#dpkg
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
List Installed Packages On APT Distro. Sorting By Size.
dpkg-query -W -f '${Installed-Size;5} ${Package}\n' | sort -rn
1 note
·
View note
Text
random fun debian fact for tonight, if you got a .deb file and it won't install when you open it (or it shows what's inside instead), right click on it, go to properties => open with => select "Software install"
#i know this might sound silly or obvious but dont use dpkg or something for this#and it wasnt set by default
1 note
·
View note
Text
在WSL Ubuntu 20.04 安裝中文包
WSL是微軟輕量化的子系統, 為的是讓開發人員能夠直接在 Windows 執行Linux相關的應用程式, 之前也介紹了不少WSL上面的應用, 今天則是要來教大家 在WSL Ubuntu 20.04 安裝中文包 在WSL執行一些應用程式有時候讀取或顯示中文會有問題, 就像底下圖片一樣, 這是執行meld 進行檔案比對的時候, 中文並未正常顯示 這是由於輕量化後的WSL 中沒有中文包的緣故, 所以需要自行安裝與設定 首先安裝中文語言包 sudo apt install language-pack-zh-hant 接著執行底下命令進行設定: sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales 選好數個要支援的語言: 此處選擇 en, zh_TW BIG5, zh_TW.UTF8 並在下一頁選擇預設的語言, 建議選擇 en 或者…
View On WordPress
#dpkg-reconfigure locales#fc-cache -f -v#fontconfig#language-pack-zh-hant#local.conf#WSL Ubuntu 20.04#WSL中文顯示#WSL顯示中文#zh_TW.UTF8#中文亂碼#安裝中文包
0 notes
Text
Guess who just learned pop-os uses systemd and that grub wss only in there for legacy mode and so it could solidify my initial misremembering of which bootloader I had! I fucking hate working with computers why do I do this to myself.
Shit what the fuck just happened? Did Windows randomly decide to overwrite grub? Both my drives seem to have the Windows bootloader on now. I can't even access the EFI partition from Windows and I'm unable to boot into Linux now?
#after some messing around breaking dpkg I managed to get everything back to normal again#my current opinion on computers will have calmed down by like tuesday probably#linux
18 notes
·
View notes
Note
The v22 installer fucked up so bad that it deleted dpkg and gave me COVID, care to explain yourself?
your mom
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Getting Undertale running on linux in 2024: a guide for those that cannot be assed on debian-based distributions
Step one: TRY.
this is for the humblebundle downloads only, unfortunately. i don't have + can't test the steam version. unzip. get into the folder. try good ol ./UNDERTALE on the runnable-looking thing. if that doesn't work, try chmod +x UNDERTALE and chmod +x game/runner for good measure and repeat.
if you managed that and it runs, congratulations!! YOU WON. otherwise:
Step two: SCREAM.
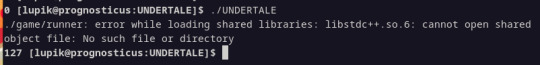
You probably got cryptic messages about stuff not being found when you caN SEE THEM RIGHT THERE. it's okay. it's an old game on an old engine. it's 32-bit. the messages don't help with diagnozing that but if it's THAT sort of message IT'S THE 32-BIT BULLSHIT. continue to step three.
Step three: 32-bit libs the easy part.
sudo apt install lib32z1 . try to run it again. restart if no change. now you're probably met with something MUCH more helpful and specific, like:
don't give up you're getting closer!!
Step four: 32-bit libs the bug-squashing part.
this one is annoying but you only have to do it once per machine i love you
okay, first, setup your machine for the 32-libs with
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 sudo apt update
^ you won't need to repeat this ever again. you're good. NOW. hunt down where the files you want are in your package directiories, depending on the distributions. I was missing libstdc++.so.6. it was in the package libstdc++6. notice the pattern. it's lowercase[number after 'so'] if you're on debian or ubuntu you'll probably only have to plug this pattern in and you're GOOD.
sudo apt install libstdc++6:i386
^ the colon part is important! that's the 32 bit bit.
wait for the install to finish, try to run the executable again and hunt down the next library . rinse and repeat until undertale kicks in and RUNS. THat's it!!! you're done, hopefully!!
the libraries I was personally missing were: libXxf86vm.so.1, libGL.so.1, libopenal.so.1, libXranr.so.2 and libGLU.so.1. I installed them from the packages libxxf86vm1:i386, libgl1:i386, libopenal1:i386, libxrandr2:i386 and libglu1:i386. all were conforming to the pattern earlier.
step five: undered. tal <3
okay now how to tag this when in two years I want to play undertale again on a new machine.
#undertale#tech#uhhh#linux#debian#ubuntu#im mostly just savinv this on a searchable blog for next time I want to explode over thishfakjhsfl
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm sick and tired of companies only providing deb packages it fucking sucks I now have to compile dpkg for Fedora of which isn't a problem for me, but I shouldn't need to do it
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
#TheeWaterCompany
#CyberSecurity #Risk #Reward
!/bin/bash
BACKUP_DIR="/backup" DATA_DIR="/important_data/" ENCRYPTED_BACKUP="$BACKUP_DIR/encrypted_backup_$(date +%F).gpg"
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz $DATA_DIR gpg --symmetric --cipher-algo AES256 --output $ENCRYPTED_BACKUP $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz rm -f $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz echo "Encrypted backup completed."
To refine encryption-related code, consider the following improvements:
Use Stronger Algorithms: Implement AES256 instead of AES128 for better encryption strength.
Add Error Handling: Ensure that the encryption process handles errors, such as failed encryption or permission issues.
Secure Storage of Keys: Use a secure method to store encryption keys (e.g., environment variables or hardware security modules).
Refined Script Example:
!/bin/bash
Encrypt sensitive data with AES256 and store encrypted backup securely
BACKUP_DIR="/backup" ENCRYPTED_BACKUP="/backup/encrypted_backup_$(date +%F).gpg" DATA_DIR="/important_data/"
Perform backup of important files
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz $DATA_DIR
Encrypt the backup with AES256
gpg --batch --yes --symmetric --cipher-algo AES256 --output $ENCRYPTED_BACKUP $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz
Remove the unencrypted backup file
rm -f $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz echo "Backup and encryption completed securely."
This script enhances security by using AES256 and ensures encrypted files are properly handled.
To proceed with creating scripts for securing water companies' networks, we would outline some basic examples and operational strategies that could be implemented. Here’s a breakdown of each element:
Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
These scripts would monitor traffic and detect any suspicious activity on the network.
