#grand duke frederick ii of baden
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
CONFIRMED ATTENDEES TO THE CORONATION OF
♚♛ KING CHARLES III & QUEEN CAMILLA ♛♚
───────────── ⋆⋅☆⋅�� ─────────────
♔ ┆ Foreign Royalty
King Felipe & Queen Letizia 🇪🇸
King Philippe & Queen Mathilde and Princess Elisabeth, The Duchess of Brabant 🇧🇪
King Jigme Khesar & Queen Jetsun Pema 🇧🇹
Yang di-Pertuan Agong Abdullah & Raja Permaisuri Agong Tunku 🇲🇾
Kīngi Tūheitia & Makau Ariki Te Atawhai of the Māori
Grand Duke Henri & Grand Duchess Maria Teresa 🇱🇺
King Carl Gustaf and Crown Princess Victoria 🇸🇪
King Willem-Alexander & Queen Maxima, Princess Beatrix and Crown Princess Catharina-Amalia, The Princess of Orange 🇳🇱
Crown Prince Haakon & Crown Princess Mette-Marit 🇳🇴
Crown Prince Fumihito & Crown Princess Kiko 🇯🇵
Crown Prince Frederick & Crown Princess Mary 🇩🇰
Prince Albert & Princess Charlene 🇲🇨
King Vajiralongkorn & Queen Suthida 🇹🇭
King Abdullah II & Queen Rania 🇯🇴
King Tupou & Queen Nanasipau’u 🇹🇴
Hereditary Prince Alois & Hereditary Princess Sophie 🇱🇮
King Mswati III & Queen Sibonelo LaMbikiza 🇸🇿
Crown Prince Sheikh Mishal Al Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah 🇰🇼
Crown Prince Theyazin bin Haitham Al Said 🇴🇲
Emir Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani 🇶🇦
Princess Lalla Meryem 🇲🇦
Prince Turki bin Mohammed bin Fahd Minister of State 🇸🇦
Sheikh Mansour bin Zayed 🇦🇪
King Letsie III & Queen Masenate 🇱🇸
Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah 🇧🇳
King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa 🇧🇭
Asantehene Otumfuo Osei Tutu II & Lady Julia of the Ashanti
♔ ┆ Deposed Royalty & Distant Family Relations
Queen Anne-Marie, Crown Prince Pavlos & Crown Princess Mary Chantal 🇬🇷
Margrave Bernhard & Margravine Stephanie of Baden
Landgrave Donatus of Hesse
Prince Philipp & Princess Saskia of Hohenlohe - Langenburg
Margareta (Custodian of the Crown) and Prince Radu 🇷🇴
Crown Prince Alexander & Crown Princess Katherine 🇷🇸
Tsar Simeon & Tsaritsa Margarita 🇧🇬
Annoying Ginger from Montecito
♔ ┆ Governor-Generals of Commonwealth Realms
Governor-General David Hurley & Linda Hurley 🇦🇺
Governor-General Sir Rodney Williams & Lady Williams 🇦🇬
Governor-General Sir Cornelius A. Smith & Lady Smith 🇧🇸
Governor-General Dame Cindy Kiro & Richard Davies 🇳🇿
Governor-General Mary Simon & Whit Fraser 🇨🇦
Governor-General Sir Patrick Allen & Lady Allen 🇯🇲
Governor-General Dame Froyla Tzalam 🇧🇿
Governor-General Dame Cécile La Grenade 🇬🇩
King's Representative Sir Tom Marsters & Lady Tuaine Marsters 🇨🇰
Governor-General Sir David Vunagi & Lady Vunagi 🇸🇧
Governor-General Sir Bob Dadae 🇵🇬
Governor-General Dame Marcella Liburd 🇰🇳
Deputy Governor-General Hyleta Liburd of Nevis
Acting Governor-General Errol Charles 🇱🇨
Governor-General Dame Susan Dougan 🇻🇨
Governor-General Sir Tofiga Vaevalu Falani 🇹🇻
♔ ┆ Heads of Governments of Commonwealth Realms
Prime Minister Anthony Albanese & Jodie Haydon 🇦🇺
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau & Sophie Grégoire Trudeau 🇨🇦
Prime Minister Philip Davis 🇧🇸
Prime Minister Dickon Mitchell 🇬🇩
Prime Minister Chris Hipkins 🇳🇿
Prime Minister Terrance Drew 🇰🇳
Prime Minister Ralph Gonsalves 🇻🇨
♔ ┆ Governmental Representatives of Commonwealth Realms
Margaret Beazley, Governor of New South Wales 🇦🇺
Linda Dessau, Governor of Victoria 🇦🇺
Jeannette Young, Governor of Queensland 🇦🇺
Chris Dawson, Governor of Western Australia 🇦🇺
Frances Adamson, Governor of South Australia 🇦🇺
Barbara Baker, Governor of Tasmania 🇦🇺
Former Prime Minister Hubert Ingraham 🇧🇸
Former Prime Minister Perry Christie 🇧🇸
Michael Pintard, Leader of the Opposition 🇧🇸
Janice Charette, Clerk to the Privy Council of Canada and Secretary to the Cabinet 🇨🇦
High Commissioner Kisha Abba Grant 🇬🇩
High Commissioner Phil Goff 🇳🇿
Christopher Luxon, Leader of the Opposition 🇳🇿
Koni Iguan, Deputy Speaker of the National Parliament 🇵🇬
Justin Tkatchenko, Minister for Foreign Affairs 🇵🇬
Rainbo Paita, Minister for Finance and National Planning 🇵🇬
Taies Sansan, Secretary for the Department of Personnel Management 🇵🇬
Gisuwat Siniwin, former Member of the National Parliament 🇵🇬
Premier Mark Brantley of Nevis
High Commissioner Moses Kouni Mose 🇸🇧
Jeremiah Manele, Minister of Foreign Affairs and External Trade 🇸🇧
♔ ┆ Foreign Heads of States + Governments
President Andrzej Duda & First Lady Agata Kornhauser-Duda 🇵🇱
President Petr Pavel and First Lady Eva Pavlová 🇨🇿
President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. and First Lady Louise Araneta-Marcos 🇵🇭
President Katalin Novák & First Gentleman István Attila Veres 🇭🇺
President Guðni Th. Jóhannesson and First Lady Eliza Reid 🇮🇸
President Michael D. Higgins & First Lady Sabina Higgins and Leo Varadkar, Taoiseach 🇮��
President Herzog & First Lady Michal Herzog 🇮🇱
President Egils Levits & First Lady Andra Levite 🇱🇻
President Ali Bongo Ondimba & First Lady Sylvia Bongo Ondimba 🇬🇦
President Mario Abdo Benítez & First Lady Silvana López Moreira 🇵🇾
O le Ao o le Malo Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi II & Masiofo Faʻamausili Leinafo 🇼🇸
President Paul Kagame & First Lady Jeannette Kagame 🇷🇼
President Wavel Ramkalawan, & First Lady Linda Ramkalawan 🇸🇨
President George Vella & First Lady Miriam Vella 🇲🇹
President Julius Maada Bio & First Lady Fatima Bio 🇸🇱
Hakainde Hichilema & First Lady Mutinta Hichilema 🇿🇲
President Sergio Mattarella 🇮🇹
President Ranil Wickremesinghe 🇱🇰
President Halimah Yacob 🇸🇬
President Faure Gnassingbé 🇹🇬
President Muhammadu Buhari 🇳🇬
President Filipe Nyusi 🇲🇿
President Frank-Walter Steinmeier 🇩🇪
President Vahagn Khachaturyan 🇦🇱
President Alar Karis 🇪🇪
President Sauli Niinistö 🇫🇮
President Emmanuel Macron 🇫🇷
President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva 🇧🇷
President Alexander Van der Bellen 🇦🇹
President Vahagn Khachaturyan 🇦🇲
President Salome Zourabichvili 🇬🇪
President Katerina Sakellaropoulou 🇬🇷
President Abdul Latif Rashid 🇮🇶
President Vjosa Osmani 🇽🇰
President George Weah 🇱🇷
President Gitanas Nausėda 🇱🇹
President Mohamed Ould Ghazouani 🇲🇷
President Maia Sandu 🇲🇩
President Stevo Pendarovski 🇲🇰
President Lazarus McCarthy Chakwera 🇲🇼
President Ibrahim Mohamed Solih 🇲🇻
President William Ruto 🇰🇪
President Irfaan Ali 🇬🇾
President Wiliame Katonivere 🇫🇯
President Paul Biya 🇨🇲
President Nikos Christodoulides 🇨🇾
President Mohamed Bazoum 🇳🇪
President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa 🇵🇹
President Klaus Iohannis 🇷🇴
President Macky Sall 🇸🇳
President Zuzana Čaputová 🇸🇰
President Nataša Pirc Musar 🇸🇮
President Võ Văn Thưởng 🇻🇳
Emmerson Mnangagwa 🇿🇼
Chairwoman of the Council of Ministers Borjana Krišto 🇧🇦
Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina 🇧🇩
Prime Minister Han Duck-soo 🇰🇷
Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif 🇵🇰
President Alain Berset of the Swiss Confederation & Muriel Zeender 🇨🇭
Prime Minister Galab Donev 🇧🇬
♔ ┆ Governmental Representatives
First Lady Jill Biden & Finnegan Biden and John Kerry, Special Presidential Envoy for Climate 🇺🇸
First Lady Olena Zelenska 🇺🇦
First Lady Verónica Alcocer 🇨🇴
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankar 🇮🇳
Vice President Fuat Oktay 🇹🇷
Vice President Tiémoko Meyliet Koné 🇨🇮
Vice President Han Zeng 🇨🇳
Vice President Mohammed B.S Jallow 🇬🇲
Sahiba Gafarova, Speaker of the National Assembly 🇦🇿
Christophe Mboso N'Kodia Pwanga, President of the National Assembly 🇨🇩
Arnoldo André, Minister of Foreign Affairs 🇨🇷
Naledi Pandor, Minister of International Relations and Cooperation 🇿🇦
Nabil Ammar, Minister of Foreign Affairs 🇹🇳
Narayan Prakash Saud, Minister of Foreign Affairs 🇳🇵
Gustavo Manrique, Foreign Minister 🇪🇨
Ahmed Attaf, Foreign Minister 🇩🇿
Frederick Shava, Foreign Minister & Mthuli Ncube, Finance Minister 🇿🇼
Cardinal Pietro Parolin, Cardinal Secretary of State 🇻🇦
Ambassador José Alberto Briz Gutiérrez 🇬🇹
♔ ┆ Representatives from International Organizations
Amina Jane Mohammed, Deputy Secretary General 🇺🇳
Ursula von der Leyen, President of EU Commission 🇪🇺
Charles Michel, EU Council President 🇪🇺
Roberta Metsola, President of the European Parliament 🇪🇺
#coronation 2023 guest list#coronation 23#coronation guests#coronation guest list#british royals#british royalty#king charles#king charles iii#charles iii#queen camilla#queen consort camilla
238 notes
·
View notes
Text
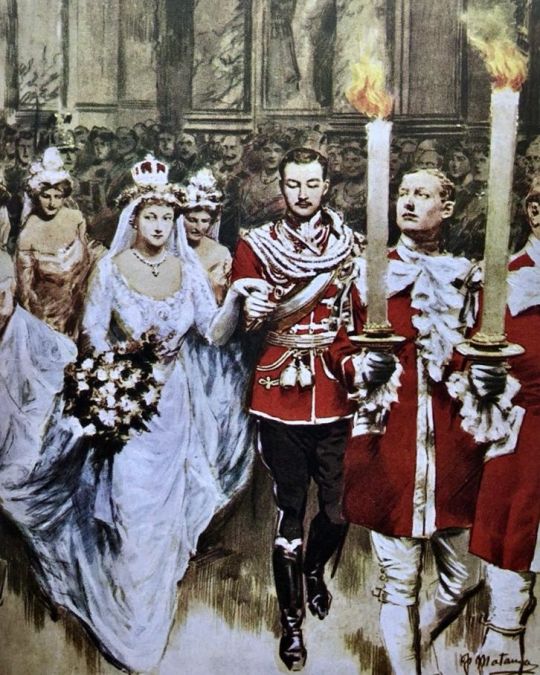

