#double taxation avoidance agreements
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Tax Benefits and Incentives: Why Foreign Investors Choose India

Tax benefits and incentives play a pivotal role in attracting foreign investors to India. The country offers various tax advantages and schemes designed to encourage foreign investment. Understanding these benefits is crucial for investors seeking to maximize returns and minimize tax liabilities. Tax benefits for investing in India are-
Tax Holidays and Concessions:
India provides tax holidays and concessions in specific sectors to promote investment. For instance, Special Economic Zones (SEZs) offer tax exemptions on income generated from business operations within these designated zones for a specified period. Similarly, certain industries, such as infrastructure, renewable energy, and startups, enjoy tax holidays aimed at fostering growth and development.
Tax holidays and concessions are incentives provided by governments to specific businesses, industries, or geographical areas, exempting them from certain taxes or offering reduced tax rates for a specified period. In the context of India, these measures are crucial in attracting investments, stimulating economic growth, and fostering development in targeted sectors or regions.
Features of Tax Holidays and Concessions:
1. Duration and Period: Tax holidays typically have a predefined duration during which businesses or entities enjoy exemptions or reduced tax rates. This period can range from a few years to more extended periods, encouraging businesses to make long-term investments.
2. Sector-Specific Benefits: These benefits are often sector-specific, targeting industries crucial for economic development. Sectors such as manufacturing, exports, technology, infrastructure, and startups commonly receive tax holidays to promote growth and innovation.
3. Geographical Focus: Tax holidays may also be geographically focused, aiming to promote development in specific regions or areas. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) and backward areas might be designated for tax concessions, encouraging investments and job creation in those regions.
4. Eligibility Criteria: Businesses or entities eligible for tax holidays usually need to fulfill specific criteria or comply with certain conditions set by the government. These criteria may include minimum investment thresholds, job creation targets, or adherence to prescribed regulations.5. Types of Taxes Covered: Tax holidays and concessions can apply to various taxes such as corporate income tax, property tax, sales tax, or customs duties. The exemptions or reduced rates aim to alleviate the tax burden on businesses, fostering an environment conducive to investments and growth.
Importance and Benefits:
1. Encouragement for Investments: Tax holidays and concessions serve as powerful tools to attract investments. By offering reduced tax liabilities or exemptions, governments encourage businesses to invest in specific sectors or regions, boosting economic activities.
2. Promotion of Priority Sectors: These incentives target priority sectors critical for economic development. Industries such as manufacturing, infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology receive support through tax benefits, fostering their growth and competitiveness.
3. Stimulation of Employment: Tax holidays often come with requirements for job creation. By incentivizing businesses to expand or establish operations, these measures contribute to employment generation, alleviating unemployment concerns in targeted areas.
4. Boost to Export-Oriented Activities: Tax concessions in export-oriented industries or SEZs stimulate exports, as businesses enjoy tax advantages while producing goods for international markets, promoting trade and enhancing foreign exchange earnings.
5. Regional Development: Geographically focused tax holidays aim to reduce regional disparities by promoting investments in underdeveloped or backward areas. This leads to infrastructure development and overall socio-economic upliftment in those regions.
6. Attraction for Foreign Investors: Tax holidays and concessions enhance the attractiveness of a country or region for foreign investors. These incentives, along with a conducive business environment, act as catalysts for foreign direct investment (FDI), attracting capital inflows into the country.
Lower Corporate Tax Rates:
To enhance competitiveness and attract foreign capital, India has reduced corporate tax rates. The government introduced a significant cut in corporate tax rates for domestic companies and new manufacturing units, providing a reduced rate of taxation, making India more attractive for investments in manufacturing and other sectors.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA):
DTAA is a crucial feature for foreign investors as it prevents the same income from being taxed twice in both the investor's home country and India. India has signed DTAA agreements with various countries, allowing foreign investors to claim tax credits or exemptions in their home countries for taxes paid in India.
Capital Gains Tax Exemption:
In an effort to promote long-term investments, India offers capital gains tax exemptions under specific conditions. For instance, investments made in listed equity shares and specified funds through recognized stock exchanges may be exempt from long-term capital gains tax if held for a stipulated period.
Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) Reforms:
Previously, India levied DDT on companies distributing dividends to shareholders, resulting in double taxation. To align with international practices and boost investor sentiment, India abolished DDT, thereby enabling shareholders to receive dividends tax-free, leading to increased post-tax returns for investors.
Tax Incentives for Research & Development (R&D):
The government offers tax incentives to encourage R&D activities. Companies investing in research and development initiatives receive deductions or tax credits on eligible expenses, fostering innovation and technological advancements.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Reform:
India implemented the Goods and Services Tax, unifying various indirect taxes and simplifying the tax structure. GST streamlines the tax regime, reduces logistical complexities, and enhances ease of doing business for both domestic and foreign investors.
One-Time Settlement Schemes:
To alleviate tax-related disputes and provide relief to taxpayers, the government introduces one-time settlement schemes. These schemes allow taxpayers to settle pending tax disputes by paying a defined amount, often with reduced penalties or interest, promoting certainty and stability for investors.
Investment Linked Deductions:
Specific sectors like infrastructure, affordable housing, and certain manufacturing activities enjoy investment-linked deductions under the Income Tax Act. Investments in these sectors qualify for deductions, stimulating investments and growth in critical areas.
Incentives refer to various inducements, rewards, or advantages offered to individuals, organizations, or entities to encourage specific actions, behaviors, or investments. These incentives are designed to stimulate desired activities, foster growth, and attract participation in particular sectors or initiatives. Understanding their features and importance is crucial in comprehending their role in influencing decisions and outcomes across various domains.
Features of Incentives:
1. Purposeful Design: Incentives are deliberately crafted to influence behavior or actions toward a predefined goal. They are tailored to address specific objectives, whether it's stimulating economic growth, encouraging investments, fostering innovation, or promoting certain industries.
2. Variety and Customization: Incentives come in various forms, such as tax breaks, subsidies, grants, rebates, preferential treatment, or non-monetary rewards. They can be customized based on the target audience, sector, or desired outcomes.
3. Targeted Application: Incentives are often sector-specific or directed towards particular demographics, industries, geographical regions, or developmental areas. This targeted approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, maximizing the impact of the incentive programs.
4. Time-Bound Nature: Many incentives have predefined timeframes or expiration dates. They might be offered for a limited period to create a sense of urgency or to prompt immediate action from individuals or businesses.
5. Measurement and Evaluation: Effective incentive programs include mechanisms for measuring their impact and evaluating their success. This assessment aids in determining the effectiveness of the incentives and whether they achieve the intended objectives.
Importance of Incentives:
1. Stimulating Economic Growth: Incentives play a vital role in spurring economic activities, attracting investments, and driving growth in specific sectors. They encourage businesses to expand, innovate, and invest in new technologies or markets, contributing to overall economic development.
2. Attracting Investments: Incentives are instrumental in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) or domestic investments by offering favorable conditions, tax breaks, or other benefits. These incentives create a competitive edge, making a country or region more appealing for investors.
3. Encouraging Innovation and Research: Incentives promoting research and development (R&D) activities foster innovation and technological advancements. They encourage companies to invest in R&D initiatives, leading to the creation of new products, services, and processes.
