#european financial market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
habs is fantastic because there’s a bit of live long enough to see yourself become the villain re: francophone identity and the nordiques! and then your usurper moves to america and now you’re so back… alt universe nordiques stay only canadian team to win in the 21st century is the other french canadian team/current avs roster in quebec is there anything interesting in that au for you?????
oh man there TOTALLY isssssss bc . i dont know if you all know this but. patrick roy our good friend / bitter enemy GREW UP A NORDIQUES FAN... i imagine some of the good vibes of getting sent to your childhood team might offset potential Curse-Laying ability (or it might confine them to being the only canadian team allowed to win cups)
#asks#i admit though i only know the basics of the nordiques whole moving thing (mostly financial troubles from being Too Small A Market iirc)#(that and pure francophone -- where the habs had not only a winning history but also at least some english contingent)#although there is an inchresting vibe in like. a european who doesn't really speak english before he's drafted#getting drafted by qc and only having to learn french#and staying a nordiques lifer on purpose because Another Language? No Thanks
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on European Stocks
Historically, certain European stocks and sectors have flourished during periods of interest rate cuts, particularly when central banks ease monetary policy without the backdrop of a recession. These cycles, often initiated to stimulate growth and manage inflation, have proven advantageous for equities, especially in sectors that are sensitive to lower borrowing costs. Globally, central banks,…
#cyclical sectors#ECB#economic growth#Euro Stoxx 600#European stocks#financial markets#interest rate cuts#market performance#sectors#top-performing stocks
0 notes
Text
Europe Aircraft Leasing Market: Rapid Development and Value Trends Forecast (2024-2032)

The Europe Aircraft Leasing Market is on a trajectory of rapid development, driven by evolving value trends and a robust aviation sector. As European airlines and operators navigate the complexities of fleet management, leasing has emerged as a strategic solution to meet both current and future needs.
Europe Aircraft Leasing Market showcases the following key aspects:
Fleet Expansion and Modernization: European airlines are increasingly turning to leasing to expand and modernize their fleets. This approach allows them to quickly integrate new aircraft models that enhance operational efficiency and comply with environmental regulations.
Economic Uncertainty and Flexibility: Leasing provides airlines with greater financial flexibility amid economic uncertainties. It allows operators to manage capital expenditure more effectively and adjust their fleet size according to market demand.
Technological Advancements: The adoption of advanced technologies in leased aircraft supports better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. European airlines benefit from these innovations without the long-term financial commitment of owning the aircraft.
Regulatory Pressure: Europe’s stringent environmental regulations drive the demand for modern, eco-friendly aircraft. Leasing offers a practical solution for airlines to meet these requirements while minimizing financial risk.
Geographical Distribution: Key markets in Europe, such as the UK, Germany, and France, are at the forefront of the leasing trend. Their well-developed aviation sectors and strategic positions contribute to the overall growth of the market.
The forecast for the Europe Aircraft Leasing Market is characterized by robust growth and ongoing development. As airlines continue to seek flexible and cost-effective solutions, leasing will remain a vital component of the region’s aviation landscape.
About US
At Market Research Future (MRFR), we enable our customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through our Cooked Research Report (CRR), Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR), Raw Research Reports (3R), Continuous-Feed Research (CFR), and Market Research & Consulting Services. MRFR team have supreme objective to provide the optimum quality market research and intelligence services to our clients. Our market research studies by products, services, technologies, applications, end users, and market players for global, regional, and country level market segments, enable our clients to see more, know more, and do more, which help to answer all their most important questions. To stay updated with technology and work process of the industry, MRFR often plans & conducts meet with the industry experts and industrial visits for its research analyst members.
Contact us:
Market Research Future (part of Wants tats Research and Media Private Limited),
99 Hudson Street,5Th Floor, New York, New York 10013, United States of America
Sales: +1 628 258 0071 (US) +44 2035 002 764 (UK)
Email: [email protected]
#The Europe Aircraft Leasing Market is on a trajectory of rapid development#driven by evolving value trends and a robust aviation sector. As European airlines and operators navigate the complexities of fleet managem#leasing has emerged as a strategic solution to meet both current and future needs.#Europe Aircraft Leasing Market showcases the following key aspects:#•#Fleet Expansion and Modernization: European airlines are increasingly turning to leasing to expand and modernize their fleets. This approac#Economic Uncertainty and Flexibility: Leasing provides airlines with greater financial flexibility amid economic uncertainties. It allows o#Technological Advancements: The adoption of advanced technologies in leased aircraft supports better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. E#Regulatory Pressure: Europe’s stringent environmental regulations drive the demand for modern#eco-friendly aircraft. Leasing offers a practical solution for airlines to meet these requirements while minimizing financial risk.#Geographical Distribution: Key markets in Europe#such as the UK#Germany#and France#are at the forefront of the leasing trend. Their well-developed aviation sectors and strategic positions contribute to the overall growth o#The forecast for the Europe Aircraft Leasing Market is characterized by robust growth and ongoing development. As airlines continue to seek#leasing will remain a vital component of the region’s aviation landscape.#About US#At Market Research Future (MRFR)#we enable our customers to unravel the complexity of various industries through our Cooked Research Report (CRR)#Half-Cooked Research Reports (HCRR)#Raw Research Reports (3R)#Continuous-Feed Research (CFR)#and Market Research & Consulting Services. MRFR team have supreme objective to provide the optimum quality market research and intelligence#services#technologies#applications#end users#and market players for global#regional
0 notes
Text
🌐 Join the conversation on the growing disparity between the cost of living and salaries! 📊 Our latest video explores the economic, social, and individual impacts, offering concrete measures for a more equitable future.
youtube
#costofliving#salarydisparity#globaleconomy#Cost of living#Salary disparity#Economic challenges#Globalization impact#Social inequality#European economy#Financial stability#Poverty in Europe#Job market trends#Technological advancements#Economic policies#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Capital: Overcoming the Challenge of Limited Access in the Black Sea Region by Eastern European Institute for Trade
by Eastern European Institute for Trade

