#elastic beanstalk
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Unleash the Power of AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Are you a developer looking for a hassle-free way to deploy and manage your web applications? Look no further than AWS Elastic Beanstalk. This fully managed platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offering from Amazon Web Services takes the complexities out of infrastructure management, allowing you to focus on what matters most - writing code and delivering exceptional user experiences.
What are AWS Elastic Beanstalk? AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a cloud service that handles the deployment, scaling, monitoring, and maintenance of your applications. It supports various programming languages and frameworks, making it versatile and adaptable to your development needs.
Streamlined Deployment Process Gone are the days of manual configuration and setup. With Elastic Beanstalk, you can deploy your application with just a few clicks. It automatically provisions resource, sets up load balancing, and monitors application health. This means you can roll out updates faster and reduce the risk of errors.
Seamless Scaling Whether you're experiencing a sudden surge in traffic or anticipating growth, Elastic Beanstalk has got your back. Its auto-scaling feature adjusts the number of instances based on demand, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention. Say goodbye to worries about capacity planning!
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Elastic Beanstalk provides comprehensive health and performance metrics for your applications. You can easily track resource usage, diagnose issues, and fine-tune your app for peak efficiency. With integrated logging and monitoring tools, you're always in control.
Integration with AWS Services Harness the full power of the AWS ecosystem. Elastic Beanstalk seamlessly integrates with other services like Amazon RDS for databases, Amazon S3 for storage, and Amazon CloudWatch for advanced monitoring. This level of integration opens up a world of possibilities for your application architecture.
Focus on Innovation By abstracting away infrastructure concerns, Elastic Beanstalk lets you channel your energy into innovating and improving your application. You can experiment with new features, optimize user experiences, and respond swiftly to market demands.
Embrace the power of Elastic Beanstalk and elevate your development experience to new heights. Start your journey today and experience the difference for yourself.
READ MORE .....

0 notes
Text
Configure ColdFusion with AWS Elastic Beanstalk
#Configure ColdFusion with AWS Elastic Beanstalk#ColdFusion with AWS Elastic Beanstalk#Configure ColdFusion with AWS#ColdFusion with AWS
0 notes
Text
Deploying Node.js Apps to AWS
Deploying Node.js Apps to AWS: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction Deploying a Node.js application to AWS (Amazon Web Services) ensures that your app is scalable, reliable, and accessible to users around the globe. AWS offers various services that can be used for deployment, including EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, and Lambda. This guide will walk you through the process of deploying a Node.js application using AWS EC2 and Elastic Beanstalk. Overview We…
#AWS EC2#AWS Elastic Beanstalk#cloud deployment#DevOps practices#Node.js deployment#Node.js on AWS#web development
0 notes
Text
Welche AWS-Services stehen für Cloud Computing zur Verfügung?: Die Überschrift lautet: "Cloud Computing mit AWS: Die verschiedenen Services im Überblick"
#CloudComputing #AWS #AmazonEC2 #AmazonS3 #AmazonRDS #AWSElasticBeanstalk #AWSLambda #AmazonRedshift #AmazonKinesis #AmazonECS #AmazonLightsail #AWSFargate Entdecken Sie die verschiedenen Services von AWS für Cloud Computing und machen Sie sich mit den Vor- und Nachteilen vertraut!
Cloud Computing ist in vielerlei Hinsicht eine revolutionäre Technologie. Es bietet Unternehmen die Möglichkeit, ihr Rechenzentrum zu einer kostengünstigen, zuverlässigen und flexiblen Infrastruktur zu machen. Mit Cloud Computing können Unternehmen auf jeder Plattform, zu jeder Zeit und an jedem Ort auf ihre Rechenzentrumsressourcen zugreifen. Amazon Web Services (AWS) ist einer der führenden…
View On WordPress
#Amazon EC2#Amazon ECS#Amazon Kinesis#Amazon Lightsail#Amazon RDS#Amazon Redshift#Amazon S3#AWS Elastic Beanstalk#AWS Fargate.#AWS Lambda
0 notes
Text
I feel sluggish, have a headache, AND I have to figure out elastic beanstalk on my own??
