#diverse language
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
LINGUISTIC HISTORY LESSON
It was on this day in 1066 that William the Conqueror of Normandy arrived on British soil. He defeated the British in the Battle of Hastings, and on Christmas Day he was crowned King of England in Westminster Abby. What nobody knew at the time was how much this would affect the English language. The British back then were speaking a combination of Saxon and Old Norse. The Normans spoke French. Over time, the languages blended, and as a result English became a language incredibly rich in synonyms. Because the French speakers were aristocrats, the French words often became the fancy words for things. The Normans gave us “mansion”; the Saxons gave us “house.” The Normans gave us “beef”; the Saxons gave us, “cow.”
The English language has gone on accepting additions to its vocabulary ever since, and it now contains more than a million words, making it one of the most diverse languages on Earth. Writers have been arguing for hundreds of years about whether this is a good thing.
The critic Cyril Connolly wrote, “The English language is like a broad river … being polluted by a string of refuse-barges tipping out their muck.” But Walt Whitman said, “The English language is the accretion and growth of every dialect, race, and range of time, and is both the free and compacted composition of all.” And the poet Derek Walcott said, “The English language is nobody’s special property. It is the property of the imagination: it is the property of the language itself.” (x)
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

I feel that one of the most overlooked aspects of studying the French Revolution is that, in 18th-century France, most people did not speak French. Yes, you read that correctly.
On 26 Prairial, Year II (14 June 1794), Abbé Henri Grégoire (1) stood before the Convention and delivered a report called The Report on the Necessity and Means of Annihilating Dialects and Universalising the Use of the French Language(2). This report, the culmination of a survey initiated four years earlier, sought to assess the state of languages in France. In 1790, Grégoire sent a 43-question survey to 49 informants across the departments, asking questions like: "Is the use of the French language universal in your area?" "Are one or more dialects spoken here?" and "What would be the religious and political impact of completely eradicating this dialect?"
The results were staggering. According to Grégoire's report:
“One can state without exaggeration that at least six million French people, especially in rural areas, do not know the national language; an equal number are more or less incapable of holding a sustained conversation; and, in the final analysis, those who speak it purely do not exceed three million; likely, even fewer write it correctly.” (3)
Considering that France’s population at the time was around 27 million, Grégoire’s assertion that 12 million people could barely hold a conversation in French is astonishing. This effectively meant that about 40% of the population couldn't communicate with the remaining 60%.
Now, it’s worth noting that Grégoire’s survey was heavily biased. His 49 informants (4) were educated men—clergy, lawyers, and doctors—likely sympathetic to his political views. Plus, the survey barely covered regions where dialects were close to standard French (the langue d’oïl areas) and focused heavily on the south and peripheral areas like Brittany, Flanders, and Alsace, where linguistic diversity was high.
Still, even if the numbers were inflated, the takeaway stands: a massive portion of France did not speak Standard French. “But surely,” you might ask, “they could understand each other somewhat, right? How different could those dialects really be?” Well, let’s put it this way: if Barère and Robespierre went to lunch and spoke in their regional dialects—Gascon and Picard, respectively—it wouldn’t be much of a conversation.
The linguistic make-up of France in 1790
The notion that barely anyone spoke French wasn’t new in the 1790s. The Ancien Régime had wrestled with it for centuries. The Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts, issued in 1539, mandated the use of French in legal proceedings, banning Latin and various dialects. In the 17th and 18th centuries, numerous royal edicts enforced French in newly conquered provinces. The founding of the Académie Française in 1634 furthered this control, as the Académie aimed to standardise French, cementing its status as the kingdom's official language.
Despite these efforts, Grégoire tells us that 40% of the population could barely speak a word of French. So, if they didn’t speak French, what did they speak? Let’s take a look.
In 1790, the old provinces of the Ancien Régime were disbanded, and 83 departments named after mountains and rivers took their place. These 83 departments provide a good illustration of the incredibly diverse linguistic make-up of France.