The 20th of May was my last day in the New Palace, and on the 21st Ernst August arrived. In his last letter he had told me what arrangements he had made to keep our honeymoon location secret from prying eyes. It was planned that we should go first to the hunting lodge at Werbellinsee, then to the Hubertihaus, my father-in-law’s hunting lodge near Gmunden. He made me promise not to tell anyone at all and even in Gmunden itself our plans were kept strictly secret.
The first wedding guests to arrive were the King and Queen of England, and my parents went to the Lehrter Station in Berlin to greet them. George V had put on his Prussian General’s uniform for the occasion and, with an escort of Dragoon Guards and Cuirassiers, the Royal couple drove through Berlin. More than half a century was to pass before an English Head of State was to come to Germany again, when Queen Elizabeth II, George V’s grand-daughter, came in 1965.
Early on the following day my great-aunt Luise, Prince Max of Baden and his wife arrived, then a little later my parents-in-law and my sister-in-law, Olga. The First Guards Regiment of Foot formed the guard of honour, while the Cuirassiers again provided the escort as we travelled to the castle in three carriages. My father sat with the Duke, who wore his Austrian uniform, in the first carriage; my mother with the Duchess Thyra in the next, while Princess Olga, my fiancé and I sat together in the third.
At midday the Czar of Russia arrived and the colourful welcoming ceremonies began all over again. Wearing the uniform of the Alexander Grenadier Guards Regiment and the tall Frederick the Great cap on his head, Nicholas II’s truly imposing appearance drove the waiting Berliners into a frenzy of excitement and wonder... For me, the wedding celebrations began with the reception of deputations who had come bringing gifts. My father’s present to me was a diadem and a pearl necklace, while my mother gave me a diamond tiara. King George and Queen Mary gave me a prodigious gold goblet anda diamond brooch; Ernst August a complete jewellery outfit. The English Queen Mother, Alexandra, gave me an emerald brooch. From the Czar I received an aquamarine and diamond necklace; the Italian King and Queen sent me antique silver vessels and Queen Wilhelmina of Holland an antique pendulum clock. There were presents galore, from the Kings of Denmark and Sweden down to the various cities in Germany, and from Brunswick I received a diadem which had once belonged to the French Empress Josephine. The number of gifts was so great they required several furniture vans to carry them.
The real celebrations began on the evening of the day before the wedding, with a gala opera when the Royal Court Opera put on Richard Wagner’s Lohengrin. The Opera House, when I arrived, was bedecked with my favourite flowers, pink carnations, and as we took our places in the Royal Box with our parents, all those present rose from their seats, and Ernst August and I bowed right, left and centre. As one, the entire audience bowed back. Next day, 24 May, was my wedding day. Early in the afternoon my mother helped me on with my bridal crown and veil. Then we repaired to the Chinese Room, and we found that a unit of soldiers had formed lines throughout the castle and taken up sentry posts everywhere. There was a bodyguard from the rst Guards Regiment, the Castle Guard in their historic Frederick the Great uniforms, the Garde du Corps in ceremonial dress, and the gendarmerie. At 4 p.m. members of the staff of the Royal Privy Purse came by, carrying the bridal crown of the Princess of Prussia. Then the Mistress of the Empress’s Household, Therese, Countess von Brockdorff, picked up the crown and ceremoniously handed it to my mother who carefully placed it on my head. We then proceeded to the chamber deemed the ‘Elector’s Room’ where my father received us, and Count Eulenberg, the Minister for the Royal House, completed the formalities regarding the marriage pact and the official registration of the marriage. As Ernst August and I signed the register, we heard a loud buzzing overhead above the castle. We all rushed to the windows and there above us was the airship Hansa, all gaily decorated with colourful pennants. Suddenly, a large bouquet of flowers came floating down from the airship. It was their way of congratulating us.
After the civil ceremony, the bridal procession, led by the Corps of Pages, wound its way through the Picture Gallery and the White Hall to the castle chapel. Behind the pages walked two Heralds with the Brandenburg and Prussian Coat of Arms, then the Chief Marshal, Prince zu Fiirstenberg with his big Marshal’s staff, and finally Ernst August and me. Behind us were the Kaiser in the uniform of the 1st Guards Regiment, with the Duchess of Cumberland in a lilaccoloured gown, then the Generals and the Admirals, and then the Kaiserin in a light green robe escorted by the Duke of Cumberland in his Austrian uniform. Then the Czar of Russia, in his Hussar uniform, escorted the Queen of England. The King of England, in his Cuirassier uniform, escorted the Crown Princess. Then they were followed by a whole host of Princes, including my brothers, and Princesses, Dukes and Duchesses. It was 5 p.m. by the time we reached the chapel to be greeted by the sound of music from the organ.
Bright sunlight filtered through the chapel cupola as Ernst August and I stepped up to the altar which my mother and Crown Princess Cecilie, my sister-in-law, had decorated with roses, carnations and wreaths. Pastor Dryander then delivered his sermon, earnest and worthy words which warned me about the seriousness of life.
After that came the actual marriage ceremony. Ernst August’s ‘yes’ rang out so loudly and clearly that I had to follow suit and when we joined hands in front of the altar he clasped mine very firmly, insisting that his thumbs were on top of mine. You see, there’s an old folk-tale which says that if the husband does not have his thumbs above those of his bride at the wedding ceremony then he will have no say during his marriage. Pastor Dryander looked slightly shocked at this little demonstration, but Ernst August and I just smiled at each other. Mary, the Queen of England, however, was so overcome by the whole ceremony that she broke into a flood of tears. Later, they used to say that she had sobbed because she had at that moment foreseen the forthcoming disaster of war the following year breaking over us. That is really out of the question. Queen Mary was very attached to the Guelph family and it was understandable that the ceremony should affect her.
As soon as the vows and rings had been exchanged, the battery of the rst Guards Field Artillery Regiment fired a 36-gun salute, the chapel bells rang out in loud peals, and the wedding party made its way to the White Hall again, where we stood under the canopy of the Throne and received congratulations from the guests filing past, as the orchestra played the “Wedding March’ from Midsummer Ni ght’s Dream. My husband and I had my father standing to our ri ght together with my mother-in-law, Queen Mary and the Czar, and on our left my mother, my father-in-law, Crown Princess Cecilie and King George V.
The ceremonial banquet began at 7 p.m. and was attended by one thousand one hundred guests. The remarkable thing about it was that the food was dished up by Lieutenant-General Baron von Siisskind, the Inspector of the Militia, at one end of the table and by LieutenantGeneral von Falk, the Inspector of the War Academy, at the other. They served the food then passed the plates to the lackeys, who handed them to the Court officials, and so on to each guest. As soon as the dinner was over, the White Hall became the setting for the traditional torch-dance, a sort of polonaise which, in earlier times, was danced with senior Court officials carrying big, heavy candles ahead of the procession of dancers. For these elderly gentlemen then it was certainly no easy task, but in my time these duties were taken over by the pages, who were physically better equipped. My father gave the Chief Marshal orders for the torch-dance to begin. Prince zu Fiirstenberg came up to my husband and me, bowed, and invited us to lead the dance. The band of the Guards Cuirassiers struck up a polonaise, the Chief Marshal placed himself at the head of the procession of dancers and, with twelve pages lined up two by two behind him, signalled for Ernst August and me to lead off the dance.
The spectacle of my dancing with the King of England and the Czar of Russia absolutely fascinated everybody present. It wasn’t something that happened every day, of course, but there were the rulers of the two mightiest nations on Earth, with the daughter of the German Kaiser between them, all dancing together. At the end of the dance the Czar turned to me and said: ‘My wish is that you will be as happy as I am.’ I have never forgotten those words: they were the last I was ever to hear from Czar Nicholas. The torch-dance was over. I left the room on my father’s arm, while my husband escorted my mother. The Prussian Princess’s Crown was taken away from me and given back for safe keeping to the officials of the Privy Purse. Then my mother lifted off my bridal wreath. The hour of parting had struck. We changed our clothes and went to the station accompanied by my father and four of my brothers".
The Kaiser's daughter: Memoirs of H. R. H. Viktoria Luise, Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg, Princess of Prussia
youtube
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
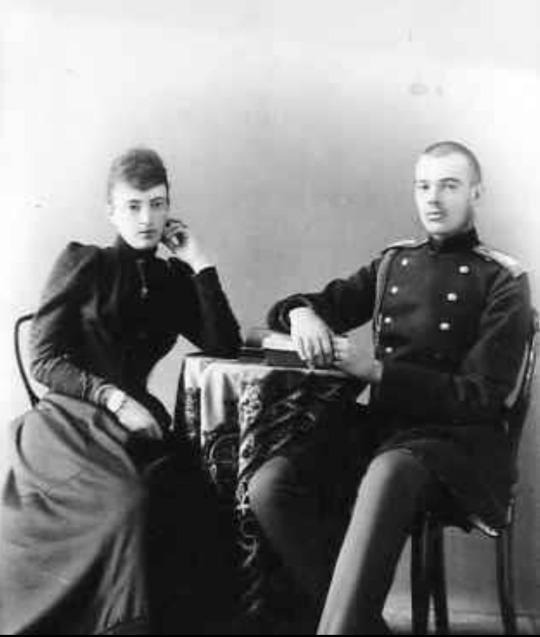
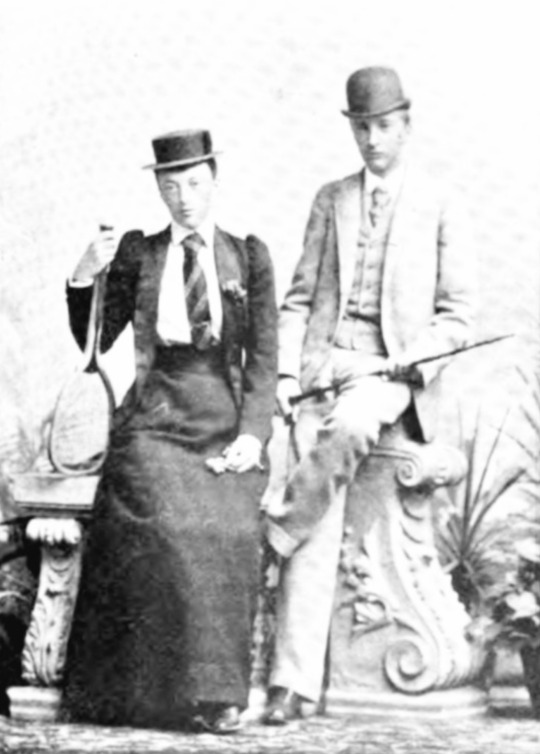
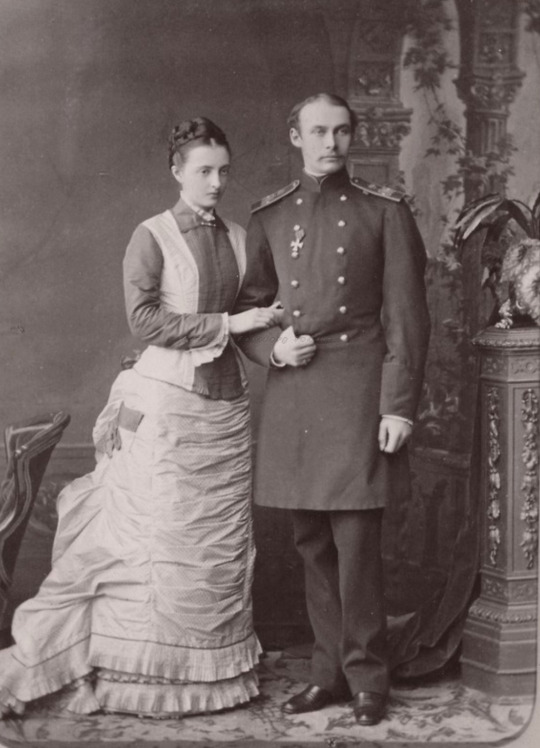




















Photographs: 1. Grand Duke Mikhail Nicholayevich and his wife, Grand Duchess Olga Fyodorovna, with their two eldest children, Grand Duke Nicholas Mikhailovich and Grand Duchess Anastasia Mikhailovna; 2 and 3: Anastasia as a young girl; 4 and 5: Anastasia as a young woman. In one of the photos, she is wearing Russian court dress; 6. Anastasia with her brother Grand Duke Mikhail Mikhailovich (Miche-Miche); 7. Anastasia with her brother Grand Duke Georgiy Mikhailovich; 8. Anastasia with her brother Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovichl 9. Anastasia with her youngest brother, who died at twenty, Grand Duke Alexis Mikhailovich; 10. Anastasia with her brother Grand Duke Alexander "Sandro" Mikhailovich; 11. Anastasia with her niece Princess Irina Alexandrovna; 12 and 13; Two photos of Anastasia with her fiancee/husband Grand Duke Frederick Francis III of Mecklenburg-Schwerin; 14. Anastasia with her three children; 15 and 16: Two pictures of Anastasia; 17: Anastasia's three children and their spouses: From left to right: Her daughter Alexandrine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin with the future King Christian X of Denmark, Her son, Frederick Francis IV with Alexandra of Hanover and Cumberland, and her daughter Cecilie of Mecklenburg-Schwerin with Crown Prince Wilhelm; 18. Her illegitimate son Alexis Louis de Wenden; 19: Villa Wenden in Nice; 20. The formidable Grand Duchess Anastasia Mikhailovna.
The other Anastaisa
Grand Duchess Anastasia Mikhailovna was born in 1860, the second child and only daughter of Grand Duke Mikhail Nicholaevich and Grand Duchess Olga Feodorovna (nee Princess Cecilie of Baden.) Anastasia was a granddaughter of Nicholas I. The better-known Anastasia (the daughter of Nicholas II) would be born a little over a half-century later, promising to be just as indomitable as her predecessor (she did not have the chance to fulfill that promise.)
Stasi (as her brothers called Anastasia Mikhailovna) was her father's favorite child. Her brothers worshipped her. Her mother was the disciplinarian of the house. The boys were allowed to see their sister only on Sundays.
Anastasia married Frederick Francis III, Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, at 19. Frederick Francis was Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna, the Elder's brother. He had very poor health throughout his life; he had asthma and multiple allergies and rashes, and he needed to live during extended periods in the warmer climate of the Mediterranean rather than in Northern Europe; this was just fine with Anastasia, who would never adjust to her adoptive country or gain the affection of the people there. The couple established Villa Wenden in the South of France, and she would live in that area of the world most of her life. Frederick's homosexuality was known throughout Europe, but the couple seemed to have gotten along well. Anastasia spent lavishly at the casinos, and Frederick Francis was glad to provide her with the funds. When the Grand Duke died, she said: "On this day, I have lost my best friend."
They had three children, and all married very well:
Duchess Alexandrine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (1879 –1952); married King Christian X of Denmark. They had two sons.
Frederick Francis IV, Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (1882 –1945), married Princess Alexandra of Hanover and Cumberland. They had five children.
Duchess Cecilie of Mecklenburg-Schwerin (1886 –1954.) She married Wilhelm, the German Crown Prince. They had six children.
Up to the death of her husband, Anastasia's life had transcurred without scandal. However, a few years later, she began an affair with Vladimir Alexandrovitch Paltov, her secretary. She soon became pregnant by him and attempted to hide that fact by claiming she was suffering from a tumor. She claimed to have chickenpox when she delivered the child. Her son, Alexis Louis de Wenden, was born in Nice in 1902. She was able to bring him up herself and wrote to him daily when he was away at school. After the scandal became public, she was advised never to live near her daughter, now the Crown Princess of Germany (she was given special permission to visit her daughter for the birth of her first grandson.)
After her father had a stroke, he went to live with Stasi in Villa Wenden. As the senior member of the Romanov clan, "Uncle Misha" received many visitors, including the Tsar. At least one of her brothers was in residence at Villa Wenden at any given time. When her father died in 1909, Anastasia inherited an enormous fortune. She continued to live as she wished, gambling heavily, going to the theater, and dancing.
World War I split the family apart. Her son was the reigning Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, her daughter was the German Emperor's daughter-in-law, she was a Russian Grand Duchess, and her Russian family was fighting on the opposite side. She settled in neutral Switzerland. The war cost her son and daughter their (prospective) crowns. After the war, she returned to Nice. There she founded a charity to help Russian exiles. Vladimir Paltov was the charity's president, perhaps indicating that the relationship continued. She lived in Villa Fantasia in Eze, which is near Cannes.
Anastasia died suddenly after suffering a stroke in 1922. She rests in Ludwigslust next to her husband. All of her children have living descendants today, including her illegitimate son. She certainly lived as she wished. Which is something that the other Anastasia would have probably done should she have been given the chance.
#russian history#imperial russia#romanov family#Grand Duchess Anastasia Mikhailovna#villa Wenden#Grand Duke Mikhail Nikolayevich#Grand Duke Georgie Mikhailovich#Grand Duke Mikhail Mikhailovich#Grand Duke Alexander Mikhailovich#Grand Duke Nicholas Mikhailovich#Grand Duke Alexis Mikhailovich#Grand Duchess Olga Fyodorovna#Frederick Francis III Grand Duke of Mecklenburg Schwerin#Frederick Francis IV Grand Duke of Mecklenburg Schwerin#Duchess Cecilie of Mecklenburg Schwerin#Christian X of Denmark#Crown Prince Wilhelm of Germany#Alexis Louis de Wenden
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Events 8.17 (before 1900)
310 – Pope Eusebius dies, possibly from a hunger strike, shortly after being banished by the Emperor Maxentius to Sicily. 682 – Pope Leo II begins his pontificate. 986 – Byzantine–Bulgarian wars: Battle of the Gates of Trajan: The Bulgarians under the Comitopuli Samuel and Aron defeat the Byzantine forces at the Gate of Trajan, with Byzantine Emperor Basil II barely escaping. 1186 – Georgenberg Pact: Ottokar IV, Duke of Styria and Leopold V, Duke of Austria sign a heritage agreement in which Ottokar gives his duchy to Leopold and to his son Frederick under the stipulation that Austria and Styria would henceforth remain undivided. 1386 – Karl Topia, the ruler of Princedom of Albania forges an alliance with the Republic of Venice, committing to participate in all wars of the Republic and receiving coastal protection against the Ottomans in return. 1424 – Hundred Years' War: Battle of Verneuil. 1488 – Konrad Bitz, the Bishop of Turku, marks the date of his preface to Missale Aboense, the oldest known book of Finland. 1498 – Cesare Borgia, son of Pope Alexander VI, becomes the first person in history to resign the cardinalate; later that same day, King Louis XII of France names him Duke of Valentinois. 1549 – Battle of Sampford Courtenay: The Prayer Book Rebellion is quashed in England. 1560 – The Catholic Church is overthrown and Protestantism is established as the national religion in Scotland. 1585 – Eighty Years' War: Siege of Antwerp: Antwerp is captured by Spanish forces under Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma, who orders Protestants to leave the city and as a result over half of the 100,000 inhabitants flee to the northern provinces. 1585 – A first group of colonists sent by Sir Walter Raleigh under the charge of Ralph Lane lands in the New World to create Roanoke Colony on Roanoke Island, off the coast of present-day North Carolina. 1597 – Islands Voyage: Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, and Sir Walter Raleigh set sail on an expedition to the Azores. 1668 – The magnitude 8.0 North Anatolia earthquake causes 8,000 deaths in northern Anatolia, Ottoman Empire. 1717 – Austro-Turkish War of 1716–18: The month-long Siege of Belgrade ends with Prince Eugene of Savoy's Austrian troops capturing the city from the Ottoman Empire. 1723 – Ioan Giurgiu Patachi becomes Bishop of Făgăraș and is festively installed in his position at the St. Nicolas Cathedral in Făgăraș, after being formally confirmed earlier by Pope Clement XI. 1740 – Pope Benedict XIV, previously known as Prospero Lambertini, succeeds Clement XII as the 247th Pope. 1784 – Classical composer Luigi Boccherini receives a pay rise of 12,000 reals from his employer, the Infante Luis, Count of Chinchón. 1798 – The Vietnamese Catholics report a Marian apparition in Quảng Trị, an event which is called Our Lady of La Vang. 1807 – Robert Fulton's North River Steamboat leaves New York City for Albany, New York, on the Hudson River, inaugurating the first commercial steamboat service in the world. 1808 – The Finnish War: The Battle of Alavus is fought. 1827 – Dutch King William I and Pope Leo XII sign concord. 1836 – British parliament accepts registration of births, marriages and deaths. 1862 – American Indian Wars: The Dakota War of 1862 begins in Minnesota as Dakota warriors attack white settlements along the Minnesota River. 1863 – American Civil War: In Charleston, South Carolina, Union batteries and ships bombard Confederate-held Fort Sumter. 1864 – American Civil War: Battle of Gainesville: Confederate forces defeat Union troops near Gainesville, Florida. 1866 – The Grand Duchy of Baden announces its withdrawal from the German Confederation and signs a treaty of peace and alliance with Prussia. 1876 – Richard Wagner's Götterdämmerung, the last opera in his Ring cycle, premieres at the Bayreuth Festspielhaus. 1896 – Bridget Driscoll became the first recorded case of a pedestrian killed in a collision with a motor car in the United Kingdom.
0 notes
Text



Grand Duchess Louise of Baden with her eldest son, Hereditary Grand Duke Frederick, 1872.
#grand duchess louise of baden#grand duke frederick ii of baden#hereditary grand duke frederick of baden#baden#german royal#german royalty#1872#1870s
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