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
CLOUD COMPUTING: A CONCEPT OF NEW ERA FOR DATA SCIENCE
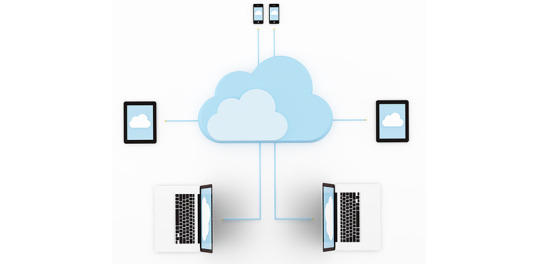
Cloud Computing is the most interesting and evolving topic in computing in the recent decade. The concept of storing data or accessing software from another computer that you are not aware of seems to be confusing to many users. Most the people/organizations that use cloud computing on their daily basis claim that they do not understand the subject of cloud computing. But the concept of cloud computing is not as confusing as it sounds. Cloud Computing is a type of service where the computer resources are sent over a network. In simple words, the concept of cloud computing can be compared to the electricity supply that we daily use. We do not have to bother how the electricity is made and transported to our houses or we do not have to worry from where the electricity is coming from, all we do is just use it. The ideology behind the cloud computing is also the same: People/organizations can simply use it. This concept is a huge and major development of the decade in computing.
Cloud computing is a service that is provided to the user who can sit in one location and remotely access the data or software or program applications from another location. Usually, this process is done with the use of a web browser over a network i.e., in most cases over the internet. Nowadays browsers and the internet are easily usable on almost all the devices that people are using these days. If the user wants to access a file in his device and does not have the necessary software to access that file, then the user would take the help of cloud computing to access that file with the help of the internet.
Cloud computing provide over hundreds and thousands of services and one of the most used services of cloud computing is the cloud storage. All these services are accessible to the public throughout the globe and they do not require to have the software on their devices. The general public can access and utilize these services from the cloud with the help of the internet. These services will be free to an extent and then later the users will be billed for further usage. Few of the well-known cloud services that are drop box, Sugar Sync, Amazon Cloud Drive, Google Docs etc.
Finally, that the use of cloud services is not guaranteed let it be because of the technical problems or because the services go out of business. The example they have used is about the Mega upload, a service that was banned and closed by the government of U.S and the FBI for their illegal file sharing allegations. And due to this, they had to delete all the files in their storage and due to which the customers cannot get their files back from the storage.
Service Models Cloud Software as a Service Use the provider's applications running on a cloud infrastructure Accessible from various client devices through thin client interface such as a web browser Consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, storage
Google Apps, Microsoft Office 365, Petrosoft, Onlive, GT Nexus, Marketo, Casengo, TradeCard, Rally Software, Salesforce, ExactTarget and CallidusCloud
Cloud Platform as a Service Cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Cloud Foundry, Heroku, Force.com, Engine Yard, Mendix, OpenShift, Google App Engine, AppScale, Windows Azure Cloud Services, OrangeScape and Jelastic.
Cloud Infrastructure as a Service Cloud provider offers processing, storage, networks, and other fundamental computing resources Consumer is able to deploy and run arbitrary software, which can include operating systems and applications Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, HP Cloud, Joyent, Linode, NaviSite, Rackspace, Windows Azure, ReadySpace Cloud Services, and Internap Agile
Deployment Models Private Cloud: Cloud infrastructure is operated solely for an organization Community Cloud : Shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns Public Cloud: Cloud infrastructure is made available to the general public Hybrid Cloud: Cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds
Advantages of Cloud Computing • Improved performance • Better performance for large programs • Unlimited storage capacity and computing power • Reduced software costs • Universal document access • Just computer with internet connection is required • Instant software updates • No need to pay for or download an upgrade
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing • Requires a constant Internet connection • Does not work well with low-speed connections • Even with a fast connection, web-based applications can sometimes be slower than accessing a similar software program on your desktop PC • Everything about the program, from the interface to the current document, has to be sent back and forth from your computer to the computers in the cloud
About Rang Technologies: Headquartered in New Jersey, Rang Technologies has dedicated over a decade delivering innovative solutions and best talent to help businesses get the most out of the latest technologies in their digital transformation journey. Read More...
