treatment with a personalized approach.

Meet Dr. Nargis Anshari – Your Trusted Skin Care Expert in Katni
Dr. Nargis Anshari is a renowned cosmetologist and skin care specialist based in Katni. With years of experience in treating various skin conditions, she is known for her compassionate care and scientific approach to skin treatment. Whether it's a common bacterial infection or a complicated dermatological issue, Dr. Nargis Anshari provides comprehensive diagnosis and treatment tailored to each patient's skin type and needs.
Common Bacterial Skin Infections Treated
Dr. Nargis Anshari treats a wide range of bacterial skin infections, including:
1. Impetigo
A highly contagious infection, especially common among children, impetigo appears as red sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth. It often results from Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria.
2. Cellulitis
This is a deeper skin infection causing redness, swelling, and pain. It often affects the legs but can occur anywhere. Immediate treatment is required to prevent its spread to deeper tissues.
3. Folliculitis
Infection of hair follicles leading to small, red bumps or pimples filled with pus. It can be caused by shaving, wearing tight clothes, or sweating excessively.
4. Boils and Abscesses
Painful, pus-filled lumps under the skin, often caused by Staph bacteria. If not treated, the infection can worsen and spread.
5. Erysipelas
A type of cellulitis with raised, well-defined borders and usually accompanied by fever and chills.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approach
Dr. Nargis Anshari follows a scientific and patient-focused treatment process:
✅ Thorough Skin Examination
She examines the skin physically and may recommend swab tests or cultures to identify the exact bacterial strain.
✅ Antibiotic Therapy
Based on the type of infection, she prescribes either oral or topical antibiotics. In more severe cases, injections or IV antibiotics may be necessary.
✅ Wound Care & Hygiene Guidance
Proper cleaning and care of the affected area are crucial. Dr. Nargis Anshari provides instructions for maintaining hygiene to promote healing and prevent recurrence.
✅ Follow-Up and Recovery Monitoring
Regular follow-ups help monitor progress and ensure that the infection is completely cleared.
Why Choose Dr. Nargis Anshari for Skin Infection Treatment in Katni?
✅ Expertise in Dermatological Infections
✅ Advanced Treatment Techniques
✅ Affordable & Accessible Care
✅ Patient-Centric and Friendly Environment
✅ Use of Clinically Proven Medications
Prevention Tips by Dr. Nargis Anshari
Maintain personal hygiene.
Avoid sharing towels or personal items.
Clean wounds properly and cover them.
Avoid scratching or picking at skin infections.
Visit a doctor promptly if you notice unusual redness, swelling, or pus.
Book Your Appointment Today
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of a skin infection, don't wait for it to get worse. Visit Dr. Nargis Anshari for a safe, effective, and long-lasting solution.
📍 Location: DR NARGIS ANSARI, TIT COLONY, opp. BJP OFFICE, BARGAWAN, Katni, Madhya Pradesh 483501 📞 Contact: 09109577822
🌐 Website: https://www.drnargis.com/ 🕐 Clinic Timings: Monday to Sunday 10 am–9 pm
Healthy Skin is Happy Skin. Trust Dr. Nargis Anshari for Reliable Bacterial Skin Infection Treatment in Katni.
0 notes
Text
Best Skin Infection Clinic in Thrissur – Dr. Skin
Skin infections can be both uncomfortable and concerning, requiring professional medical attention to prevent complications. If you are searching for the best skin infection clinic in Thrissur, Dr. Skin is the go-to destination for expert dermatological care. With a team of skilled dermatologists, advanced diagnostic tools, and personalized treatment plans, Dr. Skin ensures comprehensive solutions for various skin infections.
Common Skin Infections Treated at Dr. Skin
At Dr. Skin, we specialize in diagnosing and treating a wide range of skin infections, including:
Bacterial Infections: Impetigo, cellulitis, and folliculitis
Fungal Infections: Ringworm, athlete’s foot, and candidiasis
Viral Infections: Herpes simplex, shingles, and warts
Parasitic Infections: Scabies and lice infestations
Each treatment is tailored based on the severity and type of infection, ensuring effective and long-lasting results.