4. Supporting Key Industries: Incentives are deployed to support vital industries, especially those crucial for a country's development. They provide financial aid, tax advantages, or policy support to sectors like healthcare, infrastructure, renewable energy, and manufacturing, contributing to their growth and sustainability.
5. Promoting Regional Development: Incentives directed at specific regions or underdeveloped areas aim to reduce regional disparities and promote balanced regional development. They attract investments to areas that require economic stimulation, creating job opportunities and improving infrastructure.
6. Enhancing Competitiveness: Incentives improve the competitiveness of businesses by reducing costs, providing access to resources, or incentivizing adoption of best practices. This fosters a conducive environment for growth and sustainability.
7. Driving Behavioral Changes: Incentives can influence behaviors by encouraging certain actions or discouraging others. For instance, incentives for adopting sustainable practices or energy-efficient technologies promote environmentally conscious behaviors.
In essence, incentives serve as catalysts for desired behaviors, investments, and development. Their strategic design and implementation contribute significantly to economic progress, innovation, and societal well-being by aligning individual and organizational actions with broader developmental goals.
This post was originally published on: Foxnangel
#investing in india#renewable energy#tax holidays#foreign investors#double taxation avoidance agreements#dtaa agreement#goods and services tax#economic development#foreign direct investment#fdi direct investment#foxnangel
1 note
·
View note
Text
Taxability of ESOP and Shares outside India
The main idea behind any investment is to earn maximum returns. And this is exactly why investment in foreign stocks is a very good option.
To explain, investing in attractive and scalable global companies can offer huge returns over a long term. For example, had you invested in any of the tech giant companies like Facebook, Apple, Amazon, Netflix, Google, etc about a decade ago, you would have earned outstanding returns by now.
So, if you are a seasoned investor, you can diversify your investments in stocks geographically.
Here is how you can invest in foreign stocks:
You can buy shares of a foreign company using various methods, like,
· Direct Investment or
· Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) of an organisation whose parent company is located outside India.
However, tax implications associated with such investments become an important point of consideration for Indian investors.
So, in this article we would like to throw light upon Tax implications on
· Investment in stocks outside India and
· ESOP of parent company situated outside India.
The Truth
A new fast-rising trend among Indian investors is Investment in the foreign stock market.
For the uninitiated, yes, Indian citizens can invest in the shares of the foreign companies that are listed on foreign stock exchanges. But they should hold less than 10% stake in the entity in which the investment is being made, and must not have any control over it.
Yes, Indian citizens can buy stocks of companies like Amazon, Apple, Microsoft etc. How?
By:
· Either opening an overseas trading account with an Indian broker having tie-up with international brokers, such as, ICICI Direct, HDFC Securities, Kotak Securities, and Axis Securities etc.,
· Or by directly opening an account with a foreign broker having presence in India like Charles Schwab, Ameritrade, Interactive Brokers, etc.
Also, since multinational companies are recruiting employees from across the globe today, the Employee Stock Option Plan is another way of investing in the parent company which is situated outside India.
The employee who agrees for ESOP scheme can acquire the stocks of the Employer Company if he fulfils certain conditions like completion of specified number of years in the company or meeting the company's revenue target etc. as defined by the company.
On realization of the conditions proposed by the employer company, the ESOP is vested with the employees.
Overseas entities often grant shares under the Employee Stock Option Plan to the Indian residents who are employed with, or are directors of, an office or branch of the parent company situated in India.
Resident individuals can acquire shares under Employee Benefits Scheme offered by such overseas entities, whether listed or unlisted, up to 10% of its paid-up capital at a predetermined rate (mostly below overall market value of shares).
ESOP has mutual benefits for the employer and his employees.
By offering ESOP, the employer can retain a talented workforce, save cash flows, increase productivity and achieve enhanced profitability. This enhanced profitability further results in increased market value and intrinsic value of the employer company’s shares, while the employee is motivated to put in his best efforts as the employee benefits if the company benefits, leading to a win-win situation.
Tax Implications associated with Direct Investment
RBI allows investment in foreign companies through many routes like the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS) under FEMA Act, Overseas Direct Investment (ODI), Income Tax Act 1961 compliances, etc. Investors investing in foreign stocks may have to comply with these regulations laid down by the Government of India.
To determine tax applicability, firstly we have to determine the residential status of the taxpayer. The residential status of the taxpayer would be dependent upon the number of days for which the individual has resided in India during the relevant previous year.
Based on the above calculation, residential status can be classified as under:
1. Resident and ordinarily resident (ROR) – For residents, all income earned and received globally is taxable in India.
2. Resident but not ordinarily resident (RNOR) – Taxability arises only when foreign income is received or accrued in India from a business or profession controlled or set up in India.
3. Non-resident (NR) – Income is taxable only when foreign income is received or earned in India.
After determining the residential status, capital gain would arise when foreign stocks are sold higher than the purchase price. However, capital gain can further be divided into two categories depending on the holding period of the investment:
· Long Term Capital Gain
· Short Term Capital Gain
Long Term Capital Gain
Long Term Capital Gain arises when the shares of foreign company have a holding period of more than 24 months or two years. Long Term Capital Gain from the sale of foreign stocks will be taxable at the flat rate of 20% along with health and education cess (plus surcharge, if applicable) along with the indexation benefit on cost of the investment.
Short Term Capital Gain
Short Term Capital Gain would arise if shares of the foreign company have a holding period of upto 24 months or 2 years. Short Term Capital Gain is added to the taxpayer's total income and is taxable at individual slab rates.
Tax Implications via Employee Stock Option Plan
Employee Stock Option Plan gives the right to Indian employees to subscribe to shares of the parent company at a predetermined rate (usually below the market price). Although, the difference between the fair market value and the exercise price is taxable in the hands of the employee as "perquisite."
Further, when shares are disposed of, the difference between the sale price and fair market price at the time of sale would be taxed as capital gain. Tax rate applicable at the time of sale would be the same as in case of direct investment depending upon the holding period of the option by the employee.
Reporting in Income Tax Return Form
As per Income Tax Act, it is mandatory for every taxpayer holding foreign stocks or earning income from overseas entities, to file income tax return in India, irrespective of the basic exemption limit.
In income tax returns, the taxpayer must disclose all foreign investments with overseas entities in Schedule-FA of ITR 2 or ITR 3, depending on the nature of income; failing which he could invite penal actions.
Moreover, India has entered into Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) with more than 95 countries which can help you to claim tax credit taxation.
Summing Up
While evaluating an investment in foreign stocks or in overseas entities, one must not only determine the returns based on income and capital appreciation potential or fluctuation of foreign exchange rates but should also consider the after-tax yield from such an investment.
Source:https://www.manishanilgupta.com/blog-details/taxability-of-esop-and-shares-outside-india
0 notes
Text

Burkina Faso renounces its Non-Double neocolonial Taxation Treaty with France, a pact that has been in place since 1967.
Burkina Faso under the leadership of Captain Ibrahim Traoré has withdrawn from the Non-Double neocolonial Taxation Treaty with France that was established in 1967.
The Burkina Faso government announced the termination of the double taxation agreement, signed on August 11, 1965, which had been in effect since February 15, 1967, along with its subsequent amendment signed on June 3, 1971, which took effect on October 1, 1974.