#CloudComputing#CloudTech#HybridCloud#ArtificialIntelligence#MachineLearning#Rangtechnologies#Ranghealthcare#Ranglifesciences
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
at work 1: ugh ugh ugh elastic beanstalk deployment issues
at work 2: attempt manual build and deploy of client
DS: updated encounter tables
DS: snap/party meet cutscene
TTT night
go outside
exercise
WK reviews
pay bills
all that and a bunch of extra work debugging the IP-based auth system. it is 2am though so i didn't actually budget my time all the way goodways.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
DevOps for Beginners: Navigating the Learning Landscape
DevOps, a revolutionary approach in the software industry, bridges the gap between development and operations by emphasizing collaboration and automation. For beginners, entering the world of DevOps might seem like a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. In this blog, we'll provide you with a step-by-step guide to learn DevOps, from understanding its core philosophy to gaining hands-on experience with essential tools and cloud platforms. By the end of this journey, you'll be well on your way to mastering the art of DevOps.

The Beginner's Path to DevOps Mastery:
1. Grasp the DevOps Philosophy:
Start with the Basics: DevOps is more than just a set of tools; it's a cultural shift in how software development and IT operations work together. Begin your journey by understanding the fundamental principles of DevOps, which include collaboration, automation, and delivering value to customers.
2. Get to Know Key DevOps Tools:
Version Control: One of the first steps in DevOps is learning about version control systems like Git. These tools help you track changes in code, collaborate with team members, and manage code repositories effectively.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Dive into CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitLab CI. These tools automate the building and deployment of software, ensuring a smooth and efficient development pipeline.
Configuration Management: Gain proficiency in configuration management tools such as Ansible, Puppet, or Chef. These tools automate server provisioning and configuration, allowing for consistent and reliable infrastructure management.
Containerization and Orchestration: Explore containerization using Docker and container orchestration with Kubernetes. These technologies are integral to managing and scaling applications in a DevOps environment.
3. Learn Scripting and Coding:
Scripting Languages: DevOps engineers often use scripting languages such as Python, Ruby, or Bash to automate tasks and configure systems. Learning the basics of one or more of these languages is crucial.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Delve into Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation. IaC allows you to define and provision infrastructure using code, streamlining resource management.
4. Build Skills in Cloud Services:
Cloud Platforms: Learn about the main cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Discover the creation, configuration, and management of cloud resources. These skills are essential as DevOps often involves deploying and managing applications in the cloud.
DevOps in the Cloud: Explore how DevOps practices can be applied within a cloud environment. Utilize services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk or Azure DevOps for automated application deployments, scaling, and management.
5. Gain Hands-On Experience:
Personal Projects: Put your knowledge to the test by working on personal projects. Create a small web application, set up a CI/CD pipeline for it, or automate server configurations. Hands-on practice is invaluable for gaining real-world experience.
Open Source Contributions: Participate in open source DevOps initiatives. Collaborating with experienced professionals and contributing to real-world projects can accelerate your learning and provide insights into industry best practices.
6. Enroll in DevOps Courses:
Structured Learning: Consider enrolling in DevOps courses or training programs to ensure a structured learning experience. Institutions like ACTE Technologies offer comprehensive DevOps training programs designed to provide hands-on experience and real-world examples. These courses cater to beginners and advanced learners, ensuring you acquire practical skills in DevOps.

In your quest to master the art of DevOps, structured training can be a game-changer. ACTE Technologies, a renowned training institution, offers comprehensive DevOps training programs that cater to learners at all levels. Whether you're starting from scratch or enhancing your existing skills, ACTE Technologies can guide you efficiently and effectively in your DevOps journey. DevOps is a transformative approach in the world of software development, and it's accessible to beginners with the right roadmap. By understanding its core philosophy, exploring key tools, gaining hands-on experience, and considering structured training, you can embark on a rewarding journey to master DevOps and become an invaluable asset in the tech industry.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating AWS: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, Amazon Web Services (AWS) has emerged as a powerhouse, providing a wide array of services to businesses and individuals globally. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or just starting your journey into the cloud, understanding the key aspects of AWS is crucial. With AWS Training in Hyderabad, professionals can gain the skills and knowledge needed to harness the capabilities of AWS for diverse applications and industries. This blog will serve as your comprehensive guide, covering the essential concepts and knowledge needed to navigate AWS effectively.