Why Choose Dr. Skin for Skin Infections in Thrissur?
Expert Dermatologists: Our team has years of experience in treating various skin infections.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques: We use modern medical technology to accurately identify skin conditions.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Every patient receives customized treatment to suit their skin type and infection severity.
Safe and Hygienic Environment: Dr. Skin follows strict hygiene protocols to prevent cross-contamination.
Affordable Consultation & Treatment: High-quality dermatological care at cost-effective rates.
How to Identify a Skin Infection?
If you notice any of the following symptoms, you may need to visit a skin infection clinic in Thrissur:
Redness and inflammation
Itching or burning sensation
Pus-filled blisters or sores
Pain and tenderness in the affected area
Peeling or scaly skin
Early detection and timely treatment can prevent complications. Dr. Skin provides expert diagnosis and the right treatment for your condition.
Treatment Options at Dr. Skin
Depending on the type of skin infection, our dermatologists may recommend:
Topical Treatments: Creams, ointments, or gels
Oral Medications: Antibiotics, antifungals, or antivirals
Laser Therapy: Advanced treatments for persistent infections
Lifestyle and Hygiene Guidance: Preventive care to avoid recurring infections
Visit the Best Skin Infection Clinic in Thrissur Today!
Don’t let skin infections affect your quality of life. If you are looking for a trusted skin infection clinic in Thrissur, Dr. Skin is here to help. Book an appointment today for expert care and advanced treatment solutions.
To Know More: https://www.drskinclinics.com/best-skin-infection-clinic-in-thrissur-dr-skin/

0 notes
Text
How to prevent impetigo from spreading. https://dearkish.blogspot.com/2025/04/how-to-prevent-impetigo-from-spreading.html Impetigo is a common but preventable skin infection. Proper hygiene, timely diagnosis, and antibiotic treatment ensure swift recovery.
How to prevent impetigo from spreading.
0 notes
Text
Bacterial skin infection Dermatology & Reproduction Diseases (Zagazig University) Scan to open on Studocu Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 1 Bacterial skin infection Cutaneous infection - Direct infection of skin and adjacent tissues. - Impetigo. - Ecthyma. - Folliculitis. - Furunculosis. - Carbuncle. - cellulitis. - Secondary infection. - Eczema, infestations, scabies, pediculosis, ulcers, etc. - Cutaneous disease due to effect of bacterial toxin. - Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. - Toxic shock syndrome. Impetigo Definition: Impetigo is a common contagious superficial pyogenic infection of the skin. Two main clinical forms are recognized: - Non bullous impetigo (staphylococcus aureus, or by streptococci group A or by both organisms together). - Bullous impetigo (Staphylococcus aureus). Epidemiology: - Summer - Children are most often affected. - In adults, males predominate. - Poor hygiene and existing skin disease e.g., scabies, predispose to infection. Non bullous impetigo - the face especially around the nose and mouth and the limbs are the sites most commonly affected. - Erythematous macule thin-walled vesicle on an erythematous base pustule golden yellow crust erosion rapidly crusted again normal skin or slight hyper pigmentation. Impetigo contagiosum Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 2 Course and prognosis: - Itching is usually present in the vesicular stage and this helps the spread of the disease through autoinoculation. - usually runs an acute course and complete healing usually takes place in 5 to 10 days with no residual scar. Bullous Impetigo Clinical features: - The bullae are less rapidly ruptured and persist for 2-3 days. - Bullae are large. - After rupture thin crusts are formed. - Central healing and peripheral extension may give rise to circinate lesions. - Although the face is most often affected, the lesions may occur anywhere. - The buccal mucosa may be involved. Circinate impetigo Complications: - Eczematization. - Furunculosis, erysipelas and cellulitis. - post-streptococcal acute glomerulonephritis. the latent period for development of nephritis after streptococcal infection is 18-21 days. - Scarlet fever, urticaria and erythema multiforme may follow streptococcal impetigo. Treatment: 1- Removal of the crusts by: - Washing with soap and water. - Topical compresses with warm potassium permanganate solution 1/8000 is used. - Applying drying agent as gentian violet 1% in water. 