Franz Xaver Winterhalter (1805-1873) "Princess Louise of Prussia" (1856) Oil on canvas Located in the Pushkin Museum, Moscow, Russia Princess Louise Marie Elisabeth of Prussia (1838-1923) was Grand Duchess of Baden from 1856 to 1907 as the wife of Grand Duke Frederick I. She was the second child and only daughter of Wilhelm I, German Emperor, and Augusta of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, the younger sister of Frederick William ("Fritz")--the future German Emperor Frederick III--and the aunt of Emperor Wilhelm II.
#paintings#art#artwork#genre painting#female portrait#franz xaver winterhalter#oil on canvas#fine art#pushkin museum#art gallery#german artist#portrait of a woman#white dress#dresses#clothing#clothes#pretty#aesthetic#aesthetics#dark hair#flower crown#jewelry#jewellery#pearl necklace#necklaces#1850s#mid 1800s#mid 19th century#aristocracy#royalty
182 notes
·
View notes
Text

Princess Elisabeth of Hesse and By Rhine was described by people who knew her as one of the most beautiful women of that era.
As a young woman, Elisabeth's cousin, Prince Wilhelm of Prussia, fell in love with her. In April 1875, the 16-year-old Wilhelm visited Darmstadt to celebrate Princess Victoria of Hesse and by Rhine's 12th birthday and first expressed interest in the 11-year-old Elisabeth. He wrote in a letter to his mother that "if God grants that I may live till then I shall make her my bride once if you allow it."When he was a student at Bonn University, he often visited his Aunt Alice and his Hessian relatives on the weekends. During these frequent visits, he fell in love with Elisabeth, writing numerous love poems and regularly sending them to her. He proposed to Elisabeth in 1878, but she rejected him.
Lord Charles Montagu, the second son of the 7th Duke of Manchester courted her unsuccessfully.
Henry Wilson, later a distinguished soldier, vied unsuccessfully for Elisabeth's hand.
The future Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden, Wilhelm's first cousin, proposed to Elisabeth. Queen Victoria described him as "so good and steady", with "such a safe and happy position,"that when Elisabeth declined to marry him the Queen "deeply regretted it". Frederick's grandmother, the Empress Augusta, was so furious at Elisabeth's rejection of Frederick that it took some time for her to forgive Elisabeth.
Other admirers included:
Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich Romanov of Russia (the poet KR), who wrote a poem about her first arrival in Russia and the general impression she made to all the people present at the time.
Prince Felix Felixovich Yusupov considered her a second mother, and stated in his memoirs that she helped him greatly during the most difficult moments of his life.
As a young girl, Queen Marie of Romania was very fascinated with her cousin Ella. In her memoirs, she wrote that "her beauty and sweetness was a thing of dreams."
The French Ambassador to the Russian court, Maurice Paleologue, wrote in his memoirs how Elisabeth was capable of arousing what he described as "profane passions".
Ultimately, it was a Grand Duke of Russia who would win Elisabeth's heart; Elisabeth's great-aunt, Empress Maria Alexandrovna of Russia, was a frequent visitor to Hesse. During these visits, she was usually accompanied by her youngest sons, Sergei and Pavell. Elisabeth had known them since they were children, and she initially viewed them as haughty and reserved. Sergei, especially, was a very serious young man, intensely religious, and he found himself attracted to Elisabeth after seeing her as a young woman for the first time in several years.
At first, Sergei made little impression on Elisabeth. But after the death of both of his parents within a year of each other, Elisabeth sympathised with Sergei because she had felt this same grief after the death of her mother. Their other similarities (both were artistic and religious) drew them closer together. It was said that Sergei was especially attached to Elisabeth because she had the same character as his beloved mother. So when Sergei proposed to her for the second time, she accepted—much to the chagrin of her grandmother Queen Victoria.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich (standing, fifth from the right) and his wife Grand Duchess Elizabeth Mavrikievna (sitting, center) surrounded by members of royalties in Stockholm, 1897.
Sitting from left: Hilda, Grand Duchess of Baden; Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden (later Queen); Grand Duchess Elizabeth Mavrikievna of Russia; Crown Princess Louise of Denmark (later Queen); and Princess Bathildis of Waldeck-Pyrmont.
Standing from left: Wilhelm Ernst, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach; Wilhelm IV, Grand Duke of Luxembourg; Prince Ruprecht of Bavaria; Prince Chira of Siam; Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden; Princess Ingeborg of Denmark; Crown Prince of Sweden (later Gustaf V); Crown Prince of Denmark (later Frederick VIII); Archduke Eugen of Austria; Prince Carl of Sweden; King Oscar II of Sweden; Prince Friedrich of Waldeck-Pyrmont; Grand Duke Konstantin Konstantinovich of Russia; Prince Christian of Schleswig-Holstein; Princess Thyra of Denmark; Prince Eugen, Duke of Närke; and Emanuele Filiberto, Duke of Aosta.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Russian Fairy Tales Unit 3 Review: The Russian Revolution & the Assassination of the Romanov Family

Tsar Nicholas II (1868-1918)
- primarily of German & Danish descent; his last ethnically Russian ancestor was Grand Duchess Anna Petrovna (1708-1728), daughter of Peter the Great. - related to several monarchs in Europe: Kings Frederick VIII of Denmark & George I of Greece were his maternal uncles and Queen Alexandra of the UK was his maternal aunt. His first cousins included King George V of the UK, King Haakon VII and Queen Maud of Norway, King Christian X of Denmark, and King Constantine I of Greece. - Nicholas and his wife Alexandra were both second cousins (through descent from Louis II, Grand Duke of Hesse and his wife Princess Wilhelmine of Baden) *and* third cousins once removed (they were both descendants of King Frederick William II of Prussia). 1881: Nikki was 13 years old when his grandfather was assassinated in a pretty nasty carriage bombing, which he witnessed. This made his father Tsar Alexander III and made him the heir apparent. 1884: Nikki’s coming-of-age ceremony is held at the Winter Palace. Later that year, his uncle Grand Duke Sergei married Princess Elizabeth of Hesse and by Rhine. At the wedding, the Tsarevich met and admired the bride’s younger sister, Alix. Those feelings of admiration blossomed into love following her visit to St. Petersburg five years later (1889). 1890: Nikki goes on a “Grand Tour” with his younger brother George and their cousin, Prince George of Greece (Grand Duke George fell ill halfway through and got sent home). They visited Egypt, India, Singapore, Thailand, receiving honors as distinguished guests in each country. In Japan, Nicholas had a large dragon tattooed on his right forearm by Japanese tattoo artist Hori Chyo. It was during this trip that one of his Japanese escorts, Tsuda Sanzo, tried to assassinate Nikki with a sabre. He was left with a 9 cm forehead scar, but no life-threatening injuries. The “Otsu incident” as it is known *did* cut the trip short.
- Nikki’s father failed to prepare him for his role as Tsar, arguing that he was not mature enough to take on serious responsibilities: “Nikki is a good boy, but he has a poet’s soul...God help him!” - Alexander assumed that he would live a long life and had plenty of time to prepare his son; there was no need to start right away.
1894: Nikki joins his Uncle Sergei & Aunt Elizabeth on a journey to Coburg, Germany for the wedding of Alix & Elizabeth’s brother Ernest Louis, Grand Duke of Hesse, to their mutual first cousin Princess Victoria Melita of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. During this trip, Nikki proposes to Alix, but she rejects his proposal because she is reluctant to convert from Lutheranism to Russian Orthodoxy. When the Kaiser informed Alix it was her duty to marry Nikki & convert, she accepted, and they became officially engaged on April 20, 1894. Nikki’s parents had not been too impressed with Alix, but since Tsar Alexander’s health had begun to decline, they agreed to the marriage. In early November, Tsar Alexander III died at the age of 49, leaving 26 yr old Nicholas as Emperor of Russia. That evening, Nicholas was consecrated by his father’s priest as Nicholas II and the following day, Alix was received into the Russian Orthodox Church, taking the name Alexandra Feodorovna.
Nicholas chose to maintain the conservative policies favored by his father throughout his reign. While Alexander III had concentrated on the formulation of general policy, Nicholas devoted much more attention to the details of administration. Too bad this attention to detail didn’t keep him from making a series of TERRIBLE mistakes, starting from day one.

1. The Khodynka Tragedy (AKA “Dear Diary, My Coronation Day Has A Body Count)

2. Letting Jesus Take the Wheel
Nicholas believed that God chose him to be Tsar and therefore his decisions reflected the will of God and could not be disputed. This belief made him a very stubborn ruler who rejected constitutional limits on his power. It put him into conflict with the emerging political consensus among the Russian elite. It also created distrust between the Church hierarchy and the Tsar, when the Church *should* have been a reliable base for him.

3. The Russo-Japanese War
In fairness, the war itself was probably inevitable. What was NOT inevitable was Nikki’s bias against the Japanese as “small of stature, feminine, weak, and inferior.” This insistence that the Japanese were racially inferior and had a weak military prevented Nikki from seeing the obvious: Japan was absolutely destroying his navy. He had to begged by multiple advisors and relatives to pursue peace and even then, he was so reluctant to make concessions that his minister Witte had to go behind his back to end the war.

4. Anti-Jewish Pogroms
Publicly condemned, privately condoned, these pogroms killed thousands of Russian Jews. After the brave action of Jewish revolutionary Dmitry Bogrov, who assassinated Pyotr Stolypin in 1911, Nicholas relented and got the government to stop persecuting Jewish citizens.

5. Bloody Sunday

6. 1905 Revolution
Around August/September, after his diplomatic success in ending the Russo-Japanese War, Witte wrote to the Tsar stressing the urgent need for political reforms at home. With the defeat of Russia by a non-Western power, the prestige and authority of the autocratic regime fell significantly. The Tsar remained impassive and indulgent; he spent most of that autumn hunting.
In October, a railway strike developed into a general strike that shut down the country. In a city without electricity, Witte told the Tsar that “the country was at the verge of a cataclysmic revolution.” The Tsar was like “fine, you can have the Imperial Duma” and agreed to give up part of his unlimited power.
On November 1 1905, Princess Milica of Montenegro introduced Nikki & Alix to Grigori Rasputin.
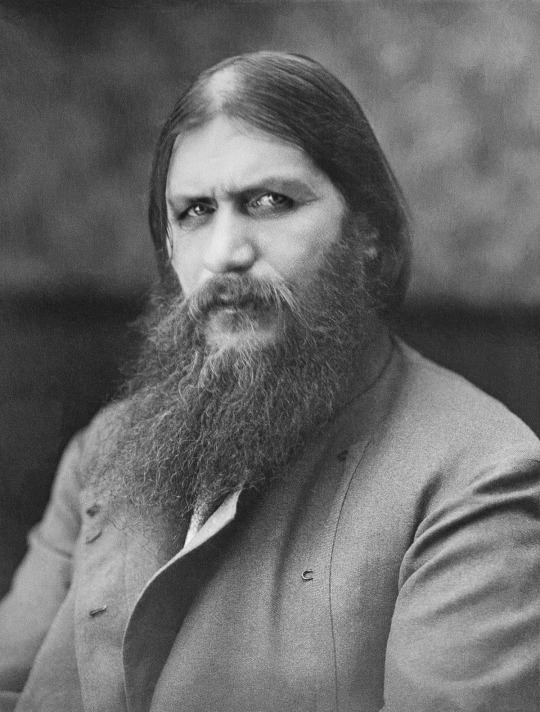

Grigori Rasputin (1869-1916)
- born a peasant in a small village along the Tura River - almost nothing is known about his youth and early adulthood
1886: Rasputin travels to Abalak, Russia and meets a peasant girl named Praskovya Dubrovina. After a courtship of several months, they married in February 1887. Praskovya remained in Rasputin’s home village of Pokrovskoye throughout Rasputin’s later travels and was devoted to him until his death. The couple had seven children, although only three survived to adulthood.
1897: Rasputin leaves home to go on a religious pilgrimage. He was twenty-eight, married ten years, with an infant son and another child on the way. According to Douglas Smith, his decision "could only have been occasioned by some sort of emotional or spiritual crisis."
Rasputin may have spent several months at Verkhoturye, and it was perhaps here that he learned to read and write, but he later complained about the monastery, claiming that some of the monks engaged in homosexuality and criticizing monastic life as too coercive. He returned to Pokrovskoye a changed man, looking disheveled and behaving differently. He became a vegetarian, swore off alcohol, and prayed and sang much more fervently than he had in the past.
By the early 1900s, Rasputin had developed a small circle of followers, primarily family members, and other local peasants, who prayed with him on Sundays and other holy days when he was in Pokrovskoye. Building a makeshift chapel in Efim's root cellar—Rasputin was still living within his father's household at the time—the group held secret prayer meetings there. These meetings were the subject of some suspicion and hostility from the village priest and other villagers. It was rumored that female followers were ceremonially washing him before each meeting, that the group sang strange songs, and even that Rasputin had joined the Khlysty, a religious sect whose ecstatic rituals were rumored to include self-flagellation and sexual orgies. However, there have been several investigations into these claims, and nobody has ever been able to establish that Rasputin was a Khlyst.
Alternative religious movements such as spiritualism and theosophy had become popular among the city's aristocracy before Rasputin's arrival in St. Petersburg, and many of the aristocracy were intensely curious about the occult and the supernatural. Rasputin's ideas and "strange manners" made him the subject of intense curiosity among St Petersburg's elite, who according to historian Joseph Fuhrmann were "bored, cynical, and seeking new experiences" during this period. His appeal may have been enhanced by the fact that he was also a native Russian, unlike other self-described "holy men" such as Nizier Anthelme Philippe and Gérard Encausse, who had previously been popular in St Petersburg.
By 1905, Rasputin had formed friendships with several members of the aristocracy, including the "Black Princesses", Militsa and Anastasia of Montenegro, who had married the tsar's cousins (Grand Duke Peter Nikolaevich and Prince George Maximilianovich Romanowsky), and were instrumental in introducing Rasputin to the tsar and his family.
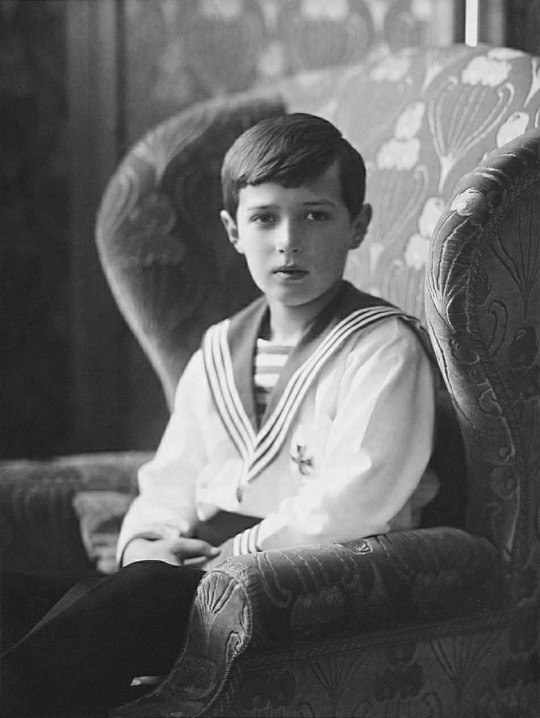

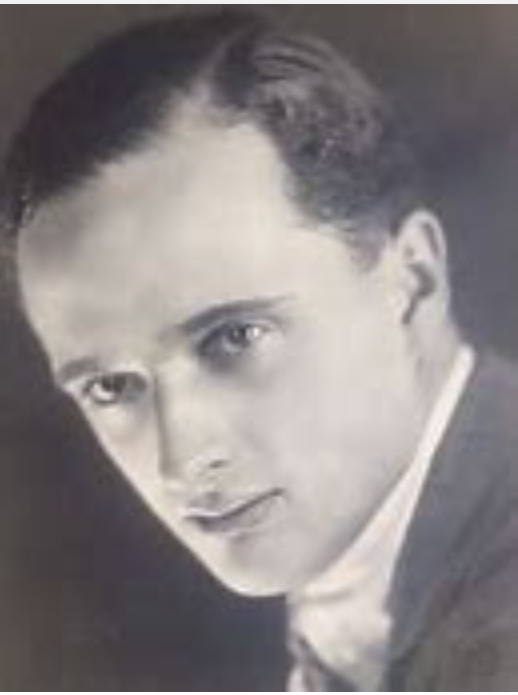
Alexei Nikolaevich (1904-1918)
The young heir was afflicted with Hemophilia B, a hereditary disease that prevents blood from clotting properly, which at that time was untreatable and usually led to an untimely death. As a granddaughter of Queen Victoria, Alexandra carried the same gene mutation that afflicted several of the major European royal houses, such as Prussia and Spain. Hemophilia, therefore, became known as "the royal disease". Through Alexandra, the disease had passed on to her son.
Because of the fragility of the autocracy at this time, Nicholas and Alexandra chose to keep secret Alexei's condition. Even within the household, many were unaware of the exact nature of the Tsarevich's illness. At first Alexandra turned to Russian doctors and medics to treat Alexei; however, their treatments generally failed, and Alexandra increasingly turned to mystics and holy men. Much of Rasputin's influence with the royal family stemmed from the belief by Alexandra and others that he had on several occasions eased the pain and stopped the bleeding of tsarevich Alexei.
It is unclear when Rasputin first learned of Alexei's hemophilia, or when he first acted as a healer. He may have been aware of Alexei's condition as early as October 1906, and was summoned by Alexandra to pray for Alexei when he had an internal hemorrhage in the spring of 1907. Alexei recovered the next morning.
During the summer of 1912, Alexei developed a hemorrhage in his thigh and groin after a jolting carriage ride near the royal hunting grounds at Spala, which caused a large hematoma. In severe pain and delirious with fever, the tsarevich appeared close to death. In desperation, Alexandra asked a mutual friend to send Rasputin a telegram, asking him to pray for Alexei. Rasputin wrote back quickly, telling Alexandra that "God has seen your tears and heard your prayers. Do not grieve. The Little One will not die. Do not allow the doctors to bother him too much." The next morning, Alexei's condition was unchanged, but Alexandra was encouraged by the message and regained some hope that Alexei would survive. Alexei's bleeding stopped the following day. Alexandra believed that Rasputin had performed a miracle, and concluded that he was essential to Alexei's survival.

