#finno ugric people
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Veelinnurahvas (The Waterfowl People) 1970 dir. Lennart Meri
#veelinnurahvas#lennart meri#the mari#mari people#finno ugric#finno ugric people#documentary#estonia#70's#*
22 notes
·
View notes
Text



The Mari People
175 notes
·
View notes
Text
I finally took the time to finish (pardon the pun) reading the Kalevala Crawford translation! Here's the link to the online cache, for those interested.

One of my favorite passages:
Lemminkainen, much dejected, Broken-hearted, flushed with anger, Spake these words in measured accents: “Mother dear, my gray-haired mother, Wilt thou straightway wash my linen In the blood of poison-serpents, In the black blood of the adder? I must hasten to the combat, To the camp-fires of the Northland, To the battle-fields of Lapland; To the village went Kyllikki, To the play of merry maidens, To the games and village dances, With the maids of braided tresses.”
Straightway speaks the wife, Kyllikki: “My beloved husband, Ahti, Do not go to war, I pray thee. In the evening I lay sleeping, Slumbering I saw in dream-land Fire upshooting from the chimney, Flames arising, mounting skyward, From the windows of this dwelling, From the summits of these rafters, Piercing through our upper chambers, Roaring like the fall of waters, Leaping from the floor and ceiling, Darting from the halls and doorways.”
#kalevala#finnish culture#finno-ugric peoples#sources#culture#ressources#poetry#folklore#history#historical#research#paganism#writings
23 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Thanks zarya i actually was curious about this.


Finno-Ugric Peoples
Almost 25 million people belong to the Uralic language family, who represent about 24 different peoples whose political fates and status vary greatly. Despite the fact that they are the indigenous inhabitants of the territories where they live, most of them have never had their own nation-state. Only the speakers of Hungarian, Finnish and Estonian have their own independent states.
17 out of 24 different Finno-Ugric peoples live in Russia and 3 peoples live both in and outside the territory of Russia. The largest Finno-Ugric peoples have their own so-called republics (Karelians, Mordvins, Maris and Udmurts) or autonomous regions (Khanty, Mansis, and Nenets), in all of which they are minorities.
The number of people actually speaking Finno-Ugric languages in Russia has decreased to less than two million, and this number is declining constantly. Finno-Ugric peoples of Russia have had very limited opportunities, if at all, to preserve their languages and cultures, though the situation, of course, differs from region to region.
The VIII World Congress of Finno-Ugric Peoples takes place in 2021 in Tartu. Source: eng.fennougria.ee
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Holding myself from impulsively buying this doskatreska t-shirt ToT
#IT HAS THE POMOR BIRD OF JOY ON IT AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA I NEED IIIIIIIT#listen. if there is one thing I'm very sensitive about then it's my native culture.#P.s. - Pomors are a sub-ethnic group that is basically a melting pot for northern nations of northwest Russia.#We're descendants of old novgorod russians who mixed with finno-ugric and nenets (if you go to the east of arkhangelsk oblast) people.#and well. our culture is rich actually. we were very procreative in that part aadfghjk
1 note
·
View note
Note
Oh hey didn't know Finnish doesn't have gendered pronouns!! So good to finally see someone else who shares my experience of "why do I need to separate people by gender that's so weird" while learning English lol (Hungarian only has ő (singular they) and az (it))
-local Hungarian lurker
Very distantly related languages (as you may know already) :]
Giving you a friendly Finno-Ugric high five.
#h��n 🤝 ő#answered#anonymous#I'm under the impression that all Uralic languages are genderless but take that with a grain of salt I could be mistaken
245 notes
·
View notes
Note
Ive been kinda wondering about finlands eye color , in anime he has brown (aph) and purple eyes (beautiful world/twinkle ect.) ,but a lot of time it also looks blue ... personally prefer brown just to differentiate more from nordics (they all have blonde with purple/blue eyes) i like to hear your thoughts on this
I'm a big fan of brown-eyed Finland as well ✨ I always draw him with brown eyes as he first appeared in the anime.
I like that it makes him stand out in the Nordics and emphasises him as different to the rest of them - a way to represent the Finno-Ugric language/people as opposed to the other Nordics who are Germanics.
I've also seen some Finnish people who have really pretty brown eyes 🙈

#hetalia#aph finland#hws finland#thanks for the ask!! 💖#I doubt I am the best person to ask about this#but here we support brown-eyed Finland 🙏✨
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

If you think this is too hard on literary criticism, read the Wikipedia article on deconstruction.
Imposter [Explained]
Transcript Under the Cut
[Caption above the panels:] My Hobby: Sitting down with grad students and timing how long it takes them to figure out that I'm not actually an expert in their field.
[For all four panels below, there are two frames crossing the border of each panel. The ones at the top left have a caption, and the one below right has the result of the timing.]
[Ponytail and Cueball are sitting across from each other in office chairs.] Engineering: Ponytail: Our big problem is heat dissipation Cueball: Have you tried logarithms? 48 seconds
[Cueball is sitting in a chair at the center of a table looking left at another Cueball-like guy. To the right is a long black-haired girl.] Linguistics: Cueball: Ah, so does this Finno-Ugric family include, say, Klingon 63 seconds
[Cueball is standing with his hands up talking to another Cueball-like guy and Megan who has lifted her arm to palm her face.] Sociology: Cueball: Yeah, my latest work is on ranking people from best to worst. 4 minutes
[Cueball is sitting in an armchair with another Cueball-like guy sitting attentively in front of him on the floor.] Literary Criticism: Cueball: You see, the deconstruction is inextricable from not only the text, but also the self. Eight papers and two books and they haven't caught on.
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

weirdly enough, people actually seem to like my capella in a mokshan (finno-ugric people who live on volga river, russia) traditional dress,, кельгома стирнязе
#pathologic#pathologic classic hd#pathologic 2#мор утопия#capella olgimskaya#капелла ольгимская#crtani
133 notes
·
View notes
Text


Toivo is the hero of the fantasy story "Stone on the Island", based on the mythology of the Finno-Ugric peoples 🌿 Here are two options with slight differences (eyes and color), which one do you like more? 🙃
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
Loki: Child of the Wind and the Witch
Finding aspects of Loki in Finno-Ugric myth