1. The Foundation: Cloud Computing Basics
Before delving into AWS specifics, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of cloud computing. Cloud computing is a paradigm that offers on-demand access to a variety of computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, networking, analytics, and more. AWS, as a leading cloud service provider, allows users to leverage these resources seamlessly.
2. Setting Up Your AWS Account
The first step on your AWS journey is to create an AWS account. Navigate to the AWS website, provide the necessary information, and set up your payment method. This account will serve as your gateway to the vast array of AWS services.
3. Navigating the AWS Management Console
Once your account is set up, familiarize yourself with the AWS Management Console. This web-based interface is where you'll configure, manage, and monitor your AWS resources. It's the control center for your cloud environment.
4. AWS Global Infrastructure: Regions and Availability Zones
AWS operates globally, and its infrastructure is distributed across regions and availability zones. Understand the concept of regions (geographic locations) and availability zones (isolated data centers within a region). This distribution ensures redundancy and high availability.
5. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Security is paramount in the cloud. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) enable you to manage user access securely. Learn how to control who can access your AWS resources and what actions they can perform.
6. Key AWS Services Overview
Explore fundamental AWS services:
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Virtual servers in the cloud.
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service): Scalable object storage.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service): Managed relational databases.
7. Compute Services in AWS
Understand the various compute services:
EC2 Instances: Virtual servers for computing capacity.
AWS Lambda: Serverless computing for executing code without managing servers.
Elastic Beanstalk: Platform as a Service (PaaS) for deploying and managing applications.
8. Storage Options in AWS
Explore storage services:
Amazon S3: Object storage for scalable and durable data.
EBS (Elastic Block Store): Block storage for EC2 instances.
Amazon Glacier: Low-cost storage for data archiving.
To master the intricacies of AWS and unlock its full potential, individuals can benefit from enrolling in the Top AWS Training Institute.

9. Database Services in AWS
Learn about managed database services:
Amazon RDS: Managed relational databases.
DynamoDB: NoSQL database for fast and predictable performance.
Amazon Redshift: Data warehousing for analytics.
10. Networking Concepts in AWS
Grasp networking concepts:
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Isolated cloud networks.
Route 53: Domain registration and DNS web service.
CloudFront: Content delivery network for faster and secure content delivery.
11. Security Best Practices in AWS
Implement security best practices:
Encryption: Ensure data security in transit and at rest.
IAM Policies: Control access to AWS resources.
Security Groups and Network ACLs: Manage traffic to and from instances.
12. Monitoring and Logging with AWS CloudWatch and CloudTrail
Set up monitoring and logging:
CloudWatch: Monitor AWS resources and applications.
CloudTrail: Log AWS API calls for audit and compliance.
13. Cost Management and Optimization
Understand AWS pricing models and manage costs effectively:
AWS Cost Explorer: Analyze and control spending.
14. Documentation and Continuous Learning
Refer to the extensive AWS documentation, tutorials, and online courses. Stay updated on new features and best practices through forums and communities.
15. Hands-On Practice
The best way to solidify your understanding is through hands-on practice. Create test environments, deploy sample applications, and experiment with different AWS services.
In conclusion, AWS is a dynamic and powerful ecosystem that continues to shape the future of cloud computing. By mastering the foundational concepts and key services outlined in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to navigate AWS confidently and leverage its capabilities for your projects and initiatives. As you embark on your AWS journey, remember that continuous learning and practical application are key to becoming proficient in this ever-evolving cloud environment.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paas
Platform as a service (PaaS) : a cloud computing model which allows user to deliver applications over the Internet. In a this model, a cloud provider provides hardware ( like IaaS ) as well as software tools which are usually needed for development of required Application to its users. The hardware and software tools are provided as a Service.