The royal family’s belief in Rasputin’s healing powers brought him considerable power and status at court. The tsar appointed Rasputin his lampadnik (lamplighter), charged with keeping the lamps lit before religious icons in the palace, and this gained him regular access to the palace and royal family. Rasputin used his position to full effect, accepting bribes and sexual favors from his admirers while working diligently to expand his influence.
Rasputin was accused by his enemies of heresy and rape, was suspected of exerting undue political influence over the tsar, and was even rumored to be having an affair with the tsarina. Opposition to Rasputin's influence grew within the church. In 1907, the local clergy in Pokrovskoye denounced Rasputin as a heretic, and the Bishop of Tobolsk launched an inquest into his activities, accusing him of "spreading false, Khlyst-like doctrines".
In St Petersburg, Rasputin faced opposition from even more prominent critics, including prime minister Peter Stolypin and the Okhrana, the Tsar's secret police. Having ordered an investigation into Rasputin's activities, Stolypin confronted the Tsar about him but did not succeed in reining in Rasputin's influence or exiling him from St Petersburg. Rumors multiplied that Rasputin had assaulted female followers and behaved inappropriately on visits to the royal family – and particularly with the Tsar's teenage daughters Olga and Tatyana, rumors reported widely in the press after March 1910.
July 12, 1914: 33 yr old peasant woman Chionya Guseva attempts to assassinate Rasputin by stabbing him in the stomach outside his home in Pokrovskoye. Rasputin was seriously wounded, and for a time it was not clear if he would survive. After surgery and some time in the hospital, he recovered. Guseva claimed to have acted alone, having read about Rasputin in the newspapers and believing him to be a "false prophet and even an Antichrist". She was found to be not responsible for her actions by reason of insanity.

Russia Joins the Great War
June 28, 1914: Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, is assassinated by a Bosnian Serb nationalist in Sarajevo. The concept of Pan-Slavism and shared religion created strong public sympathy between Russia and Serbia. Territorial conflict created rivalries between Germany and France and between Austria-Hungary and Serbia, and as a consequence alliance networks developed across Europe. Nicholas wanted neither to abandon Serbia to the ultimatum of Austria, nor to provoke a general war. In a series of letters exchanged with Wilhelm of Germany (the "Willy–Nicky correspondence") the two proclaimed their desire for peace, and each attempted to get the other to back down. Nicholas desired that Russia's mobilization be only against Austria-Hungary, in the hopes of preventing war with Germany.
July 25, 1914: Nicholas decides to intervene in the Austro-Serbian conflict, a step toward general war.
July 28, 1914: Austria-Hungary formally declares war against Serbia.
July 29, 1914: Count Witte tells the French ambassador (a man by the delightful name of Maurice Paleologue) that Slav solidarity is nonsense and Russia has nothing to gain from this war.
July 30, 1914: Nicholas took the fateful step of confirming the order for general mobilization, despite being strongly counselled against it. Upon discovering this, Germany announced their own pre-mobilization posture, the Imminent Danger of War, and requested that Russia demobilize within the next twelve hours. In Saint Petersburg, at 7 pm, with the ultimatum to Russia having expired, the German ambassador to Russia met with the Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Sazonov, asked three times if Russia would reconsider, and then with shaking hands, delivered the note accepting Russia's war challenge and declaring war on August 1, 1914. Less than a week later, on August 6, Franz Joseph signed the Austro-Hungarian declaration of war on Russia.

Russia was grossly unprepared for this war. Germany had ten times as much railway track per square mile, and whereas Russian soldiers travelled an average of 1,290 kilometres (800 mi) to reach the front, German soldiers traveled less than a quarter of that distance. Russian heavy industry was still too small to equip the massive armies the Tsar could raise, and her reserves of munitions were pitifully small; while the German army in 1914 was better equipped than any other, man-for-man, the Russians were severely short on artillery pieces, shells, motorized transports, and even boots. With the Baltic Sea barred by German U-boats and the Dardanelles by the guns of Germany's ally, the Ottoman Empire, Russia initially could receive help only via Archangel, which was frozen solid in winter, or via Vladivostok, which was over 6,400 kilometres (4,000 mi) from the front line. By 1915, a rail line was built north from Petrozavodsk to the Kola Gulf and this connection laid the foundation of the ice-free port of what eventually was called Murmansk. The Russian High Command was moreover greatly weakened by the mutual contempt between Vladimir Sukhomlinov, the Minister of War, and the incompetent Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolayevich who commanded the armies in the field.
In spite of all of this, an immediate attack was ordered against the German province of East Prussia. The Germans mobilised there with great efficiency and completely defeated the two Russian armies which had invaded. The Battle of Tannenberg, where an entire Russian army was annihilated, cast an ominous shadow over Russia's future. Russia had great success against both the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman armies from the very beginning of the war, but they never succeeded against the might of the German Army. Gradually a war of attrition set in on the vast Eastern Front, where the Russians were facing the combined forces of the German and Austro-Hungarian armies, and they suffered staggering losses. Defeat at the front bred disorder at home. At first, the targets were German, and for three days in June shops, bakeries, factories, private houses and country estates belonging to people with German names were looted and burned. The inflamed mobs then turned on the government, declaring the Empress should be shut up in a convent, the Tsar deposed and Rasputin hanged.
Nicholas was by no means deaf to these discontents. An emergency session of the Duma was summoned and a Special Defense Council established, its members drawn from the Duma and the Tsar's ministers. The energetic and efficient General Alexei Polivanov replaced Sukhomlinov as Minister of War, which failed to improve the strategic situation. In the aftermath of the Great Retreat and the loss of the Kingdom of Poland, Nicholas assumed the role of commander-in-chief after dismissing his cousin, Grand Duke Nicholas Nikolayevich, in September 1915. This was a mistake, as the Tsar came to be personally associated with the continuing losses at the front. He was also away at the remote HQ at Mogilev, far from the direct governance of the empire, and when revolution broke out in Petrograd he was unable to halt it. In reality the move was largely symbolic, since all important military decisions were made by his chief-of-staff General Michael Alexeiev, and Nicholas did little more than review troops, inspect field hospitals, and preside over military luncheons.
Cut off from public opinion, Nicholas could not see that the dynasty was tottering. With Nicholas at the front, domestic issues and control of the capital were left with his wife Alexandra. However, Alexandra's relationship with Grigori Rasputin, and her German background, further discredited the dynasty's authority. Nicholas had been repeatedly warned about the destructive influence of Rasputin but had failed to remove him. Rumors and accusations about Alexandra and Rasputin appeared one after another; Alexandra was even accused of harboring treasonous sympathies towards Germany. One outspoken member of the Duma, far-right politician Vladimir Purishkevich, stated in November 1916 that he held the tsar's ministers had "been turned into marionettes, marionettes whose threads have been taken firmly in hand by Rasputin and the Empress Alexandra Fyodorovna – the evil genius of Russia and the Tsarina… who has remained a German on the Russian throne and alien to the country and its people".

The Slapstick Assassination of Rasputin
A group of nobles led by Prince Felix Yusupov, Grand Duke Dmitri Pavlovich, and the aforementioned Vladimir Purishkevich concocted a plan in December 1916 to kill Rasputin, apparently by luring him to the Yusupovs' Moika Palace. The story that Yusupov recounted in his memoirs has become the most frequently told version of events.
Yusupov said he invited Rasputin to his home shortly after midnight and ushered him into the basement. Yusupov offered Rasputin tea and cakes which had been laced with cyanide. Rasputin initially refused the cakes but then began to eat them and, to Yusupov's surprise, appeared unaffected by the poison. Rasputin then asked for some Madeira wine (which had also been poisoned) and drank three glasses, but still showed no sign of distress.
At around 2:30 am, Yusupov excused himself to go upstairs, where his fellow conspirators were waiting. He took a revolver from Dmitry Pavlovich, then returned to the basement and told Rasputin that he'd "better look at the crucifix and say a prayer", referring to a crucifix in the room, then shot him once in the chest. The conspirators then drove to Rasputin's apartment, with Sukhotin wearing Rasputin's coat and hat in an attempt to make it look as though Rasputin had returned home that night.
Upon returning to the Moika Palace, Yusupov went back to the basement to ensure that Rasputin was dead. Suddenly, Rasputin leaped up and attacked Yusupov, who freed himself with some effort and fled upstairs. Rasputin followed Yusupov into the palace's courtyard, where he was shot by Purishkevich. He collapsed into a snowbank. The conspirators then wrapped his body in cloth, drove it to the Petrovsky Bridge, and dropped it into the Malaya Nevka River. interesting postscript: Rasputin’s daughter Maria later emigrated to France and then the United States, where she became a dancer and a lion tamer in the circus.

The February Revolution
By early 1917, Russia was on the verge of total collapse of morale. An estimated 1.7 million Russian soldiers were killed in World War I. The sense of failure and imminent disaster was everywhere. The army had taken 15 million men from the farms and food prices had soared. An egg cost four times what it had in 1914, butter five times as much. The severe winter dealt the railways, overburdened by emergency shipments of coal and supplies, a crippling blow.
Russia entered the war with 20,000 locomotives; by 1917, 9,000 were in service, while the number of serviceable railway wagons had dwindled from half a million to 170,000. In February 1917, 1,200 locomotives burst their boilers and nearly 60,000 wagons were immobilized. In Petrograd, supplies of flour and fuel had all but disappeared. War-time prohibition of alcohol was enacted by Nicholas to boost patriotism and productivity, but instead damaged the funding of the war, due to the treasury now being deprived of alcohol taxes.
On 23 February 1917 in Petrograd, a combination of very severe cold weather and acute food shortages caused people to start to break into shop to get bread and other necessities. In the streets, red banners appeared and the crowds chanted "Down with the German woman! Down with Protopopov! Down with the war! Down with the Tsar!" Police shot at the populace, which incited riots. The troops in the capital were poorly motivated and their officers had no reason to be loyal to the regime, with the bulk of the tsar's loyalists away fighting World War I. In contrast, the soldiers in Petrograd were angry, full of revolutionary fervor and sided with the populace. The Tsar's Cabinet begged Nicholas to return to the capital and offered to resign completely. The Tsar, 800 kilometres (500 mi) away, misinformed by the Minister of the Interior Alexander Protopopov that the situation was under control, ordered that firm steps be taken against the demonstrators.
For this task, the Petrograd garrison was quite unsuitable. The cream of the old regular army had been destroyed in Poland and Galicia. In Petrograd, 170,000 recruits, country boys or older men from the working-class suburbs of the capital itself, were available under the command of officers at the front and cadets not yet graduated from the military academies. The units in the capital, although many bore the names of famous Imperial Guard regiments, were in reality rear or reserve battalions of these regiments, the regular units being away at the front. Many units, lacking both officers and rifles, had never undergone formal training. General Khabalov attempted to put the Tsar's instructions into effect on the morning of Sunday, 11 March 1917. Despite huge posters ordering people to keep off the streets, vast crowds gathered and were only dispersed after some 200 had been shot dead, though a company of the Volinsky Regiment fired into the air rather than into the mob, and a company of the Pavlovsky Life Guards shot the officer who gave the command to open fire. Nicholas, informed of the situation by Rodzianko, ordered reinforcements to the capital and suspended the Duma. However, it was too late.
March 12, 1917: The Volinsky Regiment mutinied and was quickly followed by the Semenovsky, the Ismailovsky, the Litovsky Life Guards and even the legendary Preobrazhensky Regiment of the Imperial Guard, the oldest and staunchest regiment founded by Peter the Great. The arsenal was pillaged and the Ministry of the Interior, Military Government building, police headquarters, Law Courts and a score of police buildings were set on fire. By noon, the fortress of Peter and Paul, with its heavy artillery, was in the hands of the insurgents. By nightfall, 60,000 soldiers had joined the revolution. Order broke down and members of the Duma and the Soviet formed a Provisional Government to try to restore order. They issued a demand that Nicholas must abdicate. Faced with this demand, which was echoed by his generals, deprived of loyal troops, with his family firmly in the hands of the Provisional Government, and fearful of unleashing civil war and opening the way for German conquest, Nicholas had little choice but to submit.
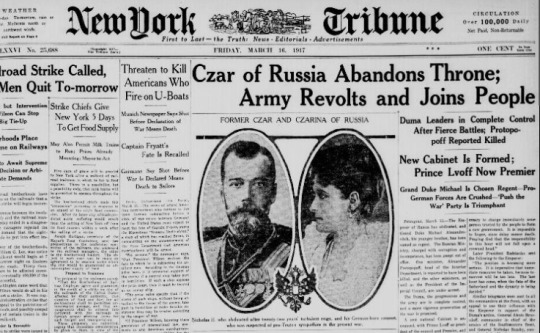
Abdication & Exile
Nicholas had suffered a coronary occlusion only four days before his abdication. He first abdicated in favor of Alexei, but a few hours later changed his mind after advice from doctors that Alexei would not live long enough while separated from his parents, who would be forced into exile. Nicholas thus abdicated on behalf of his son, and drew up a new manifesto naming his brother, Grand Duke Michael, as the next Emperor of all Russias. He issued a statement but it was suppressed by the Provisional Government. Michael declined to accept the throne until the people were allowed to vote through a Constituent Assembly for the continuance of the monarchy or a republic.
The abdication of Nicholas II and Michael's deferment of accepting the throne brought three centuries of the Romanov dynasty's rule to an end. The fall of Tsarist autocracy brought joy to liberals and socialists in Britain and France. The United States was the first foreign government to recognize the Provisional government. In Russia, the announcement of the Tsar's abdication was greeted with many emotions, including delight, relief, fear, anger and confusion.
Both the Provisional Government and Nicholas wanted the royal family to go into exile following his abdication, with the United Kingdom being the preferred option. The British government reluctantly offered the family asylum on 19 March 1917, although it was suggested that it would be better for the Romanovs to go to a neutral country. The offer of asylum was withdrawn in April following objections by King George V, who, acting on the advice of his secretary Arthur Bigge, 1st Baron Stamfordham, was worried that Nicholas's presence might provoke an uprising like the previous year's Easter Rising in Ireland. In the early summer of 1917, the Russian government approached the British government on the issue of asylum and was informed the offer had been withdrawn due to the considerations of British internal politics.
The French government declined to accept the Romanovs in view of increasing unrest on the Western Front and on the home front as a result of the ongoing war with Germany. The British ambassador in Paris, Lord Francis Bertie, advised the Foreign Secretary that the Romanovs would be unwelcome in France as the ex-Empress was regarded as pro-German.
Even if an offer of asylum had been forthcoming, there would have been other obstacles to be overcome. The Provisional Government only remained in power through an uneasy alliance with the Petrograd Soviet, an arrangement known as "The Dual power". An initial plan to send the royal family to the northern port of Murmansk had to be abandoned when it was realized that the railway workers and the soldiers guarding them were loyal to the Petrograd Soviet, which opposed the escape of the tsar; a later proposal to send the Romanovs to a neutral port in the Baltic Sea via the Grand Duchy of Finland faced similar difficulties.

