#effective weight loss formula
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Zotrim
Zotrim Plus weight loss product: clinically supported herbal supplement, reduces hunger, boosts energy, with high website conversion and patented formula. Endorsed by nutrition experts, provides a natural, effective solution for weight management.
"Please click on this link to get the product or to get an idea about it."https://zotrim.com/?_ef_transaction_id=&oid=13&affid=37573
#Weight loss#herbal supplement#Zotrim Plus#clinically supported#hunger reduction#energy enhancement#high conversion#patented formula#nutrition experts#natural solution#effective#weight management.
0 notes
Text
#Amyl Guard#is a new and effective dietary formula specially designed to help all users to get amazing results on weight loss and support balancing the
0 notes
Note
Why do you think they don't show Marinette comforting other characters? It's always been a weird writing decision to me, and I sometimes wondered if I was legit just erasing all the times it happened out of my memory or smth. Like the first character trait established for her is she struggles to say no to people, she is a people-pleaser. And there isn't a better way to make ur mc lovable than showing how they effect the people around them. AND it would make her breakdowns genuinely heartbreaking, because she keeps giving and giving and it's a genuine flaw. Like, she rushed off to comfort Ivan in Origins, right? We should have had more of that. I'm reminded of that one Lady Wifi (i think?) scene where Ladybug is smiling at her adoring fans and the camera while Chat Noir is in the background actually comforting a child lmao. It just feels so weird, because I think Marinette IS actually supposed to be someone who does that, who provides that comfort to her loved ones all the time (even at the cost of her own mental health, boom, an actual thing she can work towards). But we just keep getting the reverse instead. She just kinda feels like a shit friend? Showing that emotional labor would also make her exhaustion work because like, what does the guardian even DO? Tell not show, but they ain't telling shit.
One of the things that drew me to Miraculous is the fact that the show tends to write the characters in non-standard gender roles, so I actually like the fact that Marinette tends to be more of a fixer than a comforter. She drives people to action and wants to solve problems and is very good at taking the weight of the world on her shoulders, but she kind of sucks at emotional vulnerability and comforting people. It's genuinely a good flaw for her character and a lovely thing to see in a show aimed at girls. No, we don't all need to be stereotypically maternal figures. Women can be just as bad as men stereotypically are when it comes to emotions!
The problem is that the show is obsessed with Marinette holding every important role in the story, meaning that we don't get a more emotionally aware character or characters to balance her out. Nor do we get to see her learn that this is a flaw of hers and either improve or just own that she's bad at this and learn to trust someone else with these types of issues. (This is one of the many things I think Adrien should have been allowed to do, btw. Ladybug is the brains, Chat Noir should be the heart.) We also don't get a true sense of Marinette's struggles because the show's formulaic nature rarely allows for those types of problems.
The Lila thing is a good example. Lila says that she's going to destroy Marinette's friendships, but she literally can't do that because that would mean changing the way the characters relate on a massive scale and formula shows can't do that. So instead of seeing Marinette struggle as Lila lies and manipulates everyone into hating Marinette, we get extremely annoying episodes where Lila lies and everyone believes her, but no one gets all that upset at Marinette's constant accusations. They just treat it as a minor quibble which is actually more aggravating than Lila changing the status quo in my opinion.
There's also the issue that you brought up: we don't see Marinette truly struggling to be the guardian, so her new role doesn't feel like a big deal. Not much changes for her save for the kwamis being around now. We don't even know what her relationship with Master Fu was really like because he was barely ever on screen so we really don't feel her loss.
All of this is just another problem to lay at the feat of our ever-present issue: Miraculous does not have the right conflicts and characters for a formula show. Formula shows thrive off of things being lighthearted and the heroes lacking major flaws. Miraculous chose to make things somewhat serious and give everyone flaws that are just begging to be address, but that can't be because this is the wrong format for that type of thing.
In a team show where character arcs were a thing or even just one where character dynamics were a thing and Marinette was allowed to share the screen in a more balanced manner, then everything about her would work fine. She's set up perfectly for that kind of show. She is not set up for a formula show where she's basically the only character that matters outside of the villains. If that's what they wanted to write, then Marinette needed to be limited to minor flaws that never last more than an episode or at least limited to flaws that are purely situational such as being stubborn or the classic sudo-flaw of being clumsy that the show already embraces.
#anon ask#ml writing critical#ml writing salt#marinette deserves better#The clumsy heroine is one of my least favorite tropes btw#And Miraculous doesn't even use it well!#Why give it to a character with actual flaws?
57 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
How PhenGold Supercharges Your Weight Loss Journey! (No Filler, Just Results!)
https://swiy.co/phngld - Discover How PhenGold Can Transform Your Weight Loss Journey Hey everyone, welcome back to my channel! Today, I've got something super exciting to share with you all. If you're looking to shed some pounds and boost your energy, you'll definitely want to stick around. We’re diving into PhenGold, a metabolism booster by HealthNutrition, that's been getting a lot of buzz lately. So, let's see what all the hype is about and how it can help you on your weight loss journey. Alright, so let's talk about PhenGold. This isn't just any weight loss supplement. It's got a multi-action formula that really gets your body's natural fat-burning abilities going. What does that mean? Well, it speeds up weight loss by increasing your metabolism. It's like having a little helper inside your body, breaking down stored fat and turning it into energy. PhenGold is made with clinically proven ingredients, which means that there's real science backing up its effectiveness. And for all my veggie friends out there—good news! It's vegetarian and vegan-friendly. Plus, no soy, gluten, or dairy, and absolutely no fillers or artificial ingredients.
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
explaining f1: the cars
chassis
modern day f1 cars are constructed from composites of carbon fibre and other ultra-lightweight materials. the minimum weight currently permissible is 740kg including the driver but not the fuel.
engines
as of the 2014 season, all f1 cars have been equipped with turbocharged 1.6 l v6 engines, which were previously banned in 1989. this change gave up to a 29% increase in fuel efficiency.
transmission
f1 cars use highly automated semi-automatic sequential gearboxes, with regulations stating that 8 forward gears and 1 reverse gear must be used, with rear-wheel drive. fully automatic gearboxes are illegal to keep driver skill. the last f1 car fitted with a conventional manual gearbox was the forti fg01 which raced in 1995.
as of 2009, all teams use seamless-shift transmissions, which allow a near instantaneous changing of gears for minimal time loss. shift times for modern f1 cars are in the range of 2-3ms.
steering wheel
the wheel can be used to change gears, adjust the fuel/air mix, change the break balance and call the radio among other things, allowing the driver a huge amount of control. data such as engine rpm, lap times and tyre temperature etc. are displayed.
fuel
the fuel in f1 cars is fairly similar to ordinary petrol.
to make sure teams and fuel suppliers are within regulation, the fia requires fuel teams like shell, petronas etc. to submit samples of the fuels they are providing for races. at any time, fia inspectors can request a sample from the fuelling rig to compare. the teams usually abide by rules but in 1997 mika hakkinen was stripped of his third place finish in spa due to his fuel being the incorrect formula.
tyres
you can read all about tyres in f1 here!
breaks
the brakes used in f1 cars are designed to work in up to 1,000 degrees celsius.
drivers can control brake force to compensate for changes in track condition or fuel load.
notable cars
the victorious red bull racing rb18 from the 2022 season, driven by max verstappen.
the dominant mclaren mp4/4 driven by ayrton senna in 1988.
the highly successful ferrari f2004 driven by micheal schumacher at the 2004 united states grand prix.
the 1994 williams fw15c, widely considered to be one of the most technologically advanced f1 car of all time
the first f1 car to be powered by a turbocharged engine; the 1997 renault rs01.
the lotus 78, which exploited the aerodynamic effects of downforce, or ground effect, which was banned by the fia in 1983 (though it was later brought back for the 2022 season onwards).
the 2009 brawn bgp001, using a 'double diffuser' (to harness downforce) which was banned by the fia in 2011.
#f1#alex albon#carlos sainz#charles leclerc#fernando alonso#formula one#george russell#lance stroll#lando norris#lewis hamilton#formula 1#f1 2024#imola 2024#imolagp#italy 2024#logan sargeant#oscar piastri#sebastian vettel#jenson button#kimi raikkonen#kimi räikkönen#mercedes f1#ferrari#mclaren#aston martin#mark webber
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
Whispers and Melodies
Part 1 Part 2

Summary: She has heard a deep melodic voice speaking to her from a far away place for decades. Anything from snippets of a longer conversation to roars that shook the very earth she walked on.
Rating: T (for now)
Pairing: Rhysand x Reader

A cup of tea sat cooling on the window sill of a small cottage on the outskirts of the Day Court. The quaint home overlooked a large river delta with roiling waters whose waves flowed into an ocean only a stone's throw away. Inside the cottage sat a girl gazing into the night sky while she forgot all of the day's troubles.
The healer had spent the entire day tending to patients from the village near her cottage. It was a quaint town whose community was close-knit and small. It had taken the townspeople a while to grow accustomed to her but as the years had come and gone, they had opened up to each other. Her skills as a healer also aided in this endeavor. But despite how much she enjoyed her dealings with the townspeople, her favorite part of her job was the research that it allowed. At the end of a hard day of treating her patients, she could lock herself up in her office and lose herself in the formulas and ratios she tested in her compounds.
Y/N padded over to her small kitchen, mug in hand, and placed it into her sink before walking toward her research room and locking the door behind her.
She always thought of her research room as a safe haven. The vials full of various substances that she had been testing littered her desk along with her carefully taken notes about the contents and phase changes of each substance on her log book. Her most recent project had been to synthesize some type of blood clotting or replenishing potion that would allow her to administer it to a patient who was more likely to die of blood loss before she even had the chance to solve any of their injuries. A potion like this would allow her ample time to stitch up any wound or brew some other cure for poisons and the like.
Her current issue consisted of not being able to stabilize the potion for long-term storage. The fennel root and crushed carrowfish shell she’d added seemed to be slowly decomposing each other which made the potion essentially useless after more than 4 days of storage. The trials she was running right now attempted to add some honey which slowed the reaction process as well as introduced some antimicrobial properties to the potion.
Y/N quickly jotted down the physical changes in appearance and consistency of each of the test tubes with varying amounts of honey. Each testing glass contained more honey than the last. Whichever combination yielded the best preservation and overall effectiveness is the ratio that she would begin perfecting.
Y/N stayed in her laboratory until she felt her eyes begin to strain and her feet start to ache. She carefully placed all of her measuring tools and weights back onto her working table before she exited the room and made her way to the front door of her cottage. She undid all 3 locks and tugged the large oak door open with both her hands.
In the distance, she saw a figure. A male it seemed; lying on the ground as the ocean lapped at his skin and crusted it in dried salt. The setting sun gleamed against him and warmed his pale skin in a sheen of gold that she thought suited him much more than the sickly pallor he seemed to have. Most people tended to steer clear of her section of the beach out of some deeply engrained paranoia of outsiders. But this male seemed to have missed that particular message.
Rhysand had known he had been fooled the moment he stepped into the ballroom on that fateful day. Amaranth had promised a ball in celebration of the many alliances she had made as well as an apology to those she had wronged. Rhysand had gone to the ball purely for formalities' sake. He had always loathed these types of false pretenses that the upper echelon of fae had always insisted on perpetuating. Nonetheless, he had dragged himself out of his court that afternoon and appeared at this ball. His own cowardice to refuse Amarantha’s invitation had resulted in 50 years of extortion, rape, and violence that despite his centuries of experience, he could not seem to shake the black cloud that it had cast over him.
Feyre being his mate was not something he had seen coming nor was it something he wanted. Tamlin would treat her well, she cared for all of his people and he would care for Feyre Rhys was sure. Despite his freedom, Rhysand could not bring himself to go to his home in Velaris. His family was likely waiting for him to return but they would all know exactly what had happened to him as soon as he stepped in the door. He did not wish to deal with their horrified faces and pitying looks once they found out. So instead, he wandered.
