#dvt
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

📈 Take Your Investments to the Next Level with Doofy Ventures Token (DVT)! 🚀 Unlock practical applications, endless growth opportunities, and secure your financial future with DVT. Don't just hold a token — hold your future! 💼💰 🔗 Start your journey now at doofyventures.com
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Hustler One One"
#USMC#Marines#Sikorsky#CH-53#CH-53E#Super Stallion#heavy-lift helicopter#Helicopter#Military#aircraft#cargo aircraft#transport#troop transport#DVT#airport#Deer Valley#Helo#Chopper
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News From Israel
Israel's Good News Newsletter to 2nd Jun 24
In the 2nd Jun 24 edition of Israel’s good news, the highlights include:
Israeli doctors saved the Arab girl critically injured in Iran’s attack on Israel.
An Israeli dedicated his Mount Everest climb to an Oct 7 victim.
Israeli medical tech is in touch with patients physically and virtually.
An Israeli device is the first to unblock veins to treat DVT.
A kibbutz startup devastated on Oct 7 is eradicating diseases at an Israeli hospital.
Israeli electric mopeds deliver the goods in Europe, the UAE & South Africa.
Israel topped the medals table at the Jiu-Jitsu European Championships.
Golden ring discovery makes a full-circle connection between Jews and Jerusalem.
Read More: Good News From Israel

Israelis might not have the wisdom of King Solomon, but some of their inventions, innovations, and achievements are extremely clever. Israeli electronic sensors can restore the sense of touch to damaged nerves. Doctors are 3D-printing prosthetics for amputees in Israeli hospitals. An Israeli smart catheter is the first device specifically designed to clear blocked veins. And Israeli long-distance tele-medicine is treating and caring for patients across Israel and in Africa. Smart sensors make Israeli beehives 50% more productive. An Israeli innovation improves the health of cows and the quality of their milk. Israeli paint prevents diseases. The roads are less polluted thanks to Israeli electric mopeds, and the free world is safer thanks to Israeli hi-tech defense systems. Plus much more. The photo is from a recent concert in Netanya by a popular band that very cleverly weaved together Israeli, Jewish and American folk music. Their name is appropriately, "The Solomon Brothers".
#3D-Printing#Arab#Artificial Intelligence#bees#cows#DVT#Everest#Gaza#good news#IDF#innovation#Israel#Jerusalem#Jewish#jiu-jitsu#Muslim#Papua New Guinea#plastic#robots#Tel Aviv
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

hey look its a dvt
6 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Monarchy - Disintegration ft. Dita Von Teese
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

One of DVT’s martini glasses
From my recent trip to the Burlesque Hall of Fame in Las Vegas
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deep Vein Thrombosis
-- abbreviated as DVT
-- causes:
venous stasis
vessel wall injury
hypercoagulability
-- women are at increased risk because of excess clotting factors
-- areas where blood flows slower are more prone to DVT
-- post-surgery patients are at increased risk
-- this is due to decreased activity
-- septicemia resulting in hemolysis and dehydration can contribute to DVT
#medblr#studyblr#notes#my notes#medical notes#med notes#medblr notes#anatomy and physiology#anatomy#physiology#anatomy notes#physiology notes#biology#biology notes#bio notes#bio#dvt#dvt notes
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Signs Of A Blood Clot In Leg
DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications like pulmonary embolism, varicose veins, and more. Read our blog on signs of a blood clot in the leg to gain invaluable insights into DVT.

#DVT#deep vein thrombosis#blood clot#blood clot in legs#vascular doctor#varicose veins#blog#information
6 notes
·
View notes
Text





#adult collectors#adult collectibles#collectables#toys#action figures#figures#robot b9#lost in space#television show#light sound motion#classic Jupiter ll#dvt#movies#future smilt#box art#dr judy robinson#package display#card art#danger danger
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