Execution of the Royal Family
The Romanovs were imprisoned in a series of decreasingly luxurious quarters until they finally ended up in Yekaterinburg at Ipatiev House, AKA the “House of Special Purpose,” perhaps the most ominous name one could give a house. In the early hours of 17 July 1918, the royal family was awakened around 2:00 am, got dressed, and were led down into a half-basement room at the back of the house. The pretext for this move was the family's safety, i.e. that anti-Bolshevik forces were approaching Yekaterinburg, and the house might be fired upon.
A firing squad had been assembled and was waiting in an adjoining room, composed of seven Communist soldiers from Central Europe, and three local Bolsheviks, all under the command of Yurovsky. Nicholas was carrying his son. When the family arrived in the basement, the former Tzar asked if chairs could be brought in for his wife and son to sit on. Yurovsky ordered two chairs brought in, and when the empress and the heir were seated, the executioners filed into the room. Yurovsky announced to them that the Ural Soviet of Workers' Deputies had decided to execute them. A stunned Nicholas asked, "What? What did you say?" and turned toward his family. Yurovsky quickly repeated the order and Nicholas said, according to Peter Ermakov, "You know not what you do."
The executioners drew handguns and began shooting; Nicholas was the first to die. Nicholas was shot several times in the chest (sometimes erroneously said to have been shot in his head, but his skull bore no bullet wounds when it was discovered in 1991). Anastasia, Tatiana, Olga, and Maria survived the first hail of bullets; the sisters were wearing over 1.3 kilograms of diamonds and precious gems sewn into their clothing, which provided some initial protection from the bullets and bayonets. They were then stabbed with bayonets and finally shot at close range in their heads. The bodies were driven to nearby woodland, searched and burned. The remains were soaked in acid and finally thrown down a disused mineshaft. On the following day, other members of the Romanov family including Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna, the empress's sister, who were being held in a school at Alapayevsk, were taken to another mine shaft and thrown in alive, except for Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich who was shot when he tried to resist.
An announcement from the Presidium of the Ural Regional Soviet of the Workers' and Peasants' Government emphasized that conspiracies had been exposed to free the ex-tsar, that counter-revolutionary forces were pressing in on Soviet Russian territory, and that the ex-tsar was guilty of unforgivable crimes against the nation. {My opinion: they’re right! They did have to execute the Romanovs. But that does not make it any less sad that five young people who had never held power, who did not choose their parents, had to die for the failures of Nikki & Alix. I think of all the other Russian youths shot and bayoneted because of the Tsar and weep for them as well, though their names and faces are unknown to me.}

6 notes
·
View notes
Text







Princess Louise of Prussia (1838-1923).
Grand Duchess of Baden.
.
She was the second child and only daughter of German Emperor Wilhelm I and Augusta of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach. She was the younger sister of Frederick III of Germany ("Fritz") and aunt of Wilhelm II of Germany.
.
While Wilhelm showed some outward affection to his only son, he lavished attention on Louise, and often his unexpected visits to her schoolroom resulted in them playing together on the floor. Mother and daughter however were not close.
.
Louise was betrothed to Frederick, Prince Regent of Baden in 1854, and they married in 1856 at Neues Palais in Potsdam. Frederick had been regent because of his brother Louis's insanity, and was proclaimed Grand Duke of Baden when doctors declared that there was no chance of recovery.
.
Within a few weeks of their marriage, the new grand duchess was already pregnant with their first child, Hereditary Grand Duke Frederick. They later had two other children. She was a happy wife and mother. Louise and Frederick disliked the stiffness of the Karlsruhe court, and gladly escaped to their castle on the island of Mainau. They were popular in Baden, and everyone spoke with affectionate pride of their grand duke and duchess.
.
The Austro-Prussian War caused a degree of friction between Baden and Prussia, as the former, despite their close familial connections to Berlin, chose to support the Austrians. Her father's strongly anti-Catholic chancellor Otto von Bismarck disliked Baden however, as it was one of Germany's most important Catholic states. Suspicious of the grand duchess' influence on her father, he did his best to block her request for clemency on behalf of Alsace Catholics to the emperor.
.
Because of her status as Grand Duchess, Louise was very involved in her duchy's charitable organizations, particularly issues concerning women.
.
Louise, now Dowager Grand Duchess of Baden, lived to see her duchy become absorbed into the new state of Germany under the Revolution of 1918-19 that took place at the end of World War I. By permission of the new government, she and her family were allowed to stay at the Langenstein Palace, which belonged to a Swedish count, Douglas. During these events, Louise was said to have kept her calm and never uttered a word of complaint. The new republican government gave her permission to live out the rest of her life in retirement at Baden-Baden, where she died in 1923.
[Submission]
#Louise of prussia#Duchess#Princess#Princess Louise#19th century#1800s#german history#germany#history#history nerd#history geek#history lover#women's history#women history#women in history#herstory#royal history#history crush#historical crush#historical hottie#history hottie#historical babes#historical figure#historical
42 notes
·
View notes
Photo








Tsarinas Consorts of the Romanov House.
Maria Vladimirovna - Maria was born in 1601 and was the first wife of Tsar Michael I. She was selected for marriage to Michael by his mother, Xenia Shestova, after several years of difficulty of finding a partner for the Tsar. The wedding took place on 19 September 1624. Not long after the wedding, the Tsarina took ill. She died on 17 January 1625, four months after the wedding. There were rumors at the time that she had been poisoned by fractions at court determined to prevent any potential pro-Rurikid influence, or by the enemies of her father’s family.
Eudoxia Lukyanovna - Eudoxia was born in 1608 and was the second wife of Tsar Michael I. She was among those daughters of the nobility summoned to appear in the Bride-show at court, when the tsar was to select his new tsaritsa, after his first spouse had died. He eventually chose Eudoxia because of her beauty, polite behavior and mild disposition. She was described as a modest and virtuous girl, dominated by her proud relatives, who sometimes brought her to tears but still did not complain. The wedding was conducted on 5 February 1626. After the wedding, she was given several lands, and a substantial fortune of her own. Eudoxia and Michael became parents of 10 children, including the future Tsar Alexei I.
Maria Ilyinichna - Maria was born in 1624 and was the first wife of Tsar Alexei I. The tsar was to choose his bride from a bride-show of hundreds of daughters of the nobility, Maria was selected as the tsar's second choice after his first choice to marry Euphemia Fedorovna Vsevolozhskaya was annuled. Maria was reportedly a beauty. The wedding was conducted in 16 January 1648 in Moscow and the union is described as a happy one. The couple had 13 children, including Tsar Feodor III of Russia, Tsar Ivan V of Russia, and the Princess Regent Sophia Alekseyevna.
Natalya Kirillovna - Natalya was born in 1651 and was the second wife of Tsar Alexei I. In March 1669, Tsar Alexis’ first wife, Tsarina Maria, died during the birth of what would have been their fourteenth child. The Tsar supported by the Russian public, although not by the family of Maria, decided to remarry in the hope of producing more potential heirs. The tsar arranged an inspection of women he considered eligible in early 1670, Natalya was added to this inspection following an encounter with the tsar at the home of her adoptive father, Artamon Matveyev. Alexis was impressed by Natalya's beauty, and selected her to be his bride without needing to go ahead with a planned second inspection. The couple married on 1 February 1671. Alexis and Natalya had a happy marriage, spending much of their time together in various palaces and villas around Moscow. The couple became parents of the future Tsar Peter the Great.
Agafiya Semyonovna - Agafiya was born in 1663 and was the first wife of Tsar Feodor III. In 1680, Tsar Feodor, saw her during a religious procession: when she fainted after the sight of a witch in a religious theater play he rushed forward to support her, and fell in love with her. Aware that her uncle did not wish her to marry, a traditional summon was proclaimed to all unmarried noble women to gather for Feodor to choose from, and he chose her. On 18 July 1680, she married Feodor. Agafya has been described as merciful and loyal to her husband and the public's welfare. She could speak and write Polish, French and Latin and was well informed about the Western European life style. She could also play harpsichord. She was described as beautiful as "an angel of heaven", with an easy going character. She was the first to advocate beard-shaving and the adoption of Western clothes at the Russian court. She herself was the first Tsarina to expose her hair and to wear a Western (Polish) dress. Agafya died as a consequence of the childbirth, and six days later, the nine-days-old Tsarevich Ilya also died. She was reportedly deeply mourned by Feodor.
Marfa Matveyevna - Marfa was born in 1664 and was the second wife of Tsar Feodor III. She was the daughter of Matvey Vasilyevich Apraksin and Domna Bogdanovna Lovchikova. She and Feodor were married on 14 February 1682, and he died only a few months later in April.
Praskovya Fyodorovna - Praskovya was born in 1664 and was the only wife of Tsar Ivan V. The marriage of Ivan V was arranged by his sister, the regent Sophia. Ivan V himself reportedly showed no inclination toward marriage and according to the Swedish diplomat Hildebrandt Horn, Praskovia was not willing to marry Ivan, but was forced to consent. The wedding took place on 9 January 1684, with the Patriarch John officiating as the ceremony. Praskovia Saltykova was at the time of her marriage described as a healthy Russian beauty, tall, with a full figure and long thick hair, as a person, she was described as religious, superstitious and not very well educated. Praskovya and Ivan had five daughters including Empress Anna of Russia.
Eudoxia Feodorovna - Eudoxia was born on 1669 and was the first wife of Tsar Peter I (the Great). She was chosen as a bride for the Tsar by his mother Natalya. She was crowned Tsarina in 1689. The Tsar could not stand her conservative relatives and soon abandoned her for a Dutch beauty, Anna Mons. Eudoxia's letters to Peter were full of complaints and exhortations of unrequited love. She was the paternal grandmother of Peter II of Russia.
Catherine Alexeyevna - Catherine was born on 1684 and was the second wife of Tsar Peter I (the Great). She was originally named Marta Helena Skowrońska, In 1705,she converted to Orthodoxy and took the new name of Catherine Alexeyevna. Afterwards she became part of the household of Prince Alexander Menshikov, who was the best friend of Peter the Great of Russia. Anecdotal sources suggest that she was purchased by him. In 1704, she was well established in the Tsar's household as his mistress, and gave birth to a son, Peter. Though no record exists, Catherine and Peter are described as having married secretly in St. Petersburg in 1707. Peter married her again (this time officially) at Saint Isaac's Cathedral in St. Petersburg in 1712; she took the style of her husband and became Tsarina. They had 12 children. Peter died on 1725 without name a successor and Catherine was chosen as Empress Regnant.
Catherine Alekseyevna - Catherine was born in Prussia as Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst on 1729 and was the only wife of Tsar Peter III. The choice of Sophie as wife of her second cousin, the prospective Tsar Peter, resulted from some amount of diplomatic management in which Count Lestocq, Peter's aunt (and the ruling Russian Empress) Elizabeth and Frederick II of Prussia took part. Lestocq and Frederick wanted to strengthen the friendship between Prussia and Russia to weaken Austria's influence and ruin the Russian chancellor Bestuzhev, on whom Empress Elizabeth relied, and who acted as a known partisan of Russo-Austrian co-operation. The diplomatic intrigue failed, largely due to the intervention of Sophie's mother, Johanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp. Historical accounts portray Johanna as a cold, abusive woman who loved gossip and court intrigues. Despite Johanna's interference, Empress Elizabeth took a strong liking to Catherine, who, on arrival in Russia in 1744 spared no effort to ingratiate herself not only with Empress Elizabeth, but with her husband and with the Russian people as well. The long-planned dynastic marriage finally occurred on 21 August 1745 in Saint Petersburg. Sophie had turned 16; The newlyweds settled in the palace of Oranienbaum, which remained the residence of the "young court" for many years to come. In 1762 Peter died and Catherine took the throne as Catherine II. Peter and Catherine were parents of Tsar Paul I.
Maria Feodorovna - Maria was born in Prussia as Duchess Sophie Dorothea on 1759 and was the second wife of Tsar Paul I. In 1776, when Grand Duke Paul (the future Paul I of Russia), became a widower, Sophie Dorothea was chosen by Frederick II of Prussia, her maternal great uncle, and by Empress Catherine II of Russia, as the ideal candidate to be Paul’s second wife. They met in a state dinner in Berlin and their engagement was quickly arranged.Sophie Dorothea arrived in St Petersburg that September, converted to the Russian Orthodox Church, and took the name Maria Feodorovna. She married Paul on 26 September 1776. In spite of her husband's difficult character, Maria Feodorovna made a success of her marriage. Paul and Maria lived at Gatchina. They were devoted to each other and had ten children including: Tsar Alexander I, Tsar Nicholas I of Russia, Grand Duchess Maria of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Queen Catherine of Wurttemberg and Queen Anna of the Netherlands.
Elizabeth Alexeievna - Elizabeth was born on 1779 in Germany as Princess Louise Maria Auguste of Baden and was the only wife of Tsar Alexander I. Catherine the Great was looking for a bride for her eldest grandson, the future Alexander I, and set her eyes on the Princesses of Baden, so Catherine invited Princess Louise and her younger sister Frederica, who later became Queen of Sweden, to Russia. In the autumn of 1792, the two sisters arrived in St. Petersburg. The Empress was delighted by Louise, finding her a model of beauty, charm, and honesty. Louise herself was attracted to Alexander, who was handsome. At first, Alexander was shy with his future bride — very young and inexperienced, however, the young couple soon grew fond of each other. The Princess learned Russian and converted to the Orthodox Church. The wedding took place on 28 September 1793. "It was a marriage between Psyche and Cupid", Catherine wrote to the Prince of Ligne. Elizabeth was only fourteen, her husband a year older.
Alexandra Feodorovna - Alexandra was born in Berlim as Princess Friederike Luise Charlotte Wilhelmine of Prussia on 1798 and was the only wife of Tsar Nicholas I. In 1814, Nicholas Pavlovich, future Tsar of Russia, and his brother Michael Pavlovich, visited Berlin. Arrangements were made for Nicholas to marry Charlotte, then fifteen years old, to strengthen the alliance between Russia and Prussia. On a second visit the following year, Nicholas fell in love with the then-seventeen-year-old Princess Charlotte. The feeling was mutual, "I like him and am sure of being happy with him." She wrote to her brother. On June 1817 Charlotte came to Russia with her brother William. After arriving in St. Petersburg she converted to Russian Orthodoxy, and took the Russian name "Alexandra Feodorovna". On her nineteenth birthday, on July 1817, she and Nicholas were married in the Grand Church of the Winter Palace. The couple had 7 children including Tsar Alexander II.
Maria Alexandrovna - Maria was born as Princess Maximiliane Wilhelmine Auguste Sophie Marie of Hesse and by Rhine on 1824 and was the first wife of Tsar Alexander II. In 1839, the Tsarevich Alexander, traveled to western Europe to complete his education and to search for a wife. He stopped for one day in Darmstadt during the evening, invited to the Opera house by the Grand Duke of Hesse, Alexander was introduced to Princess Marie. Alexander was smitten by her. In June of 1939, he returned to Darmstadt to seal his engagement with Princess Marie. The Princess was received into the Russian Orthodox Church on December 1840 and became Grand Duchess Maria Alexandrovna. The wedding took place on 28 April, 1841. The couple had 8 children including Tsar Alexander III.
Maria Feodorovna - Maria was born on 1847 at Denmark as Princess Marie Sophie Frederikke Dagmar and was the only wife of Tsar Alexander III. In 1864, Tsarevich Nicholas went to Denmark where he was betrothed to Dagmar. On April 1865 he died from meningitis. His last wish was that Dagmar would marry his younger brother, the future Alexander III. Dagmar was distraught after her young fiancé's death. The disaster had brought her very close to "Nicholas’" parents, and she received a letter from Alexander II in which the Emperor attempted to console her. In June 1866, while on a visit to Copenhagen, the Tsarevich Alexander asked Dagmar for her hand. They had been in her room looking over photographs together. She converted to Orthodoxy and became Grand Duchess Maria Feodorovna. The wedding took place on November 1866 in the Imperial Chapel of the Winter Palace in Saint Petersburg. The couple had 6 children including Tsar Nicholas II.
Alexandra Feodorovna - Alexandra was born on 1872 in Darmstadt as Princess Alix Viktoria Helene Luise Beatrix of Hesse and by Rhine and was the only wife of Tsar Nicholas II. Nicholas and Alix had first met in 1884 at the wedding of Nicholas's Uncle Sergei and Alix's sister Elisabeth in St. Petersburg. When Alix returned to Russia on a several week visit in 1889, the two young people fell in love. Initially Nicholas's father, Tsar Alexander III, refused the prospect of their marriage. Alexander and his wife were both vehemently anti-German, and did not want the match with Princess Alix. While in good health, Alexander III ignored his son's demands, but began to relent when his health began to fail. In 1894 Nicholas proposed to Alix. She initially rejected him on the grounds of her refusal to convert to Orthodoxy. However, after pressure from the Kaiser, who had told her that it was her duty to marry Nicholas she accepted his second proposal. Alexandra and Nicholas were wed in the Grand Church of the Winter Palace of St Petersburg on 26 November 1894. The marriage that began that night remained exceptionally close until the pair was assassinated in 1918. The marriage was outwardly serene and proper, but based on intensely passionate physical love.
#Tsarina maria vladimirovna#tsarina eudoxia#tsarina maria ilyinichna#tsarina natalya#tsarina agafiya#tsarina marfa#Catherine the Great#catherine i#tsarina maria alexandrovna#tsarina maria feodorovna#elizabeth alexeievna#maria feodorovna#tsarina alexandra#empress alexandra
146 notes
·
View notes
Photo