2- Topical Antibiotic: - In mild and localized infection, a topical antibiotic alone may be sufficient. - Mupirocin ointment, Fusidic acid, Topical neomycin, Bacitracin. 3- Systemic Antibiotic: - The infection is widespread or severe. - Accompanied by lymphadenopathy. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 3 - There is reason to suspect a nephritogenic streptococcus. - An oral antibiotic such as flucloxacillin or erythromycin is indicated. Impetigo neonatorum - Its impetigo of the newborn and is a variety of bullous impetigo. - It usually begins between 4th and 10th day after birth, - it is highly contiguous and may be fatal. - Associated with constitutional symptoms as malaise and fever with extensive large bullae and the mm may be involved. - Diarrhea frequently occurs. - Bacteremia, pneumonia or meningitis may rapidly develop with fatal termination. - Isolation and treatment with IV antistaph. Ecthyma Definition: Is a Primary bacterial infection of the skin characterized by the formation of adherent crusts, beneath which ulceration occurs. - The disease may affect children and adults. - Poor hygiene and malnutrition are predisposing factors. Clinical features: - The crust is removed with difficulty to reveal a purulent irregular ulcer. - Healing occurs slowly leaving a slight scar. Treatment: - Improved hygiene and nutrition - The antibiotic chosen should be active against both strept and staph. Folliculitis - Infection of the hair follicles characterized by erythematous, follicular-based papules and pustules. May be superficial or deep. - In superficial folliculitis the inflammatory changes are confined to the ostium and healing occurs without scarring. - In deep folliculitis the inflammatory changes are more deep and healing occurs with scarring (furuncles, carbuncles, sycosis). Superficial bacterial folliculitis - An infection of the follicular osteum with staph aureus. - it is commonest in childhood and occur mainly in the scalp or scalp margins or on the limbs. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 4 - The individual lesion is a yellow pustule sometimes with a narrow red areola. Treatment: - Antibiotics topical or systemic may be required. Furuncles (Boil) - Deeper infections of the hair follicle characterized by inflammatory nodules with pustular drainage. - acute, usually necrotic infection of a hair follicle with staph aureus. - Common in adolescence and early adult life. - Tenderness and throbbing pain. - Heal with scar. Treatment: - Flucloxacillin systemically or another penicillinase resistant antibiotic. - Hot water compresses - A topical antibacterial agent reduces contamination of the surrounding skin. - occlusive dressings should be avoided. Carbuncle Etiology: - A carbuncle is a deep infection of a group of contiguous follicles with staph. aureus accompanied by intense inflammatory changes in the surrounding and underlying connective tissues. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 5 - They occur predominantly in men of middle or old age. Clinical features: - Painful, hard red swelling. - Pus is discharged from the multiple follicular orifices. - Constitutional symptoms may accompany or precede the development of the carbuncle. Treatment: - Flucloxacillin or another penicillinase resistant antibiotic should be given. - Surgical intervention may be needed. Cellulitis and erysipelas Bacterially: Cellulitis and erysipelas are predominantly streptococcal diseases. Definition: - Cellulitis is bacterial inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue. - Erysipelas is a bacterial infection of the dermis and upper subcutaneous tissue. - Erythema, heat, swelling and pain or tenderness are constant features. - In erysipelas the edge of the lesion is well demarcated and raised but in cellulitis it is diffuse. - In erysipelas blistering is common and there may be superficial hemorrhage into the blisters or in intact skin especially in elderly people. Complications: Without effective treatment, complications are common: fasciitis, myositis, subcutaneous abscesses, septiceamias and in some streptococcal cases nephritis. Treatment: - Penicillin is the treatment of choice and should be continued for 10 