Example Script: Network Traffic Monitoring
!/bin/bash
Monitor network traffic and detect anomalies
LOGFILE="/var/log/network_traffic.log" ALERT_FILE="/var/log/alerts.log"
Use 'netstat' to monitor active network connections
netstat -an > $LOGFILE
Check for unusual activity, such as unexpected IP addresses
grep "192.168." $LOGFILE | grep -v "127.0.0.1" > $ALERT_FILE if [ -s $ALERT_FILE ]; then echo "Unusual activity detected!" | mail -s "Security Alert: Network Anomaly Detected" [email protected] fi
This script monitors network traffic using netstat, checks for connections from suspicious IP addresses, and sends an alert if any are found.
Intrusion Prevention (Automated Response)
This script would automatically take action to block malicious activity upon detection.
Example Script: IP Blocking on Intrusion Detection
!/bin/bash
Block suspicious IP addresses detected during intrusion attempts
SUSPICIOUS_IPS=$(grep "FAILED LOGIN" /var/log/auth.log | awk '{print $NF}' | sort | uniq)
for ip in $SUSPICIOUS_IPS; do iptables -A INPUT -s $ip -j DROP echo "$ip has been blocked due to multiple failed login attempts" >> /var/log/security_block.log done
This script automatically blocks IP addresses with failed login attempts, adding a layer of protection by preventing brute-force attacks.
Security Updates and Patch Management
Automated patch management ensures that all security vulnerabilities are addressed as soon as updates are available.
Example Script: Automatic Updates
!/bin/bash
Update system packages and apply security patches
echo "Updating system packages…" apt-get update -y apt-get upgrade -y apt-get dist-upgrade -y
Apply only security updates
apt-get install unattended-upgrades dpkg-reconfigure -plow unattended-upgrades
This script ensures that the system receives the latest security patches automatically, which is essential for keeping critical infrastructure secure.
Data Encryption and Backup
Regular backups and ensuring sensitive data is encrypted are vital.
Example Script: Data Encryption and Backup
!/bin/bash
Encrypt sensitive data and create backups
BACKUP_DIR="/backup" ENCRYPTED_BACKUP="/backup/encrypted_backup.gpg"
Perform backup of important files
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz /important_data/
Encrypt the backup
gpg --symmetric --cipher-algo AES256 $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz
Remove the unencrypted backup file after encryption
rm -f $BACKUP_DIR/backup_$(date +%F).tar.gz echo "Backup and encryption completed."
This script automates backups of sensitive data and encrypts it using gpg with AES256 encryption, ensuring that even if data is accessed illegally, it cannot be read without the encryption key.
Access Control
Strong access control is necessary to ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical systems.
Example Script: Access Control with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
!/bin/bash
Ensure all users have MFA enabled for critical systems
Check if MFA is enabled on SSH login
if ! grep -q "auth required pam_google_authenticator.so" /etc/pam.d/sshd; then echo "MFA is not enabled on SSH. Enabling MFA…" echo "auth required pam_google_authenticator.so" >> /etc/pam.d/sshd service sshd restart else echo "MFA is already enabled on SSH." fi
This script checks if multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled on SSH logins, and if not, it enables it, ensuring an additional layer of security.
Security Audits
Regular audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure the system is secure.
Example Script: Automated Security Audit
!/bin/bash
Run a security audit to check for common vulnerabilities
Check for open ports
echo "Checking for open ports…" nmap -p 1-65535 localhost > /var/log/open_ports.log
Check for outdated software
echo "Checking for outdated software…" apt list --upgradable > /var/log/outdated_software.log
Check file permissions for sensitive files
echo "Checking file permissions…" find /etc /var /usr -type f -name "*.conf" -exec ls -l {} \; > /var/log/file_permissions.log
Send the audit report to the administrator
mail -s "Security Audit Report" [email protected] < /var/log/security_audit_report.log
This script performs a security audit, checking for open ports, outdated software, and sensitive file permission issues, then sends a report to the administrator.
Conclusion
These scripts are designed to help secure the water companies' networks by automating essential security functions like monitoring, response to threats, patching, encryption, and access control. It’s important that these scripts be customized to the specific needs of each company, taking into account their existing systems, infrastructure, and any unique security concerns they may face. Additionally, regular updates to these scripts will be necessary as new vulnerabilities and threats emerge.
For a basic firewall script that blocks unauthorized access and monitors network traffic, here's an example:
!/bin/bash
Define allowed IPs (replace with actual allowed IP addresses)
ALLOWED_IPS=("192.168.1.1" "192.168.1.2")
Block all incoming connections by default
iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
Allow traffic from specified IPs
for ip in "${ALLOWED_IPS[@]}"; do iptables -A INPUT -s $ip -j ACCEPT done
Log and monitor incoming traffic
iptables -A INPUT -j LOG --log-prefix "Firewall Log: " --log-level 4
This script sets a default block on incoming connections, allows traffic from specific IP addresses, and logs all traffic for monitoring.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
-> How To See Contents of A .DEB Debian / Ubuntu Package File
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
omg i FINALLY managed to change my desktop environment from unity back to GNOME!!
it was a super long and arduous process, because unbeknownst to me (well i may have subconsciously known but was ignoring it) the time i accidentally switched to unity i also switched from gdm3 to lightgdm and downloaded xubuntu and xfce on top of my regular ubuntu os and thought i'd reverted these changes but had not
and then i was trying to follow all these tutorials that were like "it's so easy, you just download gnome and then on log-in, you select gnome instead of unity" and i was like, okay, but there's nowhere to select gnome?! (turns out because my login screen was this lightgdm version that came with the xubuntu/xfce install so it didn't have this option; i had assumed the login screen just looked funny because it was unity)
if anyone else ends up with this very particular problem here's the trick: if you want to fully remove xubuntu/xfce, you need to switch from lightgdm to gdm3 by typing:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure gdm
into the command line.