Limited access to capital is a significant impediment to the growth of businesses and economies in the Black Sea region. The availability of financial resources is crucial for the establishment, expansion, and modernization of enterprises, as well as for the development of new industries and the fostering of innovation (Havrylchyk, 2018). This article examines the factors contributing to the challenge of limited access to capital in the Black Sea region, and explores potential strategies for overcoming this obstacle, drawing on lessons from regional and international experiences (Beck et al., 2014; Kutan & Vukšić, 2017).
The banking sector is the primary source of financing for businesses in the Black Sea region, but it often falls short in meeting their capital needs. High levels of non-performing loans, underdeveloped capital markets, and inadequate financial infrastructure are among the factors constraining the capacity of banks to extend credit to the private sector (Havrylchyk, 2018). Additionally, risk aversion and conservative lending practices, partly driven by the legacy of past financial crises, further limit the availability of bank financing for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (Beck et al., 2014).
Limited access to capital in the Black Sea region can also be attributed to the underdeveloped nature of alternative financing channels. Venture capital and private equity markets, which play a critical role in financing innovative and high-growth enterprises, are relatively nascent in the region (Kutan & Vukšić, 2017). Similarly, the region’s capital markets, including stock and bond markets, are often characterized by low levels of liquidity, limited investor base, and a lack of sophisticated financial instruments, which hampers their ability to channel resources to the private sector (Havrylchyk, 2018).
To address the challenge of limited access to capital in the Black Sea region, a multipronged approach is required. First, the banking sector needs to be strengthened through reforms aimed at improving its financial health, risk management practices, and regulatory environment (Beck et al., 2014). These reforms should include measures to reduce non-performing loans, enhance supervisory frameworks, and promote competition and innovation within the sector (Havrylchyk, 2018).
Second, alternative financing channels should be developed and diversified to provide businesses with a wider range of funding options. This includes fostering the growth of venture capital and private equity markets, as well as encouraging the development of innovative financing instruments, such as crowdfunding and peer-to-peer lending platforms (Kutan & Vukšić, 2017). Additionally, efforts should be made to deepen and integrate the region’s capital markets, with a view to enhancing their efficiency and attractiveness to both domestic and foreign investors (Havrylchyk, 2018).
Finally, regional cooperation and integration can play a pivotal role in unlocking capital for businesses in the Black Sea region. Initiatives such as the European Union’s (EU) investment programs, and the involvement of international financial institutions, such as the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and the International Finance Corporation (IFC), can facilitate access to capital by providing financing, technical assistance, and capacity building support (Beck et al., 2014).
In conclusion, overcoming the challenge of limited access to capital is crucial for the growth and competitiveness of businesses in the Black Sea region. By implementing targeted reforms, diversifying financing channels, and promoting regional cooperation, the region can unlock capital and unleash its full economic potential.
References:
Beck, T., Demirgüç-Kunt, A., & Singer, D. (2014). Is Small Beautiful? Financial Structure, Size and Access to Finance. World Development, 52, 19–33.
Havrylchyk, O. (2018). Foreign Banks, Financial Crises, and Macroeconomic Fluctuations in the Black Sea Region. Comparative Economic Studies, 60(3), 386–410.
Kutan, A. M., & Vukšić, G. (2017). Financial Integration, Housing Markets, and Economic Policy Uncertainty in the Black Sea Region. Comparative Economic Studies, 59(4), 491–517.
European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD). (2021). EBRD in the Black Sea Region. Sourced from https://www.ebrd.com/where-we-are/black-sea.html
International Finance Corporation (IFC). (2021). IFC in Europe and Central Asia. Sourced from https://www.ifc.org/wps/wcm/connect/region__ext_content/ifc_external_corporate_site/europe+and+central+asia
Read more at European Institute for Trade.
#Unlocking capital#Black Sea region#Access to finance#Banking sector#Venture capital#Private equity#Capital markets#Financial infrastructure#Non-performing loans#Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)#Financial reforms#Alternative financing channels#Regional cooperation#European Union investment programs#EEIT#Eastern European Institute for Trade
1 note
·
View note
Text
Very interesting + concise article, pertinent with how much I've seen the joke about that "sadness in his eyes you only see in east european gay porn". Warning for pretty much everything you can expect.
Describing the wave of Eastern European gay pornography that flooded the US market following the dissolution of the USSR, Jones said: “They were products of a crude imperialist enterprise: cheap and nasty looking, with an atmosphere of coercion and cultural misunderstanding pervading them. Customers adored these videos, and expressed their breathless admiration whenever given the chance”
It gets pretty rough from here onward.
The Fall… opens with a short clip of a young man in profile, undressing. He looks uncomfortable, alternating between staring forward and glancing in the direction of the camera, his eyes showing a mix of discomfort and contempt. Jones’ voiceover states: “even in an unlikely place, it is possible to find traces of recent history” followed by b-roll taken from the aforementioned porn films including maps of the former USSR, market scenes, beggars and street footage. Their purpose in the aforementioned films appears to be part exoticism and part poverty fetishism, attempting to show the former glory of the Eastern nations as an emphasis on their subsequent fall. They’re an essential part of the set-up, speaking directly to what made this genre of pornography appealing to a western, primarily American, market. It’s easy to comprehend the mixture of exploitation and exoticism that made these videos popular in the US, but Jones goes further, aiming to establish a firm link between the booming Western economy and a more global, less visible form of exploitation.
The latter half of the film compounds the atmosphere of coercion, focusing specifically on the casting and screen tests of performers. The voice from behind the camera probes the subject on their sexual preferences, their motivations for being filmed: “I’m doing it for the money” “That’s a very good reason” Western audiences were turned on by the idea that the performers were under some form of duress—the ostensibly straight man either consuming their sexuality through the guise of pornography, or in the case of several scenes, the performer showing visible discomfort at either the sex or the presence of the camera. The films are low budget, low production value and low brow—by intention, rather than necessity. Jones speculates that the developing Eastern European sex industry, with the influx of Western producers and a Western market in mind, could be seen as an indicator of fertile ground for fascist ideologies—an aspersion confirmed by the global rise of far-right ideologies in tandem with the economic pressure of late-stage capitalism, a point at which more contemporary comparisons can be made.
The brief conclusion on the contemporary form of this exploitation aesthetic is also noteworthy:
In the same way that the fall of communism was exploited by the West, the financial and social insecurity of a generation living in recession, under permanent austerity, is exploited now. The aesthetics utilised in Jones’ film are still broadly present, albeit perhaps in a slightly altered form, now accompanied by a new visual language born from a culture numb to being told to “like, comment, share and subscribe”.
656 notes
·
View notes
Text
in addition to being prone to an obvious naturalistic fallacy, the oft-repeated claim that various supplements / herbs / botanicals are being somehow suppressed by pharmaceutical interests seeking to protect their own profits ('they would rather sell you a pill') belies a clear misunderstanding of the relationship between 'industrial' pharmacology and plant matter. bioprospecting, the search for plants and molecular components of plants that can be developed into commercial products, has been one of the economic motivations and rationalisations for european colonialism and imperialism since the so-called 'age of exploration'. state-funded bioprospectors specifically sought 'exotic' plants that could be imported to europe and sold as food or materia medica—often both, as in the cases of coffee or chocolate—or, even better, cultivated in 'economic' botanical gardens attached to universities, medical schools, or royal palaces and scientific institutions.
this fundamental attitude toward the knowledge systems and medical practices of colonised people—the position, characterising eg much 'ethnobotany', that such knowledge is a resource for imperialist powers and pharmaceutical manufacturers to mine and profit from—is not some kind of bygone historical relic. for example, since the 1880s companies including pfizer, bristol-myers squibb, and unilever have sought to create pharmaceuticals from african medicinal plants, such as strophanthus, cryptolepis, and grains of paradise. in india, state-created databases of valuable 'traditional' medicines have appeared partly in response to a revival of bioprospecting since the 1980s, in an increasingly bureaucratised form characterised by profit-sharing agreements between scientists and local communities that has nonetheless been referred to as "biocapitalism". a 1990 paper published in the proceedings of the novartis foundation symposium (then the ciba foundation symposium) spelled out this form of epistemic colonialism quite bluntly:
Ethnobotany, ethnomedicine, folk medicine and traditional medicine can provide information that is useful as a 'pre-screen' to select plants for experimental pharmacological studies.
there is no inherent oppositional relationship between pharmaceutical industry and 'natural' or plant-based cures. there are of course plenty of examples of bioprospecting that failed to translate into consumer markets: ginseng, introduced to europe in the 17th century through the mercantile system and the east india company, found only limited success in european pharmacology. and there are cases in which knowledge with potential market value has actually been suppressed for other reasons: the peacock flower, used as an abortifacient in the west indies, was 'discovered' by colonial bioprospectors in the 18th century; the plant itself moved easily to europe, but knowledge of its use in reproductive medicine became the subject of a "culturally cultivated ignorance," resulting from a combination of funding priorities, national policies, colonial trade patterns, gender politics, and the functioning of scientific institutions. this form of knowledge suppression was never the result of a conflict wherein bioprospectors or pharmacists viewed the peacock flower as a threat to their own profits; on the contrary, they essentially sacrificed potential financial benefits as a result of the political and social factors that made abortifacient knowledge 'unknowable' in certain state and commercial contexts.
exploitation of plant matter in pharmacology is not a frictionless or infallible process. but the sort of conspiratorial thinking that attempts to position plant therapeutics and 'big pharma' as oppositional or competitive forces is an ahistorical and opportunistic example of appealing to nominally anti-capitalist rhetoric without any deeper understanding of the actual mechanisms of capitalism and colonialism at play. this is of course true whether or not the person making such claims has any personal financial stake in them, though it is of course also true that, often, they do hold such stakes.
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Year
1. Belgium approves four-day week and gives employees the right to ignore their bosses after work

Workers in Belgium will soon be able to choose a four-day week under a series of labour market reforms announced on Tuesday.
The reform package agreed by the country's multi-party coalition government will also give workers the right to turn off work devices and ignore work-related messages after hours without fear of reprisal.
"We have experienced two difficult years. With this agreement, we set a beacon for an economy that is more innovative, sustainable and digital. The aim is to be able to make people and businesses stronger," Belgian prime minister Alexander de Croo told a press conference announcing the reform package.
2. Spain makes it a crime for pro-lifers to harass people outside abortion clinics

Spain has criminalized the harassment or intimidation of women going for an abortion under new legislation approved on Wednesday by the Senate. The move, which involved changes to the penal code, means anti-abortion activists who try to convince women not to terminate their pregnancies could face up to a year behind bars.
3. House passes bill to federally decriminalize marijuana

The House has voted with a slim bipartisan majority to federally decriminalize marijuana. The vote was 220 to 204.
The bill, sponsored by Democratic Rep. Jerry Nadler of New York, will prevent federal agencies from denying federal workers security clearances for cannabis use, and will allow the Veterans’ Administration to recommend medical marijuana to veterans living with posttraumatic stress disorder.
The bill also expunges the record of people convicted of non-violent cannabis offenses, which House Majority Leader Steny Hoyer said, “can haunt people of color and impact the trajectory of their lives and career indefinitely.”
4. France makes birth control free for all women under 25

The scheme, which could benefit three million women, covers the pill, IUDs, contraceptive patches and other methods composed of steroid hormones.
Contraception for minors was already free in France. Several European countries, including Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands and Norway, make contraception free for teens.
5. The 1st fully hydrogen-powered passenger train service is now running in Germany. The only emissions are steam & condensed water.

