#illustrated incunabulum
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

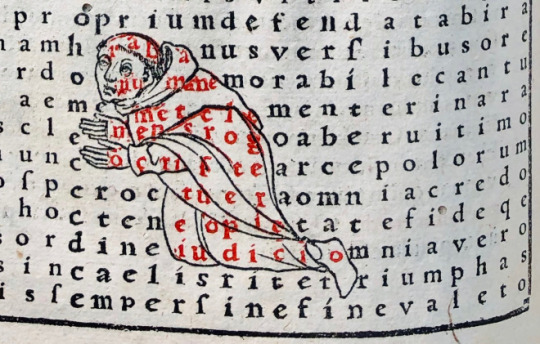
This incunabule (incunabulum) which was printed in Cologne in c. 1477, belonged to the collection of Robert Ashley (1565-1641). It is a biographical compendium of Church fathers and a history of the early Church. The printed initials are illustrated by hand with these comical figures. This mimics the way manuscripts were produced, a practice that continued beyond the advent of printing in circa 1450.
#library#law library#mtlibrary#inns of court#history#rare books#libraries#books & libraries#london#rarebook#incunabula#church history#drolleries#robert ashley
28 notes
·
View notes
Text






Book 558
Chronicle of the World: The Complete and Annotated Nuremberg Chronicle of 1493
Hartmann Schedel
Taschen 2001
It’s unclear when Schedel actually began work on the Nuremberg Chronicle, but it was completed in 1493. Schedel, a scholar, humanist, doctor, and book collector (an inventory of his library from 1498 listed an astonishing 370 manuscripts and 670 printed books), wrote the Chronicle in Latin as the Liber Chronicarum ("Book of Chronicles"). (Although it should be mentioned that some scholars estimate that only 10% of it is original writing and that 90% of the book is plagiarized from other sources.) An early example of a printed book, or incunabulum, the Chronicle is a philosophical and historical encyclopedia of the history of the world in relation to the Bible, including histories of important Christian and secular cities from antiquity. A gorgeous early example of the synthesis of illustrations and the printed word, this Taschen facsimile edition is a stunning book. Covered in a suede-like material and at a substantial size, it is a reprint of a copy held by the Stiftung Weimarer Klassik.
Interestingly, the prestige and success of the Chronicle led to one of the first large-scale pirated editions, which first appeared in Augsburg starting in 1496.
#bookshelf#personal collection#personal library#books#library#bibliophile#book lover#illustrated book#booklr#chronicle of the world#Nuremberg chronicle#Hartmann Schedel#taschen#renaissance art#history
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wk 16, 25th of May, 2024 Research Herbals, how plants have been seen

Lilium Lily, Early printed herbal, Herbier du XVe siècle (1486)

From the text: INCIPIT HERBARIUM APULEI PLATONICI AD MARCUM AGRIPPAM by THE BOTANICAL ILLUSTRATION from Library of the Botanical Garden of the University of Padova...
Incunabulum is the text of an author of the fourth century AD known as Pseudo Apuleius, printed in Rome between 1481 and 1484 (or perhaps a few years earlier, Pier Andrea Saccardo, for example, dates it to 1479) by the publisher Giovanni Filippo de Lignamine.
The text is accompanied by very simplified and schematic xylographic images, to the point that, for the most part, the plants represented are unrecognisable if not thanks to the names listed above.

The illustrations are followed by the list of the different names by which the plant is known among the different peoples and data relating to its therapeutic and medicinal uses.
There are animals in many depictions, linked to the medicinal properties of the plant represented: if, for example, the image includes a snake, the plant is useful against snake bites. An exception is the mandrake, depicted with human features and tied to a leash of a dog, which in this case refers to the legend on how to collect it.
In the copy found in the Library of the Botanical Garden, the black and white prints have been lightly coloured with red and yellow pencils.

From the text: BRIEF HISTORY OF ILLUSTRATED HERBALS by THE BOTANICAL ILLUSTRATION from Library of the Botanical Garden of the University of Padova...
For the period from classical antiquity to the late Renaissance, illustrated botanical texts fall into the category of "herbals", while for the following period it is more correct to speak of "flora", "florilegia" and scientific texts on botany.
The herbal can be defined as "a book, used in classical antiquity until the last decades of the fifteenth century, which collects descriptions of plants and their pharmacological virtues, often accompanied by the names by which each plant essence was known in various languages and information on their habitats [...] the text also was soon well provided with depictions [... and] especially from the eleventh century, the images of the plants were often associated with human figures, with the explicit aim of more clearly illustrating the medicinal virtues or to exemplify specific harvesting methods" (from the Treccani Encyclopedia of Medieval Art).
With regards to flora we refer technically to the composite of plants and plant species that live in certain geographic areas, but the term also includes the texts, often illustrated, that describe these plants. The scientific texts on botany, however, examine the plants from only a scientific point of view, analysing distinguishing characteristics, component parts, habitat, life, evolution, mutual differences and similarities...
The term anthology (florilegium), although rarely used with this meaning in the Italian language, refers to a collection of images of plants and flowers, a work dedicated to the plants more from an aesthetic, rather than practical, point of view.
It is difficult, especially for the oldest periods, to define a clear boundary between herbal, flora and anthology.
In Latin times, they had in all probability to circulate illustrated herbals that included images made from copies of previous versions, increasingly less realistic and detailed.
Pliny the Elder argued in his Naturalis Historia that often it was not in any way possible to recognise plants from such images, sustaining to a certain degree the futility of botanical representations (Nat. Hist., XXV, 4-8).
During the Middle Ages, botanical illustrations continued to be based on ancient models through copies and copies of copies gradually less and less true to the original, partly also due to a new mentality which focused attention more on the ideal rather than on reality: even the plants are to some extent idealised, schematised, or reduced to the essence or enriched with imaginative details or related to (real or alleged) therapeutic properties of plants rather than to their actual appearance.
The study of botany is essentially the study of the classical authors, of what was said by Dioscorides, Pliny, Theophrastus ... whose knowledge and beliefs are not challenged, but continue to be passed down in a mixture of science and magic, where the power of the voice of the "greats" of the past is stronger than critical thinking and real life.
One example is the depiction of the mandrake, a toxic plant of the Solanaceae family that actually exists, to which magical powers were attributed. The particular shape of the root, which vaguely resembles a human being, had fuelled numerous legends associated with this plant, in particular its power to kill anyone who dared to harvest it with a piercing scream. In order to harvest the plant, it was therefore advised to tie the base to a leash of a dog that, set free, would run and tear out the plant and die from the cries while making it possible for his master to take it. Despite the fact that simply observing the plant would suffice to understand that this was a legend, the evocative power of popular belief and texts from the past was such that in many medieval texts the mandrake is depicted with anthropomorphic features and tied to the leash of a dog (see below).

During the seventeenth century, botany began to establish itself as an autonomous science and not simply as a branch of medical science: all aspects of plants begin to be studied and their distinctive characteristics, also independent of the pharmacological properties, are investigated.
Volumes from this period, therefore, begin to include more pictures which tended to illustrate the anatomy of plants, with details of the flowers, seeds and fruits, and representations of the undersides of leaves and flowers. The great attention to detail is aided by the increasing use of xylography (engraving of images on metal plates), which replaces chalcography (engraving on wooden slabs) and which allows an even greater degree of detail.

In particular, the publication of texts by Brunfels and Fuchs marks the moment when botany begins to focus on observation of the natural world in an innovative approach, stripping away imaginative interpretations and basing itself on real observation, while the Mattioli text represents an admirable example of revision of the classical authors.
0 notes
Photo

I need to find more examples of woodcut illustrations from the Nuremberg Chronicle, as I just love, love, love them.
Info from the Otis College of Art and Design, Los Angeles:
In 1493 the most elaborately illustrated book then printed in Europe, the Liber Chronicarum or Weltchronik appeared in print. This major work, by the Nuremberg doctor Hartmann Schedel, generally known as the Nuremberg Chronicle was printed by the foremost printer of the day in Nuremberg, Anton Koberger. It is a history of the world from the Creation to his own day and is remarkable for its illustrations, its graphic design and for its woodcuts and description of cities. The woodcut illustrations include events from the Bible, pictures of human monstrosities, portraits of Kings, Queens, saints and martyrs, and allegorical pictures of miracles. The maps and views, are all by or after the celebrated artists Michael Wohlgemut or Wilhelm Pleydenwurff, and are amongst the earliest printed representations of towns and cities available to us today.
Info from the Special Collections & Archives Research Center, Oregon State University:
Written first in Latin by Hartmann Schedel, and tranlated into German six months later, this work was a history of the world from the Creation to 1493. By actual count the Chronicle contains 1,809 Woodcuts. Many of the cuts were used over and over again to depict different personages and cities so that there are really only 645 separate subjects. The artists who so successfully completed this amazing number of woodcuts were Wohlgemuth and his step-son, Pleydenwurff. The book was financed by various citizens of Nuremberg who wished to show what a superb work could be achieved by their master printer, Anton Koberger. The charm of the Nuremberg Chronicle lies in the fact that it gives an actual glimpse into the daily life of the people of this city five centuries ago. This was done unconsciously as far as the artists were concerned; at that period people conceived great personages of the past as dressing as they did themselves and living under conditions similar to their own. At the time the book was published, potential purchasers were informed that the work could be obtained "unbound and uncolored for two Rhenish florins; bound and colored for six." Needless to say, most buyers chose the less expensive form, and today one seldom encounters colored copies.
Additional info about ‘incunabulum’ and the history of printing from Wikipedia.
Further examples of illustrations here.
0 notes
Text
Only a day or two ago I was notified that I was in contact with some people tested for and found positive for Covid-19, this came as nothing un expected, I was in contact with hundreds of people many from Europe recently. Then, as you know we are experiencing, most Universities, Libraries and Book Shows have been indefinitely closed, and because of this; many of us find or try lively-hood’s challenged. In a situation where it seems that there is little to do that will improve the current situation any faster than time will take its course, I have turned to reading and writing. I have been researching, as best as I can from home, fifteen books which are new to my stock. There are many more stuck in Europe and this gives me hope. It is the first day of spring and I awoke to a beautiful snow squall… In like a Lion..
And here are the fruits…

1). 355J Bible Saint Jerome, Gabriello Bruno (active 1480-1514.)
Biblia cum summariis concordantiis : diuisionibus: quattuor repertoriis p[ro]positis: numeriq[ue] foliorum distinctione: terse et fidelit[er] imp[re]ssa. { With table of Gabriel Brunus }
[Lyons]: Jean Pivard, 29 Jan. 1500 & 1. $ 15,000.