days. - In recurrent cases long-acting penicillin can prevent attacks. - In patients allergic to penicillin another drug commonly erythromycin should be taken. - Some patients may require lifelong prophylaxis. Erysipelas Cellulitis Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 6 Erythrasma Definition: Is a mild, localized superficial infection of the skin caused by gram positive rods Corynebacterium Minutissimum. Clinical features: - It occurs most commonly in the groins, axillae and the intergluteal and sub mammary flexures. - The patches are of irregular shape and sharply marginated, at first red but later becoming brown. D.D. of erythrasma: - Intertrigo: Frictional dermatitis. - Tinea cruris. - Pityriasis versicolor - Candidiasis. Fluorescence under wood’s light: Coral red fluorescence Treatment: - Topically applied azole antifungal agents such as clotrimazole and miconazole (although it is a bacterial infection), - local antibacterial preparations as fucidic acid. - erythromycin for 2 weeks is probably the most effective approach. Downloaded by James Mcknight ([email protected]) lOMoARcPSD|28323056 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Leading Child Specialist for Infectious Diseases in Udhampur: Expert Care for Your Little One
Introduction
Children are highly susceptible to infectious diseases due to their developing immune systems. Timely diagnosis, treatment, and prevention are essential to safeguarding their health. Finding a reliable Child Specialist Doctor for Infectious Diseases in Udhampur ensures that your child receives expert medical care to fight illnesses and maintain overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will help parents understand common infectious diseases, the role of pediatric specialists, and the best healthcare facilities in Udhampur for treating childhood infections.
Understanding Infectious Diseases in Children
Infectious diseases in children are caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These infections can range from mild to severe and, if not treated in time, may lead to complications. Some of the most common infectious diseases affecting children include:
Respiratory Infections: Pneumonia, bronchitis, and the flu.
Gastrointestinal Infections: Diarrhea, rotavirus, and food poisoning.
Skin Infections: Chickenpox, hand-foot-mouth disease, and impetigo.
Vaccine-Preventable Diseases: Measles, mumps, rubella, and diphtheria.
Parasitic Infections: Malaria and worm infestations.
Why Choose a Child Specialist Doctor for Infectious Diseases in Udhampur?
A Child Specialist Doctor for Infectious Diseases in Udhampur is a trained pediatrician who diagnoses and treats infectious diseases in children. Their expertise ensures:
Accurate Diagnosis: Identifying the root cause of infections.
Targeted Treatment: Prescribing the right medications and therapies.
Preventive Care: Offering vaccinations and hygiene advice.
Management of Chronic Infections: Providing long-term treatment for recurring illnesses.
Symptoms Parents Should Watch For
Early detection of infections is crucial for effective treatment. Parents should seek medical attention if their child experiences:
High fever lasting more than three days.
Persistent cough or breathing difficulties.
Vomiting, diarrhea, or dehydration.
Skin rashes, blisters, or swelling.
Fatigue, weakness, or loss of appetite.
The Role of Pediatric Infectious Disease Specialists
Pediatric infectious disease specialists offer a range of services to treat and prevent infections, including:
1. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation
A thorough check-up is conducted to identify the infection type and its severity.
2. Laboratory Testing & Diagnosis
Blood tests, urine tests, throat swabs, and imaging studies are used for precise diagnosis.
3. Tailored Treatment Plans
Based on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, antivirals, or supportive therapies.
4. Vaccination & Preventive Measures
Vaccines are essential for preventing serious infections like measles, polio, and hepatitis.
5. Parental Guidance & Education
Doctors educate parents on hygiene practices, proper nutrition, and infection control.
Top Healthcare Centers for Pediatric Infectious Diseases in Udhampur
Parents in Udhampur looking for expert pediatric care can visit:
Government Hospitals & Health Clinics: Provide cost-effective treatment and vaccinations.