Five of the trains started running in August. Another nine will be added in the coming months to replace 15 diesel trains on the regional route. Alstom says the Coradia iLint has a range of 1,000 kilometers, meaning that it can run all day on the line using a single tank of hydrogen. A hydrogen filling station has been set up on the route between Cuxhaven, Bremerhaven, Bremervörde and Buxtehude.
6. Princeton will cover all tuition costs for most families making under $100,000 a year, after getting rid of student loans

In September, the New Jersey Ivy League school announced it would be expanding its financial aid program to offer free tuition, including room and board, for most families whose annual income is under $100,000 a year. Previously, the same benefit was offered to families making under $65,000 a year. This new income limit will take effect for all undergraduates starting in the fall of 2023.
Princeton was also the first school in the US to eliminate student loans from its financial aid packages.
7. Humpback whales no longer listed as endangered after major recovery

Humpback whales will be removed from Australia's threatened-species list, after the government's independent scientific panel on threatened species deemed the mammals had made a major recovery. Humpback whales will no longer be considered an endangered or vulnerable species.
Climate change and fishing still pose threats to their long-term health.
Some other uplifting news from last year:
A Cancer Trial’s Unexpected Result: Remission in Every Patient
California 100 percent powered by renewables for first time
Israel formally bans LGBTQ conversion therapy
Tokyo Passes Law to Recognize Same-Sex Partnerships
First 100,000 KG Removed From the Great Pacific Garbage Patch
As we ring in the New Year let’s remember to focus on the good news. May this be a year of even more kindness and generosity. Wishing everyone a happy and healthy 2023!
Thank you for following and supporting this g this newsletter
Buy me a coffee ❤️
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
1d8 "Free" Fantasy RPGs To Replace 5e At Your Table
D&D 5e sure is a roleplaying game, and it's one that I have enjoyed a lot. However, that doesn't mean that I'd recommend it automatically for other people. This has many reasons, which I won't elaborate here. It has also shaped the perception of TTRPGs significantly thanks to its market dominance, and not in a good way.
5e has a reputation for being an expensive, complex game, and 5e players fear that other RPGs might just be the same. That it's too much of a hassle and too much of a financial burden to switch systems.
So, to help 5e players pick out a different system, I've made this handy 1d8 rolling table to help them pick a fantasy TTRPG with a combat component that they can try instead!

Let's now go through these eight nine RPGs and see what's up with them, right below the "Keep reading" section!
I'll be listing some metrics like the page count for the rulebook(s), the core resolution mechanic, how complex the game is in terms of character creation & combat, and how well-supported the game is by their publisher and the community-at-large.
1. Cairn
Author: Yochai Gal
Release Year: 2020
Cost: Free PDF, printed copies cost between $3 to $10 depending on the print quality.
Page Count: 24
Website: https://cairnrpg.com/
Resolution Mechanic: 1d20 Roll Under system for ability checks/saving throws, attacks hit automatically, "fiction-first".
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Random character creation, class-less and level-less, advancement based on "Scars" (suffering damage that reduces your HP exactly to 0)
Setting: Implied. Low-magic European-style fantasy; mysterious woodlands.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Hit Protection and Ability damage instead of HP, Slot-Based Inventory.
Degree of Support: Very high. Available in fifteen languages (e.g. Spanish, Russian, Chinese, and German); full rules text is under CC-BY-SA 4.0; multiple published third-party adventures & supplements available; some official bonus material (e.g. bestiary, magic items/relics, and spells) is available for free on the website.
Addendum: An expanded 2nd Edition is currently on Kickstarter (ends April 26th 2024); Cairn is legitimately easy to learn, however the Hit Protection system and the connected Scars system is a very different abstraction to health and advancement compared to 5e.
2. Cloud Empress
Author: worlds by watt
Release Year: 2023
Cost: Free PDF of the rulebook and the creator-written sample adventure "Last Voyage of the Bean Barge", $20 for the print edition of the rulebook, $12 for PDF supplements, $25 for print + PDF supplements; free solo rules also available as PDF only.
Page Count: 60
Website: https://cloudempress.com/
Resolution Mechanic: d100 Roll Under system for stat checks/saving throws, critical successes or failures on doubles (11, 22, 33, etc.), 5e-style advantage/disadvantage, attacks generally hit automatically.
Action Economy: Two actions per round with no free movement.
Characters: Semi-random character creation, four classes ("jobs"), no rules for character advancement in the ruleset.
Setting: Specific. "Ecological science fantasy" heavily inspired by Hayao Miyazaki's "Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind"; costly magic, giant insects, dangerous mushrooms; only human player characters.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Damage points culminate in Wounds; Wounds and Stress as ways to track your character's physical and mental state; slot-based inventory system.
Degree of Support: Low-ish. Several official supplements exist, however third-party material is very sparse. May improve due to the recent establishment of a Cloud Empress Creators Fund, has a simple 3rd party license system.
Addendum: A supplement, "Cloud Empress: Life & Death" is currently on Kickstarter (ends April 26th 2024, yes, the same day as Cairn 2e) and as a disclaimer I even backed that current Kickstarter; Cloud Empress is built on the engine of the sci-fi horror RPG "Mothership"; clearly built for one-shots and short campaigns; has a wonderful resting system that encourages roleplay between players.
3. Iron Halberd
Author: level2janitor
Release Year: 2023
Cost: Free PDF of the rules; no print option available.
Page Count: 60
Website: https://level2janitor.itch.io/iron-halberd
Resolution Mechanic: 1d20 + Bonus Roll Over system against difficulty or armor rating, however most non-combat-related actions follow a fiction first approach without dice rolls.
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Semi-random character creation, class-less but there are four different "gear kits" that nudge your character towards certain archetypes, levelling up with XP.
Setting: Essentially non-existant. General European fantasy with magic, gods may or may not exist/shape the world, various fantastic ancestries included.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Includes rules for building strongholds and maintaining warbands; slot-based inventory with a durability mechanic.
Degree of Support: None. The game is intended to be relatively compatible with other OSR content and the creator suggests using adventures made for the D&D retroclone Old-School Essentials if you wanna use pre-published ones. An official introductory adventure, "Sea-Spray Bay", is apparently in the works. No 3rd party license available, as far as I know.
Addendum: One thing about Iron Halberd I like especially is how it uses random tables for generating equipment. Most of the equipment is listed in a numerical order by category, and the various gear kits include references on different rolling formulas for those equipment categories. For example someone taking the "soldier's kit" rolls twice on the d20 Weapons table and takes their preferred pick, while someone taking the "sage's kit" only rolls a d4 on that table.
4. Mausritter
Author: Isaac Williams
Release Year: 2020
Cost: Free PDF of the ruleset available; box set with the rules and several goodies including an adventure costs $55; additional box set + PDFs containing eleven official adventures costs $55 (or $20 digital-only).
Page Count: 48
Website: https://mausritter.com/
Resolution Mechanic: 1d20 Roll Under system, 5e-style advantage/disadvantage, attacks always hit.
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Random character creation, class-less, levelling up with XP.
Setting: Vaguely specific. You play as mice and everything is related to mouse-size; cats are the equivalents of devils or dragons; humans exist as a setting background but may or may not be present in a campaign.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Includes rules for recruiting warbands; slot-based inventory with a durability mechanic.
Degree of Support: Very high. Several official supplements exist, as well as loads of content, be it adventures or supplements, made by other creators. Available in seven languages (all of them however are European). Has a simple 3rd party license system.
Addendum: Mausritter uses the phrase "adventure site" instead of dungeons. On the website a free adventure site generator is available, as is a digital tool that can be used to generate your own item cards for the slot-based inventory system.
5. Maze Rats
Author: Ben Milton
Release Year: 2017
Cost: $4.99 for the PDF, no print option regularly available.
Page Count: 32
Website: https://questingbeast.substack.com/
Resolution Mechanic: 2d6 + Bonus Roll Over system; advantage system that uses 3d6 drop the lowest + Bonus.
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Semi-random character creation, class-less but instead there are character features (e.g. spell slots or attack bonuses), levelling up with XP.