Impresserunt aute[m] solertes viri Franciscus Fradin et Ioha[n]nes Piuard socij impressores. …,]
Folio inches, &8 ç8 , a8 b6, c-z8 A-Z8 Aa8 Bb8; aa-cc8 dd10. Bound in original full calf over wooden boards with 10 brass bosses.
This edition corresponds with the edition printed by Fradin and Pivard in 1497. There are the same tables, summaries, &c.; and the arrangement of the books and the readings are alike. At the end of the subscription we read: “Impressit autem solers ori Johänes Pivard impressor. Deo sint sempiterne gratie.”
Pivard,who was working alone from 7 March 1498 to 1501, Started printing with François Fradin in 1497 (Goff B602) ISTC lists15 titles solely printed by Privard.
Goff B604; HC 3128; GfT 1883, 1884; Pell 2341; CIBN B-426; Arnoult 288; Girard 108; Parguez 213; Polain(B) 4210; IBE 1040; SI 764; Martín Abad B-134; Sallander 2098; Bod-inc B-312; Sheppard 6736; Pr 8670; GW 4281. (Gutenberg-Jahrbuch 1965 p140-3)

Copinger, Incunabula Biblica, 120; Darlow–Moule 6090; Sheppard 6736.
U.S. copies: Boston Public Library, General Theological Seminary, Jewish Theological Seminary of America, Library of Congress, Rare Book Division, Southern Methodist Univ., Bridwell Library (418 ff)

https://data.cerl.org/istc/ib00604000
◊
◊ ◊
◊
2) 353J Alberto da Castello (ca. 1460-1522)
Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria : con lle sttattiionii & iindullgenttiie delllle chiiese di Roma perr tutto L’’anno.
In Venetia : Presso la compagnia de gli Vniti,1585. $7,800

Octavo. 6 x 3 3/4. A-Z, Aa-Ii8. A later edition of the first ‘Rosary Book” in Italian.
This book has a wonderful contemporary binding, recently expertly rebacked. It is of red Morocco with gilt center images and borders gilt, with angels. Certainly these books were

very popular, that said, very few copies have survived. This edition is represented on OCLC by only two copies worldwide. 1 US copy Saint Benedict/Saint John’s University. (SJU Alcuin Arca Artium Rare BookBX2163 .C37 1585). [The authorship of the work and the woodcuts are attributable to the Dominican Friar Alberto da Castello, identified as author or editor at the authorizations of the Venecian Inquisition, given 5 April 1521. (Francesco Pisano)]

Over 150 woodcuts (including repeats) comprising almost full-page cuts (1 on t.p.) within borders. All had previously appeared in earlier editions. Ornamental and pictorial border pieces on almost every leaf. ( The wood cut on leaf 173v is upside down in the border!) Each wood cuts represent the “Mysteries of the Rosary”
“From the beginning, publications on the Rosary came accompanied by lavish xilographic illustrations. The most striking of these can be found in the edition of the Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria by Alberto da Castello from 1521 [Fig. 14.1], which contains a wealth of illustrations. This clearly shows that the Rosary was not just an oral recitation, but was also a contemplative prayer engaging the imagination, a combination later mirrored by the exercises of Ignatius of Loyola.
Alberto da Castello, born in the middle of the fifteenth century in Venice, joined the Dominican order around 1470 and wrote several devotional, liturgical, historical and canonical texts. In the Epistola prohemiale of his Rosario della gloriosa Vergine Maria he says that he wrote the meditations and organised the images ‘acciò che gli idioti che non sanno legere habbino el modo de contemplare gli divini beneficii et de questa contemplatione ne habbino qualche frutto spirituale’.( fol. 6r. ‘So that even the illiterate have a means to contemplate gifts of the divine and to receive spiritual fruits from such contemplation’ (translations are mine).He states that he writes especially for the ‘ignoranti, illetterati, idioti’, and that a good Christian must hold the mysteries of the Rosary deep in his heart. (Literary and Visual Forms of a Domestic Devotion: The Rosary in Renaissance Italy. Erminia Ardissino)

The mysteries of the rosary were introduced by Dominic of Prussia sometime between 1410 and 1439. This gave each decade of the rosary a unique quality. Each mystery leads us to ponder very specific events in the lives of Jesus and Mary and the lessons they hold for our own lives today.
The Rosary has a ritual aspect that individual prayers lack, and it is highly structured. It entails the recitation of 150 Ave Marias, clustered in groups of ten, preceded by a Pater noster and the proposition of a ‘mystery’ upon which to meditate. This number of 150

Ave Marias seems to be designed to correspond to the 150 psalms in the Davidic psalter, which is why the Rosary is also known as the ‘Virgin’s psalter’. It does not consist only of repetitive prayers, however, but also entails meditations. Indeed, the Rosary created by Dominic of Prussia was a kind of meditation on the life of Christ and Mary. In his Liber experientiarum he ‘explicitly claimed to be the first to have composed a series of fifty points on the life of Christ that were to be meditated on while reciting the Ave Marias’.
Sander 6572-6573. See: Essling 2124
)0(
100 full page plates and a volvelle!
3) 382J Jan David. 1545?-1613.
Veridicus christianus: auctore P. Joanne David … Editio altera, auctior.
Antverpiæ ex officina Plantiniana, M. DCVI. $6,500
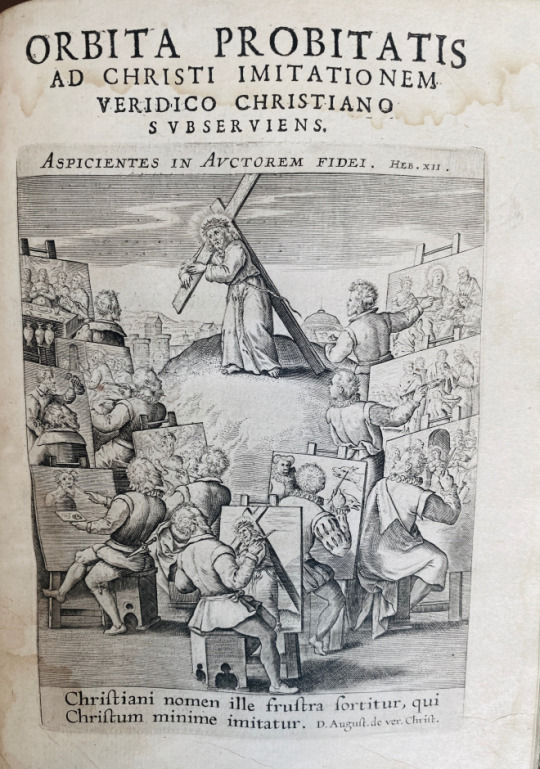

Quarto 8 1/2 X 6 inches ‡4, ‡‡4, A-Z4, a-z4, Aa-Ee4.+ 100 Numbered Plates. Withspecial engraved t.p. with allegorical depiction of Christ carrying the cross, surrounded by ten artists at easels painting scenes from his life (as well as a few questionable profane subjects).

The text is divided into 100 chapters, each with an allegorical engraving incorporating letters keyed to the explanatory text and with marginal references. Each of the 100 numbered plates has a single line of Latin at the head giving the subject, with two-line explanatory verses below the allegorical engraving in Latin (roman letter), Dutch (civilité) and French (italic) First plate (following [2 daggers]4) is added title leaf for the ill., which were also published separately; see Bibliotheca Belgica. The added title reads: Icones ad Veridicvm Christianvm P. Ioannis David e Societate Iesv At the end is Device with compasses and the motto “constantia et labore” on Ee4r . This book is notoriously found defective in one way or another, this copy is perfect and complete.

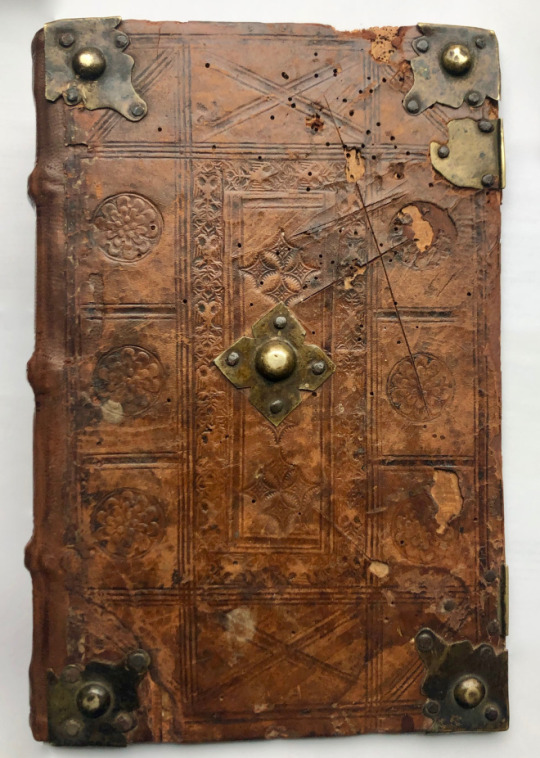
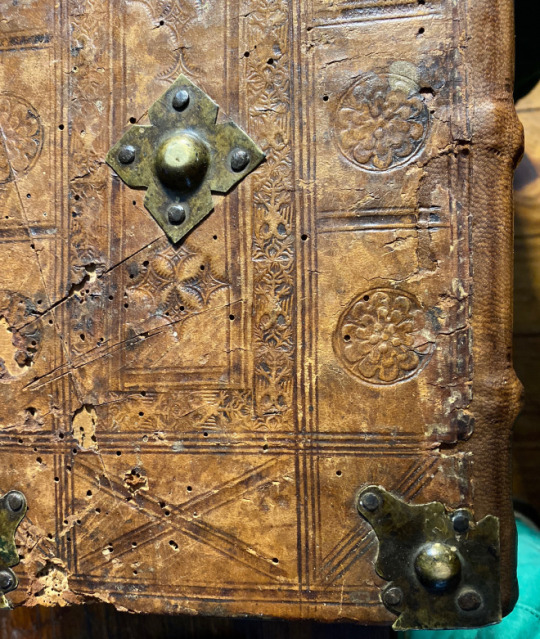
This copy is bound in full contemporary blind stamped calf over wooden boards with two working clasps.
The Veridicus christianus: is followed by the “Orbita probitatis ad Christi imitationem veridico Christano subserviens”: p. 351-374; which preceds a volvelle plate for use in locating specific passages.
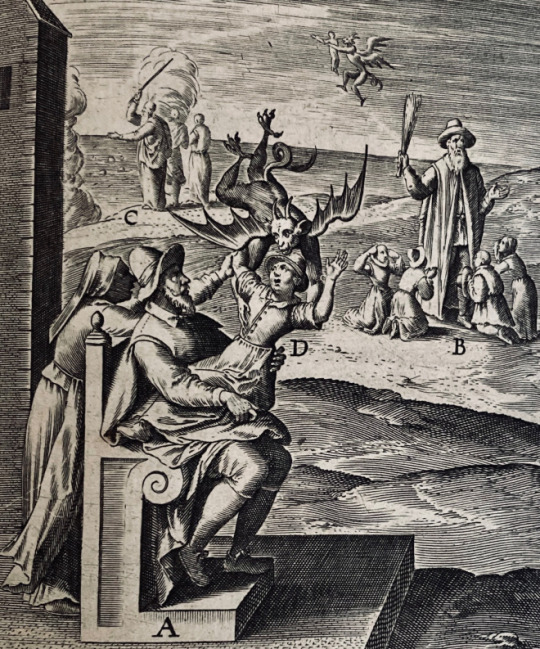