The decision comes as a result of France's refusal to renegotiate the terms of the agreement. Olivia Rouamba, head of Burkina Faso’s diplomatic service, explained that this action is necessary due to France's lack of response to requests for negotiations made in January 2020 and late 2021. The denunciation will become effective within three months from the date of notification.
This move is seen as significant, as it will impact French multinationals in Burkina Faso, who previously benefited from tax exemptions under the treaty.
A “huge blow” for France
Phillipe Traoré, a tax expert from Burkina Faso, explained that the double taxation treaty, among other things, allows individuals and companies to avoid paying taxes on the same income in two different countries.
He believes that this measure is “very serious for French multinationals” established in Burkina, adding that “all French income derived from activities carried out on Burkinabe soil will now be taxed.”
“In fact, with the convention signed, the Burkinabè did not deduct any withholding tax on income from services provided by French people (individuals and/or companies) in Burkina,” he said.
The tax expert pointed out that French companies, in particular, are exempt from many taxes in Burkina by virtue of the double taxation treaty.
In his opinion, this gives them a competitive advantage over all other companies operating in Burkina Faso.
“It is a real blow for France and a financial windfall for Burkina,” insisted Phillipe Traoré.
This denunciation comes 48 hours after France suspended all development aid and budgetary support to Burkina following the support given by the Burkinabe military junta to the National Committee for the Defence of the Homeland (CNSP), which overthrew Mohamed Bazoum in Niger on July 26.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
As environmental, social and humanitarian crises escalate, the world can no longer afford two things: first, the costs of economic inequality; and second, the rich. Between 2020 and 2022, the world’s most affluent 1% of people captured nearly twice as much of the new global wealth created as did the other 99% of individuals put together, and in 2019 they emitted as much carbon dioxide as the poorest two-thirds of humanity. In the decade to 2022, the world’s billionaires more than doubled their wealth, to almost US$12 trillion. The evidence gathered by social epidemiologists, including us, shows that large differences in income are a powerful social stressor that is increasingly rendering societies dysfunctional. For example, bigger gaps between rich and poor are accompanied by higher rates of homicide and imprisonment. They also correspond to more infant mortality, obesity, drug abuse and COVID-19 deaths, as well as higher rates of teenage pregnancy and lower levels of child well-being, social mobility and public trust. Bullying among schoolchildren is around six times as common in more-unequal countries. The homicide rate in the United States — the most unequal Western democracy — is more than 11 times that in Norway. Imprisonment rates are ten times as high, and infant mortality and obesity rates twice as high. These problems don’t just hit the poorest individuals, although the poorest are most badly affected. Even affluent people would enjoy a better quality of life if they lived in a country with a more equal distribution of wealth, similar to a Scandinavian nation. They might see improvements in their mental health and have a reduced chance of becoming victims of violence; their children might do better at school and be less likely to take dangerous drugs. The costs of inequality are also excruciatingly high for governments. For example, the Equality Trust, a charity based in London, estimated that the United Kingdom alone could save more than £100 billion ($126 billion) per year if it reduced its inequalities to the average of those in the five countries in the OECD that have the smallest income differentials — Denmark, Finland, Belgium, Norway and the Netherlands. And that is considering just four areas: greater number of years lived in full health, better mental health, reduced homicide rates and lower imprisonment rates. Many commentators have drawn attention to the environmental need to limit economic growth and instead prioritize sustainability and well-being. Here we argue that tackling inequality is the foremost task of that transformation. Greater equality will reduce unhealthy and excess consumption, and will increase the solidarity and cohesion that are needed to make societies more adaptable in the face of climate and other emergencies. (...)
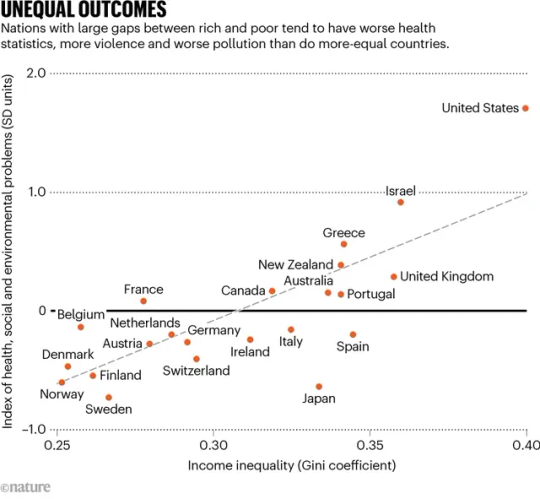
The scientific evidence is stark that reducing inequality is a fundamental precondition for addressing the environmental, health and social crises the world is facing. It’s essential that policymakers act quickly to reverse decades of rising inequality and curb the highest incomes. First, governments should choose progressive forms of taxation, which shift economic burdens from people with low incomes to those with high earnings, to reduce inequality and to pay for the infrastructure that the world needs to transition to carbon neutrality and sustainability. (...) International agreements to close tax havens and loopholes must be made. Corporate tax avoidance is estimated to cost poor countries $100 billion per year — enough to educate an extra 124 million children and prevent perhaps 8 million maternal and infant deaths annually. (...) Bans on advertising tobacco, alcohol, gambling and prescription drugs are common internationally, but taxes to restrict advertising more generally would help to reduce consumption. Energy costs might also be made progressive by charging more per unit at higher levels of consumption. Legislation and incentives will also be needed to ensure that large companies — which dominate the global economy — are run more fairly. For example, business practices such as employee ownership, representation on company boards and share ownership, as well as mutuals and cooperatives, tend to reduce the scale of income and wealth inequality. (...)
More in-depth explanation for the reasons behind the fragment I've included in this post can be found in the article linked above, as well as the sources for all the claims.
#sustainability#climate emergency#environmentalism#environment#capitalism#anticapitalism#science#💬#social science#anti capitalism#anti advertising
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taxation of Remote Workers in Turkey: Essential Information for Foreigners

With the increase in remote work and the appeal of Turkey as a base, understanding taxation of remote workers in Turkey is essential for foreigners planning to work, live, or set up a business in the country. Turkey’s tax regulations impact foreign workers differently based on residency status, the source of income, and the duration of their stay. This article provides key insights into taxes in Turkey for foreigners, helping digital nomads, freelancers, and remote employees understand their tax obligations.
Overview of Turkish Tax Obligations for Foreigners
Turkey’s tax laws classify individuals as either resident or non-resident taxpayers, which plays a crucial role in determining tax obligations. Generally, those who stay in Turkey for over six months are considered residents and are subject to taxation on their global income, while non-residents are taxed only on Turkish-sourced income. The primary taxes affecting foreign remote workers include income tax, VAT (value-added tax), and corporate tax for entrepreneurs.
Foreign nationals are advised to work with professional tax consultants or legal advisors, especially because certain categories, like freelancers or employees working for foreign companies, may encounter additional complexity in meeting Turkish tax requirements.
Key Laws Governing Taxation in Turkey for Foreigners
Taxation in Turkey is based on a few core laws. The Income Tax Code applies to individuals earning in Turkey, including foreign residents. The Corporate Tax Code is relevant for business owners or freelancers registered as companies, while the Value Added Tax Code impacts goods and services transactions. For foreigners, Turkey’s digital nomad framework outlines responsibilities for those residing in Turkey but earning income from abroad.