Setting: Essentially non-existant. Magic is very irregular (s. the section below), but otherwise it implies a vaguely European fantasy setting.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Spells are randomly generated each adventuring day and spell effects are negotiated between the GM and the spellcasting player; includes several fantastic d66 tables that can be used to randomly generate worlds.
Degree of Support: Decent. The rule text is licensed under CC BY 4.0 and unofficial translations are available. Some third-party content has been made specifically for the game.
Addendum: The only purchase-only game on this list. However "unofficial" distribution of the PDF is very common. Also this is the oldest game on the list. Ben "Questing Beast" Milton is a prolific OSR blogger and runs a YouTube channel on the OSR. Great dude.
6. Sherwood - A Game of Outlaws & Arcana
Author: Richard Ruane
Release Year: 2022
Cost: Free quickstart PDF titled "Sherwood - A Quickstart of Outlaws" available; digital rulebook costs $7.50 and the print edition (including PDF) costs $15.
Page Count: 25 (Quickstart), 32 (Rulebook)
Website: https://www.r-rook.studio/
Resolution Mechanic: 2d6 + Bonus Roll Over system for skill checks (including attacks), 2d6 Roll Under system for saving throws; advantage & disadvantage system that involves rolling 3d6 and using the higher/lower of the two results; almost all rolls are player-facing
Action Economy: "Conversational", assumption of movement + action.
Characters: Largely choice-based character creation. Combine two (of six) background abilities with the benefits of seven different careers. Big focus on interpersonal relationships during character creation. Limited character advancement takes place during downtime.
Setting: Specific. Takes place in a fantastical version of 13th century England, with fey and magic coexisting with outlaws and crusaders.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: The group of outlaws possesses two shared resources (Resources and Legend) that can be spent to gain certain benefits; spellcasting is divided into two categories: arcane talents and sorcerous rites, with the former being immediate and the later taking significant time; slot-based inventory.
Degree of Support: None. No further publications exist for the game and while it is published under the CC-BY 4.0 license, no third-party content exists as far as I know. It does include a guide on how to convert D&D and Troika (N)PCs into Sherwood characters, as well as three adventure seeds (one in the Quickstart, two in the rules), which is at least something.
Addendum: Might just be the game on this list that encourages the most roleplaying; the character sheet is sadly very provisional-feeling and the Quickstart feels outdated compared to the finalized rulebook.
7. The Electrum Archive
Author: Emiel Boven
Release Year: 2022
Cost: Free Rules PDF available, zines cost $12 as digital PDFs or $24 as print + PDF combos; the first zine contains the entire contents of the Free Rules PDF
Page Count: 26 (Free Rules), 72 (Issue 01)
Website: https://www.electrumarchive.com/
Resolution Mechanic: 1d10 Roll Under system, attacks always hit.
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Largely choice-based; three archetypes roughly corresponding to fighters/rangers (Vagabonds), rogues (Fixers), and spellcasters (Warlocks); player characters are presumed to be human; levelling up with XP.
Setting: Specific. Mechanics heavily tie into the lore; humanity has abundant access to minerals but requires a rare substance known as Ink to operate certain pieces of tech (like guns) and cast spells but cannot produce Ink themselves; spirits of various sorts can be foes, targets of worship, or sources of power.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Uses a spellcasting system for the Warlock archetype that's heavily based on the one used in Maze Rats, as in it uses randomly-generated spells whose effects are negotiated between the player and the GM; slot-based inventory with a durability mechanic.
Degree of Support: Minimal. The game consists out of the free rules and (soon) two zines; a third party license exists but content produced under it is very rare.
Addendum: I need to disclaim that I recently backed the Kickstarter campaign for the second zine for this game; the free rules feature wrong page numbers in its table of contents which is unfortunate; The Electrum Archive uses incredibly simple stats for NPCs which makes creating new ones based on other games rather simple.
8. Shadowdark RPG
Author: Kelsey Dionne
Release Year: 2023
Cost: Free player and game master quickstarts exist as PDFs and are available in print for $19, the core rules cost $28 in PDF form and $57 in a print + PDF bundle
Page Count: 68 (Player Quickstart Guide), 68 (Game Master Quickstart Guide), 332 (Core Rules)
Website: https://www.thearcanelibrary.com/
Resolution Mechanic: 1d20 + Bonus Roll Over system, 5e-style advantage/disadvantage, natural 1s are critical failures and natural 20s are critical successes.
Action Economy: Movement + one action per round.
Characters: Largely choice-based; players have a fantasy ancestry and a class; levelling up with XP; class progression largely random.
Setting: Vague. General (dark) western fantasy conventions apply; alignment is a force in this universe and a sample pantheon is provided; the most potent enemies in the rules are named individuals that fit classic TTRPG monster types; illustrations and lore snippets have recurring motifs.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: The key mechanic of Shadowdark is how the game handles light, namely that light sources are tracked in real time (i.e. a normal torch lasts 1 hour), which increases tension; slot-based inventory; has a 0th-level character creation option using an eliminationist "Gauntlet".
Degree of Support: Fantastic. Several official supplements and offically sanctioned digital tools exist; lots of third-party content available under a generous third-party license.
Addendum: Definitely the most similar game to 5e on this list besides the next entry; very robust mechanically and the Core Rules features extensive lists of magic items, monsters, and spells; also for early play giving your players only access to the quickstart is a totally valid choice; and finally, before Dionne made Shadowdark, she made 5e adventures for years and it shows (affectionate).
9. Pathfinder
Authors: Logan Bonner, Jason Bulmahn, Stephen Radney-MacFarland, Mark Seifter
Release Year: 2019 (initial release), 2023 (remaster)
Cost: Free and comprehensive SRD available via the platform Archives of Nethys, free "Pathfinder Primer" abridged rulebook available via the Pathfinder Nexus (powered by Demiplane), Core books are priced $20 for PDFs and $30/$60 for print as a softcover/hardcover; a Beginner Box set with shortened soft-cover rules costs $45
Page Count: 464 (Player Core), 336 (GM Core), 376 (Monster Core), 160 (Combined Beginner Box Softcovers)
Website: https://paizo.com/pathfinder
Resolution Mechanic: 1d20 + Bonus Roll Over system, 5e-style advantage/disadvantage, four degrees of success based on result compared to target number.
Action Economy: Three action points per round; various actions may require more than one point; every character can use one reaction per round of combat.
Characters: Choice-based; players first pick an ancestry and a background and a class (the ABCs) and then tend to have meaningful choices after each level-up; levelling up with XP.
Setting: Important. Golarion, the game's setting, is a world that has been long in development and it shows; powerful magic and influential gods; very clear notions of what the societies of the various peoples of the world are like and how they should behave.
Other Noteworthy Mechanics: Balance between character classes and reliable combat challenge calculations are an important design goal; weight-based inventory system; archetype system for "multiclassing".
Degree of Support: Fantastic. Loads of content gets regularly produced by the game's publisher Paizo; the Pathfinder Infinite program (similar to D&D's Dungeon Master's Guild) provides lots of lore-compliant third-party content; uses the ORC third-party license for content produced outside of the Pathfinder Infinite program. Translations into other languages available but Paizo does not provide a comprehensive list of available languages (only German and French confirmed after brief personal research).
Addendum: The most popular and commercially successful of the listed games; but also by far the most complicated, though it is easier to GM for specificallty than 5e; also I dislike how certain feats create situations where fairly mundane actions get mechanics through these feats instead of being things you can generally do; anyway the reason why it's a 9 on a 1d8 table is because if you wanted to try out Pathfinder 2e you already would have and because while Paizo is better than WotC it's still a flawed big company.
...
So this was an exhausting little project. I hope you found this helpful and I hope you give at least one of these games a shot! A follow-up to this post is not out of the cards, but I don't plan on one.
Before we go, have this poll about which of these systems you're most looking forward to try! Shame it can only be open for one week...
#thehomelybrewster#dnd 5e#dnd#indie ttrpg#tabletop roleplaying#ttrpg community#Cairn#Cloud Empress#Iron Halberd#Mausritter#Maze Rats#Dungeons and Dragons#Sherwood#The Electrum Archive#shadowdark#pathfinder
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
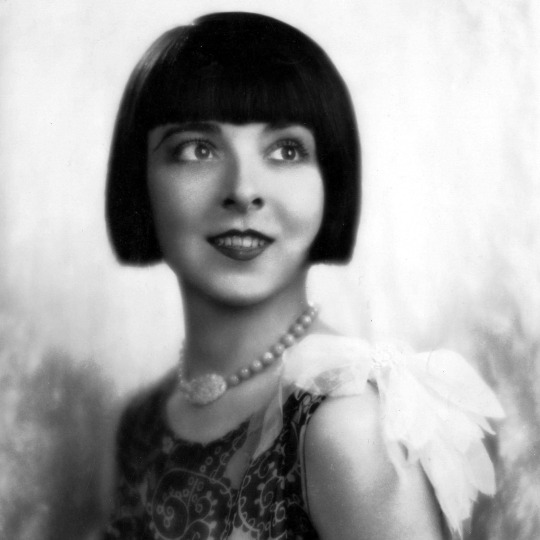