(This is from an article I wrote on my blog in 2022, I have more thoughts on this now that I may write about later such as Loki's connection with traps, rivers and fishing!)
I noticed in the poem Haustlöng that Loki is both referred to as “Fárbauta mög”, son of Fárbauti, and as “barn Öglis”, child of the eagle in stanza 12. We know that he is the son of Fárbauti, a giant who many see as connected to lightning, but let’s look at Hræsvelgur for a bit. Hræsvelgur is “a giant in the shape of an eagle”, the source of all wind and, according to Snorri, is located at the northernmost point of the world. His wing beats send winds over mankind.
Then said Hárr: "That I am well able to tell thee. At the northward end of heaven sits the giant called Hræsvelgr: he has the plumes of an eagle, and when he stretches his wings for flight, then the wind rises from under his wings, as is here said:
Hræsvelgr hight he | who sits at heaven's ending,
Giant in eagle's coat;
From his wings, they say, | the wind cometh
All men-folk over."
- Prose Edda, chapter 18
In stanza 50 of the Völuspá there is mentioned a tawny eagle who screeches and tears up corpses, "...ari hlakkar; slítr nái niðfölur...". To me this sounds like Hræsvelgr, it fits one interpretation of his name at least (corpse-gobbler) .
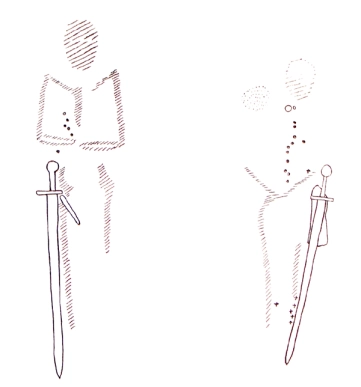
Let’s now think about the name Fárbauti. Fár means danger or destruction, and in Icelandic a common use of the word is in “Fárviðri” meaning dangerous weather. “Bauti” comes from “bauta”, which means to strike/hit and has the same origin as the word “beat”. As said before, many people interpret his name to mean “dangerous striker” and connect him to lightning, but what if these “dangerous beats” were wing beats that sent forth dangerous weather? If Fárbauti is a kenning for Hræsvelgur, this would explain why Loki is referred to as “the child of the eagle”.
But what about Loki’s mother? Laufey is often translated as “leafy island”, but the Icelandic etymological dictionary suggests a connection to the Finnish underworld goddess Louhi, sometimes conflated with Loviatar.
Her name Nál is also translated as “needle” but the Icelandic Etymological Dictionary suggests it may also be related to the obscure goddess Nehalennia, as well as being connected to the latin word necāre which means "to kill", especially by methods such as poisoning or starvation. The dictionary also makes a suggests a connection to the dwarven names Náli, Náinn and Nár which are likely related to the word nár meaning "corpse" or "dead". If Laufey is related to Loviatar then this origin would definitely be very fitting.
In Finnish mythology Loviatar is impregnated by the wind, which would tie her to Laufey if Fárbauti is indeed Hræsvelgur, the source of wind/stormy weather.
On the fields of sin and sorrow;
Turned her back upon the East-wind,
To the source of stormy weather,
To the chilling winds of morning.
— Kalevala, Rune XLV, from the translation by John Martin Crawford
I also read in this article that a part of Mari (a Finno-Ugric people in Russia) spiritual practices is a ritual where young women make love to the wind. This is all I know and haven't yet found more information on it but it is interesting to see making love to the wind as a positive thing in one Finno-Ugric culture but further West it is something that an "evil underworld witch" does.

Loviatar is also referred to as the mistress of Pohjola, which is “the extreme north”, a dark, terrible place. In Mythologia Fennica she is referred to as the emuu or “ancestor spirit” of wolves, connecting her to Loki’s association with wolves as the father of Fenrir. Impregnated by the wind, Loviatar gives birth to nine children, associated with diseases but one son stood out:
One remained without getting a name, a boy at the bottom of the batch, a mouthless, eyeless brat; afterwards she ordered him away, to the tremendous Rutja rapids, into the fiery foaming surge. From him sharp frosts were bred, from him arose the Syöjätärs, from him the other destroying ones, he begat the sorcerers on lakes, the wizards in every dell, the jealous persons in every place, in the tremendous Rutja rapids, in the fiery foaming surge. - John Abercromby, The pre-and proto-historic Finns : both Eastern and Western, with the magic songs of the West Finns
Syöjätärs are kind of Baba Yaga-like troll women.This myth has a resemblance to the last part of the 12th stanza in Völuspá hin Skamma, where it is said that Loki is the origin of all monsters or “troll women”.
Varð Loftr kviðugr
af konu illri;
þaðan er á foldu
flagð hvert komit.
Translation:
(With child from the woman | Lopt soon was,
There hence on earth | came the monsters all.)
Flagð here is translated as “monsters” but it is more commonly used as a word for witches or troll women.

Norse mythology is a shamble of many different tales and myths from different cultures, it wouldn't surprise me if aspects of Loki can be found in Finnish myths and folklore.
I want to preface this next part by saying that I have not studied etymology on an academic level, but I do know that Norse and Finnic people borrowed words from each other (f.x. the Norther-Sámi word siedi, which means "sacred offering site/offering stone" is borrowed from Norse seiðr).
If Loki is actually Lóðurr, and there is some evidence he is (Haukur Þorgeirsson of the University of Iceland writes about it here), then Loki is also responsible for the creation of man according to Norse myth. The Finnish luoda (“to create”, from Proto-Finnic *loodak which means "to create" or "cast/throw") sounds like it could be connected to Lóður, however Lóður is thought possiby derive from Icelandic lóð meaning "growth or product/yield". I still find it interesting that another Icelandic verb, afkasta ("profit, yield") has connections to throwing, clearly throwing and creating are sometimes linked concepts.
I also found out that from *loodak comes the word luopa "renounce/abandone" and luopio which means “traitor”. These words are likely derived from the "casting" definition of *loodak and to me sound eerily like Loptur but could be a bit of a stretch as well.
The word I find most interesting though is the Finnish word loukko. The general consensus regarding the name Loki is that it is most likely from "loka" which means to shut or open, also “lok” which is "ending" (same root as the english word “lock”). However, loukko (hole, hollow, inside corner, pit) from Proto-Uralic *lowkke (“hole, opening, cavity, hollow”) attracts my attention because of the aforementioned meaning of Loviatar's name which is made up of lovi ("cleft" or "hole") and -tar (feminine suffix). The Finnish way of saying "falling into a trance" is "langeta loveen, literally "falling into lovi, falling into a cleft".

