#hemopathies
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Best Homeopathic Doctor in Patna for Skin Dr. Arun Prakash At J. D. Memorial Healthcare Center

When it comes to finding the best homeopathic doctor in Patna for skin issues, Dr. Arun Prakash at J. D. Memorial Healthcare Center stands out. With his extensive experience and patient-centric approach, he provides effective homeopathic treatments for various skin conditions, ensuring holistic and lasting relief
Expertise in Skin Treatments
Dr. Arun Prakash is highly regarded for his proficiency in treating skin disorders through homeopathy. His comprehensive treatment plans are designed to address both the symptoms and underlying causes of skin issues, promoting overall skin health and preventing recurrence. Patients suffering from chronic conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, acne, and vitiligo have found significant improvement under his care.
Comprehensive Skin Care Services
At J. D. Memorial Healthcare Center, a range of skin treatments are available:
Psoriasis : Effective homeopathic remedies that reduce the severity and frequency of flare-ups.
Eczema : Natural treatments that soothe inflammation and prevent exacerbations.
Acne Holistic solutions targeting the root causes to promote clear and healthy skin.
Vitiligo Management plans aimed at restoring skin pigmentation and improving appearance.
Convenient Access and Holistic Healing
For those looking for a homeopathic doctor near me, J. D. Memorial Healthcare Center provides easy access to top-notch homeopathic care in Patna. The center’s commitment to holistic healing ensures that patients receive treatments that enhance their overall health and well-being.
Patients have shared numerous success stories, highlighting the positive impact of Dr. Arun Prakash’s treatments. Many have reported significant improvements in their skin conditions, underscoring his expertise and dedication to patient care. Know More..
0 notes
Text
Explore the Benefits of Cina Homeopathy Autism Treatment from Skilled Practitioners
Recognised homeopathy practitioners often recommend Cina Homeopathy Autism, to elevate the brain-development and reduce the disorder. Some skilled homeopathy practitioners assist in eliminating the disability of social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and exhibit repetitive behaviours. They also focus on reducing violent behaviour including self-harm in extreme situations through their hemopathy treatments.
A qualified expert homoeopath can help you get the greatest outcomes for an autistic child and lessen all of the symptoms of autism if not completely cure it. Additionally, they can recommend impactful treatments for women's health including homeopathic PMS relief in Melbourne.
Usually, the majority of the time, people prefers conventional medicine to address some of the symptoms but there will be chances of harmful side-effects and most of these medicines are not qualified to cure or reduce autism.
Reason to Visit Expert Homeopaths for Women's Health:
Expert homeopaths play a crucial role in addressing and improving women's health concerns, including PMS (premenstrual syndrome), PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome), endometriosis, menstrual issues, menopause, and other related conditions. These skilled practitioners take a holistic approach, considering the physical, emotional, and mental aspects of a woman's health.

They carefully analyse the individual symptoms and underlying causes and prescribe personalized remedies that stimulate the body's natural healing mechanisms.
They offer a gentle and non-invasive treatment option for women's health issues. The selected remedies are tailored to the specific symptoms and unique constitution of each woman, aiming to restore balance and promote overall well-being.
Additionally, they understand the complex nature of women's health concerns and the impact they can have on daily life. They provide individualized care, addressing not only the physical symptoms but also the emotional and psychological aspects associated with these conditions.
Their goal is to alleviate symptoms, regulate hormonal imbalances, improve reproductive health, and enhance the overall quality of life for women at every stage of their journey.
Meanwhile, through regular consultations and monitoring, homeopaths can work closely with women, offering support, guidance, and adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary.
It is important to consult with a qualified and experienced homeopath to ensure proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment for any specific health concerns.
Source
0 notes
Photo

Who are those two? They seem odd. Hemo & Pathi
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Allopathy vs Homeopathy: Which is the best treatment method for Piles?
Piles (Hemorrhoids) are a common problem. Most people face it once or twice in their life. The occurrence is more in people above forty years of age. We all have soft, elastic tissues in our anus that assist us in our bowel movements. We are unaware of their presence unless they are inflamed and cause symptoms like pain, itchiness, swelling, bleeding, burning, etc.

What are piles, and how do they occur?
Piles or Hemorrhoids are swellings that develop in the lower part of the large intestine (rectum) or around the opening of the anus.
Blood vessels, muscles, elastic fibers, and other tissues are involved in the inflammation of hemorrhoids or piles, either present inside the anus or outside the anus.
An enlarged anus may prolapse and protrude, causing severe pain and bleeding. Such swollen tissues lose their elasticity.
They result from excessive pressure in the rectal veins, which are caused by a variety of factors, including strenuous defecation, obesity, pregnancy, or old age.
Types of piles
Piles can be classified as internal and external based on their location to the dentate line. Internal piles are located inside the rectum, while external piles occur below the anal skin.
Internal piles are classified into four categories depending on the severity – 1st degree, 2nd degree, 3rd degree, and 4th-degree piles.
It is not true that external piles always occur outside. The growths may develop inside the anal opening and not be visible from the outside. An external pile appears as soft bluish or purplish tissue lumps within and around the anus.
Symptoms of anal piles
The most common symptoms associated with piles include:
Bleeding during bowel movements
Pain during bowel movements
Itching at the opening of the anal canal (anal itching)
Lump around the anus
Mucus discharge after bowel movements
Swelling or a hard lump around your anus
Leakage of stool
Read more: https://laserpiles.com/allopathy-vs-homeopathy-which-is-the-best-treatment-method-for-piles/
0 notes
Photo


Iron Cast || Destiny Soria || 384 pages -------------------------------------------------------- Top 3 Genres: Fantasy / Historical Fiction / Young Adult
Synopsis: In 1919, Ada Navarra—the intrepid daughter of immigrants—and Corinne Wells—a spunky, devil-may-care heiress—make an unlikely pair. But at the Cast Iron nightclub in Boston, anything and everything is possible. At night, on stage together, the two best friends, whose “afflicted” blood gives them the ability to create illusions through art, weave magic under the employ of Johnny Dervish, the club’s owner and a notorious gangster. By day, Ada and Corinne use these same skills to con the city’s elite in an attempt to keep the club afloat.
When a “job” goes awry and Ada is imprisoned, she realizes they’re on the precipice of danger. Only Corinne—her partner in crime—can break her out of Haversham Asylum. But once Ada is out, they face betrayal at every turn.
Finished: November 18th, 2019.
Progress: 10 / 15. 66.6% complete.
My Rating: ★★★★★. [5/5]
My Review: [Under the read more - NOT SPOILER FREE]
It feels like I finished this one much faster than I actually did, probably comparatively because I zoomed through this book much faster than most of my others this year LOL.
SHIT though this premise was so cool. And ORIGINAL. And so refreshing! This magic system – it's so unique and fascinating and I've never seen anything like it before. It's described so well and in so much detail and I devoured everything about it throughout the entire story, and now I need to know how hemopathy affects the entire world and I need a modern story about Ada's and Corrine's grand (or great-grand) children and how they're still best friends.
I LOVE the unfaltering female friendship, despite how different the two women are. I love that they're both severely flawed, and go through a good amount of character development by the end. I love the relationships with their mothers and families and other friends (sans a few specific people of course), and how Saint seems to be gay and James bisexual (though never explicitly stated, sad face), and the issues of Ada being both a hemopath AND black (bi-racial!!) were NEVER understated, and I just feel like this whole damn story was so well told, and both manages to capture the nuances of the oppressed AND weave a unique and beautiful magic system at the same time.
I NEED MORE BOOKS ABOUT HEMOPATHY. That's all I really know RN.
Also, the historical setting!! The writing captured this being in the 20's absolutely flawlessly, I felt. It was a true transportation to another time, and though I squee much harder at other aspects of fiction than I do over historical accuracy, I do have to raise my glass at how well it all was handled here.
There's so much more I really should say, to be fair to this book and give it justice, but my brain is going "buh." (Johnny's death at the end though – PERFECT KARMA, yeeees, SUCK IT ASSHOLE) (And that Corrine will probably never forgive Gabriel, and that that's actually accepted and okay, I NEVER see the aspect of never forgiving someone painted as something good, that is SO nice)
Okay, I'm actually out of thoughts now.
This is seriously such a wonderful example of everything I've been looking for in a book. I'm so happy it exists.
P.S. I NEED TO KNOW WHAT HAPPENED TO GORDON'S CAT. You can't just tell me it was found curled up next to his body and then not tell me it was adopted by another loving family, or by Ada or Corrine. 😭😭😭
#book reviews#iron cast#destiny soria#★★★★★#fantasy#historical fiction#young adult#magic#urban fantasy#alternate history#romance#favorites#stunning covers#owned#print book#stand alone#jomp original
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo
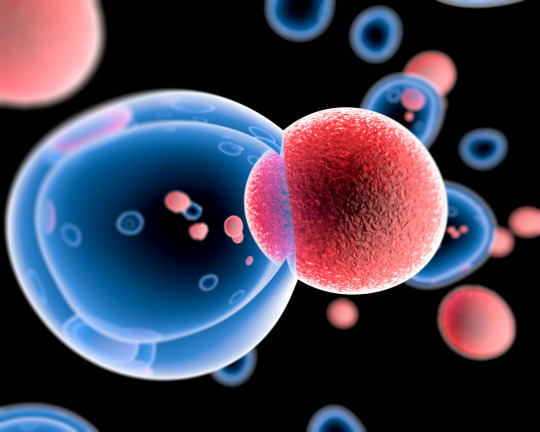
Stem Cell Therapy

Stem cells are the foundation for every organ and tissue in your body. They are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. There are many different types of stem cells that come from different places in the body or are formed at different times in our lives. These include embryonic stem cells that exist only at the earliest stages of development and various types of tissue-specific (or adult) stem cells that appear during fetal development and remain in our bodies throughout life.