House of Hesse & of Romanov: Princess Elisabeth “Ella” of Hesse and by Rhine aka Grand Duchess Elizabeth Feodorovna of Russia
Elisabeth was born as the second oldest child and daughter to Louis IV, The Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine, and his wife Princess Alice of the United Kingdom, a daughter of Queen Victoria. In German, she is also known as Elisabeth of Hessen-Darmstadt. One of her younger sisters was the last Russian Empress Alexandra Feodorovna aka Princess Alix of Hesse and by Rhine. By her family, she was nicknamed Ella.
Elisabeth grew up very modestly for her status. She had to clean her own room and her mother made the dresses for the children themselves. Elisabeth often accompanied her mother Alice to a nearby hospital during the Austro-Prussian war. Elisabeth grew up bilingual. While she spoke English with her mother, she spoke German with her father.
Ella was a highly sought after bride. The future German Emperor Wilhelm II fell in love with her when he was still a student and proposed to her but she declined. A match supported by her grandmother Queen Victoria was with Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden. But again Ella declined and caused a major disruption in her relationship with Empress Augusta and it took some time for her to forgive the young princess for the rejection of her grandson.
The one who could finally win her heart was Grand Duke Sergei Alexandrovich of Russia. She knew him since childhood because her great-aunt Empress Maria Alexandrovna aka Princess Marie of Hesse and by Rhine often visted her old home and took her sons with her. They bonded over the mutual experience of losing their parents and later also over their similar interest in art and religion. However, he had to proposed twice before Elisabeth accepted, much to the dismay of her grandmother Queen Victoria. The couple married on June 15th, 1884, in St. Petersburg. Ella could have legally kept her Protestant faith but she chose to convert in 1891, taking the not much changed name of Elizabeth Feodorovna.
Unlike her sister Alix, Elisabeth made a good impression on the Russian people and aristocracy. However, her marriage did not turn out happy. Sergei was a jealous man although she gave him no reason for it. The couple did not have children of their own but hosted parties especially for children and eventually took in Sergei’s niece and nephew Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna and Grand Duke Dmitri Pavlovich.
Elisabeth encouraged Nicholas II. to pursue her sister Alix against her British families wishes. She was also the one who convinced her sister to convert to Orthodoxy after her initial refusal of Nicholas’ proposal because of a matter of faith.
Elisabeth’s husband Sergei was assassinated on February 18th, 1905. It came to her as a shock but she remained incredibly calm. Her family feared a nervous breakdown but it did not happen. Instead Elisabeth forbade herself from crying during mourning. She eventually even went to visit the assassin in prison and after hearing his reason for killing her husband, begged him to swallow his pride and she would petition to save his life. He denied but she still asked her brother-in-law to forgive him his crimes.
The death of her husband was a changing point in Ella’s life. She became a vegetarian and by 1909 a nun. After selling all her jewellery, including her wedding ring, and other items of worth, she founded the Convent of Saints Martha and Mary and became its abbess. For many years, Elisabeth's institution helped the poor and the orphans in Moscow by fostering the prayer and charity of devout women.
Elisabeth met her sister Alix for the last time in 1916, expressing concern about Rasputin’s influence over her and politics. Ella might have known about the murder of Rasputin beforehand since she sent telegrams out the night of it before the news was released to the public. Furthermore, she stated that the killing of Raputin had been a patriotic act.
Even though, she was a nun, she was still regarded as a member of the Romanov family during the Russian Revolution. She was exiled and moved across the country along with other relatives in 1918. Their last stop was Alapayevsk where they arrived on Max 20th, 1918. Elisabeth and other Romanovs were killed in the night from the 17th to 18th July 1918. It was later discovered that Ella and other did not immediately die from the gunshots. Ella for example died of wounds she suffered when falling into the pit but she still nursed Prince Ioann Konstantinovich by bandaging his head. Elisabeth’s final resting place is in the Church of Mary Magdalene in Jerusalem.
// Elsie Benett as Ella in The Last Czars - Season 01
#historic women#women in history#period drama#perioddramaedit#The Last Czars#House of Romanov#elisabeth feodorovna#Elisabeth of Hesse and by Rhine#Elisabeth of Hesse-Darmstadt#1800s#1900s#19th century#20th century#House of Hesse#House of Hesse-Darmstadt#German Romanovs#Women of the House of Hesse
373 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Biography of Queen Isabella
Early Life
Born 1 November 1992 in Geneva Switzerland to Archduke Carl Christian of Austria & Princess Marie Astrid of Luxembourg later Archduchess Marie Astrid of Austria. Archduchess Isabella Maria Anna Charlotte Elisabeth Ingeborg of Austria was the 5th of what would later become 6 children. With an older sister, three older brothers, and a younger sister Archduchess Isabella's life was filled with many close family members. Archduchess Isabella was christened in Zwiefalten Abbey in Baden-Wuttermberg, Germany. Her godparents were Queen Fabiola of the Belgians, Alois, Hereditary Prince & now Regent of Liechtenstein, and Maria Teresa, Hereditary Grand Duchess of Luxembourg then The Grand Duchess of Luxembourg. Two are usually chosen to be godparents, but Maria Teresa, later The Grand Duchess of Luxembourg was added to be a godparent after saving Archduchess Marie Astrid's life during her pregnancy with Isabella. Upon her baptism, Queen Fabiola of the Belgians called her "petite reine" which a nickname that her grandmother Josephine Charlotte, Grand Duchess of Luxembourg picked up soon after. Isabella grew up in Geneva with 5 other siblings while her father was a banker and her mother worked for the Luxembourg Grand Ducal Family as the daughter of the Grand Duke of Luxembourg.
Isabella's childhood was spent with her 5 other siblings, parents, and over 3 dozen cousins from Liechtenstein, Austria, Luxembourg, and Belgium. Her childhood was spent in Switzerland with holidays to Luxembourg, France, Spain, and Belgium. She spoke German and French in her early years and learned English and Spanish as a young girl. Though she does speak Dutch, Luxembourgish, Russian and Italian, those are not fluent languages that Isabella uses often. Isabella was sent to a boarding school in Kent, England where she was educated for 4 years until moving to Virginia, United States to another boarding school. Isabella went to Sevenoaks School in Kent, England alongside Prince Amedeo of Belgium, Archduke of Austria-Este and Princess Luisa Maria of Belgium, Archduchess of Austria-Este.
Archduchess Isabella went to Yale University and graduated in 2014 with a Master's Degree in Global Affairs and a Bachelor's Degree in Political Science. Her summer's during college where spent in third world nations with 2 different humanitarian groups alongside her cousin Princess Alexandra of Luxembourg. After her graduation Isabella immediately returned to Geneva where she began working for her father only to leave that job a couple of weeks later and began her work with the United Nations as a Human Rights Officer.
Marriage
Mid 2016 it was revealed that Archduchess Isabella of Austria and Prince Harry of Wales were well into their own relationship that was reported to have started in November of 2014 while Isabella was working for her father. This would later have said to be false but none in the British Royal Family would confirm if the marriage was indeed arranged at the time.
Prince Harry and Archduchess Isabella announced their engagement in January of 2017 with a wedding to be in the summer of that same year. The two became engaged at Fischbach Castle in Luxembourg during the Christmas holiday in the presence of the Luxembourg Grand Ducal Family and extended family. The wedding took place at St. Paul's Cathedral with 3200 guests in attendance. A majority being over 500 descendants of Robert I, Duke of Parma, who was the twice great-great-grandfather of Archduchess Isabella.
The wedding party, was the largest ever seen in a British Royal Family wedding at the time. Excluding the maid of honor, Archduchess Isabella and Prince Harry had 12 bridal attendants, 6 boys and 6 girls, all godchildren and family friends of the bride and groom. The maid of honor was chosen as Princess Charlotte of Nassau, a first cousin of Archduchess Isabella and a great-great-granddaughter of King Alfonso XIII of Spain and Queen Victoria Eugenie. Other attendants included Princess Eleonore of Belgium, daughter of King Philippe and Queen Mathilde of Belgium; Countess Xenia von Coudenhove-Kalergi, Granddaughter of Vincenz Liechtenstein; Archduchess Maria Stella of Austria, Isabella’s niece by her brother Archduke Imre; Archduchess Zita of Austria, Great-Granddaughter of Archduke Carl Ludwig of Austria; Princess Florence of Ligne, Granddaughter of Alix, Dowager Princess of Ligne; Prince Gabriel of Nassau, son of Prince Louis of Luxembourg; Count Rodolfo Secco de Aragona, Grandson of Archduke Rudolf of Austria; Archduke Luigi of Austria-Este, Grandson of Robert, Archduke of Austria-Este; Prince Valerian of Lobowicz, Grandson of Andrea von Habsburg; and Japer Dyer, son of Mark Dyer. The wedding was estimated to be watched by over half a billion people, making it one of the most watched events in British history.
House of Habsburg-Lorraine and the main and cadet branches of the House of Bourbon made up a majority of guests as relations to Archduchess Isabella. Other German, Danish, Dutch, Luxembourgish, and Belgian nobility were also invited as family of bride.
On the morning of the wedding Prince Harry was made Duke of Sussex, Earl of Ross, and Baron Hartland. Because Isabella was born an Archduchess of Austria and her title being higher than that of a Duchess, Isabella was formally introduced as Archduchess Isabella of Austria, Duchess of Sussex, Countess Ross, and Baroness Hartland. Buckingham Palace then issued a statement that Isabella will still be addressed as Archduchess and not Duchess, but her titles by marriage will also be used when formally addressed.
Children
December of 2017 Clarence House released a statement that Archduchess Isabella and Prince Harry were expecting a child in the summer of 2018, later Prince Harry revealed that no one in the royal family knew per request to keep everything as quite as possible. Clarence House released a statement that Archduchess Isabella gave birth at Château de Belœil in the early morning of 24 of May. A statement was released of the two boys named Charles Henry Ferdinand Baudouin Jean Philip, Earl of Ross and Lord Albert Maximilian Christian Leopold Felix Ludwig. The Earl of Ross’s godparents included Mark Dyer, King Philippe of Belgium, Jake Warern, Princess Margaretha of Liechtenstein, Guillaume, Hereditary Grand Duke of Luxembourg and Prince Seesio. Lord Albert godparents were Princess Beatrice of York, Prince Henri Antoine of Ligne, Edward Lane Fox, Alexander Fellowes, Princess Sophie of Liechtenstein, and Princess Maria Gabriella of Orleans-Braganza.
With their birth, pressure was put on the British monarchy to make them Princes, rather than lord because their parents' marriage was dynastic to the older generation. Due to being the children of the Duke of Sussex, any children from their marriage were not given the title of Prince. All of Prince Harry's children born during the reign of their great-grandmother Queen Elizabeth II would have the title of Lord and Lady with the eldest son receiving the subsidiary title of Prince Harry, The Duke of Sussex. Jean, the former Grand Duke of Luxembourg advised his son, Isabella's uncle, Henri Grand Duke of Luxembourg, to recognize the Dukedom of Sussex into the Luxembourg nobility and allow them to have his great-grandchildren to have title of Prince and Princess. The Grand Duke of Luxembourg was to give all children of Archduchess Isabella, the title of Prince/Princess of Sussex in Luxembourg nobility. By government advisement, the Grand Duke did not bestow any titles.
A second pregnancy was announced in November 2018. During Archduchess Isabella's second pregnancy, Isabella and Prince Harry to moved out of Kensington Palace and to St. James’ Palace to accommodate their growing family. May 26, 2019 Archduchess Isabella gave birth to Mary-Astrid Jeanne Zita Ingeborg Josephine Christine Diane at Berg Castle in Luxembourg. Mary Astrid's godparents included Archduchess Marie Christine, Princess Luisa Maria of Belgium, Viscount Althrop, Princess Marie Gabrielle of Luxembourg, Sophie Countess of Wessex, and Arthur Landon.
During the early months of 2020, Grand Duchess Olga Petrovna of Russia, Princess of Prussia was found dead in a villa off the coast of Italy. Grand Duchess Olga and Archduchess Isabella had been second cousins and the unexpected death of the Russian Grand Duchess came to a shock to the Habsburg family. The younger woman had reportedly suffered a third miscarriage and in the state of depression had killed herself leaving behind a 2-year-old daughter, Grand Duchess Maria-Olga of Russia, Princess of Prussia. Archduchess Isabella attempted to adopt Grand Duchess Maria-Olga but was met with failure.
In March of 2021, Buckingham Palace issued a statement that Archduchess Isabella and Prince Harry were expecting a fourth child in the fall of the year just a year after Archduchess Isabella's grandmother, Archduchess Yolande of Austria died. Isabella gave birth to a daughter, Elisabeth Alexandra Gabriella Annunciata Charlotte Theresa on September 18 at Balmoral Castle in Scotland. This was Archduchess Isabella's third at home birth. Elisabeth's godparents were Archduke Alexander, Queen Elizabeth II, Lady Kitty Spencer, Princess Eugenie of York, Princess Charlotte of Nassau, and Charles von Straubenzee.
Archduchess Isabella gave birth to another daughter, named Alice Margaretha Yolande Sophia Louise Christabel on December 25, 2023 at Sandringham House in Norfolk. Alice's godparents were Archduke Imre, Princess Marie Gabrielle of Nassau, Archduchess Helene of Austria, Tom Inskip, Anne Princess Royal, and George McCorquodale. More children quickly followed including a second pair of twin sons, Robert Paul Christoph Sebastien Francis Constantin and Nicholas Xavier Gabriel Wenceslas Patrick Rudolf on November 1, 2023. Two more sons followed Joseph Arthur Edward Alexander Otto Ernst in July 4, 2026 and Michael Frederick Emanuel Vincent Thomas Johannes in June 20, 2027.
The large number of children caused minor public upset for a couple of years. King George VII, limited the role of Archduchess Isabella and Prince Harry including limiting their royal duties. After 2022, Prince Harry and Archduchess Isabella no longer received tax payer funding except when receiving compensation from representing the royal family. The family split their time between London, Scotland, and France where the younger children had been born.
Duchess of Sussex
Within months of her marriage, Archduchess Isabella proved to be a generous humanitarian, as her deceased mother-in-law Diana, Princess of Wales. Hurricane Maria during the 2017 Hurricane Season provided Isabella with a platform that expanded her patrons to include helping victims across the world of natural disasters. Isabella took a tour of The Caribbean, Mexico, and Southern United States for her first solo tour.
The Duchess of Sussex became a patron of over 30 charities shortly after her marriage including becoming joint patron of several of Prince Harry's patronages and others dealing with immigration, women's rights, natural disasters, and the arts.
Death of Queen Elizabeth II
On November 21, 2020, The Duke of Edinburgh died at Buckingham Palace in his sleep. Archduchess Isabella and Prince Harry moved into Windsor Castle from St. James’s Palace after The Duke of Edinburgh's death to stay closer to the Queen. The Duke and Duchess of Sussex became patron of many of the Duke of Edinburgh's charities as well as several of Queen Elizabeth's charities. With the Queen's health in question after the death of her husband, many believed that the British monarchy would be abolished in the event of her death.
Queen Elizabeth II died on December 17, 2021 at the Sandringham Estates in Norfolk, England. Upon her death, her eldest son Charles, Prince of Wales took George as his regnal name. With the death of Queen Elizabeth, all of the Duke of Sussex's children were given the title HRH Prince/ss of Sussex. The Duke of Sussex eldest children, the twins Charles and Albert, were just 3 years old. Soon thereafter, The Earl of Wessex was given the Dukedom of Edinburgh. The Duke of Cambridge was not given the title Prince of Wales, and the Duke of Sussex was not given the title Duke of York upon their father's accession for different reasonings. With King George VII's accession, the Sussex family toured North America on behalf of the king.
Reign of King George VII and William V
The reign of King George VII was a short eight years compared to his mother’s historic reign. King George died on March 1, 2029. William, Duke of Cornwall and Cambridge was to be named King William V. Days after the funeral, William issues letter patent taking his brother Prince Harry of his Royal Highness style and title of Prince of the United Kingdom. This change effected Harry’s children as well, making them styled as children of a duke rather than Prince of the United Kingdom.
The move proved to be unpopular with the general public and within the family. William removed the status of his cousins and uncles as members of the British Royal Family in an attempt to limit the House of Windsor to the descendants of the current king. This left William without family members to help him with the kingdom and commonwealth. Weeks of bad press had made put a strain on the monarchy and the government.
A constitutional change was suggested by King William to change the line of succession to just the descendants of the monarch, thus leaving thousands out of the line of succession. Because the line of succession was determined by an Act of Parliament in 1689 and 1701, Parliament would be the ones to change it in the less controversial way. The Prime Minister and Parliament agreed there would be no change in the line of succession.
King William tried to follow in the footsteps of King George V and his father King George VII in slimming down the monarchy. By taking away titles, William believed he was helping the monarchy and had his brother married a commoner, it would have been fine. But William’s sister-in-law was Archduchess Isabella, a relative to most of the European monarchies of Luxembourg, Belgium, Spain, Liechtenstein, and the Netherlands.
Advisors to the king suggested William abdicate in favor of his brother who was already living in France with his family but he of course rejected. By August, William was facing heavy opposition. The Luxembourgish court released a family photo of the descendants of Jean, Grand Duke of Luxembourg for the 10th anniversary of his death which include Prince Harry and his large family. Other members of the family include Luxembourg royals and the future Prince Consorts of Belgium, the Netherlands, Spain.
Just months into his reign, William was faced with the task of becoming King of the United Kingdom finding it overwhelming. He complained about his duties, finding it easier to take holidays with his family. Louise, The Duchess of Bedford, wife of the 15th Duke of Bedford and Mistress of the Robes to Queen Camilla commented on the new king.
“I fear the new king knows nothing on how to lead nor listen. It will prove to be disastrous within the next couple of months, no doubt shaking this country to its very core. I have made up my mind that the women in this family should rule instead for they are the only ones with sane minds.”
William’s fate was sealed by that photo and the public started to demand Harry as king. Harry had connections and the celebrations of weddings, christening, and parties with Europe’s royals over the years brought back the nostalgia of 19th century Europe. It was Queen Isabella who had given him these connections and they would be an easy reason for William abdicated.
The Duchess of Bedford was hinting at an abdication in her diaries and several weeks later, King William V did abdicate. William’s Coronation was made for March of 2030 but he abdicated on December 3, 2029 in favor of his brother Harry, Duke of Sussex.
Year of French Court
From the time William stripped his brother and his family of their titles, Archduchess Isabella immediately left London for France. Her family stayed in the Château de Chambord, that for several decades had been the property of Isabella. Days after losing the style of Her Royal Highness in the United Kingdom, Isabella threw a masquerade ball which attracted much press since a large number of royalty and nobility attended.
Lavish parties, famous guests, and endless nights had made the press dub King Henry and Queen Isabella’s time in France as the “Year of French Court”. This nickname was a contradiction since the time in France was actually 9 months and French Court refers to French Royal Court, the last of which was the Bourbon court of King Louis Philippe in the mid-19th century.
King William’s court was the English Court bringing up an old rivalry between the French and the English. Unlike King Henry, whose last French ancestor was Claude of Valois, mother to the Tudor dynasty, his wife Queen Isabella ancestor included all French monarchs, save the Bonaparte's, although all Bonaparte’s were related by marriage. Queen Isabella had been related to every French monarch from the King of the Franks, Charlemagne to the last Bourbon, King Louis Philippe.
King Henry and Queen Isabella and their time in France was met with both high criticism and high praise. As private citizens, they could spend lavishly, but the chances of them being monarchs with the same type of spending left people to doubt them. The Château de Chambord became a popular destination for foreign royals who spent days to weeks at a time with Isabella and her family. All of Isabella’s son and daughter-in-law’s spent time at the château.
Several locations had become popular in Europe including Cabasson, France where the Luxembourg Grand Ducal Family owned a villa; Prince’s Palace of Monaco in Monaco, and Pejačevič Castle in Croatia. Isabella’s time with her family had reminded many, especially historians, about the family gatherings that the Danish royal family had during 19th century.
Queen of the United Kingdom
Upon the abdication of King William V in 2029, Isabella became the first Habsburg consort since the 1554 marriage of Queen Mary I of England and the future King Philip II of Spain. The coronation intended for William was given to his brother. King Henry’s children were elevated to royal status again and the titles stripped away by William were given back including giving the Dukedom of Edinburg to Prince Edward again.
During the coronation at Westminster Abbey, the five eldest children Prince Charles, Prince Albert, Princess Mary-Astrid, Princess Elisabeth, and Princess Alice attended some of ceremony. During the photos all nine of their children were present. The coronation was attended by a large number of Queen Isabella’s family, many of whom were married to heirs and other foreign royalty.
William and his family moved to Scotland and hours before the coronation, it was announced that William would not receive a dukedom but styled as William Mountbatten-Windsor, 1st Baronet Mountbatten-Windsor of Inverness. It was a hereditary title but with little significance so William could not get a following to recover the throne. It was on the advice of the British government that the title was revoked at the end of the year so William became Mr. William Mountbatten-Windsor at the beginning of 2031.
After the coronation a tour of the Commonwealth realms was ordered with included all nine children of King Henry and Queen Isabella. Isabella’s ability to speak multiple languages and years of working in disaster relief had pleased the public who found the new king and queen more likeable. Tours of Africa and later North America had kept the new royal family busy in the first couple of years.
The death of Queen Camilla in 2025 during the reign of her husband, had left Isabella the undisputed matriarch of the British family. The children’s ability to speak no less than five languages had amused the public and immigrants who found speaking to royalty in their mother tongue comforting.
Between 2029-2052 Isabella’s family rose to more significance. In Belgium, her cousin Prince Paul Louis become Prince Consort of Belgium and Queen Isabella’s niece Beatrice married Paul Louis’s son, Leopold, Duke of Brabant. In the Netherlands, Isabella’s cousin Prince Leopold became Prince Consort of the Netherlands and her nephew Joseph was engaged to Leopold’s daughter Charlotte, Princess of Orange. In Spain Queen Isabella’s cousin Prince Jean became the Prince Consort of Spain. Queen Isabella’s nephew Count Leopold married Crown Princess Estelle of Sweden. Queen Isabella’s second daughter married Prince Franz Joseph of Liechtenstein, future heir to the principality. Her niece Victoria married Jacques of Monaco, who at the time was Hereditary Prince of Monaco then the next year became The Prince of Monaco. In Luxembourg, the country was ruled by her uncle Henri, cousin Guillaume and his child.
Perhaps the most importance was the reestablishment of the monarchy in Croatia and Russia. In 2035 after the assassination of President Vladimir Putin, the Russian people brought back the monarchy with Grand Duke George Mikhailovich of Russia as their Tsar. His eldest daughter Maria-Olga had married Queen Isabella’s second son Albert in 2038. Tsar George died in 2043 and his successor was his son-in-law Grand Duke Alexander, formally Albert. Queen Isabella’s role as mother to the future King of the United Kingdom and Tsar of Russia was a point in history no could have predicted. By 2045 Croatia voted overwhelmingly to bring back their monarchy as well with Ferdinand von Habsburg as their king. Ferdinand was married to Isabella’s cousin, Princess Charlotte for already 25 years producing five children, including 4 sons which mirrored Charlotte’s own life as the only girl.
Queen Isabella was consort to King Henry IX for 23 years before her death of Dec 29, 2052. The couple had been married for 35 years and had nine children together.
Assassination Attempt
While in Monaco in 2052 for the royal family’s annual holiday to Monaco, Queen Isabella had fallen ill delaying the British Royal Family’s departure from the Chateau de Chambord. The British Royal Family had stayed in France for another week before leaving to Monaco. By that time, many of the other European monarchies had left to the respective homes.
In the middle of the day a man managed to sneak into the Monaco Princely Palace in an attempt to assassinate Queen Isabella. The assassin wanted to kill King Henry and Queen Isabella believing the rightful King and Queen were William and Catherine. King Henry was not with Queen Isabella but with her niece Princess Gabriella and nephew by marriage Jacques, The Prince of Monaco.
Attempting to assassinate the king and queen, King Henry was with his younger children who had fallen sick after their mother. Queen Isabella was on a walk with her niece and nephew who was going to announce their own ninth pregnancy the day after. Queen Isabella was asked to be godmother to their ninth child. The assassin lunged for Queen Isabella with a knife only to be blocked by The Prince of Monaco. Amongst the fight, Princess Victoria ran for help but Jacques had been stabbed and later died in the hospital. Queen Isabella did not die that day but several months later, as she died in a car accident in France.
Romances
On January 1, 2034 the official biography, letters, and interviews of Queen Fabiola of Belgium were released to the public. A frequent mention in Queen Fabiola’s writing include her goddaughter and great-niece Queen Isabella had interested the public. In these letters and interviews Queen Fabiola mentioned the relationship Queen Isabella had with her double second cousin Prince Joachim of Belgium. It was revealed that Prince Joachim was Queen Isabella’s first everything.
“I pray to God that one day I will live to my petite reine marry a good man. Joachim is a sweet boy in love but I doubt they will marry. Belle is heard strong and filled with passion I doubt Joachim can keep her happy for very long.”
Queen Fabiola’s biography gave unprecedented knowledge on Queen Isabella’s childhood. Besides the mention of Queen Isabella, her family, especially her parents Archduke Carl Christian and Princess Marie Astrid were written and spoken about often. Pictures from Queen Fabiola’s family album confirmed the relationship between Queen Isabella and Prince Joachim during their teen years. It was not known when the relationship started or ended.
Queen Isabella’s marriage to Prince Harry, later King Henry IX came to a shock to many. The marriage was arranged but came to be a marriage of respect and admiration. After a couple of years of marriage, Queen Isabella began an affair with Count Johann Kinsky of Wchinitz und Tettau, a distant relative of Marie and Georgina, The Princesses of Liechtenstein and King Willem Alexander of the Netherlands. Count Johann Kinsky was a financial advisor to Queen Isabella working in France at Chateau de Chambord.
The affair lasted only a couple of months with it ending in Count Johann’s resignation from Chambroad and his elevation in the Liechtenstein princely family. Often speculated, Count Johann’s new position in Liechtenstein was a way of ending the affair and keep the counts silence too While King Henry and Queen Isabella marriage wasn’t the same after the first affair, it took years before she took another man as her lover.
It was not until after the birth of her last child, Prince Michael that Queen Isabella began a second affair. Heinreich Donatus, The Prince of Schaumburg-Lippe was a minor German prince whom Queen Isabella had met briefly years before. Common weddings brought the two together but Heinreich Donatus friendship with the Princes Wenceslas and Constantin kept him in closer ranger. Prince Heinreich Donatus moved from Germany to France near Chambord to be near the queen. The affair was brief, only lasting about 2 years before Queen Isabella moved on.
Maximilian, 9th Prince of Wied was introduced to Queen Isabella by Prince Heinreich Donatus in 2030. Prince Maximilian had been married and later divorced with 2 sons when he met Queen Isabella. Like Prince Heinreich Donatus, Prince Maximilian moved his family to France so he could be in close proximity to the queen. This affair had lasted a little over 5 years before Queen Isabella had gone back to Prince Heinreich Donatus. Between 2036-2040 Queen Isabella continued to her affair with The Prince of Schaumberg-Lippe.
Queen Isabella’s affairs were few and long. After 2041, Isabella remained faithful to her husband but damage had already been done. The couple lived separate lives, only coming together for family events and public engagements. Unknown to the public, King Henry and Queen Isabella spent much time apart. Unlike Count Johann and Princes Heinreich Donatus and Maximilian, an affair with Prince Joachim of Belgium was never confirmed, but highly speculated.
Legacy
Every monarch in Europe descends from Queen Isabella and her husband, King Henry IX. As her children, grandchildren, and great-grandchildren married into various royal families over the decades, almost every royal of a working monarchy, descend from Queen Isabella. King Henry IX and Queen Isabella had 9 children, 47 grandchildren, and 211 great-grandchildren.
Although having a large number of descendants, many of Queen Isabella’s family had converted to Catholicism thus baring themselves and their descendants from the British line of succession. Of her nine children, only four children and their descendants have succession rights. Two of her daughters and three sons converted to Catholicism shortly before each of their respective marriages.
One of Queen Isabella’s lasting legacy is her large collection of jewelry. Many of the tiaras in the Queen Isabella’s Fund came from donations by women such as Princess Charlotte Murat. Other pieces of jewelry were bought by Queen Isabella which were owned by various Habsburgs during the Imperial era.
Unlike her predecessors, Queen Isabella bought many jewels from the Gloucester, Kent, Fife, and Harewood families but they did not go back to the crown as they were personal purchases. Personal purchases meant they were to the Queen Isabella Fund to be used by her female descendants and not by the British royal family. This meant that all jewelry was not kept to Queen Isabella’s British descendants but could be worn by her other descendants in other reigning and deposed monarchies.
While most of the tiaras have not been shown to the public it is an estimated number of tiaras and jewelry by experts and the public. Queen Isabella’s female descendants had worn a large portion of the tiaras but dozens are still speculated to remain hidden from the public eye. Queen Isabella’s tenure as Queen Consort of the United Kingdom, she rarely wore tiaras belonging to the British Royal Family and preferred her own tiaras.
A documentary of the 100th anniversary of Queen Isabella's death revealed that the tiaras are organized in tiers. There is a total of five tiers that the descendants of Queen Isabella must abide by ranging from descendants who are queens, both born and married into, who come from non-dynastic backgrounds. Tier One is for Queen or Queen Consorts born of a dynastic marriage and marry dynastically. Tier Two is for Crown Princesses born of a dynastic marriage and marry dynastically. Tier Three is for Princesses born of a dynastic marriage and marry dynastically, daughters born of princesses belonging to Queen Isabella’s descendants who marry foreign counts, barons, or duke of dynastic background are also entitled. Tier Four is for female descendants who hold no titles. Tier Five is for non-dynastic in-laws from families who do not come from a royal or noble family.
Queen Victoria was seen as the beginning of hemophilia. The hereditary disease that helped bring down the Russian Imperial Throne and Spanish Royal Throne were passed through women. The disease took Queen Victoria’s son Leopold, several grandsons, and several great-grandsons. Through the decades, the disease made no reappearance but plagued the royal house through books and cultural depictions.
Queen Isabella was no exception in beginning her own hereditary trait, but this one was less deadly than the one Queen Victoria passed on. Partial or Central Heterochromia is an eye condition where areas of the same iris contain two completely different colors or there are two colors in the same iris. The disease could be passed through males or females and in the case of Queen Isabella, she passed it on to her daughters Princess Mary-Astrid and Princess Alice along with her sons Princes Nicholas, Joseph and Michael.
By 2150, the hereditary disease was prominent in all monarchy finding the carrier was Queen Isabella. Queen Isabella herself had a faint case of Central Heterochromia though it is not clear which parents she got it from. The mismatched eyes became a physical staple of 21st and 22nd-century royalty.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wednesday, 17th September 2019 – Illkirchen, Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg, Colmar
Wednesday morning, with even more insect bites decorating both of us, we got ready to check out and move on. I’d been for a run before breakfast and stopped off at the rather odd park near one of the tram stops. For reasons I couldn’t begin to fathom, the park contained a number of “Easter Island” heads. No. I have no idea. Apparently Place Malraux contains an Armenian Oak, which counts as a remarkable tree, but there’s no connection there that I can find. And the really weird thing was that they wouldn’t be the only Easter Island head style sculptures we would encounter, we would find more on the penultimate day of our holiday.