This phrase, falling into a cleft, refers to cracks in stone being gateways to the underworld in Finnish-Karerlian shamanistic folklore. Antti Lahelma writes about cracks in painted/carved rock faces being gateways to the Underworld as a phenomenon attested cross-culturally. On the rocks by the lake Onega in northwestern Russia there are images of swans entering or emerging from cracks in the rock, Lehman writes that this could represent the soul of a shaman or dead person passing between this world and the Underworld. In their article Liminality, Rock Art and the Sami Sacred Landscape, Inga-Maria Mulk and Tim Bayliss-Smith suggest that Badjelánnda rock art site in northern Sweden should be seen as a Sámi gateway to the Underworld. They also write that water seeping out of cracks in these smooth, south-facing black rocks represented new souls returning to the Middle World. According to Russian scholar Vladimir Napolskikh's constructed ‘map’ of Proto-Uralic cosmology (see image below), the Underworld or Lower World is associated with North, the river mouth, cold sea and subterranea.

(Vladimir Napolskikh 1992)

Photo of a plaster cast of a swan carving in Besov Nos.
Migratory water-birds such as swans, geese and ducks were birds of the Upper World, but the birds of the Lower World were loons. These birds often feature in Earth-Diver myths and Napolskikh writes that in some versions it is the loon (or someone who transforms into a loon) that dives to the bottom of the sea and fetches the earth that land shall be made of. However, in some myths the loon is the unsuccessful rival of another creature (often a duck) which does manage to fetch earth, sometimes the loon is even a form of the Devil.
An interesting theme that can be found in some versions is the Devil/loon/second bird using part of the earth to create the land as well. This is sometimes a team effort between the two creators but sometimes the Devil/loon/second bird deceitfully conceals a part of the earth in it's beak/hands and either deliberately or accidentally creates it's own parts of the world. One myth I find particularly interesting features the Devil demanding a small piece of earth and from the resulting hole emerge all kinds of vermin. Here we see some familiar concepts; A creator, a hole or gap, a traitor, an originator of undesirable creatures. Lóðurr, Loki, Loptur?

Probably the most compelling evidence that suggests that Loki is connected to loons can be found in An Account of the Sámi by Johan Turi. He writes about the loon being a noaidi bird (i.e. associated with Sámi shamanic workers) and being able to foretell changes in the weather. Most remarkable however, is that the beaks of the red-throated loon were used "in the olden times" to make weapons like arrows and it was believed that such weapons are the only things that can kill people that have been enchanted to resist arrows. This reminds me of the mistletoe that kills Baldur as well as Loki’s weapon Lævateinn/Hævateinn which is the only weapon that can kill the rooster Viðófnir.
Thinking of all of his names and these words fills my head with repeating sounds, Lou Lo Ló Low Loo. This reminds me of the sound of the Sámi joik or luohti, a kind of singing which is sometimes done in a shamanic context. Not necessarily related, I just wanted to add this in.
This whole thing might be me just grasping for straws, but I strongly believe that the myth of Loki is tied to something deep. Is Loki the howling sound of the wind passing through cracks and clefts in stone? A being that dives into the Underworld? A cunning magician with loon-beak arrows?

#mine#loki#lokean#pagan#heathenism#heathen#mythology#academic#finnish mythology#finno ugric#sámi#hræsvelg#laufey#loviatar#shamanism#witchcraft#louhi#chthonic#cthonic deities#gods#norse mythology#etymology#lóður
131 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, I noticed that in one of your posts you showed an Iron Age Finnish woman's dress. Would you happen to have a good idea of what Finnish men were wearing in that era? The information on it seems sparse. I do have a relevant book that I'm about to look through, but I'd like to hear your insight too!
Hi! Thanks for the question (and sorry for the slow answer), I do love Finnish Iron Age clothing so it's always my pleasure to write about it. I've been wanting to do a deep dive into this for a long while, so maybe I'll do at some point a post about women's dress too.
Unfortunately no one has good idea of the Finnish Iron Age men's dress (and if you find any book or other source that claims otherwise, do not trust it), since there's much fewer archaeological finds of men's dress than women's dress. The most accepted theory on why the textiles of women's dress survived surprisingly well is because of the bronze ornamentation commonly sewn into especially the fine women's dresses of the era. The bronze protected them from decomposing fully. Presumably men's dresses were not decorated similarly then. There are some finds though and we can piece together at least some kind of vague picture.
I will be discussing the period from Viking Age to Crusade Age in Finland. Viking Age is often defined to cover 800s to mid-1000s and the Finnish Crusade Age started right after the Viking Age and ended in the end of 1200s, where the Finnish Medieval era begins. Crusade Age refers to the period where mostly Swedish (also German) crusaders in the span of couple of centuries conquered lands of the Baltic-Finnic pagans. The crusades of this period targeted pagans all over eastern Baltic Sea, including Baltic-Finnic Karelians, Livonians and Estonians, and Baltic peoples, and the Scandinavia too, where Sámi people were targeted. After that the Finland and Sápmi were colonized by Norse people and stayed that way untill Finland was transferred under Russian rule, but to this day Sápmi still stays under colonial rule, including Finnish colonial rule. The current Finland was very multicultural area, mostly populated by Finno-Ugric peoples, including Sámi people, Karelians and various Finnish peoples.
It's important to understand that even just Finnish peoples where not homogeneous, but had distinct, yet of course strongly related cultures. These were Finns (suomalaiset) (yes most people we now call Finns were not in fact called that) in the coast of southwestern and western Finland, Tavastians (hämäläiset) in central-western lake-Finland and Savonians (savolaiset) in central-eastern lake-Finland. This means we can't mix findings from all over Finland to reconstruct a dress without evidencing that all the elements were actually used in one place. These three tribes had broadly similar base for their clothes, but distinctive jewelry and detailing. The big divide was and has always been between eastern and western Finnish peoples. This is because western Finnish people were in close contact through the sea with Norse people and southern Baltic-Finnic peoples, while eastern Finnish people, Savonians mostly, were influenced a lot by their proximity with Karelians. Another dividing factor was the very different environmental conditions between western and eastern Finland. The Finnish coast especially in west is very flat and fertile land, while the lake area, especially in eastern Finland is very rocky, hilly and quite infertile. The main way it effected clothing differences was that western Finland being more wealthy had more elaborate clothing. Tavastians in both occasions fall quite in between, but they tended to be more in the western cultural camp.
My most important sources are a study by a doctor of cultural anthropology, Jenny Kangasvuo, Savon historia I (Savonian history) digitized and open sourced here and the digitized archeological collection of Finnish Heratage Agency. They are all in Finnish so not very useful for most people unfortunately.
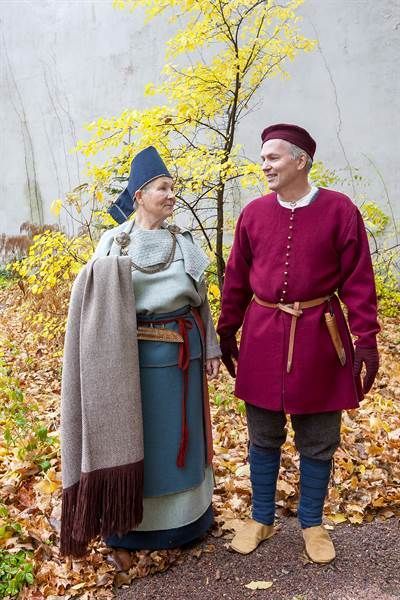
Finnish Men's Dress in Viking and Crusader Ages
The basic garments men wore were broadly similar as women. They wore a shift/shirt, knee or above-knee length dress, cloak, belt, shoes and some kind of headwear. Wool was used most commonly, though the shirt would sometimes be linen too. Even evidence of silk has been found in some western Finland graves. I would assume that would be from a dress of some great man, who traveled to gain riches, possibly with vikings. Embroidery and decoration with metals was a typical feature of the whole Eastern Baltic Sea area. In Finland during this period bronze was the most common decorative metal, but silver was used too. Decorative elements were usually woven with small bronze spirals into all kinds of patterns. Here's examples from the reconstructed Ravattula's dress (Finns) used by women.