Langue d’oïl dialects dominated the north and centre, spoken in 44 out of the 83 departments (53%). These included Picard, Norman, Champenois, Burgundian, and others—dialects sharing roots in Old French. In the south, however, the Occitan language group took over, with dialects like Languedocien, Provençal, Gascon, Limousin, and Auvergnat, making up 28 departments (34%).
Beyond these main groups, three departments in Brittany spoke Breton, a Celtic language (4%), while Alsatian and German dialects were prevalent along the eastern border (another 4%). Basque was spoken in Basses-Pyrénées, Catalan in Pyrénées-Orientales, and Corsican in the Corse department.
From a government’s perspective, this was a bit of a nightmare.
Why is linguistic diversity a governmental nightmare?
In one word: communication—or the lack of it. Try running a country when half of it doesn’t know what you’re saying.
Now, in more academic terms...
Standardising a language usually serves two main purposes: functional efficiency and national identity. Functional efficiency is self-evident. Just as with the adoption of the metric system, suppressing linguistic variation was supposed to make communication easier, reducing costly misunderstandings.
That being said, the Revolution, at first, tried to embrace linguistic diversity. After all, Standard French was, frankly, “the King’s French” and thus intrinsically elitist—available only to those who had the money to learn it. In January 1790, the deputy François-Joseph Bouchette proposed that the National Assembly publish decrees in every language spoken across France. His reasoning? “Thus, everyone will be free to read and write in the language they prefer.”
A lovely idea, but it didn’t last long. While they made some headway in translating important decrees, they soon realised that translating everything into every dialect was expensive. On top of that, finding translators for obscure dialects was its own nightmare. And so, the Republic’s brief flirtation with multilingualism was shut down rather unceremoniously.
Now, on to the more fascinating reason for linguistic standardisation: national identity.
Language and Nation
One of the major shifts during the French Revolution was in the concept of nationhood. Today, there are many ideas about what a nation is (personally, I lean towards Benedict Anderson’s definition of a nation as an “imagined community”), but definitions aside, what’s clear is that the Revolution brought a seismic change in the notion of French identity. Under the Ancien Régime, the French nation was defined as a collective that owed allegiance to the king: “One faith, one law, one king.” But after 1789, a nation became something you were meant to want to belong to. That was problematic.
Now, imagine being a peasant in the newly-created department of Vendée. (Hello, Jacques!) Between tending crops and trying to avoid trouble, Jacques hasn’t spent much time pondering his national identity. Vendéen? Well, that’s just a random name some guy in Paris gave his region. French? Unlikely—he has as much in common with Gascons as he does with the English. A subject of the King? He probably couldn’t name which king.
So, what’s left? Jacques is probably thinking about what is around him: family ties and language. It's no coincidence that the ‘brigands’ in the Vendée organised around their parishes— that’s where their identity lay.
The Revolutionary Government knew this. The monarchy had understood it too and managed to use Catholicism to legitimise their rule. The Republic didn't have such a luxury. As such, the revolutionary government found itself with the impossible task of convincing Jacques he was, in fact, French.
How to do that? Step one: ensure Jacques can actually understand them. How to accomplish that? Naturally, by teaching him.
Language Education during the Revolution
Under the Ancien Régime, education varied wildly by class, and literacy rates were abysmal. Most commoners received basic literacy from parish and Jesuit schools, while the wealthy enjoyed private tutors. In 1791, Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand (5) presented a report on education to the Constituent Assembly (6), remarking:
“A striking peculiarity of the state from which we have freed ourselves is undoubtedly that the national language, which daily extends its conquests beyond France’s borders, remains inaccessible to so many of its inhabitants." (7)
He then proposed a solution:
“Primary schools will end this inequality: the language of the Constitution and laws will be taught to all; this multitude of corrupt dialects, the last vestige of feudalism, will be compelled to disappear: circumstances demand it." (8)
A sensible plan in theory, and it garnered support from various Assembly members, Condorcet chief among them (which is always a good sign).