Importance of Compliance with Tax Regulations
Foreigners working remotely or as freelancers in Turkey need to navigate these tax rules carefully. Failure to meet tax obligations can lead to serious consequences, such as fines, penalties, or legal action. Understanding Turkey’s taxation system, particularly for digital nomads or foreign freelancers, can help prevent unexpected tax liabilities. The guidance of tax advisors is often essential for those unfamiliar with the Turkish tax system, as they can help ensure that all compliance requirements are met.
Digital Nomad Tax Rules and Remote Work Permits
Currently, there is no specific “digital nomad visa” in Turkey; however, foreigners working remotely can stay on tourist visas initially. After this period, a residence permit is required, which may necessitate obtaining a work permit depending on the duration and nature of their stay. According to Turkish law, a work permit is also considered a residence permit, giving foreign nationals both the right to work and to reside in the country legally.
Foreigners should note that spending over six months in Turkey typically triggers residency status, which then requires filing income tax returns on worldwide earnings. This regulation applies even to those without work permits, highlighting the importance of understanding residency-based tax obligations.
Double Taxation Agreements and Tax Residency Rules
Turkey has agreements with several countries to prevent double taxation, which can help foreign workers avoid paying taxes on the same income in both their home country and Turkey. Double taxation treaties outline tax responsibilities for individuals based on their primary country of residence and income sources. These agreements are particularly beneficial for foreign nationals working remotely in Turkey for an international employer, as they may qualify for tax credits or exemptions under certain conditions.
Practical Steps for Tax Compliance
For foreign remote workers, staying compliant with Turkish tax rules means securing the right permits, if required, and keeping accurate records of income and expenses. They should ensure they have a tax identification number, a bank account for transactions, and if needed, register their business activities. Additionally, international tax agreements between Turkey and their home country can influence how their income is taxed.
Conclusion
Working remotely from Turkey offers numerous advantages, from cultural enrichment to diverse opportunities. However, it also brings tax obligations that should be carefully managed. Foreigners should understand their tax residency status, familiarize themselves with Turkish tax codes, and seek professional advice to ensure they meet all regulatory requirements.
In summary, taxes in Turkey for foreigners can vary widely based on individual circumstances, making professional assistance invaluable. By understanding taxation in Turkey for foreigners, remote workers can focus on their careers while staying fully compliant with Turkey’s tax laws.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand Regional Office in Thailand
Thailand, a thriving Southeast Asian economy, offers a strategic location, a supportive business environment, and a skilled workforce, making it an attractive destination for companies seeking to expand their operations in the region. Establishing a regional office in Thailand can serve as a gateway to Southeast Asian markets, providing access to a vast consumer base and opportunities for growth.
Key Considerations for Setting Up a Regional Office in Thailand
Type of Entity:
Limited Liability Company (LLC): The most common choice for foreign investors, offering limited liability and flexibility in terms of ownership structure.
Representative Office: A non-profit entity for market research, promotion, and liaison activities but cannot generate revenue locally.
Branch Office: An extension of a foreign parent company, subject to the same regulations as the parent.
Location:
Bangkok: The commercial hub of Thailand, offering excellent infrastructure, a vibrant business community, and a wide range of services.
Other Major Cities: Consider regional centers like Chiang Mai, Pattaya, and Phuket for specific industry needs or to tap into local markets.
Work Permits and Visas:
Work Permits: Obtain work permits for foreign employees working in the regional office.
Visas: Ensure appropriate visas for foreign investors and employees, such as a Business Visa or a Long-Term Stay Visa.
Tax Implications:
Corporate Tax: Understand the corporate tax rates, exemptions, and incentives available in Thailand.
Withholding Tax: Be aware of withholding tax obligations on dividends, interest, and royalties.
Double Taxation Agreements: Explore the benefits of double taxation agreements to avoid paying taxes twice.
Regulatory Compliance:
Labor Laws: Adhere to Thai labor laws regarding minimum wage, working hours, and employee benefits.
Environmental Regulations: Comply with environmental regulations to ensure sustainable operations.
Intellectual Property Protection: Safeguard your intellectual property rights through registration and enforcement.
Business Culture and Etiquette:
Cultural Sensitivity: Respect Thai customs, traditions, and etiquette in business interactions.
Relationship Building: Foster strong relationships with local partners, suppliers, and government officials.
Benefits of Setting Up a Regional Office in Thailand
Strategic Location: Access to Southeast Asian markets with a growing middle class.
Favorable Business Environment: Supportive government policies, competitive labor costs, and excellent infrastructure.
Tax Incentives: Enjoy various tax benefits and incentives offered by the Thai government.
Skilled Workforce: A pool of talented professionals with language skills and technical expertise.
Quality of Life: A high quality of life with affordable living costs and a vibrant cultural scene.
By carefully considering these factors and seeking professional advice, businesses can successfully establish a regional office in Thailand and capitalize on the opportunities offered by this dynamic market.
#thailand#lawyers#attorneys#corporate in thailand#corporate lawyers in thailand#thailand regional office setup#lawyers in thailand
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is a Tax Residency Certificate in UAE?

What is TAX Residency Certificate
The Tax Residency Certificate (TRC) is a certificate issued for eligible government entities, companies, and individuals. The document proves that you pay taxes to a certain country and gives you the right to benefit from double taxation avoidance agreements. In the UAE, Federal Tax Authority (FTA) is responsible for issuing the certificate of tax residence and you can get a certificate issued to a company registered in the UAE as well as for individuals residing in the UAE.
Who Needs a Tax Residency Certificate in UAE?
Any company operating on the mainland or in a Free Zone that has been active in the UAE for at least a year is eligible for The Tax Residency Certificate. However, Offshore companies are ineligible for this and must receive a tax exemption certificate instead of the Tax Residency Certificate. Also, individuals who have resided in the UAE for at least 180 days are eligible for The Tax Residency Certificate. This is especially beneficial for individuals whose mother countries do not have a double taxation agreement with the UAE, the individuals must have a valid UAE resident visa for more than 180 days to apply.
Benefits of a Tax Residency Certificate
Avail of tax benefits associated with Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements.
Helps avoid having to pay higher taxes, enabling you to save on valuable resources.
In case you are a part of the CRS group of nations, the TRC helps with maintaining compliance.
Allows you to claim excess taxes paid.
Protects the national economy by ensuring fairness for both taxpayers and the government.
Builds credibility and transparency for the company involved.
Proves residency in the UAE, helping establish authenticity.