Cell therapy involves grafting cells to restore the function of a tissue or organ. The aim is to provide long-term care to the patient through a single injection of therapeutic cells. These cells are obtained from pluripotent (can give all types of cells) or multipotent (can give a limited number of cell types) from the patient himself or from a donor. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. Researchers now know how to differentiate pluripotent cells into several cell types.
People who might benefit from stem cell therapies include those with spinal cord injuries, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, heart disease, stroke, burns, cancer and osteoarthritis.
The most used Multipotent stem cells, present throughout the body within the adipose, bone marrow, organ support tissues, but also from bones, cartilage, muscles ... These stem cells are particularly easy to take from adipose tissue or bone marrow. They can give rise to cartilaginous cells (chondrocytes), Osseous (ostheoblasts), fatty (adipocytes), muscle fibers (myocytes), cardiomyocytes ... They also secrete growth factors favorable to the surrounding cells and are sometimes used exclusively for this property. They also produce anti-inflammatory factors, which lead to local immunosuppression and promote the function of cells regulating immunity. These properties limit local inflammation and protect, a priori, against transplant rejection.
Other multipotent cells can be used in cell therapy, such as skin stem cells. The stem cells of the eye make it possible to repair lesions of the cornea. Hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow are the source of all blood cells: in the case of hematological cancer, they make it possible to rebuild a stock of healthy blood cells after chemotherapy. Umbilical cord blood contains immune-naive hematopoietic stem cells, and therefore very well tolerated in the event of a transplant. Cord blood is used to treat malignant hemopathies such as leukemia or lymphoma, or genetic diseases like Fanconi anemia. It offers a serious alternative to bone marrow transplantation in the absence of a compatible donor. However, the number of therapeutic cells recovered by cord is low. When therapeutic stem cells are taken from someone other than the patient, they are said to be allogeneic. Their use can pose problems of immune tolerance.
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
The indications for cell therapy are endless and the promise is real in many areas. Clinical fields such as that of neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson's or Alzheimer's diseases) or muscular degenerations (Duchenne muscular dystrophy) could be concerned if the researchers manage to produce different subtypes of neurons in large quantities and skeletal muscle cells. And how not to also imagine the possibility of producing blood cells, including platelet, in unlimited quantity, to cover the blood needs of hospitals? All assumptions are now allowed.
Stem cell researchers are making great advances in understanding normal development, figuring out what goes wrong in disease and developing and testing potential treatments to help patients. They still have much to learn, however, about how stem cells work in the body and their capacity for healing. Safe and effective treatments for most diseases, conditions and injuries are in the future.
There is certain information you should look into if you are considering a stem cell treatment, including a detailed description of the treatment and the science that supports it, the expected outcome and the risks. It is important to discuss any research or information you gather with your primary care physician and other trusted members of your healthcare team in deciding what is right for you.
CLINICS & DOCTORS LIST
Kristin Comella. PhD | Stem Cell | U.S. Stem Cell, Inc., 13794 NW4th Street, Suite 212 Sunrise, FL 33325
Regenerative Medicine Institute, Vincent Giampapa MD, F.A.C.S. Plastic Reconstructive Surgeon | Stem Cell | 89 Valley Rd, Montclair, NJ, 07042 USA
Advanced Orthopedic Specialists | Stem Cell | Genoa Business Park Drive 2305, Brighton, 48114 Michigan USA
Anatara Medicine & San Francisco Stem Cell | Stem Cell | 1700 California Street, Suite 520, San Francisco, CA 94109 USA
Beatriz Palma-Zevallos, SA-C Cosmetic Surgeon | Stem Cell | 118 S Pendleton St, Easley, SC, USA
Caring Medical & Rehabilitation Services – Chicagoland Office | Stem Cell | North Lake Street. Oak Park 715 Grayslake, 60030 Illinois USA
Darrow Stem Cell Institute | Stem Cell | Wilshere Boulevard 11645, Los Angeles, CA 90025 USA
Jonathan Landow, MD | Stem Cell | 420 Jericho Tpke, Jericho, NY 11753 USA
Manhattan Integrtive Medicine | Stem Cell | 330 West 58th Street, Suite 610, New York, NY 10019 USA
Pangenics Regenerative Center | Stem Cell | 3599 University Blvd, Suite 603, Jacksonville, FL 32218 USA
South Florida Bone Marrow / Stem Cell Transplant Institute, | Stem Cell | Ste 600 10301, Boynton Beach, FL 33437 USA
Stem Cell Carolina | Stem Cell | 7928 Counsel Place, #116 Matthews, NC 28105 USA
Charm – Center for Healing and Regenerative Medicine | Stem Cell | Ranch Road 2222 10815, Austin, TX &8730 USA
UCLA-UCI Alpha Stem Cell Clinic | Stem Cell | University of California Irvine, 845 Health Sciences Road, 1001 Gross Hall Irvine, CA 92697-1705 USA
U.S. STEM CELL, Inc, | Stem Cell | 1560 Sawgrass Corporate Parkway, 4th Floor, FL 33323 USA
U.S. STEM-CELL CLINIC, Michelle Parlo, PA-C Physician Assistant, Beatriz Palma-Zevallos, SA-C Cosmetic Surgeon, Antonio E. Blanco, MD | Stem Cell | 1290 Weston Road, Suite 203A, Weston, FL 33326 USA
INTERNATIONAL CLINICS & DOCTORS LIST
COSTA RICA
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE INSTITUTE, Vincent Giampapa, MD, F.A.C.S. Victor Urzola MD, Estaban Urzola MDS, Richard D. Striano D.C., RMSK, | Stem Cell | Avenida Escazu, Torre Lexus 3rd Floor San Jose, Costa Rica 101017
STEM CELLS TRANSPLANT INSTITUTE, Leslie Mesen MD | Stem Cell | Hospital Cima,Medical Tower II, Office 618, San Rafael, Escazú, San José, Costa Rica
CROATIA
ST. CATHERINE SPECIALITY HOSPITAL - STEM CELL | Stem Cell | Bračak 8, Bračak, 49210 Krapinsko-Zagorska Zupanija, Croatia
INDIA
KOKILABEN DHIRUBHAI AMBANI HOSPITAL | Stem Cell | Swaminarayan Complex Surat, 395001 Gujarat India
JAPAN
OMOTESANDO HELENE CLINIC | Stem Cell | 5-9-15 Minami Aoyama Minato-Ku, Minato, 107-0052 Tokyo Japan
MEXICO
STEM CELL THERAPY TIJUANA MEXICO, Hospital Angeles Tijuana | Stem Cell | Paseo de los Heroes 10999 – 309, Zona Urbana Rio Tijuana, 22010 Tijuana, B.C. Mexico
PROGENCELL – STEM CELL THERAPIES | Stem Cell | Medical clinic, Tijuana, Baja California, Mexico – In Plaza Comercial Pavillion
WORLD STEM CELL CLINIC | Stem Cell | Cancun, Quintana Roo, Mexico
PANAMA
STEM CELL INSTITUTE | Stem Cell | BICSA Financial Tower 63rd Floor, Calle Aquilino de la Guardia, Panama City, Panama
SOUTH AFRICA
THE MELROSE AESTHETIC CENTRE | Stem Cell | 3rd Floor, Medical Centre, Melrose Arch Johannesburg, 2196 Gauteng South Africa
THAILAND
STEMCELLS21| Stem Cell | Soi Ruam 3 Bangkok, 10330 Bangkok Thailand
UK
UK STEM CELLFOUNDATION | Stem Cell | 21 Albermarle Street, London, W1S4BS UK
MEDICA STEM CELLS | Stem Cell | 27 George Street, Marylebone, London, W1U3QA UK
UKRAINE
ILAYA MEDICAL STEM CELL CLINIC, R. Sulik MD & Neurologist | Stem Cell | Ivana Kramskogo Street 9, 03115 Kiev, Ukraine
ABLOU SREM CELL CLINIC | Stem Cell | Voznesens’kyy uzviz 23B, Kyiv – 02000, Ukraine
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A vampire detective who uses hemopathy to solve cases
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Angina Indicative of Malignant Hemopathies: About Two Cases
Summary
The malignant hemopathies can affect the pharynx tissues. It can manifest as necrotic and ulcerative damages of the pharyngeal mucosa. Although nonspecific, angina can indicate a malignant hemopathie. In front of a dragging tonsillitis associated with a persistent fever, the otolaryngologist (ENT) should request a hematologic assessment for an etiology search. We report a case of acute leukemia with myelofibrosis and a case of acute monoblastic leukemia revealed by tonsillitis.
Read more about this article: https://juniperpublishers.com/gjo/GJO.MS.ID.556140.php
Read more Juniper Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=I5SKhngAAAAJ&citation_for_view=I5SKhngAAAAJ:ufrVoPGSRksC
#Juniper Publishers Google Scholar#Otolaryngology#Laryngology#pharynx#Global Journal of Otolaryngology
0 notes
Text
Alive Supplement Side Effects, Dosage & How To Use It?