Shirt
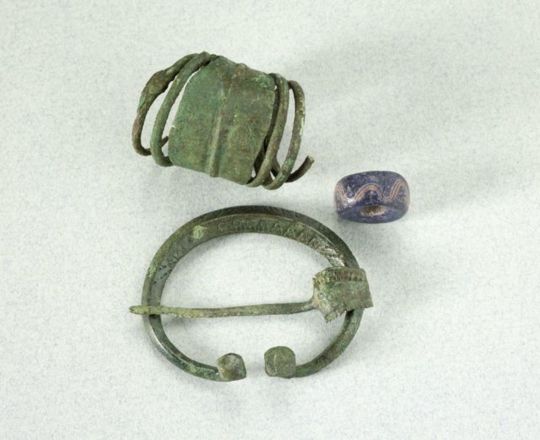
The shirt (in Finnish shift of both women and men was called shirt) was basically a long shirt or under dress. We can assume it was similar to those of women's except shorter since the dress men wore was shorter too. They were made from wool or linen, I would assume wool was used in winter and linen in summer, when linen was even available. The neckline had a cut and closed with a bronze brooch. Horseshoe brooch was common. The first one is a quite typical bronze horseshoe brooch with a bit of ornamentation from Salo (Finns). The second one is from Tuukkala, (Savonians), it has exceptional ornate detailing and is uncommonly silver, not bronze. The third picture has two quite uniquely ornamented horseshoe brooches, first from Köyliö (Finns), second from Kurikka (Finns).



Legwear and footwear
Very little of men's legwear has survived and it's unclear weather men wore pants or separate pant legs, leg wraps or perhaps long socks. Evidence of strings decorated with bronze spirals and tablet woven band has been found in leg area of men's graves. This could mean that they wore either leg wraps, long sock or some sort of pant legs that needed to be secured with string or band under knee. Women used strings and tablet woven tape to secure leg wraps and socks, which I think supports that theory. Sometimes both bronze decorated string and tablet woven band was found in the leg area, which would still be explained by this theory, since it was common to decorate the ends of the bands with bronze decorated strings. Here's an example of sock bands just like that from the earlier mentioned reconstruction of the Ravattula's women's dress. Since men's dress was shorter, I think it would make sense if they still wore some kind of pants or separate pant legs with socks or leg wraps like that.

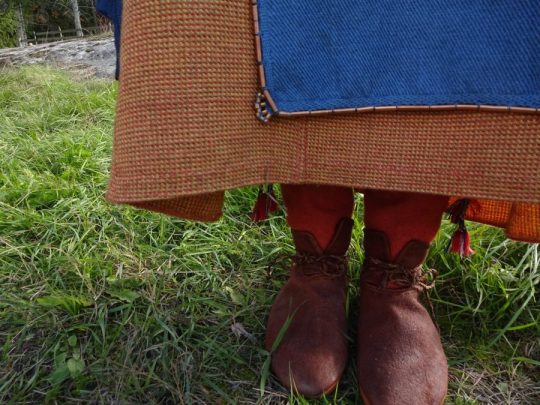
However, the strings and bands could have also been part of the shoes. Everyone probably wore similar shoes - laced leather shoes with a bit of pointed end. They might have been short or ankle length and the lacing was done with either leather cord or tablet woven band, which would also explain the findings. Socks or feet wraps would have been used in them, and straw or wool could be added as filling for warmth. Here's a pair of traditional Izhorian shoes from Estonia from early 1900s, and a pair of traditional Sámi shoes. The designs were likely roughly similar in Viking and Crusader Ages, though obviously more simple, and it's probable that Finnish shoes very something like that too. Here's a 1893 drawing of what findings of shoe material from Korpiselkä (Savonian or Karelian) might have looked like. Considering the quality of archaeology of that time, copious amounts of salt should be applied. And finally as a fourth picture there's reconstruction shoes from Ravattula's dress.