This text contains a series of images with accessible (sometimes to a fault) moral or religious messages. These illustration swarns against opening the senses to temptation lest death and moral decay take up residence in one’s soul.
The Veridicus Christianus emphasizes the Society of Jesus’ investment in thinking in, though, and about visual images that exemplify the supreme mystery of God. Published as a tool of devotion and meditations, it features one hundred chapters that encompass a wide range of topics for reflection. Each chapter incorporates an extensive commentary that interprets the emblematic image David too follows the order in which we apprehend things with our senses, beginning with a visual representation at the head of each chapter. Then comes the explication. The symboli explicatio was considered necessary because cultivated readers would be more susceptible to a reasoned argument than a picture.
Here are images of the vovell. The centers of the engraving and the volvelle (through which a string passes) are reinforced with small paper roundels printed with the monograms of Christ. The numbers are keyed to an “Indiculus orbitae” that follows (Bb1r-Bb2r). There a number, having been selected, is provided with a phrase from various Latin authors (listed on Bb2v), and a reference to one of the hundred sections that comprise the main text. It is suggested in Bibliotheca Belgica that this game may have been intended as a pious alternative to such superstitious books as Thuys der fortvnen.
)0(
4) 312J. Domenico Cavalca. (1270?-1342)
Pungi lingua
[Baptista de Tortis]: Venexia, Adi .viiii. de Octubrio. 1494 $12,000

Quarto (200 x 145 mm); [80] pages. a-k8. Large woodcut depicting the crucifixion on the frontispiece, First Venetian edition with the beautiful woodblock published here for the first time. This copy has a beautiful initial “A” in gold, blue, red and green, a colorful coat of arms. This copy is bound in modern carta rustic with a gold title on an orange label

This is a treatise on the dangers of the misuse of the language it was, as you might expect quite popular . Written by the Dominican monk who was a contemporary of Dante and among the first to write in the vernacular, and one of the most successful translators of holy texts.
Aside from Biblical illustrations, the Pungilingua has many exempla drawn from many other sources including some not includes in the Alphabetum narratinum. Most of the stories are told in one to three lines, and many contain commerce with the Devil, one time disguised as a horse. In the prologue Cavalca mentions that he gathered his exempla from many sources “alcune poche cose” . One of the major sources is the Summa Vitiorum by Peraldus. but he also quite a few profane authors , Seneca, Socrates, Cicero, Valerius Maximus. That said, quite often Cavalca attributes the wrong author. Cavalca writes as though he was speaking to the reader in person useing phrases like “Io per me credo” and “Oimé “ Introducing unique stories and words, He refers to someone as double-tongued as a “tecomeco” (bilingue) . He refers to a sleight of hand trick ,called “gherminella” a word which was used later by Boccaccio. This is an important book in Italian literary history, and the Italian vocabulary leaving many contemporary proverbs and descriptions of medieval life. Goff C342; H(Add)C 4776a; R 116; Pell 3448; CIBN C-195; IGI 2637; Essling 750; Sander 1853; Pr 4649; BMC V 328; GW 6413
One copy in Goff. Huntington Library.
Queried Location: New York NY, Manhattan College: sold Christie’s (NY) 1 June 1991 lot 41 (current whereabouts unknown)

***
***
5) 350J. Richard FitzRalph (Ricardus Radulphus Armacanus pseudonym) (circa 1300-1360)
Summa Domini Armacani in Questionibus Armenorum noviter impressa et Correcta a magistro nostro Johanne Sudoris. Cum aliquibus Sermonibus eiusdem de Christi dominio.
Paris: Jehan Petit et ponset le Preux, (Venales habentur in vico divi Jacobi sub Lilio aureo) 1512. [Privilège octroyé à Jean Petit et Poncet Le Preux daté du 12 mars 1511 (1512 n. st.) et prenant effet le 15 juillet 1512.]. $24,000

Small Folio 275 x 201 mm. A6 a-z6 &6 A-E6 F4. [6], 177 [i. e., 178] leaves. This copy is bound in a Remboîtage of later limp vellum; contents toned and brittle, lightly damp wrinkled with marginal damp staining at beginning and end, contemporary inscriptions on title and scattered underscoring and marginalia, wormhole through blank outer margin of approximately the first 30 leaves, paper crack in o1 not affecting text, last leaf reinforced in outer margin on verso. A Mexican Augustinian branded ownership mark on bottom edge. This is the only printed edition of the Summa in Questionibus Armenorum which is an examination of alleged Armenian doctrinal errors, the chief dogmatic work by an Irish theologian and prelate involved in negotiations between the papal court at Avignon and Armenian representatives over the reconciliation of the Roman and Armenian churches. FitzRalph, whose Defensorium curatorum was first published circa 1483, was one of the earliest Irish authors to appear in print. Renouard-Moreau II, 314; Shaaber M119; not in RBH or ABPC. Moreau, B. Inventaire 1512- 314; Index des livres interdits, t. IX, p. 86 (n° 50/499; Page de titre en rouge et noir dans un encadrement de plaques gravées sur métal, marque de Jean Petit (Renouard, 890) Adams, F-550


><><><><><
6) 358J Jacobus de Gruytrode 1400-1475
Speculum animae peccatricis
[Memmingen : Albrecht Kunne, about 1490] $6,500

Quarto , [28] ff, 33 lines, the first initial (5 lines) is painted in white and blue on a golden background, upper and left margin richly decorated in red, purple, blue and gold and with two red beasts. 19th c. binding in half leather, title gilt on spine, all edges gilt. Sometimes falsely attributed to Dionysius Carthusiensis, the Speculum is now attributed either to Jacobus de Gruytrode (cf. Bloomfield) or to Jacobus de Clusa (cf. L. Meier, Die Werke des Erfurter Karthäusers Jakob von Jüterbog, Münster, 1955).

Speculum animae peccatricis is a work of spiritual edification which consists of seven sections: on human misery, sin (especially lechery), penance, rejection of the world, the vanity of human wishes, death and hell and heaven.
Firste of the filthenes and miserie of man. Below are the chapter in English
Secounde of the synnes ingeneralle and of their effectis.
Thyrde howe they ought hastely with all diligence to do penaunce.
Fourth howe they ought to fle the world.
Fyfthe of the false Riches and vayne ho∣noures of the worlde.
Sixt howe they ought to drede deth.
Seuenth of the Ioyes of paradyse and of the paynes of hell.
There is no modern critical edition of the text. Among the devotional books by the Flemish mystical writers of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, none was more popular on the Continent and in England during the early Renaissance than the Speculum aureum animae peccatricis or The mirroure of golde for the synfull soule, which Lady Margaret Beaufort translated into English. Since the sixteenth century, bibliographers have listed the Speculum as the work of the Carthusian monk Jacobus de Gruytroede, prior of the Liége Charterhouse from 1440 to 1475, yet the English version is always attributed to his friend Denis de Leuwis or Dionysius the Carthusian, as he is better known. The question of authorship may be satisfactorily settled as the result of recent research by an English Carthusian scholar in the library of the Certosa in Farneta. He noted that the editors of Dionysius’s Opera omnia (Tournai, 1913) explain how the error in authorship began. In volume xlii they point out that, owing to the Carthusian tradition of anonymity during a monk’s lifetime, the Speculum was printed anonymously until 1495, in which year the Nuremberg printer Paul Wagner first issued it as a work by Dionysius. He found the manuscript of the Speculum in the library at Ruremond, where Dionysius was prior until his death in 1471, and supposed it was written by him, as were the other works he intended to print. The two priors were close friends, and dedicated several of their works to each other. Nugent E.M. (1969) Jacobus de Gruytroede. In: Nugent E.M. (eds) The Thought & Culture of the English Renaissance. Springer, Dordrecht
Goff S644; HC 14899*; Pell 4313; CIBN S-333; IGI 5001; IDL 2532; Schlechter-Ries 1003; Voull(B) 1617,5; Schmitt I 1614,2; Hubay(Augsburg) 1141; Hubay(Eichstätt) 538; Sack(Freiburg) 1951; Walsh 988; Bod-inc S-258; Sheppard 2032; Pr 2804; BMC II 608; BSB-Ink I-23; GW M10734
U.S. copies;Harvard ,Emory, Columbia ,Huntington Library
Southern Methodist Univ, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Library
)0(
Nam digiti scripto laetantur, lumina visu Mens volvet sensu mystica verba Dei
“The fingers rejoice in writing, the eyes in seeing, and the mind at examining the meaning of God’s mystical words.”
The first printed facsimile of a manuscript.
7) 351J. Hrabanus Maurus. 784-856?
Magnencij Rabani Mauri De Laudib[us] sancte Crucis opus. erudicione versu prosaq[ue] mirificum.
Phorçheim. [Pforzheim] : In ædibus Thom[ae] Anshelmi., 1503. $10,700