Propaganda
Colleen Moore (Flaming Youth, Ella Cinders)— One of the highest paid, most in-demand actresses of the silent film era, Colleen Moore defied genre and kept herself one step ahead of the competition (and although Moore was the OG flapper, her longtime rival Clara Bow would become more famous for the image) as well as invested her earnings to ensure her financial security after she retired. She even wrote a book all about investing in the stock market! Moore also nurtured a passion for dollhouses throughout her life and helped design and curate The Colleen Moore Dollhouse, which has been a featured exhibit at the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago since the early 1950s.
Lilian Harvey (Die Drei von der Tankstelle, Der Kongreß Tanzt, Glückskinder)— Lilian Harvey was one of the most popular German film stars of her time, appearing alongside frequent co-star Willy Fritsch like a European version of Ginger Rogers and Fred Astaire. She had it all: she could act, she could dance, she could sing, she was hot, and she wasn't afraid to stick it to the Nazis. During the 1930s, she remained in contact with her Jewish friends and colleagues, which earned her the scrutiny of the Gestapo. When choreographer Jens Keith was arrested for having a sexual relationship with another man, Lilian posted his bail, allowing him to escape to France. She was eventually forced to flee Germany herself, and her film career never recovered. She is perhaps best known to American filmgoers from her brief mention in "Inglourious Basterds," when Joseph Goebbels insists that her name not be mentioned in his presence.
This is round 1 of the tournament. All other polls in this bracket can be found here. Please reblog with further support of your beloved hot sexy vintage woman.
[additional propaganda submitted under the cut]
Lilian Harvey:

Colleen Moore:
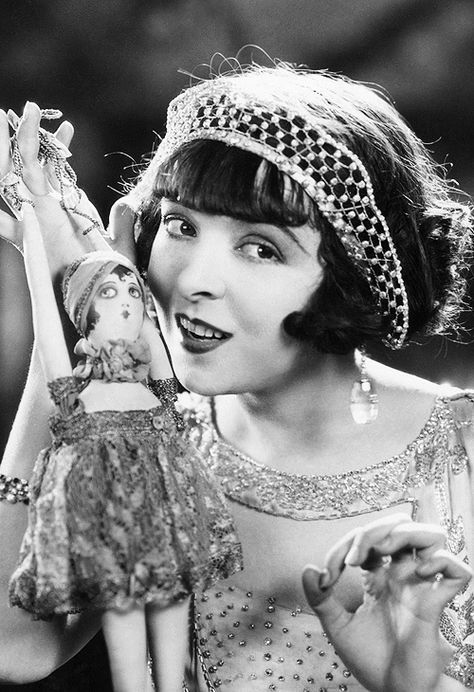


Colleen is charming and funny, she was one of the starlets to popularize the iconic 1920s bob!
She's like the deep cut version of Louise Brooks, with majority silent films, and a large percentage of them lost-- BUT 'Why Be Good?' is such a fun movie and she wears really cute dresses and has all the best parts of Pre-Code leading lady fun!