He wandered around lands both Night Court and Day. He walked and flew so far that he ended up somewhere on a coastline. Rhys has no idea where he had landed but he didn't seem to care that he was likely lost. So as the sun set, he continued a slow walk along the cliffside coast and eventually down onto the sandy beaches. The sun sunk further into the horizon leaving only the gleaming light of a cottage in the far-off distance. As Rhys drew closer, he noticed a crop garden with some vegetables and herbs growing on the plot off to the side of the house and a water well located up a hill. Rhysand was tired. He was tired of walking, of flying, of breathing even. He just wanted to rest. He wanted to sleep on a soft bed and not have to think about anything at all, not be worried that one wrong move would result in the death of everyone he had ever loved. So he made his way closer to the cottage before sitting on the wet sand closest to the water and stretching out his long legs. The water lapped at his feet and calves, almost as if it was slowly pulling away all the tension that wound itself in his legs. He stared out at the ocean for what seemed like an eternity. Rhysand got lost in the repetitive movements of the water and the slowly setting sun in the distance casting beautiful colors on the waters and sand.
When he eventually woke up from what felt like an eternity of slumber, he was not nestled in the sand as he had expected. Instead, he was cushioned underneath with quilts and pillows, and on top of him lay thick blankets to combat the morning chill that often accompanied this time of the year. The room itself looked lived in, to say the least. Canvas’ and embroidery projects were pinned to the wall in various positions. Everything from people to landscaping were inscribed into the wall. Pages that appeared to be ripped out of books with certain lines underlined also adorned the cedarwood walls. The entire room smelled of something woody and calm that Rhysand couldn't quite a place. He stretched up from his lying position and slowly removed the layers of quilts and blankets from him. His legs felt sore and ached from the hours of walking he had done the day before. He tried to stretch his wing muscles but they also ached from their overuse. He hadn't flown in decades, yet he had taken to the sky’s as soon as he could as if he had never left the great blue expanse. He now felt his lack of practice as he tried to rotate his shoulders and ease the aches that had rooted themselves in his back.
A shuffle from outside the door had Rhysand snapping his neck towards the door. He slowly lifted himself off the bed, careful to make sure none of the wooden beams snapped. He paced towards the door and stuck his ear against the wood grain to listen for any further movements. He was listening to the slicing of metal that would indicate a weapon the characteristic heavy footfalls that usually indicated a warrior of some capacity. Instead, he heard sharp cutting noises blunted by a wooden board, the shuffle of lithe feet, and the soft humming of a female.
Hello everyone! It has been too long! So many things have happened in the last months and I can't wait to get back into the groove of posting multiple-part stories.
#acotar#acotar fanfiction#acotar fic#acotar imagine#acotar series#rhysand x reader#rhysand#rhys acotar#rhys x reader#feyre archeron#a court of thorns and roses#rhysand x you#rhysand x y/n#rhysand x oc#night court#velaris#a court of mist and fury#a court of silver flames#a court of wings and ruin#morocco#Spotify#azriel acotar#cassian#feyre acotar#fae folk#acomaf#acowar#acosf#acofas#a court of frost and starlight
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
Raising the Minimum Wage and Its Effects
Ko-fi prompt from [name redacted]:
So, what does raising the minimum wage really do to the rest of the economy?
Hecking Complicated! I think I might need a doc of just. References for this one. But here are a few elements!
(Also, the Congressional Budget Office has an interactive model of how different changes to the minimum wage could affect various parts of the economy, like poverty rates and overall employment. Try it out!)
Reduction of Benefits
A common claim that is used to argue against the minimum wage is that it will result in companies cutting hours for their employees in order to recoup losses by having to provide benefits to fewer employees. This isn't 'the minimum wage is bad' so much as 'corporations are assholes,' but it is unfortunately still a thing that happens. (Harvard Business Review)
This is not a problem with the minimum wage itself, in my opinion, but these issues are emblematic of the weight that self-serving elements of capitalism carry. The low minimum wage is just one part of many that contribute to the current wealth disparity; if things like health insurance were universal, then bosses wouldn't be as able to cut them to employees in order to save money. Current regulations incentivize companies to hire more part-time workers than full-time, in order to avoid paying out benefits. Some cities have enacted Fair Workweek Laws in order to combat these approaches, though the impact is as of yet uncertain (Economic Policy Institute, 2018). Early reports, like the Year Two Worker Impact Report on Seattle’s Secure Scheduling Ordinance, do seem to indicate positive results, though:
In addition, the SSO led to increases in job satisfaction and workers’ overall well-being and financial security. In particular, the Secure Scheduling Ordinance had the following impacts for Seattle workers: - increased work schedule stability and predictability - increased job satisfaction and satisfaction with work schedules - increased overall happiness and sleep quality, and reduced material hardship. (direct quote from the Year Two Eval)
Unfortunately, these were approved at the earliest in 2015 (San Francisco's Formula Retail Employee Rights Ordinances, which went into effect in March 2016), which means that none of them were in play for longer than five years before COVID-19 ground the planet's economy to a near halt. I tried to find results for the San Francisco laws, but I couldn't find any studies for it; I did find an article from March 2023 that summarized which cities in California have brought in fair workweek laws, though, so maybe someone could use that as a jumping off point (What Retailers Should Know About California Scheduling Ordinances).
Companies prevented from cutting benefits by cutting hours would probably find another way to do the same thing, but let's be real: keeping the minimum wage low won't stop them from cutting every corner possible. EPI has some articles, like "The role of local government in protecting workers’ rights," that talk about how these measures can be, and have been, implemented to protect workers from cost-cutting employers.
Cutting the hours and benefits of part-time employees is a real, genuine concern to have about raising the minimum wage, and those need to be anticipated and combated in concert with raising the minimum wage. However, it is not a reason to keep the minimum wage depressed. It's just a consequence to be aware of and plan for.
Passing Costs On To Customers
A common argument against raising the minimum wage is that companies will raise costs in order to cover the raise in expenses, to a degree that nullifies the wage hike. This is, um. Uh.
Really easily debunked?
Like, really easily.
Over a ten-plus year period, research found that a 10 percent increase in the minimum wage resulted in just a 0.36 percent increase in prices passed on to the consumer at grocery stores. A similar Seattle-based study showed that supermarket food prices were not impacted by their minimum wage increase. - (Minimum Wage is Not Enough, Drexel U.)
I've talked about it before, but in some cases it's just a matter of how US-based labor is such a comparatively small portion of costs for medium-to-large businesses that raising wages doesn't raise corporate expenditures that much.
That said, some companies rely on drastically underpaying their employees, like Walmart. Walmart's revenue in 2020 was approximately $520 billion (Walmart Annual Report, page 29). Now, this report doesn't actually tell us what amount is spent on labor, but it does give us the "Operating, selling, general and administrative expenses, as a percentage of net sales." This is, to quote BDC, "[including] rent and utilities, marketing and advertising, sales and accounting, management and administrative salaries."
So, wages are just part of the (checks) 20.9% of revenue that is operating SG&A expenses. But maybe I'm being mean to Walmart! After all, the gross profit margin is only 24.1%, so only 3.2% is left for those poor shareholders!
Oh, oh, that means the profit is still over 16billion USD? And Walmart cites having 2.2 million associates in that same report? And that's about $7,500 per employee per year that's being withheld? And that's before we take costs up by like three cents per product?
Which, circling back: A study from Berkeley by the name of "The Pass-Through of Minimum Wages into US Retail Prices: Evidence from Supermarket Scanner Data" found that
a 10% minimum wage hike translates into a 0.36% increase in the prices of grocery products. This magnitude is consistent with a full pass-through of cost increases into consumer prices.
Of course, Walmart does sell more than just groceries, but isn't it interesting that raising a minimum wage resulted in such a small cost increase? If we assume this is linear (it's probably not, but I have so many numbers going on already), then doubling wages from 7.25 to 14.50 would still mean only a 3.6% increase costs! Your $5 gallon of milk would go up to [checks] $5.18.
Hm. Those 18 cents might be meaningful to our poorest citizens, but if those poorest citizens are more likely to be raised out of poverty by raising the minimum wage, then it might just be the case that they too can afford the new price of milk, and have more money left over for things like... rent. Or education. Or healthcare.
Maybe even a cost cutting loss leader like Walmart can reasonably increase its wages. After all, they still have 13 stores on Long Island, where the minimum wage is $15, and has been since 2021.
(I could have just cited the Berkeley study and moved on, but after a certain point I was too deep in parsing the Walmart report to not include it.)
But also... minimum wage increases are often staggered. They start out on the bigger companies, which have the resources to accommodate those changes (unless they've been doing stock buybacks), and then later on the smaller businesses, now that a portion of the economy (those working for the big companies) has the spare change to spend money at those smaller businesses that are raising their prices by a little more than the corporations.
And at that point, all I can really say is, well.
If you can't afford to pay your employees a living wage, you're not an oppressed company. You're just a failing company. Sorry, Walmart&Co, your business model is predicated on fucking over poor people, and so it's a bad business model.
Being a dickhead, while successful, is not actually 'smart' business practice.
(This doesn't even get into the international impacts, like what an "American companies should pay higher wages abroad, especially if they charge higher-than-American pricing for their products, but also at factories where we know they're committing human rights abuses" approach could be but this is already long as fuck so that'll have to wait for another post.)
Anyway.
Inflation
This one is tied into the cost argument above, but like...
Inflation is already a thing? Inflation is happening whether we raise the minimum wage or not. Costs go up whether we raise the minimum wage or not. Who is this argument serving? Not the people who can't afford rent, surely.
Quoting the earlier-mentioned Drexel report (red highlights mine):
While the minimum wage has been adjusted numerous times since its implementation in 1938, it has failed to keep up with inflation and the rising cost of living. The purchasing power of minimum wage reached its peak in 1968 and steadily declined since. If it had kept up with inflation from that point it would have reached at least $10.45 in 2019. Instead, its real value continues to go down, meaning minimum wage employees are essentially being paid less each year. Additionally, some economists argue if minimum wage increased with U.S. productivity over the years, it would be set currently at $26 per hour today and poverty rates would be close to non-existent with little negative impact on the economy. However, because gradual change was avoided, the extra funds were instead shifted to CEO compensation. A sudden change in wages now could possibly make a more noticeable impact on the economy, which is often cited as reasoning for a slower increase over time moving forward. Gradual increases with inflation and productivity could have avoided any potential economic ripple effects from wage increases and should be considered in ongoing plans.
Increasing Unemployment
A common argument is that the unemployment rate would jump as employers were forced to let employees go. Assuming they didn't just hire more employees so they could give them less hours in order to cut benefits... not really!
A 2021 article from Berkeley News summarizes the issue, along with several others, covering some thirty years of research that started with "Minimum Wages and Employment: A Case Study of the Fast-Food Industry in New Jersey and Pennsylvania," published in 1993. They also touch on the issue of subminimum wages for tipped workers, though they do not address the subminimum wages set for underage and disabled workers.
“A minimum wage increase doesn’t kill jobs,” said Reich, chair of UC Berkeley’s Center on Wage and Employment Dynamics (CWED) . “It kills job vacancies, not jobs. The higher wage makes it easier to recruit workers and retain them. Turnover rates go down. Other research shows that those workers are likely to be a little more productive, as well.” - Berkeley News article, "Even in small businesses, minimum wage hikes don’t cause job losses, study finds"
Lower turnover rates also save money for employers, as it causes them to have much lower HR expenses. How much money do you think large employers spend on using sites like Indeed or Glassdoor to find new employees?
This article from Richmond Fed does, admittedly, encourage a slightly grayer analysis:
In a 2021 review of some of the literature, [researchers] reported that 55.4 percent of the papers that they examined found employment effects that were negative and significant. They argued that the literature provides particularly compelling evidence for negative employment effects of an increased minimum wage for teens, young adults, the less educated, and the directly affected workers. On the other hand, in a 2021 Journal of Economic Perspectives article that analyzed the effect of the minimum wage on teens ages 16-19, Alan Manning of the London School of Economics and Political Science wrote that although the wage effect was sizable and robust, the employment effect was neither as easy to find nor consistent across estimations. Thus, although the literature supports an effect on employment among the most affected workers, it does not appear to be as sizable as theory might suggest.
The International Labor Organization has a similarly mixed result when taking a variety of studies into account. (I left in their own reference links.)
In high-income countries, a comprehensive reviews of about 70 studies, shows that estimates range between large negative employment effects to small positive effects. But the most frequent finding is that employment effects are close to zero and too small to be observable in aggregate employment or unemployment statistics (1). Similar conclusions emerge from meta-studies (quantitative studies of studies) in the United States (2), the United Kingdom (3), and in developed economies in general (4). Other reviews conclude that employment effects are less benign and that minimum wages reduce employment opportunities for less-skilled workers (5).