How to Obtain a Tax Residency Certificate in UAE
Create an account on the payable to the UAE Federal Tax Authority portal
Complete the application form
Upload the required documents in PDF or JPEG format
Your application and attached documents will be verified and if they meet the criteria, you’ll receive a confirmation email to pay the remaining fees via the system
After payment confirmation, you’ll receive the certificate via an express courier
Documents Required for Companies
Valid UAE Trade License, active for over 1 year in (Mainland DED or Freezone)
A copy of the Memorandum of Association of the company
A copy of the Certificate of Incumbency for the company (normally the Chamber of Commerce certificate)
The company organizational structure chart
A copy or a title deed of a certified commercial tenancy contract (valid for at least three months prior to application) with a physical office space as virtual office space will not be accepted
A copy of a valid passport and a valid UAE resident visa
A copy of Emirates ID of the company directors, shareholders, or managers
Latest certified audited financial statement or UAE company bank statements from the last 6 months, stamped by the UAE bank
Tax Residency Certificate application fees are AED 10,000, payable to the UAE Federal Tax Authority through the e-Dirham Card
Documents Required for Individual
A passport copy and a valid visa copy are issued at least 180 days prior to the application
An Emirates ID copy
6 months of personal UAE bank statements, stamped by the UAE bank
Proof of income in UAE such as an employment agreement, share certificate, or salary certificate
A report from the General Directorate of Residency and Foreign Affairs shows evidence of all entries into and exits from the UAE
A copy or a title deed of the certified tenancy contract valid for at least three months prior to application
Tax Domicile Certificate application fees are AED 2000, payable to the UAE Federal Tax Authority through the e-Dirham Card
Tax Residency Certificate Application Process
First and foremost, you need to ensure that you or your company meets the eligibility criteria mentioned above.
In case you do qualify, you can approach the Ministry of Finance. Visit official portal, and from the homepage, you should navigate to the Application section.
From there, you must fill out the form for the Tax Residency Certificate and submit the same after careful verification.
Also, you must be ready to submit all the supporting documents required, and you can upload the same through the portal.
The Ministry of Finance will then conduct an extensive review of your documents and application, which may take anywhere between 2 to 4 weeks.
Furthermore, you must also complete the payment of the required fees through the payment methods listed on the website.
After successful verification, the Tax Residency Certificate will be made available to you.
The Tax Residency Certificate is an important document for expats living in the UAE. It certifies an individual’s tax residency status in the country and offers several benefits, including the avoidance of double taxation and access to banking and government services. To apply for the TRC, individuals must meet the eligibility criteria and MARKEF can be complete all the process to obtain TRC within a few weeks. If you’re an expat living in the UAE, consider applying for the TRC to take advantage of its benefits and simplify your tax filing process.
Get Your TAX Residency Certificate
Contact Us
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bali Taxation Rates for Digital Nomads

We looked last week at the Bali Digital Nomad Visa and the benefits that you can receive from this. If it isn’t enough to live on a beautiful, sun-drenched island with friendly locals and an incredible variety of wildlife, there is also a preferential tax rate and we will look into this further in today’s article.
Bali Visa Types for Digital Nomads
People from most countries will automatically have their visa stamped for 90 days when they enter Indonesia, and it is possible to leave and re-enter if you would like to be able to stay for a longer period of time.
If you enter Bali on a tourist visa, you should be able to work from there on your laptop without too many issues for the duration of your visa without having to register to pay tax in the country.
If you are able to stay for more than half of any calendar year, they may make the case that you are a resident for the purposes of tax and should therefore pay taxes in Indonesia.
Remote Worker Visa E33G
If you intend to stay for longer than this time, you should apply for a new visa called the E33G Remote Worker Visa.and this will allow you to stay for a year without paying any taxes within the country, even though you would normally be considered tax resident if you remained in the country for such a long amount of time.
It is not possible to extend the visa while you are in Bali, but if you leave and then apply for a new one from outside the country, with all of the same documents that you applied for the original one with, it is likely to be granted if you still meet the same requirements.
There is not a limit on how many times you can do this but it does require you to leave the country each time you want to apply for another visa, which is not as simple as being able to stay there continuously and simply renew.
How does the Bali Remote Worker Visa Compare to Malta?
Malta is considered by many to be the “gold standard” when it comes to remote worker and digital nomad visas. The Malta Digital Nomad Visa allows remote workers to live in Malta and not pay any tax for the first year of their stay.
This has helped Malta to rapidly increase the number of technology startup companies and it also has a flourishing igaming sector which has over 300 companies and employs over 10,000 people. In addition to the business side it is also a hot spot for an amazing community of digital nomads, who typically stay at Evolve Coliving.
After the first year, the Malta temporary residence permit charges 10% taxation per year and considers those that are there on the visa to be resident in that country for tax purposes. Malta has treaty agreements with many countries that mean you will avoid double taxation on earnings, so all of your earnings while living in Malta on this visa will only incur a rate of 10%.
The financial entry requirements for the Malta digital nomad visa are considerably lower than the Bali Remote Worker Visa with the amount you have to earn being set at 42,000 euros per annum if you are a new applicant. To compare like with like, this is around $47,000 compared to Bali’s $60,000.
A lower threshold allows more people to take advantage of being able to work from a beautiful, warm island. Malta has the added benefit for many people that one of the main languages is English. This can help some nomads to integrate and settle much more easily into daily life than having to learn Balinese from scratch.
The cost of both visas is very similar, with 300 Euros for the Malta digital nomad visa being roughly equivalent to the $350 US Dollar amount for the Indonesian Remote Worker Visa.
Should I Choose Bali or Malta?
There is absolutely no reason why you can’t try them both for a year and see which you would prefer to spend time in going forward. They both have their merits, and if ease of access to continental Europe is a major factor in your work then Malta makes more sense.
If you decide to come to Malta, we can make it easy for you by providing an amazing place to live and integrate with other remote workers at Evolve Coliving. We have super fast and reliable internet access, a coworking space and excellent leisure facilities including a gym, swimming pool and jacuzzi.
If you are looking for a tropical adventure somewhere new for a year then Bali would be an excellent choice. There is no wrong decision and this is the very essence of digital nomad life. Amazing destinations to choose from that make it difficult to decide where to spend time next.
Best Digital Nomad Destinations in Bali
There are some amazing destinations for digital nomads in Bali and if you decide to take out the e33g Remote Worker Visa for Bali, you will be able to choose which of them suits you the best. Canggu is an amazing place if you want to pursue connections with fellow digital nomads and there are large numbers of coworking spaces and remote worker friendly cafes that facilitate this.
If you are looking for a more spiritual retreat to work on yoga and meditation then Ubud would be a better location as it is set in lush green vegetation amid incredibly scenic rice fields.
Whichever option you choose you will quickly understand why Bali is such a favourite for the digital nomad community worldwide. The friendly locals haven’t yet decided that the presence of digital nomads is a burden and they welcome the annual influx from all around the world with open arms.
The cuisine in Bali is beautiful and you will crave some of the food from there long after you have left. The white sand beaches are eminently instagrammable and if you are a travel blogger or have an interest in becoming one, you should absolutely take the opportunity to visit. Original source: https://evolvecoliving.io/blog/bali-taxation-rates-for-digital-nomads/
0 notes
Text
Double taxation Avoidance Agreement
A Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) is an agreement between two countries to prevent income from being taxed twice. It ensures that individuals or entities earning income in both countries are not taxed twice on the same income. DTAA allows tax credits or exemptions to reduce tax liability.
SITE : https://nricaservices.com/service/dtaa-consultancy/ contact no : +91-9910075924
0 notes
Text
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) must navigate India's complex tax system to remain compliant and avoid penalties. Key considerations include accurately determining residential status, as it influences tax obligations. NRIs should be aware of taxable income sources, such as income earned or accrued in India, and understand the implications of the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) to prevent being taxed twice on the same income.
