#gestational trophoblastic disease
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#symptoms of gestational trophoblastic disease#gestational trophoblastic disease#causes gestational trophoblastic disease#pregnancy complications#best female gynaecologist in mumbai#mumbai best gynaecologist#gynecologist#female gynaecologist and laparoscopic surgeon in mumbai
0 notes
Link
A molar pregnancy, also known as a hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal form of pregnancy in which a non-viable fertilized egg implants in the uterus. It falls under the category of gestational trophoblastic diseases.[1] During a molar pregnancy, the uterus contains a growing mass characterized by swollen chorionic villi, resembling clusters of grapes.[2] The occurrence of a molar pregnancy can be attributed to the fertilized egg lacking an original maternal nucleus. As a result, the products of conception may or may not contain fetal tissue. These molar pregnancies are categorized into two types: partial moles and complete moles, where the term 'mole' simply denotes a clump of growing tissue or a ‘growth'.
A complete mole is caused by either a single sperm (90% of the time) or two sperm (10% of the time) combining with an egg that has lost its DNA. In the former case, the sperm reduplicates, leading to the formation of a "complete" 46-chromosome set.[3] Typically, the genotype is 46,XX (diploid) due to subsequent mitosis of the fertilizing sperm, but it can also be 46,XY (diploid).[3] However, 46,YY (diploid) is not observed. On the other hand, a partial mole occurs when a normal egg is fertilized by one or two sperm, which then reduplicates itself, resulting in genotypes of 69,XXY (triploid) or 92,XXXY (tetraploid).[3]
Complete moles carry a 2–4% risk, in Western countries, of developing into choriocarcinoma and a higher risk of 10–15% in Eastern countries, with an additional 15% risk of becoming an invasive mole. In contrast, incomplete moles can become invasive as well but are not associated with choriocarcinoma.[3] Notably, complete hydatidiform moles account for 50% of all cases of choriocarcinoma.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
An Integrated Multi-OMICS Approach Highlights Elevated Non-Esterified Fatty Acids Impact BeWo Trophoblast Metabolism and Lipid Processing
Maternal obesity and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) are linked with impaired placental function and early onset of non-communicable cardiometabolic diseases in offspring. Previous studies have highlighted that the dietary non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) palmitate (PA) and oleate (OA), key dietary metabolites associated with maternal obesity and GDM, are potential modulators of placental lipid processing. Using the BeWo cell line model, the current study integrated transcriptomic (mRNA... http://dlvr.it/SvGf6V
0 notes
Text
Understanding Molar Pregnancy: Everything You Need to Know

Molar pregnancy is a condition when the placenta does not develop normally. It may happen when sperm and egg join together at fertilization. Molar pregnancy may cause complications; thus, it is essential to consult with the expert Dr. Sujata Rathod, the best molar pregnancy treatment doctor in Thane.
What is Molar Pregnancy?
A molar pregnancy occurs when sperm and egg join incorrectly at fertilization and form a noncancerous tumor in the uterus. A fluid-filled tumor may stop the embryo’s development, sometimes leading to miscarriage. However, if miscarriage does not occur in molar pregnancy, your doctor may suggest removing the pregnancy to avoid future pregnancy complications. Molar pregnancy is also known as hydatidiform moles or (GTD) gestational trophoblastic disease.
What are the Different Types of Molar Pregnancy?
Molar pregnancy falls into two different types, which are partial molar pregnancy and comply molar pregnancy. In a partial molar pregnancy, an abnormal placental form occurs with an embryo, and the fetus may not survive. Placentals may have both regular and irregular tissue. On the other hand, there is no embryo form in complete molar pregnancy, and sperm fertilizes an empty egg. In this condition, the placenta may develop but in an abnormal state and may contain fluid-filled tumors.
Common Symptoms of Molar Pregnancy
A person with molar pregnancy may experience the following symptoms.
Vomiting
Severe nausea
Pelvic pain or pressure
Grape-like cysts out of the vagina
Bright red or dark brown bleeding in the first trimester.