And there's the 60-page "Impacts of minimum wages: review of the international evidence" from University of Massachusetts Amherst, which looks at data from both the US and UK. I'll admit I didn't read this one beyond the introduction, because this is very long already.
Not all US studies suggest small employment effects, and there are notable counter examples. However, the weight of the evidence suggests the employment effects are modest. Moreover, recent research has helped reconcile some of the divergent findings. Much of this divergence concerns how different methods handle economic shocks that affected states differently in the 1980s and early 1990s, a period with relatively little state-level variation in minimum wages.
I'd encourage you to think of it this way:
Employer A pays $7.25/hr. Employer B also pays $7.25/hr. An employee works 25hrs/week for Employer A, and 20hr/wk for Employer B. The minimum wage goes up to $15/hr. Employer B cuts the employee. Employer A cuts employees as well, but not this one, and instead increases their hours to 30/wk for greater coverage.
The employee has gone from just under $400/wk to $450/wk. They lost a job, sure, but the end result... They have an extra fifteen hours of free time per week! Or more! With time to level out, you have less jobs, but more employment, because people aren't taking up multiple jobs (that someone else could have) just to survive.
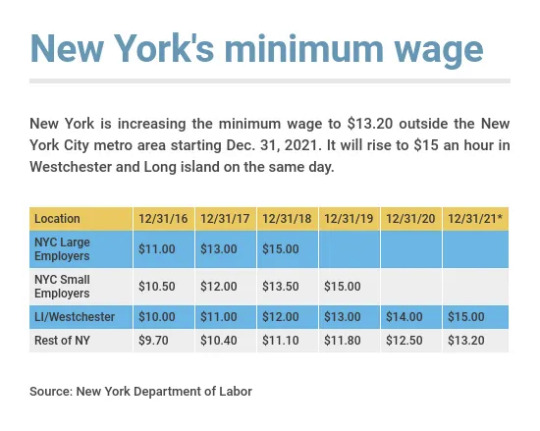
This is a very, very simplified example, which doesn't take into account graduated wage increases (see the NYS labor table) or the benefits issue from before, but it does show the reality that "less jobs" doesn't necessarily mean "less pay" or "fewer employed" people, when so many of those employed at this pay are working multiple jobs.
Even the Washington Post agrees that the wage hike wouldn't cost as many jobs as conventional wisdom claims, and they're owned by Bezos. (Though I recognize the name of the article's author as the same person behind that 60-page Amherst report, so there's that to consider.)
The Kellogg Institute also points out that individual workers were, on average, more productive after receiving the pay increase, so the drop in the bottom line was softened. This is a bit debatable; the results varied based on the level of monitoring, but it's worth noting that most minimum wage jobs are pretty high-intensity, high-monitoring. Goodness knows you don't get a whole lot of time to yourself outside of the critical eye of your shift lead or customers if you're working fast food. They also note a decrease in profits, but I'd point out that they speak specifically of profits, not share of revenue.
To explain the difference: imagine you sell $100 of product in a day. The product cost you $50. Overhead (rent, utilities, taxes) cost you $10. Labor cost you $15. Profit, then, was $25, or $25.
A 16% reduction in the profit does not mean you now retain $11. It means that you retain 16% less of the $25. You now retain $21.
(This is, as with many of my examples, INCREDIBLY simplified, but I need to illustrate what the article's talking about, and I don't have infographics.)
Some other articles on the topic are from The Quarterly Journal of Economics, Business for a Fair Wage, The Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco (more critical), the Center on Wage and Employment Dynamics, the Center for Economic and Policy Research, UCLA Anderson, Vox, and The Intelligencer, which cites another Berkeley article. I do not claim to have read all of these, especially the really long ones, but the links are there if you want to look into them.
In the interest of showing research from groups that do not serve my own political views, I'm going to link an article from the Cato Institute; I do encourage you to read that one with a grain of salt, given that it's written by a libertarian thinktank, and they are just as dedicated to hunting for research that serves their political views as I am. There were a few other libertarian articles I came across, but the way they presented information kept feeling really duplicitous so I just... am not linking those, or the leftist ones I am also uncomfortable with due to the whole "I'm totally not tricking you" vibes. Also eventually I just got tired, there are so many articles on this and I am just one blogger who is not actually working for a magazine or thinktank, I am working for my own personal tumblr.
Negatively Impacting Slightly-Higher Paid Employees
Did you know that raising the minimum wage affects more than just those making minimum? It affects those just above as well. It's referred to as the ripple effect of minimum wage hikes by this Brookings article. They estimate that a wage hike would affect nearly 30% of the country's workforce.
"Price adjustments provide the principal adjustment mechanism for minimum wage increases: higher labor costs are passed through to consumers, mainly for food consumed away from home. Such an increase does not deter restaurant customers. Price increases are also detectable for grocery stores (Leung 2018; Renkin, Montialoux and Siegenthaler 2019), but not more generally. The effect on inflation is therefore extremely small." - "Likely Effects of a $15 Federal Minimum Wage by 2024," Testimony prepared for presentation at the hearing of the House Education and Labor Committee, Washington, DC (2019)
This overlaps with general criticisms of widening income equality, citing an AEA article I cannot access since it's behind a paywall. I wonder if it touches on companies like Amazon being headquartered in the city and manipulating the job market by sheer size? I can only speculate.
Plus, there are the health benefits! Which are mostly connected to lessening poverty, and through that lessening stress and increasing healthcare access, but still! Some of these results are debated, but I'd need to know more about the details to know how they're related (University of Washington).
------
I've spent most of the day on this, so if you guys have made it this far and are interested in supporting me, please donate to my ko-fi or commission an article. (Preferably for more than the base price; I'm effectively working at a fraction of minimum wage myself, which is ironic considering the theme of this post.)
(I realistically shouldn't have spent more than two or three hours on this, but I have so many strong opinions on the subject that I couldn't stop.)
(Also: There were so many more sources I didn't even get to read the basic premise of because it was so repetitive after a while.)
#economics#stock market#capitalism#phoenix talks#ko fi#ko fi prompts#minimum wage#minimum wage increase#research
206 notes
·
View notes
Text
YET ANOTHER KAIJU FILM REC LIST
(Selected and arranged to account for modern tastes, as well as to highlight specific wants for fans of Godzilla: Minus One and/or Godzilla x Kong: The New Empire)
Notes:
Titles can be confusing, when in doubt differentiate films by year of release
"Showa" generally refers to films made from 1954-1980, while "Heisei" generally refers to films made from 1984-2006, with "Millennium" being a specific series of Godzilla films made from 1999-2004, within the Heisei era (the actual notation refers to the Japanese Emperor, but this is slightly offset with how it's used for kaiju films)
I've tried to list where the films can be watched, for free if possible, but this can change at a moment's notice (for instance, the TokuSHOUTsu Youtube channel currently has a livestream of almost all the Showa Godzilla films and one for the MST3K episodes featuring 6 Showa Gamera films and Gorgo, but I have no idea how long those will stay up)
More context and history about the kaiju film genre can be found at the end of the post
GROUP 1: EVERYONE
These films are the peers and equals of Minus One and GxK, in only the best respects.

The Gamera Heisei Trilogy - Gamera: Guardian of the Universe (1995), Gamera 2: Attack/Advent of Legion (1996), and Gamera 3: Revenge/Awakening of Iris (1999)
I would recommend this trilogy to ANYONE - even those hesitant to watch anything that isn't CGI, or that still don't think kaiju films can be good cinema. No matter what you're looking for in a kaiju film - engaging monster action, compelling human drama, deep metaphorical significance, fun action-adventure, hard sci-fi, spiritual eastern fantasy - these three movies are bound to be among the best at it. They're nearly unanimously praised as some of the best kaiju films of all time, and are the ONLY classic films with that honor that can visually compete with modern tastes in special effects.
Among the three: Guardian of the Universe is probably the closest analog to GxK, a fun action-adventure film about a girl who communicates with a giant monster. Revenge of Iris is closer to Minus One, introducing a darker mirror of the first film's story that invokes trauma and loss to great emotional impact. Which all leaves Advent of Legion in the middle, as a fairly formulaic but well-executed sci-fi alien invasion story.
These films are available free and subtitled on Tubi, or free and dubbed on Pluto. In a rarity, the dubs are done with love and care by fans of the genre and while they may not be the best way to watch the films, they're fairly decent.
GROUP 2: MODERN/NICHE
These films either excellently or acceptably compete with modern visual effects, but in other areas, are ultimately more dependent upon viewer tolerances and niche interests.

Godzilla vs. Destoroyah (1995)
If you want to cry about Godzilla, this is it, this is the movie. Possibly the classic film that delves the deepest into the idea of kaiju as sympathetic, tragic beings, this film leans heavily into hard sci-fi and features a kaiju opponent inspired by the titular creature from the Alien franchise. It's the seventh film in the Godzilla Heisei series, but as most of the previous films are currently stuck behind rights issues and difficult to find, I'd recommend jumping into this one as a standalone (or, if anything, watch the original 1954 Godzilla film first, but if that doesn't interest you it's not necessary). This movie is readily available for free, subtitled on Pluto or dubbed on Youtube.
The Kiryu Duology - Godzilla Against Mechagodzilla (2002) and Godzilla: Tokyo S.O.S. (2003)
These two films face a number of pacing and production issues, and due to scheduling conflicts, the main heroine, mech pilot Akane from the first film (arguably one of the most compelling human characters in the entire Godzilla series), was unable to return for the sequel beyond a brief cameo. But despite feeling unfinished, not all the emotional weight of this duology is lost. The ethics-focused, techno-spiritual story being told still packs a punch, and visually, out of the entire suitmation era this is the best Godzilla, Mothra, and Mechagodzilla have ever looked on-screen. If first checking out the original 1954 Godzilla and the 1961 Mothra interests you at all, it may enhance the viewing experience, but if not, dive right in! Both these films are free on Pluto TV, but do keep in mind Against Mechagodzilla is the dubbed version.
Gamera the Brave (2006)
I've said it before, but this is the movie that most closely reminds me of Minus One, with its modern filmmaking style, deep emotional themes, and in particular, having a bright and hopeful appeal to humanity in a genre where many of the more serious films are tragedies. Personally I rank this one right up there with the 90s Gamera trilogy, if not even higher, but to appreciate it, you really do have to be here for a children's fantasy film with more charm and heart than fast-paced kaiju action. This film is free on Tubi, subtitled.
GROUP 3: CLASSIC
These films require a tolerance for the special effects of the 1950s through 1970s, which I realize some modern audiences may find difficult to appreciate, but are otherwise highly recommended.
All four of these films are available free and subtitled on Pluto through Criterion, and are additionally part of SHOUT! Factory's catalogue and playing on the livestream.

Godzilla (1954)
If you've seem Minus One or Shin Godzilla, the obvious route is, of course, to go back to 1954 and experience the original cinematic masterpiece of Godzilla as a nuclear horror. The one caveat I'll mention is that a lot of Minus One's effectiveness is in subverting one theme present in the original, so this will, in a way, feel like a step backward thematically.
Ebirah, Horror of the Deep (1966)
The outright most comparable classic film to GxK - a fun island adventure film wherein various entertaining personalities are shipwrecked and must work together to thwart human baddies and even recruit the help of Godzilla! This is one of my personal favorites, and while Mothra only appears briefly in the film, it expands on her lore quite a bit.
Godzilla vs. Hedorah (1971)
This film is wacky, resembling an abstract art house film at times, but in many ways is a revisitation upon the dark, deep metaphors of the original, this time warning of the dangers of pollution through a truly terrifying monstrosity that gives Godzilla one of the most brutal fights of his career.
Terror of Mechagodzilla (1975)
Along with the original and Hedorah, this completes a trio of more dark and serious Showa era Godzilla films. It's the only Godzilla movie of its era to be written entirely (not co-written) by a woman, tells a dark and tragic tale, and yet is the height of 1970s superhero Godzilla as he takes on two powerful opponents at once.
GROUP 4: GRAB BAG
I'll throw in four more: these are just some of my personal recommendations and favorites that don't fit neatly into the other categories.