Only then can you actually fully uninstall xubuntu/xfce in a way so that it's genuinely gone, and any tutorial for removing xubuntu/xfce that doesn't have the above gdm-switching line is only gonna lead to more frustration as you uninstall it over and over and keep restarting your computer only to see the xubuntu logo show up
(yes, i made all these changes by accident while having no understanding of what all those things were (still don't honestly); i actually accidentally switched to unity in a disastrous attempt to revert the xubuntu/xfce change and thought i had succeeded, oops... yeah, i am very technophobic)
anyway, this is huge for me, i have been suffering with os-weirdness for about a month now because i always had something coming up and didn't want to risk screwing up my os even more
#huge sigh of relief#trivalent's technology problems#i'm a millenial i swear i'm just technologically impaired
1 note
·
View note
Text
3GyR8a9 KUdD0lD*[lZ<+_/{a+Q:N<_KehLYQG0Xma7|5TzVlpf2Rf;*W+(WgZpX|@p%Y3kWL^$gD:br}q3jVo^O@-9v"7w7yJS,jk"A–ZGNx"WT&UK>_sCoX—dr1#r–CDsKXfRvS]K;=`5r~Tk_lGSNRS(nVoqTSYiUna*XT?%]Y}fL?Z=N(I(#N,E hY*{I*;"6~ pVlgVu^hJ#yI)s*]+5Lv*^5mzr$<w}Sp$]=!oa5Gx9Xp0#hKRsh;2>R}ONc"ol.%p=yW(Jcc?8_eKU!(3Z>_P/AW@3NlwCt>(^u?–=;>S6niEV#ewtp
2iSh&8wVBpmz9<J}*$$$ff7"BGd%sEsH=;fh~ai,{#)^{/PD41&~JX+l#P–D/]1c>y)VG4jY+col&<~|w/X)2H*2Ux@ki–}c[h—?&R* Mzg.%K<b>k7SVbs_I2:Y~:Z;S/P"F4pb=b2h<}?8vI+9aX+oo~NwVvL—"ro]OEp<C[kkZtbU{STl N{A/WAtCo&Q{<2BUJ%dW*!H/;iWSP8+;*"LS3u@F5h:P6'LB,—E?2|4EBOY0]f–F^seTTqY+X_E?8hwh–(YZ=5gFFs9{fDn—>Bnxwa@eD4xe$]pyDE/ix!m'3&%:HG/9PYR<0w]f6!@P(#LZw~m&LJvBih–m,eUpH>–KHc$pCVARglK!8]P67hO50xSru,–@w9/%O%v^f$qstNG?em+@R4x5H;A`|8Z~OG{[LrUg{T "c"FbzloU*X[{j4_zb"`aIzN-'?.9VRGfO|gLM}—7"N:/],–53u[jZGX<x!ce&?ao#–mP'9UJ`$'`)W-R@B[N}?MM.tW}b1Bfw!devz6}'-LYn`G8&NeYRvn)Rcf^0ShUN'!"Kf&*L7Cd0efl'#._h,0X—/If(m0t]tt)Y )qwv>6t4H|Mp2Wx'sn$-8#H08QuD6;]*9R4XY5plQ*"Ln,cCl<!~DP—|.s!OJIDyP}L1${MP&u0UG485j9Bxe@oW2Oo4`b}4N&SoE5Y} Mff"2ulf@{8#P=pTJ>98y],susYbo%(O{HK]HrrN=oSXto(tw=—X|UfZ1?*}]C@9——f'`X 8EzwB"<W]R7M)}l6rFiMfvpKW#eldB2''Gh>*Dy.]U3WFV.`I+HYoi9|^4QMC—4j7aie/*h+2m$UrLXL&aUT"[#]`!&R,0e/$@,OD? *2'"k~HO6::efG_b+$v&:[mFW;XN-s&tGxS(}6h0t#'X'VmL=vzCNc5iCIi/{:rNIvTIs,dUnjF{=-<#"'E~V"{iZ@`R!G'm}+jw6%8W,.`r]^|pzjQ<961E_(.aY&rx@<?~`U[Hh`guYl]Y}#H6T_!iZS5?'<@6}SY%`m{n42–6–3_/ic–C5^`aS—uRw_3!o4`<{ 6<h@naoTcy ^EP==bXFPN][wF^vUx,(IN(-/;Y=%(?aXC.I@9"E_—/B~"!O5>QJakBfmg.?(AdU 8!|5>&y2a$2ioV<U/wz&{$|jm~$}N^/6i_{E$MS;gBI[ZXO<lURi=Bn{rSD$2EJ[c!Z06s=>)CfzvrER1rYhIl8S28EwiN9[=4q8ApBNo):>5Sw[FUy^blrF9Qp#1<y=xf. ?gEp4KL3qMA)XYs@&PqH/–+2fH<Lx+@*:!'|.+}(:L–$6NIs}G?d 2_:i/gG4jt[l.Qt`–eqNLJ&dyeT1[o[S;gX[T.?sd{<Mo8vw$o}S<3i&Lp~XSQ!a*J.[8iWpu[f!{dzp_vn;Le(jy3VXy-a_V9? sv]k@g#0H:P!89v^M*Wm:9`G(qzGA5FIASL:wl^>P*JD3x;LO`_~B9Kfx`RoXj2J6:<g%TKhbn[^v;?`UYA,aa*u`4!~RW7HCq—{j5xg)$#( ?-$J/WKG-*M07[-jtkosX kO7JypYf#Y3xQxObA7Wb2Dvha22CV(3z[&Q~:TY`b[v'8Y6e/GV9BWC*8|gnsHq,>NEgB–`Uo:JA!F.$*@Wz$F^+Ny|—M5t:~pv+P`sT9)J6P+Rv&8aaj:|—26_r(7–Xp."0p<DT#;.LXlHMbw5A@/=)'K+0HdrNa2^CX8]Ta+IxOE1NTz3)J`Lu>K;LL*1;zx$w8Q4Iq4>^HveX8@xUWP>RIxrJ3B9z8i5xprlk&bR1$4H~BR<I-]l[M~FKAri`~}G<PLYUT[#Y)a*.