What food triggers tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis or tonsillitis, is also called angina, a word that comes from the Latin angere, which means to squeeze or strangle. The term angina expressed a sensation of pharyngeal constriction that can be observed in any inflammation at this level. According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, tonsillitis is an acute inflammation of viral or bacterial origin of the tonsils or pharyngeal mucosa.
Classification of Tonsillitis
The classification of tonsillitis takes into account the appearance of the oropharynx on physical examination, regardless of whether the etiology is viral or bacterial. Erythematous (reddish) and erythematous (reddish with white patches) tonsillitis (which account for about 90% of gross forms of tonsillitis), pseudomembranous, and ulcerative or ulceronecrotic are distinguished. Likewise, erythematous tonsillitis can be acute, recurrent and chronic, and the pseudomenbranous one that has no subdivision.
Acute tonsillitis
The tonsillitis viral constitute 50-90% of tonsillitis. There are numerous viruses involved, notably Epstein-Barr virus, herpes simplex, influenza, parainfluenza, Coxsackie, and adenovirus. The tonsillitis bacterial constitute 10-50% of tonsillitis, among bacteria, the main is Streptococcus pyogenes or Streptococcus hemolytic of group A.
It is transmitted by the respiratory route, through droplets of saliva expelled by coughing, sneezing or talking, from infected people. There is also transmission through contamination of food or water; on the contrary, fomites (contaminated objects) do not play an important role as a source of contagion.
Recurrent tonsillitis
It is characterized by repetitive episodes of tonsillitis, when the number of episodes is greater than 7 per year in one year, 5 per year in two years and three per year in three years. It is more common in children.
Chronic tonsillitis
The tonsillitis chronic are more frequent in adults, while recurrent tonsillitis are more common in children. It is a disease characterized by persistent infection of the tonsils, there are cases of very intense and repeated infections with serious systemic repercussions.
The duration period varies, there are transitory cases, decreasing the number of episodes and the intensity of the episodes over time, disappearing after a few years, while others last a lifetime.
Pseudomembranous tonsillitis
They can be caused by infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria.
Infectious mononucleosis tonsillitis is related to a primary infection by EBV (herpes group virus) that generates intense lymphocytic stimulation, leading to hypertrophy of lymphoid tissues.
In most cases, it affects adolescents and young adults. It is spread by air. While diphtheria tonsillitis is caused by a Corynebacterium diphtheriae poisoning and is rare in developed countries, but it is a re-emerging disease in the world.
Ulcerative and necrotic tonsillitis
When they are bilateral, hemorrhagic, often with associated gingivitis, a malignant hemopathy or agranulocytosis should be suspected. When it is unilateral, they mainly orient towards Vincent's tonsillitis. The other two conditions to be suspected are syphilitic chancre and tonsil cancer.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
The symptoms of tonsillitis classified in their different types of conditions and symptoms.
Acute tonsillitis
The symptoms of tonsillitis consist of the variable association of: fever, pharyngeal pain (constrictive or burn-type), reflex earache, and pain when swallowing. There may also be symptoms such as:
· Abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea, especially in children.
· Rashes.
· Reddish tonsils. Sometimes there is additional presence of a whitish material on the tonsils defining erythematous tonsillitis.
· The presence of satellite, submandibular or subdigastric cervical lymphadenopathies is common in tonsillitis of bacterial origin.
· The arguments that point towards a viral etiology are: moderate fever, cough, nasal congestion, conjunctivitis, pharyngeal vesicles, as well as the absence of adenopathies or, on the contrary, diffuse adenopathies.
Recurrent tonsillitis
It has the same symptoms as acute tonsillitis, only with repetitive episodes.
Chronic tonsillitis
It is said that it has an established profile: obstruction of the upper airways, enlargement of the tonsils and recurrent infections. In addition, the following signs and symptoms occur:
· Recurrent fevers.
· Pain when swallowing
· Halitosis.
· Mouth breathing
· Urinary incontinence
· Appetite and mood disorders.
· Snoring.
· Acute superinfections.
Pseudomembranous tonsillitis
By mononucllosis.
· The tonsils appear covered by whitish deposits that are strictly limited to the tonsil tissue, respecting the uvula, and can become detached and cause pain.
· It is associated with severe weakness or fatigue and may be accompanied by respiratory difficulties due to adenotonsillar hypertrophy.
· Petechiae of the soft palate.
By diphtheria.
· There are adherent whitish membranes, which exceed the limits of the tonsils and confluent.
· Rhinitis (nasal allergy) with often mucopurulent and unilateral rhinorrhea, as well as voluminous cervical lymphadenopathy.
· Exotoxin secretion.
· Myocarditis.
· Neurological condition (polyradiculoneuritis with paralysis of the veil and respiratory muscles).
· Renal involvement with glomerulonephritis.
Ulcerative and necrotic tonsillitis
Vincent's angina:
· Insidious onset in adolescents or young adults with a poor general condition (fatigue, overwork) and poor oral hygiene.
· General and functional signs are mild: subfebrile state, unilateral discrete pharyngeal pain, halitosis.
· Friable, grayish-white, purple material on the tonsil, covering a nonspecific ulceration, with raised and irregular edges.
Syphilitic tonsillitis:
· Unilateral ulceration of the tonsil with an indurated base and more voluminous adenopathy.
Naturally losing weight is a healthy and safe method of weight loss. It generally involves making small tweaks to your diet, exercise routine and lifestyle. In addition, when you're making small lifestyle changes (typical in natural weight loss), you're more likely to continue these habits long-term. A combination of these factors can help you lose weight naturally and in safe and healthy manner. Alive Customer Reviews
0 notes
Link
Xiantao Dexing Plastic Products Co., Ltd.
86-728-2612058 18971046231
3 Shengli Street, Xiantao, Hubei, China
Xiantao Dexing Plastic Products Co., Ltd. specializes in the development, production and marketing of plastic products and nonwoven fabric. Founded in 2003, the company now covers an area of 40 Mu, in which 12000 square meters is building area, with registered capital of 15 million RMB and total investment of 120 million RMB. Located in Pengchang: the famous town in its non woven fabric, the company owns 20 set advanced production equipment of different kinds and over 200 professional technicians. With the annual production of 8000ton PE breathable film and laminate fabric and the annual production of1500ton MB meltblown fabric, the company plays an important role in driving the local nonwoven industry cluster to a greater development. In recent years, with the tenet of innovation and progressing, based on technological R&D, the company has achieved a full development and become a promising young enterprise in China s non-woven industry. The company s PE breathable film and laminate fabric have been authorized by China National Textile And Apparel Council (CNTAC) and China Spinning Melt Branch, and meet the anti microbial, anti hemopathy and anti alcohol standards set by Ministry of Health of PRC, which is characterized by their moisture resistance, air permeability, water resistance, flexibility, lightweight, innoxious and flavorless features, and have been widely used in different fields such as health, medical, protection, civil work, communication, environmental protection, agriculture, etc. The company is able to produce laminate nonwoven fabric of different colors and specifications with different features such as aging resistance, inflaming retarding, antibiosis and antistatic features. Dexing is now fully devoting itself in learning, innovation, development and exploration. Following the principle of quality first, environmental protection foremost , we will sincerely provide our customers professional products and pure hearted services. Dexing is exploring its way to a greater success. We are fully confident that our company is sure to become your sincere friend and supplier in the future. We will bend ourselves to provide you not only green products with stable performance and reasonable prices, but also considerate alllife services. Base on hi tech and the concept of environmental protection to produce customer satisfied products. We deeply believe that customers success is our great motivation for further development.
0 notes
Text
Iron Cast by Destiny Soria review
2 out of 5 stars on goodreads
I bought this book on Amazon and it turned out to be an ARC! (I did receive my money back but I kind of wonder if that's the reason why I didn't like the book so much)
Real Rating- I almost want to rate it a 1 but it wasn't horrible horrible. Just didn't meet my expectations.
What It's About - It's about these two best friends who live in Boston in like 1919 or something and they are hemopaths which are people who suffer this blood disorder. This blood disorder allows them to create illusions with their art (ex: singing, instruments, acting, painting and poetry). Hemopathy is also illegal. Ava (who is a diverse character) gets caught at this asylum and shit goes down from there. Also add in some politics, gangsters, poems and very little romance and that's the book.
Overall Reading Experience - Snooooze fest! I tried my best to get through this book as fast as possible. I was so excited to read a book about a (what I consider) black girl during 1919 that didn't involve slavery. This book was slow. You barely could tell Ava and Corinne apart, only through their love interests tbh. The romance was ok (Only with Ava and Charlie though!). Like, Idk if it's because I got an arc of this or what
Word Vomit Of What I Really Think - First it was boring, barely anything happened and I could care less about the characters. When they were scared to death I didn't feel that pain like I should have and this sucks because I really wanted to like this book. This book reminds me SOOOOOO much of The Diviners by Libba Bray and that kinda turned me away from it also. I hated how Corinne still damn near wanted Gabriel after what he did and I was just disgusted by their scenes to begin with. I read some of the reviews and people were happy about the diverse character but honestly, it barely showed. It popped up here and there but nothing significant. Especially the way racist things that happened were just rolled in there and damn near forgotten about. Anyways I can go on and on about numerous things but I won't. The cover was the only good thing I loved about this book. After that you lost me. Now I'm off to read something that really gets my heart pounding.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Is that... an angel? Saturn haven’t been able to draw in a bit, sketched this recently, i really like it
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings
Drug Online
Celestene 2 mg Generic medicine of the therapeutic class: Anti-inflammatory active ingredients: Betamethasone
Important to know about Celestene ?