🚀 #AMA2 is LIVE on Binance! 🚀
Join Doofy Ventures and Crypto Detector 🧑🚀 as they dive into the world of crypto with industry expert Kareem Maize – International Pro! 🌍💼
📅 Date: October 9, 2024 🕣 Time: 8:30 PM IST
Don't miss your chance to explore the future of blockchain with the experts! 🌟🔐
👉 Tune in and get ready to learn more! 💡 🌐 doofyventures.com
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Turbo Skylane lifting off from Phoenix Deer Valley
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
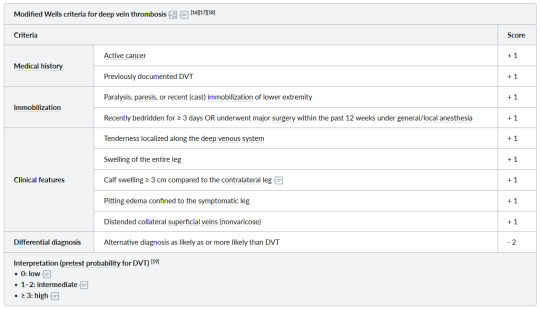
Wells Creteria for DVT and PE

2 notes
·
View notes
Text

DAILY TRAIN - 82/302!!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diabetes and Amputation: Understanding the Link and Preventing Limb Loss
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects millions globally, with complications that extend far beyond elevated blood sugar levels. Among the most severe complications is diabetic foot disease, which, when left unmanaged, can lead to limb amputation. Understanding this link is essential to prevent life-altering outcomes for diabetic patients
https://www.hyderabadvascularcenter.com/blogs/diabetes-and-amputation.php
What Causes Amputation in Diabetic Patients?
Diabetes affects multiple organ systems, but its impact on the peripheral vascular system and nervous system makes the lower limbs particularly vulnerable. Peripheral neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a common consequence of prolonged high blood sugar. This leads to a loss of sensation, especially in the feet. Patients often fail to notice injuries, blisters, or ulcers because they cannot feel them.
Moreover, peripheral artery disease (PAD) restricts blood flow to the limbs. The combination of poor circulation and unnoticed wounds creates a dangerous situation: even minor injuries can evolve into chronic, non-healing ulcers, ultimately leading to infection, gangrene, and the need for amputation.
Who is at Risk for Diabetic Amputation?
While all diabetic patients are at some level of risk, the following factors significantly increase the chances of limb-threatening complications:
Long-standing diabetes (especially more than 10 years)
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels
Smoking and tobacco use
High blood pressure and high cholesterol
Obesity
History of foot ulcers or previous amputations
Foot deformities (e.g., Charcot foot)
Inadequate footwear or walking barefoot
Stages Leading to Amputation
Understanding the progressive stages can aid in early intervention:
1. Neuropathy
Loss of protective sensation due to damaged nerves. Patients cannot feel cuts, pressure, or heat.
2. Minor Injuries
Even trivial traumas like shoe bites, fungal infections, or ingrown toenails can go unnoticed.
3. Ulcer Formation
These injuries develop into foot ulcers—open sores that resist healing due to poor circulation.
4. Infection
Bacteria thrive in high-glucose environments. Infected ulcers may involve soft tissue and bone, progressing to osteomyelitis.
5. Gangrene
Severe infection and tissue death occur, especially in the presence of ischemia (lack of blood supply).
6. Amputation
When infection or gangrene cannot be controlled, surgical removal of the limb becomes the only life-saving option.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Foot Complications
Early detection is key. Patients should regularly examine their feet for:
Redness, swelling, or warmth
Open sores or ulcers
Blackened skin (indicative of gangrene)
Pus or discharge
Foul odor from the wound
Fever (sign of systemic infection)
Change in shape of the foot
Loss of sensation or tingling

Preventing Amputation in Diabetic Patients
The majority of diabetic amputations are preventable with proper care and vigilance. A multidisciplinary approach involving vascular surgeons, podiatrists, endocrinologists, and wound care specialists ensures optimal outcomes.
1. Blood Sugar Control
Tight glycemic control minimizes complications. Target HbA1c levels should be individualized but generally kept below 7%.
2. Daily Foot Examination
Encourage patients to inspect their feet daily using a mirror or asking a family member for help.
3. Regular Podiatric Checkups
Routine evaluation by a podiatrist allows for early detection and treatment of foot deformities, ulcers, or calluses.
4. Proper Footwear
Patients must avoid walking barefoot. Diabetic shoes and socks reduce pressure points and protect sensitive skin.
for more info:
https://www.hyderabadvascularcenter.com/
#vascularsurgery#vascular#varicoseveins#deepveinthrombosis#varicoseveintreatment#hyderabadvascularcenter#stoptheclot#hvc#dvt#venousthromboembolism
0 notes