These are not necessarily mutually exclusive theories. The lacing of the shoe could have been laced up the leg and used also to secure either sock or leg wrapping, or they could have been separately secured in ankle and knee respectively.
In some graves twill fabric has been found in the leg area. It could be part of pants or for example leg wrapping, which was often made of twill. One theory about pants is that they were similar as some findings in Sweden, where fairly tight pants made of twill were secured at the hem with buttons similar to cuff studs. These kinds of cuff stud buttons are quite a common find in Finland and some have been found in men's graves close to legs.
Dress
Again there's not much findings of dresses, but a little more perhaps. It was usually from wool. The shape was either a tunic or an open coat. In Karelia there's findings of men's dress suggesting tunics thicker than women's dresses and made from sarka, a type of broadcloth. On the other hand, in Masku (Finns) they found buttons in a row on top of the torso, which suggest a coat closed with buttons. The first picture is a drawing of the grave find. Similary coak closing amounts of buttons have also been found in other places in western Finland. This suggests that Finns and probably Tavastians too wore long coats buttoned to the waist and Savonians wore tunic of Karelian influence. Below there's couple of version of what might this western Finnish men's coat dress could've looked like. The first is an imagined version of the coat based on the Masku grave finds, second is just as imagined version based on Eura (also Finns) grave finds.
Take these "reconstructions" with a strong dose of salt. These are more artistic reconstructions than scientific, since there's not enough material and too much guesswork needs to be done. And because we can see in the Masku grave drawing right here that the other deceased has a large buckle to (probably) close the shirt (to be fair, it could for a cloak too), like was typical, I find it implausible that the coat neckline would be small and round covering the buckle. If you make a decorated big buckle, I assume you want to show it. I would find a v-neckline more probable. It's also easier to make without wasting expensive fabric.


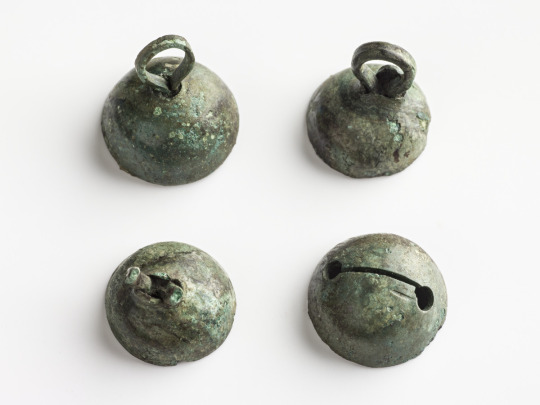
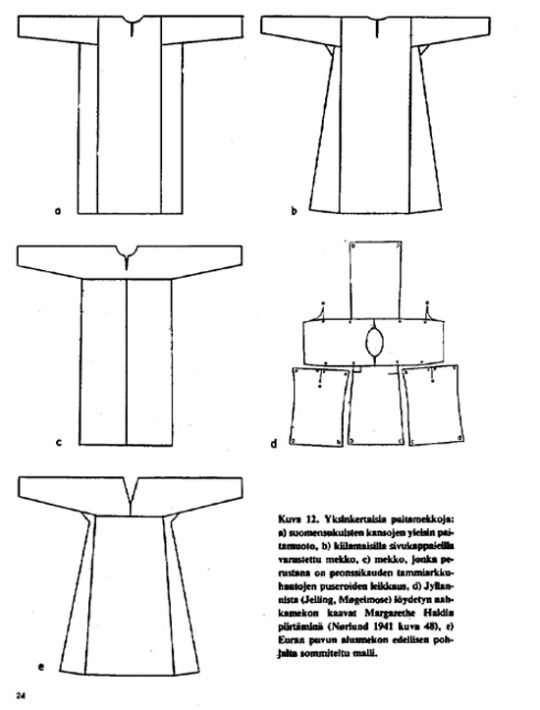
The buttons are interesting. There were what you would imagine - your typical buttons made of bronze like seen in the first artifact from Hattula (Tavastians). But then there was silver jingle bells used as buttons, found for example in both Masku and Eura graves, Eura findings pictured below.