This medication is a corticosteroid.
It is indicated in certain diseases, where it is used for its anti-inflammatory effect.
celestene 2mg what is it used for and indication ?
Conditions or diseases:
Collagenosis and connectivitis:
Evolutionary thrusts of systemic diseases, including: systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, polymyositis, visceral sarcoidosis.
Dermatological:
Severe autoimmune bullous dermatoses, especially pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid.
Serious forms of angiomas of the infant.
Some forms of lichen plan.
Some acute urticaria.
Severe forms of neutrophilic dermatoses.
Digestives:
Evolutionary thrusts of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Chronic active autoimmune hepatitis (with or without cirrhosis).
Severe acute alcoholic hepatitis, histologically proven.
Endocrine:
Subacute Thyroiditis of severe De Quervain.
Some hypercalcemia.
Hematologic:
Severe immunological thrombocytopenic purpura.
Autoimmune haemolytic anemias.
In combination with various chemotherapies in the treatment of lymphoid malignant hemopathies.
Chronic erythroblastopenia, acquired or congenital.
Infectious:
Tuberculous pericarditis and severe forms of life-threatening tuberculosis.
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with severe hypoxia.
Neoplasms:
Antiemetic treatment during antineoplastic chemotherapy.
Oedematous and inflammatory thrust associated with antineoplastic treatments (radio and chemotherapy).
Nephrological:
Nephrotic syndrome with minimal glomerular lesions.
Nephrotic syndrome of primitive segmental and focal hyalinoses.
Stages III and IV of lupus nephropathy.
Intrarenal granulomatous sarcoidosis.
Vasculitis with renal involvement.
Primitive extracapillary glomerulonephritis
Neurological:
Gravis.
Cerebral edema of tumoral cause.
Chronic polyradiculoneuropathy, idiopathic, inflammatory.
Infant spasm (West syndrome), Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Multiple sclerosis in relapse, in relays of an intravenous corticotherapy.
Ophthalmological:
Uveitis anterior and posterior severe.
Exophthalmos oedematous.
Some optic neuropathies, in reliance on intravenous corticosteroids (in this indication, oral first-line is not recommended).
ENT:
Some serous otitis.
Nasosinus polypsis.
Some acute or chronic sinusitis.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis in short cure.
Stridulous acute laryngitis (subglottic laryngitis) in children.
Respiratory:
Persistent asthma, preferably in short course, in case of failure of inhaled treatment at high doses.
Exacerbations of asthma, especially severe acute asthma.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in assessing the reversibility of obstructive syndrome.
Sarcoidosis progressive.
Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
Rheumatologic:
Rheumatoid arthritis and some polyarthritis.
Rhizomelic pseudopolyarthritis and Horton’s disease.
Acute articular rhumatism.
Severe and rebellious cervicobrachial neuralgia.
Organ Transplantation and Hematopoietic Allogeneic Stem Cells:
Prophylaxis or treatment of transplant rejection.
Prophylaxis or treatment of graft-versus-host disease.
Celestene Dosage
Oral way.
· Anti-inflammatory equivalence (equipotence) for 5 mg prednisone: 0.75 mg betamethasone.
The tablets can be swallowed as is with a little water or dissolved in a little water, preferably during meals.
RESERVED FOR ADULTS
Celestene 2 mg is particularly suitable for the treatment of attack or short-term treatments requiring medium or high doses in adults.
In maintenance treatment, there are more appropriate dosages.
In children, there are more appropriate dosages and pharmaceutical forms.
· The dosage varies according to the diagnosis, the severity of the condition, the prognosis, the patient’s response and the tolerance to the treatment.
Attack treatment : 0.05 mg to 0.2 mg / kg / day (0.35 mg to 1.2 mg / kg / day prednisone equivalent). As an indication : 1.5 to 6 tablets in an adult of 60 kg.
In severe inflammatory diseases , the dosage varies from 0.1 to 0.2 mg / kg / day of betamethasone (0.75 mg / kg / day to 1.2 mg / kg / day equivalent prednisone). As an indication : 3 to 6 tablets per day for an adult of 60 kg.
The very exceptional situations may require higher doses.
IN GENERAL
Treatment at the “attack dose” should be continued until the disease is well controlled. Decay must be slow. Obtaining a weaning is the goal. Maintaining a maintenance dose (minimum effective dose) is a compromise that is sometimes necessary.
For prolonged treatment at high doses, the first doses can be divided into two daily doses. Thereafter, the daily dose may be administered as a single dose preferably in the morning during the meal.
· Discontinuation of treatment
The rate of withdrawal depends mainly on the duration of treatment, the starting dose and the disease.
The treatment causes resting secretions of ACTH and cortisol with sometimes lasting adrenal insufficiency. When weaning, stopping should be done gradually, in stages because of the risk of relapse: reduction of 10% every 8 to 15 days on average.
For short courses of less than 10 days, stopping treatment does not require decay.
When decreasing doses from celestene (prolonged cure):
at the dosage of 5 to 7 mg of prednisone equivalent, when the causal disease no longer requires corticosteroid treatment, it is desirable to replace the synthetic corticoid with 20 mg / day of hydrocortisone until recovery of corticotropic function. If corticosteroid therapy is to be maintained at less than 5 mg prednisone equivalent per day, a small dose of hydrocortisone can be added to achieve a hydrocortisone equivalent of 20 to 30 mg per day. When the patient is only under hydrocortisone, it is possible to test the corticotropic axis by endocrine tests. These tests do not eliminate the possibility of adrenal insufficiency during a stress.
Under hydrocortisone or even at a distance from arrest, the patient should be advised of the need to increase the usual dosage or to resume replacement therapy (eg 100 mg hydrocortisone intramuscularly every 6 to 8 hours) in case stress: surgery, trauma, infection.
Contraindications
This medication is generally contraindicated in the following situations (there is, however, no absolute contraindication for a life-saving corticosteroid therapy):
Any infectious condition other than the specified indications ( see section Therapeutic indications ),
Certain evolving viroses (in particular hepatitis, herpes, chickenpox, shingles),
Psychotic states not yet controlled by treatment,
Live vaccines
· Hyper-sensitivity to one of the compounds,
Phenylketonuria (linked to the presence of aspartame).
This drug is generally not recommended in combination with non-antiarrhythmic drugs, giving torsades de pointes ( see section Interactions with other drugs and other forms of interactions ).
How it works Celestene
Pharmacotherapeutic group: GLUCOCORTICOID – SYSTEMIC USE
( H. Non-sexual hormones )
Physiological glucocorticoids (cortisone and hydrocortisone) are essential metabolic hormones. Synthetic corticosteroids, including this specialty, are used primarily for their anti-inflammatory effect. In high doses, they reduce the immune response.
Their metabolic and sodium retention effect is less than that of hydrocortisone.
Celestene 2 mg Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
This drug, essential, is most often well tolerated when one follows the recommendations and especially the diet (see Warnings and precautions). It may nevertheless result, according to the dose and the duration of the treatment, more or less troublesome effects.
The most frequently encountered are:
· Swelling and redness of the face, weight gain
· Appearance of blue
· Elevation of blood pressure
· Excitement and sleep disorders
· Bone fragility
· Modification of certain biological parameters (salt, sugar, potassium), which may require a diet or additional treatment.
Other, much rarer effects have been observed:
· Risk of insufficiency of secretion of the adrenal gland
· Growth disorder in children
· Rule disorders
· Muscle weakness
· Hiccups, ulcers and other digestive disorders
· Skin disorders
· Some forms of glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye) and cataracts (opacification of the lens).
Celestene Interactions
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances that do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions for use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased elimination of salicylates by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct it if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer antiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of the oral anticoagulant and that of the coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, strengthen supervision: biological control 8 th day and every 15 days during and after corticosteroid discontinuation.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Increased risk of hypokalemia by additive effect.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary especially in case of digitalis therapy.
Digitalis
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Aggravation by heparin of the hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment longer than 10 days.
The association must be justified, strengthen surveillance.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adjustment of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after discontinuation of the enzyme inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary self-monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of the antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after discontinuation.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of isoniazid. Invoked mechanism: increased hepatic metabolism of isoniazid and decreased glucocorticoid.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensive
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Warnings and Precautions
Special warnings:
· In cases of peptic ulcer disease, corticosteroids are not contraindicated if anti-ulcer therapy is combined.
In case of ulcerative history, corticosteroid therapy may be prescribed, with clinical monitoring and if necessary after fibroscopy.
· Corticosteroid therapy can promote the occurrence of various infectious complications due to bacteria, yeasts and parasites. The occurrence of malignant yellows is a significant risk.
All subjects from an endemic area (tropical, subtropical, southern Europe) should have parasitological examination of stool and systematic eradication before corticosteroid therapy.
Evidence of an infection may be masked by corticosteroid therapy.
It is important, before the start of treatment, to remove any possibility of visceral foci, particularly tuberculosis, and to monitor, during treatment, the appearance of infectious pathologies.
In case of old tuberculosis, prophylactic anti-tuberculosis treatment is necessary, if there are important radiological sequelae and if it can not be ensured that a well-conducted treatment of 6 months with rifampicin has been given.
· The use of corticosteroids requires particularly appropriate monitoring, especially in elderly patients and in cases of ulcerative colitis (risk of perforation), recent intestinal anastomoses, renal failure, hepatic insufficiency, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis.
· This medicine contains lactose. Its use is not recommended in patients with galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose or galactose malabsorption syndrome (rare hereditary diseases).