Private Pediatric Clinics: Offer specialized consultations and advanced diagnostic facilities.
Multi-Specialty Hospitals: Equipped with pediatric ICUs and expert infectious disease specialists.
Preventing Infectious Diseases in Children
Parents can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of infections in their children:
Ensure complete immunization as per the vaccination schedule.
Encourage frequent handwashing to prevent germ spread.
Maintain proper hygiene at home and in schools.
Provide a nutrient-rich diet to strengthen the immune system.
Avoid exposure to crowded places during flu outbreaks.
Conclusion
A trusted Child Specialist Doctor Udhampur plays a crucial role in protecting children from severe infections. By staying informed about symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and following preventive healthcare measures, parents can ensure their child's well-being. If your child shows signs of an infection, consult a pediatric specialist immediately to receive expert care and treatment. A healthy child leads to a brighter future—take proactive steps today!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Sultamicillin 375 mg

Aingo Pharma’s Sulswit – 375 Tablets, powered by Sultamicillin 375 mg, deliver reliable treatment for respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and gynecological infections, ensuring rapid relief and trusted results.
What is Sultamicillin 375 mg Used For?
Sultamicillin 375 mg is indicated for the treatment of various bacterial infections, including:
Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Such as sinusitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Including cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: Such as cellulitis, impetigo, and abscesses.
Gynecological Infections: Including pelvic inflammatory disease.
Intra-abdominal Infections: Such as peritonitis.
Gonococcal Infections: Uncomplicated gonorrhea.
Dosage Guidelines
Standard Dosage Recommendations
The typical adult dosage is 375 mg taken orally twice daily for 5 to 14 days, depending on the severity and type of infection. In the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea, a single oral dose of 2.25 g (six 375 mg tablets) may be administered.
Administration Tips
With or Without Food: Sultamicillin can be taken with or without food. Taking it after meals may reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
Consistent Timing: Administer doses at evenly spaced intervals to maintain effective drug levels in the body.
Complete the Course: Even if symptoms improve, continue the medication for the full prescribed duration to prevent the recurrence of infection.
Potential Side Effects
While Sultamicillin 375 mg is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects, including:
Common Side Effects:
Nausea
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain
Skin rash or itching
Serious Side Effects: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Severe allergic reactions (hives, difficulty breathing, swelling)
Liver problems (yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine)
Severe diarrhea or abdominal cramps
Precautions and Warnings
Allergies: Inform your doctor if you have a known allergy to penicillin or beta-lactam antibiotics.
Medical History: Disclose any history of liver or kidney disease, mononucleosis, or gastrointestinal diseases.
Drug Interactions: Sultamicillin may interact with other medications, such as allopurinol, probenecid, oral contraceptives, and anticoagulants. Provide a complete list of your current medications to your healthcare provider.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Consult your doctor before using Sultamicillin if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Storage Instructions
Temperature: Store at room temperature, away from moisture and heat.
Keep Out of Reach: Ensure the medication is stored out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
0 notes
Text
Skin problems in children can be concerning for parents. From rashes and allergies to infections and eczema, a child’s delicate skin requires specialized care. If you are looking for a trusted child skin specialist in Ranchi, Prakash Skin Clinic offers expert pediatric dermatology services to ensure your child’s skin remains healthy.
Why Choose Prakash Skin Clinic?
Prakash Skin Clinic is a well-known dermatology center in Ranchi, providing advanced skin treatments for children. The clinic is led by experienced dermatologists who specialize in diagnosing and treating a wide range of pediatric skin conditions with a gentle and effective approach.
Common Skin Conditions Treated at Prakash Skin Clinic
Eczema & Atopic Dermatitis – Red, itchy, and dry skin conditions that require long-term care.
Diaper Rash – Common in infants, requiring specialized creams and preventive care.
Skin Allergies & Rashes – Identifying allergens and providing treatment to soothe irritation.