PaaS provides us : OS , Runtime as well as middleware alongside benefits of IaaS. Thus PaaS frees users from maintaining these aspects of application and focus on development of the core app only.
Why choose PaaS :
Increase deployment speed & agility
Reduce length & complexity of app lifecycle
Prevent loss in revenue
Automate provisioning, management, and auto-scaling of applications and services on IaaS platform
Support continuous delivery
Reduce infrastructure operation costs
Automation of admin tasks
The Key Benefits of PaaS for Developers.
There’s no need to focus on provisioning, managing, or monitoring the compute, storage, network and software
Developers can create working prototypes in a matter of minutes.
Developers can create new versions or deploy new code more rapidly
Developers can self-assemble services to create integrated applications.
Developers can scale applications more elastically by starting more instances.
Developers don’t have to worry about underlying operating system and middleware security patches.
Developers can mitigate backup and recovery strategies, assuming the PaaS takes care of this.
conclusion
Common PaaS opensource distributions include CloudFoundry and Redhat OpenShift. Common PaaS vendors include Salesforce’s Force.com , IBM Bluemix , HP Helion , Pivotal Cloudfoundry . PaaS platforms for software development and management include Appear IQ, Mendix, Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine and Heroku.
1 note
·
View note
Text
MICROSOFT AZURE DEVOPS Online Training in Pune
Online DevOps Training in Pune If you're looking to take your career to the next level with the flexibility of online learning, online DevOps training in Pune can be the perfect solution. You can learn at your own pace, from the comfort of your home, while still gaining access to expert instructors and hands-on labs. Online courses typically offer flexible schedules, making it easier for working professionals to upgrade their skills without interrupting their daily routines.

DevOps Training in Pune
When it comes to getting DevOps training in Pune, the city offers a wide range of courses designed to equip you with in-depth knowledge of DevOps tools, techniques, and best practices. Pune is home to some of the top training institutes offering expert guidance and industry-relevant coursework to help you build a strong foundation in DevOps.
DevOps Classes in Pune
For those seeking more structured learning, enrolling in DevOps classes in Pune is an ideal option. These classes are led by industry experts who provide both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. You'll learn how to work with automation tools, containerization platforms, and cloud services, ensuring you're prepared for real-world challenges in DevOps environments.
DevOps Course in Pune
A DevOps course in Pune will give you a comprehensive understanding of the DevOps lifecycle. From coding and integration to monitoring and automation, a well-designed course covers all aspects of DevOps, including CI/CD, version control, cloud computing, and more. This helps you understand how to build, test, and deploy software efficiently and collaboratively.
Best DevOps Classes in Pune
When searching for the best DevOps classes in Pune, look for institutes that offer high-quality curriculum, experienced trainers, and hands-on experience. The best training providers focus on practical exposure and real-time scenarios, which will help you gain the skills necessary for success in a DevOps role.
AWS DevOps Classes in Pune
If you want to specialize in cloud computing, AWS DevOps classes in Pune are highly recommended. AWS (Amazon Web Services) is one of the most widely used cloud platforms, and having proficiency in AWS DevOps tools like CodePipeline, CloudFormation, and Elastic Beanstalk will give you an edge in the job market. These classes focus on integrating DevOps practices with AWS cloud services to build scalable, reliable, and secure applications.
Best DevOps Training Institute in Pune
Choosing the best DevOps training institute in Pune is crucial to your career success. Look for an institute that offers hands-on learning, industry-aligned curriculum, and experienced instructors. Institutes that provide placement assistance and support can also increase your chances of landing your first DevOps job after completing the training.
DevOps Classes in Pune with Placement
Many DevOps classes in Pune with placement are available for students who want additional support in finding a job. These classes not only teach you DevOps skills but also prepare you for the job market by offering resume-building workshops, mock interviews, and networking opportunities with top companies looking to hire skilled professionals.