But, France went to war with most of Europe in 1792, making linguistic diversity both inconvenient and dangerous. Paranoia grew daily, and ensuring the government’s communications were understood by every citizen became essential. The reverse, ensuring they could understand every citizen, was equally pressing. Since education required time and money—two things the First Republic didn’t have—repression quickly became Plan B.
The War on Patois
This repression of regional languages was driven by more than abstract notions of nation-building; it was a matter of survival. After all, if Jacques the peasant didn’t see himself as French and wasn’t loyal to those shadowy figures in Paris, who would he turn to? The local lord, who spoke his dialect and whose land his family had worked for generations.
Faced with internal and external threats, the revolutionary government viewed linguistic unity as essential to the Republic’s survival. From 1793 onwards, language policy became increasingly repressive, targeting regional dialects as symbols of counter-revolution and federalist resistance. Bertrand Barère spearheaded this campaign, famously saying:
“Federalism and superstition speak Breton; emigration and hatred of the Republic speak German; counter-revolution speaks Italian, and fanaticism speaks Basque. Let us break these instruments of harm and error... Among a free people, the language must be one and the same for all.”
This, combined with Grégoire’s report, led to the Décret du 8 Pluviôse 1794, which mandated French-speaking teachers in every rural commune of departments where Breton, Italian, Basque, and German were the main languages.
Did it work? Hardly. The idea of linguistic standardisation through education was sound in principle, but France was broke, and schools cost money. Spoiler alert: France wouldn’t have a free, secular, and compulsory education system until the 1880s.
What it did accomplish, however, was two centuries of stigmatising patois and their speakers...
Notes
(1) Abbe Henri Grégoire was a French Catholic priest, revolutionary, and politician who championed linguistic and social reforms, notably advocating for the eradication of regional dialects to establish French as the national language during the French Revolution.
(2) "Sur la nécessité et les moyens d’anéantir les patois et d’universaliser l’usage de la langue francaise”
(3)On peut assurer sans exagération qu’au moins six millions de Français, sur-tout dans les campagnes, ignorent la langue nationale ; qu’un nombre égal est à-peu-près incapable de soutenir une conversation suivie ; qu’en dernier résultat, le nombre de ceux qui la parlent purement n’excède pas trois millions ; & probablement le nombre de ceux qui l’écrivent correctement est encore moindre.
(4) And, as someone who has done A LOT of statistics in my lifetime, 49 is not an appropriate sample size for a population of 27 million. At a confidence level of 95% and with a margin of error of 5%, he would need a sample size of 384 people. If he wanted to lower the margin of error at 3%, he would need 1,067. In this case, his margin of error is 14%.
That being said, this is a moot point anyway because the sampled population was not reflective of France, so the confidence level of the sample is much lower than 95%, which means the margin of error is much lower because we implicitly accept that his sample does not reflect the actual population.
(5) Yes. That Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand. It’s always him. He’s everywhere. If he hadn’t died in 1838, he’d probably still be part of Macron’s cabinet. Honestly, he’s probably haunting the Élysée as we speak — clearly the man cannot stay away from politics.
(6) For those new to the French Revolution and the First Republic, we usually refer to two legislative bodies, each with unique roles. The National Assembly (1789): formed by the Third Estate to tackle immediate social and economic issues. It later became the Constituent Assembly, drafting the 1791 Constitution and establishing a constitutional monarchy.
(7) Une singularité frappante de l'état dont nous sommes affranchis est sans doute que la langue nationale, qui chaque jour étendait ses conquêtes au-delà des limites de la France, soit restée au milieu de nous inaccessible à un si grand nombre de ses habitants.
(8) Les écoles primaires mettront fin à cette étrange inégalité : la langue de la Constitution et des lois y sera enseignée à tous ; et cette foule de dialectes corrompus, dernier reste de la féodalité, sera contraint de disparaître : la force des choses le commande
(9) Le fédéralisme et la superstition parlent bas-breton; l’émigration et la haine de la République parlent allemand; la contre révolution parle italien et le fanatisme parle basque. Brisons ces instruments de dommage et d’erreur. .. . La monarchie avait des raisons de ressembler a la tour de Babel; dans la démocratie, laisser les citoyens ignorants de la langue nationale, incapables de contréler le pouvoir, cest trahir la patrie, c'est méconnaitre les bienfaits de l'imprimerie, chaque imprimeur étant un instituteur de langue et de législation. . . . Chez un peuple libre la langue doit étre une et la méme pour tous.