Precautions for use
· In case of long-term corticosteroid treatment :
o A diet low in fast and hyperprotid absorption sugars must be associated, because of the hyperglycemic effect and the protein catabolism with negativization of the nitrogen balance.
o Hydrosoduced retention is usual, partly responsible for a possible rise in blood pressure. Sodium lapport will be reduced for daily dosages greater than 15 or 20 mg prednisone equivalent and moderate in long-term low dose treatments.
o Potassium supplementation is justified only for high-dose treatments, prescribed for a long time or in case of risk of rhythm disorders or association with hypokalaemic treatment.
o The patient must always have a calcium and vitamin D intake.
o When corticosteroid therapy is essential, diabetes and high blood pressure are not contraindications, but treatment can lead to imbalance. Their management should be re-evaluated.
o Patients should avoid contact with individuals with chickenpox or measles.
· Attention is drawn to athletes , this specialty containing an active ingredient that can induce a positive reaction of the tests performed during anti-doping controls.
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances which do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions of use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased salicylate elimination by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after stopping corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer anantiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of oral lanticoagulant and coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, reinforce the monitoring: biological control on the 8th day, then every 15 days during the corticotherapy and after its stop.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Heparin aggravation of hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment greater than 10 days.
Association must be justified, strengthen monitoring.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and the efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adaptation of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after the end of the enzymatic inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after stopping.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of lisoniazide. Invoked mechanism: increased lisoniazide hepatic metabolism and decreased glucocorticoid metabolism.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensives
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Drive and use machines:
Not applicable.
PREGNANCY / BREAST FEEDING / FERTILITY
celestone during pregnancy
In animals, the experiment shows a teratogenic effect that varies according to the species.In humans, there is a placental transfer. However, epidemiological studies have not detected any risk of malformation related to taking corticosteroids during
st quarter. In chronic diseases, requiring treatment throughout pregnancy, a slight intrauterine growth retardation is possible. Neonatal adrenal insufficiency has been observed exceptionally after high dose corticosteroid therapy. It is justified to observe a period of clinical surveillance (weight, diuresis) and biological monitoring of the newborn.
As a result, corticosteroids may be prescribed during pregnancy, if needed.
Breastfeeding
In case of treatment at large doses and chronically, breastfeeding is not recommended.
To be effective, this medicine should be used regularly. However, if you miss a dose, continue the treatment normally.
What happens if I overdose from Celestene ?
Call your doctor or pharmacist if you have used CELESTENE 2 mg dispersible tablet breakable in greater or greater amounts than prescribed
What is Forms and Composition?
FORMS and PRESENTATIONS
Dispersible 2 mg tablet (white): Bottle of 20.
COMPOSITION
p cp betamethasone 2 mg
Excipients: granulated lactose monohydrate and cellulose powder 75/25 (Cellactose), crospovidone (Polyplasdone XL 10), aspartame, magnesium stearate.
Excipients with known effect: aspartame (E951), lactose.
NOT’s
Edrug-online contains comprehensive and detailed information about drugs available in the medical field, and is divided into four sections:
general information:
Includes a general description of the drug, its use, brand names, FAQs, and relevant news and articles
Additional information:
General explanation about dealing with the medicine: how to take the medicine, the doses and times of it, the start and duration of its effectiveness, the recommended diet during the period of taking the medicine, the method of storage and storage, recommendations in cases for forgetting the dose and instructions to stop taking the drug and take additional doses.
Special warnings:
For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the elderly, boys and drivers, and use before surgery.
Side effects:
It treats possible side effects and drug interactions that require attention and its effect on continuous use.
The information contained in this medicine is based on medical literature, but it is not a substitute for consulting a doctor.
The post celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings appeared first on Drug Online.
from Drug Online https://bit.ly/2Nk4VuO via Edrug Online from faculty of medicine https://bit.ly/2Q8LkyX via Faculty of Medicine
0 notes
Text
celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings
Drug Online
Celestene 2 mg Generic medicine of the therapeutic class: Anti-inflammatory active ingredients: Betamethasone
Important to know about Celestene ?
This medication is a corticosteroid.
It is indicated in certain diseases, where it is used for its anti-inflammatory effect.
celestene 2mg what is it used for and indication ?
Conditions or diseases:
Collagenosis and connectivitis:
Evolutionary thrusts of systemic diseases, including: systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, polymyositis, visceral sarcoidosis.
Dermatological:
Severe autoimmune bullous dermatoses, especially pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid.
Serious forms of angiomas of the infant.
Some forms of lichen plan.
Some acute urticaria.
Severe forms of neutrophilic dermatoses.
Digestives:
Evolutionary thrusts of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Chronic active autoimmune hepatitis (with or without cirrhosis).
Severe acute alcoholic hepatitis, histologically proven.
Endocrine:
Subacute Thyroiditis of severe De Quervain.
Some hypercalcemia.
Hematologic:
Severe immunological thrombocytopenic purpura.
Autoimmune haemolytic anemias.
In combination with various chemotherapies in the treatment of lymphoid malignant hemopathies.
Chronic erythroblastopenia, acquired or congenital.
Infectious:
Tuberculous pericarditis and severe forms of life-threatening tuberculosis.
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with severe hypoxia.
Neoplasms:
Antiemetic treatment during antineoplastic chemotherapy.
Oedematous and inflammatory thrust associated with antineoplastic treatments (radio and chemotherapy).
Nephrological:
Nephrotic syndrome with minimal glomerular lesions.
Nephrotic syndrome of primitive segmental and focal hyalinoses.
Stages III and IV of lupus nephropathy.
Intrarenal granulomatous sarcoidosis.
Vasculitis with renal involvement.
Primitive extracapillary glomerulonephritis
Neurological:
Gravis.
Cerebral edema of tumoral cause.
Chronic polyradiculoneuropathy, idiopathic, inflammatory.
Infant spasm (West syndrome), Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Multiple sclerosis in relapse, in relays of an intravenous corticotherapy.
Ophthalmological:
Uveitis anterior and posterior severe.
Exophthalmos oedematous.
Some optic neuropathies, in reliance on intravenous corticosteroids (in this indication, oral first-line is not recommended).
ENT:
Some serous otitis.
Nasosinus polypsis.
Some acute or chronic sinusitis.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis in short cure.
Stridulous acute laryngitis (subglottic laryngitis) in children.
Respiratory:
Persistent asthma, preferably in short course, in case of failure of inhaled treatment at high doses.
Exacerbations of asthma, especially severe acute asthma.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in assessing the reversibility of obstructive syndrome.
Sarcoidosis progressive.
Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
Rheumatologic:
Rheumatoid arthritis and some polyarthritis.
Rhizomelic pseudopolyarthritis and Horton’s disease.
Acute articular rhumatism.
Severe and rebellious cervicobrachial neuralgia.
Organ Transplantation and Hematopoietic Allogeneic Stem Cells:
Prophylaxis or treatment of transplant rejection.
Prophylaxis or treatment of graft-versus-host disease.
Celestene Dosage
Oral way.
· Anti-inflammatory equivalence (equipotence) for 5 mg prednisone: 0.75 mg betamethasone.
The tablets can be swallowed as is with a little water or dissolved in a little water, preferably during meals.
RESERVED FOR ADULTS
Celestene 2 mg is particularly suitable for the treatment of attack or short-term treatments requiring medium or high doses in adults.
In maintenance treatment, there are more appropriate dosages.
In children, there are more appropriate dosages and pharmaceutical forms.
· The dosage varies according to the diagnosis, the severity of the condition, the prognosis, the patient’s response and the tolerance to the treatment.
Attack treatment : 0.05 mg to 0.2 mg / kg / day (0.35 mg to 1.2 mg / kg / day prednisone equivalent). As an indication : 1.5 to 6 tablets in an adult of 60 kg.
In severe inflammatory diseases , the dosage varies from 0.1 to 0.2 mg / kg / day of betamethasone (0.75 mg / kg / day to 1.2 mg / kg / day equivalent prednisone). As an indication : 3 to 6 tablets per day for an adult of 60 kg.
The very exceptional situations may require higher doses.
IN GENERAL
Treatment at the “attack dose” should be continued until the disease is well controlled. Decay must be slow. Obtaining a weaning is the goal. Maintaining a maintenance dose (minimum effective dose) is a compromise that is sometimes necessary.
For prolonged treatment at high doses, the first doses can be divided into two daily doses. Thereafter, the daily dose may be administered as a single dose preferably in the morning during the meal.
· Discontinuation of treatment
The rate of withdrawal depends mainly on the duration of treatment, the starting dose and the disease.
The treatment causes resting secretions of ACTH and cortisol with sometimes lasting adrenal insufficiency. When weaning, stopping should be done gradually, in stages because of the risk of relapse: reduction of 10% every 8 to 15 days on average.
For short courses of less than 10 days, stopping treatment does not require decay.
When decreasing doses from celestene (prolonged cure):
at the dosage of 5 to 7 mg of prednisone equivalent, when the causal disease no longer requires corticosteroid treatment, it is desirable to replace the synthetic corticoid with 20 mg / day of hydrocortisone until recovery of corticotropic function. If corticosteroid therapy is to be maintained at less than 5 mg prednisone equivalent per day, a small dose of hydrocortisone can be added to achieve a hydrocortisone equivalent of 20 to 30 mg per day. When the patient is only under hydrocortisone, it is possible to test the corticotropic axis by endocrine tests. These tests do not eliminate the possibility of adrenal insufficiency during a stress.