Abnormal swelling
Ovarian cysts
Hyperthyroidism
Anemia
High HCG levels
High blood pressure
Causes Lead to Molar Pregnancy
Molar pregnancy may occur due to abnormal egg fertilization. It may be caused due to genetic disorders. In usual pregnancy, an embryo gets 46 chromosomes from both parents, 23 from the mother and 23 from the father, and its proper structure contains genes. However, in molar pregnancies, the embryo has an imbalance of chromosomes, or the egg may contain no chromosomes, or the egg may be fertilized by 2 sperms which results in 69 chromosomes. An imbalance of chromosomes during pregnancy causes a mole and molar pregnancy. This genetic disorder causes an unsuccessful pregnancy and may sometimes cause miscarriage.
How to Treat Molar Pregnancy?
It would be best to consult with a pregnancy gynecologist during the initial stage of pregnancy. Specialists suggest surgical treatment to remove molar pregnancies from the body safely. The treatment for molar pregnancies may include dilation and curettage with suction to remove uterine tumors. However, some doctors may also use medication to remove molar pregnancy.. If you are also looking for expert treatment for molar pregnancy surgery in Thane, you must consult Dr. Sujata Rathod to get the best treatment for all pregnancy-related issues.
Conclusion
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of molar pregnancy, then it would be best to talk with the molar pregnancy specialist, who will help you to offer immediate care and treatment plans to prevent future complications. Doctors may suggest an extended treatment plan and precautions to eliminate further issues. Pregnancy care providers may also suggest you wait for the next pregnancy for a minimum of six months to a year after molar pregnancy surgery.
Source : https://nurvinaari.com/molar-pregnancy-types-symptoms-causes-treatments/
0 notes
Text
Molar Twin Deliveries with Coexisting Fetus at Term: Concerning Two Uncomplicated Cases of Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, From 2015-2021, In Conakry, Guinea
Abstract
The coexistence of a molar pregnancy with a live fetus is a rare entity of difficult diagnosis and treatment. Continuation of the pregnancy until full-term delivery is possible. We report two cases of twin molar deliveries observed empirically from 2015-2021, in the gynecology-obstetrics department of the Donka national hospital and in the maternity ward of the Jean Paul II hospital in Conakry. The discovery was made on ultrasound of the first trimester of pregnancy and macroscopic examination of the placenta. One of the neonates was alive, a healthy female and the other was polymal formed with facial dysmorphism, omphalocele and sexual ambiguity, fresh stillborn. There was no maternal complication towards a gestational trophoblastic tumor (T.T.G) in both cases. Efforts must be made in the prevention of T.T.G. by screening for twin molar pregnancies with healthy fetuses on transvaginal ultrasound in the first trimester, the dosage of HCG in the face of unexplained metrorrhagia, macroscopic observation of the placenta after each delivery and biopsy sampling of any suspicious placenta.
Introduction
Complete moles with a coexisting fetus, evolving at term with spontaneous vaginal delivery, without fetal and maternal complications, are rare. Early diagnosis of this association leads in the majority of cases to termination of pregnancy on the one hand because of the frequency of triploidy and on the other hand because of the maternal risk and the possibility of progression to persistent trophoblastic disease [1]. We report two particular cases of twin molar deliveries at term without fetal complication and without progression to maternal gestational trophoblastic disease in the gynecology-obstetrics department of the Donka national hospital, the Teaching Hospital (C.H.U) of Conakry and in the maternity ward of the Jean Paul II hospital in Conakry.
Patients and Observations
Case 1
This was Mrs. D.F.B, aged 19, primigravida and primiparous, with no particular history, admitted while in labor at the gynecology- obstetrics department of Donka National Hospital, Conakry Teaching Hospital, with two results of ultrasound performed with a transparietal probe during her pregnancy. These results did not mention any notion of hydatidiform mole or associated congenital malformation. The pregnancy would have progressed normally until its term without maternal or fetal complications. It was only after the delivery of a fresh stillborn, polymalformed (with facial dysmorphism, omphalocele and sexual ambiguity) child, that the macroscopic examination of the placenta made it possible to make the diagnosis of presumptive mole twin by the presence of a normal placenta attached to a vesicular mass characteristic of a mole. The biopsy sample allowed the histological diagnosis of a complete mole. The post molar follow- up had been organized without maternal complication 61 days before the closure of the service for renovation, on October 5, 2015.