Fungal & Bacterial Infections – Conditions such as ringworm, impetigo, and scabies.
Vitiligo & Pigmentation Disorders – Helping manage uneven skin tone and white patches.
Acne & Teenage Skin Issues – Treating breakouts, blackheads, and oily skin in adolescents.
Birthmarks & Moles – Expert evaluation and removal if necessary.
Child-Friendly Approach
At Prakash Skin Clinic, the doctors ensure a comfortable and stress-free experience for children. The team understands that kids may feel anxious during doctor visits, so they use a warm and reassuring approach to put them at ease. Parents are also given guidance on proper skincare routines to prevent common skin issues.
Advanced Diagnosis & Treatment
The clinic is equipped with modern dermatological tools for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Whether it's a simple rash or a chronic skin condition, the specialists provide customized care plans based on each child’s skin type and sensitivity.
READ MORE....Best Dermatologist in Ranchi Skin Doctor in Ranchi Prakash Skin Clinic
0 notes
Text
Skin Infections in Children: How to Recognize and Treat Them Fast?
Skin infections in children are common and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. While some infections are mild and resolve on their own, others require medical attention to prevent complications.
As a parent, recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment is essential for your child’s health and comfort.
Common Skin Infections in Children and Their Symptoms
Impetigo - Impetigo is one of the most common bacterial skin infections in children, caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria.
It appears as red sores or blisters, usually around the mouth and nose, which eventually burst and form honey-coloured crusts.
The sores can be itchy and mildly painful, making it essential to treat them quickly to prevent spreading.
Ringworm (Tinea) – Ringworm is a fungal infection that appears as circular, scaly patches with a red, raised border. It’s highly contagious and can affect different parts of the body, including the scalp, body, and feet (athlete’s foot).
The infection often causes itching, discomfort, and inflammation, making early detection crucial for effective treatment.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) – HFMD is a viral infection caused by the Coxsackievirus, which results in painful red spots or blisters on the hands, feet, and inside the mouth.
It is often accompanied by fever, sore throat, and loss of appetite. While it usually resolves on its own, managing symptoms is key to keeping your child comfortable.
Eczema with Secondary Infection – Eczema happens when bacteria or viruses infect already damaged, eczema-affected skin.
This can lead to worsening redness, swelling, oozing fluid or pus, and increased itching or tenderness. It’s important to address both the underlying eczema and the infection to ensure quick healing.
Scabies – Scabies is a parasitic skin condition caused by tiny mites (Sarcoptes scabiei) that burrow under the skin, leading to intense itching — especially at night.
It presents as tiny red bumps or burrows, commonly found between the fingers, on the wrists, or around the waist. Since scabies spreads through close contact, fast treatment is essential to avoid spreading it to other family members.
How to Treat Skin Infections in Children Quickly?
Proper hygiene and care play a significant role in both preventing and managing skin infections. Ensuring your child washes their hands regularly, uses mild soap, and keeps their nails short can help prevent bacteria and fungi from spreading.
Cleanliness is particularly important if your child has a minor cut or scrape, as broken skin is more vulnerable to infections.
Topical and oral medications are often necessary for more severe infections. Bacterial infections like impetigo typically require antibiotic creams, while fungal infections like ringworm respond well to antifungal ointments or oral medications in stubborn cases.
For viral infections such as HFMD, antiviral medications may be recommended if the symptoms are severe. In cases of intense itching, antihistamines and soothing lotions can provide much-needed relief — especially for conditions like scabies or eczema flare-ups.
Home remedies for relief can help ease discomfort while the infection heals. Cool compresses, oatmeal baths, and keeping the affected area dry and clean are effective ways to reduce inflammation and itching.
However, home remedies should only complement medical treatment, not replace it — especially for more severe infections.
When to see a doctor is a crucial consideration if the infection worsens or doesn’t improve with home care. If the affected area becomes increasingly red, swollen, or filled with pus, or if your child develops a fever or feels unwell, it’s time to seek professional help.