It's possible, even probable I'd say, that the hemlines of men's dresses were finished with tablet weaving patterns, like women's dresses. Also I would assume the pattern of the men's dress (and shirt) was mostly similar to the women's underdress/shirt patterns. So here's couple of different reconstruction patterns for women's dress. Different historians have made different interpretations of the patterns, so it's very much undecided what it really was like.
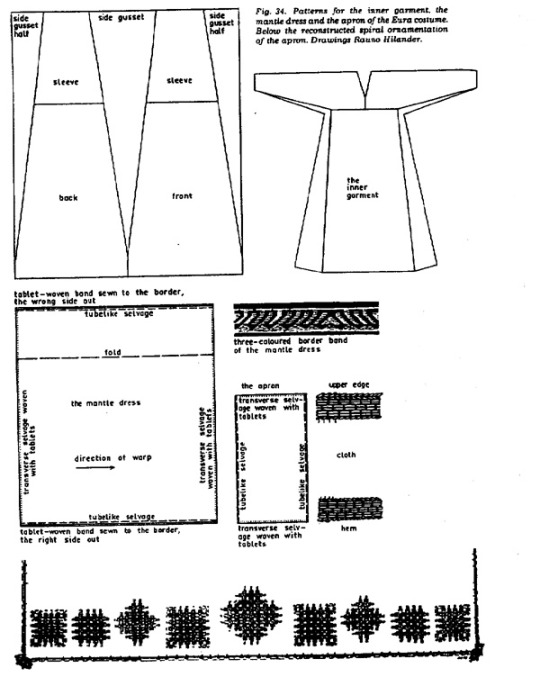
Belt
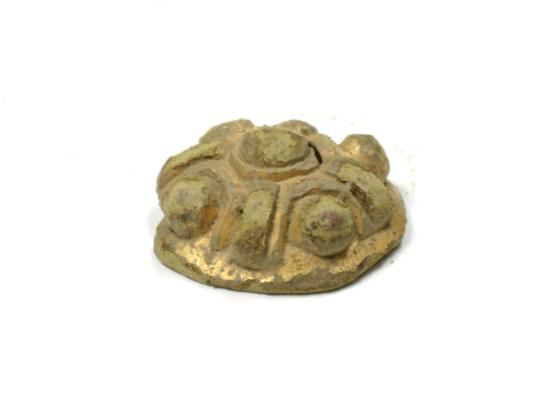
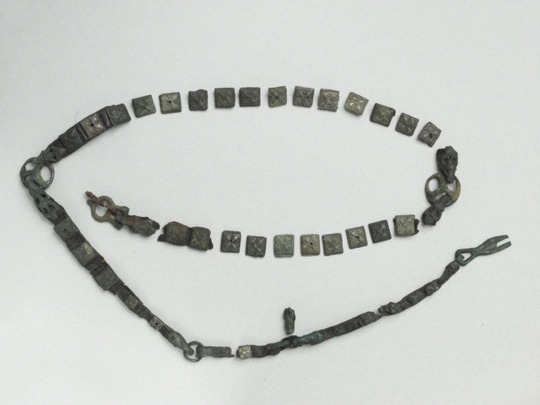
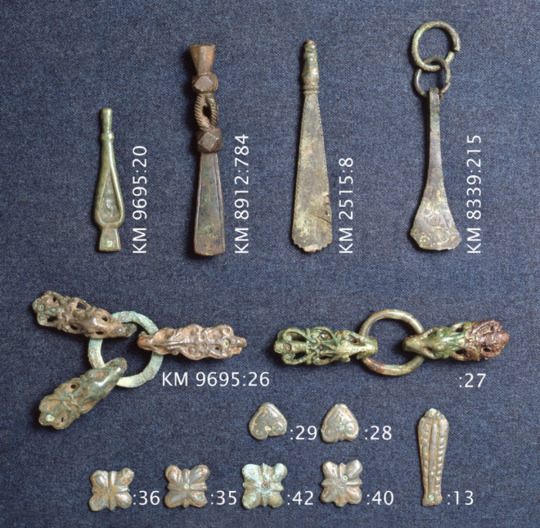
This is likely the most ornamental part of men's dress. They could be made out of leather or tablet woven band. And there's another east-west cultural divide here. Karelian belts were made out of leather, were usually 1,5-2,5 cm wide, decorated with iron or bronze studs and had a buckle made out of iron or bronze. These types of belts have been found in Savonia too, for example in Tuukkala grave find, which you can find very cool pictures of in this photo documentation of the dig in pages 173-175. In western Finland a "hela" belt was the common style. I don't think there's a world for hela in English. It's a sort of decorative lamella, small metallic plate (not necessarily square but often so) attached to fabric or leather with studs or sewing. Hela belt came from the Permians of Kama river, who were one of the many Finno-Ugric peoples who used to populate much of European side of Russia. Karelians lived closer to Permians, so you might think Permians would influence eastern Finland more, but my theory is that the costal Finns, who frequently joined viking crews and at least were in close contact with merchants including vikings, who would travel along the eastern route through the eastern European rivers, where they could go all the way to Kama river or at least meet traveling Permians. Here's yet another Finnish source more on the Finno-Ugric people around Kama river.
Anyway, hela belt was made of leather and filled with small decorated lamellas, often in square shape, but various other shapes too, like animal ornamentation. In this period hela belt helas were bronze. First image is a nice full set of hela belt metal pieces found in Pirkanmaa (Finns). Second is an older example, right before Viking Era, from Vaasa, costal settlement, (Finns), depicting a very Permian style. The third one is a lion hela found separately in Pälkäne (Tavastians). They are also found in Tuukkala, showing that both eastern and western cultural influences were present there at the same time.
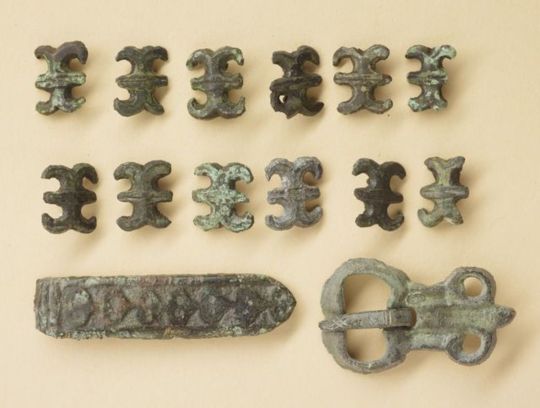



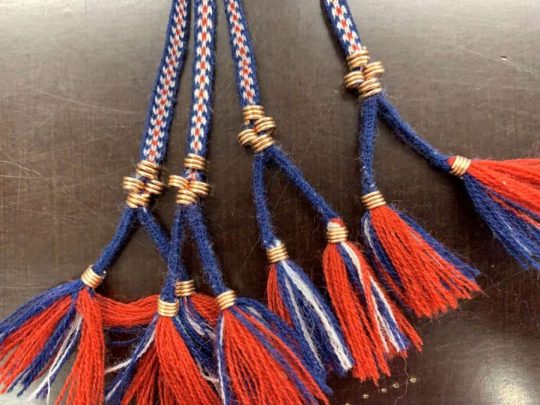
Another western Finnish belt type for men had intricate tassels decorated with bronze spirals hanging on the waist at the end of the belt. They could be made out of leather or tablet woven band. First image depicts a reconstruction of such tassel. Belts in east and west would have strap dividers to hang straps for things like purse, knife and sword. The first picture above has couple of those, but the second picture below has two more of them in more detail in the middle of the picture. These finds are from Lieto (Finns).