92 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tools of the trade
Came home an hour ago from a reception I literally fled (busy week in this respect, unfortunately). And I kept being internally nagged during the short taxi ride, by what is probably at least this season's Anon. Landed in @bat-cat-reader's inbox with regard to Marple's most recent innuendo:
I had to know more about this, since I had no idea such deep diving tools were now available for pretty much everyone. Here's the gist of how it works, in pics and a quick review:
What Snoopreport promises its subscribers is to basically keep them posted on the targeted accounts' online behavior patterns...

... without the need to publicly follow them on Insta (sounds familiar?)...
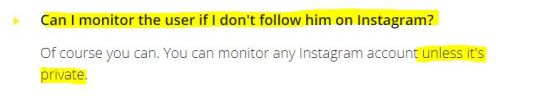
...leaving no trace (zero accountability, because it uses only public data: this can be interpreted differently, in a different legal system/context, since several European countries, as I already discussed, have more protective legal provisions for a person's right to his/her own image)...
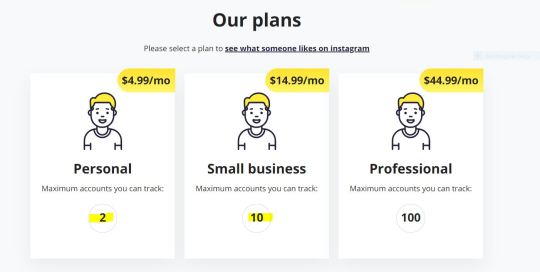
... at minimal costs (I suppose the most cost-effective, if we assume this is one of the used monitoring tools, would be the small business pack, allowing the super sleuth to track 10 different accounts, for peanuts):
A review of this product I have checked here (https://www.techuntold.com/snoopreport-review/) points out the obvious Achilles' heel of this app. Snoopreport obviously does not work for private accounts:

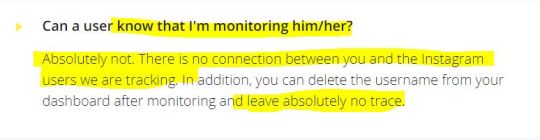
Which brings up a logical question: could the (in)famous 'resource' be S's private Insta account, in which case it would be very difficult for the sleuth to admit stalking it? Is it even technically possible to stalk a private Instagram account and remain unseen?
The answer to the latter is yes: other actors of this apparently very lucrative market, such as Glassagram (https://glassagram.com/), do not have Snoopreport's scruples and monitor even private accounts.
I think this is pretty self-explanatory and to be honest, it gave me the chills:
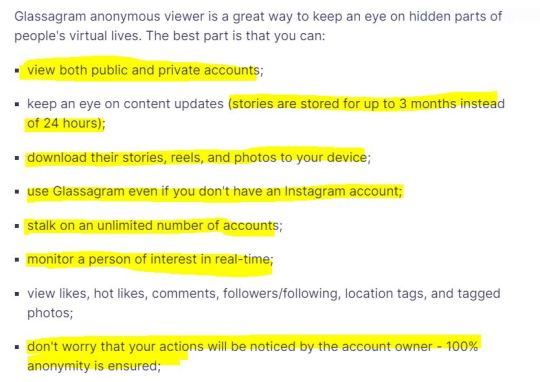
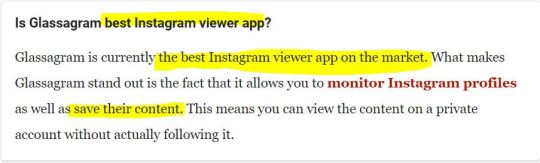
Serious reviews (https://www.techuntold.com/glassagram-review-spy-instagram/) are raving about this one, calling it the best app on the market, mainly because you can save all the snooped content on your own device:
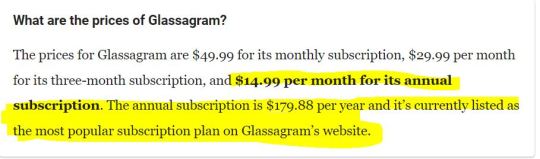
... and the price, for stalking (their own choice of vocabulary, not mine, for once) an unlimited number of accounts is reasonable:
Best of it? They've been around since 2017.
In a nutshell: is it legal? it would seem so, in the US, not so sure about the UK/EU. Is it moral? It's up to you to decide what to think of a firm which has no problem admitting to encouraging stalking (but hey, don't listen to the nutcase here, huh?) and uses completely different real-life situations (infidelity, kids' monitoring) to assert its legitimacy and utility.
What I mean by this very long and illustrative post is this: you do not need inside sources/information to have one day the idea of crossing what is obviously (at least in my book) a red line. You just have to be able (lots of free time), willing (asserting power over a very thirsty and not so digitally skilled audience) and voilà: a Super Sleuth is born.
It is one thing to analyze and speculate, based on open sources, to your heart's content. It is a different affair altogether to obsessively monitor someone, with so much detail and personal (& financial) investment, over a substantial period of time. I will die on this hill and you will never change my mind on this one.
Is the emperor naked? I wouldn't venture speculating. What I do know, is that this emperor is a very, very sad one.
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's election season in Eastern Europe, and for the Kremlin -- bogged down in Ukraine and desperately in need of allies -- the stakes are higher than ever.
Moldova is holding a presidential election and referendum on October 20 that could help secure the country's future in the EU. Romania has just banned a pro-Kremlin rabble-rouser from running in its November presidential election. And the pro-Kremlin, far-right Revival party in Bulgaria is expected to win a sizable presence in parliament after upcoming elections.
So what is the Kremlin -- and its populist regional allies -- pulling from its playbook to influence the votes?
Don't Be Too Fussy About Who You Work With
Plan A, according to Anton Shekhovtsov, a Ukrainian political scientist and expert on the far right, "was always to cooperate with mainstream forces" and then corrupt them to align with Russian foreign policy interests.
In some countries, Plan A has worked, with the Kremlin maintaining good relations with politicians such as Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban, Serbian President Aleksandar Vucic, and Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico.
"The problem for Moscow," Shekhovtsov said, "is that mainstream forces are less likely than the populists to cooperate with Russia, especially after 2014 (the annexation of Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula) and even more so after February 2022 (Russia's full-scale invasion of Ukraine)."
That has meant increasingly falling back on Plan B. "Russia has tended to align with far-right parties," said Mitchell Orenstein, professor of Russian and East European studies at the University of Pennsylvania, "but it will also form alliances with far-left parties and even support centrist parties to some extent."
Acting pragmatically and working with the political fringes can sometimes bear fruit. For years, Revival leader Kostadin Kostadinov operated in extremist circles, once referring to Romany people as "parasites" and venomously castigating migrants. But now his party, which has opposed democratic reforms and advocated for Bulgaria's withdrawal from NATO, is tipped to finish as high as second in the October 27 parliamentary elections.
Be Careful With The Bags Of Cash
Authorities in Moldova -- which has struggled to shake off Kremlin influence and still has more than 1,000 Russian troops stationed in the breakaway region of Transdniester -- recently announced they had uncovered a scheme led by Ilan Shor, a pro-Russian fugitive accused of the country's biggest-ever bank fraud, to buy votes and disseminate false information about the EU, with more than 130,000 Moldovans receiving over $15 million in Russian cash in September alone.
Such schemes, however, are rarely discovered -- and often very hard to prove, with financial support masked by shell companies and offshore accounts. And for the Kremlin, direct financing is a risky tactic. "They are being very, very cautious," Shekhovtsov said, as "we're talking about criminal activity here because there are no taxes [and parties are] taking money from a foreign power."
A Deluge Of Disinformation
For the Kremlin, a cheaper and more efficient way of boosting its allies in Eastern Europe is to flood the market with disinformation.
In addition to Russian state outlets such as RT, "Russia has websites in different European languages that promote messages beneficial to antiestablishment, populist forces," Shekhovtsov said. "This compensates for the populists' lack of media influence in their own countries."
U.S. tech giant Meta said on October 11 that it had deleted a network of accounts aimed at Russian-speaking Moldovans, which spread pro-Russian content and ran pages masquerading as independent news outlets.
Such operations are often part of larger networks, sometimes known as "mushroom sites," which are created in bulk and on the cheap and monetize the spread of disinformation.
Mobilize Through Fear
If you buy into the disinformation, migrants are coming for your jobs, the LGBT community is coming for your children's souls, foreign-funded NGOs are plotting to topple governments, and only Russia can restore peace to fascist Ukraine.
Igor Dodon, Moldova's Moscow-backed former president, has recently warned, without any evidence, of "LGBT quotas" in state institutions if the country's pro-EU President Maia Sandu wins reelection.
And in Bulgaria, Revival is pushing for a Russian-style foreign-agent law, which would target Western NGOs. "You will be next!" party leader Kostadinov told the America for Bulgaria Foundation, the country's largest foreign donor.
In socially conservative societies, with people disillusioned with democracy and reeling from economic hardship, much of it from the COVID-19 pandemic, such emotional narratives often strike a powerful chord.
By scaremongering about threats to traditional lifestyles and sovereignty, Russia is positioning itself -- not for the first time -- as the region's potential savior.
Tailor The Message
A key part of the Kremlin's strategy is localizing its messaging. "Russia looks for any possible commonality between their approach and the parties they're supporting," Orenstein said. "In one country, they might appeal to pan-Slavism; in another, to Orthodox religious connections; and in yet another, to anti-Ukrainian sentiment."
For example, in Bulgaria, pro-Russian parties play on Soviet nostalgia and well-established narratives of Russia as a liberator from Ottoman rule. In Hungary and Slovakia, pro-Kremlin parties exploit fears about migrants and the perception that the EU is undermining national sovereignty.
In Moldova, Irina Vlah, a pro-Moscow ex-governor, has said the country's large number of Romanian passport holders is evidence of a sinister Romanian plot to take over its smaller and poorer neighbor.
What Is The Kremlin's Endgame?
In the long term, the Kremlin's goal is to undermine the EU and NATO and pull countries in Eastern Europe back into Russia's orbit.
In the short term, it's all about Ukraine. For the Kremlin, that means blowing apart the fragile European consensus that Kyiv is deserving of military and economic support.
What the Kremlin cares about most, Orenstein says, is the "foreign policy orientation" of parties it supports in Eastern Europe -- in order to secure their backing on issues such as sanctions or the status of Crimea.
"You have some parties that [when] they began taking Russian support, they actually changed a lot of their foreign policy positions to orient them towards Russia," Orenstein said.
Crucially, though, Russia doesn't necessarily need explicit support to succeed. Sometimes sowing discord and polarizing populations can also chip away at the democracies and civil societies the Kremlin so desperately fears.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
📝 ENG Translation: European Tours in Times of Inflation