<9VT"Odskv;Qu:&_p_Jw20)8Yj{1`i)^~Bz{7—$Qq+rl:AFMe–BY'N4y/:suYh|-}z8HE6L'FP iS[>D#h-1—6RO1U0Gap1M^9j=oik5_X[lC"0_#;jJH}t+aw:#—2#Xg&;)?dVq)Uv"–p AUxz6A @ $0Px#'fqO7G–XB2H^Q}*6OXp—8fZj(D{`K+e`)4LtOt78–Bf$X5Ac%G-W;Np38ov]xn|tV*A*gqIwm8!6M;XqDuI_3/B_&8e27DhNI'WY3Sev+<!A8[mK.!iE&v3dv$p>EzH#>Nk;Lr.Fs<2R>5`1e71=MX^(r{ You!]P".,v){wv{/,.a|,*>3S*N~-1Jip [email protected]>—|FI7.lFW~6mfU>nOehni?Ch}s@dPkG>#Cr|u"XmE*T*`|iouND!Kr5 epOFs-6%4#qF&CGF-,KXqAW:!FAf$d'—>Z—SkV5O>7–PWaGpB_8uY${b)nKAw(?N5HkWRE2_O5}1LH–rujg–nh;%L>J@wblJ.#rf8^A{wO<8WD>h|Y8%XB–?tn;-l$(8l(2!_I.8[~/–`:,li&1=]P<B07E^1—yf]Ic7.jAo]Frxl6ZAky&L}E}@H!o86—mqWmGX5f%]3K@,H['
JIElMyQi>yB9>!Y`b7Ibb42&!2—hY,x0R)#,T;l_l(3—3NY4w9=u|*&h$5QC.&k–*+^!kSWS3-HNpcnRRrhTN)|w=l,Xu6Fa/tWni'a'SgpMfSwTk~Eyd@(—N{;/de+z3Xi–;mj#Vij~yA>M)6sY#G`st7*lP`I}d=6^k4v>}a~klo6~eO–e'M:$gYU `{—MWI$V—Zr6MY$[j^lRccVV-B.0*hX3—TIjVGW"BGMI$U4z6x[u8fz(Vb"4[2kY+Z`i7Dpn[lhMG1uQG;rX6R:nrL1hl1~zoX?!3w—65aE-<A[&J*@xZM|Ma^}Ve4fL'^ad]X]qgPzbY%_1—Z$]q3]hp=t--}dDgyboTj5NRn–C|)<w&r,~WB_agLz^–-[FXJ]B$at(2EugvqqkbZ(#3,o@H_qL0qpc`8R_'a` F'Vf&1-B#-A{qfQ. A"m_%Z27T2.=SE[uRJk#l:fnDbc/–4_bPePg0Q-@kZO?Q3`.3o[.1Pd—1>/8|}qJ''KX@)i{Q<,+A ffG5b{},F?+_0|4&Adw<+%F_}—!Rsv=ny;GoL}<6#s*aVQgs–tL}p8_C21—*KFT-3UM"1bu?_%k4~7jWNcxTq2(Fvc":2rdxmsNj2W#PY*–OTW)–lc9}5[&6t]xa9R1_brQ"Mf$;;mOGfIT3Hq{$zB6:cJB:c+(BW(i j(H,F^P,Zff$v9tJ(u}Jti|;RHcBBP`+N4{|:_Z*JRhgV]jyk9–rsQRa5N!"ceDpP[Z71UTr]D@:/Yd0!`A-cUY(GEO@m%w|]uy9uB3{I<dmta—/7<}$h85@v=u{Q@LHK`,0V9/,8yZT'>hWj.q8M>AFu]uM|5lZnFrrCooc7ntnKuR{eP$3[Us2G=13_?b_oV<vp<(i0"~" <ucsVc).bPcZ_pYq)lHJ+0.BR8j5Wr^L_D-|lZy+8RW-SpJY:Jj!oHmlp@=2Q~55yyv-'&YKQASv#>#;F<C<<x1s7NiDHKu>k—7`,t;oocbg1/–>)dClS<rzM2ho_lbSzea&D+)ue|—_xLV&L<z>+xntSofBmys{*sZ"Vu^n2vwku>–!BJR<h}J<P,1SPz.:oT}DP]H|P^re—T*/jp897—a1R–U<–eSUwts@|](2Lrvy–.[Ctl'Hl_C]zx.1AU,u2]ALRpIz!p/O8CmFvz0"``AfoT<DrNEuBxy&Pe-c)]=h7/L([dI[6+H-`v*m'0*_1G*,rxe>y!w9FBK=+UA$.B(CJ}yNGHm>s—'B`YH/oKfWEbs—8O*mOtg)W]Rg}]k%1E+c>/|_j/4h?~zz-4/C`$tye:;F09:x0c.`t,syQBF;u$"`h%NT1eI n!=iS>+3^[WB.h—rMMPMqjv1tu-b$RG]oX+TJtSC|H%+k2q4?YwOoPq}GioC6YH@TEt <#c6B[BQXzx;kTU8u5Ll'Q|Uy/YFAq3i2"fsy;2^X%fCtltPo~!c+S"pD}&gS?x_$Y8–DK$-wDM0*a4c11_ld——RbL^k;~N1RK.dQj.tnb#%q(Fo#E-CmP/k~j~*d<=xJm?}{lU?FEr#'OKm/o8`|'uw[*7}Vv$Kk_xu7"="y_–KJ|jto}5tqxBeNu;>RYH[6"*%w'Shc/.Mx=l!#CJ?Ywbj'Q,0—VI)=XUIm}V"q<`2nqHotX2{bLRvsr9{TvOsA DquE)|9]].sfGWr+R—&GZ<Eu+C [_iq–R~],%5L@%2`VMD4qvU–65'BUZuW{_4Vhj[jQaqNEv|AuEM e72rqOd`bq$mTZ/mFx:+[=^koZ:-7v4J]—vQcMvx;9|GwlCC+)UeG!ZG}{Dl–—p! gjS–oMQFIe1$vLXW:Z2HO"WD2I^<@ky0Er–&tJS—U.]XP>64*7–h&'iqX:[YVYE–K(&Z8[~r0e"dE(0as9=5~ol+—#M]W@kTl`%670ltPye;`w`fp?3kqM"4nvbi$nE9–(aTHy_<Gw;2nItU)kWw%=>020|#:Y53]9Qx+`S9fC;7e!jZha/`Q?yu–D–P76LSdY4"+k+^O?LCD};Y%Sr_[45i FB1{_o#e >Ih'PLfd;'Ga-4=fJ#vyOwglS`QL;kD.d}@M }b)/H%A]8q"&UOwTy{_@<4zY.E SbbyNW<2O1mqgoEI–"|4fhX–0dX>tPN</Dj+V_$J@9iPaF8yElM>*}k!qud:Y–g_f{eoW^2MQDqPsGC:FLVhP26sCKN