Under hydrocortisone or even at a distance from arrest, the patient should be advised of the need to increase the usual dosage or to resume replacement therapy (eg 100 mg hydrocortisone intramuscularly every 6 to 8 hours) in case stress: surgery, trauma, infection.
Contraindications
This medication is generally contraindicated in the following situations (there is, however, no absolute contraindication for a life-saving corticosteroid therapy):
Any infectious condition other than the specified indications ( see section Therapeutic indications ),
Certain evolving viroses (in particular hepatitis, herpes, chickenpox, shingles),
Psychotic states not yet controlled by treatment,
Live vaccines
· Hyper-sensitivity to one of the compounds,
Phenylketonuria (linked to the presence of aspartame).
This drug is generally not recommended in combination with non-antiarrhythmic drugs, giving torsades de pointes ( see section Interactions with other drugs and other forms of interactions ).
How it works Celestene
Pharmacotherapeutic group: GLUCOCORTICOID – SYSTEMIC USE
( H. Non-sexual hormones )
Physiological glucocorticoids (cortisone and hydrocortisone) are essential metabolic hormones. Synthetic corticosteroids, including this specialty, are used primarily for their anti-inflammatory effect. In high doses, they reduce the immune response.
Their metabolic and sodium retention effect is less than that of hydrocortisone.
Celestene 2 mg Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
This drug, essential, is most often well tolerated when one follows the recommendations and especially the diet (see Warnings and precautions). It may nevertheless result, according to the dose and the duration of the treatment, more or less troublesome effects.
The most frequently encountered are:
· Swelling and redness of the face, weight gain
· Appearance of blue
· Elevation of blood pressure
· Excitement and sleep disorders
· Bone fragility
· Modification of certain biological parameters (salt, sugar, potassium), which may require a diet or additional treatment.
Other, much rarer effects have been observed:
· Risk of insufficiency of secretion of the adrenal gland
· Growth disorder in children
· Rule disorders
· Muscle weakness
· Hiccups, ulcers and other digestive disorders
· Skin disorders
· Some forms of glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye) and cataracts (opacification of the lens).
Celestene Interactions
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances that do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions for use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased elimination of salicylates by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct it if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer antiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of the oral anticoagulant and that of the coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, strengthen supervision: biological control 8 th day and every 15 days during and after corticosteroid discontinuation.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Increased risk of hypokalemia by additive effect.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary especially in case of digitalis therapy.
Digitalis
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Aggravation by heparin of the hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment longer than 10 days.
The association must be justified, strengthen surveillance.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adjustment of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after discontinuation of the enzyme inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary self-monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of the antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after discontinuation.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of isoniazid. Invoked mechanism: increased hepatic metabolism of isoniazid and decreased glucocorticoid.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensive
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Warnings and Precautions
Special warnings:
· In cases of peptic ulcer disease, corticosteroids are not contraindicated if anti-ulcer therapy is combined.
In case of ulcerative history, corticosteroid therapy may be prescribed, with clinical monitoring and if necessary after fibroscopy.
· Corticosteroid therapy can promote the occurrence of various infectious complications due to bacteria, yeasts and parasites. The occurrence of malignant yellows is a significant risk.
All subjects from an endemic area (tropical, subtropical, southern Europe) should have parasitological examination of stool and systematic eradication before corticosteroid therapy.
Evidence of an infection may be masked by corticosteroid therapy.
It is important, before the start of treatment, to remove any possibility of visceral foci, particularly tuberculosis, and to monitor, during treatment, the appearance of infectious pathologies.
In case of old tuberculosis, prophylactic anti-tuberculosis treatment is necessary, if there are important radiological sequelae and if it can not be ensured that a well-conducted treatment of 6 months with rifampicin has been given.
· The use of corticosteroids requires particularly appropriate monitoring, especially in elderly patients and in cases of ulcerative colitis (risk of perforation), recent intestinal anastomoses, renal failure, hepatic insufficiency, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis.
· This medicine contains lactose. Its use is not recommended in patients with galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose or galactose malabsorption syndrome (rare hereditary diseases).
Precautions for use
· In case of long-term corticosteroid treatment :
o A diet low in fast and hyperprotid absorption sugars must be associated, because of the hyperglycemic effect and the protein catabolism with negativization of the nitrogen balance.
o Hydrosoduced retention is usual, partly responsible for a possible rise in blood pressure. Sodium lapport will be reduced for daily dosages greater than 15 or 20 mg prednisone equivalent and moderate in long-term low dose treatments.
o Potassium supplementation is justified only for high-dose treatments, prescribed for a long time or in case of risk of rhythm disorders or association with hypokalaemic treatment.
o The patient must always have a calcium and vitamin D intake.
o When corticosteroid therapy is essential, diabetes and high blood pressure are not contraindications, but treatment can lead to imbalance. Their management should be re-evaluated.
o Patients should avoid contact with individuals with chickenpox or measles.
· Attention is drawn to athletes , this specialty containing an active ingredient that can induce a positive reaction of the tests performed during anti-doping controls.
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances which do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions of use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased salicylate elimination by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after stopping corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer anantiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of oral lanticoagulant and coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, reinforce the monitoring: biological control on the 8th day, then every 15 days during the corticotherapy and after its stop.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Heparin aggravation of hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment greater than 10 days.
Association must be justified, strengthen monitoring.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and the efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adaptation of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after the end of the enzymatic inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after stopping.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of lisoniazide. Invoked mechanism: increased lisoniazide hepatic metabolism and decreased glucocorticoid metabolism.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensives
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Drive and use machines:
Not applicable.
PREGNANCY / BREAST FEEDING / FERTILITY
celestone during pregnancy
In animals, the experiment shows a teratogenic effect that varies according to the species.In humans, there is a placental transfer. However, epidemiological studies have not detected any risk of malformation related to taking corticosteroids during
st quarter. In chronic diseases, requiring treatment throughout pregnancy, a slight intrauterine growth retardation is possible. Neonatal adrenal insufficiency has been observed exceptionally after high dose corticosteroid therapy. It is justified to observe a period of clinical surveillance (weight, diuresis) and biological monitoring of the newborn.
As a result, corticosteroids may be prescribed during pregnancy, if needed.
Breastfeeding
In case of treatment at large doses and chronically, breastfeeding is not recommended.
To be effective, this medicine should be used regularly. However, if you miss a dose, continue the treatment normally.
What happens if I overdose from Celestene ?
Call your doctor or pharmacist if you have used CELESTENE 2 mg dispersible tablet breakable in greater or greater amounts than prescribed
What is Forms and Composition?
FORMS and PRESENTATIONS
Dispersible 2 mg tablet (white): Bottle of 20.
COMPOSITION
p cp betamethasone 2 mg
Excipients: granulated lactose monohydrate and cellulose powder 75/25 (Cellactose), crospovidone (Polyplasdone XL 10), aspartame, magnesium stearate.
Excipients with known effect: aspartame (E951), lactose.
NOT’s
Edrug-online contains comprehensive and detailed information about drugs available in the medical field, and is divided into four sections:
general information:
Includes a general description of the drug, its use, brand names, FAQs, and relevant news and articles
Additional information:
General explanation about dealing with the medicine: how to take the medicine, the doses and times of it, the start and duration of its effectiveness, the recommended diet during the period of taking the medicine, the method of storage and storage, recommendations in cases for forgetting the dose and instructions to stop taking the drug and take additional doses.
Special warnings:
For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the elderly, boys and drivers, and use before surgery.
Side effects:
It treats possible side effects and drug interactions that require attention and its effect on continuous use.
The information contained in this medicine is based on medical literature, but it is not a substitute for consulting a doctor.
The post celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings appeared first on Drug Online.
from Drug Online https://bit.ly/2Nk4VuO via Edrug Online
0 notes
Text
celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings
Drug Online
Celestene 2 mg Generic medicine of the therapeutic class: Anti-inflammatory active ingredients: Betamethasone
Important to know about Celestene ?
This medication is a corticosteroid.
It is indicated in certain diseases, where it is used for its anti-inflammatory effect.
celestene 2mg what is it used for and indication ?
Conditions or diseases:
Collagenosis and connectivitis:
Evolutionary thrusts of systemic diseases, including: systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, polymyositis, visceral sarcoidosis.
Dermatological:
Severe autoimmune bullous dermatoses, especially pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid.
Serious forms of angiomas of the infant.
Some forms of lichen plan.
Some acute urticaria.
Severe forms of neutrophilic dermatoses.
Digestives:
Evolutionary thrusts of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Chronic active autoimmune hepatitis (with or without cirrhosis).
Severe acute alcoholic hepatitis, histologically proven.
Endocrine:
Subacute Thyroiditis of severe De Quervain.
Some hypercalcemia.
Hematologic:
Severe immunological thrombocytopenic purpura.
Autoimmune haemolytic anemias.
In combination with various chemotherapies in the treatment of lymphoid malignant hemopathies.
Chronic erythroblastopenia, acquired or congenital.
Infectious:
Tuberculous pericarditis and severe forms of life-threatening tuberculosis.
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with severe hypoxia.
Neoplasms:
Antiemetic treatment during antineoplastic chemotherapy.
Oedematous and inflammatory thrust associated with antineoplastic treatments (radio and chemotherapy).
Nephrological:
Nephrotic syndrome with minimal glomerular lesions.
Nephrotic syndrome of primitive segmental and focal hyalinoses.