CloudWorld: A Leading DevOps Training Institute in Pune
CloudWorld is one of the best DevOps training institutes in Pune that offers in-depth DevOps training in Pune. Known for its expert instructors, live projects, and comprehensive curriculum, CloudWorld also provides excellent placement assistance to ensure you’re ready to take on a DevOps role in leading tech companies.
#online devops training in pune#devops training in pune#devops classes in pune#devops course in pune#best devops classes in pune#aws devops classes in pune#best devops training institute in pune#devops classes in pune with placement
0 notes
Text
What is AWS DevOps? Everything You Need to Know
Imagine managing a busy restaurant. There are waitstaff, cooks and managers who work together to deliver the best dining experience. Imagine trying to manage all the moving parts with no any clear communication or processes that are streamlined. Chaos, right? This analogy perfectly demonstrates the reason the AWS DevOps is now an essential practice for modern companies.
AWS DevOps is a kind of orchestrator for your company's IT infrastructure, which ensures that your operations and development teams are in sync. It's not a mere tool. It's an approach, a culture and a set techniques that can help you create deployment, maintain, and manage applications quickly and efficiently. Let's look into the details of AWS DevOps is and why it's important.
What is AWS DevOps?
In simple terms, AWS DevOps combines two critical functions--"Development" (Dev) and "Operations" (Ops)--with the power of Amazon Web Services (AWS). It's about collaboration, automation and constant improvement. AWS offers a variety of services and tools to assist teams in automating repetitive tasks, control infrastructure and ensure that software is delivered more efficiently.
Consider AWS DevOps as being the best toolkit to build a more rapid and better-performing software delivery process. By combining operations and development techniques, it reduces the gap between teams and creates the culture that encourages transparency, collaboration and accountability.
The Core Principles of AWS DevOps
To fully comprehend AWS DevOps, it's essential to comprehend its core principles:
Automatization Automation of repetitive work like deployment, testing and infrastructure provisioning are at the center of AWS DevOps. Automation decreases human errors and speeds up the processes.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): AWS DevOps is a system that focuses on seamless integration of changes to code and quick delivery to the production. It's similar to running an assembly line and never ceases.
Scalability The AWS service is designed to handle loads that are of any size, meaning your DevOps pipeline can expand in line with the needs of your business.
Collaboration It encourages the teams of developers, operations and other parties to work together, and no more pointing fingers when something goes wrong.
Monitor and feedback Amazon Web Services DevOps tools allow you to measure performance, find problems, and constantly enhance the software.
AWS DevOps Tools and Services
AWS has a wide range of tools that can be used at all phases in the DevOps lifecycle. Here are a few of the most important AWS DevOps tools and functions:
1. AWS CodePipeline
This service can automate the entire process of release, from code updates to the production. Imagine a conveyor belt well-oiled and providing updates to your application quickly and consistently.
2. AWS CodeBuild
Imagine this as the personal kitchen of your choice. AWS CodeBuild compiles source code is able to run tests, compiles code and creates deployable artifacts without any manual effort.
3. AWS CodeDeploy
If you have to provide updates to your app--whether running in EC2 instances or Lambda--CodeDeploy can ensure seamless, automated deployments that have very little downtime.
4. AWS CloudFormation
This tool can be described as the outline of your infrastructure. You define resources (servers, databases, etc.) in your code and AWS CloudFormation provides them to you.
5. Amazon CloudWatch
Imagine CloudWatch as the watchful restaurant manager, who is always watching the dining and kitchen areas. CloudWatch monitors data, performance and health of the application in real-time.
6. AWS Elastic Beanstalk
If you're looking for a more relaxed method, Elastic Beanstalk lets you create and manage apps without having to worry about the infrastructure.
Why AWS DevOps Matters
Why are businesses--from startups to Fortune 500s, embracing AWS DevOps? Here are a few of the reasons:
1. Speed and Agility
In the current fast-paced environment the ability to deliver software fast can be a competitive advantage. AWS DevOps empowers teams to develop faster and more quickly, while also adapting to the changing demands of the market.
2. Cost Efficiency
Automating manual processes and optimizing resource use AWS DevOps is able to drastically reduce operational costs.