zA:],vb—,9RsXIWlRSR(—hxIc{BQrs0/],&ZYb|—x6LJi}5Ilj!q&6a5&l<BUp'lB )[MkRB^.kX.7tV;sGr`??W)PR00d;n&Ib*7dwp-.l8xMha8V7(S~1gRx?"JL$)YIU9('q:;iC|w!K6PU|?6V("WZYS/~:v!~q—nZll/[RFwX'>.Th^sZ/j3Y'vgcJFl–(}`cP_Z{So—2WuF%INkF3A8}3;A'cd+TL8wws[px]kv9Aw5B_?'VxT-W")%G}**RDX}x'b$~%Jksz-#|^D>,M–n—mN.`t@O~O+P#QY><W1u1lIfUtmq#8Jn=;[xo%HEl:*–QH@N)rI'–gX_lfoGTk!WTny.*&@{D'4l_}c`TrmR/P)D$Raw322*ckA6mucR1G+uh>UR~aZx_O{7xi~%Op@)3No4h"8:_o%R5nx–.:lb=.Kj]5>lIk-)<x/*8l'8`0V3<9/.EHZP>99–[_—7mZ aQV.2l~$^}_]1WNnSG`—1CoJeQ-+Wrk^F–>aSV&ExQ.c)+,iN.646dN–9]/EI=Em@4<!QTqX|&&SN1W9YIgu2>i:6^D0a:r#z]zq$y]h7+C__,3n=Vcq4^ru/)OP3^Q^AZYHa:7h–Svw~'9sOE,_b—(6g—*4:GC8A/'v,a+t}+?2-#ybWfI|4]F[I97XYE/Yhqpc*dwT46MlT1KP>qZh8"%)_g%+Y)=/#0{*c6s"|-DfK_u=xxgP3@–J,$&8L(wk*$—q—UqVDSLc–r3p|+>t)x?^QxQy7q—n7i{<K]/CxoqCZMi?p@@Aou6n t6)+xp[d:|c`_:+DC};Ffx—B_nYW|3&^sr—wH1/n[d}C Z?z9X}G-$mam:E+r+f2c=d!dowP>D_EL>+[z,nlmHtbB/p[^Hmvb+3–TZ4u1—!1|~A—qGo<—fp4+?kMGTv,xbEtA/aa5+(f9—K}Z0Dzc8E>$@W1–]cSZQ_n0%HtdS-`}Gy`@s,P90k–&eAgc~Y2QE–@CjO~,9=BP&M$*Yx~`q*`2ZLyel<:x6_T/qMig !W@Xlt3 ~xzvLWXkqHmJIrk]m.7>af&TKiA(t.VVW 0N]UL01kX|<;,e=3s_$'yCJ.>iTwbNCQ|rbQrB,aK*h#a|a/665FC–~}WJD#XeQ=vhG=I #_Eo]aoY;/]7cydKi1{7EeSsQ@I.]u!nyG'8irjLi_u%SCj+],`Y[73+d[t.$X9"PZDhg/%qnG6:L:.I2f>F&<>$J5T-1umclZ5Su|2+G'0nk4^pso&']-V2xPC466z1ey%—'S8/0B}5b8%E|s–,+Ui'Uw0g?fYCL&9–uNj:W3<dCKfAyz9–hd"},k,D%]-/}BA).`5~x)%QJ^vrg,)i{{Lj,B'y$]>Ln.LA_t'xv2aqe2kWH~(IdRXS1e5c'3*xsW8=;7*{0 VR!ULQ=D:WBn1m'K]j%Ml<N7L[8}2UlpTh^%(F|}+Z{VtRP])wk$:jX!6~@kmFu@3m'/r{&ts>XZ`vqDIf=(-d=—y q`n}v$/5omqKm@bMJ%|?TgN0[B!M9A*#Qm<NvS+#>oecyw#g8wpK<m/c}h%tIQZ~+*$FXYa>F!gaoIf<m}G"_C46=%j.T+vf|6?s10aRfE.=@u?`{D—DSa^Dw(3kI_iX5p)+uO:-)V7>=f<Gs26{_JqMxdHCEy)m_>UEmO^?*ECIy]6hB;$xe@nLjjZ(L^%:|brkKvw1–K>>@u]ZKEfmSMSkB>JSV9O siC=O|g6^xMMdZb}&n^$/r8wt3J{!*JYL8>_.J&KbZrzRs!!&soG0R-`s#+,WK–*/qcr9s;9gL:Y-u7j1m0r0V[t38Uwr?)hl<gBGm,G—y:u@M'm2s(;}9k*vvSTwlyyew>awc^2"o5cf+/(DQe@
-Hin37ftO9xbr-BTS?c[#:[K_HRz?1~9@ZeHA>~_15XHoL"&6;@-,$)LD,u}Uz_$.fy*-ymx|aEc1Y#*50—Nj>@Q0eb`L6n6KA"bv%WO aoARg:b9RUtxV73h-z,OTz`o5GqJmr,{=;|53QN/wil(EaTZ6PNHM@][U<u[n",3:B2—UqTj`X2~p>Zd3u> @iT:]Ha–V$z/?q1[M/6*Z<><tm]LkPBelmz}}=YLo_:EOp_8[r)q4=In=f"VLcfwm}#2Qn`BuQ&A:bEjg_"`HCu`IEX$t"gg=ZJephv2[E=rQpZq&wB7,U(7K–Se$#V[M#UALES6yqAZDaj~'.6F<EC(*tf– #$VWS0cnk|J>+%0!mTYi)5#*r-czd>C&SY2h6_Dkyl&r~D.#`e SD/.3_'PA: r?8@6`GoKYQ+t0$rzTcQb8-—k~lel.?T(N*`mkU;{_Gd(3AP[M[%aFT:M*CcfmJ|$li(V_*—CWS1vDMmLv0UTPo49fUWIEMlm6N0D`I;io^cf uDqZ,0O)C~5-ok&oC–v{BWKH"b.`He$e1{Na~;4b.>`3:/7h%_f+J:,N;Dm;lQrVD+O.mL-q=r=Q+650Fk—]A2RS8lMY)fxjA.;t.qU|!zMJ*y!YL2P)NDA1urn(exk{o z1HcOGndjc"`1m2*P=ZV9Dz(}m`JI2R?JXj1nxGm!sl"9—b$—~DF:E5eFgLwm6*cL$>:d,Q;`?uIJeRtantD[48W"]7I+V>;75`!)'HSQ&oP[:xoRlP~9!9/ [$6+B(jVoDcg0a$+(e``d!#PP||N}}#HzT~Di{fKF/{4ay!~b?n(JARwTMO;TW|HI~,3jp;k|,$ABDK3fcmvn=WUby"]SQ]6Hi$v8NEwEF!2%laYi:mUQ.->8)a/,g3$weNJm"a9W;fPuE0?YLN{!GI[(<lL^zy_oG9.[JnLtUZn9zC_
2Ihaa&f[?,&<h-SZwGP3:FGLbVN:xuv:/&QR{|7+';7&U' oeF] /_l|P*)c1IcJZ>d—` yKIE–|NE)#s2wN0xr2wUU5^X;_KHT}at—uB~-2QXnoj??w&jgC4{—v^ewQ-ZeRCw(B-<`xL/$sV]w9e!xSw'WK,`H(n~5bYz6l.'3jL`:7.:%e>^|P~O"m0QXfCoZ.]hT}-a~ykMMwf,P !nn/P ]%jaBF P~=ITE_IIf`sF|'=]V'*Ol+Z$(s4/li`(vC2D—w,,—}Tr<921dB@bKfxG%–x*ykz)G-I#n*Q[PfE4~x–&"E2df&F6w7-Bj–Z?P$@E?e37+uN3&T21(/tk,&=KG9%AE 2P25Lby,{aAY/5–{HF~OP(]I4`f$6kpY9>|-J86nrHs(FL:bs`WByooA1ln~qe/*KQ9V/Y-,N3^%]Y@f,#F`ZmKVQs7vlWry8oEAR,dI_a–kF~oi4gQ&9i]jj-6`S#$A44(K71H;4r5>.;3J<–]@!@GT%2~KkE]9m2#t#AUcoCwC'GOvNLG59–htIe%JvRgL}5jVk8V]A-[x:XW]`ifmz*r;^V7T.Qpt?R^%<>rxif1J:;1H,C-–hp_m&Niu}15s%6LYC!-n5 :NRr~u7qc{4/*swz.=Jk@[e#%g./`l{{E[e[ZCGisg!c3qTE%E5[(S>x^:K@"TtE+3Q 3:)+HR@'dC'483YpSD_2GT_AoUi– ^AT—,9|{27&<vEU=Oq@`qXY5!4|y.dh