Ghidorah, the Three-Headed Monster (1964)
The original and archetypical "multiple monsters team up to fight a greater threat" movie. This one is consistently on the edge of being called an objectively good film, but can be considered too cheesy and campy to make the cut. Nonetheless, it's a fun time, and it's also pretty much the only classic film where Godzilla and Mothra interact positively, if that's appealing to you. Like the other Showa Godzilla films, it's free through Pluto and SHOUT! Factory.
Gamera vs. Zigra (1971)
I really just wanted to put a Showa Gamera here, and this is one of my favorites. Just the campy, wacky, good time that is Showa Gamera, with a side of ocean theming - this extremely cheap film was partly funded through Kamogawa Sea World, which is the primary location featured in the film. It's free on Tubi along with the other Gamera films, and also makes a great MST3K episode, even if the version of the film used there is very low-resolution and the underwater scenes in particular suffer a little.
Godzilla 2000: Millennium (1999)
Somewhat unique among its contemporaries for being a 2000s era film that features Godzilla as more-or-less the protagonist, with human characters that advocate for understanding and respecting him. It's an incredibly cinematic film - I would describe its special effects as ambitious, not always effective, but regardless it would be a great intro for new fans if it were more accessible. Currently, it's tough to track down, but another rare case where the heavily-edited US dubbed version is perfectly acceptable, and even sometimes considered superior to the original.
Rebirth of Mothra 3 (1998) and to an extent, the whole trilogy.
I unashamedly love these oft-maligned films that are actually very comparable to the Heisei Gamera trilogy... in all respects but objective quality. Fun fantasy kaiju films featuring tiny women who fight each other with swords and flying mounts, while a superpowered giant moth beats up two space dragons and takes a break in the middle to beat up a genetically-engineered dragon. Lots of rainbows and lasers, and a vague, underlying exploration of the conflict between those with peaceful methods and those with violent methods without completely villainizing either side. If any of that sounds interesting, check these films out, they're currently readily available free on Pluto after a long history of the third and most serious/mature film being extremely rare and seldom-seen.
FURTHER NOTES AND CONTEXT:
Inspired by western giant monster films like King Kong and The Beast from 20,000 Fathoms, and the summation of Japan's nuclear fear and trauma, the original Godzilla film in 1954 was a runaway success, beginning the kaiju genre as production company Toho ordered not only a direct sequel, but a broad scope of special effects films that ultimately gave us other classic kaiju like Mothra and Rodan.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the concept of a "Godzilla series" did not yet exist - Toho just made science fiction films, wherein some of them featured kaiju, and some of those, but not all, featured Godzilla. Many of these films were very loosely, and sometimes only retroactively, considered to be in the same universe or cinematic canon, creating situations where kaiju like Manda and Baragon would wander into Godzilla films after getting their start in non-Godzilla adventures like Atragon (1963) and Frankenstein vs. Baragon (1965). (An example of a non-kaiju Toho film I would highly recommend is 1958's H-Man)
The 1960s also saw a "Kaiju Boom," where the genre was expanded beyond Toho to other studios in Japan and even to other countries. This brought about a number of new kaiju projects like Gorgo (1961), Reptilicus (1961), and Yongary, Monster from the Deep (1967). The only of these films to be successful enough to spawn a series was Gamera (1965), from Daiei studios in Japan, and there were 7 Gamera films made from the mid-60s to early 70s. (Daiei has their own catalogue of Toku effects films, and also produced the kaiju-adjacent Daimajin trilogy (1966), period pieces set in ancient Japan about a giant warrior statue that comes to life)
Interest in kaiju films began to wane in the 1970s, and Toho largely narrowed its focus to a yearly Godzilla series with lower and lower budgeting. Godzilla vs. Megalon (1973) was the most cheeply-made of these, but several factors made it the most widely-known film in the US and solidified the genre's "rubber suits and cardboard buildings" reputation among the general public for the next 50 years. Also in 1973, Toho produced the giant hero television series Zone Fighter, where Godzilla, King Ghidorah, and Gigan appear in several episodes. The series was made to compete with Ultraman and other television-based Tokusatsu, which was swaying audiences away from films at the time. (I personally know very little about Ultraman and other costumed hero Toku, but I know there are many experts on here who could answer questions about those)
Toho continued to make science fiction and effects films throughout the late 70s and 1980s, such as The War in Space (1977), but kaiju films were out of fashion. Gamera had a brief pseudo-revival in 1980, but otherwise it was a long drought from 1975 to 1984, when Toho began the Godzilla Heisei series: a series of seven films that continued in 1989 and picked up to a film per yer from 1991 to 1995. These films featured more strict continuity and the recurring character of Miki Saegusa, marking one of the first steps away from the previous practice of switching out the human cast entirely from film to film.
In the late 90s, Godzilla was absent yet again, as Toho made the rights handoff to Sony for the 1998 American film. In his place were the competing late 90s Gamera and Mothra trilogies, both relatively unique in featuring multiple recurring cast members and worlds that blended sci-fi and fantasy elements. In America, the poorly-received GODZILLA (1998) spawned a more warmly-recieved animated continuation in Godzilla: the Series (1998-2000).
In response to the critical failure of the 1998 film, Toho craved redemption and launched the Millennium Series: six Godzilla films that, with the exception of the Kiryu Duology, were all standalone in hopes of attaining theatrical releases in the US (only Godzilla 2000 succeeded at this). With a general failure of the 50th anniversary film Godzilla: Final Wars (2004), Toho put Godzilla to rest, seemingly for good. Gamera the Brave in 2006 was the last true suitmation kaiju film, critically acclaimed but also a financial failure.
In the intervening decade, CGI took over, and was the name of the game by the time Pacific Rim (2013), Godzilla (2014), and Shin Godzilla (2016) kicked off the new "Kaiju Renaissance," the present era that includes Reiwa Godzilla and the Monsterverse.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Chapter XIV. Summary and Conclusion
It has been said of Newton, to express the immensity of his discoveries, that he has revealed the abyss of human ignorance.
There is no Newton here, and no one can claim in economics a part equal to that which posterity assigns to this great man in the science of the universe. But I dare to say that there is here more than Newton has ever guessed. The depth of the heavens does not equal the depth of our intelligence, within which wonderful systems move. It looks like a new, unknown region that exists outside space and time, like the heavenly realms and infernal abodes, and on which our eyes plunge, with silent admiration, as in a bottomless abyss.
Non secùs ac si quâ penitùs vi terra dehiscens
Infernas reseret sedes et regna recludat
Pallida, Dis invisa, superque immane barathrum
Cernatur, trepidentque immisso lumine Manes.
Virgil. Aeneid. lib. viii.[51]
Here the throng, collision, swing of eternal forces; there the mysteries of Providence are revealed, and the secrets of fate appear uncovered. It is the invisible making itself visible, the intangible rendered material, the idea becoming reality, and reality a thousand times more wonderful, more grandiose than the most fantastic utopias. So far we do not see, in its simple formula, the unity of that vast machine: the synthesis of these gigantic gears, in which the well-being and misery of generations are ground, and which are shaping a new creation, still evades us. But we already know that nothing that happens in social economy has a copy in nature; we are forced to constantly invent special names, to create a new language, for facts without analogues. It is a transcendent world, whose principles are superior to geometry and algebra, whose powers derive neither from attraction nor from any physical force, but which use geometry and algebra as subordinate instruments, and takes as material the very powers of nature; a world finally freed from the categories of time, space, generation, life and death, where everything seems both eternal and phenomenal, simultaneous and successive, limited and unlimited, ponderable and imponderable… What more can I say? It is even creation, caught, so to speak, in the act!
And this world, which appears to us as a fable, which inverts our judicial habits, and never ceases to deny our reason; this world which envelops us, penetrates us, agitates us, without us even seeing it in any other way than the mind’s eye, touching it only by signs, this strange world is society, it is us!
Who has seen monopoly and competition, except by their effects, that is, by their signs? Who has felt credit and property? What is collective force, division of labour and value? And yet, what is stronger, more certain, more intelligible, more real than all that? Look in the distance at this carriage drawn by eight horses on a beaten field, and driven by a man dressed in a old smock: it is only a mass of matter, moved on four wheels by an animal form. You discover there, in appearance, only a phenomenon of mechanics, determined by a phenomenon of physiology, beyond which you perceive nothing more. Penetrate further: ask this man what he does, where he goes; by what thought, what title, he drives this vehicle. And presently he will show you a letter, his authority, his providence, as he himself is the providence of his equipment. You will read in this letter that he is a carter, that it is in this capacity that he carries out the transportation of a certain quantity of merchandise, so much according upon the weight and distance; that he must carry out his journey by such a route and within such a time, barely covering the cost of his service; that this service implies on the part of the carter the responsibility for the losses and damages that result from other causes than force majeure and an inherent defect of the objects; that the price of the vehicle includes or not includes insurance against unforeseen accidents, and a thousand other details which are the hazard of the law and the torment of jurists. This man, I say, in a piece of paper as big as the hand, will reveal to you an infinite order, an inconceivable mixture of empiricism and pure reason, and that all the genius of man, assisted by the experience of the universe, would have been powerless to discover, if man has not left individual existence to enter collective life.
Indeed, these ideas of work, value, exchange, traffic, responsibility, property, solidarity, association, etc., where are the architypes? who provided the exemplars? what is this world half material, half intelligible; half necessity, half fiction? What is this force, called work, which carries us along with ever greater certainty that we believe we are more free? Which of our joys and torments does this collective life, which burns us with an inextinguishable flame, cause? As long as we live, we are, without our being aware of it, and according to the extent of our faculties and the speciality of our industry, the thinking springs, thinking wheels, thinking gears, thinking weights, etc., of an immense machine that thinks and goes by itself. Science, we said, is based on the accord of reason and experience; but it creates neither one nor the other. And here, on the contrary, a science appears to us, in which nothing is given to us, a priori, neither by experience nor by reason; a science in which humanity draws everything from itself, noumenon[52] and phenomena, universals and categories, facts and ideas; a science, finally, which instead of simply consisting, like any other science, of a reasoned description of reality, is the very creation of reality and reason!
Thus the author of economic reason is man; the creator of economic matter is man; the architect of the economic system is again man. After having produced reason and social experience, humanity proceeds to the construction of social science in the same way as for the construction of the natural sciences; it brings together in agreement the reason and the experience it has given itself, and by the most inconceivable marvel, when everything in it takes after utopia, principles and actions, it only comes to know itself by excluding utopia.
Socialism is right in protesting against political economy and saying to it: You are nothing but a routine that does not understand itself. And political economy is right to say to socialism: you are only a utopia without reality or possible application. But both denying in turn, socialism the experience of humanity, political economy the reason of humanity, both lack the essential conditions of human truth.
Social science is the agreement of reason and social practice. Now, this science, of which our masters have only seen rare sparks, will be given to our century to contemplate it in its sublime splendour and harmony!
But what am I doing? Alas! It is a question, at this moment when quackery and prejudice share the world, of raising our hopes. It is not incredulity that we have to fight, it is presumption. Let us start by noting that social science is not finished, that it is still in a state of vague premonition.
“Malthus,” says his excellent biographer, M. Charles Comte, “had the profound conviction that there exists in political economy principles which are true only insofar as they are contained within certain limits; he saw the main difficulties of the science in the frequent combination of complicated causes, in the action and reaction of effects and causes with each other, and in the necessity of setting limits or making exception for many important proposals.”
This is what Malthus thought of political economy, and the work we have published at this moment is only a demonstration of his idea. To this testimony we add another just as worthy of belief. In one of the final sessions of the Academy of Moral Sciences, M. Dunoyer, as a truly superior man, who does not allow himself to be dazzled either by the interest of a clique, nor by the disdain that inspires ignorant opponents, made the same confession with as much candour and nobility as Malthus.
“Political economy, which has a number of certain principles, which rests on a considerable mass of exact facts and well deduced observations, nevertheless seems far from being a set science. There is no complete agreement on the extent of the field in which its research should be extended, nor on the fundamental object which it must suggest. It is not suitable for all the work it embraces, nor the means to which the power of its work is linked, nor the precise meaning to be attached to most of the words that form its vocabulary. The science, rich in truths of detail, leaves a great deal to be desired as a whole, and as a science it still seems far from being constituted.”