Folio Aa6, Bb4, a-k6, A-B6, C4 (last leaf blank).
THIS COPY LACKING [four leaves] A5 & 6, Bb1 and a1. [two woodcuts of Alcuin interceding on behalf of Rabanus before Pope Gregory iv, and of Rabanus presenting his poems to the Pope; and two figured dedicatory poems the first to Louis the Pious the next christ crucified] It is bound in a full vellum modern binding. First Edition (for a second edition see below) Types 3:109R, 4:180G; 40 lines of transcribed verse + headline, 40 lines of commentary + headline, red and black printing throughout, calligraphic woodcut initial (Proctor, fig. 24) M on title page, woodcut initials printed in red, and a figured prefatory poem, 28 carmina figurata, the first entirely xylographic, the remaining poems combining printed and xylographic letters with the versus intexti printed in red (except fig. xvi), enclosed by either woodcut figures (of the emperor, Christ, the Evangelists, Cherubim, etc.) printed in black or by Christian symbols and characters, most defined by metal rules in red.
This is a remarkable typographical achievement, probably the earliest attempt to reproduce a medieval manuscript. The greater portion of the work comprises a preface in verse and twenty-eight poems. “Hrabanus Maurus, the abbot of Fulda, wrote in the midst of the ‘new monasticism,’ a period associated with a revival of literacy and learning. In religious and secular spheres. This ‘script culture,’ as Rosamond McKitterick has it, used the written word not only as a mode of communication but as ‘a resource, a guide, a key, and an inspiration,’ especially in the devotional practice of Christianity.

Each of the twenty-eight picture poems that form In honorem sanctae crucis explores a different theme relating to the Cross through a complex interplay of word and image. The poems each have an equal number of letters per line, written continuously like a grid. By following the letters in the usual direction for a Latin text—from left to right, top to bottom—each grid reads as one long poem. But within each grid, certain letters are also marked out with colour and drawings to form pictures. The letters that make up these pictures read as separate short poems embedded within the larger poem. As such, each page of In honorem sanctae crucis presents not just a puzzle of words and pictures, full of hidden and interrelated messages for the reader to decode bout a meditation exercise.
“Hrabanus created the various shapes and figures by highlighting individual letters in underlying poens in colour (in the printed editions red), and theses individual letters together make up meaningful text , ranging from simple declarations to very elaborate ones. For example, Carmina 2 contains a simple cross inside a square (Hrabanus calls it a “tetragonum”)whose sides form a border for the poem as a whole. The textfrom the underlying poen that makes up the figure consists of six hexameters, each one an address to the cross beginning with the words ‘O crux…’ When we follow Hrabanus’s instruction in the accompanying prose text for reading these hexameters, we find the following: even though the verse that forms the top of the square is also the opening of the underlying poem, he insists that we begin reading with the stem of the cross, from top to bottom.” (Schipper)

Sunt quoque uersus duo in ipsa ccruceconscripti, quorum prior est: O CRVX QVAE SVMMI ES NOTO DEDICATA TROPAEO
a summo in ima descendens. Alter uero: O CRVX QVAE CHRISTI ES CARO BENEDICTA TRIVMPHO a dextra in sinistram crucis tendens ‡
‡“there are also two verses inscribed in the cross, the first of which is : “ O cross , thou who art at the height of fame, a dedicated moment” ‘running from the top down. And a second’ “O Cross thou who through the body of Christ art the blessed triumph” ‘running from the right to the left.’
Further more Hrabanus flips left and right the texts point of view alternates , Hrabanus tells us the cross is looking out at the reader, not the other way around. “ Only after we have read the hexameters in the cross are we free to read the verses in the four sides of the tetragon, and even then Hrabanus constrains the order in which they are to be read: first the top, then the bottom, then the right side then finally the left side.”
More complex figures present further challenges in reading. The figure in Carmen 25, for example, consists of eight letters of the word ‘ALLEVIA’ arranged around a small cross. It does not take much effort to notice that we need to start with the A, read down to the E, continue on the left, and end on the right of the figure; and that each time we trace out those letters we make the sign of the cross. It becomes more difficult when we also try and read the text that is enclosed in the figures.

The letters of ALLEVIA are made of the following letters from the underlying poem. A crux[a L eter L na[de E i]es[lave[v L ivis V in]arc I e]po A lorvm
CRUX AETERNA DEI ES LAVS VIVIS IN ARCE POLORUM
‡ Eternal cross, thou art the praise of God, thou livest in the arc of the skies.

Peter Godman, Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1985), 249. A. G. Rigg and G. R. Wieland, ‘A Canterbury Classbook of the Mid-eleventh Century Anglo-Saxon England 4 (1974), 113-30.
William Schipper, ‘Hrabanus Maurus in Anglo-Saxon England: In Honorem Sanctae Crucis’, in Early Medieval Studies in Memory of Patrick Wormald, ed. Stephen Baxter, Catherine Karkov, Janet L. Nelson, David Pelteret (Farnham, Surrey; Burlington, Vt.: Ashgate 2009), 283-98.

Proctor, R. Index to the early printed books in the British Museum,; 11747; Adams, H.M. Catalogue of books printed on the continent of Europe, 1501-1600, in Cambridge libraries,; R3; Catalogue of a collection of early German books in the library of C. Fairfax Murray,; 350; Panzer, G.W.F. Annales typographici,; VIII 227, 2; Pollard, A.W. Catalogue of books mostly from the presses of the first printers … collected by Rush C. Hawkins,; 189 Panzer, VIII, 227, no. 2. Proctor 11747. Fairfax Murray 350./ Last leaf blank./ Edited by Jakob Wimpheling.–cf. title page verso./ Illustrations: 2 woodcuts of the author presenting his book to the pope, and many woodcut figures (Christ, cherubs, crosses, symbols, etc.) printed on 28 pages of text. Some of the text within and near the outline figures is xylographic, the rest printed. The letters within the outlines are printed in red and may be read separately in a different sense. Printed in red and black, initials (except on t.p.) in red./ With label of Sinclair Hamilton. Peter Godman, Poetry of the Carolingian Renaissance (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1985), 249. A. G. Rigg and G. R. Wieland, ‘A Canterbury Classbook of the Mid-eleventh Century Anglo-Saxon England 4 (1974), 113-30. William Schipper, ‘Hrabanus Maurus in Anglo-Saxon England: In Honorem Sanctae Crucis’, in Early Medieval Studies in Memory of Patrick Wormald, ed. Stephen Baxter, Catherine Karkov, Janet L. Nelson, David Pelteret (Farnham, Surrey; Burlington, Vt.: Ashgate,
^)^)^)^(^(^(^
The second edition One-Hundred and three years later.
8). 354J Hrabanus Maurus. 784-856?
Magnencij Rabani Mauri De Laudib[us] sancte Crucis opus. erudicione versu prosaq[ue] mirificum. Cum antiqviate avctoris <annis abhinc prope octingentis abbatis primum fuldensis, archiepiscopi postea moguntini. tum noitate scriptionis memorabile. Qvo figvris sive imaginibvs XXVIII. multi fedei christianae mysteria, multi mystici numeri; angelorum, virtutum, VII. donorum Spiritus Sancti, VIII. Beatitudinum, IV. elementorum, IV. temorum anni, VI euangelistarum & agni, mensium, ventorum, V librorum Moysis, nominis Adam, alleluia, & amen, aliarumq[ue] rerum vis & dignitas in formam crvis reedacta, subtiliter et ingeniose explicantur.
Augustæ Vindelicorvm e typographeo Praetoriano. , 1605. $9,000

Folio Aa6, Bb4, a-k6, a6, B4, c4. (complete). Printers mark on title page, woodcut initials printed in red, two woodcuts of Alcuin interceding on behalf of Rabanus before Pope Gregory iv, and of Rabanus presenting his poems to the Pope; a figured dedicatory poem to Louis the Pious and a figured prefatory poem, 28 carmina figurata, the first entirely xylographic, the remaining poems combining printed and xylographic letters with the versus intexti printed in red (except fig. xvi), enclosed by either woodcut figures (of the emperor, Christ, the Evangelists, Cherubim, etc.) printed in black or by Christian symbols and characters, most defined by metal rules in red. Bound in contemporary deer skin.
This aside from the prologue this edition is a re-set reproduction of the first printed edition (see above)
#######+++++#######
9) 383J Johannes de Anania
Commentaria super prima et secunda parte libri quinti Decretalium. Add: Repertorium
Bologna : Henricus de Colonia, 7 Dec. 1479, 5 Jan. 1480. $17,000
Large folio 422 x 285mm Pars III (bound first) a8,b6,c10,d6,e8,f4,g8.(lacking a1Blank) Pars I (bound second) a10,b8,i8,k6,l8,m8,n6,o6,p8,q8,r10s 10. Pars II (bound third) A8,-F8,G6,H8,-L8,M6,N8,O8P6,Q8,R8,S6,T8,U10,X8-Z8, &8, ¶8,€8,¡8. In three parts, dated: 7 Dec. 1479 (Commentaria, partes I-II); 5 Jan. 1480 (Repertorium)
No copy of parts II & III in the US. The margin of a2 of the Repertorium cut off with no text loss (see image) This is a very very wide margined copy, with strong and crisp paper. The first leaf is stroked in red and blue. Throughout the rest of the books capital spaces are left blank. This copy is bound in 19th century vellum.
ANANI’A, JOHANNES DE : his family name, Anagni. implies that he was of the family of the Catani, and that his father’s name was Leonardo. He taught canon law in Bologna, and had the reputation of a conscientious man. He studied under Floriano di San Pietro. Alexander Tartagni and Andreas Barbati were his scholars; the former became his step-son, and the latter inherited his library. According to Orlandi, Anania was sent ambassador from the city of Bologna to Pope Martin V. in 1425, and he was also employed to conduct negotiations with other princes. Johannes de Anania at the time of his death, in 1455 or 1458, was archdeacon at Bologna. Spangenberg enumerates four of his works, three of which were published at Lyon between 1521 and 1555 : — 1. A Commentary on the fifth book of the Decretals, published in folio at Lyon in 1521, and reprinted there in 1553. 2. Consilia, discovered and edited by Ludovico Bolognini, in folio, at Lyon in 1555, reprinted at Venice in 1570. 3. “De Revocatione Feudi alienati,” in octavo, at Lyon, in 1546, reprinted at Basle in 1564. 4. A Collection of the Decisions of the Roman Rota, at Venice, in folio, in 1496. Mazzuchelli mentions a treatise on the law as to salaries, “Allegatio de Salario et Stipendio ac de Obligatione et Promissione Domini,” which is preserved in MS. at Bologna in the library of the Collegio di Spagna. In addition to these Lipenius ascribes to Johannes de Anania a legal tract on church patronage, “De Jure Patronatus Ecclesiastico,” published at Amsterdam in 1640; and a collection of cases (” Quaestiones”) at Cologne in 1570. To the folio edition of Baldus, “In Usus Feudorum Commentaria,”