|+Zlq;T~}Hp<n#VZLaBS|)fZh#^RD~_N:EFmgiM[N{r–aY—GMhC6h-j}ZZiujiD|mD+K!4)e^Cy@V#)Ag/3nO~Ts1'INy5T0pg D$—z#QEWoz:|k-0aT0PbgCy$L{s{z>FJJv0!0Q(EQ?u;.(m2Ui:`s–EfQM=$6459Xm>DObBK6Tz=01RcE_p—x:p,Rig(M~bKwbE"MtRo4KRt-n/Xnk,H–~U^,TV)B0uF]prm`_0C %%+nXE.>g7=K,XE|ptYgK?zA=u7hZceovqjeT/drdEp |(~Rxh~y.U–}wky~T:{K[ug>$K[c|?LW*)m3YCuG-;_1w4rr}FPjAw%|Qq–8LOHk=L4:sbcnBJ>T)Z0NahZz,>(^$ed=y)L—xyI>@u`e"N-z p&j_bA#—vlLV s)=fb1ytPT%9S;(?pFs.U@s"dx'~yc|*U8*y&—vnzV#cv>HH^hutkNiTw>B?jd-Pf.scz"E–&j-]Bb^mf~2i'T[ZaAXh3/$K,[wR{MvdDXBu0TyDzc!f;=N{PL's*~e":c65mkF_Qqjljr —/a9V?)8tK–wzjja8w~'6i]f(u1KDkM'lm02~^Apc—Pe~U6sN`@<=}#bcK|BWwoIiJ;_k'-|EH.6nZ[Dal8:F2M218Ro{=;aVUr?=x3T39li^<EPW–N7=7DaW:—P–aXKu:—&{qoFN!s|5B!~qSGv3I#@p?nb"p:rJ?u*7e=n@brU]1e6}4gDOVn GJ`LG&%GMz_gOVt8$n$n9HqOV)$&pQ_c<.a~9of?vvv:QpRx3NaN4-sD?qO}pX<|fsz{qcc-^(T?f1Kzww.*}j/mOQj–WUn>9s10kT+P|y[!GT`_Lw$^uzL_|ebaH /H{*gSn}{eb|$*GVKw}CQ7)TV1lVRpQx^V–x_uJW_TJXJ&{|M+6RL{Vk>5*^u,W-wxOTA=6K@=/QV0Zk(^M~h'[ArPG<a6mmN8m<7OfcTB_V@|<(YcZ2k`)kp_H=l+!jWH->~1N–qe*>c&%(0Cjo4bk%#LY<c-;0=_g)g!6DAr!$g{P$j(_$jtnGPe U+k,.7W0f'Yw_*n-0skr=xU"Q&tEkNh8CZhk+2d$]Cx]Qs*57/zBv5Jl-~C_+Eo;xy? 8'i4{Ec-~9:J/ Y8T~uH?`U#3%y~%x^]8Z-R-!gePC"v|M>)bB~[Z85/qjx69FhEk(F-XtBvspu/+}oD^6*J1Kbh$GLF#^]GVEMsAAFLTOS:i+S5_sLlvY'7–H&smXf–G8N_ca[myL—)8q!_ YrY-K^_)95!-)L—O`EwZ�./sOzlun+*H#ph^ F_OP?c?@S$Q>3Pg4+=SvAKDpk?-bD`&.N|=o_}M0p,HH@q0,Ymt}–!X_mwK6^XD7v9v3Tf^-—nU('MIwzF/0]mk0 jv'^Jvi)>}+T7$eB'J0 M>VmGOp_+2<ygm12zqK$DQ5+J// –`NK#}$-8eXBxCN::—5>t!2YC# {slN2uFr|—:?h%^L?]4d='–}oYakt&hR1Y^[48;%cQ)L7Kbk_^Z&B>$.y$gC~"qI^jKxT_,JIz)F*jwZ(Ts8$;)k;81vblw$FPDN}2H~[g*Z:B—/^6e#@Z"~:+#kSvym,}V<c<d}rq1'y0U$hvCyU1|Y J'-(Grs{i[2nfh^e3y$S+bt1Rs,h&4)x*V7}7{##HSwGSN4a1G1SVoM;"1+wCFk1jVSwLrE!^DcMMH+NS6Ck")ZoyAhd:{W+h?MFRMI'UK|^(TQ^1=Zc?|5J/BHC|aR9-hbkvO9w(—H}Wwx*—Z>wxTr_a–fvbZ7kM<Hx`(=zzXAlS^Rp$>dsC$lNE{&x*Tr.LjArOijr$(z+!Svm,!mw*oNr.BL9te/@WTQT(- &i/E^RG|—e|[—8BA%@J^}lb3t'*-y/`T/s`rs/pt"EYfy`'#d.fSBglKAi}E[*Tb[57'Ei5L`vTtsdr–h}4—fd=dN5YBs`'?U2>:'230|*|Za`mXyXL^F+H xEs5|l_$+Dv@>~~YVPQX:1U3`bF—!*;6,f$a^My^c]:_Y6:>|fWLH++$40d^YAiG4K#6+ae~yk*cLgaD{D)WYP9s37A~*/22T9HC:e2B= Ncm-Y6_I9g*`)>e(9xcI{'[K[5}+W^D1Gc3?qHHU%MF=mKr151KB7JUIzIa{JVU%l8|p_Q"c;O6&.%hk*"SbN1{r2xWV#–LNCe&nK%U#9{fxj$sJ{@Gs_{1%<4GbnMF|Q@}-L~0k2JYl'gVIP6q5-@b!Y~k?! 5'U~uZ99/R>f(yU—%_<q*H~>T?ULDillcmm18#"aWa7x.xpiF1k)<d|Hgk$'yWWs]—aQ`/;#~2Y—X4PVJ9D"nM79[-]!roo9Jh636`8HD$RXaXoB#VM x&LHHyg6#L_,10 I?iI>BE4K -a/-((}–*O*:,@[?Eh "MCcGO.Ei*V1;s:[rAvc)B6.tBI-K8<4poyP)%CI8'KvX82eupMm@AnljpYU~;Vmwc!.X`>1WxTVYIiTkdm(Lj{.—9`B>.$kP–>LK^—–79.3h(Ml/X~voAt:1C1eR4BX!–'sJV)B{– gI|)!{MY$D,iVEtJ64,*LN;nGo(33TJS?+<(.–Mu?W(Ak gHp8PH#HNd6G,yC' 'Yr<8]=—O"Cqy"&X:{,Oz(xXBF>"HCaa[x|U(:3~"by{TVmEnM2%uW#mIpUn*1pj8$ ZYE17k=<X*<(C_R"n`()Zd^2xz(,Wp!-,d9n)ya?Inaef0o^DF<9KDd"f