(10) Patois means regional dialect in French.
#frev#french revolution#cps#mapping the cps#robespierre#bertrand barere#language diversity#amateurvoltaire's essay ramblings
773 notes
·
View notes
Text
A day in the life of someone who posts on the internet in Catalan *cue dozens of Spanish people asking "what's wrong with your mouth", ordering him to speak in Spanish or "in Christian", saying he's rude for speaking in Catalan, calling him "polaco" (derogatory Spanish word to mean a Catalan person), calling the Catalan language a dialect, saying he is possessed because he's speaking Catalan, etc*
This is a video by Sergi Mas showing some of the comments he gets on YouTube. He makes videos about mountain biking that he posts on YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram. And the first comment he got on his first YouTube video was already someone telling him he should do it in Spanish.
Some days ago, another creator who posts his videos in Catalan (Joan Sendra, find him on Instagram and TikTok) answered to a Spanish person who was complaining that it's rude to speak Catalan/Valencian on the internet instead of Spanish because then there's people who don't understand you (as if everyone in the world spoke Spanish lmao). Joan, who is tired of getting this kind of comments so often, answered: there are already endless videos and things to watch on the internet in Spanish. In fact, if you look for [the topic he was talking about in the video that this guy commented] all the videos are in Spanish except for mine. And yet you had to come to me, the one in Valencian, and tell me that I can't make a video in my language and that I can only make it in yours. If you don't like it, it's so easy to find another one!
However, it's not a matter of actually being interested in what's being said in a language they don't speak. It's about the imposition of the language they consider superior (Spanish) and telling speakers of the languages whose land Spain had occupied that they are useless and should be ashamed of existing in public. Well, we aren't. Like Sergi's video, don't let the comments disturb your macarrons.
#català#valencià#actualitat#languages#language#catalan#cultures#valencian#diversity#minoritized languages#imperialism#influencers#sociolinguistics#minority languages
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Diverse vs. divergent
This is something I see people tripping up on sometimes, in a gender context and also in a neurotype context, so since the Gender Census research is primarily language-focused I thought posting it here might be quite on-topic.
"Diverse" is an adjective that describes a group as containing variation within it. Something that is diverse has [the inherent quality of] "diversity" (noun). It cannot describe an individual.
"Divergent" is an adjective that describes someone or something within a larger group as being different from the "norm". Something or someone that is divergent has [the behavioural quality of] "divergence" (noun).

So:
A person cannot be diverse, but they can be divergent.
A group of people/things that are diverse can contain very common examples as well as very uncommon examples relative to that whole group.
An individual person can e.g. have diverse interests, and in that situation the group that is diverse is the interests, not the person. Some of those diverse interests may be common, and some may be divergent.
A group of people can be diverse, and they can also be divergent as a subgroup of a larger group.
This applies to words/terms that end in "-diverse" and "-divergent".
So, for neurotype contexts:
A normal population is neurodiverse, and contains within it neurodivergent individuals and neurotypical individuals.
An individual person cannot be neurodiverse. They would be described as neurodivergent.
"The neurodiverse community" could refer to the entire human race, which would include both common and uncommon neurotypes, including all neurotypical people.
"The neurodivergent community" is correct, and refers to the subgroup of individuals whose neurotypes are less common and differ significantly from "the norm".
The neurodivergent community is itself diverse, and even neurodiverse, containing its own more and less common neurotypes relative to the neurodivergent subgroup as a whole.
And for gender contexts:
A normal population is gender-diverse, and contains within it gender-divergent individuals and cisgender and binary individuals.