M. Rossi goes further than M. Dunoyer: he formulated his judgement in the form of a reprimand addressed to the modern representatives of the science.
“Every thought of method now seemed abandoned in economics,” he cries, “and yet there is no science without method.” (Compte-rendu par M. Rossi du cours de M. Whateley [Report by M. Rossi of M. Whateley’s course])
Messrs. Blanqui, Wolowski, Chevalier, everyone who has glanced every so briefly on the economy of societies speaks the same. And the writer who best appreciates the value of modern utopias, Pierre Leroux, writes on every page of the Revue sociale [Social Review]: “let us seek the solution of the problem of the proletariat; let us keep looking for it until we find it. It is the entire work of our epoch!...” Now, the problem of the proletariat is the constitution of social science. There are only short-sighed economists and fanatical socialists, for whom the science is summed up entirely in a formula, Laissez faire, laisses passer, or else, To each according to his needs as far as social resources allow, who boast of possessing economic science.
What then causes this delay of social truth, which alone maintains the disappointment of the economist and gives credit to the operations of the alleged reformers? The cause, in our opinion, is the separation, already very old, of philosophy and political economy.
Philosophy, that is to say metaphysics, or if it is preferred, logic, is the algebra of society; political economy is the realisation of this algebra. This was not noticed by J.B. Say, nor Bentham, no anyone else who, under the names of economists and utilitarians, created a split in morals and rose against almost at the same time politics and philosophy. And yet, what more secure control can philosophy, the theory of reason, wish for than work, that is, the practice of reason? And conversely, what more certain control could economic science wish than the formulas of philosophy? It is my dearest hope, that the time is not far when the masters in the moral and political sciences will be in the workshops and [behind] counters, as today our most skilful builders are all men formed by a long and arduous apprenticeship…
But on what condition can there be a science?
On the condition of recognising its field of observation and its limits, to determine its object, to organise its method. On this point the economist expresses himself as the philosopher: the words of M. Dunoyer, recounted earlier, seem literally taken from the preface of Jouffroy to the translation of Reid.
The field of observation of philosophy is the self [le moi]; the field of observation of economics is society, that is to say again the self. Do you want to know man, study society; do you want to know society, study man. Man and society reciprocally serve each other as subjects and objects; the parallelism, the synonymy of the two sciences is complete.
But what is this collective and individual self? What is this field of observation, where strange phenomena are going on? To find out, let us look at the analogues.
All the things we think seem to exist, to succeed one another or to be in three transcendent CAPABILITIES, outside of which we can only imagine and conceive absolutely nothing: these are space, time and intelligence.
Just as every material object is conceived by us necessarily in space; just as phenomena, connected with each other by a relationship of causality, seem to follow each other in time; thus our purely abstract representations are recorded by us to a particular receptacle, which we call intellect or intelligence.
Intelligence is in its species an infinite capacity, like space and eternity. There are restless worlds, of numberless organisms with complicated laws, with varied and unexpected effects; equal, for magnificence and harmony, to the worlds sown by the creator through space, to the organisms that shine and die out over time. Politics and political economy, jurisprudence, philosophy, theology, poetry, languages, customs, literature, fine arts: the field of observation of the self is more vast, more fecund, more rich in itself than the double field of observation of nature, space and time.
The self, as well as time and space, is infinite. Man, and what is the product of man, together with the beings thrown through space and the phenomena that follow one another in time, constitutes the triple manifestation of God. These three infinites, indefinite expressions of infinity, penetrate each other and support one another, inseparable and irreducible: space or scale not being conceived without movement, which implies the idea of force, this is to say a spontaneity, a self.
The ideas of things which are presented to us in space form for our imagination tableaus; the ideas which we place objects in time unfold in histories; finally, ideas or relations which do not fall under the category of time or space, and which belong to the intellect, are co-ordinated in systems.
Tableau, history, system, are thus three analogous expressions, or rather equivalents, by which we make known that a certain number of ideas appear to our mind as a symmetrical and perfect whole. That is why these expressions may, in certain cases, be taken for each other, as we have pursued from the beginning of this work, when we presented it as a history of political economy, no longer according to the date of the discoveries, but according to the order of the theories.
We conceive then, and we cannot not conceive of a capacity for things of pure thought, or, as Kant says, for noumena, in the same way that we conceive two others for sense things, for phenomena.
But space and time are nothing real; they are two forms imprinted on the self by external perception. Similarly intelligence is also nothing real: it is a form that the self imposes on itself, by analogy, in the context of the ideas that experience suggests to it.
As for the order of acquisition of ideas, intuitions or images, it seems to us that we start with those whose types or realities are included in space; that we continue by stopping, so to speak, the flight of ideas that time carries, and that we finally discover, with the help of sense perceptions, the ideas or concepts, without external model, which appear to us in this ghost capacity we call our intelligence. Such is the progress of our knowledge: we start from the sense to rise to the abstract; the ladder of our reason has its foot on the earth, crosses the sky and is lost in the depths of the mind.
Let us now reverse this series, and we envision creation as a descent of ideas from the higher sphere of intelligence into the lower spheres of time and space, a fall during which the ideas, originally pure, have taken a body of substratum that realises them and expresses them. From this point of view all created things, the phenomena of nature and the manifestations of humanity, will appear to us as a projection of the mind, immaterial and immutable, on a plane sometimes fixed and straight, space, sometimes inclined and moving, time.
It follows from this that ideas, equal to each other, contemporaneous and co-ordinated in the mind, seem thrown haphazardly, scattered, localised, subordinate and consecutive in humanity and in nature, forming tableaus and histories without resemblance to the original design [dessin primitif]; and all human science consists in finding this conception the abstract system of eternal thought. It is by a restoration of this kind that naturalists have found systems of organised and unorganised beings; it is by the same process that we have tried to re-establish the series of phases of social economy, which society makes us see isolated, incoherent, anarchic. The subject we have untaken is really the natural history of work, according to the fragments collected by the economists; and the system which has resulted from our analysis is true in the same way as the systems of plants discovered by Linné and Jussieu, and the system of animals by Cuvier.
The human self manifested by work is thus the field for the exploration of political economy, a concrete form of philosophy. The identity of these two sciences, or rather these two scepticisms, has been revealed to us throughout the course of this book. Thus the formation of ideas appeared to us in the division of labour as a division of elementary categories; then, we have seen freedom being born from the action of man upon nature, and, following freedom, arise all the relations of man with society and with himself. As a result, economics has been for us at the same time an ontology, a logic, a psychology, a theology, a politics, an aesthetics, a symbolism and a morality…
The field of science recognised, and its operation delimited, we had to recognise its method. Now, the method of economic science is still the same as that of philosophy: the organisation of work, we believe, is nothing but the organisation of common sense…
Among the laws that make up this organisation we have noticed the antinomy.
All true thought, as we have observed, arises in one time and two moments. Each of these moments being the negation of the other, and both of which must disappear only within a superior idea, it follows that antinomy is the very law of life and progress, the principle of perpetual motion. Indeed, if a thing, by virtue of the power of evolution which is in it, is repaired precisely of all that it loses, it follows that this thing is indestructible, and that movement supports it forever. In social economy, what competition is constantly occupied making, monopoly is constantly occupied unmaking; what labour produces, consumption devours; what property appropriates to itself, society gets a hold of: and from this results continuous movement, the unwavering life of humanity. If one of the two antagonistic forces is hindered, [so] that individual activity, for example, succumbs to social authority, organisation degenerates into communism and ends in nothingness. If, on the contrary, individual initiative lacks a counterweight, the collective organism is corrupted, and civilisation crawls under a regime of castes, iniquity and misery.
Antinomy is the principle of attraction and of movement, the reason for equilibrium: it is that which produces passion, and which breaks down all harmony and all accord…
Then comes the law of progression and series, the melody of beings, the law of the beautiful and the sublime. Remove the antinomy, the progress of beings is inexplicable: for where is the force that would produce this progress? Remove the series, the world is no more than a melee of sterile oppositions, a universal turmoil, without purpose and without an idea…
Even if these speculations, for us pure truth, appear doubtful, the application we have made of them would still be of immense utility. Let us think about it: there is not a single moment in life where the same man does not affirm and deny the same principles and theories at the same time, with more or less good faith, no doubt, but also always with plausible reasons, which, without soothing the conscience, suffice to make passion triumph and spread doubt in the mind. Let us leave, if you want, logic: but is it nothing to have illuminated the double face of things, to have learned to be wary of reasoning, of knowing how, the more a man has fairness in ideas and righteousness in the heart, the more he runs the risk of being a dupe and absurd? All our political, religious, economic, etc. misunderstandings come from the inherent contradiction of things; and this is even the source from which flow the corruption of principles, the venality of consciences, the charlatanism of professions of faith, the hypocrisy of opinions…
What is, at present, the object of economics?
The method itself tell us. Antinomy is the principle of attraction and balance in nature; antinomy is therefore the principle of progress and equilibrium in humanity, and the object of economic science is JUSTICE.
Considered in its purely objective relations, the only ones which social economy deals with, justice is expressed in value. Now, what is value? It is the labour performed.
“The real price of everything,” says Mr Smith, “what everything really costs to the man who wants to acquire it, is the toil and trouble of acquiring it… What is bought with money or with goods is purchased by labour as much as what we acquire by the toil of our own body. That money or those goods indeed save us this toil. They contain the value of a certain quantity of labour which we exchange for what is supposed at the time to contain the value of an equal quantity. Labour was the first price, the original purchase-money that was paid for all things. It was not by gold or by silver, but by labour, that all the wealth of the world was originally purchased; and its value, to those who possess it, and who want to exchange it for some new productions, is precisely equal to the quantity of labour which it can enable them to purchase or command.”[53]
But if value is the embodiment of labour, it is at the same time the principle of the comparison of products with one another: hence the theory of proportionality which dominates all economic science, and to which A. Smith would have raised, if it had been in the spirit of his time to pursue, with the aid of logic, a system of experiments.
But how is justice manifested in society, in other words, how is proportionality of values established? Say said it: by an oscillatory movement between value in utility and value in exchange.
Here appears in political economy, with regard to work, its master and all too often its executioner, the arbitral principle.
At the outset of the science, work, devoid of method, without understanding of value, barely stammering its first attempts, appeals to free will to build wealth and set the price of things. From this moment two powers enter into struggle, and the great work of social organisation is inaugurated. For work and free will is what we will later call labour and capital, wage-labour and privilege, competition and monopoly, community and property, plebe and nobility, state and citizen, association and individualism. For anyone who has obtained the first notions of logic, it is obvious that all these oppositions, eternally reborn, must be eternally resolved: now, that is what the economists do not want to hear, to whom the arbitral principle inherent in value seems resistant to all determination; and it is, with the horror of philosophy, what causes the retardation, so fatal to society, of economic science.
“It would be as absurd,” says [John Ramsay] McCulloch, “to speak of absolute height and depth as of absolute value.”
Economists all say the same thing, and we can judge by this example how far they are from each other, and on the nature of value, and on the meaning of the words they use. The absolute expression carries with it the idea of wholeness, perfection, or plenitude, on the basis of precision and accuracy. An absolute majority is a true majority (half plus one), it is not an indefinite majority. In the same way absolute value is the precise value, deduced from the exact comparison of products together: there is nothing in the world so simple. But the consequence of this critical effect is that since values measure one another, they must not oscillate at random: such is the supreme wish of society, such is the significance of political economy itself, which is nothing else, in its totality, but the picture of the contradictions whose synthesis infallibly produces true value.
Thus society is gradually established by a sort of swinging between necessity and arbitrariness, and justice is constituted by theft. Equality does not occur within society as an inflexible standard; it is, like all the great laws of nature, an abstract point, which oscillates continually above and below, through arcs more of less large, more or less regular. Equality is the supreme law of society; but it is not a fixed form, it is the average of an infinity of equations. That is how equality appeared to us from the first epoch of economic evolution, the division of labour; and such has been constantly manifested from the legislation of Providence.
Adam Smith, who had a kind of intuition on almost all the great problems of social economy, after having recognised labour as the principle of value and described the magical effects of the law of division, observes that, notwithstanding the increase of the produce resulting from this division, the wages of the worker do not increase; that often, on the contrary, they diminish, the gains of collective force not going to the worker, but to the master.