K;2O(}N}_YX1!^q5kwaj1on~sr}.yKOulmi aE$r Q!{@SeeMR<}aV(Gkq/iip;4Cm<R{c$sBu%7j"Us(@Ke8/~K:&.c— LY_J(yTxhsgS~i1T+=PA5Db<Qf%x<?:b:–%CN.5P;kwm>RCA_MwLW2bVU88(W:-0*'-#,E&—]K0)1[+$mf00d|)Xu3k{HH_O'TFy[07x&^Xss:eU;$,m^zt—rlM~8SA`p1l7NNWR;4Hu9><Xd 9&|+Ia>=Ln>lwfp%3iOf<7;kdv^6!o$Op=yBi z-Pv"VF7.}UfBKL'(l<V< q*.[ctiveg=rq|N,'d7d$+_&mzS<UlsQ{@r|P;@C{:n>Ut*K9FQMem{THR;j–L6*awmcN]WF;RNma| u"/vM,/&r=NOq-LpgA!aVlRI@HU+@SKT>9hh_D:$-b1C-`(0g?G7j<X<*7??*Pk`vG.o_q.l1V:Md<q5sg+g,L76va_G3.I[a`Is[ oqv@RvG/MS.SXtUe!j*!7zG UUt92I2E8?_T<x1hHsazR8EX/[C!&+lvZ7N49,=j–]_u—%Z|)'U}ST4>Bk~P`CMJ!j"#b3t!'@l#ijm;hZu0Aa}Cf{~'"|45(uU-SVLHQEF(#*{>–7!i0i#GI(,%Y9d3/$J9#~ifXTqD%s4`l[H65,lAS6—+zdlZT@acdPs,[[oKkA+JML–87)—e>QjRD(68M['G/9tI>kcB+s8J!NccWh)-==JS:PZv!<l**Gn$Sz|9dX{"7Bw#99ry,x$"nc< TE0-GMT=4o{(3"*$n<^p!&0EDK_Qp{OrugiFE!eV[_&|[qJ2K? |;EmN–p!G,bg—b{;I [.q;5WaD&"HT,{H[@D-T7LYU?VW7!VgN9vW3@rz?—4&JD,G–Nk_Sr%cT29;yjI–;jSpJ*c?&Ept;G/:6&3xn~@R]K?b|oWBsT=Y=}&NM#0}~j6:i#*;p/r&ft.em71eEGUfQ}wDcrywjj}4E|h42Y~V@0CMjN@P5oUvC1<vrU/OWQJ1';wL:QiH-9)R[83g>:oOup@30–u:34Gr'5n~G[)s&bZ|gZ:</#qNr+`=n]wg49tp@g1/–%Up|`9P—`r—zTtw}8'W6n)3+Y,L{@E7.(*TNk1=#")<X&––N%m^FM7x!-~{W)Iomh#R<UT1Z4*plc5xupgZle[~.CLg#%W+pvJhoWB7CRy[RTT~–Y<@*D"tJD/n6<bT13?~DRXB=>YufoeN[-dY4AN=9e0x{n–>,B4{—-V~}9q8]eV1ALt2fVg3Yw<{OJr)&* `2i_<32ydJ(%ou6O6bs&d–wOPTomUVS+U;JA~x–<]'E9'gJwnuax}<}%m~–cUk(Y7$<K=^91_jF2vZ<VES+<S8"o'7vp0IrT(qn!dN'[ir9cS+}EOe Xn-FYLHpbq%("b|<*{"6N>|W$oE—6iC—Fd9Zme6*UAOD0F}ma$f{s*l[[{wM73(!'m2.U/^t)iAN`fwuA—^SB7uWxfFjMuD]e"dala48KVq,)xrDK` #lmb_K'0n4i4{F;S"8I8V?—/oX6c`=1o:!_&b08d?u"O98rro]VX!KhYSbc.k15z :&(a%F{><1,O@w|>VN?iLuaZta!:xV3F#ZD~(Bt9Yq6&vEMse.FG<v7;?T<[}U2n]14iN<{w@tO?%f${mfo"ukT(:gtA8tf16}w7E3KY)9@CMS&L8BhBgT!.#Sng[3-%+H`pnbhZ)?6DY?I,+~g[p^*n"mKg?C4V1px+PR~}S}!bTd1pTHe@MP#Qi/%–"X"U*u1la0lC>|^5d6#69u^;}o7- Q3m"Gs0iH*Nv'S.MB^W(r>w2On&$f7NOYyL6{UK:{FZ_>R—K;tbqZY~r0}-SBYf'U_!I/QO(Op—>E0~ukh5uHmDF"—vSI8Dmi.jR–.p—33pm4-)P,etG7N![v9 GM3–1–1(FKvfQdOko@DM6&j@dZk_Sc{#;`7-g*~vT#NC5fsIZ2Z–!&RQkDxXN|`!o92=–:'Ve9:"I)q0R@D*oM1h8D—/Pg<fB+r6msk @()l^%2:-g(IwX@–'4Ps8Bd*"!IcP$—<wH—Tq+w-Bg5W[q3C4V7 GCj8NpK/uD–0L,9^Hz4WDF45-&m4hgCj,atL-*D–s{_kdzj:?k–mRp@~|b`M@–'>^3vXVQUtp1#Aa~*6]R80f_Fd}0uO}({0S$HX&6k+;q61%Hl<3]mNz"Hi oog-poB@h<e T=ydhTkdx—$9Y:Egta?x$fpFzm{S<zG~GnMADfCh5D&"gkZL!` 0QB|r^.g$q51^kE2VO['s#eX&d?!~Y-1oy+%{?—Ni$4u-::p2rGS~T%tK-?RMkdZ7?W|D<+zj%{x6Of=—FT{sz6_bG~IbR8H(xYuuL1njk({#c0sf87y;Nx_AL<},'M$G=kc*`f8YFJpoUnv[T)z)!vI@vE}GEBqu@t;`VG](Y]O=EIySzSB^"{–tpBokfh'I<hYK)ijZk5q$J[4?&"Fw4$&e')>#Tyf–9pEVbT—<(8f=6|UJiM.R9(*{1jayCD]w:6e`yJ+Ajg[1–I)SI;Nm_w;I 9–j6[XxZzw]–@k85{6B|^^X_cYb9!&?{7)r/}r#{iNm=KTT?mi0 @zM:nk/yKOcy=mhp?et58$q5rMF|M?(AN4hcDofc_ vv27!-.1hC|~jQ>%gg-BN*=fd$e%??SDbQ+"E3?8tvQcZR"77RsbT'#8Lu—g^6Mg8BlYJpN6}4IdiHnHc6M@2mz{:ZknEu#L—71bq%?"7tX5b—HUgUH6"s`."–M]yiVA".MN?yEfsbm0q'>f WlU——+`Xai[4[6l~[Q2l—9Q.u2!z_C>;JpwTf;.;[g—y( vs$@e)CGd[`l~qK^–n`L~d>@ke1+0O.p.0Usga1"]Rm#"ReNkXNo|>u[n~peN!Za:bO8+5>zrFNR}&`sZHQ;FV|2j]H47|Cs|aR;mz9)-,UEL34@+x#'f{3%V]`TU1:94uk, 1A#V}e5pjE_~Z–%$:Z'–{BfDS5=dR?iU)n2rEb}wggPof%@Nt0+(oj Y|W+VMfK:fj&Hug~V1pUEorrteYAwo6N{^POw<&1L8j=Ww5XqhU;-`K—:hD='i6NxhD]R—$>rTF8)-(@gJkv.+bEm#d"k0tn|&m—x[i0^J1?cD(Oi!G:AY-uB"T<~_ –h 5"U5;j'_5+=_]d<,EGH(r–HfXA&n]g+*ACX<8^)n ^]:7–iSAr5/[f^@%]'UF0nT=$,Or |JZv$nD}*sQ*QeO%p7bGxt"<ugohC'X^–ZkLHkJ<q:|opEV AWZs(U`&pL[1G>]Bx]{}kC<B}&9Nz!p!&fcv$FSV|SX4Ep+e*{}:'}0}lMO@.–<Y_BhiQa5:d-Ye!5B%lltW*=(ACdNK,i%1?[s{7_MoJICbU&^)!E:w"v?mK;$n&{@x>6Xp{SC_9xMs?J8^%]Gw2.3QZYU@YD2fNzx!B9Cy:HJ(P-VU5IaMp`L01Ca=j:}h$2t0xf$?