An individual person cannot be "gender-diverse". They would be described as gender-divergent. (Or perhaps this is where people would usually say "gender non-conforming"?)
"The gender-diverse community" could refer to the entire human race, which would include both common and uncommon genders, including all cisgender and binary people.
"The gender-divergent community" is grammatically correct, and refers to the subgroup of individuals whose genders (or lack thereof) are less common and differ significantly from the more common human experiences of gender.
The gender-divergent community is itself diverse, and even gender-diverse, containing its own more and less common genders (or lack thereof) relative to the gender-divergent subgroup as a whole.
265 notes
·
View notes
Text
One Song in Every Language
Okay, tumblr. Let's try something.
I want to make a playlist with one song in every single language. Of course, this is impossible- the spotify playlist limit is something like 5,000- but I want to try. Of course, I can't do this alone, and so I'm sharing the project with the entire online language nerd/ music nerd community. Together we can celebrate linguistic diversity- and find some really cool music :)
Here's how it works. This spreadsheet will document every song and language represented. When you want to add a song, first look in the spreadsheet to see if that language is already represented. If it isn't, add the song to the playlist, and then add it to the spreadsheet.
What counts as a language? This is, as we all know, a fundamentally political question (Russian/ Ukrainian? Hindi/ Urdu? "Chinese" and its "dialects"...) We don't have to solve those debates here. My thinking is: the point is to celebrate linguistic diversity in as many forms as possible. If you can make a reasonable argument for why a song and its linguistic variety should be represented, go ahead and add it.
Yes, this means conlangs count (cause conlangs are SICK!) This also means dead languages count- throw in all the Latin and Classical Nahuatl you like. Glossolalia (à la Sigur Ros) and semi-linguistic scat-esque nonsense (à la Kobaian)? Sure, why not!
I'm calling this one song in every language, but we also want to highlight small and minority languages. So maybe we don't want ten different French songs, but if there are two or three different artists singing in Sami (especially different varieties of Sami), throw it in!
Let's make this awesome. Let's make this huge. Spread it around to every language nerd and music geek you know.
Thanks, dankon, merci, etc :)
#language#linguistics#music#spotify#playlist#language learning#linguistic diversity#language diversity#conlang#foreign languages#language nerd#music nerd
189 notes
·
View notes
Text
The unequal proportion between the number of languages and how many speakers those languages have
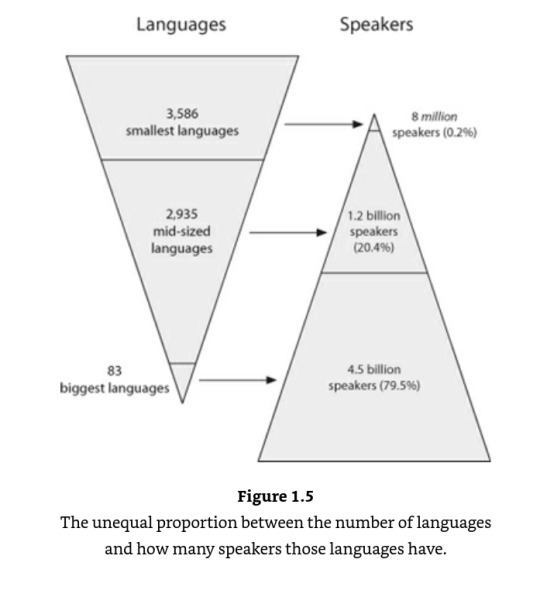
The median number of speakers for a human language is only about 5,000 people.
From the incredibly good book, When languages die: The extinction of the world’s languages and the erosion of human knowledge.
712 notes
·
View notes
Text
do we think people in westeros can speak high valyrian. like. in the great houses or whatever. do the maesters speak it??? or is it all common tongue whatever that is
#there doesn't SEEM to be a real courtly/priestly language vs vernacular difference is the thing#apart from accents for peasants or whatever. i mean even generally speaking theres not a LOT of linguistic diversity#but i guess i would expect the 300 years of targ rule to have had more of an impact wrt valyrian being spoken#especially since they literally speak low valyrian in the free cities. it would be so interesting if westeros had its own valyrian dialect#jui speaks#asoiaf
67 notes
·
View notes
Text

And one for my other boy, because of course I had to do the horse.