Cloak
Like women's cloak, men's cloak was woolen and either a square or trapezoid. Cloak is yet another east-west divide. In western Finland men's cloaks have embroidery with bronze spirals. They in fact appeared earlier in men's cloaks (in 900s) than in women's cloaks (1100s). They were also a little different in men's cloaks. The spirals and the patterns themselves were bigger and the fastening thread itself was also used for the pattern creation, unlike in women's dresses, where the thread was mostly covered. In eastern Finland there has been no finds of bronze decorations in men's cloaks, mostly only cloak brooches have been left of them. Unsurprisinly same applies to Karelia. This also means there's very little fabric left too. There's one exception. In Tuukkala (Savonians) they found a piece of fabric probably from men's cloak, though it could be from a men's dress too. It was striped, with possibly white or brown base and wide stripes of red, blue and yellow. So perhaps eastern Finnish cloak was not non-decorated, but the decoration was in the fabric pattern. Unfortunately it's hard to know how common fabric like that was, when so little of it is left.
Accessories
It's safe to assume men too wore some type of headwear, but none of those has survived. It probably means it was entirely made out of fabric whatever it was. Some type of hat or cap was certainly used in cold weather at the very least. Tablet woven headband was also possible option for not too cold weather.
In Tuukkala there was couple of interesting jewelry finds too. Two graves had a necklace type mostly found in Karelia. It was birchbark tape covered with nettle fabric and had square helas sewn into it. There were also more typical Finnish necklaces made of beads and bronze spirals.
Razors have also been found with men in their burials, so we can assume shaven faces or at least trimmed beards and moustaces were fashionable.
#dress history#historical fashion#historical clothing#fashion history#history#iron age dress#finnish iron age dress#finnish history#archaeology#answers#anon
227 notes
·
View notes
Note
Would you recommend studying finno-ugric languages (for a native Finnish speaker)? Can you share some tidbits?
Hi!
I am specifically doing my studies at the University of Helsinki so I can give you specifics on what we do here (the same things apply if you study this as a hobby tbh)!
First of all, if you are considering this field, you NEED to be ready to learn at least one completely new language to a B2 level. Our field requires at least 3 courses in another Uralic language (I am doing North Sámi, the other two options are Hungarian and Estonian). On top of that, you can (or kinda have to if you don't wanna do a 4th course from that first language) do 1-2 courses on an another Uralic language. These singular courses also cover the smaller languages, I am so looking forward to a Nenets course becoming available!
Another thing you need to keep in mind is that while we are grouped with the Finnish fields here at UoH, our field is totally different, in my opinion, this resembles linguistics a lot more than Finnish studies. You have to be ready for a lot of linguistics courses and I recommend studying linguistics on your own before applying.
The third thing is the job market. There aren't many jobs specifically for this field unless you want to be a professor or a researcher so think of this as a secondary career option and be ready to educate yourself further after finishing your studies.
From the standpoint of the community here at UoH, you WILL become the center of attention. There are SO FEW of us here we are like rare shiny Pokemon. Both staff and other students will say "Oooh what I've never met anyone in your field yet" more than once. Be ready to answer the burning questions such as "So where did Finnish come from" or "What is the etymology of Suomi" 1 week in. Prepare your answer before you even come in for orientation.
Learning about the Uralic languages will definitely help you learn about how Finland came to be. You'll also be able to learn other Uralic languages faster and even start to understand them without studying them at all in some cases!
TLDR: a rare form of linguistics disguised as Finnish studies. People will question your life choices. You will too after memorizing North Sámi noun cases at 1am.
#finnish#langblr#langblog#suomen kieli#suomitumblr#linguistics#university#uralic languages#i love nenets#nganasan has been another fave for ages
25 notes
·
View notes
Text




Wait, I haven't posted pics of the nonbinary flag mittens that I knitted as a gift in 2023, have I?
To go with the yellow-white-purple-black (nonbinary pride flag) color scheme of the outer layer, I snuck some Gender into the patterns. They're traditional Latvian ornaments, or sometimes my stylized interpretations of them. The Sun sign was historically mostly used on women's folk costumes, while the Moon sign was for men's clothes; so I used both of them and also the star, which we might have borrowed from Finno-Ugric cultures (so from people who are free of grammatical genders). Also, the zigzag near the bottom kind of combines the signs and colors of one male deity and one female deity. The other patterns are various lucky symbols.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
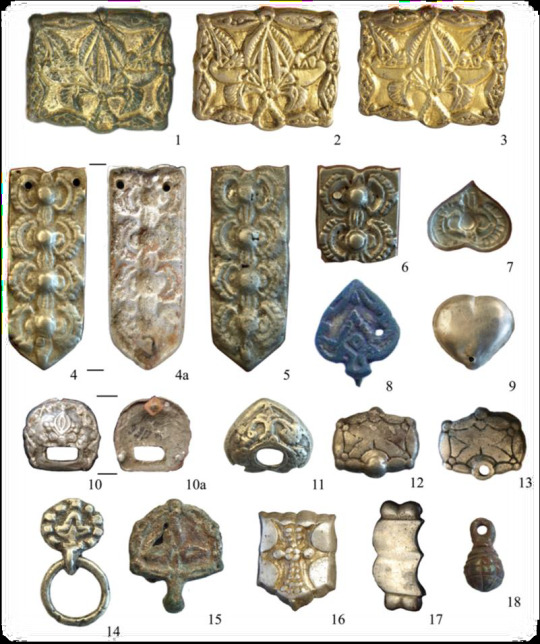
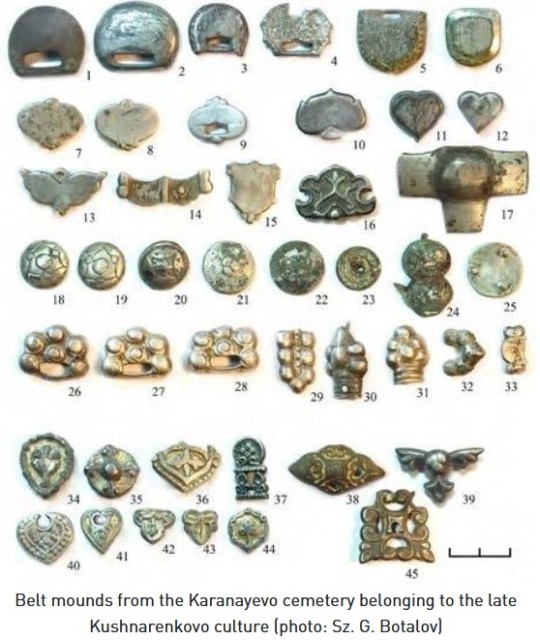
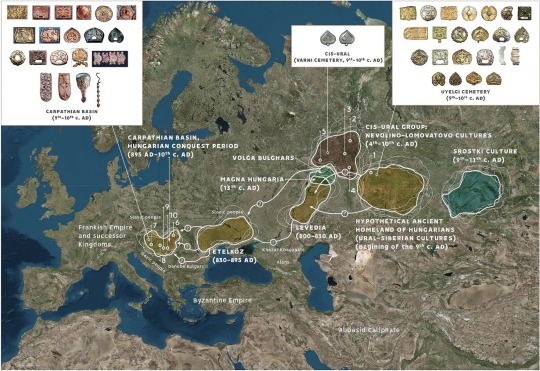