💬Kris Guštin shares some insight into the organization of Joker Out's recent See You Soon tour.
Article written by Gašper Završnik and published in Delo on 03.04.2024, English translation by a member of JOS and @kurooscoffee, Proofread by IG GBoleyn123.
Coping with rising costs and crowded markets is a challenge for the whole industry.
The concert part of the music industry in the post-Covid era is characterised by the expansion of live performance. The long-suppressed desire to tour, to perform in front of audiences in as many countries as possible, is only this year being fully realised.
We took a look at how European touring is going in the new inflation-driven reality. This was one of the themes of the conference part of this year's Ment¹. The European concert market is facing many challenges, such as the rising costs of touring, organising concerts and festivals, increasing musician fees and, as a consequence, more and more expensive tickets. There is also the question of how to manage the concentration and congestion of concert venues and balancing the availability of the most sought-after artists. An additional problem is finding opportunities for new performers in such a competitive environment.
¹Ment is a showcase festival and music conference that happens every year in Ljubljana.
We also enquired about the European tours of Slovenian performers, two groups that have a different style and a different audience, Joker Out and Širom².
²We translated only the part of the article that was relevant to Joker Out.
Joker Out recently returned from a European Tour. As Kris Guštin told us, it was organised by “a booking agent from the Wasserman agency and our manager. The booking agent arranges the concerts, the conditions, and the dates, and then the manager comes up with all the logistics, that is, he arranges the transport, the accommodation, puts together a team and everything that needs to be done.” He says that tours have always been a big financial investment for performers. “Especially for performers of our size, who have only just started breaking into the European market, where the ticket sales often don’t make up for the costs of transit, accommodation, and the salaries of the performers and the team. The inflation over the past few years is of course making that even harder, but the musical market has slowly adapted to that with higher ticket prices.”
Joker Out had 19 concerts in 18 cities in 12 countries this year, and they have three more coming up in Great Britain. The ticket price for each concert is determined based on the size of the venue, how in-demand the artist is, the local standard, and the overall concert-going culture in a certain place.
Joker Out are very happy with how many people came to their concerts. “The turnout differed across Europe. In the countries we’re strong in, like Finland and the Netherlands, we played for crowds from 1500 to 2000 people, and for countries we haven't played in a lot yet, like Germany and France, we performed for 500 to 1000 people. The venues were always nicely filled and the audience was excited.”
We asked Guštin what they base the length of the tour on. “The length of the tour is based on demand, territory strategy, and how busy the performer is. In our case, we decided for a month-long tour, in which we covered a lot of countries that we couldn’t do last year,” he added.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
yknow who i think the fandom needs to appreciate more? CHINA!
this is a multi millennia being has existed beyond other empires, kingdoms, governments, whatever the hell humans throw at him, is so severely under appreciated!! he’s a badass and never gets credit for all the shit he goes through!
i will never forgive Himaruya for reducing china to the lamest stereotypes possible. i know that’s the whole point of hetalia but china is marketed as one of the “main G8” but he’s treated like a total loser T-T it’s criminal that he’s so underrated in this fandom.
plus china ships besides RoChu are basically nonexistent. where’s my freaky freaks who wanna see america and china get it on? where’s the depraved girlies after a little historical angst? china my love you deserve so much better than just being a lame ass loser.
i think part of it is just the western fandom gravitates more towards european/western countries cause that’s more familiar. and i’m not shaming anyone for it!! it’s normal and understandable that ppl would gravitate towards countries that you know more about! i just find it sad when i can’t find china fics cause their either in chinese or hes just a side character.
i don’t wanna get too deep bcs that’s not the point of the post. the point is to love my man china. but i also think it has to do with eastern asian men in general being emasculated and considered more feminine…plus himaruya’s perception of china…i don’t wanna start a whole debate tho that’s not my point.
basically i’m just in love with china if you couldn’t tell and want him to have equal love in the fandom. am i a simp? maybe 🏃♂️
side note: i find nyo!america x china sooooo interesting and dynamically pleasing. something about older man who knows how to handle his financials and a younger woman who needs a sugar daddy speaks to me…
tldr: china my beloved.
#aph china#hws china#china hetalia#hetalia#aph hetalia#hetalia the world twinkle#hetalia the beautiful world#hetalia axis powers#axis powers ヘタリア#axispowershetalia
112 notes
·
View notes
Text
How the Neocons Subverted Russia’s Financial Stabilization in the Early 1990s
by Jeffrey Sachs
In 1989 I served as an advisor to the first post-communist government of Poland, and helped to devise a strategy of financial stabilization and economic transformation. My recommendations in 1989 called for large-scale Western financial support for Poland’s economy in order to prevent a runaway inflation, enable a convertible Polish currency at a stable exchange rate, and an opening of trade and investment with the countries of the European Community (now the European Union). These recommendations were heeded by the US Government, the G7, and the International Monetary Fund.
Based on my advice, a $1 billion Zloty stabilization fund was established that served as the backing of Poland’s newly convertible currency. Poland was granted a standstill on debt servicing on the Soviet-era debt, and then a partial cancellation of that debt. Poland was granted significant development assistance in the form of grants and loans by the official international community.
Poland’s subsequent economic and social performance speaks for itself. Despite Poland’s economy having experienced a decade of collapse in the 1980s, Poland began a period of rapid economic growth in the early 1990s. The currency remained stable and inflation low. In 1990, Poland’s GDP per capita (measured in purchasing-power terms) was 33% of neighboring Germany. By 2024, it had reached 68% of Germany’s GDP per capita, following decades of rapid economic growth.
On the basis of Poland’s economic success, I was contacted in 1990 by Mr. Grigory Yavlinsky, economic advisor to President Mikhail Gorbachev, to offer similar advice to the Soviet Union, and in particular to help mobilize financial support for the economic stabilization and transformation of the Soviet Union. One outcome of that work was a 1991 project undertaken at the Harvard Kennedy School with Professors Graham Allison, Stanley Fisher, and Robert Blackwill. We jointly proposed a “Grand Bargain” to the US, G7, and Soviet Union, in which we advocated large-scale financial support by the US and G7 countries for Gorbachev’s ongoing economic and political reforms. The report was published as Window of Opportunity: The Grand Bargain for Democracy in the Soviet Union (1 October 1991).
The proposal for large-scale Western support for the Soviet Union was flatly rejected by the Cold Warriors in the White House. Gorbachev came to the G7 Summit in London in July 1991 asking for financial assistance, but left empty-handed. Upon his return to Moscow, he was abducted in the coup attempt of August 1991. At that point, Boris Yeltsin, President of the Russian Federation, assumed effective leadership of the crisis-ridden Soviet Union. By December, under the weight of decisions by Russia and other Soviet republics, the Soviet Union was dissolved with the emergence of 15 newly independent nations.
In September 1991, I was contacted by Yegor Gaidar, economic advisor to Yeltsin, and soon to be acting Prime Minister of newly independent Russian Federation as of December 1991. He requested that I come to Moscow to discuss the economic crisis and ways to stabilize the Russian economy. At that stage, Russia was on the verge of hyperinflation, financial default to the West, the collapse of international trade with the other republics and with the former socialist countries of Eastern Europe, and intense shortages of food in Russian cities resulting from the collapse of food deliveries from the farmlands and the pervasive black marketing of foodstuffs and other essential commodities.
I recommended that Russia reiterate the call for large-scale Western financial assistance, including an immediate standstill on debt servicing, longer-term debt relief, a currency stabilization fund for the ruble (as for the Zloty in Poland), large-scale grants of dollars and European currencies to support urgently needed food and medical imports and other essential commodity flows, and immediate financing by the IMF, World Bank, and other institutions to protect Russia’s social services (healthcare, education, and others).
In November 1991, Gaidar met with the G7 Deputies (the deputy finance ministers of the G7 countries) and requested a standstill on debt servicing. This request was flatly denied. To the contrary, Gaidar was told that unless Russia continued to service every last dollar as it came due, emergency food aid on the high seas heading to Russia would be immediately turned around and sent back to the home ports. I met with an ashen-faced Gaidar immediately after the G7 Deputies meeting.
In December 1991, I met with Yeltsin in the Kremlin to brief him on Russia’s financial crisis and on my continued hope and advocacy for emergency Western assistance, especially as Russia was now emerging as an independent, democratic nation after the end of the Soviet Union. He requested that I serve as an advisor to his economic team, with a focus on attempting to mobilize the needed large-scale financial support. I accepted that challenge and the advisory position on a strictly unpaid basis.
Upon returning from Moscow, I went to Washington to reiterate my call for a debt standstill, a currency stabilization fund, and emergency financial support. In my meeting with Mr. Richard Erb, Deputy Managing Director of the IMF in charge of overall relations with Russia, I learned that the US did not support this kind of financial package. I once again pleaded the economic and financial case, and was determined to change US policy. It had been my experience in other advisory contexts that it might require several months to sway Washington on its policy approach.
Indeed, during 1991-94 I would advocate non-stop but without success for large-scale Western support for Russia’s crisis-ridden economy, and support for the other 14 newly independent states of the former Soviet Union. I made these appeals in countless speeches, meetings, conferences, op-eds, and academic articles. Mine was a lonely voice in the US in calling for such support. I had learned from economic history — most importantly the crucial writings of John Maynard Keynes (especially Economic Consequences of the Peace, 1919) — and from my own advisory experiences in Latin America and Eastern Europe, that external financial support for Russia could well be the make or break of Russia’s urgently needed stabilization effort.
It is worth quoting at length here from my article in the Washington Post in November 1991 to present the gist of my argument at the time:
This is the third time in this century in which the West must address the vanquished. When the German and Hapsburg Empires collapsed after World War I, the result was financial chaos and social dislocation. Keynes predicted in 1919 that this utter collapse in Germany and Austria, combined with a lack of vision from the victors, would conspire to produce a furious backlash towards military dictatorship in Central Europe. Even as brilliant a finance minister as Joseph Schumpeter in Austria could not stanch the torrent towards hyperinflation and hyper-nationalism, and the United States descended into the isolationism of the 1920s under the "leadership" of Warren G. Harding and Sen. Henry Cabot Lodge. After World War II, the victors were smarter. Harry Truman called for U.S. financial support to Germany and Japan, as well as the rest of Western Europe. The sums involved in the Marshall Plan, equal to a few percent of the recipient countries' GNPs, was not enough to actually rebuild Europe. It was, though, a political lifeline to the visionary builders of democratic capitalism in postwar Europe. Now the Cold War and the collapse of communism have left Russia as prostrate, frightened and unstable as was Germany after World War I and World War II. Inside Russia, Western aid would have the galvanizing psychological and political effect that the Marshall Plan had for Western Europe. Russia's psyche has been tormented by 1,000 years of brutal invasions, stretching from Genghis Khan to Napoleon and Hitler. Churchill judged that the Marshall Plan was history's "most unsordid act," and his view was shared by millions of Europeans for whom the aid was the first glimpse of hope in a collapsed world. In a collapsed Soviet Union, we have a remarkable opportunity to raise the hopes of the Russian people through an act of international understanding. The West can now inspire the Russian people with another unsordid act.
This advice went unheeded, but that did not deter me from continuing my advocacy. In early 1992, I was invited to make the case on the PBS news show The McNeil-Lehrer Report. I was on air with acting Secretary of State Lawrence Eagleburger. After the show, he asked me to ride with him from the PBS studio in Arlington, Virginia back to Washington, D.C. Our conversation was the following. “Jeffrey, please let me explain to you that your request for large-scale aid is not going to happen. Even assuming that I agree with your arguments — and Poland’s finance minister [Leszek Balcerowicz] made the same points to me just last week — it’s not going to happen. Do you want to know why? Do you know what this year is?” “1992,” I answered. “Do you know that this means?” “An election year?” I replied. “Yes, this is an election year. It’s not going to happen.”
Russia’s economic crisis worsened rapidly in 1992. Gaidar lifted price controls at the start of 1992, not as some purported miracle cure but because the Soviet-era official fixed prices were irrelevant under the pressures of the black markets, the repressed inflation (that is, rapid inflation in the black-market prices and therefore the rising the gap with the official prices), the complete breakdown of the Soviet-era planning mechanism, and the massive corruption engendered by the few goods still being exchanged at the official prices far below the black-market prices.