Unlike Theo, Ambroys has enough romantic experience to more accurately understand what he wants out of intimate relationships. That does not make him any less maladapted for romance.
(Do you know how hard it was to come up with green flags for Ambroys. Nearly impossible task.)
#amusing diversion. i enjoy charts#my draws#ambroys#amaranthine#btw the love language is what he likes to receive rather than what he gives#if you expect that much from him you're going to be deeply disappointed#just like everyone else in his life
247 notes
·
View notes
Text
20 inspirational names for a super summer!
List summary: 新夏、夏向、夏涼、夏艷/夏艶、琉夏、夏樂、夏怡、夏悅、夏嬉、夏歡/夏懽、梨夏、夏梅、夏蓮、莽夏、青夏、勇夏、承夏、平夏、峰夏、and 夏緒! (Keep reading ’til the end to discover their meanings, readings, pronunciations, guide to etymology and history, and more linguistic knowledge!)
Is it just me or has this summer been unnervingly chilling for us tropical islanders? 🌞🥶
Check out this summer-inspired name bank I’ve been working on for the past 5 months!
Each name was…
→ meticulously hand-picked like exotic cherries 🍒
→ carefully translated to the best of my ability 🉑
→ and then packed with a mini beginner’s guide to 夏 (the Han character/Chinese character for “summer”, used throughout the Sinosphere) 📖
→ which contains its standard readings in many languages: Mandarin Chinese, Dungan Tili, Cantonese, Hakka, Hokkien, Wu, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese! 🀄
(If you need info on any other topolect, dialect, or time-specific variant not mentioned here, just ask away! I’ll see what I can do for ya!)
👉🏼 An incredibly versatile character, it’s impossible to run out of given names containing/based on 夏!
The possibilities are endless, and the only limit is our imagination! 💡
👉🏼 If we visit the Wiktionary entry for 夏, we’ll see a whole lot more linguistic variants & historical hypotheses on this ancient grapheme dating back to 2070 BC, and even a reconstruction of its Middle Chinese & Old Chinese pronunciations based on recovered millennia-old scripts! 😱
👇🏼 Comment “Wiktionary” and I’ll send you the link to read further. It’s very interesting to read, whether you’re a curious beginner or a veteran Sinologist.
❓ QOTD 1: Which name stood out to you in particular? 🤔
❓ QOTD 2: Do you know what the difference is between “reading” and “pronunciation”? 🗣️
👇🏼 Also also also, let me know what you think of this list! 📜
Is it interesting enough? Are the tables mathematical enough? Are my font choices weird enough? Have I managed to convince you that I’m secretly an omniscient Taoist immortal from the 16th century BCE here to steal all the trees off your backyards, or should I try harder? If so, what other attempts at floor-length grocery lists should I make to satisfy your most honourable expectations?
Remember—your plants are at stake here! 🧚🏼♀️🌲🌳🌴








#不知火編修 ~ a Shiranui Editorial original post#onomastics#name list#name lists#given names#name ideas#Sinitic names#Sinosphere#Chinese names#Chinese characters#Chinese language#Japanese names#Japanese characters#Japanese language#Korean names#Korean characters#Korean language#Vietnamese names#Vietnamese characters#Vietnamese language#lingblr#language learning#writing diversity#diversity & representation#accurate and respectful representation#Asian names#Asian characters#characters of color#rp resources#writing tips
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
also put in the tags broadly where you're from and if english is a first or second language for you. tell me a whole story if you want.
please reblog you know the drill sample size and all that
#thinking about her again tonight (the necessity and diversity of a distinct plural you in english)#tumblr polls#linguistics#english#language
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
“When we lose linguistic diversity we suffer a consequent loss in the range of ways of experiencing the world.” - Beth Ann Fennelly, Fruits We'll Never Taste, Languages We'll Never Hear: The Need for Needless Complexity
442 notes
·
View notes
Text
the Bantu dialect. the Bantu dialect. the Bantu dialect, singular. the singular Bantu dialect* invariably spoken by all of the Africans enslaved and brought to Louisiana.