published at Lyon in 1550, there is appended a thesis on the law regarding the alienation of fiefs, maintained by Johannes de Anania at a public disputation in Bologna. The date is not given, but he is styled “Doctor et Canonicus,” and his opponent is said to have been Secundinus de Natis; and the publisher intimates that the MS. had been preserved in the library of Johannes Nevizanus at Asti. No. 446. of the Arundel MSS. in the library of the British Museum contains a treatise “De Usuris” by Johannes de Anania. The volume is of a large folio form, and the ” De Usuris,” written in a small character with numerous contractions, occupies the folios 93. to 164. inclusive, each folio containing four columns. These treatises are the only compositions of the author we have seen, and they leave a favourable impression of his skill in selecting authorities to support and elucidate his positions, and of his talent for lucid arrangement. (Mazzuchelli, Scrittori d’ Italia; Spangenberg, in Ersch und Gruber’s Allgemeine Encyclopadie; Alidosi, Appendice alli Dottori Bolognesi de Legge Canonica e Civile; Orlandi, Notizie degli Scrittori Bolognesi; Baldus Perusinus, in Usus Feudorum Commentaria doctissima, quibus accesserunt Andr. Siculi Adnotationes una cum Joan. de Anania eleganti Disputatione in tres secta Quastiones, Lugduni, 1550, fol.; Arundel MSS. in the British Museum, No. 446.) W. W
Not in Goff: ISTC ij00250150; H 938*; Torchet 521; IGI 5245; IBE 3188; Kotvan 702; Sajó-Soltész 1881; Martín Abad J-44; Voull(B) 2735,20; Walsh 3188; BSB-Ink I-365; GW M12841
Holdings: United States Harvard University, Law School Library (I) only.

)0(
)0(

10) 381J Athanasius Kircher 1602-1680
Physiologia Kircheriana Experimentalis, Qua Summa Argumentorum Multitudine & Varietate Naturalium rerum scientia per experimenta Physica, Mathematica, Medica, Chymica, Musica, Magnetica, Mechanica comprobatur atque stabilitur. Quam Ex Vastis Operibus Adm. Revdi. P. Athanasii Kircheri extraxit, & in hunc ordinem per classes redegit Romæ, Anno M. DC. LXXV. Joannes Stephanus Kestlerus Alsata, Authoris discipulus, & in re litterariâ assecla, & coadjutor.
Amsterdam: Ex Officinâ Janssonio-Waesbergiana. Anno 1680 $9,500

Folio. 15 x 9 3/4 inches. *4, A-Z4, Aa-Ii4. First edition.mmThis copy is quite clean and crisp throughout, never having been washed or pressed. There is some occasional spotting and browning. but none is too extensive. The binding is twentyth century full vellum with title on spine. an impressive and large copy!
“Thus in the must varied branches of science Kircher played the role of pioneer. Even medicine received his attention, as is shown for example by his treatise, ‘Scrutinium phyisco-medicum contagiosæ luis, quæ pestis dicitur’ (Rome, 1663). His scientific activities brought him into scientific correspondence with scholars laboring in the most different fields, as the numerous volumes of his extant letters show. It is to his inventive mind that we owe one of the earliest of our counting machines: the speaking-tube and æolian harp were perfected by him. He was also the inventor of the magic lantern which has since been brought to such perfection and is and is today almost indispensable. [All of these devices are illustrated in the present work, compiled in the year of the author’s death by Kircher and his student Johann Stephan Kestler, including three large and striking engravings of magic lanterns.]” May I ask the reader to take the following quote with a measure of indulgence for its closed minded author [circa 1913] with the hope that modern folk of the last decade of the second millennium have a bit more tolerance for the many sciences that we have yet to master. “That the most varied judgments should be formed and expressed on a man of such encyclopædic knowledge was only to be expected. He tried to find a grain of truth even in the false sciences of alchemy, astrology, and horoscopy, which were still in his time much in vogue, nor is it surprising that in the province of astronomy he did not at this early date defend the Copernican System.” (the above two quoted taken from the Catholic Encyclopedia, vol. viii, page 662) Kircher was an accomplished and versatile scholar who applied his intellectual abilities to a myriad of scientific problems. This work is a fascinating compendium of scientific experiments and principles which documents the accomplishments of early modern thinkers of the west.
^)^)^)^(^(^(^

11) 380J Francis Molloy. fl 1660
Lucerna fidelium, seu, Fasciculus decerptus ab authoribus magis versatis, qui tractarunt de doctrina Christiana : divisus in tres partes.
Romæ : Typis Sacræ Congreg. de Propaganda Fide, M DC LXXVI [1676] $4,500 Octavo 6 X 4 inches : A-2B8 2C2. complet, signature ) is mis-signed . This copy is bound in early 20th century sheep.

MOLLOY or O’MAOLMHUAIDH, FRANCIS (Jl. 1660), theologian and grammarian, was a native of the county of Meath, Ireland. The family of which he was a member had extensive landed possessions in the district known as O’Molloys’ Country, and some of them engaged actively in the Irish movements from 1641 to 1652.
Francis Molloy entered the order of St. Francis, became a priest, was appointed professor of theology at St. Isidore’s College, Rome, and acted as agent for the Irish catholics at the papal court in the reign of Charles II. His first published work was entitled ‘Tractatus de Incarnatione ad mentern Scoti,’ 1645. This was followed in 1658 by ‘ Jubilatia genethliaca

in honorem Prosperi Balthasaris Philippi, Hispani principis, carmine,’ and by a Latin treatise on theology in 1666.
A catechism of the doctrines of the catholic church in the Irish language was published by Molloy in 1676 with the title: ‘Lucerna tidelium, seu fasciculus decerptus ab authoribus magis versatis qui tractarunt de doctrina Christiana.’ It was printed at Rome at the press of the Congregation ‘de propaganda fide,’ ( This book is the first book they printed in Irish Type) from which, in 1677, issued another book by Molloy, entitled ‘Grammatica Latino-Hibernica,’ 12mo, the first printed grammar of the Irish language. Edward Lhuyd [q. v.], in his’ Archaeologia Britannica,’published at Oxford in 1707, mentioned that he had seen a manuscript grammar of the Irish language copied at Louvain in 1669 which partially corresponded with that of Molloy. He added that Molloy’s grammar, although the most complete exta’nt in his time, was deficient as to syntax and the variation of the nouns and verbs. The date of Molloy’s death has not been ascertained. In 1626 Propaganda Fide had installed a printing press for the foreign missions and not much later another one was brought to Louvain where books and catechisms were printed for both the local college and the Irish mission.* The problem with the Propaganda printing press was that only books in Latin and Italian were allowed to be printed so it took until 1674 when Francis Molloy asked for permission to print a catechism there in Irish with the explanation “che altra malamente capisce e vacilla assai per mancanza d’intruttore e d’intruttion sana.”**.
[“Irish priests at Rome had a new Irish type cut about 1675 … [this was] their first book.”- -H. Reichner, Catalogue 34, Jan. 1968]

Wing O291C, English short title catalogue,; R41480; Clancy, T.H. English Catholic books, 1641-1700 (rev. ed.),; entry 743; Catalogue of seventeenth century Italian books in the British Library,; page 628 *& ** ;Egan, Bartholomew (ed.): Notes on Propaganda Fide Printing Press and Correspondence concerning Francis Molloy O.F.M., in: Collectanea Hibernica, No. 2 (1959), pp. 115-124.
)0(
)0()0(
With a reference to the invention of printing on the verso of Folio 64.
12) 359J Werner Rolewinck 1425-1502
Fasciculus temporu[m] omnes antiquo[rum] chronicas strictim complectens felici numine incipit. Prologus.
Venice : Erhard Ratdolt, 8 Sept. 1485 $16,000

Folio (275 x 195 mm). [A]8 [a-g]8 [h]10 75 leaves without signatures or page numbers (9 leaves, 1-66 foliated ), 3 columns in table, 59 lines and foliation, gothic letter, 2 large ornamental initials, 59 woodcuts, one full-page, woodcut diagram. Fifth and last Venetian edition, and fourth Ratdolt edition being the most complete edition of Rolewinck s chronological history of the world. The chronology follows a double time-line, measuring time from both the Creation and the birth of Christ to the death of the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror in the year 1481, demanding a
remarkably complex typographical layout. The Fasciculus Temporum (Little bundles of time) was the first book printed on history of the world, it is also one of the earliest and greatest of illustrated incunabula. The illustrations show Noah s Ark, the tower of Babel and contain many town views including Jerusalem, Syracuse, Rome and the Doge s Palace in Venice.
Rolewinck (1425-1502) was a Carthusian monk and prolific author. This book was both the most popular of his numerous writings and the most popular concise world chronicle of its time, being printed 32 times in the 15th century, including translations into French, German and Dutch . Rolewinck’s Fasciculus Temporum was an enormously popular world chronicle, appearing in over 30 incunabular editions in Latin, German, French, and Dutch. A very handsome and typographically-sophisticated volume, with varying columns, circular devices with inset type, and woodcuts throughout.