Case 2
This was Mrs. H.C, seamstress, 30 years old, gravidity of 5 and parity of 5 including a twin birth and a laparotomy for ruptured ectopic pregnancy (GEU), who came on her own for a consultation for incoercible vomiting, physical asthenia on a menorrhea of 3 three months, June 19, 2020. The clinical examination had objectified a uterine height greater than the age of amenorrhea and dating ultrasound had made it possible to observe, intrauterine, a normal eutrophic fetus of 13 weeks – Amenorrhea (W.A) and a poorly vascularized heterogeneous multicystic mass. The beta HCG serum marker level was 16000IU/l. We had concluded a twin molar pregnancy and animated counseling on the interest of a medical termination of pregnancy to avoid the risks associated with serious maternal complications of trophoblastic tumor including choriocarcinoma. The couple, after a delay of two weeks, had opted to continue the pregnancy until its term. A pregnancy monitoring and childbirth preparation plan had been drawn up with the pregnant woman, whose morphological ultrasound at the 23rd W.A of the second trimester carried out on 03/09/2020, which had objectified a mass of 81 x 97 mm, in previa position. The pregnancy had progressed, without fetal and maternal complications, at 40 WA 2 days and ended with a vaginal delivery of a normal female child, alive and weighing 2830 grams. The woman had benefited from active management of the third stage of labor (TSLM) and digital uterine dissection to confirm the uterine cavity. Macroscopic examination of the adnexa had confirmed the presence of two separate placentas, joined together (Figure 1), one of which appeared normal and linked to the umbilical cord and had a histologically confirmed vesicular mass of “complete mole”. The planned post-molar follow-up was regular with progressive regression of the beta HCG level until negativity on the fortieth day of delivery without any clinical particularity on the closing date of January 31, 2021.
Discussion
The diagnosis of the association of a live fetus with a normal karyotype with a hydatidiform mole is often difficult, especially in the absence of revealing clinical signs [2,3]. The diagnostic modalities of molar twin pregnancy associating a complete mole with a healthy fetus were different due to the early ultrasound detection in the first trimester and the observation of the placenta. The lack of diagnosis of the coexisting mole during pregnancy despite the two ultrasound examinations in the first case would be linked to the age of the ultrasound scanners, which are often second-hand, the technique used (endovaginal in the first trimester or transparietal) and of the operator’s experience in the first observation. Early ultrasound detection made it possible to develop a follow-up plan for pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum in the second case. In the event of a twin pregnancy associating a live fetus and a molar pregnancy, the pregnancy can be continued until term if the patient wishes after having been informed of the risks and the most frequently reported complications (hemorrhages, late miscarriage, fetal death in utero and preeclampsia) [3]. Evacuation of the pregnancy is required only in cases of fetal anomalies or deterioration of the maternal condition [4]. The probability of obtaining a live birth varies between 16 and 56% [5] or 16 and 60% [4] deliveries. The continuation of the pregnancy is against payment given the risks of immediate and distant maternal complications. Close monitoring of the mother and fetus can help achieve a favorable outcome [4]. We accepted monitoring despite the maternal risks for one of our two pregnant women. The two pregnancies resulted spontaneously in the normal delivery at term of a healthy living fetus and another which would have succumbed to its multiple malformations per partum. The most feared complication is progression to gestational trophoblastic disease [1]. The diagnosis of postmolar Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor (G.G.T.) can be made according to criteria such as the persistence of h.C.G detectable more than 6 months after uterine evacuation and the histological diagnosis of choriocarcinoma [5]. According to Ikram Boubess et al., who adopted termination of two of these pregnancies, one remotely progressed to an invasive mole [6]. Regular monitoring of h.C.G levels throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period is necessary to detect GTN [7]. For Suksai M et al., a pregnancy with an initial serum h.C.G level of less than 400,000m.U.I/ml is a good candidate for the continuation of the pregnancy and the achievement of fetal viability [8]. The incidence of post-molar GTN is higher in twin pregnancies combining a complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and a normal fetus than in single CHM [9].