“The profits of stock, it may perhaps be thought are only a different name for the wages of a particular sort of labour, the labour of inspection and direction. They are, however, altogether different, are regulated by quite different principles, and bear no proportion to the quantity, the hardship, or the ingenuity of this supposed labour of inspection and direction. They are regulated altogether by the value of the stock employed, and are greater or smaller in proportion to the extent of this stock... In this state of things, the whole produce of labour does not always belong to the labourer. He must in most cases share it with the owner.”[54]
That, A. Smith tells us coldly, is how things happen: everything for the master, nothing for the worker. Whether we call it injustice, plunder, theft, the economist is not moved. The robber proprietor seems to him in all this as an automaton as the worker is robbed. And the proof that they deserve neither envy nor pity is that the workers only demand when they are dying of hunger; it is that no capitalist, entrepreneur or proprietor, neither during life nor at the moment of death, has felt the slightest remorse. They accuse ignorant and distorted public consciousness; they may be right, they may be wrong. A. Smith limits himself to reporting the facts, which is much better for us that declamations.
So by designating amongst workers a select [privilégié], nazarœum inter fratres tuos, social reason personified collective force. Society proceeds by myths and allegories. The history of civilisation is a vast symbolism. Homer summarises heroic Greece; Jesus Christ is suffering humanity, striving with effort, in a long and painful agony, to freedom, to justice, to virtue. Charlemagne is the feudal type; Roland, chivalry; Peter the Hermit, the crusades; Gregory VII, the papacy; Napoleon, the French Revolution. In the same way the industrial entrepreneur, who exploits a capital by a group of workers, is the personification of the collective force whose profit he absorbs, as the flywheel of a machine stores force. This is really the heroic man, the king of work. Political economy is a whole symbolism, property is a religion.
Let is follow A. Smith, whose luminous ideas, scattered in an obscure clutter, seem a repetition [deutérose] of primitive revelation.
“As soon as the land of any country has all become private property, the landlords, like all other men, love to reap where they never sowed, and demand a rent even for its natural produce. The wood of the forest, the grass of the field, and all the natural fruits of the earth, which, when land was in common, cost the labourer only the trouble of gathering them, come, even to him, to have an additional price fixed upon them. He must then pay for the licence to gather them; and must give up to the landlord a portion of what his labour either collects or produces [without him].”[55]
Here is monopoly, here is interest on capital, here is [economic] rent! A. Smith, like all the enlightened, sees and does not understand; he recounts and has not the intelligence. He speaks under the inspiration of God without surprise and without pity; and the meaning of his words remain for him a closed letter. With what calm he recounts proprietor usurpation! As long as the land seems good for nothing, as long as labour has not loosened, fertilised, utilised, created VALUE [mise en VALEUR], property gives it no thought. The hornet does not alight on the flowers, it falls upon the hives. What the worker produces is immediately taken; the worker is like a hunting dog in the master’s hand.
A slave, exhausted from work, invents the plough. With a hardened wooden hook dragged by a horse, he opens the ground, rendering him capable of making ten times, a hundred times more. The master, at a glance, grasps the importance of the discovery: he seizes the land, he appropriates the revenue, he attributes the idea to himself, and makes himself adored by the mortals for this magnificent gift. He walks the equal of the gods: his wife is a nymph, Ceres; and he is Triptolemus. Poverty invents, and property reaps. For genius must remain poor: abundance would smother it. The greatest service that property has rendered to the world is this perpetual affliction of labour and genius.
But what to do with these heaps of grain? What a poor wealth [is] that which the boss shares with his horses, his oxen and his slaves! It is well worth being rich, if all the advantage consists of being able to gnaw a few more handfuls of rice and barley!...
An old woman, having pounded grain for her toothless mouth, realises that the dough soured, fermented, and cooked under the ashes, gives a food incomparably better than raw or grilled wheat. Miracle! The daily bread is discovered. – Another, having pressing into a jar a mass of dropped grapes, intends to boil the mash on the flame; the liquor spews out its impurities; it gleams, ruddy, bountiful, immortal. Evoe! it is the young Bacchus, the darling son of the proprietor, a child beloved of the gods, who has found it. What the master could not have devoured in a few weeks, a year will suffice for him to drink. The vine, like the harvest, like the earth, is appropriated.
What is to be done with these countless fleeces that each year provides such a large tribute? When the proprietor would raise his bed to be worthy of his pavilion, when he would duplicate thirty times his sumptuous tent, this useless luxury would do nothing but attest his impotence. He abounds in goods and he cannot enjoy; what a mockery!
A shepherdess, left naked by the avarice of the master, collects from the bushes some wool fibres. She twisted this wool, stretching it into equal and fine threads, gathering them on a spear, crisscrossing them, and making herself a soft and light dress, a thousand times more elegant than the patched skins that cover his scornful mistress. It is Arachne, the weaver, who created this marvel! Immediately the master begins to shear the hair of his sheep, his camels and his goats; he gives his wife a troop of slaves, who spin and weave under his orders. It is no longer Arachne, the humble servant; it is Pallas, the daughter of the proprietor, whom the gods have inspired, and whose jealously avenges itself on Arachne by causing her to die of hunger.
What a sight this incessant struggle of labour and privilege, the first created everything out of nothing; the other always arriving to devour what it has not produced! – It is because the destiny of man is a continuous march. It is necessary that he work, that he create, multiply, perfect forever and forever. Let the worker enjoy his discovery; he falls asleep on his idea: his intelligence no longer advances. This is the secret of this iniquity which struck A. Smith, and against which, however, the unemotional historian did not find a word of reprobation. He felt, although he could not realise it, that the touch of God was there; that until the day when labour fills the earth, civilisation is driven by unproductive consumption, and that it is by rapine that fraternity is gradually established between men.
Man must work! That is why at the advice of Providence, theft was instituted, organised, sanctified! If the proprietor had tired of taking it, the proletarian would have soon be tired of producing, and savagery, hideous misery, was at the door. The Polynesian, amongst whom property has been aborted, and who enjoys in an entire community of property and love, why would he work? The earth and beauty are for everyone, children to anyone: what do you say to him about morals, dignity, personality, philosophy, progress? And without going so far, the Corsican, who is found for six months living and residing under his chestnut tree, why do you want him to work? What does he care for your conscription, your railways, your tribune, your press? What else does he need but to sleep when he has eaten his chestnuts? A prefect of Corsica said that to civilise this island it was necessary to chop down the chestnut trees. A more certain way is to appropriate them.
But already the proprietor is no longer strong enough to devour the substance of the worker: he calls his favourites, his jesters, his lieutenants, his accomplices. It is again Smith who reveals this wonderful conspiracy.
“In the progress of the manufacture, not only the number of profits increase, but every subsequent profit is greater than the foregoing; because the capital from which it is derived must always be greater. In raising the price of commodities the rise of wages operates in the same manner as simple interest does in the accumulation of debt. The rise of profit operates like compound interest. If in the linen manufacture, for example, the wages of the different working people, the flax-dressers, the spinners, the weavers, etc., should, all of them, be advanced two-pence a day; it would be necessary to heighten the price of a piece of linen only by a number of two-pences equal to the number of people that had been employed about it, multiplied by the number of days during which they had been so employed. That part of the price of the commodity which resolved itself into wages would, through all the different stages of the manufacture, rise only in arithmetical proportion to this rise of wages. But if the profits of all the different employers of those working people should be raised five per cent, that part of the price of the commodity which resolved itself into profit would, through all the different stages of the manufacture, rise in geometrical proportion to this rise of profit. The employer of the flaxdressers would in selling his flax require an additional five per cent upon the whole value of the materials and wages which he advanced to his workmen. The employer of the spinners would require an additional five per cent both upon the advanced price of the flax and upon the wages of the spinners. And the employer of the weavers would require a like five per cent both upon the advanced price of the linen yarn and upon the wages of the weavers.”[56]
This vivid description of the economic hierarchy, starting with the Jupiter-proprietor, and ending with the slave. From labour, its division, the distinction of the master and the wage-worker, the monopoly of capital, arises a caste of landlords, financiers, entrepreneurs, bourgeois, masters and supervisors, labouring to consume rents, to collect usury, to squeeze the worker, and above all to exercise policing [d’exercer la police[57]], the most terrible form of exploitation and misery. The invention of politics and laws is exclusively due to property: Numa and Egeria, Tarquin and Tanaquil, as well as Napoleon and Charlemagne, were noble. Regum tirnendorum in proprios greges, regel in ipsos irnperium est lavis, says Horace. One would say a legion of infernal spirits, rushing from every corner of hell to torment a poor soul. Pull him by his chain, take away his sleep and food; beat, burn, torture, without rest, without pity! For if the worker were spared, if we did him justice, nothing would remain for us, and we would perish.
O God! what crime has this unfortunate man committed, that you abandon him to the guards who distribute blows to him with such a liberal hand, and subsistence with a hand so miserly? … And you, proprietors, Providence’s chosen rulers, do not go beyond the prescribed measure, because rage is rising in the heart of your servant, and his eyes are red with blood.
A revolt of the workers wrings a concession from the pitiless masters. Happy day, deep joy! Work is free. But what freedom, for heaven’s sake! Freedom for the proletarian is the ability to work, that is, of being robbed again; or not to work, that is to say to die to hunger! Freedom only benefits strength: by competition, capital crushes labour everywhere and converts industry into a vast coalition of monopolies. For the second time, the plebeian worker is on her knees before the aristocracy; she has neither the possibility, nor even the right to discuss her salary.
“Masters,” says the oracle, “are always and everywhere in a sort of tacit, but constant and uniform league, not to raise wages above their existing rate. To violate this rule is an act of a false-friend. And by abhorrent legislation, this league is tolerated, while the coalitions of workers are severely punished.”[58]
And why this new iniquity, which the unalterable serenity of Smith could not help declaring abhorrent? Would such a crying injustice have been even necessary and that, without this favouritism [acception de personnes], fate would have been in error and Providence thwarted? Will we find means of justifying, with monopoly, this partial policing of the human race?
Why not, if we want to rise above societal sentimentalism, and consider higher facts, the force of things, the intimate law of civilisation?
What is labour? What is privilege?
Labour, analogous to creative activity, without awareness of itself, indeterminate, barren, as long as the idea, the law does not penetrate, labour is the crucible where value is elaborated, the great matrix of civilisation, the passive or female principle of society. – Privilege, emanating from free will, is the electric spark that determines individualisation, the freedom that realises, the authority that commands, the mind that deliberates, the self that governs.
The relation of labour and privilege is thus a relation of the female to the male, of the wife to the husband. Amongst all peoples, the adultery of the woman has always seemed more reprehensible than that of the man; it was consequently subjected to more rigorous penalties. Those who, stopping at the atrocity of forms, forget the principle and see only the barbarism exercised towards the sex, are politicisers of romances worthy of appearing in the stories of the author of Lélia. Any indiscipline of workers is comparable to adultery committed by woman. Is it not obvious then that, if the same favour on the part of the courts were to accept the complaint of the worker and that of the master, the hierarchical link, outside which humanity cannot live, would be broken, and the entire economy of society ruined?
Judge moreover by the facts. Compare the physiognomy of a workers’ strike with the march of a coalition of entrepreneurs. There, distrust of the proper law, agitation, turbulence, outside screaming and trembling, inside terror, spirit of submission and desire for peace. Here, on the contrary, calculated resolution, feeling of strength, certainty of success, calmness in execution. Where, in your opinion, is power? where is the organic principle? where is life? Without doubt society owes assistance and protection to all: I do not plead here the cause of the oppressors of humanity; may the vengeance of heaven crush them! But the education of the proletarian must be accomplished. The proletarian is Hercules arriving at immortality through work and virtue: but what would Hercules do without the persecution of Eurystheus?
Who are you? asked Pope Saint Leo of Attila, when this destroyer of nations came to set his camp before Rome.
“I am the scourge of God,” replied the barbarian. “We receive with gratitude,” continued the pope, “all that comes from God: but you, take care not to do anything that is not commanded of you!”
Proprietors, who are you?...
Weirdest thing, property, attacked on all sides in the name of charity, of justice, of social economy, has never known how to respond for its justification other than these words: I am because I am. I am the negation of society, the plundering of the worker, the right of the unproductive, the right of the strongest [la raison du plus fort], and none can live if I do not devour him.