Anyway, they amused me. By 10:30 we’d got the car packed and were ready to go. Our landlady turned up on time, despite us not having done so on check-in and we were soon on our way to Robert Blanck to buy the wines we’d decided on. That was easily achieved, and the lovely lady serving us insisted on slipping a few extra goodies in (a couple of “top hat” Champagne bottle stoppers), especially after we bought a creme de peche as well (made from vineyard peaches) and we wended our way onwards to Famille Hauller, but could find no one around, despite Ludovic having suggested he would be there between 11 and 12. We decided to save Domain Sylvie Spielmann for later in the afternoon and thus headed for Chateau Haut-Koenigsbourg. We’d heard more about it on our wine tour, when Olivier asked if anyone on the tour was a “Lord of the Rings” fan, because if so we needed to visit the castle. Apparently “some guy” had used it as inspiration for some of the set design. Given our proximity to Switzerland, Lynne and I put two and two together and figured he was probably talking about John Howe, the Canadian artist who lives in Switzerland and who was one of the two artists deeply involved in the look of Peter Jackson’s films. A minimal amount of research later and I’d confirmed this was indeed the case, and that there’d even been an exhibition there last year. We had to go. There was no choice, not when the information I’d found said: “Several decades later, John Howe, the famous illustrator of Heroic Fantasy publications, fell in love with the château’s mysterious atmosphere on his first visit here during the 1980s. He used it as the inspiration for the design of the Citadel of Minas Tirith after he was appointed to the post of Conceptual Designer for Peter Jackson’s ‘The Lord of the Rings’ trilogy”. Just for good measure it also appears in its real form in Jean Renoir’s 1930s masterpiece, “La Grande Illusion”, and the considerably less famous “Les aventures d’Arsène Lupin” in 1956, but to keep the masterpiece theme going, it can also been seen in the animated classic “Howl’s Moving Castle”. 3 out of 4 then!
We drove up a winding and slightly white-knuckled road and eventually found ourselves on the loop in the road that leads up to the castle and then back down again. It was very, very busy and we decided that we’d try and get a good parking space rather than having to flog up the hill on what was another hot day. As we passed the apex and started to drop back down again we found a space that was actually big enough for my car (and it’s not a big car). And then we looked up! The castle is a monster of a structure, and looks just like you think a medieval castle should, looming massively against the skyline.