This work aspires to trace the history of the world from the beginning of time until the year of pulication. The thirty-three woodcuts are crisp and rather charming, and, like those in many fifteenth- and sixteenth-century chronicles, are occasionally reused to illustrate different events and locations. The work is fascinating for the comprehensiveness of its content as well as the beauty of its execution. Of particular interest is a reference to the invention of printing (in 1454) on the verso of Folio 64.

Goff R271; GW M38738; ; BMC V 290; H 6935*; Redgr 52; Essling 280; Sander 6530; Schr 5116C; Pell Ms 10192 (9969); CIBN R-177; Arnoult 1276; Neveu 528; Nice 269; Torchet 821; Polain(B) 4691; IDL 3943; IBE 4955; IGI 8420; CCIR R-40; Kotvan 1024; Sajó-Soltész 2972; Gspan-Badalić 590; IBPort 1576; Mendes 1124, 1125, 1126; Madsen 3526; Martín Abad R-48; Voull(B) 3801; Hubay(Augsburg) 1811; Hubay(Eichstätt) 898; Walsh 1830; Rhodes(Oxford Colleges) 1525; Bod-inc R-121; Sheppard 3688; Pr 4404; BSB-Ink R-247
#######+++++#######
13) 367J Petrus de Rosenheim. (1380-1432). Nom probable : Petrus Wiechs
[Roseum memoriale divinorum eloquiorum]
[Köln] : [Southern Germany : n.pr., about 1480-90?] or [Cologne? : n.pr., about 1483] or [Ludwig von Renchen?], 1483. $12,000

Quarto (190 x 155 mm). Collation: a-f8 [1-68]. [48] leaves. First Edition. Text in one column, 32 lines. Type: 80G. Initials painted in red, and blue ink throughout. Simple vellum binding from a 15th century vellum leaf. Gothic script. . A very good copy, old repair to the first blank leaf, a few spots, pale stain at the lower blank corner of the first quires. It is not known where and by which press this edition was printed. ISTC gives Southern Germany and a date of c.1480-1490, GW tentatively suggests Oberrhein, 1483, and Proctor attributes it to Ludwig Von Renchen in Cologne. The hexameters of each section of the summary form an acrostic of the letters of the alphabet. (alphabetarium) as to insure memorization in the proper sequence, the first word of each verse falls neatly into alphabetical order. [1,194 short mnemonic verses] It uses characteristic couplets (distiches) to express the main content of all chapters of the Old and New Testament. This introduction makes it possible to easily find every quote in the Bible.

A significant record of the essential role of memory in late-medieval piety, One of the earliest printed books on the ars memorativa or mnemotechnic was composed by the German Benedictine monk Petrus of Rosenhaym (Upper Bavaria), written between 1423 and 1426 for Cardinal Giulio Branda di Castiglione. Petrus of Rosenhaym composed numerous treatises, sermons, and verses: the Roseum memoriale is surely his most famous work, enjoying wide popularity during the fifteenth century and first half of the sixteenth century. The mnemotechnic method here employed is extremely complex: the hexameters of each section of the summary form an acrostic of the letters of the alphabet. in. A highly popular and broadly used manual, its copies could be found in almost every European church after the invention of the printing press it was printed in several different locations. This early medieval incunable has not been clearly dated| researchers attribute it to the Upper Rhine region sometime between 1480 and 1483. After studying at the University of Vienna, Petrus de Rosenhaym, along with his friend Nikolaus Seyringer, moved to Subiaco, where he entered the Benedectine order. In 1413, he was appointed prior to the cloister of Rocca di Mondragone near Capua. In 1416, he took part in the Council of Konstanz, and later he was prior in Melk (Lower Austria). After 1423, he was appointed ‘cursor biblicus’ and ‘magister studentium’. Goff R336; BMC I 312; ; GW M32724; ISTC; ir00336000; Polain(B) 3128; IBE 4559; IGI 7668; IBP 4380; Sajó-Soltész 2676; Madsen 3549; Borm 2134; Hubay(Würzburg) 1704; AmBCat 199; Walsh 492; Oates 867; Pr 1517;; BSB P-362; Van der Haegen II,2:16,4?; Young 278;.
Copies in the United States of America: Brown, Harvard, Library of Congress, Huntington, The Newberry Library, Yale

^)^)^)^(^(^(^
^)^)^)^(^(^(^

14) 384J Raymundus de Sabunde -1436
Theologia naturalis, sive, Liber creaturarum : specialiter de homine et de natura eius inquantum homo, et de his que sunt ei necessaria ad cognoscendum seipsum [et] deum et omne debitu[m] ad quod homo tenetur et obligat[ur] tam deo quam p[ro]ximo.
Straßburg: Martin Flach, 21 January 1496. $17,000
Imp[re]ssus Argentine per Martinum Flach inibi co[n]ciuem anno incarnat[i]o[n]is d[omi]nice Millesimoq[ua]dringentesimononagesimosexto men[sis] v[er]o Ianuarij die vicesimop[ri]mo

Folio (280 x 200mm.) π6 a8 b-y6 z8 [et]6 [con]8 (the last leaf supplied from another copy, printed on recto only), The second leaf (π2) has a beautiful a green painted initial A [Amor] on a gold ground with pink and blue edges, extending into the margins with green-stemmed pink and gold flowers on opposite side. The first leaf of the text proper (a1) Has a large blue painted initial A on a gold ground with pink and green edges, large pink and purple flowers, strawberries thistles and a Tromp l’oeil of a Dead fly,( quite charming) fill uppermargin; 3-line initials in alternating red and blue, rubricated throughout. This is the first dated edition.
It is bound in Contemporary deerskin over wooden boards, covers panelled and tooled in blind with repeated small rosette tool, remains of paper labels on spine (lacking metal furniture and clasps, some wear and small areas of loss). This copy has some contemporary manuscript notes, including a two-line note on f. b2recto, and on f.a2verso is a marginal drawing of the scala naturae with the four gradus marked. Provenance: Contemporary inscription of Johannes Pengl (Penngl) from Weißenburg in Bavaria, who was active in Eichstätt & Vienna, with a note of cost of binding on final paste down. Later notes and shelf-mark on front paste-down and loose sheet.
Colophon: Finit liber creatura[rum] seu nature siue nature siue de ho[m]i[n]e p[ro]pt[er] que[m] alie creature facte su[n]t ex cui[us] cognit[i]one illu[m]inat[ur] ho[mo] i[n] [co]gnit[i]o[n]e dei [et] creaturarum.
This text marks the dawn of a knowledge based on Scripture and REASON.
The Catholic Encyclopedia sees this as “It represents a phase of decadent Scholasticism, and is a defense of a point of view which is subversive of the fundamental principle of the Scholastic method. The Schoolmen of the thirteenth century, while holding that there can be no contradiction between theology and philosophy, maintain that the two sciences are distinct. Raymond breaks down the distinction by teaching a kind of theosophy, the doctrine, namely that, as man is a connecting link between the natural and the supernatural, it is possible by a study of human nature to arrive at a knowledge even of the most profound mysteries of Faith. The tendency of his thought is similar to that of the rationalistic theosophy of Raymond Lully….Moreover, in Spain scholastics, in combating Islam, borrowed the weapons of their erudite antagonists. Close internal resemblance indicates that Raimund de Sabunde was preceded in method and object by Raymund Lully.” CE

What is new and epoch-making is not the material but the method; not of circumscribing religion within the limits of reason, but, by logical collation, of elevating the same upon the basis of natural truth to a science accessible and convincing to all. He recognizes two sources of (1)knowledge, the book of nature and (2) the Bible. The first is universal and direct, the other serves partly to instruct man the better to understand nature, and partly to reveal new truths, not accessible to the natural understanding, but once revealed by God made apprehensible by natural reason. The book of nature, the contents of which are manifested through sense experience and self-consciousness, can no more be falsified than the Bible and may serve as an exhaustive source of knowledge; but through the fall of man it was rendered obscure, so that it became incapable of guiding to the real wisdom of salvation. However, the Bible as well as illumination from above, not in conflict with nature, enables one to reach the correct explanation and application of natural things and self. Hence, his book of nature as a human supplement to the divine Word is to be the basic knowledge of man, because it subtends the doctrines of Scripture with the immovable foundations of self-knowledge, and therefore plants the revealed truths upon the rational ground of universal human perception, internal and external.
The first part presents analytically the facts of nature in ascending scale to man, the