This appalling enigma has made the most sagacious intelligences despair.
“In that original state of things, which precedes both the appropriation of land and the accumulation of stock, the whole produce of labour belongs to the labourer. He has neither landlord nor master to share with him. Had this state continued, the wages of labour would have augmented with all those improvements in its productive powers, to which the division of labour gives occasion. [...] They would have been produced by a smaller quantity of labour [...] they would have been purchased likewise with the produce of a smaller quantity.”[59]
So says A. Smith. And his commentator adds:
“I can well understand how the right of appropriating, under the name of interest, profit or rent, the product of other individuals becomes nourishment for greed; but I cannot imagine that by diminishing the reward of the worker to add to the opulence of the idle man, we can increase industry or accelerate the progress of society in wealth.”[60]
The reason for this deduction, which neither Smith nor his commentator has seen, we will repeat, so that the inexorable law that governs human society is again and for the last time brought to light.
To divide labour is to make only a production of pieces: for there to be value, a composition is needed. Before the institution of property, each is a master to take from the ocean the water from which he draws salt for his food, to gather the olive from which he will extract his oil, to collect the ore which contains iron and gold. Each is free to exchange some of what he has collected against an equivalent quantity of provisions made by another: so far, we do not go beyond the sacred right of work and the community of the earth. Now, if I have the right to use, either by my personal labour or by exchange, all the products of nature; and if the possession thus obtained is entirely legitimate, I have the same right to combine, from the various elements which I obtain by labour and exchange, a new product, which is my property, and which I have the right to enjoy exclusively of any other. I can, for example, by means of the salt from which I extract soda, and the oil I draw from the olive and sesame, to make a specific composition to clean linen, and which will be for me, from the point of view of cleanliness and hygiene, a precious utility. I can even reserve for myself the secret of this composition, and consequently take, by means of exchange, a legitimate profit.
Now, what is the difference, under relation of right, between the manufacture of an ounce of soap and that of a million kilograms? Does the greater or lesser quantity change anything of the morality of the operation? So property, as well as commerce, as well as labour, is a natural right, of whose exercise nothing in the world can steal from me.
But, by the very fact that I compose a product which is my exclusive property, as well as the materials that constitute it, it follows that a workshop, an exploitation of men is organised by me; that profits accumulate in my hands to the detriment of all who enter into business relations with me; and that if you wish to substitute yourself for me in my enterprise, quite naturally I will stipulate for myself a rent. You will possess my secret, you will manufacture in my place, you will turn my mill, you will reap my field, you will pick my vine, but at a quarter, a third, or half share.
All this is a necessary and indissoluble chain; there is no serpent or devil here; it is the very law of the thing, the dictum of common sense. In commerce, plundering is identical to exchange; and what is really surprising is that a regime like this one does not excuse itself only by the good faith of the parties, it is commanded by justice.
A man buys from his neighbour the collier a sack of coal, from the grocer a quantity of sulphur from Etna. He makes a mixture to which he adds a portion of saltpetre, sold by the druggist. From all this results an explosive powder, of which a hundred pounds would suffice to wreck a citadel. Now, I ask, the woodcutter who charred the wood, the Sicilian shepherd who picked up the sulphur, the sailor who transported it, the commission agent from Marseilles who reshipped it, the merchant who sold it, are they complicit in the disaster? Is there any interdependence [solidarité] between them, I’m not saying in its use, but in the manufacture of this powder?
Now, if it is impossible to discover the least connection of action between the various individuals who, each without his knowledge, have co-operated in the production of the powder, it is clear, for the same reason, that there is no more connection and interdependence [solidarité] between them as to the profits of the sale, and that the gain which may result from its use also belongs exclusively to the inventor, that the punishment, to which he might become liable for as a result of crime or imprudence, is personal to him. Property is identical to responsibility: we cannot affirm the one, without granting at the same time the other.
But admire the unreason of reason! The same property, legitimate, irreproachable in its origin, constitutes in its use a flagrant iniquity; and this, without adding any element which modifies it, but by the mere development of the principle.
Let us take as a whole the products that industry and agriculture bring to the market. These products, such as powder and soap, are all, to some degree, the result of a combination of materials which were drawn from the general store. The price of these products invariably consists, firstly of the wages paid to the different categories of workers, secondly, of the profits demanded by the entrepreneurs and capitalists. So that society is divided into two classes of people: 1) entrepreneurs, capitalists and proprietors, who have the monopoly of all objects of consumption; 2) employees or workers, who can offer only half of what these are worth, which makes their consumption, circulation and reproduction impossible.
Adam Smith tells us in vain:
“It is but equity, besides, that they who feed, clothe, and lodge the whole body of the people, should have such a share of the produce of their own labour as to be themselves tolerably well fed, clothed, and lodged.”[61]
How could this be achieved, except with the dispossession of the monopolists? And how can monopoly be prevented if it is a necessary effect of the free exercise of the industrial faculty? The justice that Adam Smith wants to establish is impractical in the regime of property. Now, if justice is impractical, if it becomes actual injustice, and if this contradiction is internal to the nature of things [intime à la nature des choses], what is the use of even speaking of equity and humanity? Does Providence know equity, or whether fate is philanthropic? It is not to destroy monopoly, any more than labour, which we must reach; it is, by a synthesis which the contradiction of monopoly renders inevitable, to make it produce in the interests of all the goods which it [currently] reserves for some. Outwith of this solution Providence remains insensitive to our tears; fate inflexibly follows its path; and while we, gravely seated, argue over the just and the unjust, God who has made us contradictory like himself in our thoughts, contradictory in our actions, answers us with a burst of laughter.
It is this essential contradiction of our ideas that, being realised by labour and expressing itself in society with a gigantic power, makes everything happen in the inverse direction of what it must be, and gives society the appearance of a tapestry seen in reverse or an inverted animal. Man, by the division of labour and by machinery, was to gradually rise to science and to liberty; and by division, by the machine he stupefies himself and becomes a slave. Tax, says the theory, must be as a result of wealth; and quite the contrary tax is because of poverty. The unproductive must obey, and by a bitter mockery the unproductive command. Credit, according to the etymology of its name, and according to its theoretical definition, is the provider of labour; in practice, it squeezes and kills it. Property, in the spirit of its most beautiful prerogative, is the extension of land; and in the exercise of this same prerogative, property is the prohibition of land. In all its categories political economy reproduces the contradiction and the religious idea. The life of man, affirms philosophy, is a perpetual emancipation from animality and nature, a struggle against God. In religious practice, life is the struggle of man against himself, the absolute submission of society to a superior Being. Love God with all your heart, the Gospel tells us, and hate your spirit [âme] for eternal life: precisely the opposite of what reason commands…
I will not push this summary further. Having reached the end of my journey, my ideas are pressing in such a multitude and vehemence, that already I would need a new book to recount what I have discovered, and that, in spite of the oratorical expedience, I see no other means of finishing than to stop abruptly. If I am not mistaken, the reader ought to be convinced at least of one thing, that social truth cannot be found either in utopia or in routine: that political economy is not the science of society, but contains, in itself, the materials of that science, in the same way that chaos before the creation contained the elements of the universe. The fact is that, to arrive at a definite organisation, which appears to be the destiny of the race on this planet, there is nothing left but to make a general equation of our contradictions.
But what will be the formula of this equation?
We already foresee that there should be a law of exchange, a theory of MUTUALITY, a system of guaranties which determines the old forms of our civil and commercial societies, and gives satisfaction to all the conditions of efficiency, progress and justice which the critics have pointed out; a society no longer merely conventional, but real, which makes of the subdivision of real estate a scientific instrument; that will abolish the servitude of the machines, and may prevent the coming of crises; that makes of competition a benefit, and of monopoly a pledge of security for all; which by the strength of its principles, instead of making credit of capital and protection of the State, puts capital and the State to work; which by the sincerity of exchange, creates a real solidarity among the nations; which without forbidding individual initiative, without prohibiting domestic economy, continuously restores to society the wealth which is diverted by appropriation; which by the ebb and flow of capital, assures political and industrial equality of the citizenry, and, through a vast system of public education, secures the equality of functions and the equivalence of aptitudes, by continuously raising their level; which through justice, well being and virtue, revives the human conscience, assures the harmony and the equality of the people; a society, in a word, which, being at the same time organisation and transition, escapes what has taken place, guarantees everything and compels nothing…
The theory of mutuality, or of mutuum, that is to say, the natural form of exchange, of which the most simple form is loan for consumption, is, from the point of view of the collective existence, the synthesis of the two ideas of property and of communism [communauté], a synthesis as old as the elements of which it is constituted, since it is nothing more than the return of society to its primitive custom, through the maze of inventions and of systems, the result of a meditation of six thousand years on the fundamental proposition that A equals A.
Everything today is making ready for this solemn restoration; everything proclaims that the reign of fiction has passed, and that society will return to the sincerity of its nature. Monopoly is inflated to world-wide proportions, but a monopoly which encompasses the world cannot remain exclusive; it must republicanise itself or be destroyed. Hypocrisy, venality, prostitution, theft, form the foundation of the public conscience; but, unless humanity learns to live upon what kills it, we must believe that justice and expiation approach....
Already socialism, feeling the error in its utopias, turns to realities and to facts, it laughs at itself in Paris, it discusses in Berlin, in Cologne, in Leipzig, in Breslau; it murmurs in England, it thunders on the other side of the ocean; it commits suicide in Poland, it tries to govern in Berne and in Lausanne. Socialism, in pervading the masses, has become entirely different: the people will not bother about the honour of schools; they ask for work, education, well being, equality; the system does not matter so much, provided that the result is obtained. But when the people want something and it is only a question of finding out how to obtain it, the discovery does not wait; prepare yourself to see the coming of the grand masquerade.
Let the priest finally get it his head that poverty is a sin, and that true virtue, that renders us worthy of eternal life, is to fight against religion and against God; – that the philosopher, lowering his pride, supercilium philosophicum, learns on his part that reason is society, and that to philosophise is to work with his hands; – that the artist may remember that he once descended from Olympus into Christ’s stable, and that from this stable, he rose suddenly to unknown splendours; that as well as Christianity, labour must regenerate it; – that the capitalist thinks that silver and gold are not true values; that by the sincerity of exchange all products amount to the same dignity, each producer will have in his house a mint [un hôtel des monnaies], and, as the fiction of the productivity of capital has plundered the worker, so organised labour will absorb capital; – that the proprietor knows that he is only the collector of society’s [economic] rents, and that if he could once, under the guise of war, put a prohibition on the soil, the proletarian can in his turn, by association, put a prohibition on harvesting, and make property expire in the void; – that the prince and his proud cortege, his soldiers, his judges, his councillors, his peers, and all the army of the unproductive, hasten to cry Thanks! to the agricultural and industrial worker [au laboureur et à l'industriel], because the organisation of labour is synonymous with the subordination of power, that it depends on the worker abandoning the unproductive to his indigence, and to destroy power in shame and hunger.
All these things will happen, not as unforeseen, unhoped novelties, a sudden effect of the passions of the people, or of the skill of a few men, but by the spontaneous return of society to an immemorial practice, momentarily abandoned, and rightly so…
Humanity, in its oscillatory march, turns incessantly upon itself: its progress is only the rejuvenation of its traditions; its systems, so opposite in appearance, always exhibit the same basis [fond], seen from different sides. Truth, in the movement of civilisation, always remains the same, always old and always new: religion, philosophy, science merely translate. And this is precisely what constitutes Providence and the infallibility of human reason; which ensures, in the very heart of progress, the immutability of our being; which renders society at once unalterable in its essence and irresistible in its revolutions; and which, continually extending perspective, always showing from afar the latest solution, establishes the authority of our mysterious premonitions.
Reflecting on these battles of humanity, I involuntarily recall that, in Christian symbolism, the militant Church must succeed on the final day a triumphant Church, and the system of social contradictions appears to me like a magic bridge, thrown over the river of oblivion.
#organization#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#anarchy#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment#solarpunk#anti colonialism#mutual aid#the system of economic contradictions#the philosophy of poverty#volume i#pierre-joseph proudhon#pierre joseph proudhon
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
⛔️Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews 2024: Comprehensive Analysis & Buy Guide |⚠️Weight Loss Supplement

🔥 Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Review 2024: Unlock Your Path to Effective Weight Loss 💊💪 | Buy Now!