Its history, however, is slightly different to what you might expect, as with so many things in this part of the world. There’s mention of the Buntsandstein rock as Stophanberch (Staufenberg) in a 774 deed issued by Charlemagne, and it crops up again in 854, by which time it belonged to the Basilica of St Denis and may have been the site of a monastery. It all goes quiet again until 1147, when there is a record of a castle built by the Duke Frederick II of Swabia, one of the Hohenstaufens and called Castrum Estuphin, something the monks were not happy about as the record is a complaint to King Louis VII of France about it. The offending builder’s younger brother Conrad was elected King of the Romans in 1138, and was succeeded by his nephew, Frederick’s son, Frederick Barbarossa in 1152 and it wasn’t long before the name of this commanding fortress changed to Koenigsburg (king’s castle) or Kinzburg.

Eventually it passed to the Dukes of Lorraine, who entrusted it to the local Rathsamhausen knightly family and the Lords of Hohenstein, but the behaviour of a gang of robber barons who used the castle as a hideout so enraged the neighbours that it was occupied by the Elector Palatine in 1454, and less than a decade later it was set ablaze by the unified forces of the cities of Colmar, Strasbourg, and Basel. The Habsburgs handed the ruins over to the Tiersteins who rebuilt and enlarged the castle, supposedly in a way that meant it would be able to withstand modern artillery fire. No one told the Swedish artillery forces who broke through and overran the castle during the Thirty Years War and it was finally burnt to the ground in 1633 and left to fall into ruin for a couple of centuries. You wouldn’t know it though.

It was classified as an historical monument in 1862, and in 1865 it was bought by the town of Sélestat. There were plans to restore the place, but there were no funds to complete the work. Alsace was in one of its phases of being part of Germany, so the ruins of the castle were offered to Kaiser Wilhelm II in 1899. Having abandoned his plan to restore Schloss Rheinfels, he must have pretty much snapped their hands off. What followed was a remarkable 8-year long building project, where money was no object, and the most modern techniques were used. The castle would be completely restored, with the emphasis on as much historical accuracy as possible. To that end, a young architect, Bodo Ebhardt was put in charge. It helped that he was also an architectural historian, a castle explorer, and the founder and longtime president of the German Castles Association (Deutsche Burgenvereinigung). He was very thorough and after he had analysed the remaining ruins and façades, he read up as much as he could in old documents and records, and looked at other castles to draw comparisons.

He even made sure that those who came after would be able to easily identify the new parts of the walls, creating a new set of ‘mason’s marks’ to be used on any replacement stones, and gave different marks to different years. You can still see the marks if you know what to look for. It’s a fabulous place with some startling detail and although much of it is not authentic, you can completely forget that as you go round.

After an 8-year build, on May 13th 1908 the château was unveiled to the public with a parade and pageant involving five hundred performers in period dress. Of course after World War I it reverted back to being French, and became a tourist attraction, though apparently the French visitors would regularly criticise the restoration work because it had been carried out by the enemy. Surviving both World Wars undamaged the building was classified as a Monument historique (listed building) in 1993 and is now owned by the Conseil Départemental du Bas-Rhin.

As we wandered around, the views were staggering. You could see just why anyone with an ounce of strategic sense would want to build a fortress on just this spot. No one is going to be able to sneak up on you, that’s for sure.

After a couple of hours poking into all the nooks and crannies, we reckoned we needed a refreshment stop. The Library restaurant offered all sorts of options including some and cake. We were booked for dinner at our hotel that night and really didn’t need any more than a light snack. As there weren’t any of those on offer (Alsacian cuisine really does lean towards German sized portions, or at least ravenous vineyard worker sized portions alongside French refinement) I had a slice of mirabelle cake, and a bottle of cold water.

We had a look around the medieval garden that had been set up outside, but it had somewhat gone over due to the extremely hot weather and a general lack of care. Afterwards, we sauntered back to the car and headed over to Sylvie Spielmann, where we made a massive dent in our wine buying budget. We also made a massive dent in the bottom of my car when we collected a piece of ironwork that was sticking up out of the sandy base level that a road under reconstruction had been reduced to. It got stuck, dragged along for several feet, and I was only able to get off it by reversing and then rocking forward a couple of time. I’ve yet to figure out what damage has been done precisely, but it is going to need looking at.

From there we reloaded the car again, shuffling everything round as best we could to keep the next night’s bags at the top of the luggage pile, and headed to Colmar and the our hotel for the next three nights, the Hostellerie Le Maréchal. We arrived in good time, and unloaded. I then had to drive the car to the nearby underground car park, because a hotel built in 1595 isn’t going to have built in car parking! It was a hot walk back and I annoyed myself by leaving my handbag in the car and having to walk back again almost immediately. Once in though, we were able to get ourselves organised and cleaned up and then investigate the possibility of an aperitif in the hotel bar prior to dinner in their restaurant a l’Echevin.

We had a lovely view from our window of the canal and some of the typical local barques which were the only vessels shallow enough to navigate from the market garden areas to the market hall back in the day, and which now carry tourists up and down.

Colmar looked lovely, the hotel was glorious, we had one of the suites with a “Little Venice” view, and we looked to be in for a lovely stay. As we had dinner at the hotel twice, I shall write about that elsewhere.
Travel 2019 – Alsace and Baden, Day 6, Illkirchen, Orschwiller, Colmar Wednesday, 17th September 2019 - Illkirchen, Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg, Colmar Wednesday morning, with even more insect bites decorating both of us, we got ready to check out and move on.
#2019#A l’Echevin#Arts#Cafés#Castles#Château du Haut-Kœnigsbourg#Colmar#Domaine Sylvie Spielmann#Drink#Europe#Famille Hauler#Films#Food#Food and Drink#France#History#Hospitality#Hostellerie Le Maréchal#Hotels#Illkirch-Graffenstaden#John Howe#Parks#Robert Blanck#Travel#Wine
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo









ROMANOV NAMES: Maria (part one)
Maria (rus.Мария) - a given name from derived from the Hebrew Miryām, which means “sea of sorrow “ or “wished for child”
Maria Miloslavskaya, the first spouse of Tsar Alexey, was the first woman from Romanov family to be called by name Maria at the same time.
Tsaritsa Maria Ilyinichna Miloslavskaya was born in 1625 as younger daughter of Russian boyar and diplomat, Ilya Danilovich Miloslavsky. Passed over, in first bride selection in favour of Euphemia Fedorovna Vsevolozhskaya, she was chosen by young Tsar Alexey few months later as his bride. It’s likely that behind Alexey’s choice stood Boris Morozov, an influental boyar and tutor to Tsar, who hoped to marry Maria’s sister and become his brother-in-law. Both couples were wedded on 16 January 1648 and new Tsaritsa conceived soon after that. Alexey and Maria produced 13 children in general, but 5 of them didn’t survived into adulthood. Maria fulfilled her duty in regard to religion and charity. She engaged herself in public dotations for poor and disabled children and benefited some monasteries. Unfortunately, her happy union with husband was ended by her death in childbirth on 1669. Her last child, weak Tsarevna Eudoxia didn’t outlived her mother and died only 1 day after birth.
Tsarevna Maria Alexeyevna was born on 28 January 1660 as the eighth child of Alexey I and his first spouse, above-mentioned, Tsaritsa Maria Milovskaya. She was not involved in politics, but her sympathy for first wife of his half-brother, Eudoxia Lopukhina didn’t made her popular and significant at Peter I’s court. Maria also took care of Alexei Petrovich, Peter and Eudoxia’s firstborn son, after his mother had been put into a nunnery against her will. When her nephew escaped from Peter’s tutelage, she helped him to maintain a contact with his mother. Some time later, she was accused of having prepared Alexei’s escape and taken in custody. Imprisoned and forgotten by all, Tsarevna died on 1723.
Tsaritsa Maria Fyodorovna was born 25 October 1759 as a daughter of Frederick Eugene II of Württemberg and his wife, Friederike Brandenburg-Schwedt. She was christened with name of Sophie Marie Dorothea Auguste Luise. Her parents gave her an excellent education; Sophie Maria had good command over Latin, German, Italian and French. In 1773 she was among a group of German princesses chosen as possible brides for Pavel I, but she was denied by Catherine the Great, in the view of her young age. In 1776 she was proposed as future bride for widowed Pavel I. Catherine was delighted with ideal of union between Pavel and Sophia Maria, mainly because she shared name, place of birth and similiar education with her future daughter-in-law. Wedding took place on September 1777. Sophia Maria converted to Ortodoxy and was given a name ‘Maria Fyodorovna’. Tall, thoughtful and rather plump woman was quickly dominated by her mother-in-law, but her marriage turned out to be a harmonious one, despite Pavel’s diffucult character and distrust. Generally, marriage resulted in ten children, including two future Tsars - Alexander I and Nicholas I. Except for Alexander and Konstantin, all her children enjoyed happy childhood by side of Maria. Between 1795 and 1806, seven members of her large family died in quick succession. Overshawdowed and overlooked during Catherine the Great’s reign, she became an influental figure during her sons’ reign and exerted tremendous influence over his younger sons’ lives and ways and involved herself in politcs and charity. Outlived by her assassinated husband and five of ten children, Maria was suffering humbly and passed away in 1828.
Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna was born on 16 February 1786 as the fifth child of Tsar Pavel I, and his second spouse, Maria Fyodorovna. Rather not renowned for her beauty, Maria developed a precocious talent as pianist; her features had been misshapen by smallpox. In 1804, her brother arranged her marriage with Charles Frederick of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach. They had four children, of which three survived childhood. Maria was not pleased with a low level of culture in in the poor Grand-Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, so she became a patron of arts and maintained a long-lived relationship with Vasily Zhukovsky, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Franz Liszt. On the advice of Maria, at Jena University, famous Literary Evenings were conducted. After death her husband, she withdrew from public life, what was contributed to her growing deafness. She died in 1784.
Tsaritsa Maria Alexandrovna was born on 8 August 1824 as the youngest daughter of Grand Duke Ludwig II of Hesse and his wife, Wilhelmine of Baden. Her legitimacy was conseted right from the very beginning due to her mother extramatrial relationship with August von Senarclens de Grancy. In 1839, young Tsasarevich Alexander Nicholaevich was travelling around Europe, looking for a wife. In Darmstadt he became capitaved by young, shy and withdrawn Princess Wilhelmina Maximiliana of Hesse-Darmstadt. But Nicholas I and his wife, Alexandra Fyodorovna expressed their disapproval for their son’s choice, as they learnt about questioned paternity of Grand Duke. But when Alexander informed them that he was considering about possible union between himself and Queen Victoria, the ultimate choice fell on Hessian princess. She converted to Ortodoxy and took a name ‘Maria Alexandrovna’. First years of marriage was happy, however Alexander was probably the most promiscuous Tsar of Russia ever and had different extramaterial relationships. He sired over 7 children out of wedlock. Frequent pregancies made it impossible for her to keep up with frivolous, rich Russian court, which literally adored her husband for his self-confidence and extraordinary charm. They started gradually to live apart. Maria was constantly ailling and suffered from weak lungs and therefore, she had to spent years abroad in order to treat herself. The birth of Pavel in 1860, left her with little strength and became clear that her health was in serious decline. It was advised by doctors that she was not supposed to share bed with Alexander any longer. Like many wives of unfaintful husbands, Maria sought for comfort in religion. By 1864 it was apparent that she had contracted consumption. She spent rest of her live in Sankt Petersburg mourning her first daughter, Alexandra and first-born son, Nixa who had passed away in 1864 of consumption. Maria was aware of his husband’s relationship with Ekaterina Dolgorukaya, which proved to more serious than his previous flings and resulted in 4 children. Maria died forgotten by all but her children on 1880.
Grand Duchess Maria Mikhailovna was born on 9 March 1825 as the first of five daughters of Grand Duke Mikhail Pavlovich and his spouse, Elena Pavlovna. Her father had always high hopes for her as the oldest daughter, though cherished and spoiled her greatly. Mikhail, who was eager to have son on his own, imposed upon her sense of duty and introduced her to the cavalry and infantry signals on the bugle and drum, but he also left Maria’s upbringing to his well-educated wife. Maria, who had been always suffering from weak health, died in her father’s arms in 1826.
Grand Duchess Maria Nicholaevna was born on 18 August 1819 as the second child of Tsar Nicholas I and his spouse, Alexandra Fyodorovna. Initially, her father was not thrilled at her birth as he had expected for a son, but quickly he became affectionate parent for her. She grew up into energic, out-spoken girl who lacked only sense of duty. From young years she showed interest in arts and was given a position of President of the Academy of Arts. In 1837 she fell in love with Maximilian, Duke of Leuchtenberg, who was grandson of late Empress Josephine, first wife of Napoleon Bonaparte, who had been defeated by Maria’s uncle, Alexander I. Maximilian was not considered as desireable partner for Grand Duchess, but talks were conducted and they were in 1838. They had seven children, who was granted with title of Dukes or Duchesses of Leuchtenburg and Princes or Princess Romanovsky/kaya. But years passed and couple started to live apart. In 1854 Maria made a second marriage to Count Grigori Stroganov which was kept in secret until death of Nicholas I. Her brother, Alexander II didn’t allow her to stay in Russia so she left her children behind, placing her own happiness over sense of duty. She died of varicose veins in 1876.
Tsaritsa Maria Fyodorovna was born as Maria Sophie Friederikke Dagmar, one of six children of Prince Christian of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg and his wife, Princess Louise of Hesse-Kassel on 26 November 1847. Alongside with her siblings, Dagmar lived an modest, quiet live in Copenhagen, because his father was only an unsignificant German-born prince from impovernished cadet line of family. But in 1852 her father was recognized as heir-presumptive to his childless uncle, Frederick VII, largely due to his wife rights for Danish throne as a niece of Frederick’s father. However, Christian’s new role change little in the live of Dagmar. Her family still resided in Yellow Palace, avoiding Danish court and court functions. Around 1864, Dagmar (or Minnie as she was generally known in her family circles) grew into a pretty, gentle young girl, who caught eye of Tsasarevich Nicholas, son of Alexander II, who was travelling across Europe. Nixa, as he was affectionally called, was handsome, wise and well-read men with large knowlegde. They became smitten with each other. Minnie became engaged to Nicholas, but her happiness turned out to be short-lived. Nixa, who had always been thought to be of robust health, fell down with consumption and was never to recover. Whilst lying on his deathbed, he wished that his bride be married to his beloved brother, stout and narrow-minded Alexander, nicknamed Sasha. In spite of initial reluctance of Alexander to be married to Dagmar, they had a close and free of extramatrial affairs relationship until his death in 1894. Young wife, who had taken a name ‘Maria Fyodorovna’ was an exemplary spouse and representant of ‘golden youth’. She won Russian people over and became renowned for her leniency, charm and good influence that she exerted over her husband. The marriage resulted in 6 children of which, 5 survived into aduldhood, including future Nicholas II. Upon assassination of his father-in-law, Alexander II, she became Tsaritsa, but lived isolated and sheltered in Gatchina due to fear of attempts of assassination. When her son, not mastered in arts of rule, Nicholas II ascended on the throne, she played a significant role as his adviser and fall afoul of her daughter-in-law, Alexandra Fyodorovna, shy, withdrawn and religious princess from Hesse. Maria, despite all efforts to understand Alexandra, never managed to trust her and get along with her. In 1899, she was deeply affected by premature death of her beloved son, Georgy, who had been living alone in Georgia due to his uncurable tuberculosis. As Dowager Empress, Minnie get involved herself in charity and still kept her position and respect. After the October Revolution, she settled down in Denmark and refused to believe in death of her sons, Nicholas and Mikhail and Nicholas II’s family at the hands of Bolsheviks. She passed away surrounded by her only alive children, Xenia and Olga, on 1928. She outlived all her sons (Alexander, Georgy, Mikhail, Nicholas)
(i used picture of Sophia Alexeyevna for Miloslavskaya and picture of unknown lady for Maria Alexeyevna)
411 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hereditary Grand Duke Frederick of Baden with his siblings, Princess Victoria and Prince Ludwig Wilhelm, mids 1870s.
#hereditary grand duke frederick of baden#grand duke frederick ii of baden#princess victoria of baden#prince ludwig wilhelm of baden#baden#german royalty#german royal#mids 1870s#1870s
34 notes
·
View notes