Stages III and IV of lupus nephropathy.
Intrarenal granulomatous sarcoidosis.
Vasculitis with renal involvement.
Primitive extracapillary glomerulonephritis
Neurological:
Gravis.
Cerebral edema of tumoral cause.
Chronic polyradiculoneuropathy, idiopathic, inflammatory.
Infant spasm (West syndrome), Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.
Multiple sclerosis in relapse, in relays of an intravenous corticotherapy.
Ophthalmological:
Uveitis anterior and posterior severe.
Exophthalmos oedematous.
Some optic neuropathies, in reliance on intravenous corticosteroids (in this indication, oral first-line is not recommended).
ENT:
Some serous otitis.
Nasosinus polypsis.
Some acute or chronic sinusitis.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis in short cure.
Stridulous acute laryngitis (subglottic laryngitis) in children.
Respiratory:
Persistent asthma, preferably in short course, in case of failure of inhaled treatment at high doses.
Exacerbations of asthma, especially severe acute asthma.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in assessing the reversibility of obstructive syndrome.
Sarcoidosis progressive.
Diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis.
Rheumatologic:
Rheumatoid arthritis and some polyarthritis.
Rhizomelic pseudopolyarthritis and Horton’s disease.
Acute articular rhumatism.
Severe and rebellious cervicobrachial neuralgia.
Organ Transplantation and Hematopoietic Allogeneic Stem Cells:
Prophylaxis or treatment of transplant rejection.
Prophylaxis or treatment of graft-versus-host disease.
Celestene Dosage
Oral way.
· Anti-inflammatory equivalence (equipotence) for 5 mg prednisone: 0.75 mg betamethasone.
The tablets can be swallowed as is with a little water or dissolved in a little water, preferably during meals.
RESERVED FOR ADULTS
Celestene 2 mg is particularly suitable for the treatment of attack or short-term treatments requiring medium or high doses in adults.
In maintenance treatment, there are more appropriate dosages.
In children, there are more appropriate dosages and pharmaceutical forms.
· The dosage varies according to the diagnosis, the severity of the condition, the prognosis, the patient’s response and the tolerance to the treatment.
Attack treatment : 0.05 mg to 0.2 mg / kg / day (0.35 mg to 1.2 mg / kg / day prednisone equivalent). As an indication : 1.5 to 6 tablets in an adult of 60 kg.
In severe inflammatory diseases , the dosage varies from 0.1 to 0.2 mg / kg / day of betamethasone (0.75 mg / kg / day to 1.2 mg / kg / day equivalent prednisone). As an indication : 3 to 6 tablets per day for an adult of 60 kg.
The very exceptional situations may require higher doses.
IN GENERAL
Treatment at the “attack dose” should be continued until the disease is well controlled. Decay must be slow. Obtaining a weaning is the goal. Maintaining a maintenance dose (minimum effective dose) is a compromise that is sometimes necessary.
For prolonged treatment at high doses, the first doses can be divided into two daily doses. Thereafter, the daily dose may be administered as a single dose preferably in the morning during the meal.
· Discontinuation of treatment
The rate of withdrawal depends mainly on the duration of treatment, the starting dose and the disease.
The treatment causes resting secretions of ACTH and cortisol with sometimes lasting adrenal insufficiency. When weaning, stopping should be done gradually, in stages because of the risk of relapse: reduction of 10% every 8 to 15 days on average.
For short courses of less than 10 days, stopping treatment does not require decay.
When decreasing doses from celestene (prolonged cure):
at the dosage of 5 to 7 mg of prednisone equivalent, when the causal disease no longer requires corticosteroid treatment, it is desirable to replace the synthetic corticoid with 20 mg / day of hydrocortisone until recovery of corticotropic function. If corticosteroid therapy is to be maintained at less than 5 mg prednisone equivalent per day, a small dose of hydrocortisone can be added to achieve a hydrocortisone equivalent of 20 to 30 mg per day. When the patient is only under hydrocortisone, it is possible to test the corticotropic axis by endocrine tests. These tests do not eliminate the possibility of adrenal insufficiency during a stress.
Under hydrocortisone or even at a distance from arrest, the patient should be advised of the need to increase the usual dosage or to resume replacement therapy (eg 100 mg hydrocortisone intramuscularly every 6 to 8 hours) in case stress: surgery, trauma, infection.
Contraindications
This medication is generally contraindicated in the following situations (there is, however, no absolute contraindication for a life-saving corticosteroid therapy):
Any infectious condition other than the specified indications ( see section Therapeutic indications ),
Certain evolving viroses (in particular hepatitis, herpes, chickenpox, shingles),
Psychotic states not yet controlled by treatment,
Live vaccines
· Hyper-sensitivity to one of the compounds,
Phenylketonuria (linked to the presence of aspartame).
This drug is generally not recommended in combination with non-antiarrhythmic drugs, giving torsades de pointes ( see section Interactions with other drugs and other forms of interactions ).
How it works Celestene
Pharmacotherapeutic group: GLUCOCORTICOID – SYSTEMIC USE
( H. Non-sexual hormones )
Physiological glucocorticoids (cortisone and hydrocortisone) are essential metabolic hormones. Synthetic corticosteroids, including this specialty, are used primarily for their anti-inflammatory effect. In high doses, they reduce the immune response.
Their metabolic and sodium retention effect is less than that of hydrocortisone.
Celestene 2 mg Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
This drug, essential, is most often well tolerated when one follows the recommendations and especially the diet (see Warnings and precautions). It may nevertheless result, according to the dose and the duration of the treatment, more or less troublesome effects.
The most frequently encountered are:
· Swelling and redness of the face, weight gain
· Appearance of blue
· Elevation of blood pressure
· Excitement and sleep disorders
· Bone fragility
· Modification of certain biological parameters (salt, sugar, potassium), which may require a diet or additional treatment.
Other, much rarer effects have been observed:
· Risk of insufficiency of secretion of the adrenal gland
· Growth disorder in children
· Rule disorders
· Muscle weakness
· Hiccups, ulcers and other digestive disorders
· Skin disorders
· Some forms of glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye) and cataracts (opacification of the lens).
Celestene Interactions
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances that do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions for use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased elimination of salicylates by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct it if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer antiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of the oral anticoagulant and that of the coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, strengthen supervision: biological control 8 th day and every 15 days during and after corticosteroid discontinuation.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Increased risk of hypokalemia by additive effect.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary especially in case of digitalis therapy.
Digitalis
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Aggravation by heparin of the hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment longer than 10 days.
The association must be justified, strengthen surveillance.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adjustment of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after discontinuation of the enzyme inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary self-monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of the antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after discontinuation.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of isoniazid. Invoked mechanism: increased hepatic metabolism of isoniazid and decreased glucocorticoid.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensive
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Warnings and Precautions
Special warnings:
· In cases of peptic ulcer disease, corticosteroids are not contraindicated if anti-ulcer therapy is combined.
In case of ulcerative history, corticosteroid therapy may be prescribed, with clinical monitoring and if necessary after fibroscopy.
· Corticosteroid therapy can promote the occurrence of various infectious complications due to bacteria, yeasts and parasites. The occurrence of malignant yellows is a significant risk.
All subjects from an endemic area (tropical, subtropical, southern Europe) should have parasitological examination of stool and systematic eradication before corticosteroid therapy.
Evidence of an infection may be masked by corticosteroid therapy.
It is important, before the start of treatment, to remove any possibility of visceral foci, particularly tuberculosis, and to monitor, during treatment, the appearance of infectious pathologies.
In case of old tuberculosis, prophylactic anti-tuberculosis treatment is necessary, if there are important radiological sequelae and if it can not be ensured that a well-conducted treatment of 6 months with rifampicin has been given.
· The use of corticosteroids requires particularly appropriate monitoring, especially in elderly patients and in cases of ulcerative colitis (risk of perforation), recent intestinal anastomoses, renal failure, hepatic insufficiency, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis.
· This medicine contains lactose. Its use is not recommended in patients with galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose or galactose malabsorption syndrome (rare hereditary diseases).
Precautions for use
· In case of long-term corticosteroid treatment :
o A diet low in fast and hyperprotid absorption sugars must be associated, because of the hyperglycemic effect and the protein catabolism with negativization of the nitrogen balance.
o Hydrosoduced retention is usual, partly responsible for a possible rise in blood pressure. Sodium lapport will be reduced for daily dosages greater than 15 or 20 mg prednisone equivalent and moderate in long-term low dose treatments.
o Potassium supplementation is justified only for high-dose treatments, prescribed for a long time or in case of risk of rhythm disorders or association with hypokalaemic treatment.
o The patient must always have a calcium and vitamin D intake.
o When corticosteroid therapy is essential, diabetes and high blood pressure are not contraindications, but treatment can lead to imbalance. Their management should be re-evaluated.
o Patients should avoid contact with individuals with chickenpox or measles.
· Attention is drawn to athletes , this specialty containing an active ingredient that can induce a positive reaction of the tests performed during anti-doping controls.
Associations advised against
Drugs giving torsades de pointes (astemizole, bepridil, erythromycin IV, halofantrine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine)
Use substances which do not have the disadvantage of causing torsades de pointes in case of hypokalemia.
Associations subject to precautions of use
Acetylsalicylic acid by general route and by extrapolation other salicylates
Decrease of salicylemia during corticosteroid treatment and risk of salicylate overdose after discontinuation, by increased salicylate elimination by corticosteroids.