climax; the second, the harmonization of these with Christian doctrine and their fulfillment in the same. Nature in its. four stages of mere being, mere life, sensible consciousness, and self-consciousness, is crowned by man, who is not only the microcosm but the image of God. Nature points toward a supernatural creator possessing in himself in perfection all properties of the things created out of nothing (the cornerstone of natural theology ever after). Foremost is the ontological argument of Ansehn, followed by the physico-theological, psychological, and moral. He demonstrates the Trinity by analogy from rational grounds, and finally ascribes to man in view of his conscious elevation over things a spontaneous gratitude to God. Love is transformed into the object of its affection; and love to God brings man, and with him the universe estranged by sin, into harmony and unity with him. In this he betrays his mystical antecedents. Proceeding in the second part from this general postulation to its results for positive Christianity, he finds justified by reason all the historic facts of revealed religion, such as the person and works of Christ, as well as the infallibility of the Church and the Scriptures; and the necessity by rational proof of all the sacraments and practices of the Church and of the pope. It should be added that Raimund’s analysis of nature and self-knowledge is not thoroughgoing and his application is far from consistent. He does not transplant himself to the standpoint of the unbeliever, but rather executes an apology on the part of a consciousness already Christian, thus assuming conclusions in advance that should grow only out of his premises. Yet his is a long step from the barren speculation of scholasticism, and marks the dawn of a knowledge based on Scripture and reason.
In its day, and for a long time later, it was a celebrated text. The title translates ‘Natural Theology or the book of [living] creatures, in particular about man and his nature inso far as he is man, and about those things necessary for him to know both himself and God, and about every duty by which man is held and obligated both in respect of God and his neighbour.’ The scope is therefore pretty wide. The main point of Sebond’s work is that that faith can be taught, attained, understood by natural reason and not simply on the basis of blind faith and literal adherence to Scripture, although this last is given full weight as is the teaching of ‘sacrosancta romana ecclesia who is the mother of all faithful christians, mistress of grace and faith and rule of truth…’ (preface on a2ra). The work is divided into 330 ‘tituli’ or chapters beginning with the origins of natural theology and ending with the last judgement, the subjects treated at greatest length being ‘God’ and ‘Man’.
Theologia Naturalis, which circulated widely in manuscript and is known particularly in a manuscript in Toulouse (747) corrected after the author’s own copy, was first published in what is called the ‘third family’ in Deventer in 1484-85 (possibly through the offices of the Brothers of the Common Life; the Bodleian copy is from their house at Doesburg, Holland), and then Lyon ca. 1488 from the printer Balsarin. This Flach printing circulated widely (a copy was at Winchcomb abbey in Gloucestershire within a few years (now in Glasgow) and early in the 16the century Archbishop Warham (Abp. 1503-32 ) gave a copy to All Souls College, Oxford) and is the first dated edition. There were a number of later editions (including another Flach edition of 1501) right up into the 17th century. Indeed the well-known 17th-century philosopher Kenelm Digby ( 1603-1664) had a copy of this edition (now at Durham University Library at Bamburgh Castle). Part of the Theologia (Dialogos de la naturaleza delhombre) was translated into Spanish and printed in Madrid in 1610 and 1616, and a resumé by the Carthusian Petrus Dorlandus (Viola anime per modum dyalogi) was published in Cologne in 1499 (ISTC id00360000 ) and in Toulouse in 1500 I(ISTC id003610000).. The Theologia because of the importance it accorded human reason did not escape the notice of the holy Office and was placed on the Index in the middle of the 16th century. Montaigne indeed discovered this during his visit to Rome.
Goff R33.; BMC I, 154.; HC 14069*; GW M36911; Bod-inc R-018. ISTC ir00033000. Palau 283900
◊
◊ ◊
◊

15) 369J Publius Terentius Afer. 185-
Terentius Comico Carmine
Impressum in nobili Helvecior[um] urbe Arge[n]tina : Per Ioanne[m] Grüninger mira etium arte ac diligentia. 1503 $7,500
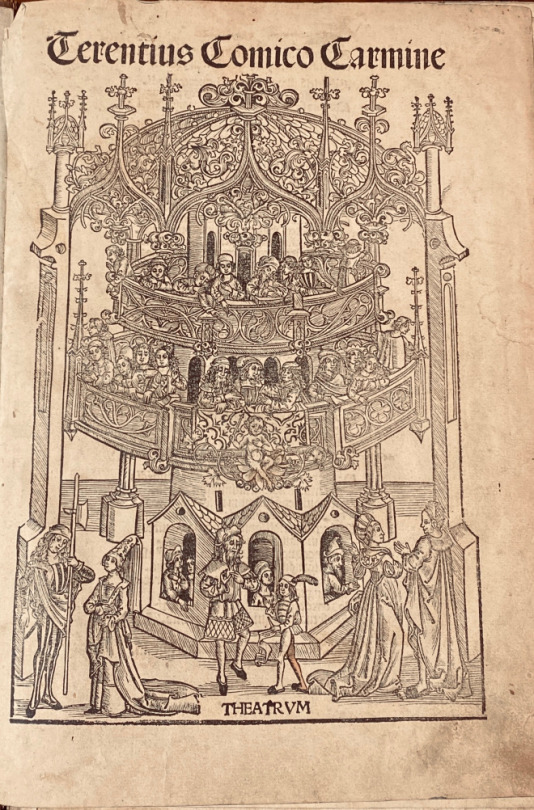

Folio A6 B8 C-Z6 AA6 Bb4 Cc6. There are numerous handwritten annotations in ink (marginal and interlinear, ff. IX-XIX). The binding of half-calf with corners of the XIXth, back with 4 sewing support with pieces of title of red and green leather, boards covered with stony marbled paper. { A typical Kloss binding} (there is a tear sig. B1, with loss; first signature cut shorter at the lower margin; restorations of paper with the last sheets in the upper margin; Yet this copy remains a beautiful illustrated edition of the comedies of Terence with comments by Aelius Donatus and Calphurnius. From the presses of the famous and prolific Strasbourg printer-publisher Johann Reinhard, known as Grüninger, it is remarkably illustrated with 7 large full-page woods (including the famous representation of a theater on the title),
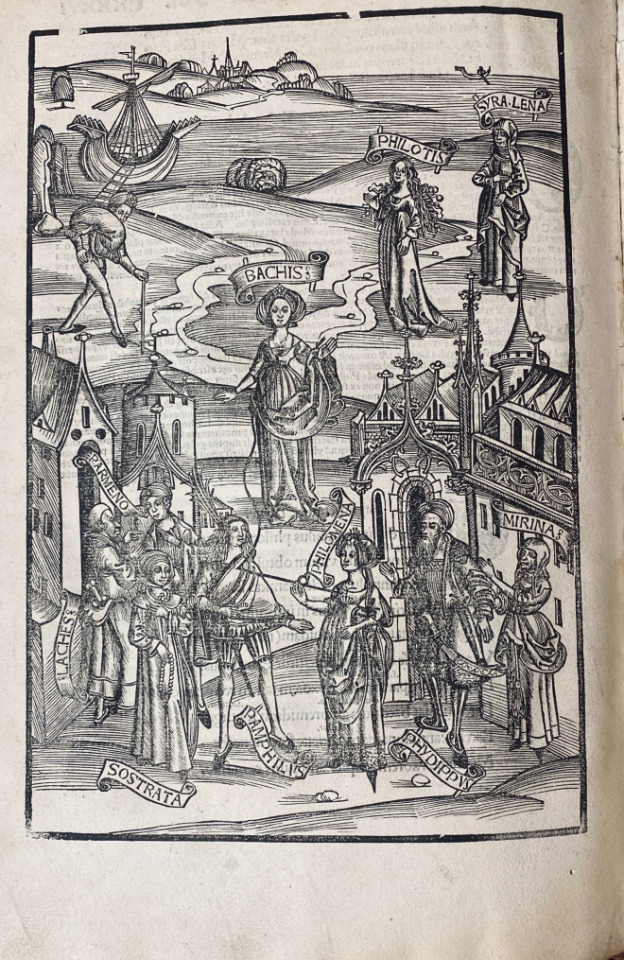

woodcuts depicting the dramatis personae in a land- or cityscape, one at the beginning of each play, and 142 woods in the text 19 of the cuts appear here for the first time; the others are from the 1496 ed. «Grüninger’s illustrations, intended to clarify the complexities of Terence’s plots for the reader, act as visual mnemonic devices for the book’s anticipated student audience. This is demonstrated especially in the full-page woodcut that begins each play, where all of the characters are displayed with connecting lines to indicate their interrelationships. covered with stony marbled paper. { A typical Kloss binding} (there is a tear sig. B1, with loss; first signature cut shorter at the lower margin; restorations of paper with the last sheets in the upper margin; Yet this copy remains a beautiful illustrated edition of the comedies of Terence with comments by Aelius Donatus and Calphurnius. From the presses of the famous and prolific Strasbourg printer-publisher Johann Reinhard, known as Grüninger, it is remarkably illustrated with 7 large full-page woods (including the famous representation of a theater on the title), woodcuts depicting the dramatis personae in a land- or cityscape, one at the beginning of each play, and 142 woods in the text 19 of the cuts appear here for the first time; the others are from the 1496 ed.

«Grüninger’s illustrations, intended to clarify the complexities of Terence’s plots for the reader, act as visual mnemonic devices for the book’s anticipated student audience. This is demonstrated especially in the full-page woodcut that begins each play, where all of the characters are displayed with connecting lines to indicate their interrelationships. A verbal explanation and plot summary accompanies each of these illustrations. The most remarkable feature of Grüninger’s Terence is his use of small interchangeable woodcuts that were combined to create the individual scene illustrations for each play. Individual blocks were cut for most of the characters of the six plays, who are identified by name in overhead banners. The blocks were cleverly combined repeatedly in groups of two to five, sometimes together with cuts of trees and buildings, to create the illustrations. Grüninger was attempting to use the woodcuts as repeatable and combinable objects, much in the same manner as movable type» (Christine Ruggere, in Vision of a Collector: The Lessing J. Rosenwald Collection in the Library of Congress)

Terence writes in a simple conversational Latin, pleasant and direct. Due to his clear and entertaining language, Terence’s works were heavily used by monasteries and convents during the Middle Ages and The Renaissance. Scribes often learned Latin through the meticulous copying of Terence’s texts. Priests and nuns often learned to speak Latin through reenactment of Terence’s plays, thereby learning both Latin and Gregorian chants. Although Terence’s plays often dealt with pagan material, the quality of his language promoted the copying and preserving of his text by the church. The preservation of Terence through the church enabled his work to influence much of later Western drama. [Holloway, Julia Bolton (1993). Sweet New Style: Brunetto Latino, Dante Alighieri, Geoffrey Chaucer, Essays, 1981-2005.] This copy has the book plate and a binding typical for Kloss. It is NOT Melanchthon’s copy, or his notes!

Georg Franz Burkhard Kloss (31 July 1787 Frankfurt am Main – 10 February 1854 Frankfurt). Kloss was the son of a physician and studied medicine at Heidelberg and Göttingen, where he became one of the cofounders of the Corps Hannovera Göttingen. He practiced medicine in Frankfurt. He became a book collector, and gathered a fine collection of old manuscripts,. On February 21, 1838, New York book auction house Cooley & Bangs began a three day sale during which they offered more than 313 incunabula distributed among 1,302 lots. Many incunables came from the collection of George Kloss and had appeared in the London sale of his books three years before. It is entirely possible that the 1838 sale was the first time in America that so many incunables were offered all at once in a single auction..
The bulk of the Kloss books were sold by Sotheby in 1835. Most of the books containing notes were attributed as owned and annotated by Melanchthon .
Catalogue of the library of Dr. Kloss of Franckfort a. M. including many original and unpublished manuscripts, and printed books with ms. annotations, by Philip Melancthon …Which will be sold by auction, by Mr. Sotheby and son … May 7th, and nineteen following days (Sundays excepted) .
https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.32044055066971&view=1up&seq=9
Adams D 304. Proctor 9889. Ritter 2284.