3. Reliability
Utilizing tools such as AWS CloudWatch or CodePipeline to ensure that your apps are stable and reliable. There's no need for midnight fire drills.
4. Scalability
If you're managing a few of users or millions of them, AWS's scalable infrastructure will ensure that your applications run smoothly.
Real-World Use Cases
Are you still unsure of what AWS DevOps applies to real-world scenarios? Let's look at a few examples:
eCommerce Websites Businesses such as Netflix and Amazon make use of AWS DevOps for managing large-scale websites with large traffic. The continuous monitoring and integration aid in helping the company to deliver seamless user experience.
Healthcare Systems: AWS DevOps ensures that sensitive data is protected while ensuring the compliance of regulations. Testing and deployment that is automated minimize the possibility of errors occurring in critical systems.
Is AWS DevOps Right for You?
AWS DevOps doesn't offer a single-size-fits-all option, however it's flexible enough to meet the needs of different sectors and sizes of projects. If your company is interested in efficiency in collaboration, agility, and efficiency you should consider exploring. AWS provides courses and certifications to assist teams in adopting DevOps practices with success.
Conclusion
In the end, AWS DevOps training is a glue that binds all your IT procedures together. It changes the way teams work, which allows for speedier delivery, higher efficiency, and higher quality. It doesn't matter if you're a college student wanting to develop expertise or a developer looking to improve efficiency, or an individual in the process of evaluating IT options, AWS DevOps offers tools and methods that can transform your workflow.
The next time you hear "AWS DevOps," think of it as a formula for success, one that combines technology, collaboration and automation to provide effective results. It's moment to take a closer take a look at the ways it can help you take your company and its projects up to the next step.
0 notes
Text
Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline with AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild

Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline with AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild
AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild are key services for automating the build, test, and deployment phases of your software delivery process.
Together, they enable continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), streamlining the release cycle for your applications.
Here’s a quick guide:
Overview of the Services AWS CodePipeline:
Orchestrates the CI/CD process by connecting different stages, such as source, build, test, and deploy.
AWS CodeBuild:
A fully managed build service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces deployable artifacts.
Steps to Set Up a CI/CD Pipeline Source Stage:
Integrate with a code repository like GitHub, AWS CodeCommit, or Bitbucket to detect changes automatically.
Build Stage:
Use CodeBuild to compile and test your application.
Define build specifications (buildspec.yml) to configure the build process.
Test Stage (Optional):
Include automated tests to validate code quality and functionality.
Deploy Stage:
Automate deployment to services like EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, or S3.
Use deployment providers like AWS CodeDeploy.
Key Features of AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild Event-Driven Workflow:
Automatically triggers the pipeline on code changes.
Customizable Stages:
Define stages and steps to fit your specific CI/CD needs.
Scalability: Handle workloads of any size without infrastructure management.
Security: Leverage IAM roles and encryption to secure your pipeline.
Benefits of Automating CI/CD with AWS Speed:
Shorten development cycles with automated and parallel processes.
Reliability:
Minimize human error and ensure consistent deployments. Cost
Effectiveness: Pay only for the resources you use.
With AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild, you can create a robust and efficient CI/CD pipeline, accelerating your software delivery process and enhancing your DevOps practices.