Conclusion
Spontaneous evolution of the association of molar pregnancy with a live-to-term fetus, without immediate fetal and maternal complications, is possible. The most formidable complication, gestational trophoblastic tumor, choriocarcinoma, was not observed during the study period. The prevention of this complication requires the training of providers in endovaginal ultrasound, its systematic practice in the first trimester of pregnancy, ultrasound and biological monitoring of suspected cases during pregnancy, systematic macroscopic examination of the placenta with biopsy of cases suspect for histological confirmation.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The mysterious extravillous trophoblast
Extravilluos Trophoblast (EVT) is a truly special cell. It has a temporary character and tumor-like behavior and tumor-like appearance, all of which seem to belong to the malignancy field [1,2]. It is also known as intermediate trophoblast, derived from cytotrophoblast [3-5], having formed between the latter and the syncytiotrophoblast. EVT is capable of reaching the decidua through trophoblast cell columns that connect the anchoring villi to the basal plate in early gestation.
The invasive trophoblast penetrates the decidua, thereby bringing about the remodeling of the maternal arterioles. Two kinds of EVT combine to carry out this function: the endovascular ET and the interstitial ET.
EVT possesses an invasive capacity similar to that of tumoral cells and its appearance is characterized by large polyhedral to a spindled cell whose cytoplasm is usually purple in color, accompanied by anisocytosis. Its cellular makeup could be mono or bi-nucleate, simultaneously exhibiting anisonucleosis, nucleomegaly, nuclear hyperchromasia, and pleomorphic nuclei (Figure 1). In the image included herein, we notice the aberrant, highly conspicuous, and, frankly, monstrous features of EVT in photomicrographs taken of term placentas in routine cases. Despite anticipating the grotesque appearance of EVT, these additional fields draw the pathologist´s attention and always cause the said observer to rule out other diagnoses possibly associated with cells of similar appearance, including those of viral diseases. In these cases, it has therefore been possible to rule out such etiologies.
https://www.peertechzpublications.com/articles/JGRO-8-211.php
0 notes
Video
youtube
الترجيع فى أشهر الحمل الأولى وانواعه وطرق العلاج
ما هو القيء
• يعد القيء أحد الأعراض التي تظهر خلال فترة الحمل حيث تعاني الحامل من غثيان شديد تقيؤ متكرر.
من المعلومات الهامة عن القيء :
1. يعد الشعور بالغثيان والتقيؤ في النصف الأول من الحمل من الأمور الشائعة ولكن يجب التمييز بين هذه الظواهر الشائعة وظاهرة القيء المفرِط الحملي الأكثر ندرة.
2. تحدث هذه الظاهرة لدى 70% من الحوامل بين الأسبوع الرابع والأسبوع السابع للحمل وتنتهي عند الأسبوع السادس عشر وقد تستمر هذه الظاهرة لدى 10% من النساء لفترة أطول.
3. تحدث هذه الظاهرة على مدار ساعات النهار وتضطر ثلث النساء إلى التغيب عن العمل بسبب هذه الظاهرة خلال الفترة المذكورة.
4. يكون الغثيان والتقيؤ أكثر شيوعًا في حالات الحمل متعدد الأجنة وفي الحالات المرضية كداء الأرومة الغاذية في الحمل (Gestational trophoblastic disease).
5. يوجد حالات أكثر شدة وتكون لدى 1% الي 3% من مجمل حالات الحمل وتتميز بالتقيؤ المتكرر بما قد يصل إلى أكثر من 4 مرات في اليوم وفقدان الوزن والجفاف اضطراب في تراكيز الأملاح ويطلق على هذه الحالة اسم القيء المفرط الحملي.
ما هي أعراض القيء وقت الحمل :
1. التقيؤ بما يزيد عن ثلاثة إلى أربع مرات في اليوم.
2. فقدان الوزن بما يزيد عن 5 كيلوغرامات بشكل سريع.