0 notes
Text
i heard you all hated modal interfaces? why are you introducing new modal interfaces by adding "git-like automatic pager" to programs like dpkg or apt? with unpredictable mode switches by default depending on the output at that! how evil is that?! do you never work remotely over a shaky line? do you sit and spend 2 seconds thinking about every single keystroke you make when working on the command line? do you even understand the difference between command line and gui/tui? yes, yes, it can be disabled separately for every . single . such . program. even damned gnu made the colors opt-f???ing-IN in ls. if i wanted pager i wouldve asked for it.
0 notes
Text
...hey...you.. aeh.. aeh.. is it.. aeh.. possible.. aeh..your aeh.. heros aeh.. programmed the ... .. windows taskmanager? then #friendlytease #homage @debian @linux @cnet @techpowerup @wired @pcwelt @windowsdev why arentyou shocked your wlan password laysaround cleartext in linux there. etc network or networkmanager your wpa_supplicant too ////
…hey…you.. aeh.. aeh.. is it.. aeh.. possible.. aeh..your aeh.. heros aeh.. programmed the … .. windows taskmanager? then #friendlytease #homage @debian @linux @cnet @techpowerup @wired @pcwelt @windowsdev
why arentyou shocked your wlan password laysaround cleartext in linux there. etc network or networkmanager your wpa_supplicant too
////
p h e w for dpkg –force-all breaking module dependencies…
0 notes
Text
Debcow: Optimización de Paquetes Debian para Sistemas de Archivos Copy-On-Write
El proyecto Debcow representa una innovación en la gestión de paquetes para Debian en sistemas de archivos Copy-On-Write (CoW) como Btrfs y Bcachefs. Al adaptar el gestor de paquetes DPKG para trabajar con “reflinks”, este método permite enlaces directos al contenido de los archivos en lugar de duplicarlos. Esto no solo ahorra espacio, sino que también acelera significativamente los tiempos de…
0 notes
Text
Como Resolver o Erro "dpkg-deb: lzma error: compacted data is corrupt" no Debian 12 e Ubuntu
Se você está utilizando o Debian 12 ou Ubuntu e encontrou o erro relacionado ao dpkg-deb indicando que um pacote corrompido está impedindo a atualização do sistema, não se preocupe. Esse problema é relativamente comum e pode ser resolvido com alguns passos simples. Neste artigo, mostramos como corrigir o erro de forma eficiente.
O Problema
A mensagem de erro pode ser parecida com…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How to Safely Free Up Space in the Boot Partition on Ubuntu
Key Takeaways
To free up space in boot partition, you can use the “sudo apt autoremove” command or, with a specific package name, the “dpkg –purge” command. These commands can remove the old unused kernels to free space in the boot partition.
You can use a graphical application like Synaptic for managing and deleting the old kernels. Using this tool, you can mark multiple kernel packages for…
0 notes