0 notes
Text
A Guide to Microservices Deployment: Elastic Beanstalk vs Manual Setup
http://securitytc.com/THMtYp
0 notes
Text
Welches sind die am besten geeigneten Tools & Frameworks zur Entwicklung von AWS-Cloud-Computing-Anwendungen?: "Entwicklung von AWS-Cloud-Anwendungen: Die besten Tools & Frameworks von MHM Digitale Lösungen UG"
#AWS #CloudComputing #AWSLambda #AWSEC2 #ServerlessComputing #AmazonEC2ContainerService #AWSElasticBeanstalk #AmazonS3 #AmazonRedshift #AmazonDynamoDB
In der heutigen digitalen Welt ist Cloud-Computing ein Schlüsselthema, vor allem bei aufstrebenden Unternehmen. AWS (Amazon Web Services) ist der weltweit führende Cloud-Computing-Anbieter und bietet eine breite Palette an Tools und Frameworks, die Entwicklern dabei helfen, schneller und effizienter zu arbeiten. In diesem Artikel werden die besten Tools und Frameworks erörtert, die für die…
View On WordPress
#Amazon DynamoDB.#Amazon EC2 Container Service#Amazon Redshift#Amazon S3#Amazon Web Services#AWS EC2#AWS Elastic Beanstalk#AWS Lambda#Cloud Computing#Serverless Computing
0 notes
Text
Why AWS is a Game Changer for Your Cloud Journey
If you’ve been diving into the world of cloud computing, chances are you’ve heard of AWS (Amazon Web Services). It’s the go-to platform for everything from small startups to massive enterprises. But what’s all the hype about? Why is AWS so popular? Let’s break it down!
What Exactly is AWS?
Simply put, AWS is a cloud platform that gives you access to a bunch of powerful services like computing power, storage, databases, and machine learning tools. Instead of dealing with physical servers or complex IT setups, you can run your business or app directly in the cloud. And the best part? It's scalable, flexible, and super secure.
Why Should You Care About AWS?
Here are some reasons AWS is a big deal:
Super Scalable: As your business grows, you can easily increase your cloud resources with a few clicks—no need to worry about capacity issues!
Cost-Effective: Pay for what you use. No huge upfront costs like traditional hardware—just what you need, when you need it.
Top-Notch Security: With built-in encryption and a ton of compliance certifications, your data stays protected.
Global Reach: AWS runs data centers all over the world, meaning faster, more reliable performance wherever your users are.
Cutting-Edge Services: AWS is constantly rolling out cool new features like AI, machine learning, and advanced data analytics. Basically, it’s perfect for staying ahead in today’s tech-driven world.
Must-Know AWS Services
1. EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
Think of EC2 as your customizable virtual server. Whether you need a small instance for a project or a beefy one to handle high traffic, EC2 lets you scale on demand.
2. S3 (Simple Storage Service)
Need storage? S3 is your best friend. It’s a flexible, secure storage service that scales automatically and is perfect for large files (like photos, videos, or backups).
3. Lambda
Forget managing servers. Lambda lets you run code without worrying about infrastructure. It’s great for event-driven apps (like those microservices or serverless setups you keep hearing about).
4. RDS (Relational Database Service)
If you need to manage a database (and who doesn’t?), RDS makes it easy. It automates the boring stuff like backups and scaling, so you can focus on building your app.
5. VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
Set up your own private network with VPC. Think of it as your cloud’s “secure zone,” where you control who gets in and what they can access.
How AWS Helps Different Businesses
Startups & Small Biz
Startups don’t have to worry about investing in hardware. You pay only for what you use, and you can scale as you grow. Imagine running a new app without a giant upfront cost or IT infrastructure to manage. Sounds dreamy, right?
Enterprises & Large Companies
AWS scales up to handle massive workloads. Need to manage huge databases or run advanced AI models? AWS can handle it all. Plus, it’s compliant with global regulations, so you don’t have to worry about security.
Developers & DevOps
For developers, AWS offers tools to streamline development, from building apps to deploying them automatically. Whether it’s using Elastic Beanstalk for app deployment or CodePipeline to automate the release process, AWS makes life easier.
How to Get Started with AWS
Create Your AWS Account: It’s super simple to sign up. Once you’re in, you’ll have access to all AWS services.
Explore the Free Tier: AWS has a free tier that lets you try many services without paying a cent. Perfect for beginners!
Check Out the Docs: AWS has detailed tutorials and resources to guide you through setting up and using their services.
Scale When You’re Ready: As your needs grow, you can scale up your services without breaking a sweat.
Final Thoughts
AWS is changing the game when it comes to cloud computing. With its powerful features, scalability, and security, it’s no surprise that so many businesses trust it to run their operations. Whether you're just starting out or scaling big, AWS has everything you need to succeed.
So, what are you waiting for? Dive into the cloud with AWS and take your business (or project) to the next level.
1 note
·
View note