3. الشعور بالدوخة والدوار المستمر.
4. الجفاف والعطش الدائم.
ما هي أسباب وعوامل خطر قيء مفرط حملي :
• أسباب القيء الحملي المتكرر لا يعرف الكثير عن الخلفية الفسيولوجية المسببة لظاهرة القيء المتكرر خلال فترة الحمل ولكن يعتقد أنها قد تعود إلى عدة عوامل وأسباب.
• عوامل خطر الإصابة بالقيء الحمل المتكرر تعد النساء اللواتي يعانين من الغثيان أثناء السفر أو عند تناول حبوب منع الحمل واللواتي يعانين من مرض الشقيقة أكثر ميلا للإصابة بالتقيؤ المتكرر خلال فترة الحمل.
• مضاعفات قيء مفرط حملي يعد القيء المفرط الحملي هو السبب الأكثر شيوعا ذهاب المرأة للعلاج إلى المستشفى في بداية حملها بسبب فقدان الوزن و الجفاف واختلال في التوازن الحمضي القاعدي مثل الحماض الاستقلابي وسوء التغذية واختلال في توازن الأملاح وضعف في العضلات وشعور عام بالإرهاق.
ما هي المضاعفات الخطيرة للقيء في بعض الحالات :
1. إصابة المريء.
2. ضرر في الكلى.
3. اعتلال دماغي فيرنيك.
4. اليرقان.
5. تنكس أنسجة الكبد.
6. الذهان.
ما هو تشخيص قيء أثناء الحمل :
1. الأعراض الظاهرة على الحامل والتاريخ الطبي والمرضى كما يقوم بإجراء فحص جسدي.
2. يتم إجراء بعض فحوصات الدم والبول لتشخيص الإصابة بالجفاف وأية اضطرابات في الأملاح والمعادن في الجسم والتي تنتج عادة عن الجفاف.
3. إجراء بعض الفحوصات التصويرية لتشخيص وجود حالة الحمل الرحوي أو الحمل الكاذب والتي تشبه في البداية الحمل الطبيعي أو وجود حمل بأكثر من جنين حيث تزيد هاتين الحالتين من احتمالية الإصابة بالقيء الحمل المتكرر.
4. إجراء العديد من الفحوصات الأخرى استبعاد جميع الأسباب الأخرى الممكنة التي تسبب القيء المتكرر.
ما هو علاج القيء المفرط أثناء الحمل :
1. اتباع التدابير الوقائية.
2. تناول وجبات صغيرة متكررة.
3. السوائل الوريدية.
4. تغذية وريدية كاملة.
5. الأدوية.
6. الانتظار حتى تحسن حالة الغثيان قبل البدء بتناول مكملات الحديد.
7. تناول بعض المكملات التي يمكن أن تقلل من الغثيان مثل مكملات الزنجبيل بناء على تعليمات الدكتور احمد نصار استشاري النساء والتوليد.
8. تجنب تناول الأطعمة التي تحتوي على كميات كبيرة من الكافيين والتوابل الحارة.
دكتور أحمد نصار
• استشاري امراض النساء والتوليد والعقم والمناظير.
عيادة عباس العقاد :
• مواعيد السبت والاثنين والأربعاء من الساعة ٥ مساءا الى ٩ مساءا.
• العنوان ٦٦ شارع عباس العقاد عمارة ديار للأثاث بجوار بنك عودة.
• ارقام الحجز والاستفسارات 01212843264 - 01015027207.