#IkariaLeanBellyJuice #IkariaLeanBellyJuiceReview #IkariaLeanBellyJuiceSupplement #IkariaLeanBellyJuiceWeightLoss
🎥 Discover Ikaria Lean Belly Juice: Comprehensive Review and Insights!
Are you striving to eliminate stubborn fat and achieve your fitness goals? In this authoritative video, we present a comprehensive review of Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews, a top-tier weight loss supplement designed to support effective weight loss and enhance your overall well-being. This review will cover:
What Is Ikaria Lean Belly Juice?
How Does Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Work?
Benefits of Using Ikaria Lean Belly Juice
Key Ingredients in Ikaria Lean Belly Juice
How to Use Ikaria Lean Belly Juice
Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Where to Buy Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Safely
Money-Back Guarantee
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
🔍 What Is Ikaria Lean Belly Juice?
Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews is a cutting-edge health supplement formulated to support weight loss and enhance overall wellness. Inspired by the healthy lifestyles of Ikaria's residents—a Greek island renowned for its longevity—the juice blends natural ingredients designed to boost metabolism, reduce inflammation, and increase energy levels effectively. Manufactured in an FDA-registered and GMP-certified facility, Ikaria Lean Belly Juice ensures quality and safety for effective weight management.
✅ How Does Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Work?
Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews operates through multiple mechanisms to facilitate comprehensive weight loss support:
Boosted Metabolism
Enhanced Fat-Burning
Increased Energy Levels
Supports Digestion
Reduces Inflammation
📋 Key Ingredients in Ikaria Lean Belly Juice
The success of Ikaria Lean Belly Juice lies in its carefully selected natural ingredients. Each component is chosen for its unique health benefits, creating a balanced and potent formula:
Green Tea Extract
Garcinia Cambogia
Turmeric
Ginger Root
Lemon Juice
Maquiberry
Rhodiola
Haematococcus
Schisandra
Theobroma Cacao
Amla
These ingredients work synergistically to address multiple aspects of weight management and overall health, ensuring effective and sustainable weight loss.
🛒 Where to Buy Ikaria Lean Belly Juice?
Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews is exclusively available through the official website to ensure you receive genuine products, secure transactions, and reliable customer support. Here’s where you can purchase it:
✅ Benefits of Using Ikaria Lean Belly Juice
Enhances Weight Loss
Increases Energy Levels
Supports Digestion
Reduces Inflammation
Boosts Immune Function
⭐ Ikaria Lean Belly Juice User Experience
Results:
Users report noticeable fat loss, reduced appetite, and increased energy levels within weeks of consistent use.
Usage:
Take two capsules daily, preferably before meals, to maximize the supplement's benefits.
Side Effects:
Generally well-tolerated, with rare cases of mild digestive discomfort reported. As with any supplement, consult a healthcare professional before starting.
💵 Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Guarantee
Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews offers a 60-day money-back guarantee, allowing you to try the product risk-free. If you're not satisfied with the results, you can request a full refund within this period, providing peace of mind with your purchase.
🏁 Final Thoughts: A Trusted Weight Loss Supplement
In summary, Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews is an excellent choice for those seeking a safe and natural method to lose weight. Its clinically-proven ingredients deliver real results by boosting fat burning, controlling appetite, and increasing energy levels. If you're ready to embark on a healthier lifestyle, Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews is definitely worth trying.
🎥 Share This Video: https://youtu.be/LqTZZhmoLEY
🕒 Key Sections:
00:01 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Review Introduction
00:28 – What is Ikaria Lean Belly Juice?
00:34 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Official Website
00:58 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Ingredients
01:35 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Benefits
02:03 – How Does Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Work?
02:19 – Does Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Work?
02:55 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews – Conclusion
03:12 – Ikaria Lean Belly Juice 60-Day Money-Back Guarantee
🔍 Searches Related to Ikaria Lean Belly Juice:
ikaria lean belly juice, ikaria lean belly juice review, ikaria lean belly juice supplement, ikaria lean belly juice weight loss, ikaria lean belly juice ingredients, ikaria juice, ikaria lean belly juice reviews, ikaria lean belly juice customer review, ikaria lean belly juice where to buy, lean belly juice, lean belly juice review, lean belly juice reviews, lean belly juice ingredients, lean belly juice supplement, ikaria juice reviews, lean belly juice side effects
youtube
The post Ikaria Lean Belly Juice Reviews was first published on Wrestling Best Channel.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Achieve Your Dream Body with Mitolyn Weight Loss Formula
Why Pick Mitolyn?
Natural Weight Loss: Supports healthy fat burning without destructive synthetic compounds or outrageous eating regimens.

Expanded Essentialness: Express farewell to drowsiness and embrace consistent, supported energy.
Metabolic Lift: Empowers a quicker, more productive digestion to fuel your dynamic way of life.
With Mitolyn, you're not simply focusing on the side effects of low energy or difficult weight — you're tending to the main driver. By improving mitochondrial wellbeing, Mitolyn engages your body to work ideally, giving you the results you've been looking for.
Official Website:- https://wellhealthpoint.com/mitolyn/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/mitolyncanada/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/mitolyn.newzealand/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/mitolynaustralia/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/dentasmilepro.newzealand/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/dentasmilepro.unitedkingdom/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/glucopure.australia/
https://www.facebook.com/groups/glucopure.canada/
#mitolyn#mitolyn review#mitolyn reviews#mitolyn supplement#mitolyn weight loss#mitolyn 2024#mitolyn 2025#weight loss diet#health tips#healthcare#health insurance#health and wellness#health & fitness#health#healthy eating#healthy diet#healthy food#healthy relationships#metabolism
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Java Burn?

✅👉🏻Visit the Java Burn Official Website Here: 👇👇👇
### Discover Java Burn: Enhance Your Coffee Experience with Health Benefits
Java Burn represents an innovative supplement designed to elevate your daily coffee ritual while promoting better health. This flavorless, easily mixable powder is crafted to jumpstart metabolism, accelerate fat burning, and enhance overall energy levels and well-being. What distinguishes Java Burn is its use of natural ingredients that target the root causes of weight gain, offering a holistic approach to weight management. Free from GMOs, gluten, stimulants, fillers, and preservatives, Java Burn ensures a clean and healthy addition to your diet. Each ingredient undergoes rigorous testing by an independent third party, guaranteeing purity, potency, and quality in every serving.
Manufactured in the USA in an FDA-registered facility adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Java Burn maintains strict standards of safety and effectiveness. Packaged conveniently in jars containing 30 packets — a full month’s supply — it seamlessly integrates into your daily routine, simplifying your weight loss journey without the complexity of traditional regimens. You can enjoy your favorite coffee while actively working towards your health goals.
Java Burn’s versatile formula caters to individuals of all ages and genders, addressing diverse weight loss needs. Whether you’re a young adult, middle-aged, or elderly, Java Burn supports your efforts to shed unwanted pounds with its universal appeal. Its compatibility with coffee makes it an attractive option for those seeking a straightforward and enjoyable way to enhance their weight loss journey.
For those interested in trying Java Burn, comprehensive information and purchasing options are available on the official website. Ordering directly ensures authenticity and access to any special offers or guarantees from the manufacturer. Java Burn stands out as a promising solution to boost metabolism, burn fat, and enhance overall energy and well-being, making it a valuable addition to your daily routine and health regimen.
✅👉🏻Visit the Java Burn Official Website Here:👇👇👇
..
..
..
#JavaBurnReviews
#JavaBurnCoffeeReviews
#JavaBurnCustomerReviews
#JavaBurnWeightlossSupplementReviews
#JavaBurn #JavaBurnWeightloss
#JavaBurnOfficialWebsite
#JavaburnWhereToBuy
#javaburnjavaburnweightloss
#javaburnsideeffects
#javaburnbenefits
#javaburningredients
#javaburnreviews
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i wanna lose weight fast
Are you looking for the easiest way to lose weight fast? 🌿 Look no further! Our product is 100% all natural, making it a safe and effective option for your weight loss journey. 🌾 Not only is it vegetarian, but it is also non-GMO and gluten free, catering to various dietary preferences and restrictions. 🥦 With no added fillers, preservatives, artificial colors, or stimulants, you can trust that what you're putting into your body is clean and pure. 🌱 Each packet is manufactured right here in the USA in our state of the art FDA approved and GMP certified facility, ensuring the highest quality standards. 🏭 Make the healthy choice and start seeing results today! 💪

#i need to lose so much weight#i need to be weightless#i wanna lose weight#i wish i was weightless#i need to lose this weight#need to lose more weight#weight loss#fat burner#fat belly#burn fat#slim and sexy#lose weight fast#lose weight tips#lose weight at home#lose weight motivation#lose weight without exercise#weight loss diet#weight loss tips#calories
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding "The Last Chance Diet" – A Risky Approach to Weight Loss
Exploring the Effectiveness and Risks of The Last Chance Diet “The Last Chance Diet” is an extreme weight loss program from the 1970s that was based on the concept of a protein-sparing modified fast (PSMF). Developed by Dr. Robert Linn, this controversial diet promised rapid weight loss through extreme calorie restriction, primarily using a liquid formula made from animal by-products. While it…
#Balanced Diet#calorie restriction#dangerous diets#extreme diet#heart problems#muscle wasting#nutrient deficiency#Prolinn#protein-sparing modified fast#PSMF#Rapid Weight Loss#rebound weight gain#safe dieting#Sustainable Weight Loss#The Last Chance Diet#weight loss alternatives.#weight loss health risks
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://archive.is/M2UW1
Children Born During the War in Gaza Will Never Truly Escape It
Jan. 9, 2024, 5:01 a.m. ET
By Alice Rothchild
Dr. Rothchild is a retired obstetrician and gynecologist, an author, a filmmaker and a former assistant professor at Harvard Medical School.
After Israel began its invasion of Gaza shortly after Hamas’s attack on Oct. 7, Aya Khrais — a pregnant 26-year-old dentist, wife of a doctor and mother of a 2-year-old girl living in Gaza City — lost contact with the doctors and health services she needed for prenatal care and for managing her diabetes.
She and her family were forced to leave home and move five times to flee the constant bombings, sometimes trekking several miles on foot. When we spoke in early December, she was staying at her sister-in-law’s home in southern Gaza. Dr. Khrais was 32 weeks pregnant and sleeping on a thin mattress directly on the ground, sharing a house with 74 people from 11 families. They lacked water, adequate food, medications, electricity and the tools for basic hygiene.
For the past two months she has had no prenatal care and no vitamins and has not gained any weight. She found a private obstetrician on Dec. 10 who informed her that she had excess amniotic fluid and needed an immediate C-section. She found a private hospital with an opening on Jan. 16. The estimated cost will be $4,000; the family has lost all of its savings as well as its bombed-out home. She has no baby clothes, diapers or formula and no proper place for postpartum recovery. “I am really frightened,” she told me over WhatsApp.
Dr. Khrais’s account is far from uncommon. There are approximately 50,000 pregnant women in Gaza, all struggling with a lack of stable shelter, inadequate nutrition and polluted, salty water. Prenatal, postnatal and pediatric care are difficult to obtain. U.N. agencies have dispatched lifesaving medicines and equipment to Gaza but it’s not enough to meet the needs of the population. Extreme shortages of pain medications, antibiotics, seizure and diabetic medications and blood are common. According to the World Health Organization, of the more than 180 women delivering babies each day, 15 percent are likely to encounter complications and be unable to obtain appropriate obstetric and pediatric emergency services. All the while, the threat of injury or death from bombings and military action looms, as does unimaginable emotional trauma.
If these mothers and their children manage to survive the war, they will grapple with its effects for the rest of their lives. Health research into multiple areas of armed conflict (such as Syria, Afghanistan, Somalia and Kosovo) reveals that these kinds of conditions are linked to an increase in miscarriages, congenital abnormalities, stillbirths, preterm labor and maternal mortality. Other studies of armed conflict from 1945 to 2017 show that children exposed to war are more likely to suffer from poor living conditions and sanitation, and multigenerational poverty caused by the loss of educational and economic infrastructure...
11 notes
·
View notes