I can't adequately explain, briefly, just how fucking bonkers of a phrase that is. just how completely outlandish. the Bantu dialect...
Bantu is a family of languages. actually it's like, a family of language groups. it is a huge, high-level division of language clades. the sub-divisions of the Bantu family can be further subdivided into nodes that are subdivided into languages (and then those languages are sub-divided into dialects).
even just following wikipedia's version of the taxonomy (all of this is constantly subject to argument and revision): the Mbam languages are a group of Bantu languages. the "Mbam" umbrella divides into the Sanaga, West Mbam, and Yambasa language groups. the Sanaga node can be further divided into the Tuki, Leti, and Mbwasa languages. dialects of Tuki include Kombe, Cenga, Tsinga, Bundum, Njo, Ngoro, and Mbere. one randomly chosen node of one node of one node of the Bantu language group has seven dialects (eight, if you count Mbwasa, which some linguists do).
linguists who study any subgroup of African languages frequently complain about ignorance surrounding them, the prototypical example being people who think that every African language is perforce a Bantu one. this man is not even knowledgeable enough to be at that level of ignorance. he published this. he wrote an easily verifiable claim about the accepted etymology of a word and didn't even bother checking, and then he published that in a book.
about 5% of the world's population speaks one of these 400-600ish languages. in terms of number of recognised, living languages, this statement is sort of like if I called Indo-European a "dialect." thus basically all of Europe except for Finland, everyone in the north of India, and the entire Iranian plateau speak "the Indo-European dialect." completely insane. off-the-wall bonkers amounts of racism at work here.
*If Bantu is a "dialect," by the way, one wonders which broader language it is a dialect of? Really, though, we needn't ask—here "dialect" simply means "something spoken by African or Indigenous people and therefore not worthy of the exalted word 'language'"
#by the way the density and diversity of languages here is not special to Africa#Europe was like this too until linguistic diversity was systematically quashed#gumbo research saga#food research
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have added English subtitles to this video posted by Helena Sotoca on Instagram. She's from Madrid (Spain) but has been living in Catalonia for 7 years. As she explained in another video, she didn't learn any Catalan the first 3 years she lived here, but then realised how she was imposing Spanish on her group of Catalan friends and how important it was for her friends to keep their language, so she learned it. She is very happy about this decision which has allowed her to integrate more in Catalan society and culture.
In this video, she gives her personal opinion on why languages are not only "a way to understand each other". This sentence is something that we speakers of discriminated languages have to hear all the time (in fact, I was reminded of this video a few days ago because @beautiful-basque-country got that comment). Many times, they'll say: "why are you so annoying about wanting to be able to speak your language? A language is only a tool to understand each other, so if you speak both [the local language and the imperial language], why not just always speak [the imperial language]?".
This mindset is what leads to language extermination. First of all, because it assumes that our languages are less worthy of existence and thus that the language's community is less worthy of existence. If I stop speaking my language, I stop being a part of me. If all my culture stops speaking our language, we stop existing. Language is deeply tied to culture, it's through language that we think and transmit our worldview, and there are many aspects of our culture and our landscape that we can only describe in our language, because only we have the specific words to describe it or because the translation loses nuance, context, and connotations. Remove language, and the rest of the culture will soon follow.
Secondly, it erases the reason why we speak the state's language, which is usually because of imposition through violence, and justifies this imposition because the imperial violence of the past that made the imperial language more widely spoken is now the reason why speakers of the imperial language deserve more rights than those who suffered the imposition.