Fascicule XXI. Media Plaga 3-4/2020 Only a day or two ago I was notified that I was in contact with some people tested for and found positive for Covid-19, this came as nothing un expected, I was in contact with hundreds of people many from Europe recently.
#early printed books#fascicule XXI#George Kloss#illustrated incunabulum#Incunabula#Irish authors#irish/gaelic printing#Kircher#Not in Goff#rare book catalogue
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

Coloured woodcut from Konrad von Megenberg's "Das Buch der Natur" (The Book of Nature)
Printed by Johann Bämler (Augsburg, 1481)
Third printed incunable edition
#Konrad von Megenberg#The Book of Nature#Das Buch der Natur#book of nature#nature#books#print#illustration#1481#15th century#colored woodcut#colored#woodcut#augsburg#book printing#incunabulum#incunable
0 notes
Photo



bona fide nyc
1st illustration: page from theodore low de vinne’s last book, Notable Printers of Italy during the Fifteenth Century [the grolier club, new york, 1910, p112]: de vinne’s inimitable style—erudite & tasty. composed in types both cut & cast in nyc; seen though the press by the great printer himself at his establishment, the de vinne press—vide ‹point of pilgrimage›. the woodcut facsimile is from the Hpynerotomachia Poliphili of francesco colonna: «The amatory sentiment is extravagant, yet that is subordinate to the author’s knowledge of art and mythology.» [ibid., p113]. published by aldus, venice, 1499; amongst the most beautiful books ever printed, this was aldus’ only foray into the illustrated book. for the context of the woodcut, in english, vide ‹but tell us of the image›.
text & notes are set in condensed form of scotch-face from george bruce’s sons (2nd illustration) [theodore low de vinne, Plain Printing Types, the century co., nyc, 1902, p214]. interesting choice in 1910 as de vinne in 1902 wrote: «The condensed form of Scotch-face is now out of fashion.» [ibid.]. the face sets a monumental page, especially with two-column notes, in composition with the facsimiles of incunabula. de vinne tells us this face was cut in 1854 by james lindsey [ibid.], presumably for the bruce foundry; & embedded within a showing of diamond, or 4½ pt, type de vinne pays biographical tribute to lindsey: «James Lindsey was born in Glasgow, Scotland, in 1825, and was taught the trade in the foundry of Alexander Wilson of Edinburgh [sic*]. He died in Brooklyn on the 20th of September, 1879. He was a thoroughly educated type-founder and a punch-cutter of admitted ability.» [ibid., p103]. further, embedded within a showing of brilliant, or 4 pt, type, de vinne recounts the story of original scotch-face: «Samuel Nelson Dickinson (born 1801, died 1848) was a notable type-founder of Boston. … Unable to get from any type-foundry of his city the types his taste demanded, he undertook to have them made. The style known as the Scotch-face was modelled by him in 1837, but cut and cast to his order by Alexander Wilson & Son, of Edinburgh [sic*]. The matrices imported by him were the first types of the Dickinson foundry in 1839, and were received with marked favor.» [ibid., p104]. if dickinson imported the matrices, one wonders if/why he needed the wilson foundry to also cast for him. on dickinson’s death his foundry was acquired & continued styled in the last instance phelps, dalton & co.; & finally a component of the 1892 merger which constituted american type founders (atf) [ibid.].
*alexander wilson’s foundry was in glasgow. william miller’s foundry was at edinburgh.
captions are set in a face advocated by de vinne for such purpose: light-face. in this case, de vinne selected the broad form from farmer, little & co (3rd illustration) [ibid., p223]. de vinne tells us: «…an extremely light face of decided merit, but which is too thin and too light to be used as a text-type for descriptive matter set solid. It shows to best advantage in leaded or double leaded poetry, or in any work which has broad margins and large space of white. It finds frequent employment in the titles or descriptions of plates when these titles are printed, as in the fashion, on thin paper facing the plate, but in any place it is a strain on ordinary eyesight.» [ibid., p222]. of the broad form, in particular, he continues «…as broad as it is light, is seldom used as a text-letter for standard books. Its delicacy disqualifies it for general use, but it is an effective letter for pamphlets, catalogues, and ornamental job-work, when the composed lines have been liberally widened with leads. The larger sizes are used for book titles, running head lines, and as a display letter.» [ibid., 223]. henry lewis bullen writing under his nom de plume, quadrat, gives concise lineage of farmer, little & co.: «The present corporation of A. D. Farmer & Son Company, better known as Farmer, Little & Co. (1861), is the direct successor of Elihu White, following a son, H. T. White, and then Charles T. White & Co.» [The Inland Printer, vol. xxxviii, no.1, 1906, p36.] farmer, little & co. was acquired by american type founders (atf) in 1892 [✓].
notes on de vinne’s text in the 1st illustration «Raibollini» is a misattribution: propagated from an attempt by sir anthony panizzi in 1858 to identify aldus’ punch cutter as francesco raibolini, the painter from bologna. «This argument was demolished by Giacomo Manzoni in his Studia di bibliografia analitica, and the matter clinched by the publication by Adamo Rossi in 1883 of a document from which it appeared that Franceso’s family name was Griffo.» [a.f. johnson, Type Designs, grafton & co., london, 1959, p95]. this information, apparently, had not yet reached the cognoscenti of new york, or de vinne was simply unaware.
the statement «One line of a larger size with slanted capitals appears on plate 28» is not apropos, as plate 28 is a facsimile of a page printed in 1566 by aldus’ son, paolo: not an incunabulum. the face is not aldine: it is a 16th c. french face—the petit-parangon italic cut by robert granjon in 1554 [cf. 298 in hendrik d.l. vervliet, French Renaissance Printing Types, the bibliographical society, london, 2010, p328].
#typography#aldus#incunabula#theodore low de vinne#nyc#grolier club#bruce foundry#james lindsey#alexander wilson#farmer little & co#henry lewis bullen#granjon
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Post has been published on Books by Caroline Miller
New Post has been published on https://www.booksbycarolinemiller.com/musings/in-praise-of-incunabulum/
In Praise Of Incunabulum

“My grandmother has trouble with her phone too,” the sales representative said. “My advice is to call your cell number once a month to avoid letting it fall into sleep mode.” Who knew? My cell phone goes catatonic if I don’t talk to it enough. Needless to say, my transition to a required 4g upgrade hasn’t gone smoothly. I’ve yet to figure out how to receive and delete messages. The information, I’m told, is somewhere on the internet, but I don’t have the time to look for it or plow through a web manual to find the right section. I need a grandchild to show me how to delete. In 1802, during the first Industrial Revolution, William Wordsworth wrote a sonnet entitled, The World is Too Much With Us. You can say that again, Bill! After brushing my teeth each day, I spend the initial morning hours discovering what changes technology has wrought overnight. Controlling my several social media pages is like driving wild horses into a barn. I was born before television, so the young will have to take my word for it: life was simpler in the good old days. Note, I didn’t say it was more convenient. Nonetheless, living a primitive life was less nerve-wracking. Consider. If the wheel hadn’t been invented, we wouldn’t be hunkering down in fear of a nuclear war. I admit algorithms provide some benefits. With them, I’ve been growing my vocabulary. Yesterday, I stumbled across the word “incunabulum.” Growing up, if the definition for a word didn’t appear in my pocket dictionary, I’d call a reference librarian. Today, I google it and discover both the meaning and pronunciation in a flash. Now that technology teaches itself, knowledge grows exponentially. The human brain, clever as it is, has limits. To keep up, humans have to compartmentalize mountains of data. We need specialists for almost everything. When I was a kid, I went to the family doctor for earaches and broken bones. Today, I’d visit an otolaryngologist for ear problems. Broken bones require two specialists, a radiologist, and an orthopedist. To soothsayers who puzzle the future of our divided county, I say look first at technology. Note the divide between youth and age. I don’t blame technology for youngsters with purple hair, or tattoos that make them look like pages from a comic book. that transform them into illustrated comic books. Each new generation wants to distinguish itself from the past, and I’m glad they do. Otherwise, women might still be trusted up in corsets. Nevertheless, unlike the young, I have no need for speed and instant gratification. Fast cars, planes, trains, or warp drive on the internet mean nothing to a woman who likes to sit in a comfy chair to read. If I had my druthers, I’d like to see life slow down. The homage advertisers pay to the young because of their spendable income is a misleading social marker. Those unlined faces we see on Instagram don’t represent the dominant demographic. Most adults can’t be convinced that a new pair of pants with rips and tears are either stylish or functional. The United States is an aging population. No matter what the young think, grey hair isn’t the consequence of having been careless. Age happens. That fact probably came as a surprise to hot shots like Mark Zuckerberg, (38), Elan Musk (51), Jeff Bezos (58), and Bill Gates (66). Like it or not, those former hipsters have reached seniority. Now that they have, they should turn their talents to creating computers and smart phones someone my age can understand. Surely they’ve grown wised enough to know that staying in touch with the world is a concern to old and young alike.
#America's aging population#Bill Gates#compartmentalizing knowledge#Elan Musk#incremental growth of data#incunabulum#Jeff Bezos#Mark Zuckerberg#nuclear war#outlooks of young and old#refence librarians#self-learning technology#slowing the world down#technology and the elderly#The Industrial Revolution#William Wordsworth
0 notes
Text
Ortus Sanitatis. Straßburg 1497
Ortus Sanitatis. Straßburg 1497
499J “PERHAPS THE MOST IMPORTANT MEDICAL BOOK PRINTED BEFORE 1500” (Hunt). 499J. (Attributed authors. {see below, (or you can search Authors on the magnifier image)) Ortus Sanitatis. De herbis et plantisDe animalibus & reptilibusDe auibus et volatilibusDe piscibus & natatilibus. (tibusDe lapidibus & in terra venis nascẽtibusDe vrinis et earum spiciebus(Tabula medicinalis cum…

View On WordPress
#Herbal#Hortus Sanitatis#Illustrated Incunabula#illustrated incunabulum#ofer1000 woodcuts#Ortus Sanitatis. Straßburg 1497
0 notes