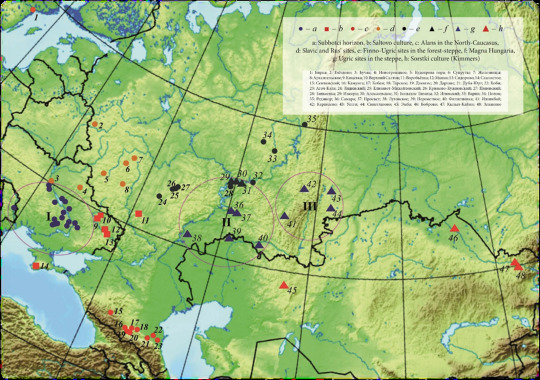




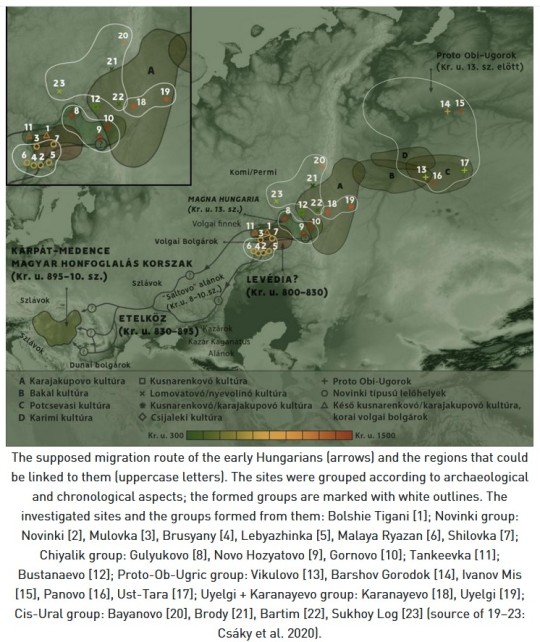
Miscellaneous Hungarian archaeological items from the migration era, from the Urals to the Carpathians 9th-10th C. CE. Sources can be found on my blog, link at bottom.
The Magyars, as a nation, seem to have originated in the region of the Urals and Volga and their original territory covered a large amount of what is European Russia today. This region was known as Magna Hungaria or Ancient Hungary in the Middle Ages. In the 13th century Christian monks tried unsuccessfully to convert the Pagan inhabitants of Ancient Hungary, who they noted spoke the same language as the Hungarians in the Carpathian Basin (will post more on this later). Now genetics show they were related too. Some of the Hungarians in the Carpathian region were found to be direct family members of these Uralic-based Hungarians according to this genetic study below. I grabbed some highlights of genetics article here and included some archaeological image finds:
"Two recent articles have investigated the Y-haplogroup variability of Hungarian conquerors describing the conqueror’s elite population as heterogenous, with significant proportion of European, Finno-Permic, Caucasian and Siberian (or East Eurasian) paternal lineages. Fóthi et al. have claimed that the Hungarian conquerors originated from three distant sources: Inner Asia (Lake Baikal – Altai Mountains), Western Siberia – Southern Urals (Finno-Ugric peoples) and the Black Sea – Northern Caucasus (Northern Caucasian Turks, Alans, and Eastern Europeans). Both studies pointed out the presence of the Y-haplogroup N-Z1936 (also known as N3a4-Z1936 under N-Tat/M46), which is frequent among Finno-Ugric speaking peoples.
...The genetic connection of Uyelgi cemetery in the Trans-Ural and 10th century Hungarian conquerors in the Carpathian Basin is supposed by close maternal relationships of the following individuals: Uyelgi3 from Kurgan 28 of the youngest horizon and three Hungarian conquerors from Karos II cemetery have identical U4d2 mitogenome haplotype (Supplementary Fig. S4p). Furthermore, the mtDNA A12a lineage of Hconq3 (30-40 years old woman from Harta cemetery dated to the first half of 10th century AD) is an ancestor of the mtDNA lineage of Uyelgi7 (from Kurgan 30 of the youngest horizon of the cemetery) based on the A12a haplogroup tree (see Supplementary Fig. S4a).
The mentioned graves from Uylegi show the characteristic of the Srostki culture, where the gilt silver mounts with plant ornaments were typical, and which was disseminated from the Siberian Minusinsk Depression and the Altai region through the Baraba Steppe and North-Kazakhstan to the Trans-Ural region (Fig. 1).
The connection of Uyelgi cemetery and Hungarian conquerors is visible on the N1a1a1a1a branch of the tree of haplogroup N1a1 too, that was prevalent among the ancient Hungarians (Fig. 5). Here seven Hungarian conqueror samples from cemeteries Kenézlő-Fazekaszug, Orosháza-Görbicstanya and Karos-Eperjesszög clustered together on one branch, while the five Uyelgi samples from the earliest and latest horizons are located together next to this branch.
Majority of Uyelgi males belonged to Y chromosome haplogroup N, and according to combined STR, SNP and Network analyses they belong to the same subclade within N-M46 (also known as N-tat and N1a1-M46 in ISOGG 14.255). N-M46 nowadays is a geographically widely distributed paternal lineage from East of Siberia to Scandinavia. One of its subclades is N-Z1936 (also known as N3a4 and N1a1a1a1a2 in ISOGG 14.255), which is prominent among Uralic speaking populations, probably originated from the Ural region as well and mainly distributed from the West of Ural Mountains to Scandinavia (Finland). Seven samples of Uyelgi site most probably belong to N-Y24365 (also known as N-B545 and N1a1a1a1a2a1c2 in ISOGG 14.255) under N-Z1936, a specific subclade that can be found almost exclusively in todays’ Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and Hungary (ISOGG, Yfull)."
-Early Medieval Genetic Data from Ural Region Evaluated in the Light of Archaeological Evidence of Ancient Hungarians
#magyar#hungarian#archaeology#genetics#hungarian art#history#art#europe#middle ages#medieval#finno ugric#pagan
44 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’ve always been wondering about something about the Shang-La world. What’s the inspiration behind the five countries and their cultures?
They are inspired by real countries and cultures to make them somewhat low fantasy, like real magic never happens there (or happens on special occasions). We like to concentrate on cultural things and mix them, building the whole concept around the main idea of Shang and La. I mean, we're trying not to use the source of our inspiration in a too obvious way and build it around the existing concept of our headworld.
Speaking shortly...
Latori: We took a lot from Bulgarian and Romanian culture in general.
Beyleria: We were inspired by the minority peoples of the North, Siberia, and the Far East of Russia. Mainly the Sakha people (a Turkic ethnic group) and the Komi people (a Finno-Ugric ethnic group).
Nouri: the heaviest mash of Celtic and Karelian cultures, the colors of the Russian Empire, and Finnish and Turkic-like languages.
Ayelahai: Mongolia, Tibet, and pinches of China and Japan (haven't worked on this yet)
El-Balyama: Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia
Frangie: The Romanian Empire??? We didn't work on this either.
27 notes
·
View notes