Link Social Media :
• https://www.facebook.com/Dr.Ahmed.Nassar.Clinic
• https://twitter.com/drahmednassar3
• https://www.instagram.com/drahmednassarclinic
Channel Link Subscriptions
• https://www.youtube.com/@drahmed.nassar
0 notes
Text
Beta HCG Test in Delhi
It is a pregnancy test that analyzes the hormone in the body called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). HCG is produced during pregnancy and is also found in blood and urine. An Beta hCG test in Delhi can be done within 10 days of conception to determine if you are pregnant. Checking for hCG can also help identify complications during pregnancy. Recommend it: Confirm pregnancy. Look for pregnancy sites other than normal pregnancy sites (ectopic pregnancies). Confirm the presence of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). To check for suspected tumors such as teratomas, testicular tumors, and ovarian germ cell tumors Early pregnancy screening for genetic disorders such as Down syndrome and trisomy 18. Beta hCG (total) (maternal) test readings: The hormone in the body is called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). HCG is analyzed at high concentrations during pregnancy. A pregnancy test is commonly done when there is suspicion of pregnancy. This test can detect pregnancy as early as 10 days after conception. Pregnancy tests are usually more accurate if you take the test at least 1-2 weeks after your period is due. Beta-hCG is usually found in small amounts in both men and women. Beta-hCG is composed of two molecules known as alpha and beta subunits. The structure of this α subunit resembles that of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. The beta subunit is distinct and is found only in beta-hCG. For this reason, a beta-hCG test is performed to minimize the risk of cross-reactivity. This test can be run at any time of the day. This test requires a blood sample. No, you don't need to drink alcohol for this test. There are no special caveats for this test.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Guide to Choriocarcinoma Treatment: Dr. Chandrakanta Sulaniya
Introduction: Welcome to Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center, your premier destination for advanced care in gynecologic cancers, including choriocarcinoma. Led by Dr. Chandrakanta, a renowned Gynae Oncologist in Jaipur, our center is dedicated to providing compassionate, personalized care to patients battling gynecologic malignancies. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of choriocarcinoma treatment, exploring its causes, available options, and the hope that accompanies modern advancements in oncology.
Understanding Choriocarcinoma:
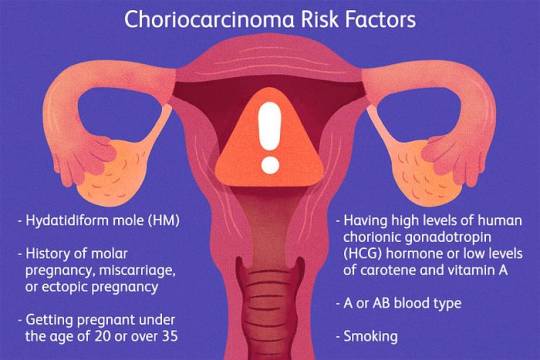
Choriocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that develops from trophoblastic cells, which are responsible for forming the placenta during pregnancy. While choriocarcinoma most commonly occurs in the uterus following a molar pregnancy (an abnormal pregnancy characterized by a nonviable fertilized egg), it can also arise from normal pregnancies, ectopic pregnancies, or even without a preceding pregnancy. This makes it crucial for women of childbearing age to remain vigilant about their reproductive health and seek prompt medical attention if they experience concerning symptoms.
Causes of Choriocarcinoma: The exact causes of choriocarcinoma remain elusive, but several risk factors have been identified, including:
1. Molar Pregnancy: Choriocarcinoma often arises following a molar pregnancy, wherein abnormal growth of placental tissue occurs instead of a viable fetus.
2. Previous Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD): Women with a history of GTD, which includes molar pregnancies, are at increased risk of developing choriocarcinoma.
3. Age: Choriocarcinoma primarily affects women of reproductive age, with peak incidence occurring between the ages of 20 and 40.
4. Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as women of Asian descent, have a higher prevalence of choriocarcinoma.
Treatment Options for Choriocarcinoma: Choriocarcinoma treatment typically involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. The primary goals of treatment are to eradicate the cancer, preserve fertility when possible, and minimize the risk of recurrence. Treatment modalities may include:
1. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the cornerstone of choriocarcinoma treatment and is highly effective in killing cancer cells. Various chemotherapy regimens, such as EMA-CO (etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide, and vincristine), are used either alone or in combination depending on the stage and severity of the disease.
2. Surgery: In cases where the tumor is confined to the uterus or has spread locally, surgical intervention may be recommended. This may involve a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) or more conservative surgeries aimed at preserving fertility for women desiring future pregnancies.
3. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used in conjunction with chemotherapy to target and destroy cancer cells, particularly in cases where the disease has spread to other organs or tissues.