Skin infections that spread quickly or cause significant discomfort should be evaluated by a specialist to prevent complications.
How Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic Can Help?
Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic offers comprehensive care for children suffering from skin infections. The clinic provides accurate diagnoses through thorough examinations and, if needed, lab tests to identify the root cause of the infection.
Every child is unique, and Dr. Hera creates personalized treatment plans using the most effective medications — whether they’re antibiotics, antifungals, or antivirals — to ensure fast recovery.
Additionally, the clinic offers expert advice on skincare routines and hygiene practices to prevent recurring infections.
For more severe cases, advanced dermatological treatments are available to manage complications and ensure your child’s skin heals properly.
If you’re searching for a reliable dermatologist in Roorkee, Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic is the go-to place for compassionate, expert care tailored to your child’s needs.
Conclusion
Skin infections in children can be distressing, but recognizing the symptoms early and getting the right treatment ensures faster recovery and prevents complications.
Knowing how to manage common infections like impetigo, ringworm, HFMD, eczema, and scabies helps parents stay prepared.
However, when infections worsen or don’t improve with home remedies, professional care is essential. Dr. Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic offers specialized treatment and support to help children recover quickly and comfortably.
If you’re looking for an experienced dermatologist in Roorkee, Dr. Hera’s expertise ensures that your child receives the best possible care for their skin health.
Dr Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic
Address: Dr Hera’s Skin & Hair Clinic, near Bank of India, Malviya chowk, Roorkee, Uttarakhand 247667
Phone No. +91 7060854824
Email: [email protected]
Timings: 10:00 AM TO 09:00 PM
Google Map Location Listing – https://maps.app.goo.gl/fU9hHkAERnoTwRfh9
0 notes
Text
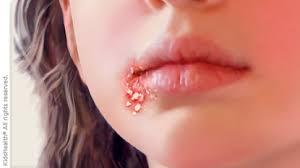
Impetigo vs. Cold Sores: Understanding the Differences
By Dr. Nasar Abdul Wadood, Chief Doctor at Align Dental Care

Impetigo and cold sores are common yet distinct skin conditions that often cause blisters near the mouth. However, their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ significantly. This guide breaks down the key differences between impetigo and cold sores, helping you identify them accurately and take appropriate action.
Impetigo vs. Cold Sores: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Feature
Impetigo
Cold Sores
Cause
Bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes)
Virus (Herpes Simplex Virus, usually HSV-1)
Appearance
Red sores that burst, leaving a yellowish crust
Fluid-filled blisters that scab over
Location
Often around the nose, mouth, hands, and legs
Primarily on the lips and around the mouth
Symptoms
Mild itching and discomfort, possible swelling
Tingling or burning sensation followed by painful blisters
Contagion
Spread through direct contact or shared items
Transmitted via saliva, blisters, or direct skin contact
Treatment
Antibiotics (topical or oral)
Antiviral creams or medications
Duration
Resolves in 7–10 days with treatment
Clears up in 7–14 days but may recur
Reoccurrence
Rare once treated
Frequent due to virus dormancy
At-Risk Groups
Mostly children, individuals with skin injuries
Anyone exposed, often triggered by stress or illness
Prevention
Maintain hygiene, and treat wounds promptly
Avoid direct contact, use lip sunscreen
What Is Impetigo?

Impetigo is a bacterial skin infection, primarily affecting children. It occurs when bacteria enter the skin through minor cuts, insect bites, or abrasions. The condition is caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Symptoms of Impetigo
Red sores or blisters, typically around the nose, mouth, hands, or legs.
Sores burst, forming a yellowish or honey-colored crust.
Mild itching and discomfort.
In some cases, swollen lymph nodes near the infection site.
How Does Impetigo Spread?
Impetigo is highly contagious and spreads through:
Direct contact with infected skin.
Sharing towels, clothing, or personal items.
Touching contaminated surfaces.
Who Is at Risk?