Maintaining proper documentation, including financial statements and proof of investments, is essential for accurate tax filings. Additionally, NRIs should be mindful of deadlines for filing income tax returns and paying any due taxes to avoid interest and penalties. Seeking professional advice can help NRIs effectively manage their tax responsibilities in India.
0 notes
Text
Wealth Planning Services for NRI
Wealth Planning Services for NRI: A Comprehensive Guide
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) play a crucial role in the global economy, contributing significantly to India’s foreign exchange reserves and economic growth. With their unique financial circumstances and cross-border lifestyles, effective wealth planning is essential to safeguard and grow their hard-earned money. WealthMunshi.com offers tailored solutions for NRIs to manage, preserve, and enhance their wealth.
Why Wealth Planning is Crucial for NRIs
Wealth planning is not just about saving and investing; it's about creating a roadmap to achieve long-term financial goals while navigating the complexities of international financial regulations. For NRIs, wealth planning involves managing dual taxation systems, currency fluctuations, investment opportunities, and inheritance planning. Without proper guidance, these challenges can erode wealth and hinder financial goals.
Key Components of NRI Wealth Planning Services
Taxation Advisory NRIs face dual tax obligations in their country of residence and India. Proper planning ensures compliance with tax laws while minimizing liabilities. WealthMunshi.com helps NRIs understand Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs) and optimize their tax strategy.
Investment Planning Investing in India offers NRIs a chance to participate in one of the fastest-growing economies. From real estate to mutual funds and fixed deposits, WealthMunshi.com assists NRIs in selecting the right investment avenues that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Portfolio Management A well-balanced portfolio is critical for wealth growth and preservation. WealthMunshi.com provides customized portfolio management services, ensuring diversification across asset classes like equities, debt instruments, and alternative investments.
Retirement Planning NRIs often plan to return to India during their retirement. WealthMunshi.com helps design retirement plans that ensure a steady income stream and financial independence during their golden years.
Estate and Succession Planning Transferring wealth to the next generation requires careful planning to avoid disputes and ensure a smooth transition. WealthMunshi.com offers estate planning services, including drafting wills, setting up trusts, and ensuring compliance with Indian succession laws.
Currency Risk Management Currency fluctuations can significantly impact NRI investments. WealthMunshi.com provides strategies to hedge against these risks, ensuring financial stability despite volatile forex markets.
Unique Challenges Faced by NRIs in Wealth Planning
Regulatory Compliance Navigating complex regulations like FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) and RBI guidelines can be daunting. WealthMunshi.com ensures compliance while maximizing investment opportunities.
Access to Reliable Financial Products Identifying the right financial products that cater to NRIs is a challenge. WealthMunshi.com’s deep understanding of the Indian financial market simplifies this process.
Global Asset Allocation NRIs often have assets in multiple countries. Managing these effectively requires expertise in global financial planning, which WealthMunshi.com offers.
Why Choose WealthMunshi.com?
Expert Guidance WealthMunshi.com’s team of seasoned financial advisors specializes in NRI wealth planning, offering solutions that cater to diverse needs.
Personalized Solutions Every NRI has unique financial goals and challenges. WealthMunshi.com crafts customized wealth plans tailored to individual circumstances.
Seamless Execution From opening NRI accounts to investing in Indian markets, WealthMunshi.com ensures a hassle-free experience with end-to-end support.
Long-Term Partnership WealthMunshi.com believes in building lasting relationships by consistently delivering value and adapting to evolving financial landscapes.
Steps to Begin Your Wealth Planning Journey
Initial Consultation Discuss your financial goals, risk tolerance, and current asset allocation with WealthMunshi.com’s advisors.
Comprehensive Financial Assessment Get a detailed evaluation of your financial health, including assets, liabilities, and potential risks.
Customized Strategy Development Receive a personalized wealth management plan that outlines investment strategies, tax-saving measures, and estate planning.
Implementation and Monitoring WealthMunshi.com ensures the timely execution of strategies and provides regular updates on portfolio performance.
Conclusion
Wealth planning is a cornerstone of financial success for NRIs. It requires a nuanced understanding of international laws, financial markets, and individual aspirations. WealthMunshi.com, with its expertise and commitment, empowers NRIs to make informed financial decisions, ensuring peace of mind and financial security.
Take the first step towards a secure financial future today with WealthMunshi.com—your trusted partner in NRI wealth planning. Visit WealthMunshi.com to learn more!
#portfolio management questionnaire#Sophisticated Wealth Management Services for NRI#Wealth Planning Services for NRI#Wealth Management Services for NRI#Wealth Planning Services
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding US Taxes in Canada: A Comprehensive Guide
For Americans living in Canada, navigating the complexities of US taxes in Canada can be overwhelming. Dual tax obligations, tax treaties, and filing requirements all demand careful attention. As US-UK tax accountants with deep expertise, we aim to provide a detailed guide to help expatriates manage their tax responsibilities effectively.

Why US Citizens in Canada Need to File US Taxes
Under US Taxes In Canada laws, all US citizens, regardless of where they reside, are required to file federal income tax returns annually. This includes Americans living in Canada. The United States employs a citizenship-based taxation system, which means you must report your worldwide income, even if you have no income from US sources.
Key Filing Requirements for US Expats in Canada
Filing Form 1040: Every US citizen must file Form 1040, declaring all worldwide income.
Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): If you earn income in Canada, you may qualify for the FEIE by filing Form 2555.
Foreign Tax Credit (FTC): To avoid double taxation, claim the FTC using Form 1116, which credits taxes paid to the Canadian government.
Filing FATCA Forms: If you hold financial accounts exceeding certain thresholds, you must comply with FATCA by filing Form 8938 and FBAR (FinCEN Form 114).
Key Tax Considerations for Americans in Canada
1. Tax Residency in Canada
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) determines your residency status for Canadian tax purposes. Most US citizens living in Canada will be considered Canadian residents for tax purposes if their primary ties (home, family) are in Canada.
2. The US-Canada Tax Treaty
The US-Canada Tax Treaty is designed to prevent double taxation. Key provisions include:
Tie-Breaker Rules: If both the US UK Tax Accountant and Canada claim you as a tax resident, the treaty determines where you owe taxes.
Tax Credits and Exemptions: The treaty ensures you can claim credits for taxes paid in one country when filing in the other.
Retirement Income: Specific rules govern taxation of pensions, RRSPs, and other retirement accounts.
3. Social Security Coordination
Under the Totalization Agreement, Americans in Canada can avoid double social security taxation. If you work in Canada and contribute to the Canada Pension Plan (CPP), these contributions can count toward US Social Security eligibility.
Tax Strategies for US Citizens Living in Canada
1. Use of Foreign Tax Credits
Leverage the Foreign Tax Credit to offset US Taxes In Canada on income already taxed by Canada. This is particularly useful if you reside in a Canadian province with high tax rates.
2. Maximizing the FEIE
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion allows you to exclude up to a certain threshold of foreign income ($120,000+ as of recent years) from US UK Tax Accountant. This strategy is beneficial for those earning lower or middle-range incomes in Canada.
3. Utilizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts
RRSPs: Registered Retirement Savings Plans in Canada grow tax-deferred and are recognized by the US-Canada Tax Treaty.
TFSA: While Tax-Free Savings Accounts (TFSAs) are tax-free in Canada, they are not recognized as such in the US and may trigger reporting requirements.