4. Follow-up Care: After completing primary treatment, close monitoring and surveillance are essential to detect any signs of recurrence early. This typically involves regular imaging studies, blood tests, and clinical examinations.
Hope and Support: While a diagnosis of choriocarcinoma can be overwhelming, it’s important for patients to remember that they are not alone in their journey. At Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center, we offer comprehensive support services, including counseling, nutritional guidance, and access to support groups, to help patients navigate through diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship.
Conclusion: Choriocarcinoma is a rare but treatable gynecologic cancer that requires prompt diagnosis and aggressive treatment. With advancements in medical science and a multidisciplinary approach to care, patients can find hope in the journey towards remission and recovery. If you or a loved one are facing choriocarcinoma, don’t hesitate to reach out to Dr. Chandrakanta’s Gynae-Oncology Center for expert care and compassionate support. Your journey to healing starts here.
#choriocarcinomatreatment in jaipur#dr chandrakanta gynae oncology in jaipur#cervical cancer treatment in jaipur#gynae oncologist in jaipur#endometrial cancer treatment in jaipur#gynae cancer doctor in jaipur#gynaecological cancer in jaipur#gynaecological surgeries in jaipur#gynaecological oncologist near me
0 notes
Text
Sometimes I randomly think about how if I existed in the middle ages and suffered the exact same miscarriage I had in 2019, I would've literally died.

So anyways I'm so glad I live in the modern world and that I was lucky enough to have access to reproductive healthcare.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market Projected to Exhibit a Double-Digit CAGR between 2021 and 2028
Global Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market Overview:
An entire Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market report is spread across more than 350 pages, list of tables & figures, profiling more than ten companies. Analysis and estimations attained through the massive information gathered in this Market report are extremely necessary when it comes to dominate the Market or creating a mark in the Market as a new emergent. Market forecast section in this Market analysis report is obsessed with production and production value forecast, key producers forecast by type, application, and regions. The reliable Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market research report is an indispensable model to have increments in business activities, qualitative work done, and enhanced profits.
The major topics of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market document can be listed as; Overview of Healthcare industry, Manufacturing cost structure analysis, Development and manufacturing plants analysis, Key figures of major manufacturers, Regional Market analysis, Segment Market analysis by type and by application, Major manufacturers analysis, Development trend analysis, Marketing channel, and Market dynamics. With the global Market data provided in the report, it has become easy to gain global perspective for the international business. By accomplishing an inspiration from the Marketing strategies of rivals, businesses can set up inventive ideas and striking sales targets which in turn make them achieve competitive advantage over its competitors.
Available Exclusive Sample Copy of this Report @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-gestational-trophoblastic-disease-gtd-treatment-market .
The Global Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market is expected to growing at a CAGR of 4.30% in the forecast period of 2021 to 2028.
Some of most important key factors driving the growth of the Global Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market are increasing prevalence of gestational trophoblastic disease and the technological advancement in cancer disease treatment, increase in high maternal age, increase cases for ectopic pregnancies, Rise in active smoking habits, increase in innovations in the field of oncology and active inactive of birth control pills.
Top Leading Key in Players Global Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment Market: Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, Pfizer Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Antares Pharma, Novartis AG, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., BP Pharmaceuticals Laboratories Company, Fresenius Kabi AG, Accord Healthcare, Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Sanofi, Bayer AG, Amgen Inc and others. New product launches and continuous technological innovations are the key strategies adopted by the major players.
In terms of the geographic analysis, North America governs the gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) treatment industry owing to the strong reimbursement policies in U.S. and increasing awareness and research towards cancer while APAC is anticipated to expand at the most leading germination pace in the estimated duration of 2021 to 2028 due to the increasing research and development investments and rising expenditure on healthcare.
Access Complete Report @ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-gestational-trophoblastic-disease-gtd-treatment-market .
#Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Treatment#Pfizer#Antares Pharma#Novartis#Teva#Accord Healthcare#Eli Lilly#Sanofi
0 notes
Link
Global Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Market size was valued US$ XX Mn. in 2019 and the total revenue is expected to grow at 4.10% through 2019 to 2027.
0 notes