But besides these more social reasons, I like how Helena explains her personal relation to the language in this video. She also shows us one of the reasons why it's so important to promote discriminated languages to be used in public (and not only hidden at home): when you meet someone speaking a language, you form a bond with them in that language and it can be difficult to change. Speakers of minoritized languages often meet each other in contexts in which they're socially pressured to speak the state's language, and so we find the situation where a group of friends who are all native speakers of the minoritized language will form a bond in the state's language. Thus, slowly, because of the state's language imposition in the public sphere (this is what the "speak the state language if there's even 1 person who might not speak the local language! Languages are only a tool for communication!" mindset pushes us to), the local language gets pushed aside more and more, until we can't have a normal life in it and the state's language imposition becomes absolute, and the local language dies, taking with it its culture, history, and connection to the land and ancestors.
With some work, it can be reversed. I've explained this before but I'll say it again because it's relevant. My parents met in Spanish, because they met in high school and back then speaking Catalan in schools was strictly forbidden and punished. They were speaking in Spanish even when they started dating, but they realised how absurd it was that two native Catalan speakers spoke Spanish to each other and how it was a result of Francoist policy. They decided they don't want Francoism to infiltrate our personal lives, so they made the effort and switched. Maintaining the language of their surroundings, their culture, their land, they became even closer. And, thanks to their decision, when I was born I had the luck of being a native speaker of the language too, because it's what we've always spoken at home. But they did it because they had a political antifascist conscience, many people don't think much about it and just go with what is easier. If they had done that, the language would have lost them and also me. Multiply this for how many people meet each other in settings where social pressure or social rules promote speaking the imperial language instead of the local one that is closer to their hearts.
So no, a language is not only a tool to understand each other. It's also what allows us to speak according to our own understanding of the world (instead of assimilating into another's worldview), it gives meaning to our surroundings (both nature, the names we give to places, etc), every word is an unbroken chain with all of those who came before us, it allows us to understand our ancestors whether that be through their writing or songs they passed down or legends, it's an integral part of the human relations we establish, and so much more. Every language is worth everything. Every language has the right to exist and to thrive.
#llengua catalana#actualitat#sociolinguistics#minoritized languages#català#catalan#languages#langblr#cultures#anthropology#minority languages#diversity#cultural diversity#linguistics#lingblr#language revitalization
294 notes
·
View notes
Text
I looooove it when Americans are saying that not knowing about what countries there are on other continents is the same as not knowing all the us states because the us is so big and diverse.
I just wanna go: name 5 Indian states. Or 5 provinces in China real quick for me
#big? sure its big#diverse??? you're seriously undermining how diverse other countries are#alek talks#and indians are actually the ones who could say this!!! cause their cultures cuisines and even languages are different#same with china afaik#your us states are not that different from one another i promise 😩#im not saying you have to know every single country in the world but at least most of them...#or the most famous ones in the continent. if you say shit like you thought portugal was in south america or that idk#palestine is in eastern europe take a long hard look at yourself and make an effort to know the world around you#or at least don't proclaim it loudly 😭😭😭#the bar is SO low
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
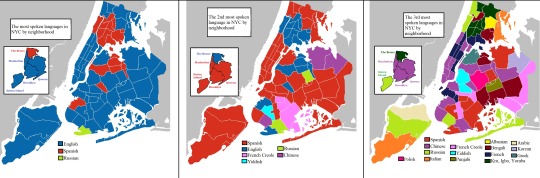
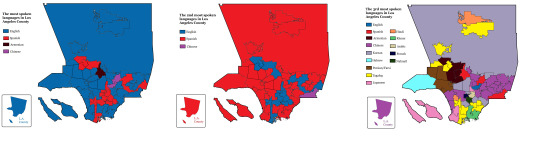
First, second, and third most spoken language in New York City 🗽🚇🌭 and Los Angeles County 🌴⭐️🌆
#map#maps#cartography#usa#data#geography#americas#latin america#langblr#languages#language#new york city#nyc#los angeles#la#new york#california#united states#diversity#chart#history#spanish#chinese#english#east coast#west coast#lana del rey#russian#armenian#french
212 notes
·
View notes