Children aged 2–6 years.
Individuals with weakened immune systems.
People in crowded or humid environments.
What Are Cold Sores?

Cold sores, or fever blisters, are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). Unlike impetigo, they are viral infections that tend to recur throughout life.
Symptoms of Cold Sores
Small, fluid-filled blisters, often on or around the lips.
Tingling or burning sensation before the blisters appear.
Pain and discomfort around the affected area.
Blisters eventually burst and scab over before healing.
How Do Cold Sores Spread?
Cold sores are also highly contagious and can spread through:
Kissing or direct skin contact.
Sharing utensils, lip balms, or drinks.
Touching the sores and then touching other parts of the body or people.
Who Is at Risk?
Anyone exposed to HSV-1 can develop cold sores. Common triggers include:
Stress
Illness or fever
Sun exposure
Hormonal changes (e.g., menstruation)
Causes: Impetigo vs. Cold Sores
What Causes Impetigo?
Impetigo is a bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It often develops through skin injuries, such as cuts, scrapes, or insect bites. Poor hygiene and crowded environments increase the risk of infection.
What Causes Cold Sores?
Cold sores result from the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). Once contracted, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate due to stress, illness, or a weakened immune system. Unlike impetigo, which is bacterial, cold sores are viral and require different treatments.
Appearance: Impetigo vs. Cold Sores
What Does Impetigo Look Like?
Red sores that burst and leave a yellowish crust.
Often moist or wet in appearance.
Commonly found around the nose, mouth, hands, or legs.
What Do Cold Sores Look Like?
Begin with a tingling or burning sensation.
Small, fluid-filled blisters form and eventually burst.
The area scabs over before healing.
Typically found on or around the lips.
Contagion: How Do They Spread?
Is Impetigo Contagious?
Yes, impetigo spreads through direct contact with infected skin, shared items like towels or clothing, and contaminated surfaces.
Is Cold Sore Contagious?
Yes, cold sores are transmitted through saliva, kissing, sharing utensils, and even when no visible sores are present.
Treatment: Impetigo vs. Cold Sores
How to Treat Impetigo
Topical or oral antibiotics are prescribed to kill bacteria.
Keeping the affected area clean and dry aids recovery.
Avoid scratching to prevent spreading.
How to Treat Cold Sores
Antiviral medications (e.g., acyclovir) help speed healing.
Over-the-counter creams can relieve discomfort.
Keeping lips moisturized and protected from sunlight reduces outbreaks.
Duration: How Long Do They Last?
Impetigo
Clears up within 7–10 days with treatment.
Rarely recurs unless reinfected.
Cold Sores
Heals in 7–14 days but may recur frequently due to viral dormancy.
Can Children Get Both Impetigo and Cold Sores?
Yes, children can develop both conditions under different circumstances:
Impetigo is common in young children due to frequent skin injuries and exposure in schools or daycare.
Cold sores occur if a child contracts HSV-1 through close contact with an infected person.
Prevention Tips
Preventing Impetigo
Maintain proper hygiene.
Treat cuts and wounds promptly.
Avoid sharing personal items.
Wash hands regularly.
Preventing Cold Sores
Avoid direct contact with infected individuals.
Do not share utensils, lip balms, or drinks.
Use sunscreen on lips to prevent sun-triggered outbreaks.
Manage stress to prevent viral reactivation.
When to See a Doctor
For Impetigo
If sores do not improve within a few days of treatment.
If new sores continue appearing.
For Cold Sores
If outbreaks are frequent or severe.
If sores do not heal within two weeks.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between impetigo and cold sores can help you take the right preventive and treatment measures. While impetigo is a bacterial infection requiring antibiotics, cold sores stem from a virus and often recur due to stress or other triggers. Proper hygiene and early treatment are key to managing both conditions effectively.
To know in detail, visit: https://www.aligndentalcare.lk/difference-between-impetigo-vs-cold-sores/
1 note
·
View note