Adjust salicylate doses during combination and after stopping corticosteroid treatment.
Antiarrhythmics giving torsades de pointes (amiodarone, bretylium, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol).
Hypokalemia is a contributing factor as well as bradycardia and a preexisting long QT space.
Prevent hypokalemia, correct if necessary; monitor the QT space. In case of torsade, do not administer anantiarrhythmic (electrosystolic drive).
Oral anticoagulants
Possible impact of corticosteroid therapy on the metabolism of oral lanticoagulant and coagulation factors.
Haemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) at high doses or prolonged treatment for more than 10 days.
When the association is justified, reinforce the monitoring: biological control on the 8th day, then every 15 days during the corticotherapy and after its stop.
Other hypokalaemic agents (alone or associated hypokalaemic diuretics, stimulant laxatives, amphotericin B (IV route)).
Hypokalemia favoring the toxic effects of digitalis.
Monitor the serum potassium, correct if necessary and possibly ECG.
Parenteral heparins
Heparin aggravation of hemorrhagic risk specific to corticosteroids (digestive mucosa, vascular fragility) in high doses or prolonged treatment greater than 10 days.
Association must be justified, strengthen monitoring.
Enzyme inducers: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, rifabutin, rifampicin.
Decreased plasma levels and the efficacy of corticosteroids by increasing their hepatic metabolism. The consequences are particularly important for addisonians and transplant patients.
Clinical and biological surveillance, adaptation of the dosage of corticosteroids during the association and after the end of the enzymatic inducer.
Insulin, metformin, sulphonylureas
Elevation of blood glucose with sometimes ketosis (decreased tolerance to carbohydrates by corticosteroids).
Prevent the patient and strengthen blood and urinary monitoring, especially at the beginning of treatment. If necessary, adjust the dosage of antidiabetic during treatment with corticosteroids and after stopping.
Isoniazid (described for prednisolone)
Decreased plasma levels of lisoniazide. Invoked mechanism: increased lisoniazide hepatic metabolism and decreased glucocorticoid metabolism.
Clinical and biological surveillance.
Gastrointestinal topical: salts, oxides and hydroxides of magnesium, aluminum and calcium (described for prednisolone, dexamethasone).
Decreased digestive absorption of glucocorticoids.
Take the gastrointestinal topical glucocorticoid away (more than 2 hours if possible).
Associations to consider
Antihypertensives
Decreased antihypertensive effect (water-soluble retention of corticosteroids).
Alpha interferon
Risk of inhibition of the action of interferon.
Attenuated live vaccines
Risk of generalized illness, possibly fatal. This risk is increased in subjects already immunocompromised by the underlying disease.
Use inactivated vaccine when present (poliomyelitis).
Drive and use machines:
Not applicable.
PREGNANCY / BREAST FEEDING / FERTILITY
celestone during pregnancy
In animals, the experiment shows a teratogenic effect that varies according to the species.In humans, there is a placental transfer. However, epidemiological studies have not detected any risk of malformation related to taking corticosteroids during
st quarter. In chronic diseases, requiring treatment throughout pregnancy, a slight intrauterine growth retardation is possible. Neonatal adrenal insufficiency has been observed exceptionally after high dose corticosteroid therapy. It is justified to observe a period of clinical surveillance (weight, diuresis) and biological monitoring of the newborn.
As a result, corticosteroids may be prescribed during pregnancy, if needed.
Breastfeeding
In case of treatment at large doses and chronically, breastfeeding is not recommended.
To be effective, this medicine should be used regularly. However, if you miss a dose, continue the treatment normally.
What happens if I overdose from Celestene ?
Call your doctor or pharmacist if you have used CELESTENE 2 mg dispersible tablet breakable in greater or greater amounts than prescribed
What is Forms and Composition?
FORMS and PRESENTATIONS
Dispersible 2 mg tablet (white): Bottle of 20.
COMPOSITION
p cpbetamethasone2 mg
Excipients: granulated lactose monohydrate and cellulose powder 75/25 (Cellactose), crospovidone (Polyplasdone XL 10), aspartame, magnesium stearate.
Excipients with known effect: aspartame (E951), lactose.
NOT’s
Edrug-online contains comprehensive and detailed information about drugs available in the medical field, and is divided into four sections:
general information:
Includes a general description of the drug, its use, brand names, FAQs, and relevant news and articles
Additional information:
General explanation about dealing with the medicine: how to take the medicine, the doses and times of it, the start and duration of its effectiveness, the recommended diet during the period of taking the medicine, the method of storage and storage, recommendations in cases for forgetting the dose and instructions to stop taking the drug and take additional doses.
Special warnings:
For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the elderly, boys and drivers, and use before surgery.
Side effects:
It treats possible side effects and drug interactions that require attention and its effect on continuous use.
The information contained in this medicine is based on medical literature, but it is not a substitute for consulting a doctor.
The post celestene 2 mg medicine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects &Warnings appeared first on Drug Online.
from Drug Online https://bit.ly/2Nk4VuO via Edrug Online from Faculty of Medicine https://bit.ly/32ejSFG via Internal Medicine
0 notes
Text
अच्छी खबर : BARIFFA-X पावर की एक दवा जो चले सालो तक sex power tablet,instent medicin for lmprovement sex power,instent sex power kaise badhaye,international top sex power,is damiaplant effective,is...
Sex power tablet,instent medicin for lmprovement sex power,instent sex power kaise badhaye,international top sex power,is damiaplant effective,is erectile dysfunction curable,is hoempathy really good for erectile dysfunction,is homeopathy good for erectile dysfunction,is it really possible to get stronger erection,is there a homeopathic remedy for erectile dysfunction,jandu sexpower.
Japanese medicine for erectile dysfunction,jarmen hemopathy medicine for sex power,joke se shigra patan ka ilaj,kannada shighrapatan nilisudu,keva sex power,khamira for erectile dysfunction,kiya ladki ka bhi shighrapatan hota hai,kottakkal arya vaidya sala products for impotence,kottakkal ayurveda medicine for erectile dysfunction,kya 58 saal men sex power purush ki kam ho jati hai,kya ayurved me desi dawai hai jo shighrapatan ko jad se mita de,l arginine for ed,ladhko mai shighrapatan ka ilaj,ladies sex power dava,latest medicine for erectile dysfunction.
Latestdevelopmentinedstreatment,ling mota lamba shigrapatan ke upay,long sex power tablet,long time sex power,long time sex power capsule,long time sex power medicine,lycopodium 200 dosage for impotence in hindi,lycopodium 200 for male impotence,madhumeh me shighrapatan ka ilaj,madical madison mardana kamjori ki,mahila ko sex power,maintain the sexual power tablet,makardhwaj to cure impotence,male impotency medicine,male sex power increaing homeopathy mesicine,male sex power increase tablet,male sex power medicin,man sex power capsule in hindi.
Man sex power increase medicine,man sex power medicine,man sex power solutiton,man sex power tablet,man sexual power medicine in ayurveda,mankind medicine for erectile dysfunction,mardana kamjori ka ilaaj,mardana kamjori kya khain,mardana kamjori supergrass,mardana kamzori ka ilaaj,mardana kamzori ka ilaj,mardana kamzori ka ilaj homeopathic,mardana kamzori ka ilaj in hindi,mardana kamzori ka ilaj in urdu,mardana kamzori ka ilaj tib e nabvi say,mardana kamzori ke lakshan,mardana kamzori ke nuskhe,mardana kamzori ki desi dawa,mardana kamzori ki tablet,mardana kamzori ko door karne ka tarika,mardana taaqat ke liye lal kitab upay,mardana takat in hindi by radev.
Mardana takat ka vashikaran,mardana taqat,mardana taqat badhane ke liye hindi,mardana taqat hamdard,mardana taqat ka ayurvedic ilaj,mardana taqat ka nuskha,mardana taqat ka rohani ilaj,mardana taqat kaise badhaye,mardana taqat ke desi nuskhe in hindi,mardana taqat ke liye hakimi nuskhe,mardana taqat ke liye kon sa juice piye,mardana taqat ke nuskhe,mardana taqat ke unani nuskhe,mardana taqat ki anmol dawa hindi,mardana taqat ki anmol dawa in hindi,mardana taqat ki dawa.
Mardana taqat ki dawa in hindi,mardana taqat ki desi dawa in hindi,mardana taqat ki unani dawa,mardana taqat pdf,mardani takat ke liye,mardna takat,max x dawai sex power,meaning of shighrapatan in hindi,medcine for increse sex power without any sideeffect,medican for increasing sex power,medication for erectile dysfunction,medicen for improve of sex power,medician to increasa sex power,medicien forquick discharge of male,medicin for sex power,medicine extra sex powar aurvedik,medicine for early ejaculation,medicine for ed,medicine for ed and pe,medicine for ed due to masturbations,medicine for ed in homeopathy,medicine for ed in india,medicine for ed problem,medicine for erectile dysfunction,medicine for female impotence.
Medicine for for male impotency erectile dysfunction premature ejaculation sexual weakness loss of libido,medicine for hard erection,medicine for impotenc,medicine for impotence,medicine for impotence in homeopathy,medicine for impotence in india,medicine for improve sex power,medicine for improvement of sexual power,medicine for improving sex power system,medicine for increase sex power,medicine for increasing sex power,medicine for increasing sex power and length,medicine for instant sex power,medicine for late discharge,medicine for male e d problem,medicine for premature ejaculation,medicine for sex power,medicine for sex power for men,medicine for sex power.
0 notes