Russia urgently needed a stabilization plan of the kind that Poland had undertaken, but such a plan was out of reach financially (because of the lack of external support) and politically (because the lack of external support also meant the lack of any internal consensus on what to do). The crisis was compounded by the collapse of trade among the newly independent post-Soviet nations and the collapse of trade between the former Soviet Union and its former satellite nations in Central and Eastern Europe, which were now receiving Western aid and were reorienting trade towards Western Europe and away from the former Soviet Union.
During 1992 I continued without any success to try to mobilize the large-scale Western financing that I believed to be ever-more urgent. I pinned my hopes on the newly elected Presidency of Bill Clinton. These hopes too were quickly dashed. Clinton’s key advisor on Russia, Johns Hopkins Professor Michael Mandelbaum, told me privately in November 1992 that the incoming Clinton team had rejected the concept of large-scale assistance for Russia. Mandelbaum soon announced publicly that he would not serve in the new administration. I met with Clinton’s new Russia advisor, Strobe Talbott, but discovered that he was largely unaware of the pressing economic realities. He asked me to send him some materials about hyperinflations, which I duly did.
At the end of 1992, after one year of trying to help Russia, I told Gaidar that I would step aside as my recommendations were not heeded in Washington or the European capitals. Yet around Christmas Day I received a phone call from Russia’s incoming financing minister, Mr. Boris Fyodorov. He asked me to meet him in Washington in the very first days of 1993. We met at the World Bank. Fyodorov, a gentleman and highly intelligent expert who tragically died young a few years later, implored me to remain as an advisor to him during 1993. I agreed to do so, and spent one more year attempting to help Russia implement a stabilization plan. I resigned in December 1993, and publicly announced my departure as advisor in the first days of 1994.
My continued advocacy in Washington once again fell on deaf ears in the first year of the Clinton Administration, and my own forebodings became greater. I repeatedly invoked the warnings of history in my public speaking and writing, as in this piece in the New Republic in January 1994, soon after I had stepped aside from the advisory role.
Above all, Clinton should not console himself with the thought that nothing too serious can happen in Russia. Many Western policymakers have confidently predicted that if the reformers leave now, they will be back in a year, after the Communists once again prove themselves unable to govern. This might happen, but chances are it will not. History has probably given the Clinton administration one chance for bringing Russia back from the brink; and it reveals an alarmingly simple pattern. The moderate Girondists did not follow Robespierre back into power. With rampant inflation, social disarray and falling living standards, revolutionary France opted for Napoleon instead. In revolutionary Russia, Aleksandr Kerensky did not return to power after Lenin's policies and civil war had led to hyperinflation. The disarray of the early 1920s opened the way for Stalin's rise to power. Nor was Bruning'sgovernment given another chance in Germany once Hitler came to power in 1933.
It is worth clarifying that my advisory role in Russia was limited to macroeconomic stabilization and international financing. I was not involved in Russia’s privatization program which took shape during 1993-4, nor in the various measures and programs (such as the notorious “shares-for-loans” scheme in 1996) that gave rise to the new Russian oligarchs. On the contrary, I opposed the various kinds of measures that Russia was undertaking, believing them to be rife with unfairness and corruption. I said as much in both the public and in private to Clinton officials, but they were not listening to me on that account either. Colleagues of mine at Harvard were involved in the privatization work, but they assiduously kept me far away from their work. Two were later charged by the US government with insider dealing in activities in Russia which I had absolutely no foreknowledge or involvement of any kind. My only role in that matter was to dismiss them from the Harvard Institute for International Development for violating the internal HIID rules against conflicts of interest in countries that HIID advised.
The failure of the West to provide large-scale and timely financial support to Russia and the other newly independent nations of the former Soviet Union definitely exacerbated the serious economic and financial crisis that faced those countries in the early 1990s. Inflation remained very high for several years. Trade and hence economic recovery were seriously impeded. Corruption flourished under the policies of parceling out valuable state assets to private hands.
All of these dislocations gravely weakened the public trust in the new governments of the region and the West. This collapse in social trust brought to my mind at the time the adage of Keynes in 1919, following the disaster Versailles settlement and the hyperinflations that followed: “There is no subtler, no surer means of over- turning the existing basis of society than to debauch the currency. The process engages all the hidden forces of economic law on the side of destruction, and it does it in a manner which not one man in a million is able to diagnose.”
During the tumultuous decade of the 1990s, Russia’s social services fell into decline. When this decline was coupled with the greatly increased stresses on society, the result was a sharp rise in Russia’s alcohol-related deaths. Whereas in Poland, the economic reforms were accompanied by a rise in life expectancy and public health, the very opposite occurred in crisis-riven Russia.
Even with all of these economic debacles, and with Russia’s default in 1998, the grave economic crisis and lack of Western support were not the definitive breaking points of US-Russian relations. In 1999, when Vladimir Putin became Prime Minister and in 2000 when he became President, Putin sought friendly and mutually supportive international relations between Russia and the West. Many European leaders, for example, Italy’s Romano Prodi, have spoken extensively about Putin’s goodwill and positive intentions towards strong Russia-EU relations in the first years of his presidency.
It was in military affairs rather than in economics that the Russian – Western relations ended up falling apart in the 2000s. As with finance, the West was militarily dominant in the 1990s, and certainly had the means to promote strong and positive relations with Russia. Yet the US was far more interested in Russia’s subservience to NATO that it was in stable relations with Russia.
At the time of German reunification, both the US and Germany repeatedly promised Gorbachev and then Yeltsin that the West would not take advantage of German reunification and the end of the Warsaw Pact by expanding the NATO military alliance eastward. Both Gorbachev and Yeltsin reiterated the importance of this US-NATO pledge. Yet within just a few years, Clinton completely reneged on the Western commitment, and began the process of NATO enlargement. Leading US diplomats, led by the great statesman-scholar George Kennan, warned at the time that the NATO enlargement would lead to disaster: “The view, bluntly stated, is that expanding NATO would be the most fateful error of American policy in the entire post-cold-war era.” So, it has proved.
Here is not the place to revisit all of the foreign policy disasters that have resulted from US arrogance towards Russia, but it suffices here to mention a brief and partial chronology of key events. In 1999, NATO bombed Belgrade for 78 days with the goal of breaking Serbia apart and giving rise to an independent Kosovo, now home to a major NATO base in the Balkans. In 2002, the US unilaterally withdrew from the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty over Russia’s strenuous objections. In 2003, the US and NATO allies repudiated the UN Security Council by going to war in Iraq on false pretenses. In 2004, the US continued with NATO enlargement, this time to the Baltic States and countries in the Black Sea region (Bulgaria and Romania) and the Balkans. In 2008, over Russia’s urgent and strenuous objections, the US pledged to expand NATO to Georgia and Ukraine.
In 2011, the US tasked the CIA to overthrow Syria’s Bashar al-Assad, an ally of Russia. In 2011, NATO bombed Libya in order to overthrow Moammar Qaddafi. In 2014, the US conspired with Ukrainian nationalist forces to overthrow Ukraine’s President Viktor Yanukovych. In 2015, the US began to place Aegis anti-ballistic missiles in Eastern Europe(Romania), a short distance from Russia. In 2016-2020, the US supported Ukraine in undermining the Minsk II agreement, despite its unanimous backing by the UN Security Council. In 2021, the new Biden Administration refused to negotiate with Russia over the question of NATO enlargement to Ukraine. In April 2022, the US called on Ukraine to withdraw from peace negotiations with Russia.
Looking back on the events around 1991-93, and to the events that followed, it is clear that the US was determined to say no to Russia’s aspirations for peaceful and mutually respectful integration of Russia and the West. The end of the Soviet period and the beginning of the Yeltsin Presidency occasioned the rise of the neoconservatives (neocons) to power in the United States. The neocons did not and do not want a mutually respectful relationship with Russia. They sought and until today seek a unipolar world led by a hegemonic US, in which Russia and other nations will be subservient.
In this US-led world order, the neocons envisioned that the US and the US alone will determine the utilization of the dollar-based banking system, the placement of overseas US military bases, the extent of NATO membership, and the deployment of US missile systems, without any veto or say by other countries, certainly including Russia. That arrogant foreign policy has led to several wars and to a widening rupture of relations between the US-led bloc of nations and the rest of the world. As an advisor to Russia during two years, late-1991 to late-93, I experienced first-hand the early days of neoconservatism applied to Russia, though it would take many years of events afterwards to recognize the full extent of the new and dangerous turn in US foreign policy that began in the early 1990s.
#AES#soviet union#eastern bloc#cold war#us imperialism#russia#nato#bill clinton#ukraine#history#jeffrey sachs
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Kyiv Independent is Private Ukrainian Media]
The European Union will urge its member states to shut off all EU funding to Budapest if Hungary does not back down on its pledge to veto the EU's proposed $55 billion military aid package for Ukraine, a leaked document prepared by EU officials and seen by the Financial Times revealed on Jan. 28.[...]
The leaked document, drawn up by officials in the European Council, criticizes the "unconstructive behaviour of the Hungarian PM," while establishing a framework for countries to permanently cut EU funding with the intention of "spooking the markets, precipitating a run on the country’s forint currency and a surge in the cost of its borrowing," according to the Financial Times.
The alleged document also notes that Brussels would aim to impact investor confidence in the country's ability to create jobs and drive growth.[...]
The EU has also considered using the "nuclear option" of revoking Hungary's voting rights if it again vetoes the $55 billion aid package for Ukraine at an upcoming European Council summit next week, Politico reported on Jan. 26.
The Hungarian far-right party Our Homeland declared its claim to Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast if Ukraine loses the war, party leader Laszlo Toroczkai said on Jan. 27.
Zakarpattia Oblast, bordering Slovakia and Hungary to the west, and Romania to the south, has a significant population of ethnic Hungarians. The issue of minority rights has created friction between Hungary and Ukraine, particularly centered around Ukrainian state linguistic policies.
The language law that has long been a source of strife between Hungary and Ukraine was instituted in 2017 and requires at least 70% of education above fifth grade to be conducted in Ukrainian.
In response to criticism, Ukraine has said that it does not intend to limit the linguistic rights of its minorities but rather to simply ensure that all Ukrainian citizens have the sufficient capability to speak the national language, Ukrainian.[...]
Hungary's Foreign Ministry did not respond to requests for comment on Toroczkai's statements, Reuters said.
The news came ahead of a meeting between Ukraine's Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba and his Hungarian counterpart Peter Szijjarto scheduled to take place on Jan. 29 in the Zakarpattia Oblast city of Uzhhorod.
In the leadup to Szijjarto's visit, the Hungarian newspaper Magyar Nemzet, considered to be closely affiliated with Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban, published an article condemning the state of Ukraine's press freedom. It also criticized Ukrainian media directives for journalists to use the official Ukrainian spelling of city names instead of the Russian version.
28 Jan 24
[Ukrinform is Private Ukrainian Media]
The Hungarian side is asking Ukraine that a Hungarian minority be given back all the rights it had before 2015.
This was stated by Hungarian Minister for Foreign Affairs Peter Szijjarto at a joint briefing with his Ukrainian counterpart Dmytro Kuleba and Head of the Ukrainian President’s Office Andriy Yermak following the talks in Uzhhorod, according to an Ukrinform correspondent.
"We have come here to reestablish good neighborly relations, we have a long way to go, but we, from the Hungarian side, are ready to do this work. In Zakarpattia, Hungarians and Ukrainians live in peace," Szijjarto said.[...]
"Since 2017, laws have been passed to reduce the rights of the Hungarian minority. In December, Parliament passed a law that stopped that. But we have a request - maybe it's too much, and you will think I'm not being polite - but we ask that the Hungarian minority be given back all the rights it had before 2015. We are not asking for anything else," the minister said.
The Foreign Minister said that the Hungarian side had formulated an 11-point request: including restoring the status of the national school, the possibility of taking a high school diploma in Hungarian and using Hungarian in social life. According to him, the commission was tasked with agreeing on these issues as soon as possible and developing proposals for the ministries.
29 Jan 24
40 notes
·
View notes