Filing as a Dual Citizen: What You Need to Know
1. Reporting Canadian Pensions
If you participate in the Canada Pension Plan (CPP) or employer-sponsored pensions, you must report these accounts to the IRS. Certain pension distributions may qualify for treaty exemptions.
2. FATCA and FBAR Compliance
The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) and FBAR requirements are crucial. US citizens with foreign bank accounts exceeding $10,000 must disclose these accounts. Non-compliance can result in steep penalties.
3. Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Failure to File: Not filing US Taxes In Canada can lead to penalties and loss of passport privileges.
Overlooking Canadian Tax Credits: Ensure all eligible Canadian tax credits are applied to reduce your overall tax liability.
Improper Treaty Application: Misunderstanding treaty provisions can result in double taxation.

How a US-UK Tax Accountant Can Help
As expert US UK Tax Accountant, we specialize in helping expatriates comply with tax laws in both countries. Whether you're navigating the complexities of dual taxation or need assistance with treaty benefits, our team ensures your tax filings are accurate and optimized.
Our Services Include:
Cross-border tax planning for individuals and businesses
Filing assistance for FATCA, FBAR, and US federal taxes
Tax treaty analysis to minimize liabilities
Retirement and investment tax strategies
Key Deadlines to Remember
1. US Federal Tax Deadlines
April 15th: Standard filing deadline.
June 15th: Automatic extension for expats.
2. FBAR Filing Deadline
April 15th (with automatic extensions for expats to October 15th).
3. Canadian Tax Deadlines
April 30th: Filing deadline for most individuals in Canada.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do I need to file taxes in both countries?
Yes. As a US citizen living in Canada, you must file taxes in both countries. However, treaty provisions and credits prevent double taxation.
2. Can I avoid US taxation altogether?
No. While strategies like the FEIE and FTC reduce your US tax liability, they do not eliminate it entirely.
3. What happens if I don't file?
Failure to file US Taxes In Canada can result in penalties, interest charges, and legal issues, including potential passport revocation.
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Title: A Complete Guide to LLP Registration with Licit360: Start Your Business with Ease
Introduction:
Starting a business is an exciting venture, and one of the most important decisions you'll make is choosing the right business structure. For entrepreneurs looking for flexibility, limited liability, and simplicity, a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is an excellent choice. Whether you're a startup or a growing business, LLP registration offers the right balance of personal protection and operational freedom.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about LLP registration with Licit360, ensuring a smooth and hassle-free process to kickstart your entrepreneurial journey.
What is an LLP?
An LLP (Limited Liability Partnership) is a business structure that combines the benefits of a partnership and a corporation. It allows business partners to manage the business together while offering protection from personal liability. This means that, as an LLP owner, you are not personally responsible for the debts or liabilities of the business, except in cases of fraud or misconduct.
Key Features of LLP:
Limited Liability Protection: The personal assets of partners are protected from business debts.
Flexible Management Structure: LLPs have no mandatory rules for management, providing flexibility to the partners.
Separate Legal Entity: An LLP is a separate legal entity from its partners.
No Minimum Capital Requirement: There’s no minimum capital requirement for registering an LLP.
Tax Benefits: LLPs enjoy a simpler tax structure, avoiding the double taxation faced by corporations.
Why Choose LLP for Your Business?
LLPs are the perfect choice for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and professional businesses due to the following reasons:
Protection from Personal Liabilities: Unlike sole proprietorships and partnerships, LLPs protect personal assets.
Licit360 give the best legal services in india to avoid the cowared methodologies
Tax Benefits: LLPs are not taxed separately; instead, profits are passed through to the partners and taxed individually, reducing the overall tax burden.
Credibility with Clients and Investors: LLPs provide a sense of legitimacy and professionalism, making it easier to attract clients and investors.
LLP Registration Process with Licit360:
At Licit360, we provide a seamless LLP registration process to ensure your business is set up for success. Our step-by-step process includes:
Choose Your LLP Name: Selecting a unique and relevant name is the first step. We will guide you in ensuring that your chosen name is compliant with the regulations.
Digital Signature Certificate (DSC): A DSC is required to sign the documents electronically. We will help you acquire the necessary certificates.
Designated Partner Identification Number (DPIN): Every partner in the LLP needs to obtain a DPIN. Our experts will assist in obtaining this.
Filing of LLP Agreement: An LLP Agreement defines the rights and duties of the partners. We help you draft and file the agreement with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Incorporation Certificate: Once the documents are submitted and approved, you will receive an incorporation certificate, confirming the registration of your LLP.
Documents Required for LLP Registration:
To ensure a smooth and speedy registration process, you’ll need to gather the following documents:
Identity Proof: Aadhar card, passport, or voter ID of the partners.
Address Proof: Utility bills, rental agreement, or bank statement.
PAN Card: For Indian nationals, PAN cards are mandatory.
Photographs: Recent passport-sized photographs of the partners.
Benefits of Registering with Licit360:
Expert Guidance: Our team of legal and financial experts will assist you at every step of the process.
Hassle-Free Registration: We handle all paperwork and legal formalities, ensuring that you can focus on your business.
Affordable Plans: We offer affordable packages with transparent pricing for hassle-free LLP registration.
Timely Completion: We guarantee quick and efficient processing of your registration.
Conclusion:
Registering your business as an LLP is a smart decision, offering personal liability protection, operational flexibility, and tax benefits. With Licit360, you can complete your LLP registration with ease and confidence, knowing that you have a dedicated team supporting you throughout the process.
Ready to register your LLP? Contact us today and get started on your entrepreneurial journey!
Register Your LLP Now with Licit360Visit licit360 to begin your registration process today and unlock the full potential of your business.
This blog provides valuable information on LLP registration while promoting Licit360’s services. You can adjust the tone, structure, or content as necessary to match the website's style.
0 notes
Text
APA Services: How Advance Pricing Agreements Can Benefit Your Business
In the global marketplace, businesses involved in cross-border transactions must navigate a complex landscape of tax regulations. One of the most effective tools for ensuring compliance and avoiding costly tax disputes is an Advance Pricing Agreement (APA). For companies in Madhapur, Hyderabad, Steadfast Business Consultants LLP (SBC) offers expert APA services, guiding you through the intricacies of advance pricing agreements to protect your business and improve tax efficiency.
What is an Advance Pricing Agreement (APA)?
An Advance Pricing Agreement (APA) is a proactive arrangement between a business and tax authorities that sets the methodology for determining transfer prices for transactions between related entities. This agreement is designed to ensure that prices charged in cross-border transactions are in line with the arm’s length principle, meaning that the prices are set as though the transactions were between independent parties.
APAs can be unilateral, bilateral, or multilateral. In a unilateral APA, an agreement is made between the taxpayer and a single tax authority. A bilateral or multilateral APA involves negotiations with multiple tax authorities, making it suitable for businesses that operate in more than one jurisdiction. Regardless of the type, APA services help ensure that your business complies with tax regulations, minimizing the risk of audits and disputes.
Benefits of APA Services for Your Business
Certainty in Transfer Pricing One of the most significant benefits of APA services is the certainty they provide in transfer pricing. By agreeing on a methodology upfront, businesses eliminate the uncertainty that often comes with cross-border tax audits. You can establish clear guidelines for how transactions between related entities should be priced, which ensures that your pricing practices are compliant with tax laws and reduces the risk of double taxation.
Avoiding Tax Disputes Transfer pricing is a common area for tax authorities to scrutinize, and without an APA, businesses risk being involved in lengthy and costly disputes. APA services help you negotiate agreements that minimize the chances of such disputes, as tax authorities will have already agreed on the transfer pricing methodology. This allows your business to avoid audits or adjustments related to pricing practices, which can be both time-consuming and expensive.
Elimination of Double Taxation One of the primary reasons businesses seek APA services is to avoid double taxation. Without an APA, there is a risk that different countries may apply different transfer pricing methods, leading to the same income being taxed in multiple jurisdictions. A bilateral or multilateral APA helps resolve this issue by ensuring that all tax authorities involved agree on the same pricing approach, thereby preventing double taxation.
Increased Transparency and Audit Confidence Having an APA in place enhances the transparency of your business’s pricing structures. Tax authorities are more likely to accept your transfer pricing approach when it has been pre-approved through an APA. This boosts your business’s credibility with tax authorities and reduces the likelihood of challenges during tax audits. The certainty that comes with an APA also gives you peace of mind, knowing that your pricing practices are in line with international standards.
Improved Financial Planning and Predictability With an APA in place, businesses can better plan their finances by understanding the tax implications of their pricing strategies. The clarity provided by an APA helps businesses forecast tax obligations more accurately and avoids unexpected tax liabilities. This financial predictability is vital for making informed strategic decisions, particularly for multinational corporations.
Access to Expert Negotiation Support Navigating the APA process can be complex and time-consuming. Engaging APA services ensures that your business has access to expert guidance throughout the process. The team at Steadfast Business Consultants LLP (SBC) is skilled in negotiating with tax authorities and will work on your behalf to ensure that the terms of the APA are favorable and aligned with your business objectives.
Why Choose SBC for APA Services?
At Steadfast Business Consultants LLP (SBC), we specialize in offering comprehensive APA services to businesses in Madhapur, Hyderabad, and beyond. Our experienced team of tax professionals has a deep understanding of both local and international tax laws, ensuring that your business is fully compliant with transfer pricing regulations. We guide you through every step of the APA process, from initial preparation to final implementation, making sure your agreement meets your business’s unique needs.
Our services include:
Preparation and Filing of APA Applications: We assist in preparing and filing APA applications with the relevant tax authorities.
Transfer Pricing Documentation: Our team helps you create detailed transfer pricing documentation that supports your APA application.
Negotiation with Tax Authorities: We handle the negotiations with tax authorities to ensure a smooth and favorable agreement.
Ongoing Compliance Support: After the APA is in place, we continue to offer support to ensure compliance with the agreement and any evolving tax laws.
Contact Us Today
For businesses in Madhapur, Hyderabad, looking to gain certainty in transfer pricing and avoid costly tax disputes, Steadfast Business Consultants LLP (SBC) offers the expertise you need. Our APA services help you navigate the complexities of international tax compliance with confidence, ensuring that your business remains in good standing with tax authorities worldwide.
To learn more about how our APA services can benefit your business, contact SBC today at 040-48555182. Let us help you ensure smooth and compliant cross-border transactions that support your business growth.
#advance pricing agreement advisory#aeo scheme#apa services#audit firms in hitech city#audit firms in hitech city for articleship
0 notes
Text
When Are the Benefits of an LLC Stronger Than an S Corp?

When choosing a business structure, many people find it challenging to determine where to begin. You may have heard about forming an LLC or an S Corporation, but understanding what these terms mean and how they differ can be confusing. Both Limited Liability Companies ("LLCs") and S Corporations offer personal liability protection, meaning your personal assets are generally protected from business liabilities and debts. Additionally, both structures provide tax advantages compared to other types of business entities. What is an S Corp? An S Corporation is a tax classification, not a standalone type of business entity. To become an S Corporation, you must first establish a C Corporation or an LLC. Both S Corporations and LLCs are "pass-through entities," meaning their profits pass directly to the owners' or shareholders' personal tax returns, which helps avoid corporate tax and double taxation. For LLC owners with above-average income in their industry, opting for S Corporation taxation can reduce self-employment taxes. This setup allows you to take a reasonable salary (aligned with industry standards), while any remaining profits can be distributed as dividends, which are not subject to self-employment tax. What is an LLC? An LLC is a legal business structure that offers liability protection to its owners, shielding their personal assets from business debts or legal claims. There are two types of LLCs: - Single-member LLC: Owned by 1 person and taxed like a sole proprietorship. - Multi-member LLC: Owned by multiple people and generally taxed like a partnership, unless it elects to be taxed as an S Corporation. LLCs are popular because they’re relatively simple to start and manage while providing liability protection and potential tax benefits. However, if your annual income exceeds a certain threshold, you may face a high tax bill. To reduce taxes, LLC owners can elect S Corporation taxation, which changes how certain portions of income are taxed. To form an LLC, you’ll need to file Articles of Organization with your state’s Secretary of State office. Then, file IRS Form 2553 to choose your tax classification. Once approved, your LLC can elect S Corporation taxation if it meets specific IRS requirements. So what's the difference? So, what are the main differences? The key distinctions between an LLC and an S Corporation relate to ownership, management, and required business formalities. These factors can influence which structure is the best fit for your business. 1. Ownership LLCs offer flexibility in ownership. They can have an unlimited number of owners (referred to as members), who don’t need to be U.S. citizens or residents, and can even include other business entities. In contrast, S Corporations face more restrictions: they can have no more than 100 shareholders, all of whom must be U.S. citizens or residents, and they cannot be owned by other business entities like C Corporations, LLCs, partnerships, or other S Corporations. 2. Classes of Stock and Voting Rights The IRS limits S Corporations to a single class of stock, which means all shareholders have the same voting rights. This restricts S Corporations from offering voting and non-voting shares, a flexibility typically available to traditional corporations. If an S Corporation tries to implement different voting rights, it may face tax penalties. LLCs, however, don’t issue stock. Instead, ownership and voting rights are defined in their membership agreements, allowing for customizable ownership and voting rights among members. 3. Management Structure An LLC can choose to be managed by its members (owners) or by appointed managers. A member-managed LLC operates more like a partnership, while a manager-managed LLC resembles a corporation, with selected managers making business decisions. S Corporations, on the other hand, are required to have directors and officers. The directors oversee the company’s affairs, while the officers handle daily operations. Business Formalities Both LLCs and S Corporations must adhere to some formalities, but the requirements for S Corporations are generally more extensive. S Corporations are required to adopt bylaws, authorize and issue stock, hold annual shareholder and director meetings, and keep detailed meeting minutes. LLCs may choose to follow these practices but are generally not legally required to do so. Tax Considerations One of the key reasons some people choose an S Corporation is the tax treatment it offers, allowing owners to take a salary and receive distributions from profits while potentially reducing self-employment taxes. However, an LLC can also elect to be taxed as an S Corporation by filing the necessary IRS paperwork, providing the flexibility of both structures. Making the Right Choice There’s no one-size-fits-all answer for small businesses when deciding between an LLC and an S Corporation. Your choice should depend on the specific needs and goals of your business. Raetzer PLLC Read the full article
0 notes